Imaging Leishmania major Antigens in Experimentally Infected Macrophages and Dermal Scrapings from Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions in Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leishmania Isolates and Culture
2.2. Rabbit Anti-L. major Immune Serum
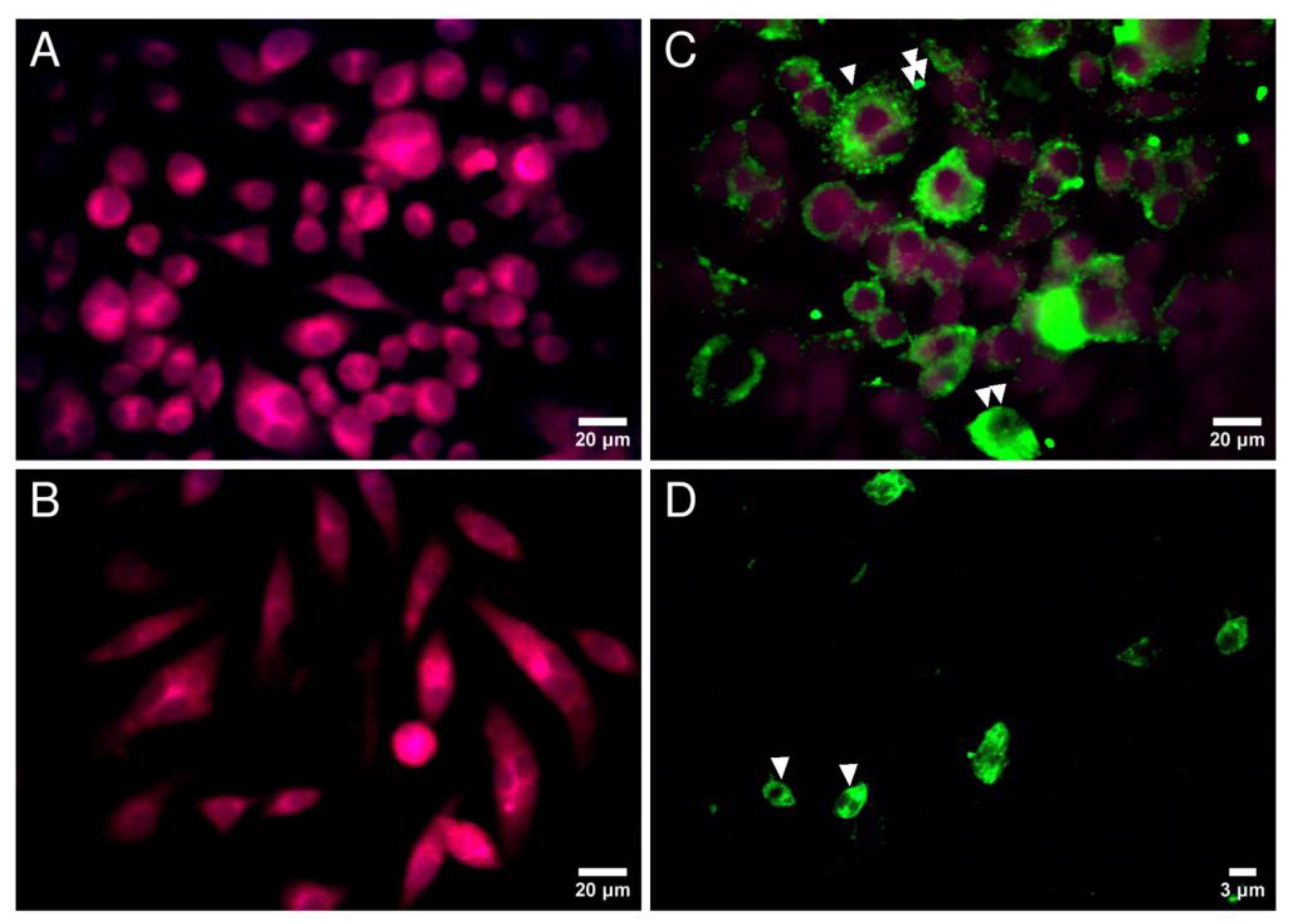
2.3. Reactivity of the Rabbit Anti-L. major Immune Serum against In Vitro Infected Macrophages and Macrophage-Derived Amastigotes
2.3.1. In Vitro Infection of Macrophages by Leishmania Promastigotes
2.3.2. Reactivity of the Rabbit Anti-L. major Immune Serum
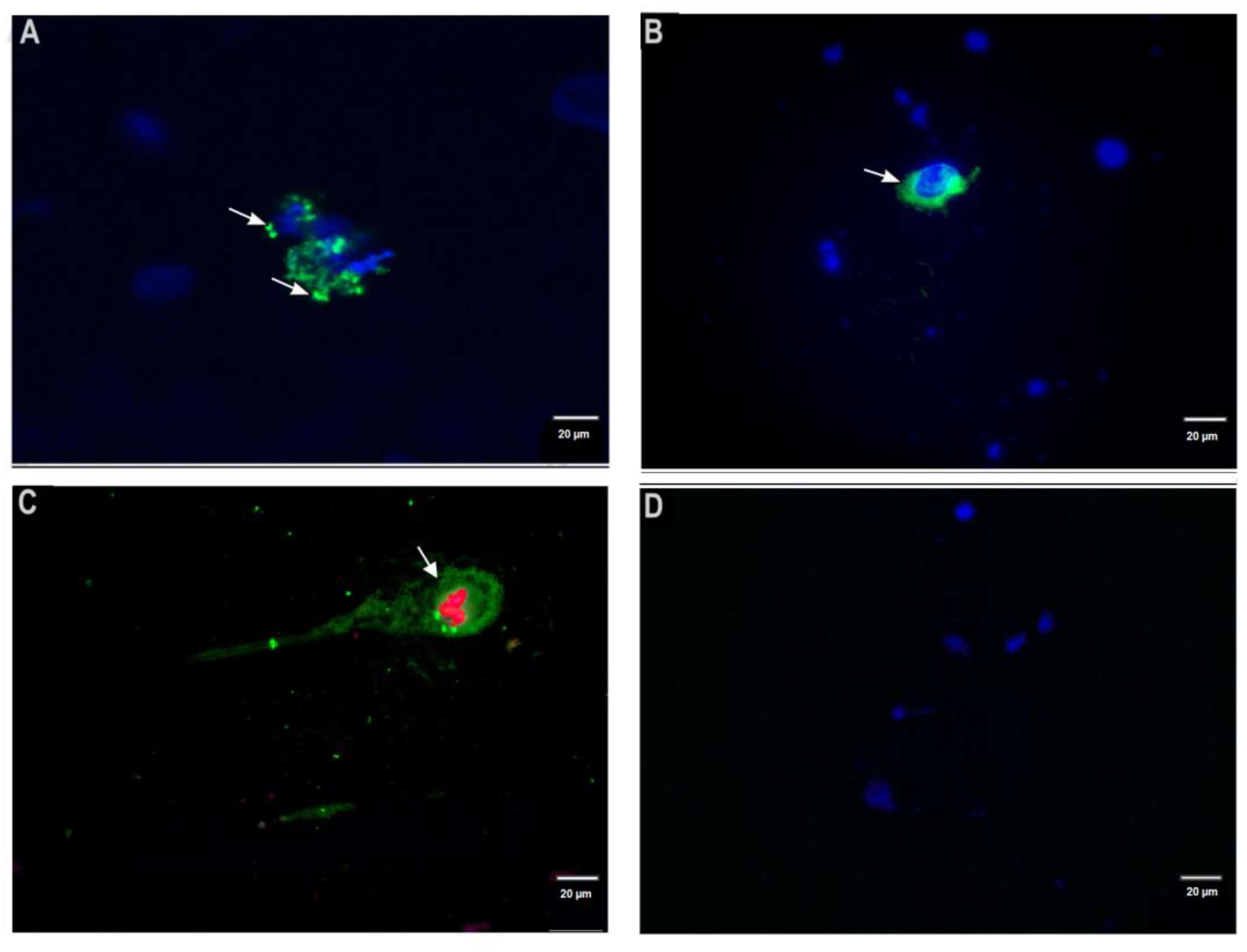
2.4. Optimization of Direct Immunofluorescence Assay (DIF) on Dermal Scrapings
2.5. Evaluation of DIF Assay in the Diagnosis of CL and Comparison to ITS1-PCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Reactivity of the Rabbit Anti-L. major Immune Serum against In Vitro Infected Macrophages and Macrophage-Derived Amastigotes
3.2. Detection of Leishmania Antigens by Direct Immunofluorescence Staining of Dermal Scrapings
3.3. Reliability of Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) Method Using FITC-Labeled Anti-L. major IgG in Comparison to Other Available Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leishmaniasis . Available online: https//www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis . Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Leishmaniasis in high-burden countries: An epidemiological update based on data reported in 2014. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2016, 91, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Postigo, J.A.R.; Jain, S.; Mikhailov, A.; Elkhoury, A.N.M.; Valadas, S.; Warusavithana, S.; Osman, M.; Lin, Z.; Beshah, A.; Yajima, A.; et al. Global Leishmaniasis surveillance: 2019–2020, a baseline for the 2030 roadmap. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2021, 96, 401–420. [Google Scholar]
- Aoun, K.; Bouratbine, A. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in North Africa: A review. Parasite 2014, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniklef, R.; Aoun, K.; Boudrissa, K.; Ben Abid, M.; Cherif, K.; Aissi, W.; Benrekta, S.; Boubidi, S.C.; Späth, G.F.; Bouratbine, A.; et al. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Algeria; Highlight on the Focus of M’Sila. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, K.; Kalboussi, Y.; Sghaier, I.B.; Souissi, O.; Hammami, H.; Bellali, H.; Bouratbine, A. Assessment of incubation period of cutaneous Leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major in Tunisia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1934–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.; Greenberger, S.; Baum, S.; Pavlotsky, F.; Barzilai, A.; Schwartz, E. Unusual forms of cutaneous Leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 7, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Manual for Case Management of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Aoun, K.; Tebrouri, M.; Ben-Abdallah, R.; Bellali, H.; Souissi, O.; Bouratbine, A. Contribution of real-time PCR in the diagnosis of cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Experience of the Institut Pasteur de Tunis. Bull. Soc. Path. Exo. 2020, 113, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, H.J.; Reedijk, S.H.; Schallig, H.D. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Recent developments in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimão, J.Q.; Coser, E.M.; Lee, M.R.; Coelho, A.C. Laboratory Diagnosis of Cutaneous and Visceral Leishmaniasis: Current and Future Methods. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, R.E.; Englund, P.T. Network news: The replication of kinetoplast DNA. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, E.; Nasereddin, A.; Jonas, F.; Schnur, L.F.; Jaffe, C.L. Comparison of PCR assays for diagnosis of cutaneous Leishmaniasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennis, I.; Verdonck, K.; El Khalfaoui, N.; Riyad, M.; Fellah, H.; Dujardin, J.C.; Sahibi, H.; Bouhout, S.; Van der Auwera, G.; Boelaert, M. Accuracy of a Rapid Diagnostic Test Based on Antigen Detection for the Diagnosis of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Patients with suggestive Skin Lesions in Morocco. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Henten, S.H.; Melkamu, R.; Dessie, D.; Mekonnen, T.; Kassa, M.; Bogale, T.; Mohammed, R.; Cnops, L.; Vogt, F.; Pareyn, M. Evaluation of the CL Detect Rapid Test in Ethiopian patients suspected for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, R.S.; García-Montero, P.P.; Chicharro, C.; Tardío, J.C. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A pathological study of 360 cases with special emphasis on the contribution of immunohistochemistry and polymerase chain reaction to diagnosis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Trujillo, E.; Gonzàlez-Farré, M.; Pujol, R.M.; Bellosillo, B.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; Alcover, M.; Barranco, C.; Martin-Ezquerra, G. Diagnostic usefulness of immunohistochemical evaluation of CD1a antigen and polyclonal anti-leishmania antibodies in cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Histol. Histopathol. 2021, 36, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, N.R.; Malavé, C.; Ifante, R.B.; Modlin, R.L.; Convit, J. In situ detection of amastigotes in American cutaneous Leishmaniasis, using monoclonal antibodies. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 80, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenner, J.R.; Aronson, N.E.; Bratthauer, G.L.; Turnicky, R.P.; Jackson, J.E.; Tang, D.B.; Sau, P. Immunohistochemistry to identify Leishmania parasites in fixed tissues. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1999, 26, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, P.G.; Burton, M. Identification of Leishmania amastigotes and their antigens in formalin fixed tissue by immunoperoxidase staining. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livni, N.; Abramowitz, A.; Londner, M.; Okon, E.; Morag, A. Immunoperoxidase method of identification of Leishmania in routinely prepared histological sections. Virchows Arch. 1983, 401, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, G.; Valderrama, L.; Palma, G.; Montes, G.; Saravia, N. Detection of amastigotes in cuteneous and mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis by the immunoperoxidase method, using polyclonal antibody sensibility and specifity compared with conventional diagnosis methods. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1989, 84, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubach, A.; Cuzzi-Maya, T.; Oliveira, A.V.; Sartori, A.; de Oliveira-Neto, M.P.; Mattos, M.S.; Araújo, M.L.; Souza, W.J.; Haddad, F.; Perez, M.D.; et al. Leishmanial antigens in the diagnosis of active lesions and ancient scars of American tegumentary Leishmaniasis patients. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2001, 96, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintella, L.P.; Cuzzi, T.; Madeira, M.D.; Okamoto, T.; Schubach, A.D. Immunoperoxidase technique using an anti-Leishmania (L.) chagasi hyperimmune serum in the diagnosis of culture-confirmed American tegumentary Leishmaniasis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2009, 51, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.F.; Alves, C.F.; Figueiredo, M.M.; Souza, C.C.; Machado-Coelho, G.L.; Melo, M.N.; Tafuri, W.L.; Raso, P.; Soares, R.P.; Tafuri, W.L. American tegumentary Leishmaniasis: Effectiveness of an immunohistochemical protocol for the detection of Leishmania in skin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chico, M.E.; Guderian, R.H.; Cooper, P.J.; Armijos, R.; Grogl, M. Evaluation of a direct immunofluorescent antibody (DIFMA) test using Leishmania genus-specific monoclonal antibody in the routine diagnosis of cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 1995, 28, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Bumb, R.A.; Ansari, N.A.; Mehta, R.D.; Salotra, P. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania tropica in Bikaner, India: Parasite identification and characterization using molecular and immunologic tools. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Späth, G.F.; Beverley, S.M. A lipophosphoglycan-independent method for isolation of infective Leishmania metacyclic promastigotes by density gradient centrifugation. Exp. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayachi, I.; Galai, Y.; Ben-Abid, M.; Saidi, N.; Ben-Sghaier, I.; Aoun, K.; Bouratbine, A. Use of Immunomagnetic Separation tool in Leishmania promastigotes capture. Acta Trop. 2021, 215, 105804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Sahu, R.; Walker, L.A.; Tekwani, B.L. A parasite rescue and transformation assay for antileishmanial screening against intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes in THP1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 70, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.Y.; Mullins, J.M. Conjugation of fluorochromes to antibodies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 588, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Schönian, G.; Nasereddin, A.; Dinse, N.; Schweynoch, C.; Schallig, H.D.; Presber, W.; Jaffe, C.L. PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousslimi, N.; Aoun, K.; Ben-Abda, I.; Ben-Alaya-Bouafif, N.; Raouane, M.; Bouratbine, A. Epidemiologic and clinical features of cutaneous Leishmaniasis in southeastern Tunisia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, C.; Faraut, F.; Lascombe, L.; Dumon, H. Quantification of Leishmania infantum DNA by a real-time PCR assay with high sensitivity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5249–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fróes, A.M.; dos Santos, C.V.; Penha-Filho, M.L.; Teixeira, M.C.; Silva, T.M.; Oliveira, G.G.; dos Santos, W.L.; Pontes-de-Carvalho, L.C.; Alcântara-Neves, N.M. Sub-clinical infection as an effective protocol for obtaining anti-Leishmania chagasi amastigote antibodies of different animal species. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 99, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, J.D.; Dwyer, D.M. Expression of Leishmania antigen on the surface membrane of infected human macrophages in vitro. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1981, 44, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Handman, E. Study of Leishmania major-infected macrophages by use of lipophosphoglycan-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kima, P.E.; Bonilla, J.A.; Cho, E.; Ndjamen, B.; Canton, J.; Leal, N.; Handfield, M. Identification of Leishmania Proteins Preferentially Released in Infected Cells Using Change Mediated Antigen Technology (CMAT). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sert, M.; CakirKoc, R.; BudamaKilinc, Y. Novel Fitc-Labeled Igy Antibody: Fluorescence Imaging Toxoplasma Gondii In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, M.J.; Ridley, D.S. Monocyte recruitment, antigen degradation and localization in cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1986, 67, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- ElHassan, A.M.; Gaafar, A.; Theander, T.G. Antigen-presenting cells in human cutaneous Leishmaniasis due to Leishmania major. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1995, 99, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraille, E.; Gounon, P.; Cazareth, J.; Hoebeke, J.; Lippuner, C.; Davalos-Misslitz, A.; Aebischer, T.; Muller, S.; Glaichenhaus, N.; Mougneau, E. Direct visualization of peptide/MHC complexes at the surface and in the intracellular compartments of cells infected in vivo by Leishmania major. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beena, K.R.; Ramesh, V.; Mukherjee, A. Identification of parasite antigen, correlation of parasite density and inflammation in skin lesions of post kala-azar dermal Leishmaniasis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2003, 30, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Ezquerra, G.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C.; Rocamora, V.; Fernández-Casado, A.; Barranco, C.; Serra, T.; Baró, T.; Pujol, R.M. Role of Leishmania spp. infestation in nondiagnostic cutaneous granulomatous lesions: Report of a series of patients from a Western Mediterranean area. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Routine Diagnosis of Suspected CL Lesions (n = 101) | Corresponding Methanol Fixed Dermal Smears (n = 101) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIFA | ITS1 PCR | ITS1 PCR-RFLP | |||||||
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | L. major | L. infantum | L. tropica | ND * | ||
| Positive (n = 59) | Positive microscopy kDNA qPCR not done (n = 42) | 42 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 38 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Negative microscopy Positive kDNA qPCR (n = 17) | 16 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Negative (n = 42) | Negative microscopy Negative kDNA qPCR (n = 42) | 0 | 42 | 0 | 42 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saïdi, N.; Galaï, Y.; Ben-Abid, M.; Boussoffara, T.; Ben-Sghaier, I.; Aoun, K.; Bouratbine, A. Imaging Leishmania major Antigens in Experimentally Infected Macrophages and Dermal Scrapings from Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions in Tunisia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061157
Saïdi N, Galaï Y, Ben-Abid M, Boussoffara T, Ben-Sghaier I, Aoun K, Bouratbine A. Imaging Leishmania major Antigens in Experimentally Infected Macrophages and Dermal Scrapings from Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions in Tunisia. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061157
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaïdi, Nasreddine, Yousr Galaï, Meriem Ben-Abid, Thouraya Boussoffara, Ines Ben-Sghaier, Karim Aoun, and Aïda Bouratbine. 2022. "Imaging Leishmania major Antigens in Experimentally Infected Macrophages and Dermal Scrapings from Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions in Tunisia" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061157
APA StyleSaïdi, N., Galaï, Y., Ben-Abid, M., Boussoffara, T., Ben-Sghaier, I., Aoun, K., & Bouratbine, A. (2022). Imaging Leishmania major Antigens in Experimentally Infected Macrophages and Dermal Scrapings from Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions in Tunisia. Microorganisms, 10(6), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061157






