Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. DNA Extraction, Metagenomic Sequencing and Sequence Assembly
2.3. Abundance Assessment of Community Composition and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Molecular Ecological Network Analysis nad Cohesion Calculated
3. Results
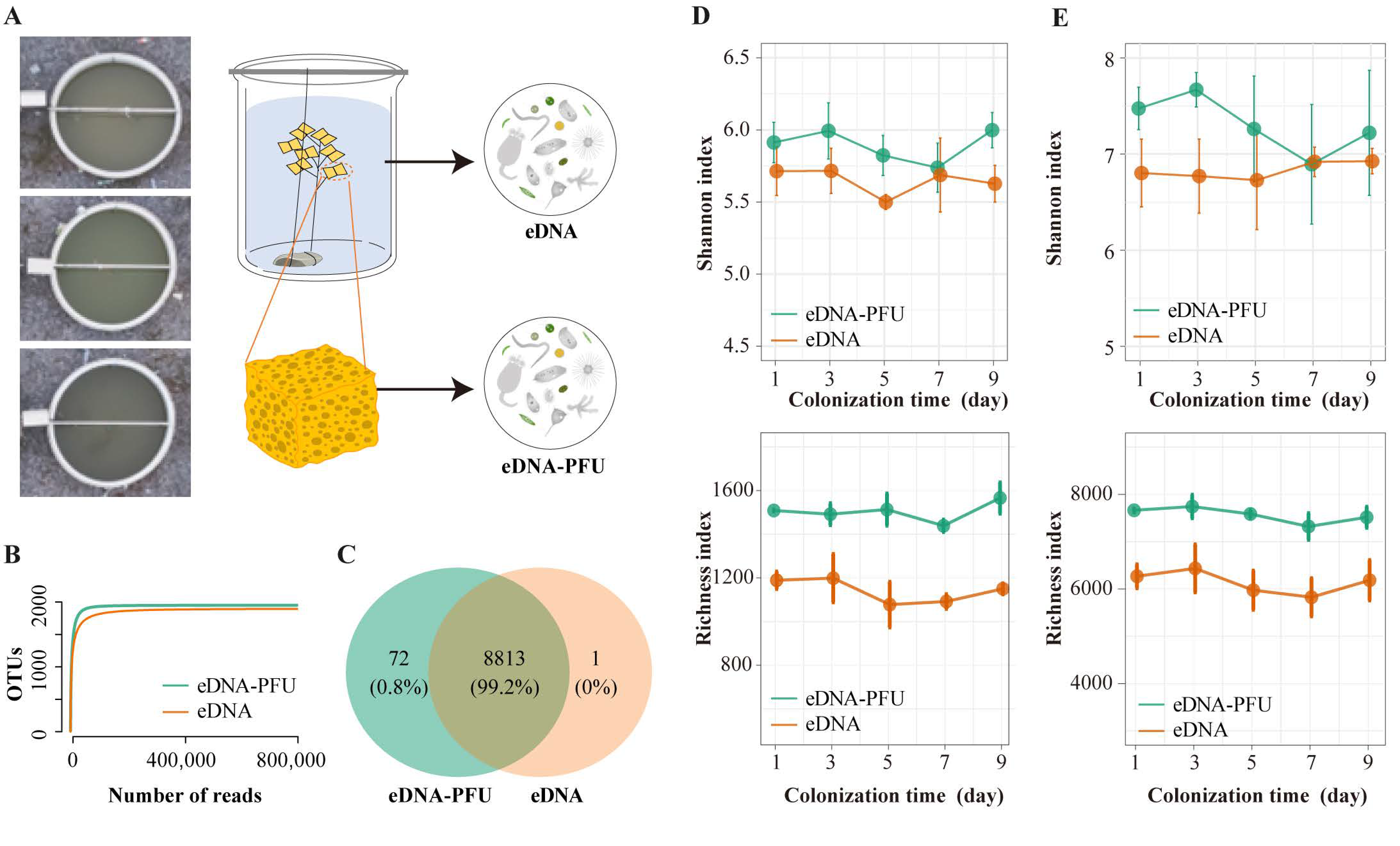
3.1. Overview of Sequencing Data and Microbe Diversity Varied
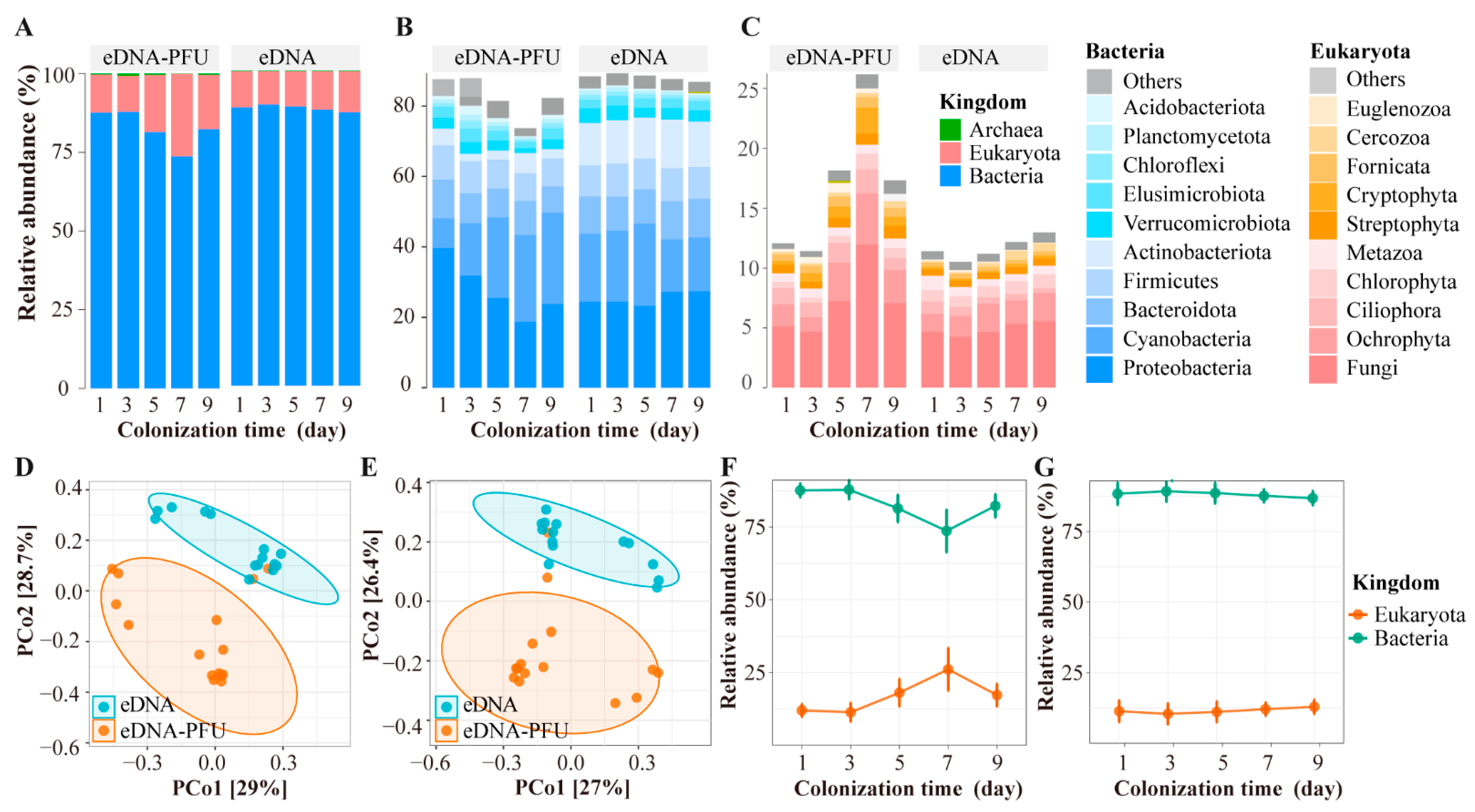
3.2. The Global Picture of Microbe Community Composition
3.3. Colonizational Dynamic Patterns of Microbial Community
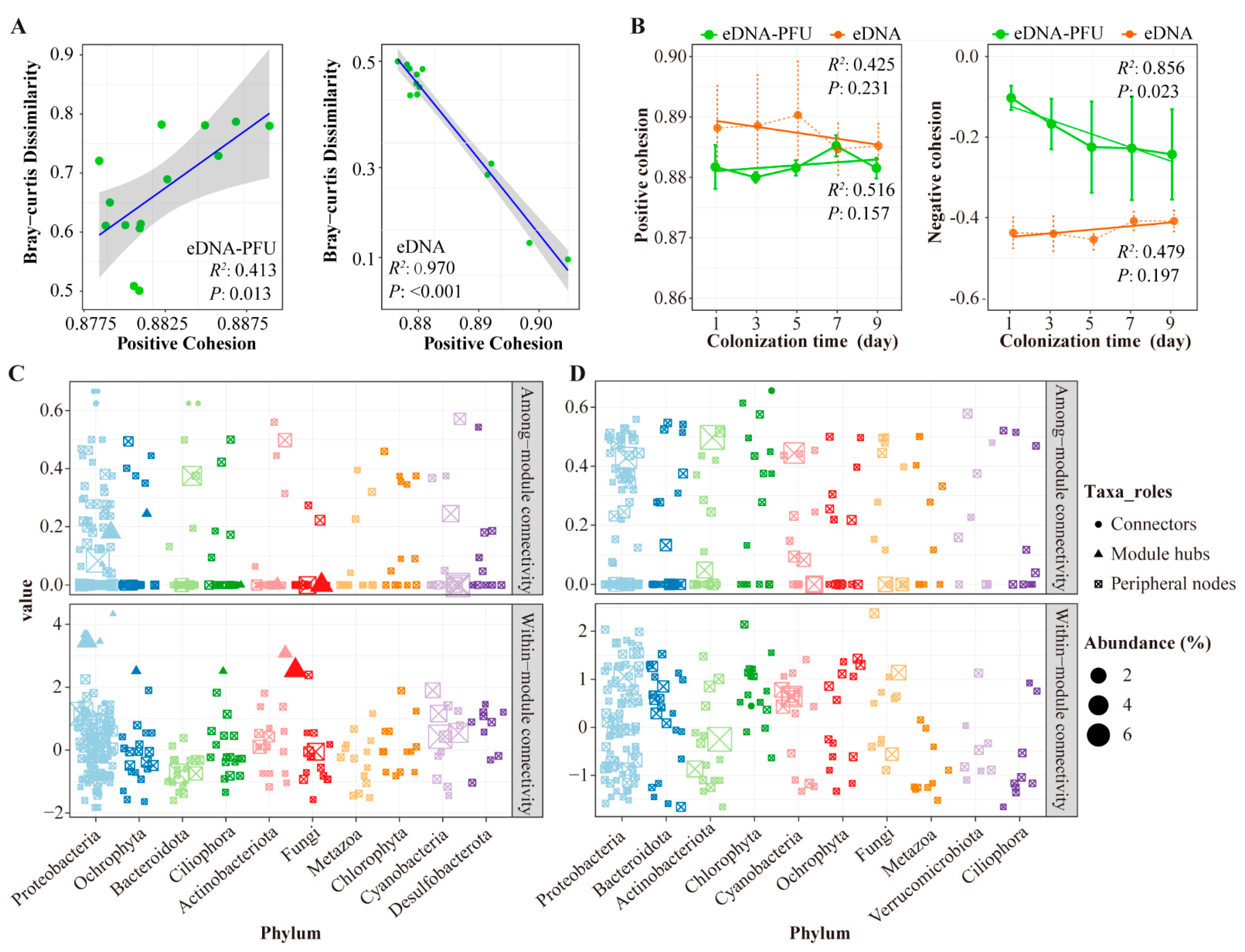
3.4. Molecular Ecological Network of Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficiency of the eDNA-PFU Method in Mesocosm Experiments for Bioassessments
4.2. Colonization Patterns of Microbial Community in Mesocosm Experiments
4.3. Molecular Ecological Network among Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimm, S.L.; Jenkins, C.N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T.M.; Gittleman, J.L.; Joppa, L.N.; Raven, P.H.; Roberts, C.M.; Sexton, J.O. The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection. Science 2014, 344, 1246752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, S.; Alatawi, A.M.M. Aquatic Ecosystem and Biodiversity: A Review. Open J. Ecol. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Silliman, B.R. Climate Change, Human Impacts, and Coastal Ecosystems in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. CB 2019, 29, R1021–R1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.; Dahlberg, M.L.; Dickson, K.L.; Smith, N.; Waller, W.T. The relationship of fresh-water protozoan communities to the MacArthur-Wilson equilibrium model. Am. Nat. 1969, 103, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Gu, M.; Gong, X.; Shi, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, X. Modern Biomonitoring Techniques Using Freshwater Microbiota; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.F.; Gong, X.J.; Gu, M. Studies of biological monitoring by using PFU protiozoa communtiy. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1985, 9, 299–308. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chung, P.R.; Cho, K.S.; Jung, Y.H.; Shen, Y.F.; Gu, M.; Feng, W.S. Biological evaluation of running waters in Korea, with special reference to bioassessment using the PFU system. Hydrobiologia 1998, 390, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Cao, H.; Xie, P.; Deng, D.; Feng, W.; Xu, J. Use of PFU protozoan community structural and functional characteristics in assessment of water quality in a large, highly polluted freshwater lake in China. J. Environ. Monit. JEM 2005, 7, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.G.; Wu, S.G.; Shen, Y.F. Effects of seasonal succession and water pollution on the protozoan community structure in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Warren, A.; Song, W. An approach to determining the sampling effort for analyzing biofilm-dwelling ciliate colonization using an artificial substratum in coastal waters. Biofouling 2011, 27, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhong, X.; Guo, C.; Gui, Y.; Xu, H. Colonization dynamics of protozoan communities in marine bioassessment surveys using two modified sampling systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.P.; Port, J.A.; Yamahara, K.M.; Martone, R.G.; Lowell, N.; Thomsen, P.F.; Mach, M.E.; Bennett, M.; Prahler, E.; Caldwell, M.R.; et al. Environmental monitoring. Harnessing DNA to improve environmental management. Science 2014, 344, 1455–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Machler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursiere-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, D.M.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New, F.N.; Brito, I.L. What Is Metagenomics Teaching Us, and What Is Missed? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, J.A.; Mahon, A.R. From molecules to management: Adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejean, T.; Valentini, A.; Miquel, C.; Taberlet, P.; Bellemain, E.; Miaud, C. Improved detection of an alien invasive species through environmental DNA barcoding: The example of the American bullfrogLithobates catesbeianus. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Q.; Xiong, J.; Huang, J.; Feng, W.S.; Gong, Y.C.; Miao, W. Microbial community biomonitoring- eDNA-PFU method. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 1400–1404. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.S.; Aschan, M.; Carr, M.R.; Clarke, K.R.; Green, R.H.; Pearson, T.H.; Rosenberg, R.; Warwick, R.M. Analysis of Community Attributes of the Benthic Macrofauna of Frierfjord-Langesundfjord and in a Mesocosm Experiment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 46, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Mitsch, W.J. Scaling considerations of mesocosm wetlands in simulating large created freshwater marshes. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 18, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.I.A.; Dossena, M.; Bohan, D.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kordas, R.L.; Ledger, M.E.; Meerhoff, M.; Moss, B.; Mulder, C.; Shurin, J.B.; et al. Mesocosm Experiments as a Tool for Ecological Climate-Change Research. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2013, 48, 71–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 12990-1991; Water Quality—Microbial Community Biomonitoring—PFU Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1991. (In Chinese)
- Stewart, C.; Via, L.E. A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR applications. Biotechniques 1993, 14, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porebski, S.; Bailey, L.G.; Baum, B.R. Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1997, 15, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockner, F.O.; Yilmaz, P.; Quast, C.; Gerken, J.; Beccati, A.; Ciuprina, A.; Bruns, G.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Westram, R.; et al. 25 years of serving the community with ribosomal RNA gene reference databases and tools. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Subgroup, G.P.D.P. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Tang, B.; Li, C.; Kou, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Kou, X.; Li, J.; et al. Protein expression landscape of mouse embryos during pre-implantation development. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3957–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinf. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.M.; McMahon, K.D. Cohesion: A method for quantifying the connectivity of microbial communities. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh, D.; Norf, H.; Weitere, M. Response of biofilm-dwelling ciliate communities to enrichment with algae. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 63, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H. Colonization dynamics of trophic-functional patterns of PFU protozoan communities in Dongchang Lake, northern China. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2012, 27, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, H. Colonization dynamics in body-size spectrum of protozoan periphytons for marine bioassessment using two modified sampling systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xu, G.; Min, G.S.; Kim, S.; Xu, H. Can tidal events influence monitoring surveys using periphytic ciliates based on biological trait analysis in marine ecosystems? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Xu, G.; Min, G.-S.; Kim, S.; Xu, H. Insight into tidal disturbance on colonization surveys for marine bioassessment using periphytic ciliates based on biological trait analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigee, D.C. Freshwater Microbiology: Biodiversity and Dynamic Interactions of Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment. Transl. Interpret. 2005, 3, 401–441. [Google Scholar]
- Mille-Lindblom, C. Interactions between Bacteria and Fungi on Aquatic Detritus—Causes and Consequences. In Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis; Uppsala University Library: Uppsala, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Romaní, A.M.; Fischer, H.; Mille-Lindblom, C.; Tranvik, L.J. Interactions of Bacteria and Fungi on Decomposing Litter: Differential Extracellular Enzyme Activities. Ecology 2006, 87, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risse-Buhl, U.; Kusel, K. Colonization dynamics of biofilm-associated ciliate morphotypes at different flow velocities. Eur. J. Protistol. 2009, 45, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, J.K.; Norf, H.; Arndt, H.; Weitere, M. Role of dispersal in shaping communities of ciliates and heterotrophic flagellates within riverine biofilms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppellotti, O.; Matarazzo, P. Ciliate colonization of artificial substrates in the Lagoon of Venice. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2000, 80, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, M.N.A.; Xu, H. Seasonal variations in colonization dynamics of periphytic protozoa in coastal waters of the Yellow Sea, northern China. Eur. J. Protistol. 2020, 72, 125643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Choi, J.K.; Yang, E.J.; Lee, K.C.; Lei, Y. Biomonitoring of coastal pollution status using protozoan communities with a modified PFU method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Min, G.S.; Choi, J.K.; Jung, J.H.; Park, M.H. An approach to analyses of periphytic ciliate colonization for monitoring water quality using a modified artificial substrate in Korean coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, I.-S.; Park, Y.-S. Food Chains and Food Webs in Aquatic Ecosystems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linglin, W.; Zhifan, C.; Jia, G.; Lihui, T.; Lijuan, R.; Boping, H.; Qinglong, W. Principle and application of co-occurrence networks for freshwater ecosystem assessment. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1765–1787. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan, S.F.M.; Ji, L.; Schädler, M.; Wu, Y.-T.; Sansupa, C.; Tanunchai, B.; Buscot, F.; Purahong, W. Future climate conditions accelerate wheat straw decomposition alongside altered microbial community composition, assembly patterns, and interaction networks. ISME J. 2022, 17, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | eDNA-PFU | eDNA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical Network | Random Network | Empirical Network | Random Network | |
| Nodes | 332 | 332 | 255 | 255 |
| Edges | 2242 | 2242 | 2550 | 2550 |
| Average degree | 13.51 | 13.50 ± 0.001 | 20 | 9.05 ± 1.18 |
| Average path length | 4.00 | 2.52 ± 0.002 | 2.64 | 2.11 ± 0.0026 |
| Network diameter | 12 | 4 ± <0.001 | 9 | 3.01 ± 0.1 |
| Clustering coefficient | 0.62 | 0.041 ± 0.002 | 0.58 | 0.078 ± 0.001 |
| Centralization degree | 0.12 | 0.035 ± 0.005 | 0.133 | 0.0517 ± 0.006 |
| Heterogeneity | 1.04 | 1.04 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Connectance | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.079 | 0.079 |
| Centralization betweenness | 0.12 | 0.01 ± 0.003 | 0.045 | 0.007 ± 0.001 |
| Centralization closeness | 0.16 | 0.09 ± 0.013 | 1.31 | 0.092 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Zhang, P.; Luo, S.; Chen, K.; Jiang, C.; Xiong, J.; Miao, W. Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102498
Gu S, Zhang P, Luo S, Chen K, Jiang C, Xiong J, Miao W. Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102498
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Siyu, Peng Zhang, Shuai Luo, Kai Chen, Chuanqi Jiang, Jie Xiong, and Wei Miao. 2023. "Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102498
APA StyleGu, S., Zhang, P., Luo, S., Chen, K., Jiang, C., Xiong, J., & Miao, W. (2023). Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems. Microorganisms, 11(10), 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102498






