Estimated Incidence of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Lublin, Poland in 2021
Abstract
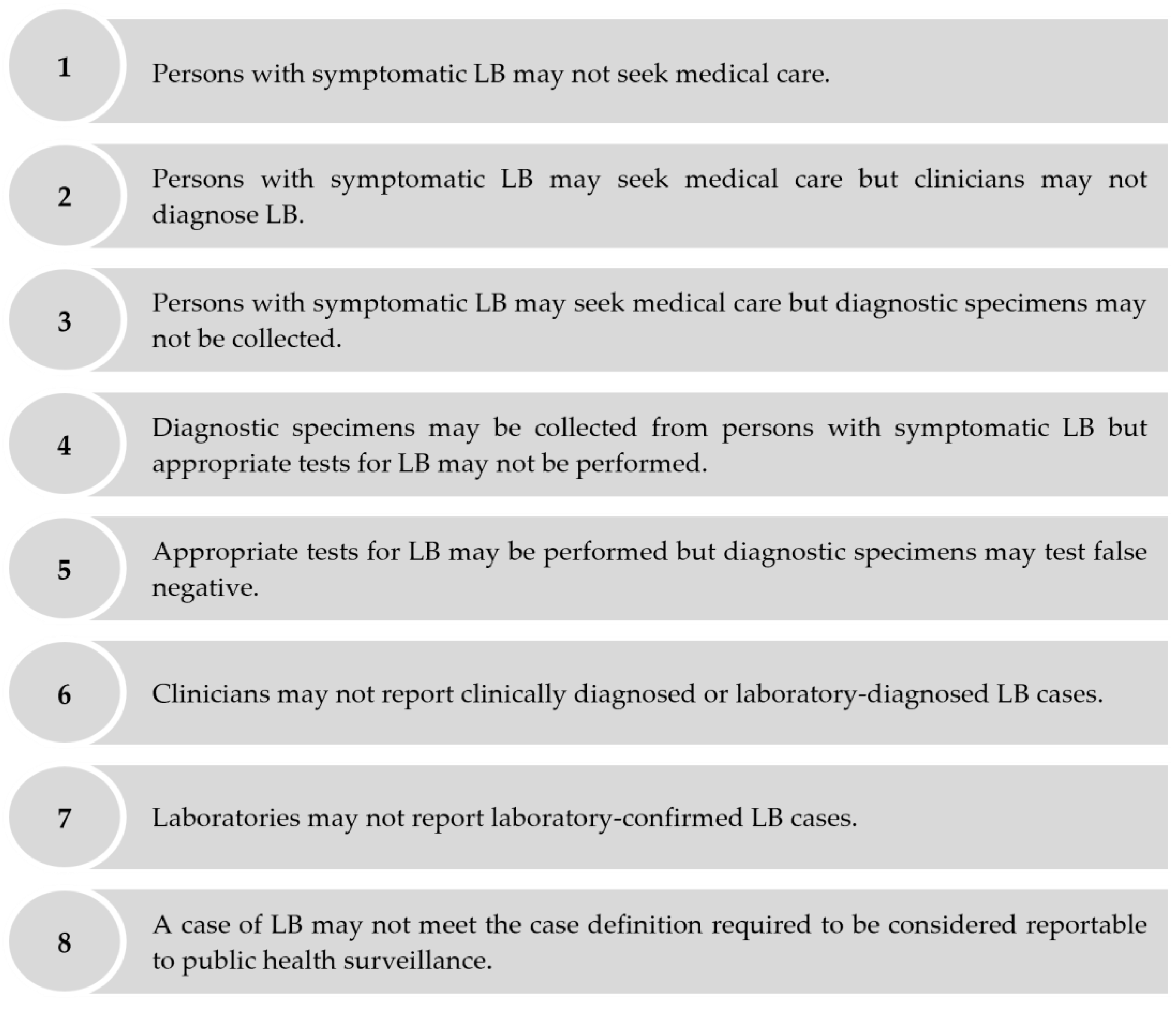
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seroprevalence Literature Search
2.2. Additional Literature Searches
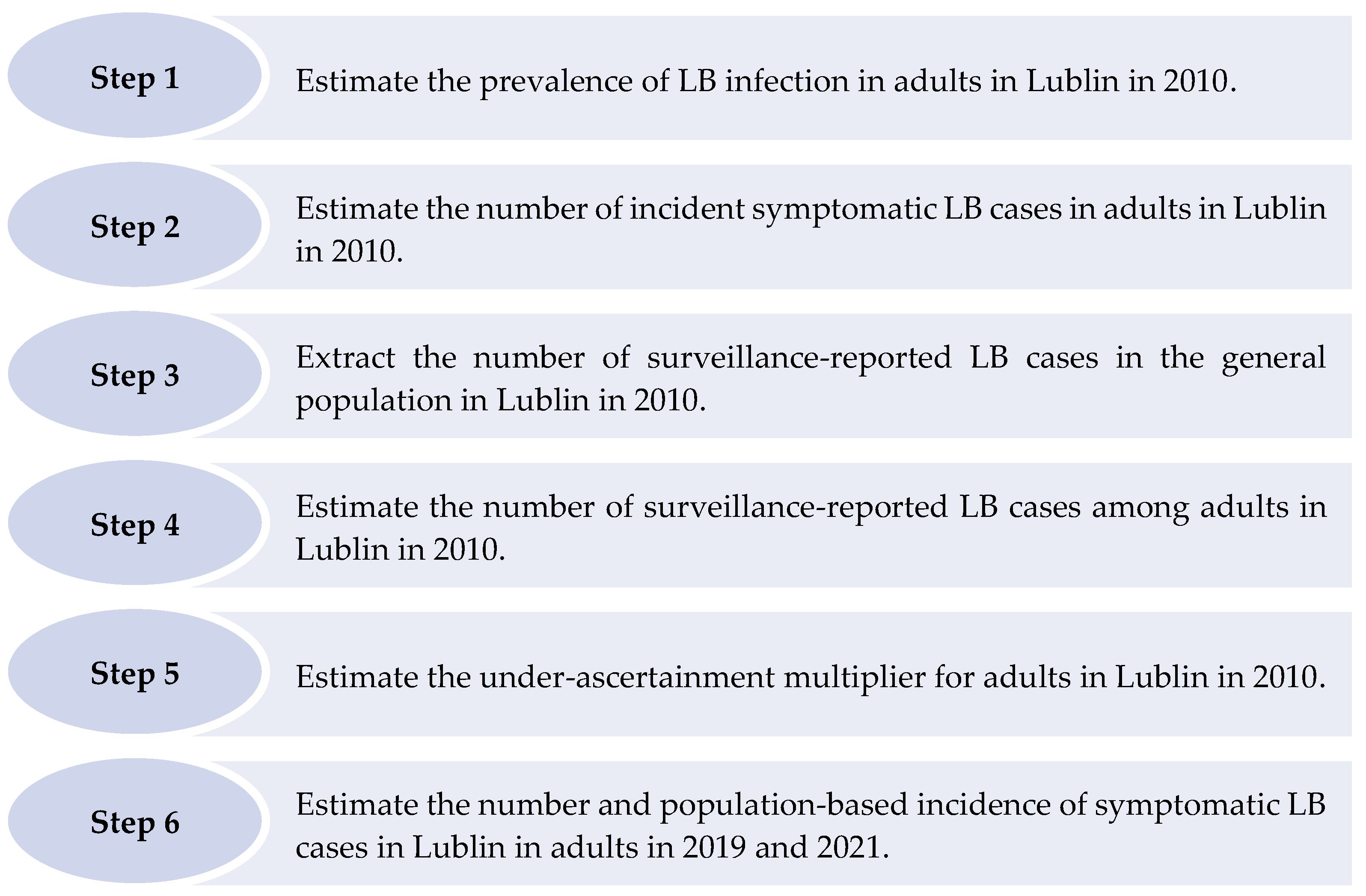
2.3. Estimation of the Number and Incidence of Adult Symptomatic LB Cases in Lublin in 2021
2.3.1. Step 1: Estimate the Prevalence of LB Infection in Adults in Lublin in 2010
2.3.2. Step 2: Estimate the Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults in Lublin in 2010
2.3.3. Step 3: Extract the Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in the General Population in Lublin in 2010
2.3.4. Step 4: Estimate the Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases among Adults in Lublin in 2010
2.3.5. Step 5: Estimate the Under-Ascertainment Multiplier for Adults in Lublin in 2010
2.3.6. Step 6: Estimate the Number and Population-Based Incidence of Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults in Lublin in 2021 (and 2019)
2.4. Duration of Antibody Detection Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Step 1: Estimate the Prevalence of LB Infection in Adults in Lublin in 2010
3.2. Step 2: Estimate the Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults in Lublin in 2010
3.3. Step 3: Extract the Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in the General Population in Lublin
3.4. Step 4: Estimate the Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases among Adults in Lublin in 2010
3.5. Step 5: Estimate the Under-Ascertainment Multiplier for Adults in Lublin in 2010
3.6. Step 6: Estimate the Number and Incidence of Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults in Lublin in 2021 (and 2019)
3.7. Duration of Antibody Detection Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Borrelia burgdorferi | B. burgdorferi |
| LB | Lyme borreliosis |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunoassay |
References
- Cardenas-de la Garza, J.A.; De la Cruz-Valadez, E.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Welsh, O. Clinical Spectrum of Lyme Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.T.; Keen, C.L.; Huntley, A.C.; Gershwin, M.E. Lyme Disease: A Rigorous Review of Diagnostic Criteria and Treatment. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 57, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.; Strle, F.; Wormser, G.P. Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradowska-Stankiewicz, I.; Zbrzeźniak, J.; Skufca, J.; Nagarajan, A.; Ochocka, P.; Pilz, A.; Vyse, A.; Begier, E.; Dzingina, M.; Blum, M.; et al. A Retrospective Database Study of Lyme Borreliosis Incidence in Poland from 2015 to 2019: A Public Health Concern. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.; Angulo, F.J.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Lipsitch, M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Jernigan, D.; Finelli, L. Estimates of the Prevalence of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009, United States, April–July 2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 2004–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, F.J.; Finelli, L.; Swerdlow, D.L. Estimation of US SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Symptomatic Infections, Hospitalizations, and Deaths Using Seroprevalence Surveys. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2033706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, P.S.; Slutsker, L.; Dietz, V.; McCaig, L.F.; Bresee, J.S.; Shapiro, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.V. Food-Related Illness and Death in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States—Major Pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Griffin, P.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Hoekstra, R.M. Foodborne Illness Acquired in the United States--Unspecified Agents. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.L.; Mangen, M.-J.J.; Plass, D.; Havelaar, A.H.; Brooke, R.J.; Kramarz, P.; Peterson, K.L.; Stuurman, A.L.; Cassini, A.; Fèvre, E.M.; et al. Measuring Underreporting and Under-Ascertainment in Infectious Disease Datasets: A Comparison of Methods. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Pilz, A.; Halsby, K.; Kelly, P.; Turunen, J.; Åhman, H.; Stark, J.; Jodar, L. Estimated Number of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Adults in Finland in 2021 Using Seroprevalence Data to Adjust the Number of Surveillance-Reported Cases: A General Framework for Accounting for Underascertainment by Public Health Surveillance. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Pilz, A.; Halsby, K.; Kelly, P.; Brestrich, G.; Stark, J.H.; Jodar, L. Estimated Number of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Germany in 2021 after Adjusting for Under-Ascertainment. Public Health 2023, 219, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gańczak, M.; Miazgowski, T.; Kożybska, M.; Kotwas, A.; Korzeń, M.; Rudnicki, B.; Nogal, T.; Andrei, C.L.; Ausloos, M.; Banach, M.; et al. Changes in Disease Burden in Poland between 1990–2017 in Comparison with Other Central European Countries: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, L.; Pilz, A.; Vyse, A.; Gutiérrez Rabá, A.V.; Angulo, F.J.; Tran, T.M.P.; Fletcher, M.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Moïsi, J.C.; Stark, J.H. Seroprevalence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: Results from a Systematic Literature Review (2005–2020). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisak, E.; Chmielewska-Badora, J.; Zwoliński, J.; Wojcik-Fatla, A.; Zajac, V.; Skórska, C.; Dutkiewicz, J. Study on Lyme Borreliosis Focus in the Lublin Region (Eastern Poland). Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2008, 15, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Tokarska-Rodak, M.; Plewik, D.; Kozioł-Montewka, M.; Szepeluk, A.; Paszkiewicz, J. Risk of occupational infections caused by borrelia burgdorferi among forestry workers and farmers. Med. Pr. 2014, 65, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, P.; Petersen, J.; Hinckley, A. Updated CDC Recommendation for Serologic Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, M.; Golestani, M.; Kerl, H.; Müllegger, R.R. Clinical Relevance of Different IgG and IgM Serum Antibody Responses to Borrelia Burgdorferi After Antibiotic Therapy for Erythema Migrans: Long-Term Follow-up Study of 113 Patients. Arch. Dermatol. 2006, 142, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammers-Berggren, S.; Lebech, A.M.; Karlsson, M.; Svenungsson, B.; Hansen, K.; Stiernstedt, G. Serological Follow-up after Treatment of Patients with Erythema Migrans and Neuroborreliosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalish, R.A.; McHugh, G.; Granquist, J.; Shea, B.; Ruthazer, R.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia Burgdorferi 10–20 Years after Active Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltomaa, M.; McHugh, G.; Steere, A.C. Persistence of the Antibody Response to the VlsE Sixth Invariant Region (IR 6 ) Peptide of Borrelia Burgdorferi after Successful Antibiotic Treatment of Lyme Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woudenberg, T.; Böhm, S.; Böhmer, M.; Katz, K.; Willrich, N.; Stark, K.; Kuhnert, R.; Fingerle, V.; Wilking, H. Dynamics of Borrelia Burgdorferi-Specific Antibodies: Seroconversion and Seroreversion between Two Population-Based, Cross-Sectional Surveys among Adults in Germany. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofhuis, A.; Herremans, T.; Notermans, D.W.; Sprong, H.; Fonville, M.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; van Pelt, W. A Prospective Study among Patients Presenting at the General Practitioner with a Tick Bite or Erythema Migrans in The Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowicz, M.; Schötta, A.-M.; Höss, D.; Kundi, M.; Schray, C.; Stockinger, H.; Stanek, G. Infections with Tickborne Pathogens after Tick Bite, Austria, 2015–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsson, P.; Lindblom, P.; Fryland, L.; Ernerudh, J.; Forsberg, P.; Lindgren, P.-E. Prevalence, Diversity, and Load of Borrelia Species in Ticks That Have Fed on Humans in Regions of Sweden and Åland Islands, Finland with Different Lyme Borreliosis Incidences. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsson, P.; Fryland, L.; Lindblom, P.; Sjöwall, J.; Ahlm, C.; Berglund, J.; Haglund, M.; Henningsson, A.J.; Nolskog, P.; Nordberg, M.; et al. A Prospective Study on the Incidence of Borrelia Burgdorferi Sensu Lato Infection after a Tick Bite in Sweden and on the Åland Islands, Finland (2008–2009). Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Péter, O.; Kondrusik, M.; Moniuszko, A.; Zajkowska, J.; Dunaj, J.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Pancewicz, S. Assessment of the Frequency of Different Borrelia Burgdorferi Sensu Lato Species in Patients with Lyme Borreliosis from North-East Poland by Studying Preferential Serologic Response and DNA Isolates. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kubiak, K.; Dzika, E.; Równiak, J.; Dziedziech, M.; Dzisko, J. Seroprevalence of Lyme Disease and Genospecies of Borrelia Burgdorferi Sensu Lato in Patients Diagnosed with Borreliosis in the Province of Warmia-Masuria in North-Eastern Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowska-Koszko, I.; Mnichowska-Polanowska, M.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Roszkowska, P.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Dołęgowska, B. Immunoreactivity of Polish Lyme Disease Patient Sera to Specific Borrelia Antigens—Part 1. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIPH-NIH-NRI Infectious Diseases and Poisonings in Poland Annual Report; National Institute of Public Health—National Institute of Hygiene—Department of Epidemiology, 2005–2021. Available online: http://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpage/epimeld/index_p.html#uu (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Statistics Poland. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/statistical-yearbooks/statistical-yearbooks/demographic-yearbook-of-poland-2022,3,16.html (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Burn, L.; Vyse, A.; Pilz, A.; Tran, T.M.P.; Fletcher, M.A.; Angulo, F.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Moïsi, J.C.; Stark, J.H. Incidence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: A Systematic Review (2005–2020). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, A.; Skufca, J.; Vyse, A.; Pilz, A.; Begier, E.; Riera-Montes, M.; Gessner, B.D.; Stark, J.H. The Landscape of Lyme Borreliosis Surveillance in Europe. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 23, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewska-Badora, J.; Moniuszko, A.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Zwoliński, J.; Piątek, J.; Pancewicz, S. Serological Survey in Persons Occupationally Exposed to Tick-Borne Pathogens in Cases of Co-Infections with Borrelia Burgdorferi, Anaplasma Phagocytophilum, Bartonella Spp. and Babesia Microti. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hens, N.; Aerts, M.; Faes, C.; Shkedy, Z.; Lejeune, O.; Van Damme, P.; Beutels, P. Seventy-Five Years of Estimating the Force of Infection from Current Status Data. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.; Mysterud, A.; Jore, S.; Viljugrein, H.; Bakka, H.; Vindenes, Y. Demographic Patterns in Lyme Borreliosis Seasonality over 25 Years. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, zph.13073, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbrzeźniak, J.; Paradowska-Stankiewicz, I. Lyme Disease in Poland in 2020. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2022, 76, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bézay, N.; Hochreiter, R.; Kadlecek, V.; Wressnigg, N.; Larcher-Senn, J.; Klingler, A.; Dubischar, K.; Eder-Lingelbach, S.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Leroux-Roels, G.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Novel Multivalent OspA-Based Vaccine Candidate against Lyme Borreliosis: A Randomised, Phase 1 Study in Healthy Adults. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Articles with Data from Poland 1 | B. afzelii | B. garinii | B. burgdorferi s.s. | B. valaisiana 2 | B. spielmenii 3 | B.miyamotoi 2 | Untypeable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grygorczuk et al., 2013 [27] (n = 30 sera samples) | 83.3% | 10.0% | 6.7% | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Kubiak et al., 2012 [28] (n = 259 sera samples) | 29.2% | 15.8% | 30.4% | -- | 4.3% | -- | 20.0% |
| Wojciechowska-Koszko et al., 2021 [29] (n = 53 sera samples) | 32.0% | 60.0% | -- | -- | -- | -- | 8.0% |
| Articles used to estimate the proportion of infections that are asymptomatic | |||||||
| Hofhuis et al., 2013 [23] (n = 56 Ixodes ricinus ticks removed from tick-bitten persons | 64.3% | 19.6% | 12.5% | 7.1% | -- | -- | -- |
| Markowicz et al., 2021 [24] (n = 194 Ixodes ricinus ticks removed from tick-bitten persons) | 68.0% | 16.5% | 7.7% | 7.2% | -- | -- | -- |
| Wilhelmsson et al., 2013 4, [25] Wilhelmsson et al., 2016 4 [26] (n = 178 Ixodes ricinus ticks removed from tick-bitten persons) | 48.3% | 23.6% | 2.2% | 7.9% | 3.0% | 1.0% | 13.0% |
| Estimated Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in Adults, 2010 | Estimated Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults, 2010 | Under-Ascertainment Multiplier(Based on 2010 Data) | Estimated Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in Adults, 2019 | Estimated Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults, 2019 | Estimated Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in Adults, 2021 | Estimated Number of Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults, 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 672 | 3975 | 5.9 | 1677 | 9894 | 1021 | 6204 |
| Estimated Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults, 2010 | Under-Ascertainment Multiplier (Based on 2010 data) | Estimated Number of Surveillance-Reported LB Cases in Adults, 2021 | Estimated Number of Incident Symptomatic LB Cases in Adults, 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Years | 20 Years | 5 Years | 20 Years | 5 Years | 20 Years | |
| 7951 | 1988 | 11.8 | 3.0 | 1021 | 12,048 | 3063 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colby, E.; Olsen, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Kelly, P.; Halsby, K.; Pilz, A.; Sot, U.; Chmielewski, T.; Pancer, K.; Moïsi, J.C.; et al. Estimated Incidence of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Lublin, Poland in 2021. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102481
Colby E, Olsen J, Angulo FJ, Kelly P, Halsby K, Pilz A, Sot U, Chmielewski T, Pancer K, Moïsi JC, et al. Estimated Incidence of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Lublin, Poland in 2021. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(10):2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102481
Chicago/Turabian StyleColby, Emily, Julia Olsen, Frederick J. Angulo, Patrick Kelly, Kate Halsby, Andreas Pilz, Urszula Sot, Tomasz Chmielewski, Katarzyna Pancer, Jennifer C. Moïsi, and et al. 2023. "Estimated Incidence of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Lublin, Poland in 2021" Microorganisms 11, no. 10: 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102481
APA StyleColby, E., Olsen, J., Angulo, F. J., Kelly, P., Halsby, K., Pilz, A., Sot, U., Chmielewski, T., Pancer, K., Moïsi, J. C., Jodar, L., & Stark, J. H. (2023). Estimated Incidence of Symptomatic Lyme Borreliosis Cases in Lublin, Poland in 2021. Microorganisms, 11(10), 2481. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11102481






