Abstract
Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) are phenotypically indistinguishable from the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus–A. baumannii (ACB) complex members using routine laboratory methods. Early diagnosis plays an important role in controlling A. baumannii infections and this could be assisted by the development of a rapid, yet sensitive diagnostic test. In this study, we developed an enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor for asymmetric PCR (aPCR) amplicon detection of the blaOXA-51-like gene in A. baumannii. A. baumannii blaOXA-51-like gene PCR primers were designed, having the reverse primer modified at the 5′ end with FAM. A blaOXA-51-like gene sequence-specific biotin labelled capture probe was designed and immobilized using a synthetic oligomer (FAM-labelled) deposited on the working electrode of a streptavidin-modified, screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE). The zot gene was used as an internal control with biotin and FAM labelled as forward and reverse primers, respectively. The blaOXA-51-like gene was amplified using asymmetric PCR (aPCR) to generate single-stranded amplicons that were detected using the designed SPCE. The amperometric current response was detected with a peroxidase-conjugated, anti-fluorescein antibody. The assay was tested using reference and clinical A. baumannii strains and other nosocomial bacteria. The analytical sensitivity of the assay at the genomic level and bacterial cell level was 0.5 pg/mL (1.443 µA) and 103 CFU/mL, respectively. The assay was 100% specific and sensitive for A. baumannii. Based on accelerated stability performance, the developed genosensor was stable for 1.6 years when stored at 4 °C and up to 28 days at >25 °C. The developed electrochemical genosensor is specific and sensitive and could be useful for rapid, accurate diagnosis of A. baumannii infections even in temperate regions.
1. Introduction
Acinetobacter baumannii has emerged as an important human health risk that is associated with nosocomial infections such as pneumonia, bacteraemia, urinary tract infection, and meningitis [1,2,3]. Infections due to A. baumannii are common among immunocompromised patients who are critically ill in intensive care units (ICUs) or among patients who have undergone major surgical procedures [4,5]. A major challenge faced by many clinicians is treatment options for patients infected with extensively multi-drug-resistant A. baumannii. Currently, there are limited antibiotic options available for the treatment of these infections, hence making A. baumannii infections a grave concern for public health worldwide [6,7,8].
Within a few decades, A. baumannii has demonstrated a remarkable ability to rapidly develop resistance against multiple antibiotics [1,9]. Using various mechanisms, multi-drug-resistant A. baumannii (MDRAB) exhibit resistance to several existing antibiotics, including β-lactams, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, and aminoglycosides [10,11,12]. Carbapenems are among the drugs of choice for treating nosocomial infections [13] but their efficiency has been increasingly compromised by the spread of carbapenem-resistant isolates, mostly following acquisition of Class D carbapenemases. Studies have shown that A. baumannii isolates with carbapenem resistance tend to be resistant to all classes of antimicrobials except polymyxins and tigecycline in some cases [8,14]. Though previously effective against MDRAB, resistance to polymyxins have been reported in some clinical strains classified as extensively resistant (XDR) or pan-resistant A. baumannii [15,16]. The most common mechanism of carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii is through the production of carbapenem-hydrolysing beta-lactamases [17]. Class D β-lactamases are the most prevalent carbapenemases in A. baumannii isolates [18,19]. In addition to acquired carbapenem-hydrolysing class D oxacillinase (CHDL) gene clusters, which are present either in the chromosome or in the plasmids of A. baumannii strains, and known mainly as blaOXA-23-, blaOXA-24/40-, and blaOXA-58-like genes [20], the chromosomal blaOXA-51-like gene, which is intrinsic to A. baumannii isolates, confers carbapenem resistance when an ISAba1 element is inserted upstream of the gene [21,22].
Antibiotic resistant pathogens contribute to increased cost of healthcare and prolonged hospitalizations [23]. The use of ineffective antibiotics results in over usage, which further leads to an increase in the already mounting challenge of drug resistance among pathogens, thereby making them more difficult to treat [24]. Hence, in addition to accurate diagnosis of A. baumannii infections, rapid differentiation of A. baumannii from other Acinetobacter species in clinical settings would significantly improve patient outcomes. A. baumannii infections are typically diagnosed in routine laboratory using conventional culture method and biochemical tests. However, these methods are time-consuming and labour-intensive, rendering them less effective for rapid diagnosis. Due to its major health threat, there is a growing demand for a rapid detection test for A. baumannii. Among emerging technologies available, DNA biosensor, an analytical device incorporating a single-stranded oligonucleotide (probe) linked with a physicochemical transducer, offers an interesting alternative test. In recent years, this technology has been studied widely as a potential novel method for the detection of DNA hybridization in various fields such as the diagnosis of diseases including cancer [25,26,27], the detection of infectious agents [28,29], drug screening [30,31,32], crops screening [33,34], and forensic applications [35,36].
Electrochemical biosensors are specific, sensitive, and rapid, making them suitable for identification of microorganisms in samples [37]. DNA biosensors (genosensors) are inherently stable physicochemically and rely on the distinctive nature of genetic information to specifically identify microorganisms in human infections [38]. Genosensors employ immobilized DNA (or RNA) probes on a physical transducer to detect a target with a complementary sequence to the probe, through hybridization. Biological signals generated by this interaction are then detected as electrical signals through transducers, using appropriate equipment. Target analytes can be detected using biosensors via indirect sensing (labelled system) or direct sensing (label-free system) [37,39]. An electrodeposited gold nanostructure-based electrochemical biosensor was reported for Enterococcus faecalis, which could detect 30.1 ng µL−1 genomic DNA [40]. A few works have also reported biosensors for A. baumannii detection. Yeh and co-workers [41] developed an electro-microchip system based on DNA hybridization of a PCR-amplified A. baumannii target using biotin-labelled primers and gold-streptavidin nanoparticles. An electrochemical biosensor that used a gold electrode labelled with electroactive β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) for A. baumannii detection has also been reported. The electrochemical signals generated by the reduction of β-CD were recorded using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) [42]. A more recent effort by Roushani and co-workers [43] showed the detection of A. baumannii from human serum samples using a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) on a glassy carbon electrode with electropolymerization of a dopamine monomer and A. baumannii template.
The use of screen-printed electrodes in biosensors confer the advantage of adaptability, ease of mass production, and selective specificity for target analytes, making biosensors suitable for rapid analysis on-site [44]. Additionally, among available transducer types, electrochemical biosensors have the advantage of having a high sensitivity, low detection limits, and flexibility for easy miniaturization [45]. Although some progress has been made towards accurate detection methods for detecting an important pathogen like A. baumannii, this study aimed to present an alternative detection for A. baumannii that is rapid, adaptable, and cost-effective, with applicability in both temperate and nontemperate climates. In this study, we developed a sequence-specific enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay for the detection of A. baumannii using a blaOXA-51-like gene as the target gene and a screen-printed carbon electrode. The adaptability and cost-effective nature of carbon electrodes in biosensor development is advantageous to this method. To facilitate more accurate detection, the zot gene was used as an internal control. We further evaluated the analytical sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic performance of this enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor. In addition, to determine the shelf-life of the assay at various temperatures, an accelerated stability evaluation of the enzyme-based, electrochemical, sequence-specific biosensor assay was performed. This novel rapid test may facilitate the early detection of infections caused by A. baumannii and consequently help doctors to make prompt decisions about appropriate antibiotic treatment for infected patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
Reference strains of A. baumannii ATCC 19606 and Shigella sonnei ATCC 25931, which served as positive and negative control templates, respectively, were used for optimization of aPCR protocol and the development of an enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor. A total of 76 clinical isolates were used in this study comprising 42 A. baumannii strains and 34 non-Acinetobacter bacterial pathogens (Table 1 and Table 2).

Table 1.
List of reference strains used in this study.

Table 2.
List of clinical strains used in this study.
2.2. Bacterial Culture and Growth
All isolates used in this study were maintained as stock culture in 15% glycerol and stored at −70 °C. For the working culture, the bacterial strains were revived from glycerol stock culture by inoculating a loop of culture into tryptone soy broth (TSB) and incubating it overnight at 37 °C. Each overnight culture was then sub-cultured overnight onto blood agar (for purity confirmation), MacConkey agar (for confirmation of the strain), and nutrient agar (NA; for lysate preparation) and incubated overnight at 37 °C.
2.3. Development and Pretreatment of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode (SPCE)
A screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCEs) was designed, and its fabrication was outsourced to a local company. The protocol was adapted from a previous study [46] with some modifications. The surface of SPCE was pre-washed with 100 µL of deionised water for 2 min (min). Subsequently, 5 µL of covalent agent [200 mM 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDAC), and 50 mM N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)] were applied on the working electrode (WE) for 10 min to activate the surface. This process allowed for hybridization between the biotinylated capture probe and the synthetic oligomer on the surface of the working electrode. Five microliters (µL) of 0.05 mg/mL streptavidin were then coated onto the WE. Next, 50 µL of 1 M ethanolamine hydrochloride was applied and incubated in the dark for 10 min to inactivate the surface of SPCEs. The carbon surface was then blocked with 50 µL of 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA). SPCE was washed with deionized water by dipping once after each incubation step. The development of the SPCE until the BSA application step was used for internal control (IC) gene detection, whereas SPCEs for target gene detection were immobilized with 5 µL of biotinylated capture probe after the washing of BSA. SPCEs were then incubated for 10 min at room temperature, followed by washing with phosphate buffer saline (PBS).
2.4. Preparation of DNA Samples for PCR Amplification
2.4.1. Lysate DNA Preparation
Lysate DNA was prepared by a boiling method. A single colony from an overnight culture on an NA plate was inoculated into 30 µL of water and boiled for 10 min. The lysate mixture was then centrifuged at 6000× g for 3 min and the supernatant containing the DNA was used for DNA templates during PCR amplification.
2.4.2. Genomic DNA Preparation
A single bacterial colony from an overnight culture was inoculated into 10 mL of TSB and incubated at 37 °C overnight. Cells were harvested on the following day by centrifuging at 8000× g for 5 min; the supernatant was discarded. A cell pellet was collected and bacterial genomic DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit® (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration of the purified genomic DNA was determined using a UV-VIS Biophotometer (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and stored at −20 °C.
2.4.3. Preparation of Internal Control (IC) Plasmid DNA
TOP10 E. coli cells were treated with chemicals (magnesium chloride and calcium chloride) to become competent cells. These chemically competent TOP10 cells were either used directly for transformation or preserved in 15% glycerol stock. IC plasmid was obtained from previously prepared laboratory stock. The transformation of plasmid into competent cells was performed using the heat-shock method. The screening of clones with desired DNA inserts was carried out, and the presence of the IC gene (zot) was checked by performing a standard PCR. IC plasmid was extracted from bacterial clones using NucleoSpin®® PlasmidQuickPure Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration of the purified IC recombinant plasmid was quantified using a UV-VIS Biophotometer (Eppendorf, Germany), and stored at −20 °C as a concentrated stock.
2.5. Preparation of aPCR Reaction Mixture
A pair of specific primers (Table 3) was designed to amplify a 135 bp-DNA sequence from the A. baumannii blaOXA-51-like gene. The employed primer pair was in an optimal 1:20 forward-to-reverse-primer concentration ratio for aPCR amplification of the target ssDNA. Twenty microliter aliquots of the aPCR mix containing 1 × Taq buffer, 2.0 mM of MgCl2, 200 µM of dNTP mix, 1.0 U of Taq DNA polymerase, 0.1 µM of blaOXA-51_F forward primer, and 1.0 µM of blaOXA-51_R reverse primer were prepared in 0.2 mL PCR tubes using PCR-grade water. The reaction mix was then amplified using the following parameters: 3 min at 95 °C followed by 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 seconds (s), 61 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. The amplification was further incubated for another 30 s at 61 °C and 5 min at 72 °C to extend any incomplete amplicons. The obtained aPCR amplicons were used directly for amperometric detection without any pretreatment or purification steps.

Table 3.
Details of oligomers used in this study.
2.6. Electrochemical Detection of Synthetic DNA and Amplicons
A complementary biotinylated capture probe (Table 3) was used for blaOXA-51-like gene detection. The biotin-labelled capture probe was immobilized on the WE electrode surface with one end free to capture the synthetic blaOXA-51-like target. After the washing step, 1 µM of the synthetic target was diluted with an equal volume of 4× sodium saline citrate (SSC) buffer and was applied on the WE surface. The SPCEs were then incubated for 20 min at room temperature. This process would allow hybridization between the biotinylated capture probe and the synthetic oligomer on the surface of the WE. Following this, the electrode was washed again with PBS to remove the unbound synthetic target. Five microliters of anti-fluorescein antibody in the ratio of 1:200 was applied onto the electrode surface and incubated for 5 min to allow binding of the enzyme with the fluorescein-labelled synthetic oligomer. The electrode was then washed with PBS prior to the addition of 70 µL of TMB:H2O2 (1:9) substrate onto the sensing area of SPCE. The electrode was subjected to 5 s incubation at 0 V standby potential, followed by amperometric measurement at −0.2 V for 60 secs with an interval time of 0.2 s. The current value at the end of the measurement period was recorded. For this electrochemical genosensor assay, aPCR technique was performed to generate single-strand DNA of the target blaOXA-51-like gene for hybridization with the complementary capture probe, whereas the internal control (IC) gene was produced in double-stranded form for streptavidin–biotin binding. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram for single-strand target blaOXA-51-like gene detection by the electrochemical genosensor assay.
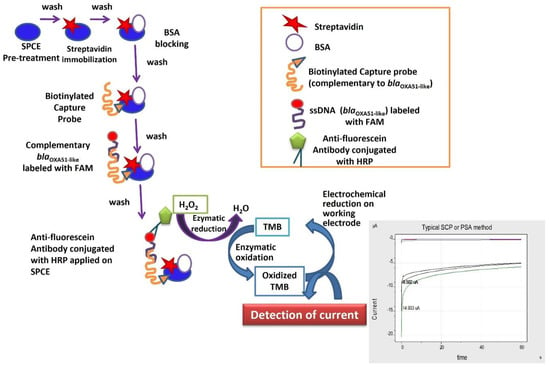
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of the developed electrochemical genosensor assay for detection of A. baumannii.
2.7. Analytical Evaluation of the Electrochemical Genosensor
2.7.1. Analytical Specificity
The analytical specificity of the electrochemical genosensor assay was conducted using 30 bacterial strains made up of 6 A. baumannii reference strains, 8 A. baumannii clinical strains, 5 other Acinetobacter species, and 11 other pathogens including nosocomial pathogens (Table 1 and Table 2). DNA obtained by lysate extraction was used as a template for PCR amplification. The analytical specificity of the electrochemical genosensor assay was compared to the standard PCR amplification used as the gold standard. The electrochemical detection was conducted in triplicate (n = 3) for each DNA sample. The current signal obtained from this experiment was used to determine the cut-off value for the genosensor assay. The cut-off value for the positive results was calculated to be greater than or equal to the mean of the current plus three times the standard deviation (BG + 3SD) of the current signals for the negative control and non-target samples [47].
2.7.2. Analytical Sensitivity at DNA and Cell Levels
The analytical sensitivity is the lowest concentration of purified genomic DNA required to give greater or equal current value to the cut-off point as determined in the analytical specificity. Purified genomic DNA of A. baumannii (ATCC 19606) was used for the genomic DNA level sensitivity evaluation. Serial dilution ranging from 0.05 pg to 1000 pg of genomic DNA was made using PCR-grade water. For the evaluation, 1 µL of the gDNA was used in the presence of 5 pg/µL of plasmid DNA in each reaction. The analytical sensitivity of the electrochemical genosensor was then compared to that from standard PCR amplification. The electrochemical detection was conducted in triplicates.
For the determination of sensitivity at the bacterial cell level, bacterial stock culture was prepared by inoculating a single colony of the A. baumannii (ATCC 19606) overnight culture into TSB broth and incubating it at 37 °C overnight. After at least 18 h, 10-fold serial dilutions were made in 0.9% NaCl and 1 mL of each dilution was washed twice with deionized water by centrifugation at 8000× g for 10 min. The pellet was then re-suspended in 100 µL water. The cell suspension was boiled for 10 min and 2 µL of cell lysate were used as a template for aPCR. The colony count for each dilution was checked in parallel by plating on TSA.
2.8. Clinical Application of the Electrochemical Genosensor
2.8.1. Calculation of Sample Size for Spiked Blood Samples
In this study, blood samples were spiked with reference strains and clinical isolates as listed in Table 1 and Table 2. Evaluation with clinical blood samples was not carried out due to limited availability of samples during the study period. The sample size for spiked blood samples was calculated according to a previously published study. Based on the calculation, at least 35 spiked samples were required for each positive and negative sample evaluation. In this study, 48 positive strains consisting of 6 reference strains and 42 clinical isolates of A. baumannii, and 40 negative clinical isolates consisting of nosocomial and other pathogens, were spiked in blood samples and subsequently used for the diagnostic evaluation (Table 1 and Table 2).
2.8.2. Preparation of Spiked Blood Sample
Spiked blood sample suspensions were prepared according to a previously described method with slight modifications. An overnight bacterial culture in TSB was diluted with 0.9% NaCl. Approximately 1 mL of 104 CFU/mL of bacteria was spiked in 1 mL of blood culture. The pellet was then washed twice with 0.9% NaCl and re-suspended in 100 mmol/L Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0). The suspension was then boiled for 10 min, and the resulting supernatant was used as a template for aPCR and the products were subsequently detected using an electrochemical genosensor assay. To determine the diagnostic performance of spiked blood samples, the obtained results were further analysed to determine the diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV).
2.9. Stability Evaluation of the Modified SPCEs
The method used to evaluate the stability of the modified SPCE was adapted from a previous study [46] with slight modification. The stability evaluation test was carried out for 28 days at 1-week intervals. The SPCEs for IC detection were modified with streptavidin, whereas for the target gene, the SPCEs were modified with a capture probe before being stored at three different temperatures (4 °C, 25 °C, and 37 °C). Trehalose at 3% and 6% concentration was used as a stabilizer and was added onto the modified SPCEs’ surfaces to retain the streptavidin and capture probe activity on the electrode surface. The prepared trehalose was applied onto the surface of SPCEs. The electrodes were then freeze-dried for 15 min using a Heto vacuum concentrator (Thermo Scientific Heto, Denmark) connected to a LyoLab 3000 freeze-dryer (Thermo Scientific Heto, Denmark). The SPCEs were then placed in an aluminium pouch containing silica gel desiccants and stored at three different temperatures (4 °C, 25 °C, and 37 °C). The stability of the stored SPCEs was evaluated on days 1, 7, 14, 21, and 28.
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Amperometric Cut-Off Value
The cut-off value was calculated based on the mean of the amperometric current plus three times the standard deviation of BG (background control without using bacterial strains) and non-target samples. Based on this analytical evaluation, the cut-off value for this genosensor was 0.618 µA [0.369 µA + 3(0.083)]. Tests with ≥0.618 µA were interpreted as positive, whereas those below this current value were regarded as negative. The negative results obtained, however, were validated with a positive current response for IC. This was to ensure that inhibition did not occur during aPCR amplification, and hence, all negative results were indeed true negative results.
3.2. Evaluation of Analytical Specificity of Enzyme-Based Electrochemical DNA Biosensor
In this study, the interpretation of results was facilitated through the determination of a cut-off value for blaOXA-51-like gene detection. As shown in Figure 2, the developed genosensor was able to distinguish positive samples from negative samples. The developed assay gave high amperometric signals to all A. baumannii tested, while a low background current was obtained with non-A. baumannii bacteria (negative samples). The negative results were validated with the presence of a high amperometric signal for IC.
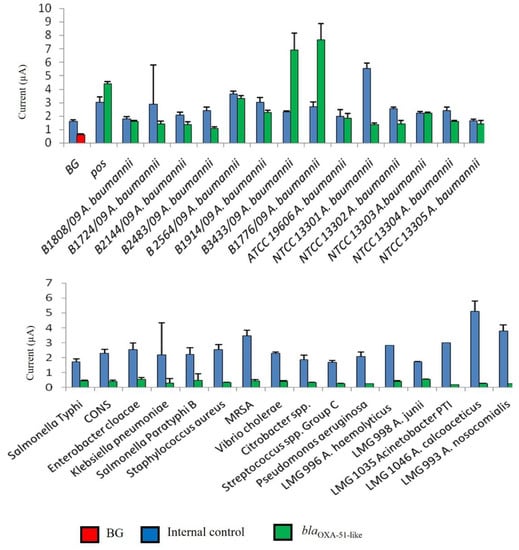
Figure 2.
Analytical specificity of an enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor using different bacterial strains. The error bars show the standard deviation for triplicate tests. CoNS—Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus; MRSA—Methicillin-resistant S. aureus; BG—background control without using bacterial strains.
3.3. Evaluation of Analytical Sensitivity of Enzyme-Based Electrochemical DNA Biosensor
The developed enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay was evaluated for its sensitivity at a genomic and bacterial level. This assay was also compared to the conventional PCR amplification with a 1:1 primer ratio through agarose gel electrophoresis analysis.
3.3.1. Limit of Detection (LoD) at Genomic DNA Level
The analytical sensitivity (lowest limit of detection) of the enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay was evaluated and compared with conventional PCR using purified genomic DNA from A. baumannii (ATCC 19606) at concentrations varying from 0.05 pg to 1000 pg of genomic DNA. The LoD for conventional PCR using agarose gel electrophoresis analysis was 5 pg of genomic DNA (Figure 3a). As shown in Figure 3b, the amperometric current response of the target gene was directly proportional to the amount of genomic DNA. However, a plateau of the current response was observed at 100 pg of genomic DNA onwards. Interestingly, the LoD for this enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay at the genomic DNA level was 0.5 pg, with an amperometric current of 1.443 µA. Based on the result, this enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay was ten times more sensitive than the conventional PCR.
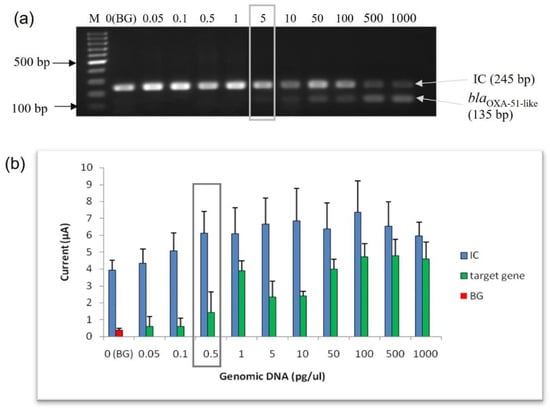
Figure 3.
Evaluation of the analytical sensitivity of the enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor using purified genomic DNA from A. baumannii ATCC 19606. (a) Agarose gel analysis; (b) enzyme-based DNA assay electrochemical DNA biosensor. The error bars show the standard deviation of triplicate tests. The limit of detection for the agarose gel analysis and the enzyme-based DNA assay are highlighted in the gray box. (M: 100 bp DNA ladder; BG: background control).
3.3.2. Limit of Detection (LoD) at Bacterial Cell Level
The sensitivity analysis of the developed enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay was also performed at the bacterial cell level. Serially diluted bacterial lysates extracted from a pure culture of A. baumannii (ATCC 19606) were used to perform the sensitivity analysis. The bacterial concentrations ranging from 101 to 107 CFU/mL were tested. The sensitivity was tested at the bacterial cell level with the developed enzyme-based DNA biosensor and agarose gel analysis; both are shown in Figure 4. The detection limit at the bacterial level was found to be 103 CFU/mL based on the calculated cut-off point. In contrast, the LoD for conventional PCR amplification (1:1 primer ratio) was 104 CFU/mL.
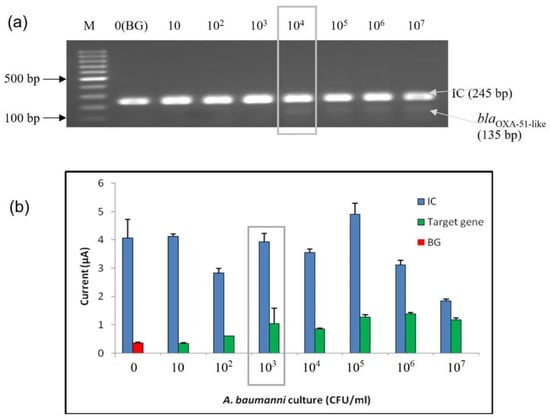
Figure 4.
Analytical sensitivity evaluation of the enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor using bacterial lysate from A. baumannii (ATCC 19606). (a) Agarose gel analysis; (b) enzyme-based DNA assay electrochemical DNA biosensor. The error bars show the standard deviation for triplicate tests. The limit of detection for the agarose gel and enzyme-based DNA assay were highlighted in the gray box. (M: 100 bp DNA ladder; BG: background control).
3.4. Diagnostic Evaluation of Enzyme-Based Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Assay Using Spiked Blood Samples
Diagnostic evaluation was carried out to test the potential use of the developed enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor for sequence-specific detection of the targeted microorganisms in clinical samples. Clinical evaluation was performed using blood samples spiked with a total of 88 bacterial strains which consisted of 48 positive samples (A. baumannii strains) and 40 negative samples (nosocomial and other pathogens). The results were interpreted based on the previously established cut-off value (0.618 µA). As shown in Figure 5, all positive A. baumannii clinical samples gave current signals above the cut-off value of 0.618 µA. On the other hand, all 40 negative samples were correctly interpreted as negative given that the current signals produced by the enzyme-based genosensor assay were all below 0.618 µA. All these negative results, however, had a positive signal for IC, indicating that these were true negative results.
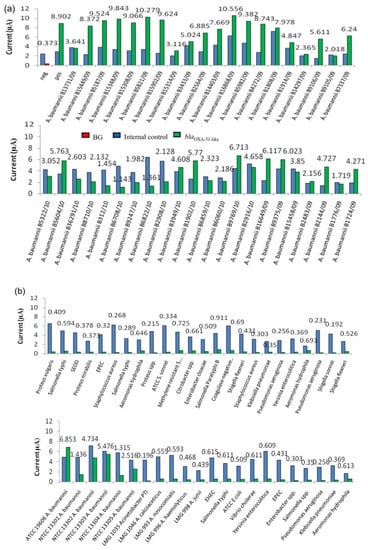
Figure 5.
(a) Diagnostic evaluation of the enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor using different A. baumannii clinical strains. (b) Diagnostic evaluation of the enzyme-based electrochemical DNA biosensor using different A. baumannii reference strains and other non-Acinetobacter pathogens.
Diagnostic evaluation results were compared to conventional PCR as the gold standard method. All the A. baumannii bacterial strains used in this study were accurately identified as true A. baumannii by amplified 16S rRNA gene restriction analysis (ARDRA), which was performed prior to this study. Clinical evaluation using spiked blood samples showed that the developed enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor correctly identified the blaOXA-51-like gene in A. baumannii strains (48 positive and 40 negative samples) without cross-reaction with other pathogens.
3.5. Accelerated Stability Evaluation of Enzyme-Based Electrochemical DNA Biosensor
As shown in Figure 6, the SPCEs were stable for 28 days when stored at all the tested temperatures. SPCEs for the target gene detection (modified with the capture probe) were more stable than the SPCEs modified with streptavidin for IC detection. The signal produced by the target gene was demonstrated to be approximately similar throughout the 28 days. The results showed that SPCEs were stable at both 25 °C and 37 °C, indicating that the modified SPCEs can be kept at room temperature. The optimal concentration of stabilizer needed to preserve the modified SPCEs surface was shown to be 6% trehalose, as the amperometric signals for the target gene were more stable compared to the amperometric signal obtained using 3% trehalose.
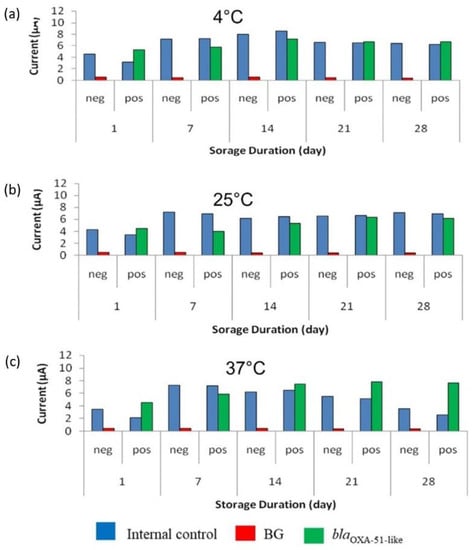
Figure 6.
Stability evaluation of the modified screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) with 6% trehalose for 28 days at (a) 4 °C, (b) 25 °C, and (c) 37 °C. BG: Background control without using bacterial strains.
According to Zheng et al. [20], one-day test kit storage at 37 °C is estimated to be equivalent to 21 days’ storage at 4 °C. Therefore, the stability of the modified SPCE at 37 °C ± 2 °C was calculated as the following:
= 28 days × 21
= 588 days at 4 °C
Hence, this result indicated that the modified SPCEs have an estimated minimum of 1.6 years of shelf-life when stored at 4 °C.
4. Discussion
The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria causing infection in humans is a major global concern [48]. A. baumannii is one of the important pathogens that is included in this antibiotic-resistant bacteria group and is responsible for many hospital-acquired infections [6,9]. Infections due to A. baumannii are commonly reported in ICUs, particularly in immunocompromised patients who are critically ill [49,50]. A. baumannii is well-known for its resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics [51]. Carbapenem resistance, particularly class D carbapenemase genes, are of concern, as these genes are observed more frequently in A. baumannii strains. A. baumannii possesses a wide range of resistance mechanisms towards carbapenem such as causing changes in penicillin-binding proteins and alterations in the structure and the activity of efflux pumps [2,17]. Hence, A. baumannii infections have been reported to contribute to high mortality among patients [6,49,52].
In routine diagnostics, the identification of A. baumannii is performed using a panel of biochemical tests or a commercially available identification system such as the API 20NE system and VITEK. This conventional identification method is time-consuming and laborious. The detection of nucleic acid from microbial pathogens has also become an alternative detection method for the identification of causative agents. The development of PCR-based assays for the detection of A. baumannii has been described in several studies [53,54,55]. A real-time PCR assay has also been developed for A. baumannii detection [56], which provides faster results compared with conventional PCR. However, PCR assays require the use of expensive equipment and thus may not be an ideal solution for some countries [57,58]. Accurate and early detection of A. baumannii infections is very essential to efficient healthcare for patients due to the high mortality rate associated with its infections [59]. In recent years, various types of electrochemical biosensors based on the detection of bacterial nucleic acid have also been developed to replace PCR and gel electrophoresis analysis. DNA biosensors have been developed against several infectious diseases such as tuberculosis [60], hepatitis [61], dengue [62], and other food-borne diseases like Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium [63]. DNA hybridization is a widely used technique for biosensor assay [64]. This process involves hybridization between single-stranded oligonucleotides and a complementary target sequence. The present study describes the development of an enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor for sequence-specific detection of the blaOXA-51-like gene in A. baumannii. This genosensor assay was used as a detection method for aPCR amplicons instead of gel electrophoresis analysis. The hybridization process occurred after the immobilization of the single-stranded capture probe on the electrode surface, where the probe identified the complementary target gene amplified by aPCR, and formed a DNA probe-target hybrid. This hybridization mechanism is known as the direct hybridization method for target DNA detection in biosensor assay. This sequence-specific detection approach has been widely used due to its effectiveness and specificity even in the presence of non-complementary sequences [65,66]. Readable electrochemical signals are then generated through the oxidation of TMB with H2O2 reduction through a reaction catalyzed by an HRP enzyme [67,68]. Some DNA biosensors have been previously developed for A. baumannii detection. The work of Yeh and co-workers [41] also applied the hybridization principle, but incorporated an electro-microchip into their design and gold-streptavidin nanoparticles plus Ag+ -hydroquinone solution to enhance detection. The LoD observed at the genomic and bacterial level showed that the developed genosensor is 10 times more sensitive than a conventional PCR assay with an LoD of 5 pg. The LoD at the genomic level for our genosensor is slightly lower than the 0.825 ng mL−1 (1.2 fM) reported by Yeh and colleagues [41]. LoDs of 0.14 nM [42] and 1.86 nM [45] have also been provided with previously reported A. baumannii biosensors. Previous studies have also reported a similar LoD for aPCR amplicons of E. coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticles [69] and V. cholerae using a magnetogenosensing assay [47].
While SPCE was used in this study for the development of an electrochemical genosensor, Eksin and co-workers [45] instead used chitosan as the material for the electrode. Although chitosan has been reported as a good natural polysaccharide for biosensor preparation [70,71,72], the use of screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) in biosensors has also been reported to confer the advantages of adaptability, low-cost, ease of mass production, and selective specificity for target analytes [44,73,74,75]. Additionally, SPEs can be easily customized in terms of their shape, substrate, and dimension, which provides for easy selectivity and calibration of SPE-based biosensors. Valuable analytical properties of biosensors such as specificity, sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility again can be easily achieved when SPEs surfaces are modified with nanomaterials [76,77].
Previous studies using PCR and other detection methods have shown that all A. baumannii isolates possessed a chromosomally located blaOXA-51-like gene. Therefore, the detection of the blaOXA-51-like gene can be used as a feasible and reliable way to identify A. baumannii from clinical and other specimens [20,78,79,80]. The present study therefore targeted the blaOXA-51-like gene of A. baumannii. Findings of this study showed that the specificity of the developed genosensor was in consonance with that obtained by a conventional PCR assay. The analytical specificity of the developed genosensor assay at genomic and bacterial cell levels was tested using a panel of bacterial strains consisting of A. baumannii and other pathogens that commonly cause infections in humans. The capture probe immobilized on the SPCE surface was proven to be 100% specific for the A. baumannii target gene (blaOXA-51-like gene), where the hybridisation process was successful and an amperometric current signal was produced. The use of the zot gene as an internal amplification control both for the PCR amplifications and amperometric readings in this study, eliminates the possibility of false negatives that could arise due to the presence of inhibitors in the sample. Other previously reported studies [41,42,43,45] that developed different biosensors for A. baumannii detection did not include any internal controls.
The diagnostic evaluation of the developed enzyme-based genosensor assay was performed using blood samples spiked with clinical isolates. Bloodstream infection in patients due to A. baumannii has been commonly reported [81,82] and because of this, blood samples are widely used in PCR assay. The most common problem in the detection of pathogens in a blood sample using PCR assay is that it includes the presence of inhibitory substances such as natural components of blood [83]. As such, in this study, a blood sample inoculated in a blood culture medium was used to minimise the inhibitory substances present in the clinical samples as well as to enhance bacterial growth. The diagnostic performance for the developed enzyme-based electrochemical sequence-specific biosensor assay using aPCR amplicons was shown to be 100% sensitive and specific, with 100% positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predicted value (NPV). These findings potentially establish that the developed biosensor can still function efficiently when blood samples are used.
In addition, an accelerated stability evaluation of this developed enzyme-based electrochemical sequence-specific biosensor assay was carried out to determine the shelf-life of the assay. Trehalose as a stabiliser was used to retain the activity of protein (streptavidin) and DNA (capture probe) on the SPCE surface for the IC and target gene, respectively. Trehalose interacted with DNA by forming a glassy intermediate, thereby reducing the fluctuations of the DNA structure. In addition, during lyophilisation, trehalose could stabilize protein by making it more rigid [84]. Findings further showed that modified SPCE surfaces treated with 6% trehalose showed more relatively stable amperometric signals at all tested temperatures over the 28-day period, than those treated with 3% trehalose. In this study, the SPCE stored at 25 °C and 37 °C maintained its performance for up to 28 days. The calculated accelerated stability of the assay was determined to be 1.6 years, when stored at 4 °C. A similar stability duration was also reported by Dash and colleagues [85] where the genosensor was stable for approximately 1 year at 4 °C. The result from this study further suggests that the modified SPCE could be stored and transported without a cold chain requirement. Hence, it would be efficient for use in tropical environments as well. Other studies that reported similar electrochemical biosensors for A. baumannii detection [41,42,43,45] did not perform any stability evaluations to determine the performance of the method under varied temperatures.
The electrochemical genosensor developed previously and in this study could serve as an easier alternative to the laborious process of agarose gel electrophoresis and conventional culture methods in detecting A. baumannii in clinical specimens. However, improvements in their performance and properties to provide more powerful, miniaturized, user-friendly, and highly sensitive biosensors for nucleic acid detection would greatly impact public health. For instance, an increase in capture efficiency will also translate to a higher sensitivity [86]. Although biosensors hold great potentials for more rapid disease diagnosis, a few limitations have been reported. For instance, most reported biosensors are not multiplexable [87]. However, the integration of nanomaterials into biosensors development and integration with other technologies hold much promise towards solving this challenge [88,89]. Generally, the use of antibodies in biosensors can face limitations such as loss of biological activities due to the immobilization step. Additionally, at high density, steric hinderances can result in a loss of activity [90]. Despite this limitation, many studies have used antibodies as biorecognition molecules in electrochemical biosensor development because the method allows for easier sample preparation and also possesses good sensitivity and specificity [37]. The use of other bioreceptors such as enzymes, phages, cells, and aptamers have also been explored.
5. Conclusions
This study successfully developed an enzyme-based electrochemical genosensor assay for the detection of A. baumannii with an internal control from the zot gene, which could be useful for early and specific detection of infections. Using amplicons generated from aPCR amplification of the blaOXA-51-like gene of A. baumannii, the electrochemical genosensor with SPCE accurately detected the presence of complementary sequence A. baumannii DNA, using the hybridization principle with the help of a sequence-specific probe immobilized on the surface of the working electrode. The genosensor showed a 10-fold higher sensitivity than conventional PCR and 100% specificity with no false results or cross-reactivity among non-A. baumannii strains tested. Although previous works reported a lower detection limit, the LoD reported in this study (0.5 pg) is within an acceptable level for A. baumannii detection, and is, as well, higher than other reported LoDs. Interestingly, the developed electrochemical genosensor retained a stable performance when stored at higher temperatures of 25 °C and 37 °C, making it suitable for use in both temperate and nontemperate climates. The use of screen-printed electrodes in this study presents the advantage of adaptability, ease of mass production, and selective specificity for the target gene, making it suitable for rapid analysis on-site. The electrochemical genosensor developed in this study combines sensitivity, specificity, ease of use, and rapidity with the potential for POCT adaptability and miniaturization; hence, it can eventually be helpful to clinicians in providing prompt and appropriate treatment and management of A. baumannii infections in patients. With the rapid detection of A. baumannii in clinical specimens, the spread of A. baumannii can be significantly prevented, thereby improving patient health and outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: K.K.B.S.; methodology: K.K.B.S., C.Y.Y., C.C., R.H.S. and G.A.O.; investigation: S.K.; validation: S.K. and K.K.B.S.; resources: K.K.B.S. and C.Y.Y.; supervision: K.K.B.S. and C.Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation: C.C., R.H.S., S.K. and G.A.O.; writing—review and editing: K.K.B.S. and G.A.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Universiti Sains Malaysia GIPS-PhD Grant (Grant number 311.PPSP.4404809) and Research University Grant (Grant number 1001.PPSP.812050).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval for this study (USM/JEPeM/18010015) was obtained from the Human Research Ethics Committee of Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) and experiments were performed following the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent Statement
JEPeM CODE:USM/JEPeM/18010015: Since blood samples used in this study were anonymously handled, informed patient consent was waived for this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Institute for Postgraduate Studies, Universiti Sains Malaysia for providing fellowship assistance to S.K. and the staff of the Department of Medical Microbiology and Parasitology, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan, Malaysia, for assistance with sample processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bergogne-Bérézin, E.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter Spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Microbiological, Clinical, and Epidemiological Features. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, F.; Hujer, A.M.; Hujer, K.M.; Decker, B.K.; Rather, P.N.; Bonomo, R.A. Global Challenge of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriamanantena, T.S.; Ratsima, E.; Rakotonirina, H.C.; Randrianirina, F.; Ramparany, L.; Carod, J.F.; Richard, V.; Talarmin, A. Dissemination of Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Various Hospitals of Antananarivo Madagascar. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2010, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R.A. Nosocomial Infection Update. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, L.C.S.; Visca, P.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of a Global Pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 71, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, T.L.; Shie, S.S.; Huang, C.T.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Quyen, T.L.T.; Pan, Y.J. Association of Capsular Types with Carbapenem Resistance, Disease Severity, and Mortality in Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsi, K.; Messai, Y.; Hamidi, M.; Ammari, H.; Bakour, R. High Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Encoding Genes BlaOXA-23-like, BlaOXA-24-like and BlaNDM-1 in Algiers Hospitals. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.A.; Biagi, M.; Tan, X.; Qasmieh, S.; Bulman, Z.P.; Wenzler, E. Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Resistance by Any Other Name Would Still Be Hard to Treat. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaha, E.L.; Gonsu, H.K.; Bughe, R.N.; Fonkoua, M.C.; Ateba, C.N.; Mbacham, W.F. Occurrence of BlaTEM and BlaCTXM Genes and Biofilm-Forming Ability among Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii in Yaoundé, Cameroon. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chai, D.; Wang, R.; Liang, B.; Bai, N. Colistin Resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii: Clinical Reports, Mechanisms and Antimicrobial Strategies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- We, I.; Adeniyi, B.A.; Soge, O.O. Prevalence of Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Eight Tertiary Hospitals in Southwestern Nigeria. N. Y. Sci. J. 2014, 77, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a Successful Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An Increasing Threat in Hospitals: Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperaki, E.T.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Miriagou, V.; Daikos, G.L. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: In Pursuit of an Effective Treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Hittle, L.E.; O’Hara, J.A.; Rivera, J.I.; Syed, A.; Shields, R.K.; Pasculle, A.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Doi, Y. Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Beyond Carbapenem Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.; Zander, E.; Stefanik, D.; Higgins, P.G.; Roca, I.; Vila, J.; McConnell, M.J.; Cisneros, J.M.; Seifert, H.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; et al. High Incidence of Pandrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Collected from Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Greece, Italy and Spain as Part of the MagicBullet Clinical Trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3277–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amudhan, S.M.; Sekar, U.; Arunagiri, K.; Sekar, B. OXA Beta-Lactamase-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 29, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Sun, J.; Bao, L.; Li, W. Distribution and Antibiotic Resistance of Pathogens Isolated from Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Patients in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. World J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 2, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, C.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Seol, S.Y.; Cho, D.T.; Kim, K.W.; Song, D.Y.; et al. Differences in Phenotypic and Genotypic Traits against Antimicrobial Agents between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter Genomic Species 13TU. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Hanneken, J.; Houchins, D.; King, R.S.; Lee, P.; Richard, J.L. Validation of an ELISA Test Kit for the Detection of Ochratoxin A in Several Food Commodities by Comparison with HPLC. Mycopathologia 2005, 159, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Woodford, N.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pike, R.; Livermore, D.M.; Pitt, T.L. The Role of ISAba1 in Expression of OXA Carbapenemase Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 258, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.H.Y.; Chan, B.K.W.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. Over-Expression of ISAba1-Linked Intrinsic and Exogenously Acquired OXA Type Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing-Class D-β-Lactamase-Encoding Genes Is Key Mechanism Underlying Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jit, M.; Ng, D.H.L.; Luangasanatip, N.; Sandmann, F.; Atkins, K.E.; Robotham, J.V.; Pouwels, K.B. Quantifying the Economic Cost of Antibiotic Resistance and the Impact of Related Interventions: Rapid Methodological Review, Conceptual Framework and Recommendations for Future Studies. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshafie, S.; Taj-Aldeen, S.J. Emerging Resistant Serotypes of Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibun, T.; Thanasapburachot, P.; Chatchawal, P.; Yin, L.S.; Jiaranuchart, S.; Jearanaikoon, P.; Promptmas, C.; Buajeeb, W.; Lertanantawong, B. A Multianalyte Electrochemical Genosensor for the Detection of High-Risk HPV Genotypes in Oral and Cervical Cancers. Biosensors 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Santana, W.; Dolabella, S.S.; Santos, A.L.S.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P. Are Nanobiosensors an Improved Solution for Diagnosis of Leishmania? Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Salcedo, R.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Dual Electrochemical Genosensor for Early Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer through LncRNAs Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Yen, H.Y.; Lai, L.T.; Perng, G.C.; Lee, C.R.; Wu, S.J. A Label-Free Impedimetric Genosensor for the Nucleic Acid Amplification-Free Detection of Extracted RNA of Dengue Virus. Sensors 2020, 20, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandong, G.; Yanqing, L.; Hongxia, G.; Xiaoqin, W.; Lifang, F. Electrochemical Detection of Short Sequences Related to the Hepatitis B Virus Using MB on Chitosan-Modified CPE. Bioelectrochemistry 2007, 70, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkhani, H.; Hughes, T.; Li, J.; Zhong, C.J.; Hepel, M. Nanostructured SERS-Electrochemical Biosensors for Testing of Anticancer Drug Interactions with DNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaníčková, M.; Lehotay, J.; Čižmárik, J.; Labuda, J. Kinetic Study of the Degradation of a Potential Local Anesthetic Drug in Serum Using the DNA-Based Electrochemical Biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2005, 66, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, S.A.; Kauffmann, J.-M.; Zuman, P. Electrochemical Biosensors for Drug Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 141–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Melo, S.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Dos Santos Junior, J.R.; da Silva Fonseca, R.A.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. A Quantitative PCR-Electrochemical Genosensor Test for the Screening of Biotech Crops. Sensors 2017, 17, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tichoniuk, M.; Ligaj, M.; Filipiak, M. Application of DNA Hybridization Biosensor as a Screening Method for the Detection of Genetically Modified Food Components. Sensors 2008, 8, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Agüí, L.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. What Electrochemical Biosensors Can Do for Forensic Science? Unique Features and Applications. Biosensors 2019, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshey, A.; Srivastava, A.; Das, T.; Nigam, K.; Shrivastava, R.; Yadav, V.K. Trends in Gunshot Residue Detection by Electrochemical Methods for Forensic Purpose. J. Anal. Test. 2021, 5, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambry, N.S.; Obande, G.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Bustami, Y.; Hamzah, H.H.; Awang, M.S.; Aziah, I.; Manaf, A.A. Utilizing Electrochemical-Based Sensing Approaches for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.V.; Cordeiro, T.A.R.; Oliveira e Freitas, G.R.; Ferreira, L.F.; Franco, D.L. Biosensors for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses: A Review. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, N.; Zhang, W. Review of Electrochemical DNA Biosensors for Detecting Food Borne Pathogens. Sensors 2019, 19, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Vanani, R.; Sattarahmady, N.; Yadegari, H.; Heli, H. A Novel and Ultrasensitive Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Based on an Ice Crystals-like Gold Nanostructure for the Detection of Enterococcus Faecalis Gene Sequence. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Chang, T.C.; Lin, H.P.; Lin, Y.C. Electro-Microchip DNA-Biosensor for Bacteria Detection. Analyst 2010, 135, 2717–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Feng, C.; Yao, Z. An Electrochemical DNA-Hybridization Assay for Acinetobacter baumannii Detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Sarabaegi, M.; Rostamzad, A. Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Polydopamine Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; Delibato, E.; Palleschi, G. Electrochemical Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Salmonella: A Critical Overview. Sensors 2017, 17, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eksin, E. An Electrochemical Assay for Sensitive Detection of Acinetobacter baumannii Gene. Talanta 2022, 249, 123696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Kamarudin, B.; Ozkan, D.A.; Lee, S.Y.; Lalitha, P.; Ismail, A.; Ozsoz, M.; Ravichandran, M. Enzyme-Linked Amperometric Electrochemical Genosensor Assay for the Detection of PCR Amplicons on a Streptavidin-Treated Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2774–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.F.; Karimah, A.; Yean, C.Y. A Thermostabilized Magnetogenosensing Assay for DNA Sequence-Specific Detection and Quantification of Vibrio Cholerae. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Rozos, G.; Vaou, N.; Bardanis, M.; Konstantinidis, T.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. Antimicrobial Evaluation of Various Honey Types against Carbapenemase-Producing Gram-Negative Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H. Clinical and Economic Evaluation of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Colonization in the Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Chemother. 2016, 48, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Du, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, T.; Tang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tao, C.; Xie, Y. Risk and Prognostic Factors for Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Complex Bacteremia: A Retrospective Study in a Tertiary Hospital of West China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancianu, C.O.; Gheorghe, I.; Czobor, I.B.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Antibiotic Resistance Profiles, Molecular Mechanisms and Innovative Treatment Strategies of Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garmendia, J.L.; Ortiz-Leyba, C.; Garnacho-Montero, J.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J.; Monterrubio-Villar, J.; Gili-Miner, M. Mortality and the Increase in Length of Stay Attributable to the Acquisition of Acinetobacter in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 1794–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Krut, O.; Seifert, H. A PCR-Based Method to Differentiate between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter Genomic Species 13TU. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, M.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, Y.T.; Chen, T.L.; Fung, C.P. Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Detection of Acinetobacter baumannii in Endotracheal Aspirates from Patients in the Intensive Care Unit. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2011, 44, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodford, N.; Ellington, M.J.; Coelho, J.M.; Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Brown, S.; Amyes, S.G.B.; Livermore, D.M. Multiplex PCR for Genes Encoding Prevalent OXA Carbapenemases in Acinetobacter Spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 27, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Chang, S.C.; Wang, W.K. High and Increasing Oxa-51 DNA Load Predict Mortality in Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremia: Implication for Pathogenesis and Evaluation of Therapy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, M.A.; Christie, J.; Yang, N.; Yao, C. A Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Assay Specific to Trichomonas Tenax Is Suitable for Use at Point-of-Care. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Meneses, A.V.; Chicharro, C.; Sánchez, C.; García, E.; Ortega, S.; Ndung’u, J.M.; Moreno, J.; Cruz, I.; Carrillo, E. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Allows Rapid, Simple and Accurate Molecular Diagnosis of Human Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania Infantum When Compared to PCR. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, L.L.; Marshall, D.R.; Pratap, S.; Hulette, R.B. Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Descriptive Study in a City Hospital. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, L.; He, D.; Wang, K.; Qin, D. Biosensing Technologies for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Detection: Status and New Developments. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2011, 193963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y. A Gold Nanorods-Based Fluorescent Biosensor for the Detection of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer. Analyst 2013, 138, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Ng, L.C.; Soh, S.H.; Leo, Y.S.; Toh, C.S. Ultrasensitive CDNA Detection of Dengue Virus RNA Using Electrochemical Nanoporous Membrane-Based Biosensor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.H.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, H.X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.C.; Cao, Y.C.; Meng, Q.H.; Lu, J.X. Aptasensors for Rapid Detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerman, K.; Vestergaard, M.; Nagatani, N.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E. Electrochemical Genosensor Based on Peptide Nucleic Acid-Mediated PCR and Asymmetric PCR Techniques: Electrostatic Interactions with a Metal Cation. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2182–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Yin, L.S.; Ravichandran, M. Electrochemical Genosensor Assay for the Detection of Bacteria on Screen-Printed Chips. In Electrochemical DNA Biosensors; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2012; pp. 499–516. ISBN 9780429066412. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, F.R.R.; Fonseca, L.P. Trends in DNA Biosensors. Talanta 2008, 77, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wan, Y.; Gau, V.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Fan, C. An Enzyme-Based E-DNA Sensor for Sequence-Specific Detection of Femtomolar DNA Targets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.; Compagnone, D.; Draisci, R.; Palleschi, G. 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine as Electrochemical Substrate for Horseradish Peroxidase Based Enzyme Immunoassays. A Comparative Study. Analyst 1998, 123, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wei, Q.S.; Wu, C.S.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, P. The Escherichia Coli O157:H7 DNA Detection on a Gold Nanoparticle-Enhanced Piezoelectric Biosensor. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksin, E.; Muti, M.; Erdem, A. Chitosan/Ionic Liquid Composite Electrode for Electrochemical Monitoring of the Surface-Confined Interaction between Mitomycin C and DNA. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Muti, M.; Mese, F.; Eksin, E. Chitosan-Ionic Liquid Modified Single-Use Sensor for Electrochemical Monitoring of Sequence-Selective DNA Hybridization. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congur, G.; Eksin, E.; Erdem, A. Chitosan Modified Graphite Electrodes Developed for Electrochemical Monitoring of Interaction between Daunorubicin and DNA. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 22, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albareda-Sirvent, M.; Merkoçi, A.; Alegret, S. Configurations Used in the Design of Screen-Printed Enzymatic Biosensors. A Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 69, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metters, J.P.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. New Directions in Screen Printed Electroanalytical Sensors: An Overview of Recent Developments. Analyst 2011, 136, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Minotti, C.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. Fully Integrated Ready-to-Use Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor to Detect Nerve Agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Basso, M.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. A Paper-Based Nanomodified Electrochemical Biosensor for Ethanol Detection in Beers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Neagu, D.; Carbone, M.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Novel Carbon Black-Cobalt Phthalocyanine Nanocomposite as Sensing Platform to Detect Organophosphorus Pollutants at Screen-Printed Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Villa, L.; Menegon, M.; Luca, M.D.; Toma, L.; De Liberato, C.; Magliano, A.; Romiti, F.; Carattoli, A.; Ciervo, A. First Evidence of BlaNDM-1 and BlaOXA-23 Carbapenemase Genes in Human Body Lice Infesting a Second-Hand T-Shirt in a Street Market in Italy. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2021, 57, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ababneh, Q.; Aldaken, N.; Jaradat, Z.; Al Sbei, S.; Alawneh, D.; Al-zoubi, E.; Alhomsi, T.; Saadoun, I. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Three Major Hospitals in Jordan. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-ahmer, S.D.; Moslim, A.M.; Al-asady, Z.H.A. Molecular Detection of Acientobacter Baumannii Isolated from Nosocomial Infections in Baghdad Hospitals. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cisneros, J.M.; Reyes, M.J.; Pachón, J.; Becerril, B.; Caballero, F.J.; García-Garmendía, J.L.; Ortiz, C.; Cobacho, A.R. Bacteremia Due to Acinetobacter baumannii: Epidemiology, Clinical Findings, and Prognostic Features. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Bischoff, T.; Tallent, S.M.; Seifert, H.; Wenzel, R.P.; Edmond, M.B. Nosocomial Bloodstream Infections in US Hospitals: Analysis of 24,179 Cases from a Prospective Nationwide Surveillance Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Soud, W.A.; Rådström, P. Purification and Characterization of PCR-Inhibitory Components in Blood Cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedoux, A.; Paccou, L.; Achir, S.; Guinet, Y. Mechanism of Protein Stabilization by Trehalose during Freeze-Drying Analyzed by in Situ Micro-Raman Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Khare, S.; Kumar, A. Omp85 Genosensor for Detection of Human Brain Bacterial Meningitis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, B.; Iqbal, M.; Mehmood, T.; Shaheen, M.A. Electrochemical DNA Biosensors: A Review. Sens. Rev. 2019, 39, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshvar, S.; Sudhakumari, C.C.; Senthilkumaran, B.; Prakash, H. Recent Advances in Biosensor Technology for Potential Applications—An Overview. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil Rosa, B.; Akingbade, O.E.; Guo, X.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Crone, M.A.; Cameron, L.P.; Freemont, P.; Choy, K.L.; Güder, F.; Yeatman, E.; et al. Multiplexed Immunosensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostic Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Jiang, H.; Juhas, M.; Zhang, Y. Multiplex Biosensing for Simultaneous Detection of Mutations in SARS-CoV-2. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25846–25859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).