Metallophore Activity toward the Rare Earth Elements by Bacteria Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Due to Coal Mining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Environmental Sampling Locations and Siderophore Screening
2.2. Rare Earth Element Metallophore Screening
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
3. Results
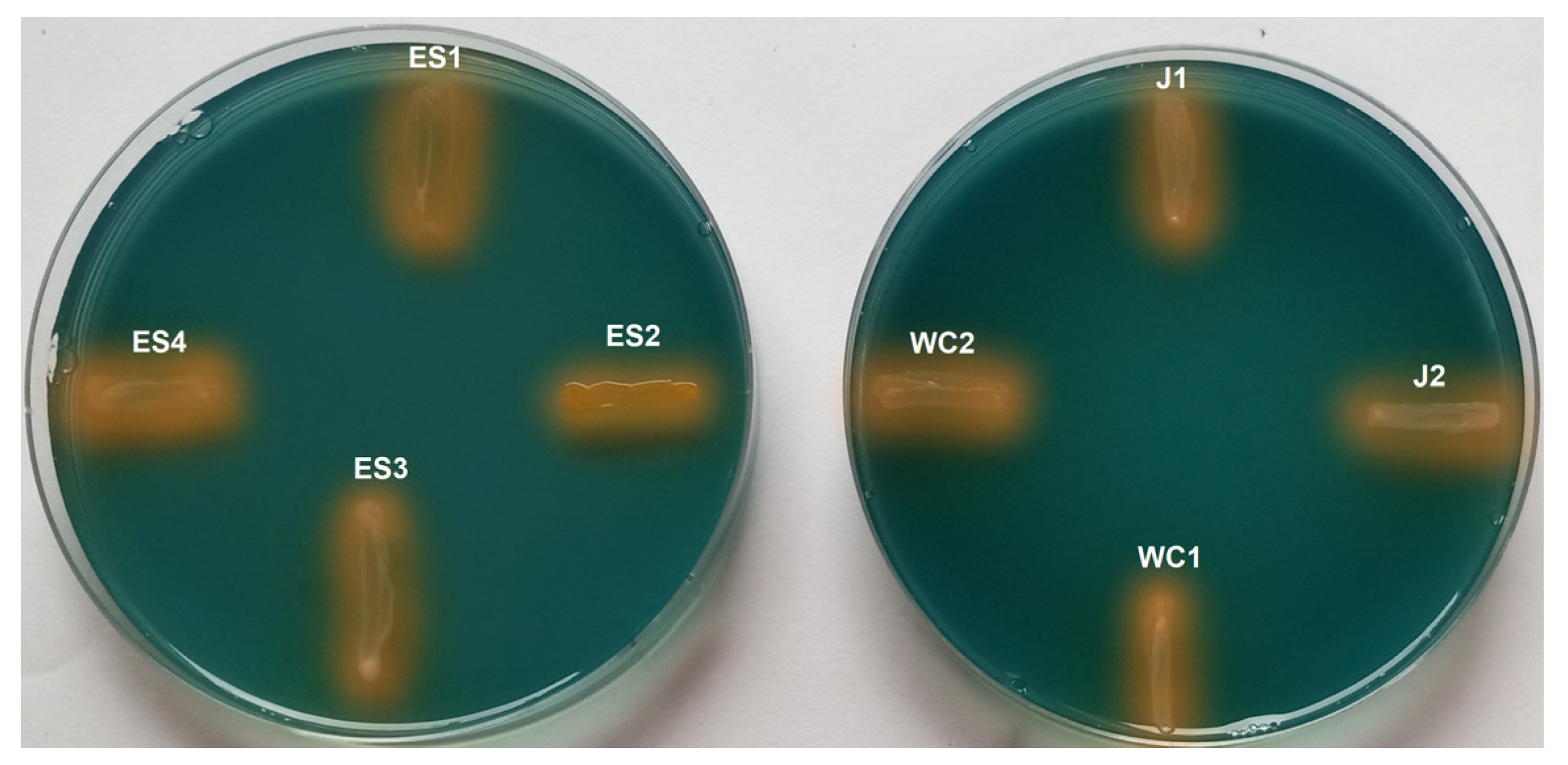
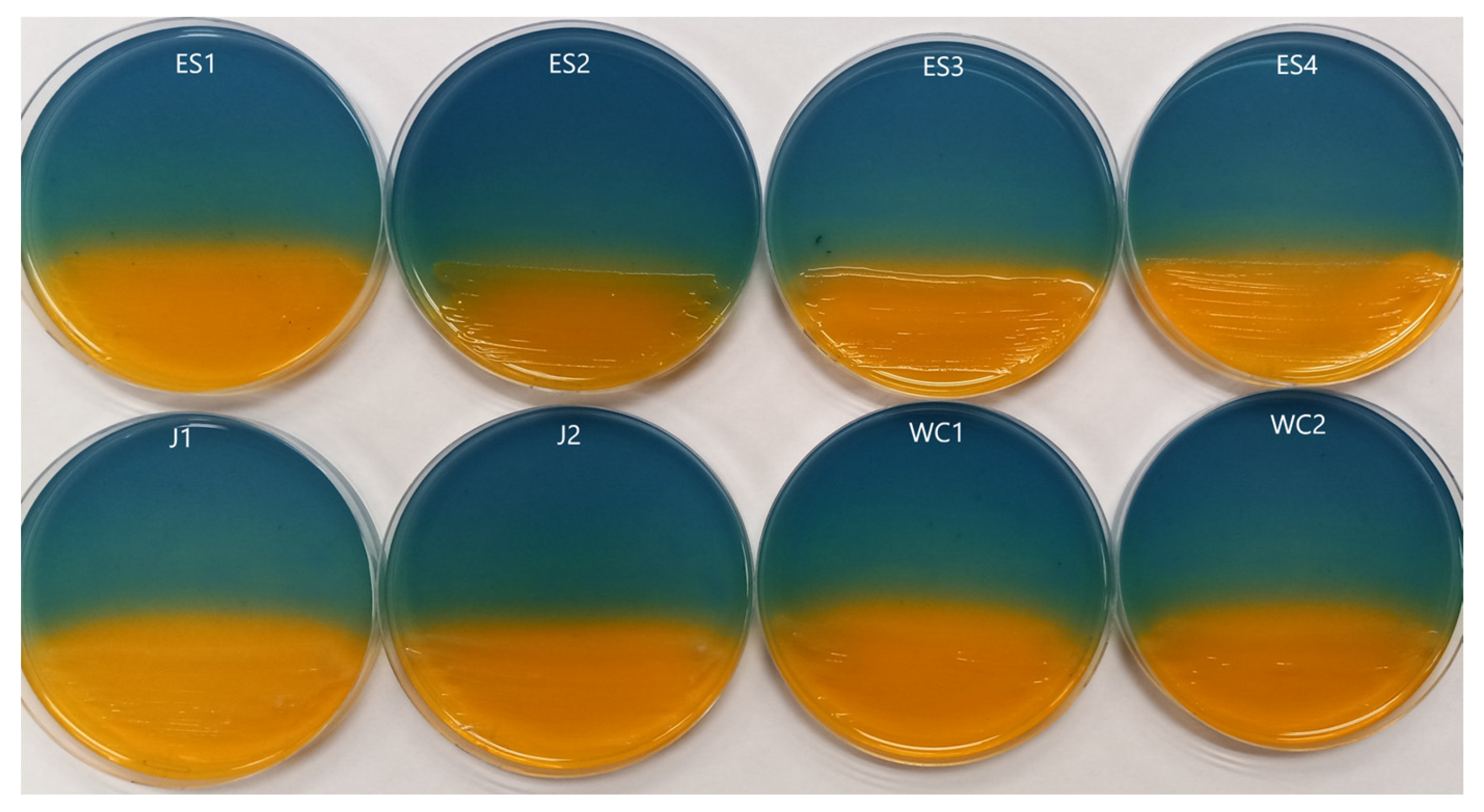
3.1. Siderophore Activity
3.2. Rare Earth Element Metallophore Activity
3.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holden, J.; Adams, M. Microbe-metal interactions in marine hydrothermal vent environments. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, H.; Faramarzi, M. Microbe-metal interactions for the biotechnological treatment of metal-containing solid waste. China Particuology 2006, 4, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltman, C.; Walter, G.; Yurkov, V. A diverse community of metal(loid) oxide respiring bacteria is associated with tube worms in the vicinity of the Juan de Fuca Ridge black smoker field. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilescu, M. Microbial recovery of critical metals from secondary sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, G.; Jiang, H.; Li, F.; et al. A critical review of mineral-microbe interaction and co-evolution: Mechanisms and applications. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nawc128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Kormoker, T.; Khan, R.; Proshad, R.; Kabir, M.; Idris, A. Strategies for heavy metal remediation from contaminated soils and future perspectives. In Soil Health and Environmental Sustainability: Application of Geospatial Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 615–644. [Google Scholar]
- Letoffe, S.; Ghigo, J.; Wandersman, C. Iron acquisition from heme and hemoglobin by a Serratia marcescens extracellular protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9876–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, V.; Hantke, K. Recent insights into iron import by bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantke, K. Iron and metal regulation in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner-Lamia, J.; Pereira, S.; Bovea-Marco, M.; Futschik, M.; Tamagnini, P.; Oliveria, P. Extracellular proteins: Novel key components of metal resistance in Cyanobacteria? Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Zhao, C.; Burkinshaw, B.; Zhang, B.; Wei, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.; Shen, X. Manganese scavenging and oxidative stress response mediated by type VI secretion system in Burkholderia thailandensis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 114, E2233–E2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, S.; Hughes, E.; Yrukov, V. Discovery of siderophore and metallophore production in the aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghssein, G.; Esseddine, Z. A review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa metallophores: Pyoverdine, pyochelin, and pseudopaline. Biology 2022, 11, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielands, J. Siderophores. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 302, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Shaikh, S.; Sayyed, R. Modified chrom azurol S method for detection and estimation of siderophore having affinity for metal ions other than iron. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 1, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Graham, D.; DiSpirito, A.; Alterman, M.; Galeva, N.; Larive, C.; Asunskis, D.; Sherwood, P. Methanobactin, a copper-acquisition compound from methane-oxidizing bacteria. Science 2004, 305, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, J.; Kehl-Fie, T. Bioinformatic mapping of opine-like zincophore biosynthesis in bacteria. mSystems 2020, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, S.; Duckworth, O.; Harrington, J.; Schenkeveld, W. Metallophores and trace metal biogeochemistry. Aquat. Geochem. 2015, 21, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkov, V.; Jappe, J.; Vermeglio, A. Tellurite resistance and reduction by obligately aerobic photosynthetic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4195–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltman, C.; Donald, L.; Yurkov, V. Tellurite and tellurate reduction by the aerobic anoxygenic phototroph Erythromonas ursincola is carried out by a novel membrane associated enzyme. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, A. A systematic review on leaching of rare earth metals from primary and secondary sources. Miner. Eng. 2022, 184, 107632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Bettinelli, M.; Boffi, A.; Botta, M.; De Simone, G.; Luchinat, C.; Marengo, E.; Mei, H.; Aime, S. Rare earth elements (REE) in biology and medicine. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2020, 31, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X. Rare earth element recycling from waste nickel-metal hydride batteries. J. Hazard. Mat. 2014, 279, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Shen, B.; Mu, G.; Zhu, X.; Han, F.; Zeng, B.; Wen, H. High-Tc superconductivity induced by doping rare earth elements into CaFeAsF. EPL 2018, 85, 67003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preinfalk, C.; Morteani, G. The industrial applications of rare earth elements. In Lanthanides, Tantalum and Niobium: Mineralogy, Geochemistry, Characteristics of Primary Ore Deposits, Prospecting, Processing and Applications, Proceedings of a workshop in Berlin, November 1986; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, E.; Wallington, T.; Sherman, A.; Everson, M.; Field, F.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R. An assessment of the rare earth element content of conventional and electric vehicles. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf. 2012, 5, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, E. Rare earth elements: Therapeutic and diagnostic applications in modern medicine. Clin. Med. Rep. 2018, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, L.; Nordberg, G.; Nurchi, V.; Aaseth, J. Gadolinium in medical imaging—usefulness, toxic reactions and possible countermeasures—A review. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, D.; Suresh, A.; Holton, G.; McKeown, C.; Wang, W.; Gu, B.; Mortensen, N. Effects of engineered cerium oxide nanoparticles on bacterial growth and viability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7981–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya, N.; Solomon, F.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. Effects of dysprosium oxide nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkes, S.; McCleskey, C. The bacteriostatic activity of cerium, lanthanum and thallium. J. Bacteriol. 1947, 54, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, T. Microbial communities in rare earth mining soil after in-situ leaching mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, N.; Hughes, A.; Lim, S.; Vernon, C. Rare earth elements: Overview of mining, mineralogy, uses, sustainability and environmental impact. Resources 2014, 3, 614–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, A.; Dohnalkova, A.; Shutthanandan, V.; Kovarik, L.; Chang, E.; Swavel, A.; Mason, H.; Reed, D.; Ye, C.; Hynes, W.; et al. Microbe encapsulation for selective rare-earth recovery rom electronic waste leachates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13888–13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalah, J.; Espina, G.; Blamey, L.; Munoz-Ibacache, S.; Blamey, J. Advantage of using extremophilic bacteria for the biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles and its potential for rare earth element recovery. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 855077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daumann, L. A natural lanthanide-binding protein facilitates separation and recovery of rare earth elements. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddanna, M.; Baral, S. Bioleaching of rare earth elements from spend fluid catalytic cracking catalyst using Acidothiobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denholm, C.; Johnson, D.; Taylor, W.; Shearer, R.; Danehy, T.; Busler, S.; Dunn, M. Case Study: The Jennings System—Over a decade of successful passive treatment. In Proceedings of the America Society of Mining and Reclamation, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–11 June 2010; pp. 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datashead. Available online: https://www.datashed.org/index.php/project-slippery-rock-elementary-wetland (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Western Pennsylvania Conservancy. Available online: https://waterlandlife.org/land-conservation/explore-our-preserves/wolf-creek-narrows-natural-area/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Yurkov, V.; Stackebrandt, E.; Holmes, A.; Fuerst, J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Golecki, J.; Gad’on, N.; Gorlenko, V.; Kompantseva, E.; Drews, G. Phylogenetic positions of novel aerobic bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacteria and description of Roseococcus thiosulfatophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., Erythromicrobium ramosum gen. nov., sp. nov., and Erythrobacter litoralis sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Kuo, T. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of gram-negative bacterial genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Jaiswal, R. Metal resistance in Pseudomonas strains isolated from soil treated with industrial wastewater. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talburt, D.; Johnson, G. Some effects of rare earth elements and Yttrium on microbial growth. Mycologia 1967, 59, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techer, D.; Grosjean, N.; Sohm, B.; Blaudez, D.; Le, M. Not merely noxious? Time-dependent hormesis and differential toxic effects systematically induced by rare earth elements in Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5640–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Ozaki, T.; Ohnuki, T.; Francis, A. Adsorption of rare earth elements by γ-Al2O3 and Pseudomonas fluorescens cells in the presence of desferrioxamine B: Implications of siderophores for the Ce anomaly. Chem. Geol. 2004, 212, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, A32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, W.; Desouky, O.; Jussien, S. Bioleaching of some rare earth elements from Egyptian monazite using Aspergillus ficuum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 11, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.; Auling, G.; Coto, O.; Nies, D. High-level resistance to cobalt and nickel but probably no transenvelope efflux: Metal resistance in the Cuban Serratia marcescens strain C-1. Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 53, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageswaran, N.; Ramteke, P.; Verma, O.; Pande, A. Antibiotic susceptibility and heavy metal tolerance pattern of Serratia marcescens isolated from soil and water. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2012, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaban, T.; Mohsen, Y.; Esseddine, Z.; Ghssein, G. Overview of Yersinia pestis metallophores: Yersiniabactin and yersinopine. Biology 2023, 12, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmaled, Y.; Halouane, A.; Hacene, H.; Fardeau, M.-L. Resistance to heavy metals and bioaccumulation of lead and zinc by Chryseobacterium solincola strain 1YB-R12T isolated from soil. Int. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 6, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, C.-E.; Gorniak, L.; Riedel, S.; Westermann, M.; Kusel, K. Lanthanide-dependent methylotrophs of the family Beijerinckiaceae: Physiological and genomic insights. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 86, e01830-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotruvo, J.; Featherston, E.; Mattocks, J.; Ho, J.; Laremore, T. Lanmodulin: A highly selective lanthanide-binding protein from a lanthanide-utilizing bacterium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15056–15061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrmann, M.; Billard, P.; Martin-Meriadec, A.; Zegeye, A.; Klebensberger, J. Functional role of lanthanides in enzymatic activity and transcriptional regulation of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent alcohol dehydrogneases in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. mBio 2017, 8, e00570-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachieng’a, L.; Unuofin, J. The potentials of biofilm reactor as a resource for the recuperation of rare earth metals/elements from wastewater: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44755–44767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.-S.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-C. Use of phosphate solubilizing bacteria to leach rare earth elements from monazite-bearing ore. Minerals 2015, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Ce | Dy | Er | Eu | Gd | Ho | La | Lu | Nd | Pr | Sm | Sc | Tb | Tm | Yb | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES1 | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + |
| ES2 | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| ES3 | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| ES4 | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | + |
| J1 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| J2 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| WC1 | ++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| WC2 | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Strain | Nearest Relative | Isolation Source |
|---|---|---|
| ES1 | Pseudomonas oryziphila (99.93%) | Slippery Rock Elementary Wetland |
| ES2 | Chryseobacterium vietnamense (98.99%) | Slippery Rock Elementary Wetland |
| ES3 | Pseudomonas rhizophila (99.48%) | Slippery Rock Elementary Wetland |
| ES4 | Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis (99.70%) | Slippery Rock Elementary Wetland |
| J1 | Yersinia entomophaga (99.63%) | Jennings |
| J2 | Serratia fonticola (99.41%) | Jennings |
| WC1 | Pseudomonas mosselii (99.80%) | Wolf Creek |
| WC2 | Pseudomonas hamedanensis (99.63%) | Wolf Creek |
| Rare Earth Element | Ionic Radii (Å) * | Average Zone of Metallophore Activity (mm) | E. coli EC50 During Exponential Phase (µM) # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scandium (Sc) | 0.87 | 21.38 | 1.10 |
| Lutetium (Lu) | 0.98 | 9.75 | 3.00 |
| Ytterbium (Yb) | 0.99 | 12.00 | 3.98 |
| Thulium (Tm) | 0.99 | 16.50 | 6.30 |
| Erbium (Er) | 1.00 | 13.54 | 8.30 |
| Holmium (Ho) | 1.02 | 9.33 | 17.40 |
| Yttrium (Y) | 1.02 | 4.67 | 7.60 |
| Dysprosium (Dy) | 1.03 | 6.25 | 18.60 |
| Terbium (Tb) | 1.04 | 13.83 | 21.90 |
| Gadolinium (Gd) | 1.05 | 5.33 | 17.20 |
| Europium (Eu) | 1.07 | 17.67 | 20.50 |
| Samarium (Sm) | 1.08 | 9.71 | 17.20 |
| Neodymium (Nd) | 1.11 | 6.50 | 19.40 |
| Praseodymium (Pr) | 1.13 | 25.25 | 27.40 |
| Cerium (Ce) | 1.14 | 11.00 | 19.70 |
| Lanthanum (La) | 1.16 | 7.17 | 18.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skeba, S.; Snyder, M.; Maltman, C. Metallophore Activity toward the Rare Earth Elements by Bacteria Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Due to Coal Mining. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112672
Skeba S, Snyder M, Maltman C. Metallophore Activity toward the Rare Earth Elements by Bacteria Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Due to Coal Mining. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkeba, Stephanie, Morgan Snyder, and Chris Maltman. 2023. "Metallophore Activity toward the Rare Earth Elements by Bacteria Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Due to Coal Mining" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112672
APA StyleSkeba, S., Snyder, M., & Maltman, C. (2023). Metallophore Activity toward the Rare Earth Elements by Bacteria Isolated from Acid Mine Drainage Due to Coal Mining. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112672





