Susceptibility Tests and Predictions of Transporter Profile in Serratia Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of Disinfectants and Inhibitors
2.3. Efflux Pump Predictions and Annotations
2.4. Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Efflux Pump Inhibitor-Supplemented Susceptibility Tests
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
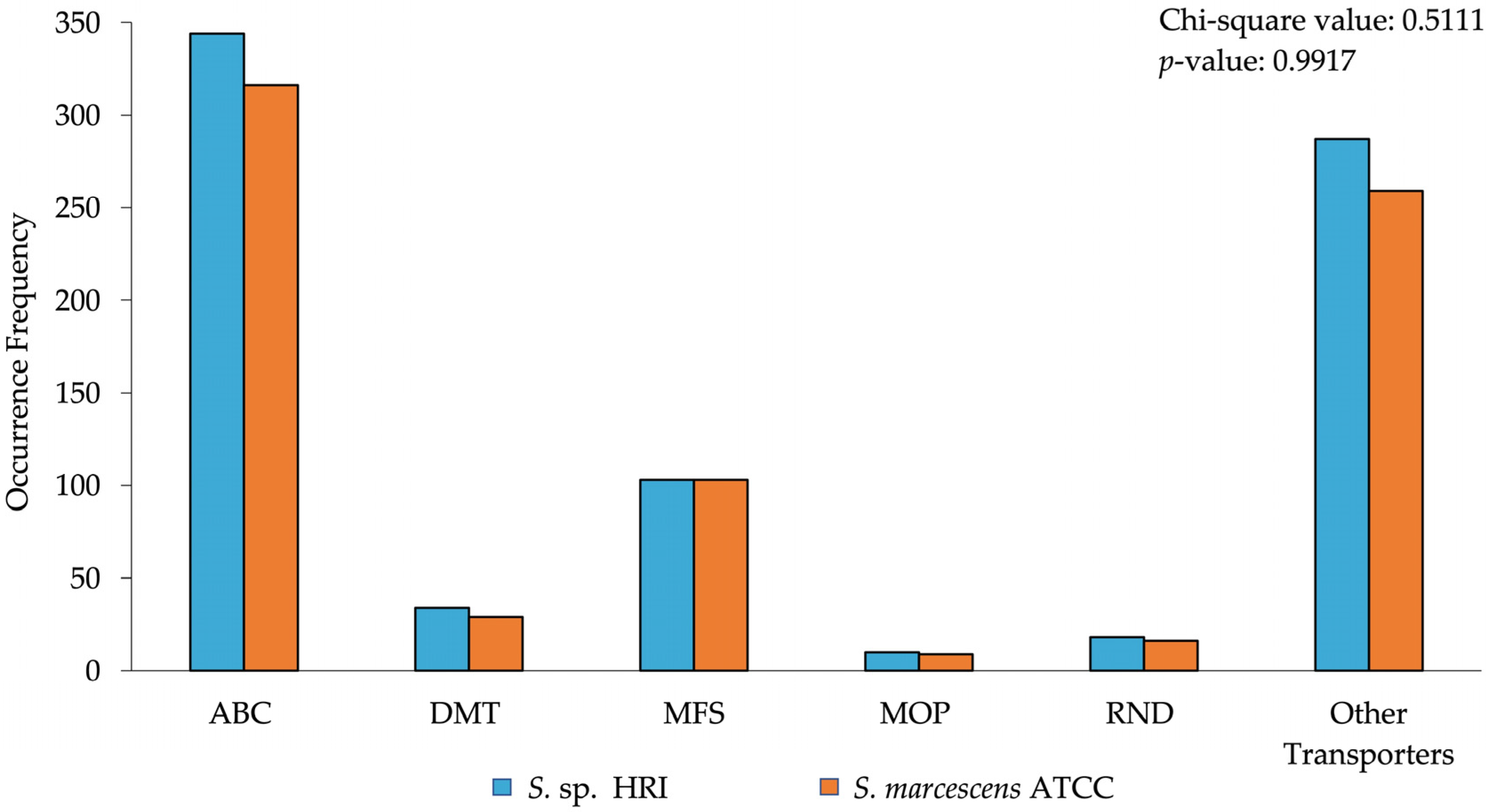
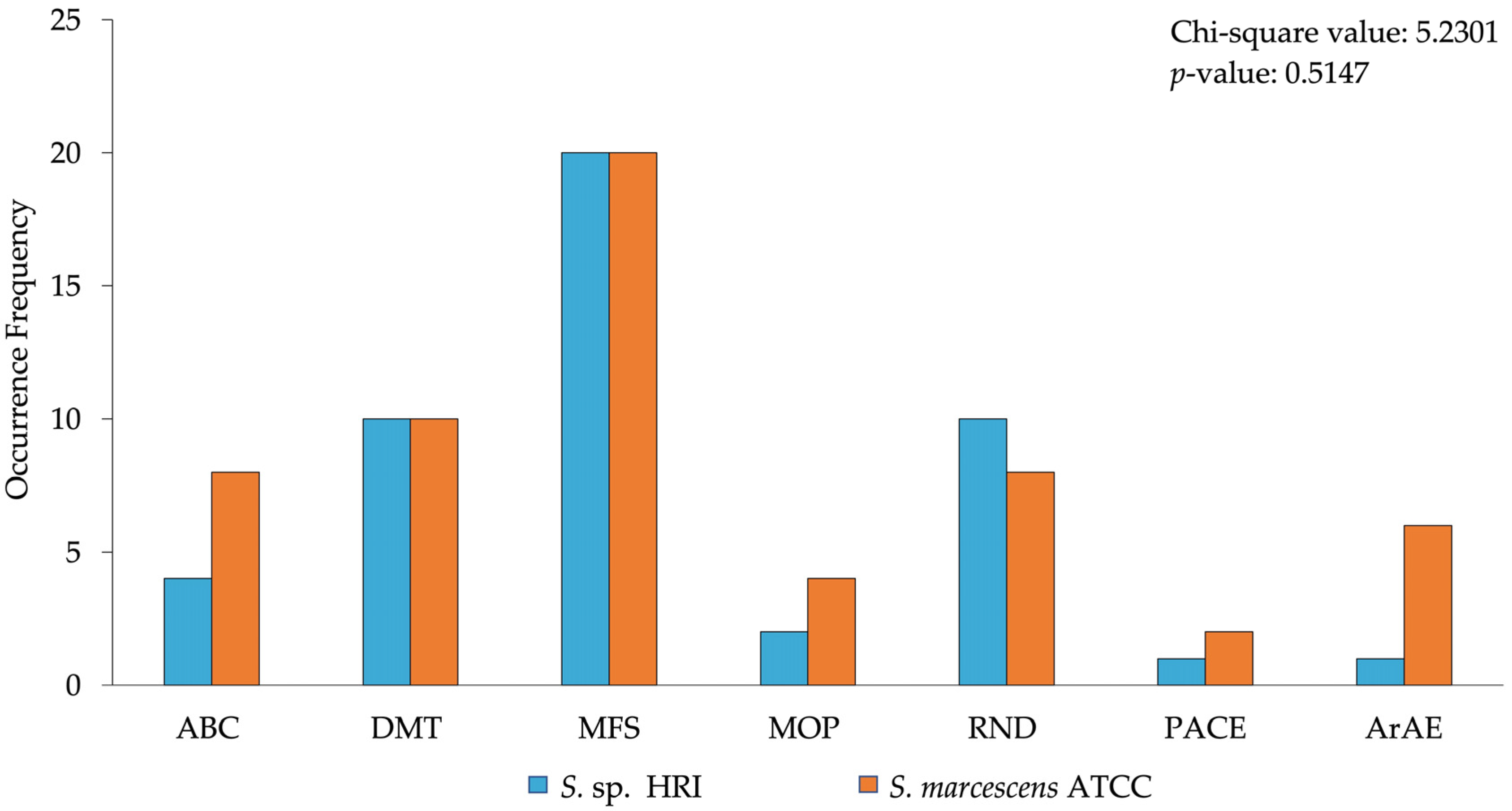
3.1. Efflux System Profile of Isolates
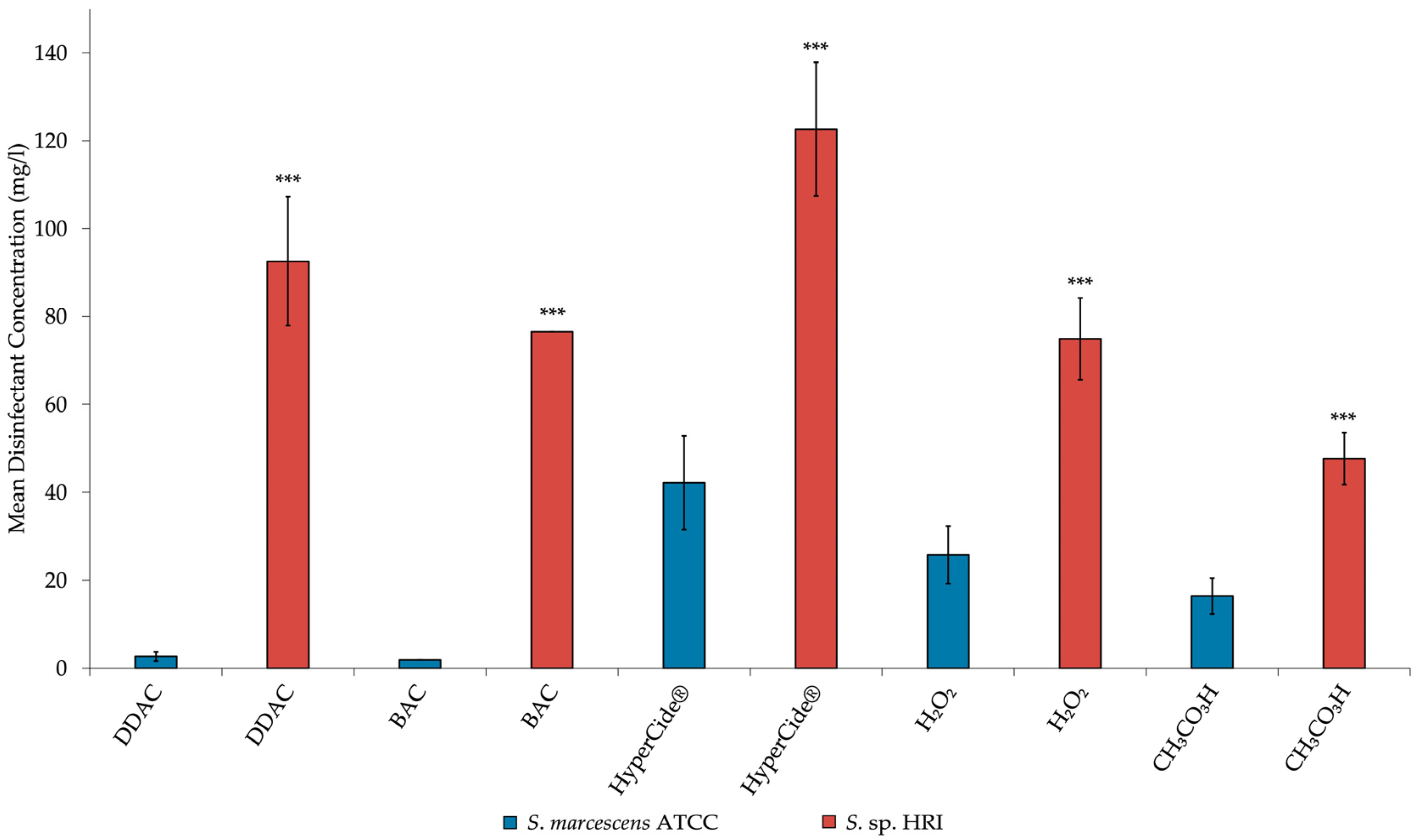
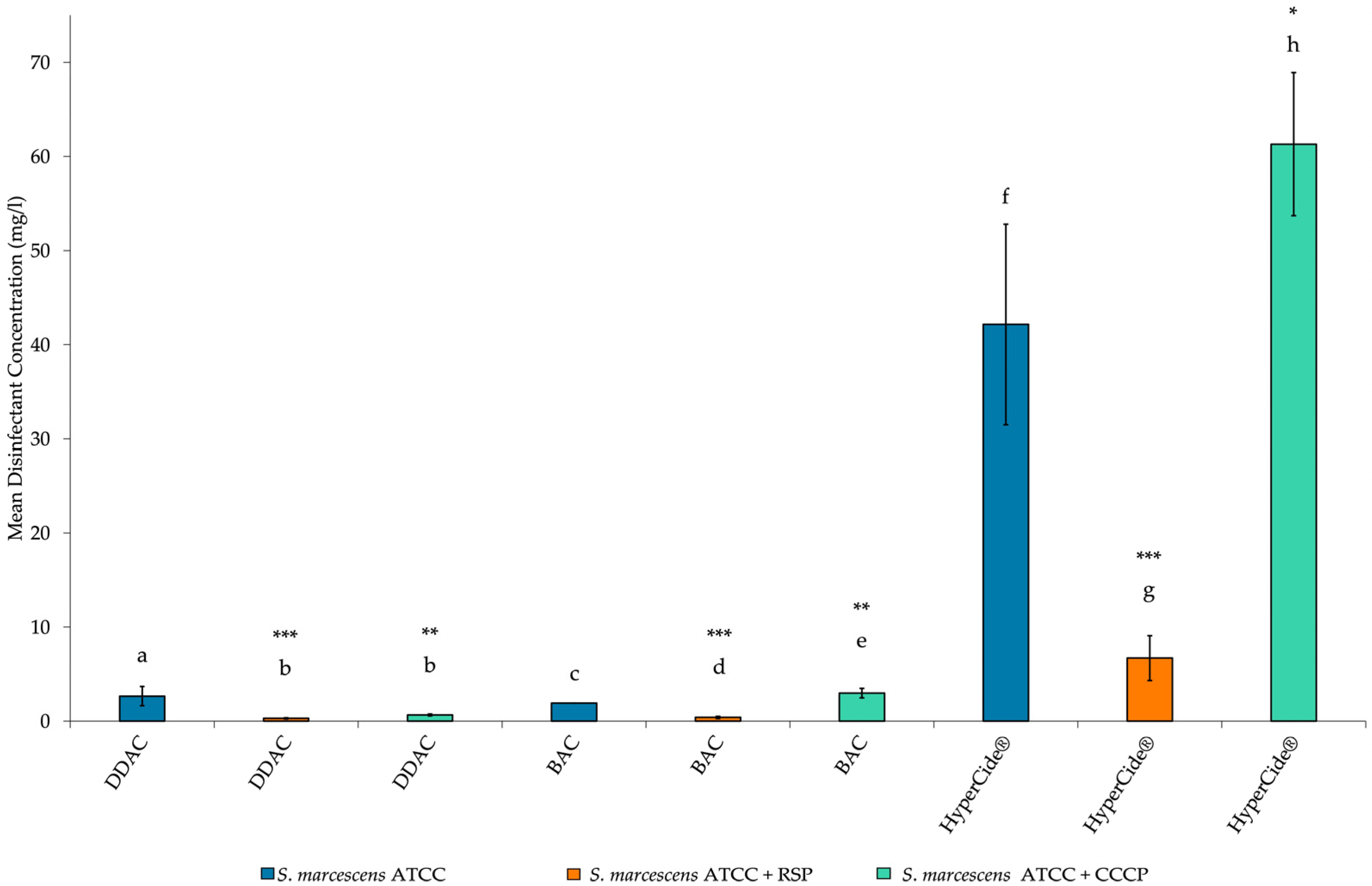
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations for Isolates
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahlen, S.D. Serratia Infections: From Military Experiments to Current Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 755–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laupland, K.B.; Parkins, M.D.; Gregson, D.B.; Church, D.L.; Ross, T.; Pitout, J.D.D. Population-Based Laboratory Surveillance for Serratia Species Isolates in a Large Canadian Health Region. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, I.; Akova, M.; Baquero, F.; Carlet, J.; Cavaleri, M.; Coenen, S.; Cohen, J.; Findlay, D.; Gyssens, I.; Heure, O.E.; et al. The Global Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance: Science for Intervention. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, R.R.; Meyburgh, C.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Coetzee, M. Potential Treatment Options in a Post-Antibiotic Era. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1052, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, C.J.; Hanlon, G.W.; Denyer, S.P. Action of Disinfectant Quaternary Ammonium Compounds against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorland, J.; Steinum, T.; Sunde, M.; Waage, S.; Heir, E. Novel Plasmid-Borne Gene qacJ Mediates Resistance to Quaternary Ammonium Compounds in Equine Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus simulans, and Staphylococcus intermedius. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3046–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennent, J.M.; Lyon, B.R.; Gillespie, M.T.; May, J.W.; Skurray, R.A. Cloning and Expression of Staphylococcus aureus Plasmid-Mediated Quaternary Ammonium Resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 27, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J.V. Understanding the Mechanisms and Drivers of Antimicrobial Resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Carlie, S.J.; Hellmuth, J.E.; Newman, J.; Boucher, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Genome Sequence of Resistant Serratia sp. Strain HRI, Isolated from a Bottle of Didecyldimethylammonium Chloride-Based Disinfectant. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00095-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, M.; Villa, L.; Fortini, D.; Bordoni, R.; Imperi, F.; Bonnal, R.J.P.; Sicheritz-ponten, T.; Bellis, G.D.; Visca, P.; Cassone, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Pyrosequencing of an Epidemic Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strain Belonging to the European Clone II Group. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M.I.; Piddock, L.J.V. The Efflux Pump Inhibitor Reserpine Selects Multidrug-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Strains That Overexpress the ABC Transporters PatA and PatB. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyfakh, A.A.; Bidnenko, V.E.; Chen, L.B. Efflux-Mediated Multidrug Resistance in Bacillus subtilis: Similarities and Dissimilarities with the Mammalian System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4781–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, M.A.; Verschoor, C.P.; Bowdish, D.; Brown, E.D. Collapsing the Proton Motive Force to Identify Synergistic Combinations against Staphylococcus aureus. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.K.; Ko, K.S. Effect of Carbonyl Cyanide 3-Chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) on Killing Acinetobacter baumannii by Colistin. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbourne, L.D.H.; Tetu, S.G.; Hassan, K.A.; Paulsen, I.T. TransportDB 2.0: A Database for Exploring Membrane Transporters in Sequenced Genomes from All Domains of Life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D320–D324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, K.A.; Liu, Q.; Henderson, P.J.F.; Paulsen, I.T. Homologs of the Acinetobacter baumannii AceI Transporter Represent a New Family of Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Systems. mBio 2015, 6, e01982-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Tiwari, M.; Tiwari, V. Efflux Pumps in Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Current Status and Challenges in the Discovery of Efflux Pumps Inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.Y.; Jamshidi, S.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Current Advances in Developing Inhibitors of Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1062–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, H.; Hashida, Y.; Konaka, R.; Shirai, A.; Kourai, H. Mutational Upregulation of a Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division-Type Multidrug Efflux Pump, SdeAB, upon Exposure to a Biocide, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, and Antibiotic Resistance in Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5230–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, J.; Ziegler, J.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Reimer, A.; Kitts, D.D.; Gilmour, M.W. Tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes to Quaternary Ammonium Sanitizers Is Mediated by a Novel Efflux Pump Encoded by emrE. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J.V. Clinically Relevant Chromosomally Encoded Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps in Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorland, J.; Sunde, M.; Waage, S. Plasmid-Borne smr Gene Causes Resistance to Quaternary Ammonium Compounds in Bovine Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, Y.; Hiasa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Omote, H. Multidrug and Toxic Compound Extrusion (MATE)-Type Proteins as Anchor Transporters for the Excretion of Metabolic Waste Products and Xenobiotics. Xenobiotica 2008, 38, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kuroda, T.; Huda, M.N.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. An RND-Type Multidrug Efflux Pump SdeXY from Serratia marcescens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabrin, A.; Gioe, B.W.; Gupta, A.; Grove, A. An EmrB Multidrug Efflux Pump in Burkholderia thailandensis with Unexpected Roles in Antibiotic Resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.-X.; Zhang, C.; Crow, R.R.; Thorpe, C.; Chen, H.; Kumar, S.; Tsuchiya, T.; Varela, M.F. SugE, a New Member of the SMR Family of Transporters, Contributes to Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3954–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouch, D.A.; Cram, D.S.; Di Berardino, D.; Littlejohn, T.G.; Skurray, R.A. Efflux-mediated Antiseptic Resistance Gene qacA from Staphylococcus aureus: Common Ancestry with Tetracycline- and Sugar-transport Proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 1990, 4, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kücken, D.; Feucht, H.-H.; Kaulfers, P.-M. Association of qacE and qacEΔ1 with Multiple Resistance to Antibiotics and Antiseptics in Clinical Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 183, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.H.; Paulsen, I.T.; Skurray, R.A. The Multidrug Efflux Protein NorM Is a Prototype of a New Family of Transporters. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, K.; Latifi, T.; Groisman, E.A. Virulence and Drug Resistance Roles of Multidrug Efflux Systems of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.A.; Jackson, S.M.; Penesyan, A.; Patching, S.G.; Tetu, S.G.; Eijkelkamp, B.A.; Brown, M.H.; Henderson, P.J.F.; Paulsen, I.T. Transcriptomic and Biochemical Analyses Identify a Family of Chlorhexidine Efflux Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20254–20259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaze, W.H.; Abdouslam, N.; Hawkey, P.M.; Wellington, E.M.H. Incidence of Class 1 Integrons in a Quaternary Ammonium Compound-Polluted Environment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahcheraghi, F.; Minato, Y.; Chen, J.; Mizushima, T.; Ogawa, W.; Kuroda, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Multidrug Efflux Pump, SmfY, from Serratia marcescens. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, S.D.; Worobec, E.A. Gene Expression Analysis of the SdeAB Multidrug Efflux Pump in Antibiotic-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Serratia marcescens. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, A.; Du, D.; Luisi, B.F. Structure and Mechanism of Bacterial Tripartite Efflux Pumps. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Lewis, K.; Matin, A. EmrR Is a Negative Regulator of the Escherichia coli Multidrug Resistance Pump EmrAB. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooun, A.; Tomashek, J.J.; Lewis, K. Purification and Ligand Binding of EmrR, a Regulator of a Multidrug Transporter. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 5131–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braoudaki, M.; Hilton, A.C. Mechanisms of Resistance in Salmonella Enterica Adapted to Erythromycin, Benzalkonium Chloride and Triclosan. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardebili, A.; Talebi, M.; Azimi, L.; Rastegar Lari, A. Effect of Efflux Pump Inhibitor Carbonyl Cyanide 3-Chlorophenylhydrazone on the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Ciprofloxacin in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, e8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulkidjanian, A.Y.; Cherepanov, D.A.; Heberle, J.; Junge, W. Proton Transfer Dynamics at Membrane/Water Interface and Mechanism of Biological Energy Conversion. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, G.; Srinivasan, V.B.; Gebreyes, W.A. Novel Role of Acinetobacter baumannii RND Efflux Transporters in Mediating Decreased Susceptibility to Biocides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Ling, B.-D.; Li, X.-Z. Distribution of the Multidrug Efflux Pump Genes, adeABC, adeDE and adeIJK, and Class 1 Integron Genes in Multiple-Antimicrobial-Resistant Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Complex. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Espada, R.; Shahrour, H.; Pitts, B.; Stewart, P.S.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Martínez-de-Tejada, G. A Permeability-Increasing Drug Synergizes with Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors and Restores Susceptibility to Antibiotics in Multi-Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasetyoputri, A.; Jarrad, A.M.; Cooper, M.A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. The Eagle Effect and Antibiotic-Induced Persistence: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, H. A Paradoxical Zone Phenomenon in the Bactericidal Action of Penicillin in Vitro. Science 1948, 107, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckay, G.A.; Beaulieu, S.; Arhin, F.F.; Belley, A.; Sarmiento, I.; Jr, T.P.; Moeck, G. Time–Kill Kinetics of Oritavancin and Comparator Agents against Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 63, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorian, V.; Silletti, R.P.; Biondo, F.X.; De Freitas, C.C. Paradoxical Effect of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics on the Growth of Gram-Negative Bacilli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1979, 5, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Nakazawa, S. Bacteriological Study on Effects of Beta-Lactam Group Antibiotics in High Concentrations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1976, 9, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nishino, T. Paradoxical Antibacterial Activities of B- Lactams against Proteus vulgaris: Mechanism of the Paradoxical Effect. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, G.; Hong, Y.; Drlica, K.; Zhaoa, X. Suppression of Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation Accounts for Paradoxical Bacterial Survival at High Quinolone Concentration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01622-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Carbonel, A.; Mondragón, B.; López-Chegne, N.; Peña-Tuesta, I.; Huayan-Dávila, G.; Blitchtein, D.; Carrillo-Ng, H.; Silva-Caso, W.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; del Valle-Mendoza, J. The Effect of the Efflux Pump Inhibitor Carbonyl Cyanide M-Chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) on the Susceptibility to Imipenem and Cefepime in Clinical Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staats, G.J.; Mc Carlie, S.J.; Boucher-van Jaarsveld, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Susceptibility Tests and Predictions of Transporter Profile in Serratia Species. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112257
Staats GJ, Mc Carlie SJ, Boucher-van Jaarsveld CE, Bragg RR. Susceptibility Tests and Predictions of Transporter Profile in Serratia Species. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(11):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112257
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaats, Gunther J., Samantha J. Mc Carlie, Charlotte E. Boucher-van Jaarsveld, and Robert R. Bragg. 2022. "Susceptibility Tests and Predictions of Transporter Profile in Serratia Species" Microorganisms 10, no. 11: 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112257
APA StyleStaats, G. J., Mc Carlie, S. J., Boucher-van Jaarsveld, C. E., & Bragg, R. R. (2022). Susceptibility Tests and Predictions of Transporter Profile in Serratia Species. Microorganisms, 10(11), 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112257





