Unraveling the Intertwined Effect of pH on Helicobacter pylori Motility and the Microrheology of the Mucin-Based Medium It Swims in
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. H. pylori J99 Culturing Conditions
2.2. PGM Preparation
2.3. pH Calibration in BB10 and PGM
2.4. Motility: Phase Contrast Microscopy Live Cell Imaging, Cell Tracking
2.5. Body Rotation and Cell Shape Analysis
3. Results
3.1. pH Dependence of Swimming Speed Distributions of H. pylori in BB10 and PGM
3.2. H. pylori Display Differences in Duration and Length of Trajectories
3.3. H. pylori Displays Broad Speed Distributions in PGM and BB10
3.4. The Effect of pH on Cell Body Rotation in BB10 and PGM
3.5. Different Types of Stuck Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobley, H.L.T.; Mendz, G.L.; Hazell, S.L. (Eds.) Helicobacter Pylori: Physiology and Genetics; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in gastric acidic territory. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimmel, C.J.; Etienne, A.; Cilluffo, T.; Ritter, C.V.; Gasser, T.; Rey, J.P.; Caradonna-Moscatelli, P.; Sabbatini, F.; Pace, F.; Bühler, H.W.; et al. Long-term ambulatory gastric pH monitoring: Validation of a new method and effect of H2-antagonists. Gastroenterology 1985, 88, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allen, A.; Flemström, G. Gastroduodenal mucus bicarbonate barrier: Protection against acid and pepsin. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 288, C1–C19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schade, C.; Flemstrom, G.; Holm, L. Hydrogen ion concentration in the mucus layer on top of acid-stimulated and-inhibited rat gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, I.N.; Bahari, H.M.M.; Turnberg, L.A. The pH gradient across mucus adherent to rat fundic mucosa in vivo and the effect of potential damaging agents. Gastroenterology 1981, 81, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, O.L.; Keener, J.P.; Fogelson, A.L. A physics-based model for maintenance of the pH gradient in the gastric mucus layer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G599–G612. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, S.; Konradt, M.; Groll, C.; Scheid, P.; Hanauer, G.; Werling, H.O.; Josenhans, C.; Suerbaum, S. The spatial orientation of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5024–5029. [Google Scholar]
- Schweinitzer, T.; Mizote, T.; Ishikawa, N.; Dudnik, A.; Inatsu, S.; Schreiber, S.; Suerbaum, S.; Aizawa, S.; Josenhans, C. Functional characterization and mutagenesis of the proposed behavioral sensor TlpD of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3244–3255. [Google Scholar]
- Croxen, M.A.; Sisson, G.; Melano, R.; Hoffman, P.S. The Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis receptor tlpB (HP0103) is required for pH taxis and for colonization of the gastric mucosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Lertsethtakarn, P.; Ottemann, K.M.; Hedrixson, D.R. Motility and chemotaxis in Campylobacter and Helicobacter. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 389–410. [Google Scholar]
- Howitt, M.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Vogelmann, R.; Joubert, L.M.; Ottemann, K.M.; Amieva, M.R. Chepep controls helicobacter pylori infection of the gastric glands and chemotaxis in the epsilonproteobacteria. MBio 2011, 2, e00098-11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antani, J.D.; Sumali, A.X.; Lele, T.P.; Lele, P.P. Asymmetric random walks reveal that the chemotaxis network modulates flagellar rotational bias in Helicobacter pylori. eLife 2021, 10, e63936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celli, J.P.; Turner, B.S.; Afdhal, N.H.; Ewoldt, R.H.; Mckinley, G.H.; Bansil, R.; Erramilli, S. Rheology of gastric mucin exhibits a pH-dependent sol-gel transition. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celli, J.P.; Turner, B.S.; Afdhal, N.H.; Keates, S.; Ghiran, I.; Kelly, C.P.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H.; So, P.; Erramilli, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori moves through mucus by reducing mucin viscoelasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14321–14326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bansil, R.; Celli, J.P.; Hardcastle, J.M.; Turner, B.S. The influence of mucus microstructure and rheology in Helicobacter pylori infection. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Z.; Chasan, B.; Bansil, R.; Turner, B.S.; Bhaskar, K.R.; Afdhal, N.H. Atomic force microscopy reveals aggregation of gastric mucin at low pH. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3458–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Clyne, M.; Labigne, A.; Drumm, B. Helicobacter pylori requires an acidic environment to survive in the presence of urea. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Kihara, M.; Macnab, R.M. Cytoplasmic pH mediated pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1981, 145, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Minamino, T.; Imae, Y.; Oosawa, F.; Kobayashi, Y.; Oosawa, K. Effect of intracellular pH on rotational speed of bacterial flagellar motors. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Kami-ike, N.; Jun-ichi, P.Y.; Kudo, S.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Effect of intracellular pH on the torque-speed relationship of bacterial proton-driven flagellar motor. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Oono, K.; Hayashi, F.; Oosawa, K.; Kudo, S.; Nakamura, S. Effect of the MotA(M206I) mutation on torque generation and stator assembly in the Salmonella H+-driven flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00727. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Lin, W.; Zhu, S.; Franco, A.T.; Liu, J. Imaging the Motility and Chemotaxis Machineries in Helicobacter pylori by Cryo-Electron Tomography. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chaban, B.; Coleman, I.; Beeby, M. Evolution of higher torque in Campylobacter-type bacterial flagellar motors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karim, Q.N.; Logan, R.P.; Puels, J.; Karnholz, A.; Worku, M.L. Measurement of motility of Helicobacter pylori, Campylobacter jejuni, and Escherichia coli by real time computer tracking using the Hobson BacTracker. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 51, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshiyama, H.; Nakamura, H.; Kimoto, M.; Okita, K.; Nakazawa, T. Chemotaxis and motility of Helicobacter pylori in a viscous environment. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez, L.E.; Hardcastle, J.M.; Wang, J.; Pincus, Z.; Tsang, J.; Hoover, T.R.; Bansil, R.; Salama, N.R. Helicobacter pylori strains vary cell shape and flagellum number to maintain robust motility in viscous environments. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 88–110. [Google Scholar]
- Constantino, M.A.; Jabbarzadeh, M.; Fu, H.C.; Bansil, R. Helical and rod-shaped bacteria swim in helical trajectories with little additional propulsion from helical shape. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601661. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Y.; Goers Sweeney, E.; Guillemin, K.; Amieva, M.R. Multiple Acid Sensors Control Helicobacter pylori Colonization of the Stomach. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006118. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.; Padra, M.; Constantino, M.A.; Sharba, S.; Thorell, A.; Lindén, S.K.; Bansil, R. Influence of the viscosity of healthy and diseased human mucins on the motility of Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9710. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C. Influence of Acid on Motility and Chemotactic Response of Helicobacter Pylori in Gastric Mucin. Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Constantino, M.A. Investigating Effects of Morphology and Flagella Dynamics on Swimming Kinematics of Different Helicobacter Species Using Single-Cell Imaging. Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, S.; Scheid, P. Gastric mucus of the guinea pig: Proton carrier and diffusion barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1997, 272, G63–G70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lieleg, O.; Jang, S.; Ribbeck, K.; Han, J. A microfluidic in vitro system for the quantitative study of the stomach mucus barrier function. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4071–4079. [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle, J.M. Studies on Helicobacter Pylori Motility: Influence of Cell Morphology, Medium Rheology, and Swimming Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Theves, M.; Taktikos, J.; Zaburdaev, V.; Stark, H.; Beta, C. A bacterial swimmer with two alternating speeds of propagation. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pincus, Z.; Theriot, J.A. Comparison of quantitative methods for cell-shape analysis. J. Microsc. 2007, 227, 140–156. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, J.; Hoover, T.R. Requirement of the flagellar protein export apparatus component FliO for optimal expression of flagellar genes in Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Kao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Lin, S.Y.; Lai, T.Y.; Sheu, B.S.; Lo, C.J.; Wu, J.J. Inactivation of ferric uptake regulator (Fur) attenuates Helicobacter pylori J99 motility by disturbing the flagellar motor switch and autoinducer-2 production. Helicobacter 2017, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lele, P.P.; Hosu, B.G.; Berg, H.C. Dynamics of mechanosensing in the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11839–11844. [Google Scholar]
- Tipping, M.J.; Delalez, N.J.; Lim, R.; Berry, R.M.; Armitage, J.P. Load-dependent assembly of the bacterial flagellar motor. MBio 2013, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bansil, R.; Hardcastle, J.; Constantino, M. Microrheology of mucin: Tracking particles and Helicobacter pylori bacteria. Epitőanyag. J. Silic. Based Compos. Mater. 2015, 67, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Beeby, M.; Ribardo, D.A.; Brennan, C.A.; Ruby, E.G.; Jensen, G.J.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Hultgren, S.J. Diverse high-torque bacterial flagellar motors assemble wider stator rings using a conserved protein scaffold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1917–E1926. [Google Scholar]
- Mirbagheri, S.A.; Fu, H.C. Helicobacter pylori couples motility and diffusion to actively create a heterogeneous complex medium in gastric mucus. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 198101. [Google Scholar]
- Bansil, R.; Constantino, M.A.; Su-Arcaro, C.; Liao, W.; Shen, Z.; Fox, J.G. Motility of Different Gastric Helicobacter spp. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
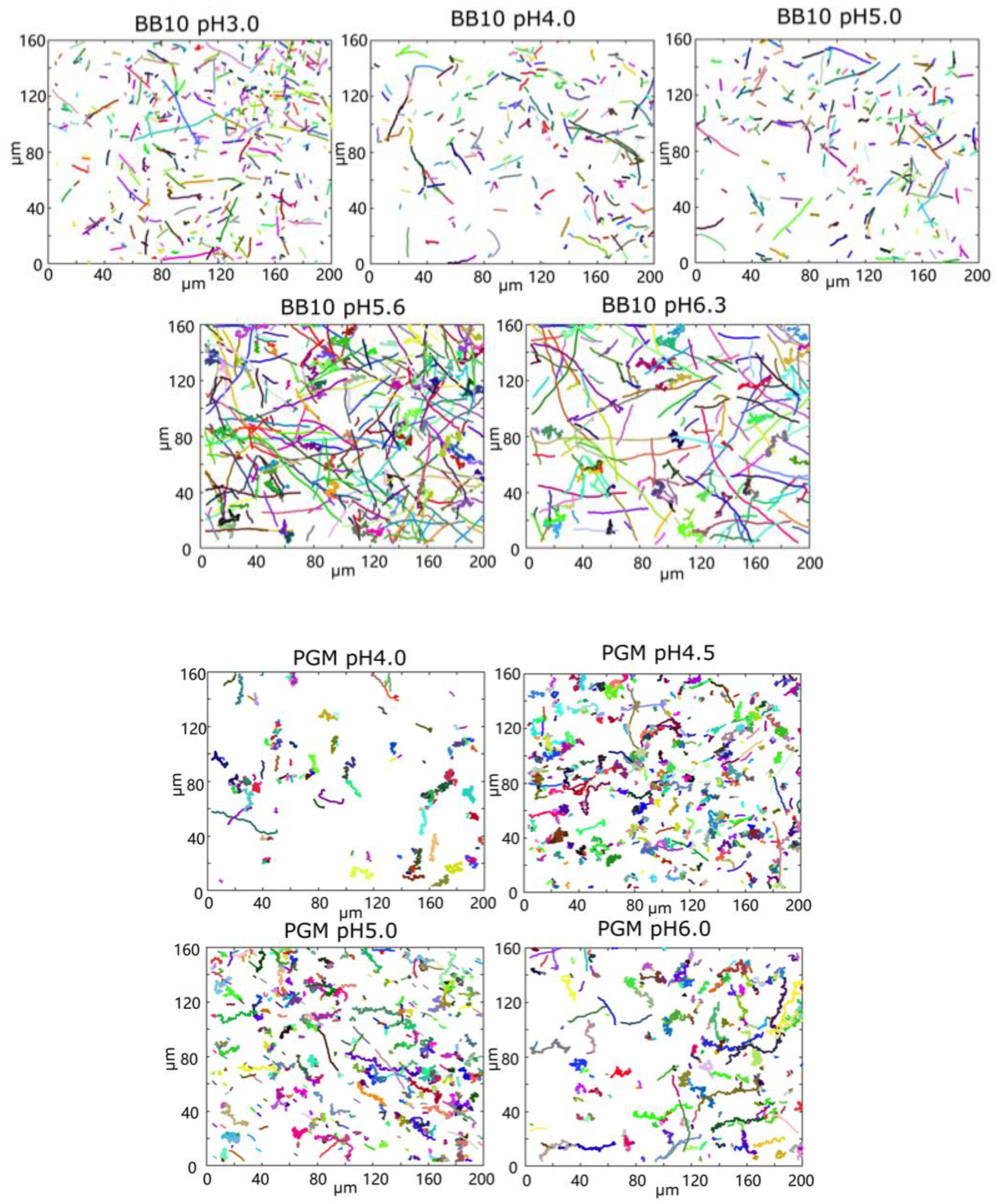
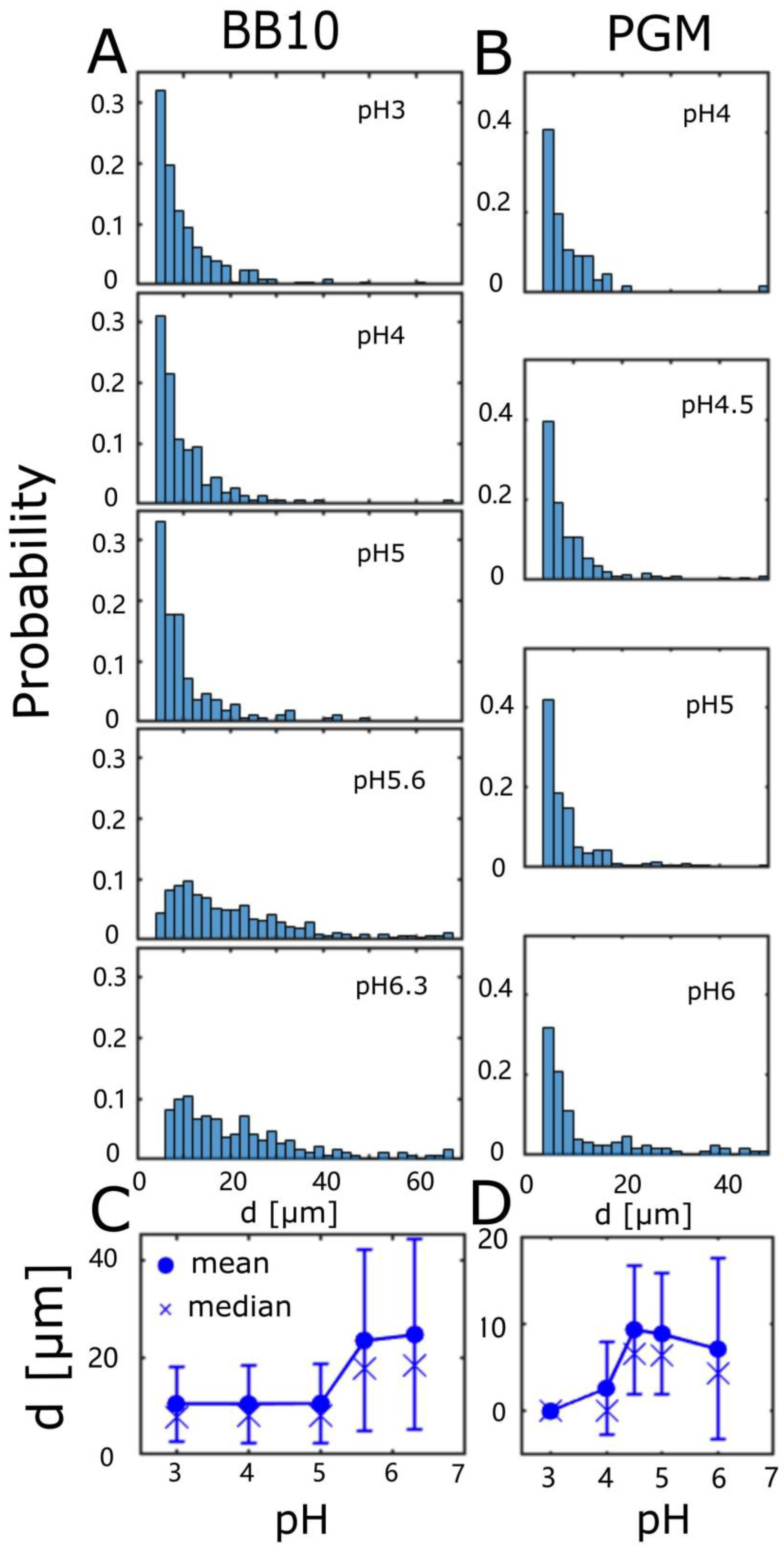
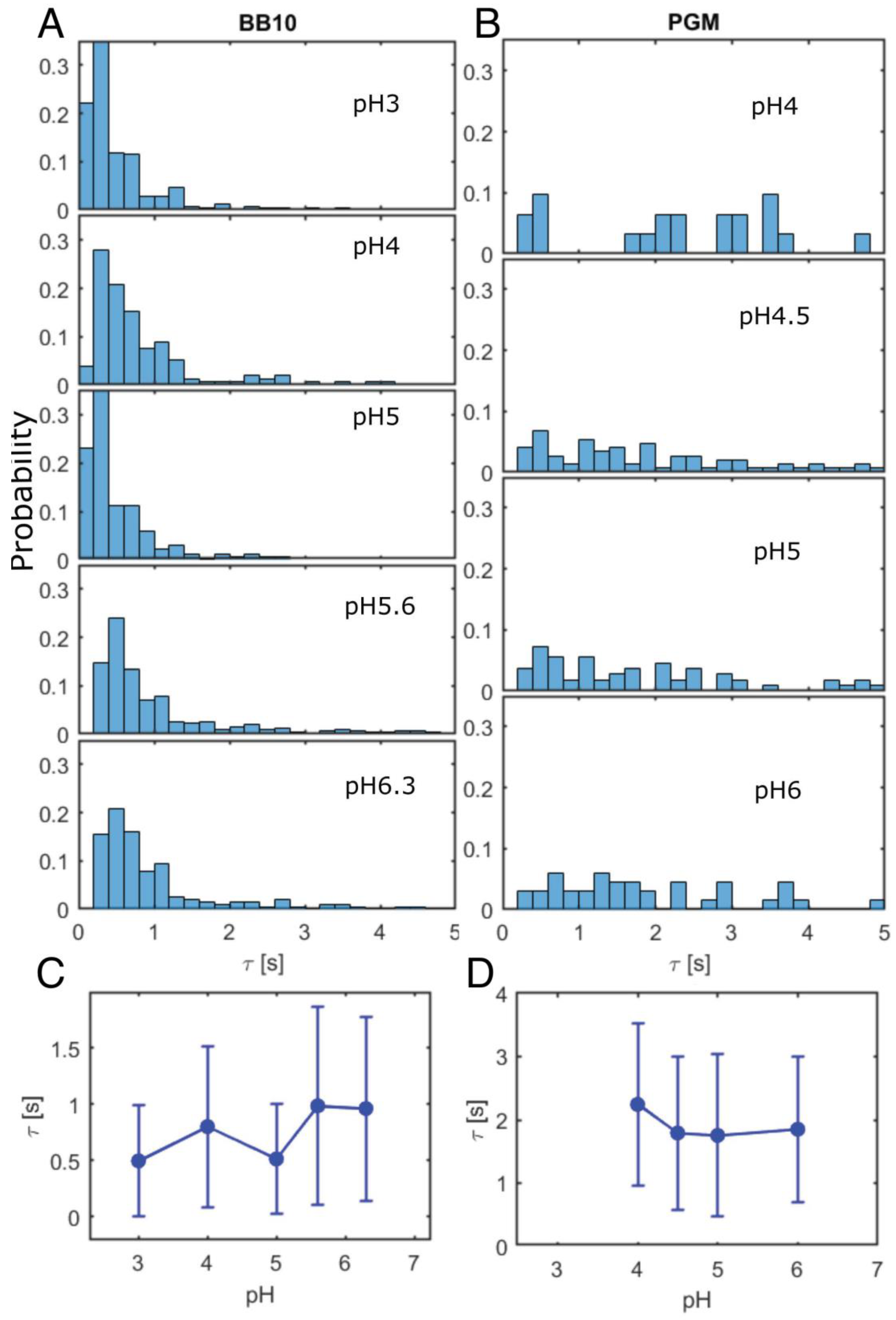
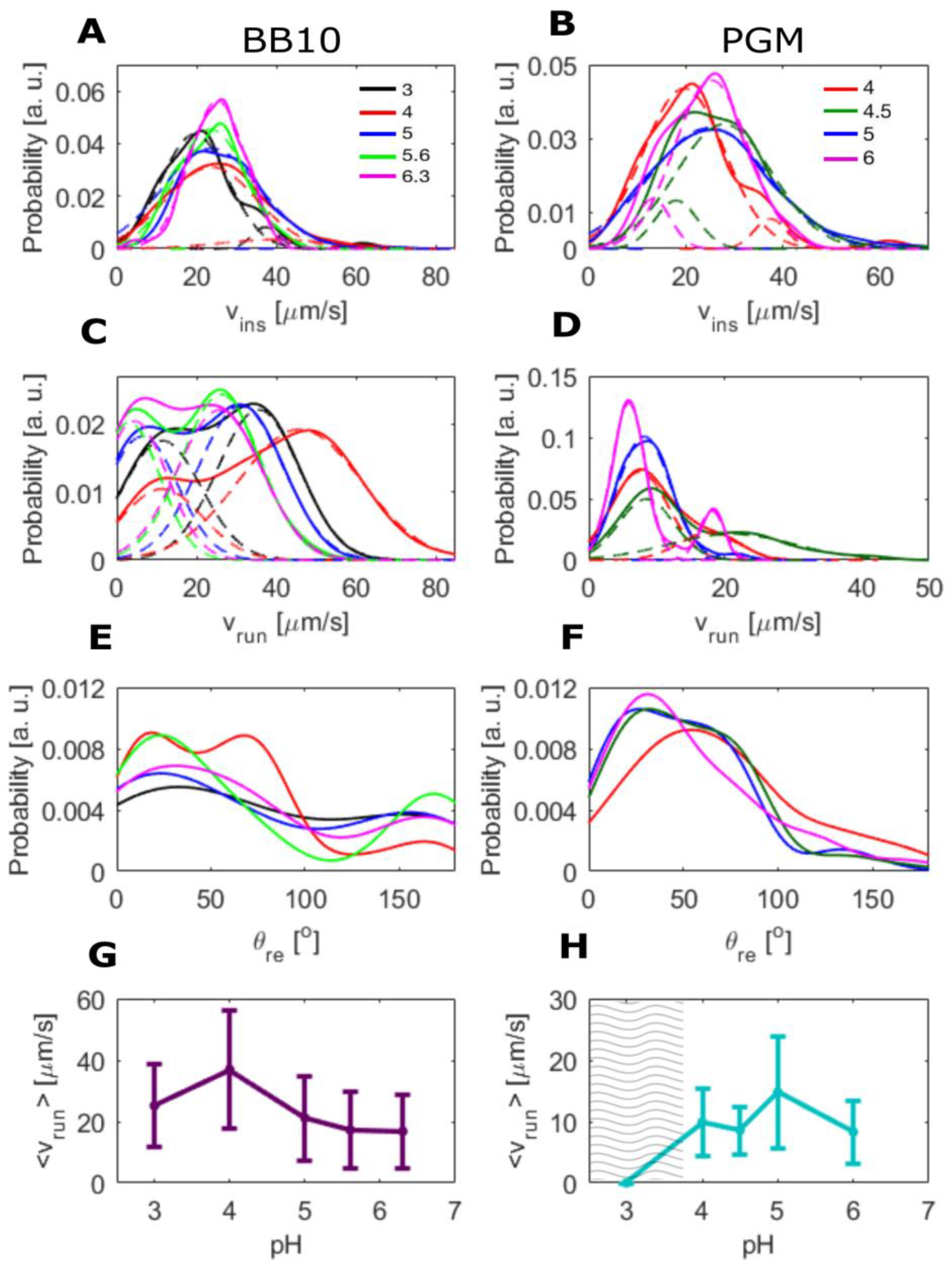
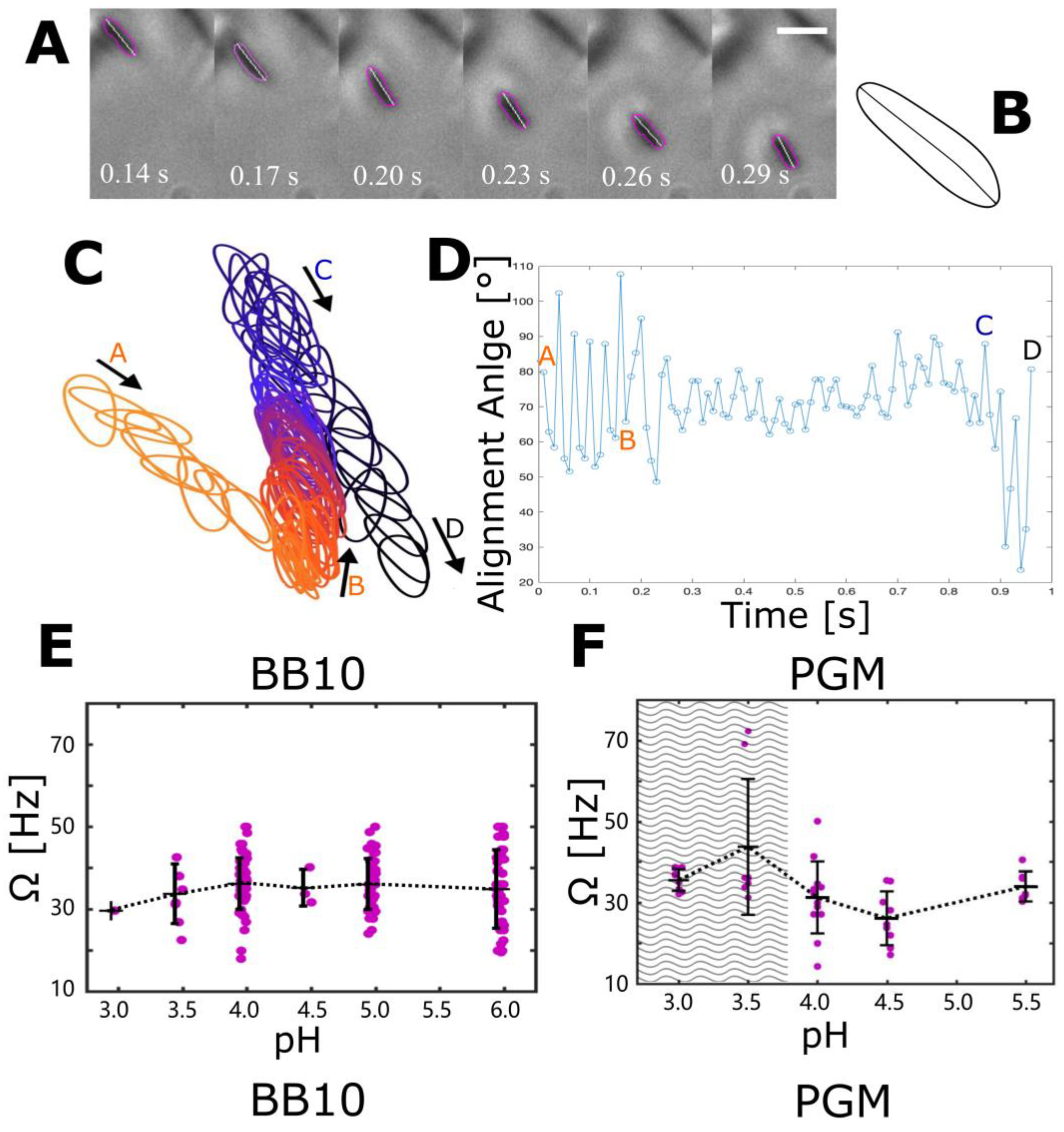
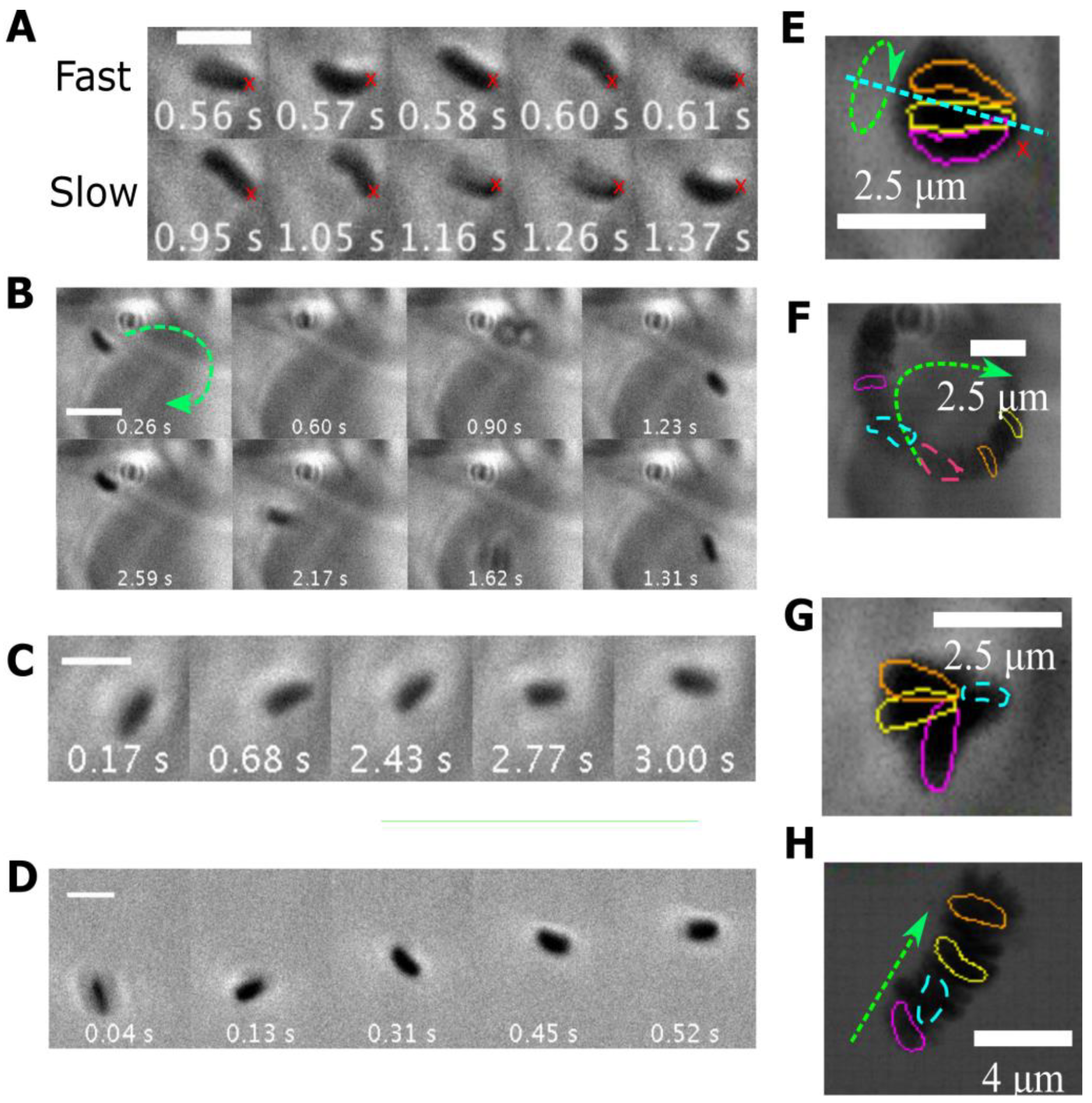
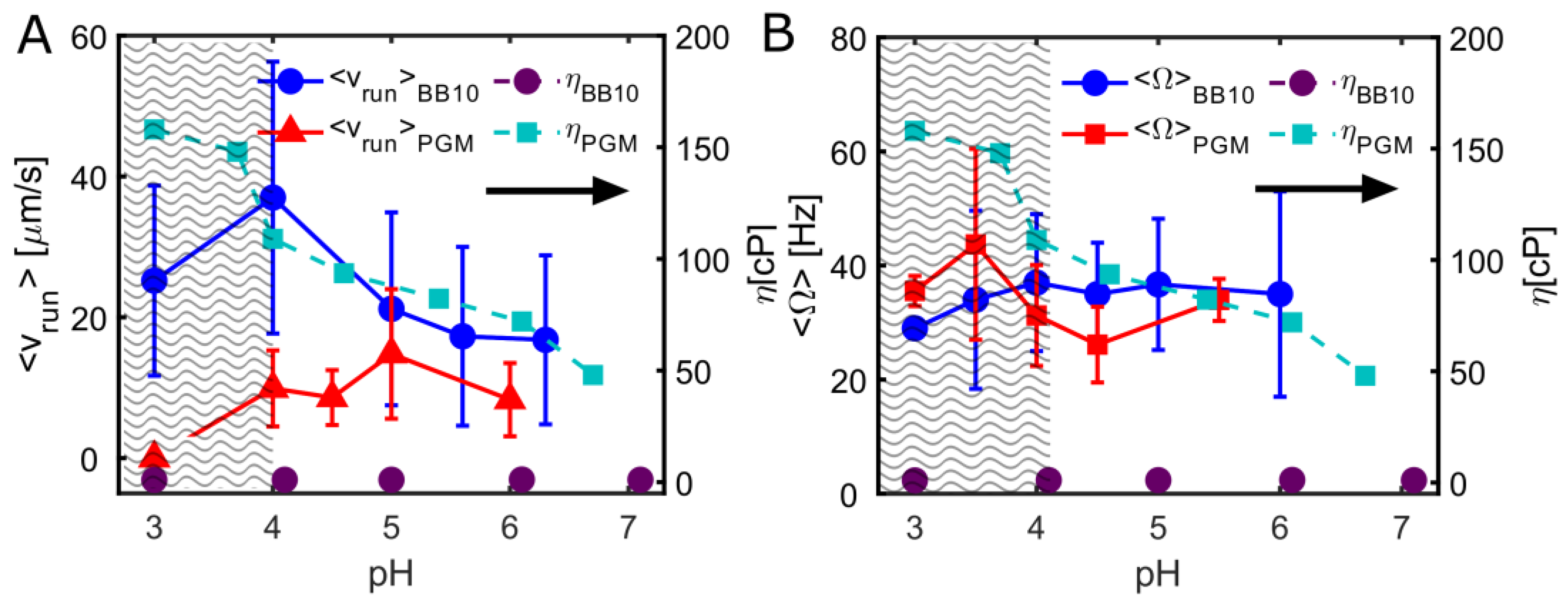
| Medium | pH | <vins> | σ | Median | <vrun> | σ | Median | Motile | Reversal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μm/s | μm/s | μm/s | μm/s | μm/s | μm/s | % | % | ||
| BB10 | 3 | 33 | 10 | 34.1 | 25.2 | 13.5 | 27.6 | 40.4 | 56.0 |
| 4 | 47.5 | 17.1 | 48.1 | 37 | 19.3 | 39.6 | 42.3 | 24.6 | |
| 5 | 29.8 | 9.3 | 30.9 | 21.2 | 13.7 | 21.7 | 60.9 | 61.5 | |
| 5.6 * | 25.2 | 6.5 | 25.4 | 17.3 | 12.7 | 23.6 | 61.2 | 70.7 | |
| 6.3 * | 24.9 | 7 | 25.3 | 16.8 | 12 | 16.8 | 59.7 | 56.3 | |
| PGM | 4 | 21.9 | 10.2 | 20.8 | 9.9 | 5.4 | 8.9 | 12.4 | 37.9 |
| 4.5 | 26.1 | 11.9 | 25.6 | 8.6 | 3.9 | 8.5 | 24.8 | 13.1 | |
| 5 | 27.1 | 10.1 | 26.3 | 14.8 | 9.2 | 10.8 | 27.3 | 8.1 | |
| 6 | 23.7 | 10.9 | 21.1 | 8.3 | 5.2 | 6.4 | 21 | 42.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su-Arcaro, C.; Liao, W.; Bieniek, K.; Constantino, M.A.; Decker, S.M.; Turner, B.S.; Bansil, R. Unraveling the Intertwined Effect of pH on Helicobacter pylori Motility and the Microrheology of the Mucin-Based Medium It Swims in. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112745
Su-Arcaro C, Liao W, Bieniek K, Constantino MA, Decker SM, Turner BS, Bansil R. Unraveling the Intertwined Effect of pH on Helicobacter pylori Motility and the Microrheology of the Mucin-Based Medium It Swims in. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112745
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu-Arcaro, Clover, Wentian Liao, Katarzyna Bieniek, Maira A. Constantino, Savannah M. Decker, Bradley S. Turner, and Rama Bansil. 2023. "Unraveling the Intertwined Effect of pH on Helicobacter pylori Motility and the Microrheology of the Mucin-Based Medium It Swims in" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112745
APA StyleSu-Arcaro, C., Liao, W., Bieniek, K., Constantino, M. A., Decker, S. M., Turner, B. S., & Bansil, R. (2023). Unraveling the Intertwined Effect of pH on Helicobacter pylori Motility and the Microrheology of the Mucin-Based Medium It Swims in. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112745








