Role of IL-17 in Morphogenesis and Dissemination of Cryptococcus neoformans during Murine Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2. Mouse Strains
2.3. Infections
2.4. Administration of TNF-α
2.5. Determination of CFUs and Fungal Morphology
2.6. Macroscopic Analysis of Brain and Lungs
2.7. Histology
2.8. Identification of Different Types of Immune Cells by Flow Cytometry
2.9. Measurement of Cytokine Concentration in Lungs and Brains
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
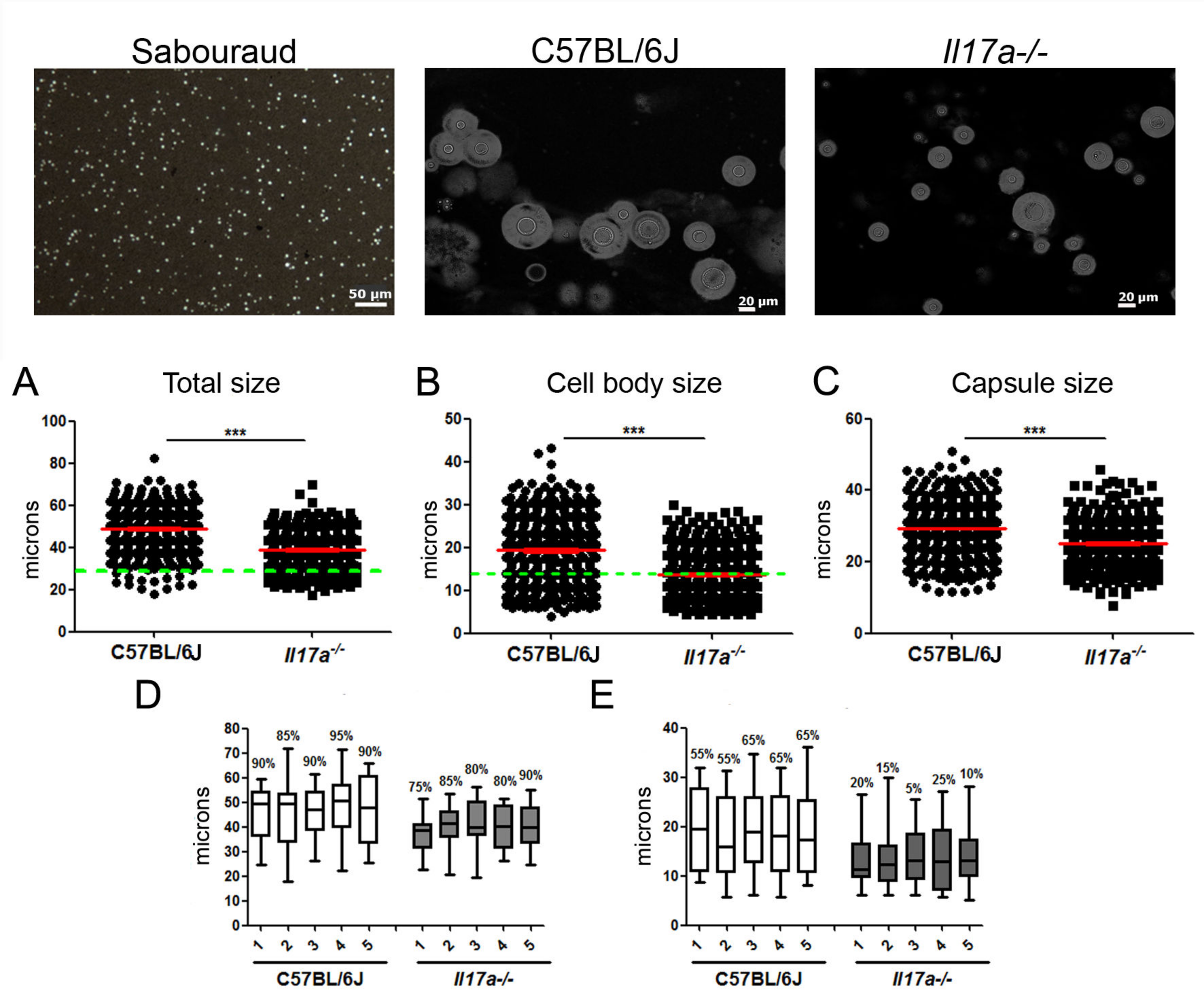
3.1. C. neoformans Formed a Lower Proportion of Titan Cells in Il17a−/− Mouse Model
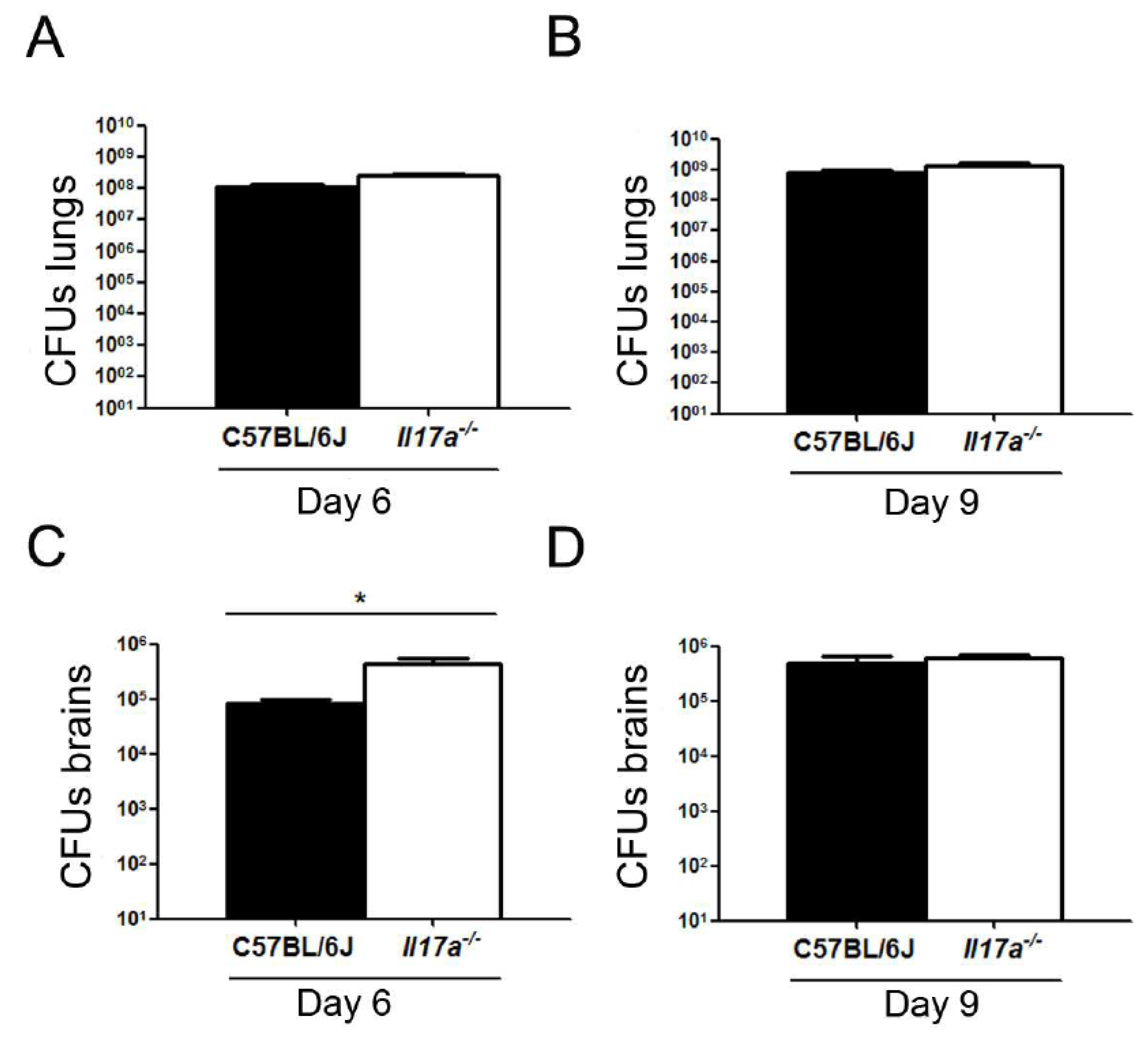
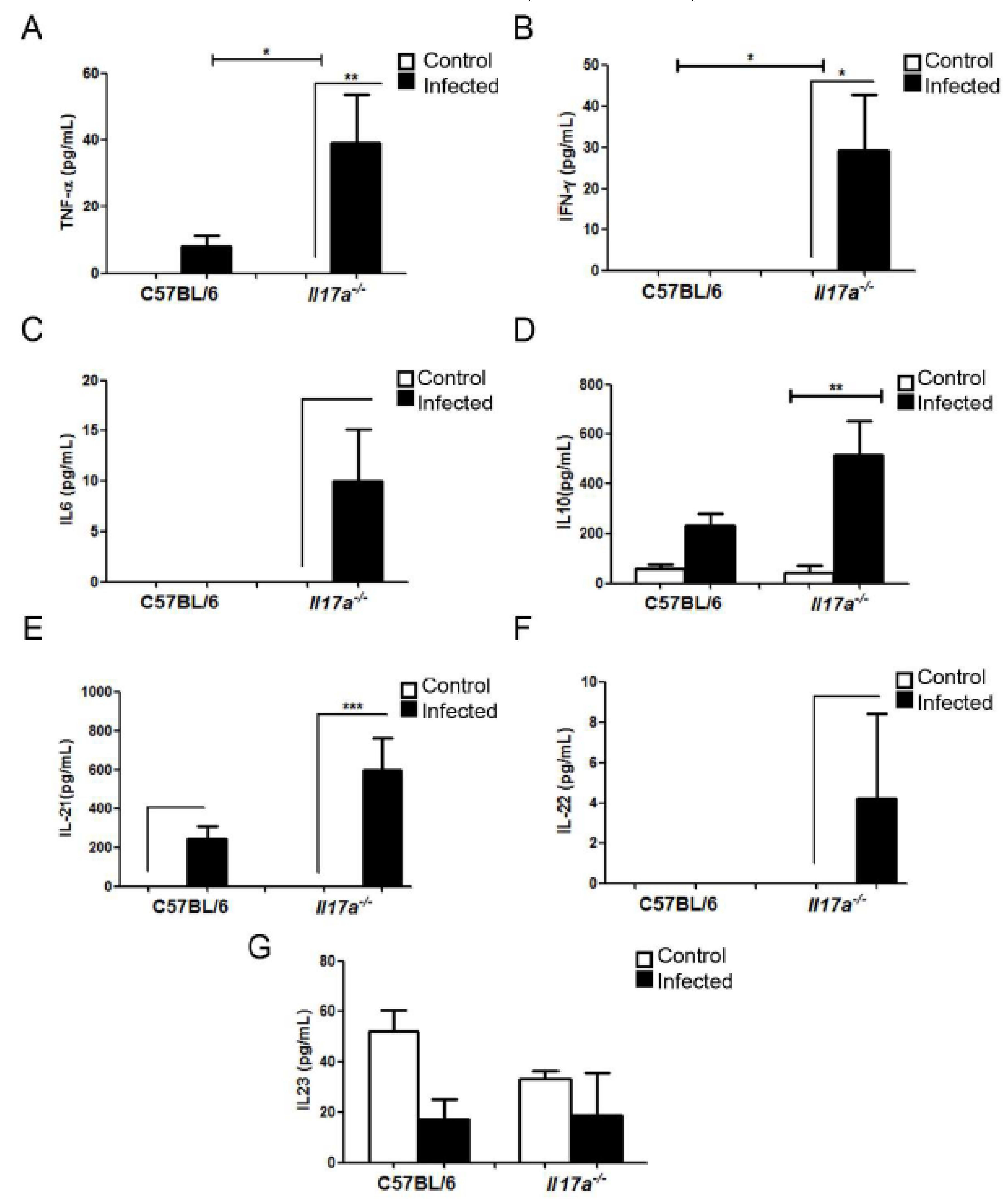
3.2. C. neoformans Caused Increased Inflammation in Brains of Il17a−/− Mice
3.3. Correlation of C. neoformans Morphology with Dissemination to Central Nervous System
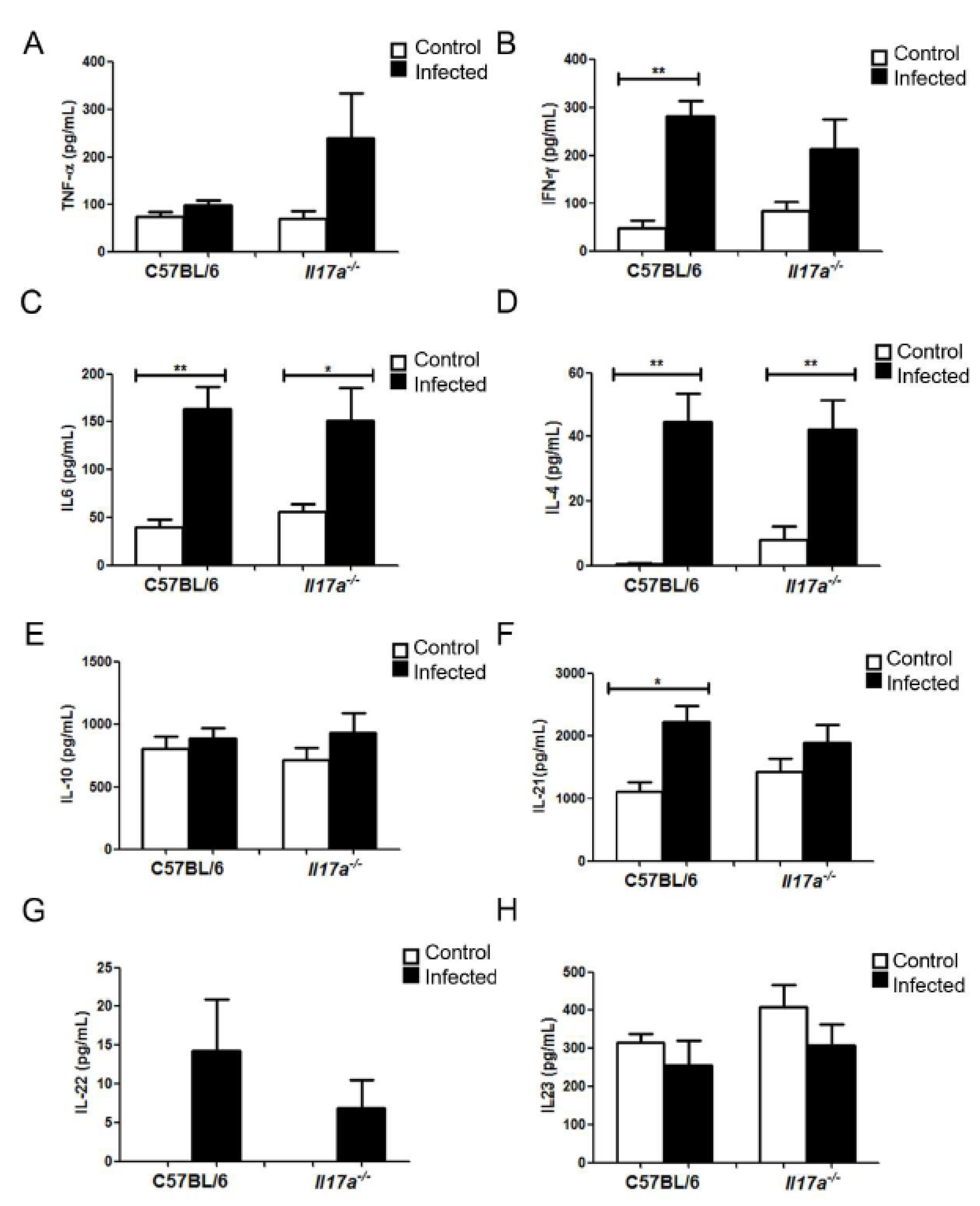
3.4. Analysis of Cytokine Production during Infection
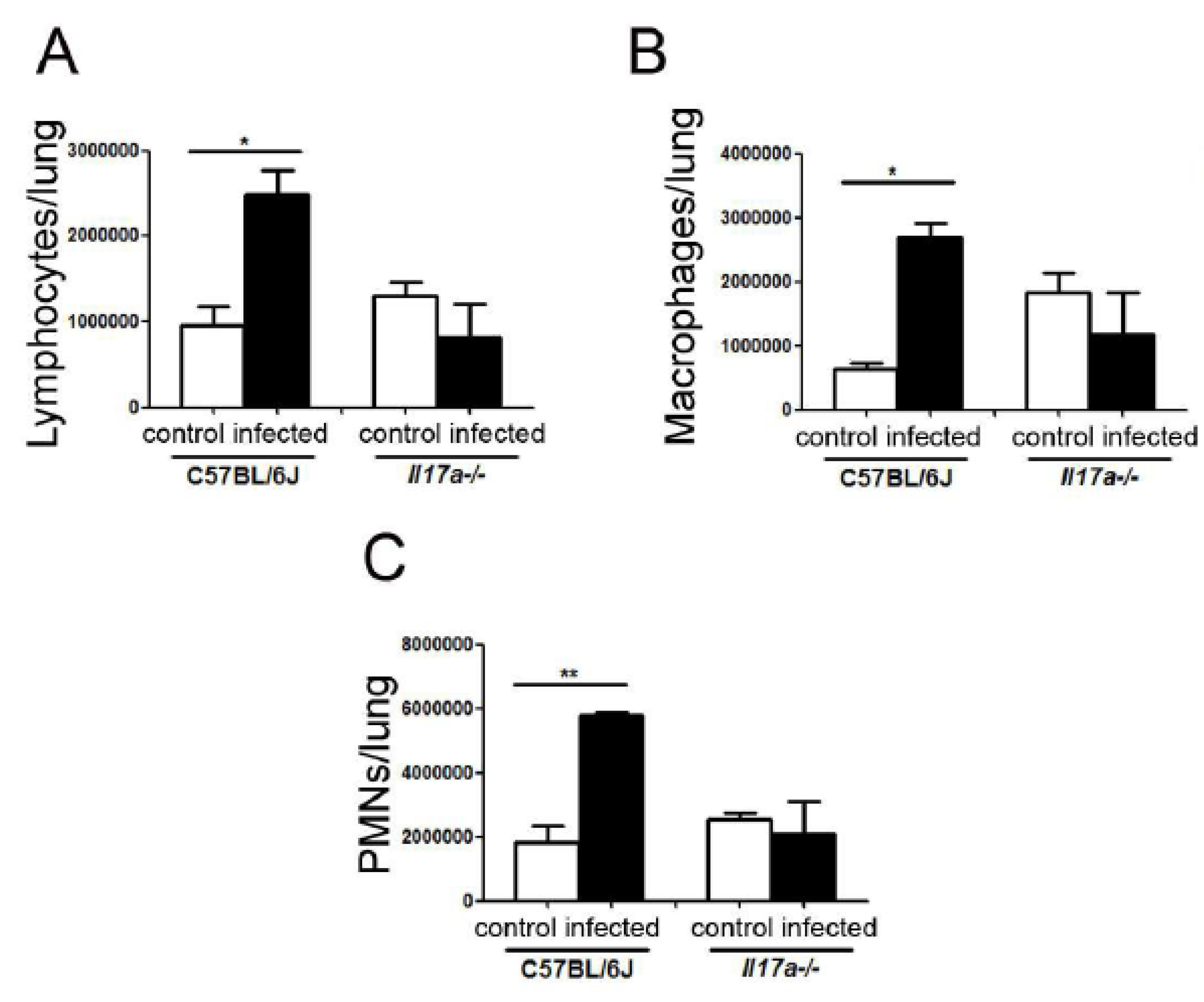
3.5. Cell Recruitment in Lungs
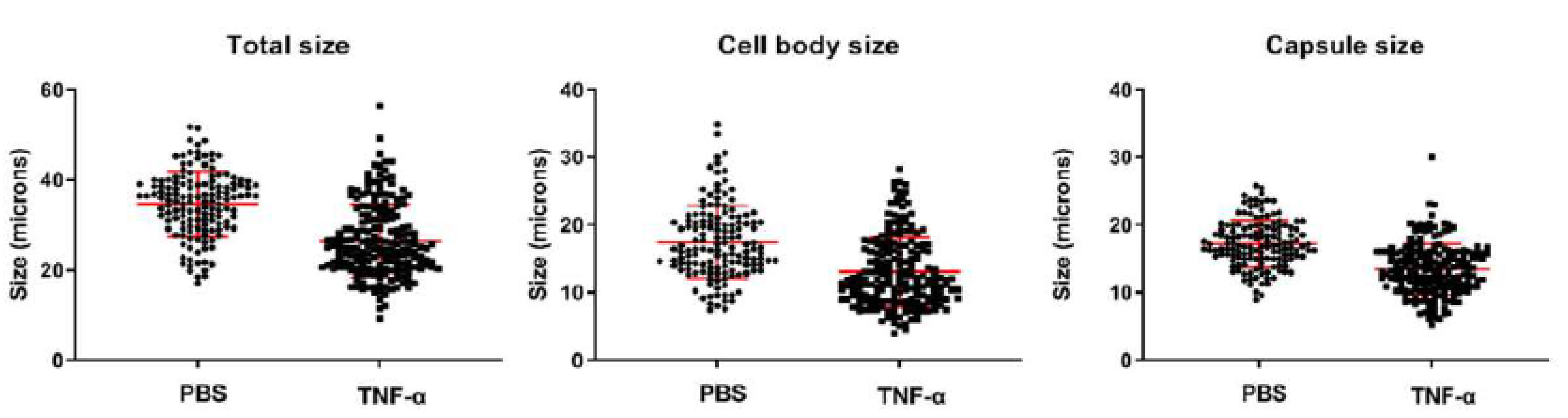
3.6. Exogenous Administration of TNF-α Reduced Proportion of Titan Cells in Lungs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perfect, J.R.; Casadevall, A. Cryptococcosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2002, 16, 837–874v–vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: An updated analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyrgos, V.; Seitz, A.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Prevots, D.R.; Williamson, P.R. Epidemiology of Cryptococcal Meningitis in the US: 1997–2009. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldmesser, M.; Kress, Y.; Novikoff, P.; Casadevall, A. Cryptococcus neoformans Is a Facultative Intracellular Pathogen in Murine Pulmonary Infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4225–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaragoza, O.; Chrisman, C.J.; Castelli, M.V.; Frases, S.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L.; Casadevall, A. Capsule enlargement in Cryptococcus neoformans confers resistance to oxidative stress suggesting a mechanism for intracellular survival. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okagaki, L.H.; Strain, A.K.; Nielsen, J.N.; Charlier, C.; Baltes, N.J.; Chrétien, F.; Heitman, J.; Dromer, F.; Nielsen, K. Cryptococcal Cell Morphology Affects Host Cell Interactions and Pathogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza, O.; García-Rodas, R.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L.; Casadevall, A. Fungal Cell Gigantism during Mammalian Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazera, M.S.; Salmito Cavalcanti, M.A.; Londero, A.T.; Trilles, L.; Nishikawa, M.M.; Wanke, B. Possible primary ecological niche of Cryptococcus neoformans. Med. Mycol. 2000, 38, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldmesser, M.; Kress, Y.; Casadevall, A. Dynamic changes in the morphology of Cryptococcus neoformans during murine pulmonary infection. Microbiology 2001, 147, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaragoza, O.; Nielsen, K. Titan cells in Cryptococcus neoformans: Cells with a giant impact. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trevijano-Contador, N.; de Oliveira, H.C.; García-Rodas, R.; Rossi, S.A.; Llorente, I.; Zaballos, Á.; Janbon, G.; Ariño, J.; Zaragoza, Ó. Cryptococcus neoformans can form titan-like cells in vitro in response to multiple signals. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hommel, B.; Mukaremera, L.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Coelho, C.; Desjardins, C.A.; Sturny-Leclère, A.; Janbon, G.; Perfect, J.R.; Fraser, J.A.; Casadevall, A.; et al. Titan cells formation in Cryptococcus neoformans is finely tuned by environmental conditions and modulated by positive and negative genetic regulators. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dambuza, I.M.; Drake, T.; Chapuis, A.; Zhou, X.; Correia, J.; Taylor-Smith, L.; LeGrave, N.; Rasmussen, T.; Fisher, M.C.; Bicanic, T.; et al. The Cryptococcus neoformans Titan cell is an inducible and regulated morphotype underlying pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Rodas, R.; de Oliveira, H.; Trevijano-Contador, N.; Zaragoza, O. Cryptococcal Titan Cells: When Yeast Cells Are All Grown up. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 422, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ballou, E.R. The Cryptococcus neoformans Titan Cell: From In Vivo Phenomenon to In Vitro Model. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Barbazán, I.; Trevijano-Contador, N.; Rueda, C.; De Andrés, B.; Pérez-Tavárez, R.; Herrero-Fernández, I.; Gaspar, M.L.; Zaragoza, O. The formation of titan cells in Cryptococcus neoformans depends on the mouse strain and correlates with induction of Th2-type responses. Cell. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufaud, C.; Rivera, J.; Rohatgi, S.; Pirofski, L.-A. Naïve B cells reduce fungal dissemination in Cryptococcus neoformans infected Rag1−/− mice. Virulence 2017, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, K.L.; Hardison, S.E.; Kolls, J.K.; Wormley, F.L. Role of IL-17A on Resolution of Pulmonary C. neoformans Infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Tompkins, K.C.; McNamara, A.; Jain, A.V.; Moore, B.B.; Toews, G.B.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Olszewski, M.A. Robust Th1 and Th17 Immunity Supports Pulmonary Clearance but Cannot Prevent Systemic Dissemination of Highly Virulent Cryptococcus neoformans H99. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, K.L.; Hole, C.R.; Yano, J.; Fidel, P.L., Jr.; Wormley, F.L., Jr. Characterization of IL-22 and antimicrobial peptide production in mice protected against pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Microbiology 2014, 160, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aujla, S.J.; Chan, Y.R.; Zheng, M.; Fei, M.; Askew, D.J.; Pociask, D.A.; Reinhart, T.A.; McAllister, F.; Edeal, J.; Gaus, K.; et al. IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, M.A.; Werner, J.L.; Lilly, L.M.; Nelson, M.P.; Metz, A.E.; Dunaway, C.W.; Chan, Y.R.; Ouyang, W.; Brown, G.D.; Weaver, C.T.; et al. Dectin-1-Dependent Interleukin-22 Contributes to Early Innate Lung Defense against Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolls, J.K., Jr.; McCray, P.B., Jr.; Chan, Y.R. Cytokine-mediated regulation of antimicrobial proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.C.; Tan, X.-Y.; Luxenberg, D.P.; Karim, R.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Collins, M.; Fouser, L.A. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Kunz, S.; Witte, E.; Friedrich, M.; Asadullah, K.; Sabat, R. IL-22 Increases the Innate Immunity of Tissues. Immunity 2004, 21, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagasse, E.; Clerc, R.G. Cloning and expression of two human genes encoding calcium-binding proteins that are regulated during myeloid differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Odink, K.; Cerletti, N.; Brüggen, J.; Clerc, R.G.; Tarcsay, L.; Zwadlo, G.; Gerhards, G.; Schlegel, R.; Sorg, C. Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 1987, 330, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwadlo, G.; Brüggen, J.; Gerhards, G.; Schlegel, R.; Sorg, C. Two calcium-binding proteins associated with specific stages of myeloid cell differentiation are expressed by subsets of macrophages in inflammatory tissues. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1988, 72, 510–515. [Google Scholar]
- Mambula, S.S.; Simons, E.R.; Hastey, R.; Selsted, M.E.; Levitz, S.M. Human Neutrophil-Mediated Nonoxidative Antifungal Activity against Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Heesemann, L.; Wagener, J.; Marcos, V.; Hartl, D.; Loeffler, J.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. NETs formed by human neutrophils inhibit growth of the pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, C.F.; Ermert, D.; Schmid, M.; Abu-Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Nacken, W.; Brinkmann, V.; Jungblut, P.R.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contain Calprotectin, a Cytosolic Protein Complex Involved in Host Defense against Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koguchi, Y.; Kawakami, K. Cryptococcal infection and TH1-TH2 cytokine balance. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 21, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, U.; Stenzel, W.; Kohler, G.; Werner, C.; Polte, T.; Hansen, G.; Schutze, N.; Straubinger, R.K.; Blessing, M.; McKenzie, A.N.; et al. IL-13 Induces Disease-Promoting Type 2 Cytokines, Alternatively Activated Macrophages and Allergic Inflammation during Pulmonary Infection of Mice with Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perfect, J.R.; Lang, S.D.; Durack, D.T. Chronic cryptococcal meningitis: A new experimental model in rabbits. Am. J. Pathol. 1980, 101, 177–194. [Google Scholar]
- Trevijano-Contador, N.; Pianalto, K.M.; Nichols, C.B.; Zaragoza, O.; Alspaugh, J.A.; Pirofski, L.-A. Human IgM Inhibits the Formation of Titan-Like Cells in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00046-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagaki, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Ballou, E.R.; O’Meara, T.R.; Bahn, Y.-S.; Alspaugh, J.A.; Xue, C.; Nielsen, K. Cryptococcal Titan Cell Formation Is Regulated by G-Protein Signaling in Response to Multiple Stimuli. Eukaryot. Cell 2011, 10, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okagaki, L.H.; Nielsen, K. Titan Cells Confer Protection from Phagocytosis in Cryptococcus neoformans Infections. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakae, S.; Komiyama, Y.; Nambu, A.; Sudo, K.; Iwase, M.; Homma, I.; Sekikawa, K.; Asano, M.; Iwakura, Y. Antigen-Specific T Cell Sensitization Is Impaired in IL-17-Deficient Mice, Causing Suppression of Allergic Cellular and Humoral Responses. Immunity 2002, 17, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, H.R.; Shen, F.; Nayyar, N.; Stocum, E.; Sun, J.N.; Lindemann, M.J.; Ho, A.W.; Hai, J.H.; Yu, J.J.; Jung, J.W.; et al. Th17 cells and IL-17 receptor signaling are essential for mucosal host defense against oral candidiasis. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, S.; Meintjes, G.; Lesosky, M.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Wilkinson, R.J. Interleukin-17 mediated differences in the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated tuberculous and cryptococcal meningitis. AIDS 2016, 30, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAleer, J.P.; Kolls, J.K. Directing traffic: IL-17 and IL-22 coordinate pulmonary immune defense. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, S.; Gurney, A.L. IL-17: Prototype member of an emerging cytokine family. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolls, J.K.; Lindén, A. Interleukin-17 Family Members and Inflammation. Immunity 2004, 21, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosci, P.; Gabrielli, E.; Luciano, E.; Perito, S.; Cassone, A.; Pericolini, E.; Vecchiarelli, A. Involvement of IL-17A in preventing the development of deep-seated candidiasis from oropharyngeal infection. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschek, M.A.; Muller, U.; Brodie, S.J.; Stenzel, W.; Kohler, G.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Straubinger, R.K.; McClanahan, T.; Kastelein, R.A.; Alber, G. IL-23 Enhances the Inflammatory Cell Response in Cryptococcus neoformans Infection and Induces a Cytokine Pattern Distinct from IL-12. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutitzky, L.I.; Bazzone, L.; Shainheit, M.G.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Cua, D.J.; Stadecker, M.J. IL-23 Is Required for the Development of Severe Egg-Induced Immunopathology in Schistosomiasis and for Lesional Expression of IL-17. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, M.A.; Huo, Y.; Burcin, T.L.; Morris, M.A.; Olson, T.S.; Ley, K. Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils Regulates Granulopoiesis via IL-23 and IL-17. Immunity 2005, 22, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salim, T.; Sershen, C.L.; May, E.E. Investigating the Role of TNF-α and IFN-γ Activation on the Dynamics of iNOS Gene Expression in LPS Stimulated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Morgan, M.J.; Choksi, S.; Liu, Z.-G. TNF-Induced Activation of the Nox1 NADPH Oxidase and Its Role in the Induction of Necrotic Cell Death. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trevijano-Contador, N.; Roselletti, E.; García-Rodas, R.; Vecchiarelli, A.; Zaragoza, Ó. Role of IL-17 in Morphogenesis and Dissemination of Cryptococcus neoformans during Murine Infection. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020373
Trevijano-Contador N, Roselletti E, García-Rodas R, Vecchiarelli A, Zaragoza Ó. Role of IL-17 in Morphogenesis and Dissemination of Cryptococcus neoformans during Murine Infection. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020373
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrevijano-Contador, Nuria, Elena Roselletti, Rocío García-Rodas, Anna Vecchiarelli, and Óscar Zaragoza. 2022. "Role of IL-17 in Morphogenesis and Dissemination of Cryptococcus neoformans during Murine Infection" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020373
APA StyleTrevijano-Contador, N., Roselletti, E., García-Rodas, R., Vecchiarelli, A., & Zaragoza, Ó. (2022). Role of IL-17 in Morphogenesis and Dissemination of Cryptococcus neoformans during Murine Infection. Microorganisms, 10(2), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020373





