Abstract
The emergence of drug-resistant strains of the parasite Leishmania infantum infecting dogs and humans represents an increasing threat. L. infantum genomes are complex and unstable with extensive structural variations, ranging from aneuploidies to multiple copy number variations (CNVs). These CNVs have recently been validated as biomarkers of Leishmania concerning virulence, tissue tropism, and drug resistance. As a proof-of-concept to develop a novel diagnosis platform (LeishGenApp), four L. infantum samples from humans and dogs were nanopore sequenced. Samples were epidemiologically typed within the Mediterranean L. infantum group, identifying members of the JCP5 and non-JCP5 subgroups, using the conserved region (CR) of the maxicircle kinetoplast. Aneuploidies were frequent and heterogenous between samples, yet only chromosome 31 tetrasomy was common between all the samples. A high frequency of aneuploidies was observed for samples with long passage history (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1), whereas fewer were detected for samples maintained in vivo (MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033). Twenty-two genes were studied to generate a genetic pharmacoresistance profile against miltefosine, allopurinol, trivalent antimonials, amphotericin, and paromomycin. MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 displayed a genetic profile with potential resistance against miltefosine and allopurinol. Meanwhile, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 were identified as potentially resistant against paromomycin. All four samples displayed a genetic profile for resistance against trivalent antimonials. Overall, this proof-of-concept revealed the potential of nanopore sequencing and LeishGenApp for the determination of epidemiological, drug resistance, and pathogenicity biomarkers in L. infantum.
1. Introduction
Leishmania infantum is a parasitic protozoan of the order Trypanosomatida (family Trypanosomatidae), known to infect and cause severe disease in dogs and other mammals which can act, in turn, as reservoirs for zoonotic transmission to humans (further developed in Hong et al., 2020) [1]. L. infantum is transmitted as an extracellular parasite (promastigote) to a mammalian host by female infected phlebotomine sand flies. Afterward, the parasites proliferate as obligate intracellular parasites (amastigotes) in phagocytic cells and spread to different organs, causing leishmaniosis. The infection in the mammalian host can occur subclinically or with clinical signs of varying severity. In humans, L. infantum infection can cause cutaneous lesions (cutaneous leishmaniosis or CL) and systemic disease (visceral leishmaniosis or VL). In dogs, the infection causes a severe systemic disease, with cutaneous lesions, lymphadenopathy, weight loss, and chronic kidney disease, among other clinical signs. Dogs are the major domestic reservoir of L. infantum, but wild mammals such as the red fox, black rats, and the Iberian hare can also be involved in the transmission cycle [1,2,3].
Several drugs are available to treat leishmaniosis, both in humans and dogs, albeit their effectiveness may vary and can be considered toxic. Trivalent antimonials and miltefosine, although potentially hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic (reviewed in van Griensven and Diro, 2019 [4]), are the first-choice treatment in dogs and are also used to treat human patients. As in many infections, diversity and selection have given rise to drug resistance and treatment failure. Given the limited therapeutic arsenal, the increasing emergence of resistant L. infantum strains is a serious global health problem.
The genome of Leishmania infantum is diploid with an approximate size of 32 Mb, organized in 36 chromosomes (plus maxicircles and minicircles, which form the kinetoplast network). Genome instability is characteristic of L. infantum and of all the Leishmania genus, and it is responsible for unique genomic characteristics such as (i) mosaic aneuploidy [5] and (ii) transcription regulation by gene copy number variation (CNV) [6]. The genome instability is triggered by heterologous recombination of direct and indirect repeats spread along its genome [7]. This stochastic rearrangement (“genome sizing and shuffling”) may introduce local or chromosome wide CNVs, reaching its characteristic mosaic subpopulations and eliciting a fast adaptation to changing environments [8]. Thus, studies that identify mutations or genetic markers as well as the underlying mechanic for drug resistance are essential for determining specific genetic variations involved in drug resistance mechanisms; reviewed in Ponte-Sucre et al., 2017 [9] as well as for parasite population genetics and epidemiology. Some genetic variations have been associated with resistance to drugs: an increase in copy number of genes in the H locus (chromosome 23) has been associated with trivalent antimonial resistance, and a reduction in METK (LinJ.30.3560) gene copies has been associated with increased allopurinol resistance [10]. Other markers, such as the coding regions of the conserved region (CR) of the maxicircle, have recently been reported as suitable for Leishmania taxonomy for phylogenetic analysis, including subspecies divisions [11,12].
Rapid aneuploidy and CNV turnover (“genome sizing and shuffling”) serve as a substrate for variability that, combined with selection, triggers a fast environment adaptation and enhances parasite evolvability under stress (i.e., culture, extra- and intracellular life cycle, drug resistance, etc.) [13]. Massive short-read sequencing has proven valuable for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery but lacks power for more complex structural variants [14]. Long reads from single-molecule sequencing span repetitive regions of the genome, facilitating subsequent assembly of genomes and offering an added advantage in quantitatively identifying and assessing structural variations and gene amplification events [14]. Furthermore, long-read technologies allow sequencing without the need for previous amplification, so it is possible to directly compare the coverage between different regions for biomarker panels or regions with very divergent GC content [15].
In this pilot study, we present the development of a genomic analysis platform (LeishGenApp) that allows sequencing and bioinformatics analyses to identify pharmacoresistance, pathogenicity, and population genetic biomarkers for L. infantum. In this proof-of-concept, the validity of direct uncorrected nanopore reads is defended for identifying and typing L. infantum samples and detecting genomic aneuploidies and gene copy number variations, (un)known markers for pathogenicity, and pharmacoresistance. Further development will be required to transform this proof-of-concept into an agile and straightforward genomic platform for use in clinical practice, and as an aid in conducting epidemiological studies or on treatment and prognosis of leishmaniosis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
Four Leishmania infantum samples were acquired to test as a proof-of-concept: (i) ATCC Control DNA from reference L. infantum strain Nicolle (ATCC 50134D, MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1) and (ii) three promastigote cultures received from Facultat de Farmàcia (Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain) collections. The cultured samples were propagated in Schneider medium (S0146-500ML, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% human urine, and 25 mg/mL gentamicin. Cultured samples correspond to MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 (isolated from dog’s skin exudate and passaged in Cricetus aureus) from the north-western Mediterranean region (Table 1).

Table 1.
Sample origin and metadata used in this study. Four cultured L. infantum samples MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 were used in this study. Columns represent the relation with their original host, type of sample, leishmaniosis presentation (visceral or VL, cutaneous or CL), organ of isolation, and year and geographical location.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
DNA was extracted from the three cultures using the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Miniprep Kit (D4300; Zymo Research Corporation; Los Angeles, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Before library preparation, extracted DNA was quantified using Qubit dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Fisher Scientific S.L; Madrid, Spain), and quality was assessed by absorbance using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific S.L; Waltham, MA, USA). The sequencing libraries were prepared using the Rapid Barcoding Sequencing Kit (SQKRBK004) from Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT, Oxford, UK), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Rapid sequencing barcodes were added to the tagged ends to analyze more than one sample in a single run (barcoding). As a final step, 12 μL of each library was loaded onto a flow cell for sequencing using the Mk1c (MinION, ONT, Oxford, UK) and run for 48 h.
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3.1. Identification, Typing, and Phylogeny
Guppy (v6.1.2; ‘SUP’ model) was used for basecalling and demultiplexing all runs. Species identification was carried out using blastn (part of BLAST+ v2.9.0 [16] with direct uncorrected reads against a local database of Trypanosomatidae, downloaded from NCBI-NIH records by taxonomical ID (nucleotide database with txid5654). Typing was conducted by reconstruction of the conserved region of the maxicircle kinetoplast by mapping the corresponding reads with minimap2 v2.17-r941 [17] against the L. infantum JPCM5 v2/2018 reference (http://leish-esp.cbm.uam.es/l_infantum_downloads.html, accessed on 1 April 2022) [18] and deriving the consensus sequencing using SAMTools v1.10 [19] and BCFtools v1.10.2 [20]. Phylogenetic data from previous studies were collected from the Leish-ESP site (http://leish-esp.cbm.uam.es/l_infantum_downloads.html, accessed on 1 April 2022) [21]. L. infantum maxicircle phylogeny was constructed by multiple sequence alignment concatenation of conserved genes sequences 12S rRNA, 9S rRNA, ND8, ND9, MURF5, ND7, CO3, CYb, ATPase 6, ND2, G3, ND1, CO2, MURF2, CO1, G4, ND4, G5 (ND3), RPS12, and ND5 using MAFFT v7.490 [22]. Phylogeny was reconstructed using the maximum likelihood method applying the Tamura–Nei 1993 model [23] with 1000 bootstraps, selecting the topology with the best log-likelihood with IQ-Tree2 v2.2.0 [24].
2.3.2. Aneuploidy and Gene Copy Number Variation Analysis
Aneuploidy and gene copy number variation were determined by calculating the log2 change of observed vs. expected copies (2N) over a sliding window of 100 kbp and 1 kbp, respectively. Thus, the copy ratio of 0 is 2N, 0.5 is 3N, 1 is 4N, or −1 is N. Both analyses were conducted using the LeishGenApp analysis platform (Nano1Health S.L., Bellaterra, Spain). Briefly, direct uncorrected nanopore reads were mapped against a reference using LRA v1.3.4 [25] and the read alignments were processed by SAMTools v1.10 [19]. The coverage in read alignments was screened with multiple sliding windows (as previously described) with CNVkit v0.9.8 [26].
Chromosome variation was significant by a threshold of ±0.2, as recommended elsewhere [26]. For instance, all the copy ratio values between −0.2 and 0.2 were determined as diploid (2N). Locally, nine genomic regions harboring 22 genes previously described as related to pathogenicity or drug resistance in L infantum have been used as a proof-of-concept for CNV characterization (Table 2). L. infantum JPCM5 v2/2018 genome assembly and annotation were used as reference for CNV (http://leish-esp.cbm.uam.es/l_infantum_downloads.html, accessed during 1 April 2022) [18]. Gene identification is conserved with previous assemblies, as described elsewhere [18]. A more stringent threshold, ±0.25, was assigned to identify variation in gene copy number than for aneuploidy detection, accounting for a greater effect of population mosaicism of smaller sliding windows. If multiple copy numbers are reported due to mosaicism, the most extreme copy number is reported by convention. Gene copy number was calculated from log2 for each of the 22 genes. CNVs were expressed as an addition to the expected number of chromosomes or gene copies (2N).

Table 2.
Summary of known biomarkers for drug resistance in L. infantum. Summary of locus, gene ID, function, and reported gene copy number variation of the nine genomic regions (22 loci) analyzed related to pathogenicity or drug resistance in L. infantum. Gene ID, Start, and End correspond to the L. infantum reference genome (L. infantum JPCM5 v2/2018) [18]. CNV: Expansion or deletion of gene copy number. R: Resistant; TF: Treatment failure. A reference is provided for studies showing threshold resistance effect by CNVs.
2.4. Data Availability
Raw sequencing data for this experiment can be accessed at NCBI-NIH SRA SRR21601459—SRR21601462, BioSamples SAMN30884654—SAMN30884657, under BioProject SUB12055562.
3. Results
3.1. Identification, Typing, and Phylogeny
Each culture (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033) was successfully identified as belonging to the Leishmania infantum species by aligning direct uncorrected nanopore reads against a local database of Trypanosomatidae sequences with blastn (best hit with e-value < 1 × 10−8). For each sample, 94% (99% L. donovani–L. infantum complex), 94% (99% L. donovani–L. infantum complex), 94% (99% L. donovani–L. infantum complex), and 96% (99% L. donovani–L. infantum complex) of total reads were assigned to L. infantum, respectively. The remaining 1% was assigned to other Leishmania spp. complexes (L. major or L. mexicana) or unannotated.
Each CR sequence could be successfully reconstructed with a variety of mean coverages: 161X for MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, 15X for MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, 8X for LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and 3X for MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033. Sequence alignment and a maximum likelihood (ML) tree of the CR of the maxicircle with the Leishmania–Trypanosoma phylogeny procured by Solana et al., 2022 placed them within the phylogenetic cluster of L. infantum (Figure S1). Moreover, as shown in Figure 1, when placing the four sequences (marked in red) in an L. donovani–L. infantum phylogeny, the novel sequences still cluster within L. infantum but are divided between the so-called JPC5 subgroup (marked in dark green) and non-JPC5 subgroup (marked in blue) clusters. MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 is the only sequence that clusters in the alternative non-JPC5 subgroup Spanish cluster. Thus, shallow coverage (<10X) does not interfere with sequence reconstruction nor with its phylogenetic placement.
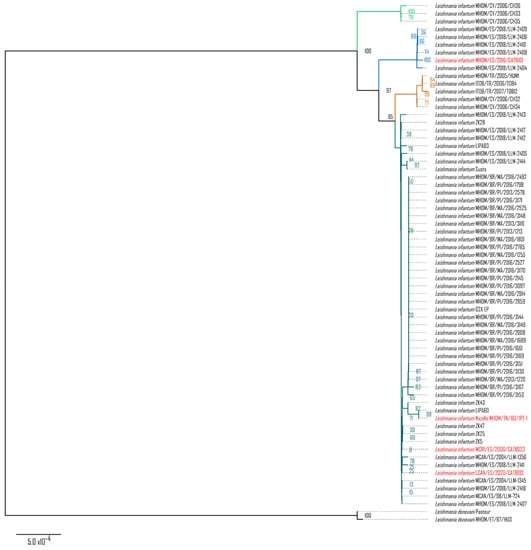

Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the L. donovani–L. infantum group. L. donovani–L. infantum consensus phylogeny was constructed using the conserved region of the maxicircle, concatenating the coding sequences of 12S rRNA, 9S rRNA, ND8, ND9, MURF5, ND7, CO3, CYb, ATPase 6, ND2, G3, ND1, CO2, MURF2, CO1, G4, ND4, G5 (ND3), RPS12, and ND5. The maximum likelihood tree (log-likelihood −21,183.118) was modeled with the Tamura–Nei 1993 model with 1000 bootstraps. Taxa highlighted in red correspond to the novel maxicircle sequences of MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033, and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 samples. Subspecies phylogenetic clusters, types, or groups are highlighted in green, blue, yellow, and turquoise, corresponding to the same clusters identified in Solana et al., 2022 [12].
3.1.1. Aneuploidy Analysis
Regarding the aneuploidy analysis, the chromosomal dotation of the samples was heterogeneous (Figure 2). Chromosome 31 was tetrasomic in all the studied samples. Total or mosaic trisomy was observed for chromosomes 5, 9, 11, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, and 29 for sample MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1; chromosomes 1, 5, 9, 11, 23, 26, and 35 for sample MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101; and chromosomes 33 and 35 for LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102. Changes involving chromosome gain (Figure 2, green, turquoise, and violet) were more common among all samples than those involving chromosome loss (red). Sample MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 harbors the highest number of chromosomal variations (nine trisomies, four tetrasomies, and one hexasomy). Other anomalies identified were hexasomy for chromosome 23 in sample MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, and partial monosomy (mosaic) for chromosome 13 in sample MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033. This finding supports the presence of intrastrain mosaicism and interstrain chromosomal diversity.
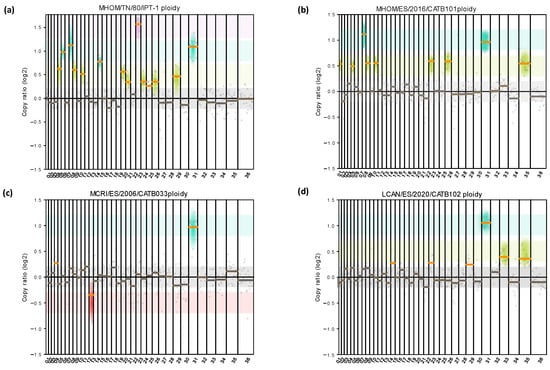
Figure 2.
Detection and quantification of different aneuploidy patterns among L. infantum cultures. Aneuploidy analysis was carried out by adapting the sliding window size to 100 kbp (gray dots) for MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 (a), MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 (b), LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 (c), and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 (d). Copy ratio represents the fold change of expected and observed chromosomal dotation. The median copy ratio is represented in orange if significantly different than 0 or in gray if not significant. Monosomy is highlighted with red shadowing, disomies with gray, trisomies with green, tetrasomies in turquoise, and hexasomies or larger in violet. No pentasomies were observed.
3.1.2. CNV for Drug Resistance and Pathogenicity Biomarkers in L. infantum
Miltefosine, allopurinol, trivalent antimonials, amphotericin, and paromomycin are the most used drugs used to treat leishmaniosis. As depicted in Table 2, CNVs of these 22 genes may act as potential biomarkers for pharmacoresistance in L. infantum. All 22 genes were detected with a coverage > 5X. CNVs were detected in all the samples: 13 genes with CNV in LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, 16 genes with CNV in MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033, 18 genes with CNV in MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, and 19 genes with CNV in MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 (Table 3). Hence, nine, six, four, and three genes remain copy-neutral (CN 0) for each sample. Variation was observed for all the genes in at least one sample. Overall, the variation in copy number compared to the diploid dotation ranged from +7 copies for the LinJ.23.0280 gene (YIP1) in MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 to −1 for the LinJ.36.6760 gene (LMPK) in MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033.

Table 3.
Detection of CNV in 22 genes suitable as potential pharmacoresistance and pathogenicity biomarkers in L infantum. Variation in its local copy number for each sample, ranging between −1 and +7 gene copies compared to the diploid dotation (0). * Tetrasomy in chromosome 31 must be considered.
The miltefosine transporter and associated genes are in chromosomes 13 (LinJ.13.1590, LdMT; LinJ13.1600, hypothetical protein gene) and 32 (LinJ.32.1040, IdRos3) [32], where local deletions (CN −1) were found in three strains (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033). Regarding the miltefosine sensitivity locus (MSL; LinJ.31.2370 to LinJ.31.2400), located in chromosome 31 (tetrasomic) [27], local expansions were detected at the population level in all four samples. In addition to the duplication of the entire diploid chromosome dotation (CN +2), additional local expansions of this entire locus were detected in sample MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 (CN +4; +4; +4, +5, and +3 in LinJ.31.2370 to LinJ.31.2400, respectively). Considering the tetrasomic dotation of chromosome 31, partial deletions (CN +1, +2) were observed in samples MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102.
Allopurinol pharmacoresistance is linked to the METK locus located in chromosome 30, which contains four genes (LinJ.30.3550, Lorien protein gene; LinJ.30.3560, METK1; LinJ.30.3570, Lorien protein gene; LinJ.30.3580, METK2) [10]. Samples MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 presented local expansion (CN +1) in all genes in the METK locus, while MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 followed a different trend with partial deletions in LinJ.30.3560 and LinJ.30.3570.
The H locus, AQP1 gene, MAPK1 gene, and SMT gene are trivalent antimonial resistance biomarkers [30,31,33]. The H locus harbors four genes in chromosome 23 (LinJ.23.0280, YIP1; LinJ.23.0290, MRPA; LinJ.23.0300, LinJ.23.0300; LinJ.23.0310, PTR1). Samples MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 showed CNV and mosaicism (CN +1). Remarkably, MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 had the greatest increase that ranged from +4 in PTR1 to +7 in YIP1. These local expansions could be related to the ploidy of chromosome 23 in the four samples (hexasomy in MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, partial trisomy in LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, trisomy in MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, and disomy in MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033). The AQP1 gene (LinJ.31.0030) is in chromosome 31 (tetrasomic). Considering the duplication of the complete chromosome dotation, an additional gene expansion was observed in sample MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 (CN +5). Total gene (CN +1) deletion was observed in sample MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, and partial (CN +1, +2 and +2, +3) deletions were observed in MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, respectively. The MAPK1 gene (LinJ.36.6760) and SMT gene (LinJ.36.2510) copy number ranged from −1 to +1 CN.
The paromomycin resistance locus entails two genes in chromosome 27 (LinJ.27.1940, D-LDH; LinJ.27.1950, B-CAT) [30]. While the D-LDH had two copies (CN 0) in all the samples except in LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 (CN 0, +1), the B-CAT gene copy number presented certain variability among the samples. MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 had CN −1 compared to the reference, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 had CN 0, and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 had CN +1.
The LACK antigen is a protein encoded by Lack1 (LinJ.28.2940) and Lack2 (LinJ.28.2970) genes, and they are related to Leishmania pathogenicity [29]. Both are located at chromosome 28. Mosaicism of both genes (CN 0, +1) was observed in MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 and MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101; Lack2 was present as a mosaic (CN 0, +1) in LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102. MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 had no CNV in this locus.
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification, Typing, and Phylogeny
All four samples (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033) were successfully identified as Leishmania infantum. Direct uncorrected nanopore reads proved to be of sufficient quality and length to successfully assign at least 94% (max. 96%) of the total reads to L. infantum with e-value < 1× 10−8, further validating the technology as a feasible approach for pathogen identification. The remaining reads were assigned to members of the L. donovani–L. infantum complex (5%) or were unassigned or misassigned to other Trypanosomatidae members (1%). Differentiation between L. infantum and L. donovani can be difficult due to their high nucleotide identity (i.e., chromosome 36 is 99.16% similar between references L. donovani BPK282A1 and L. infantum JPCM5); thus, it is not striking that a small percentage of reads (5%) is assigned as L. donovani. The remaining 1% consists of a mixture of assignments to other Trypanosomatidae, to high error reads or sequences belonging to the maxicircle and minicircle kinetoplasts, for which there is no complete reference for L. infantum yet [12,21].
In addition to species identification by random sequence fragments, maxicircle kinetoplast sequences from Trypanosomatidae have been previously described as a suitable molecular marker for species [11,21] and strain [12] phylogenies, akin to mitochondrial sequences from the kingdoms Plantae, Fungi, or Animalia. As shown in Figure S1, reconstruction of the L. infantum conserved region (CR) of the maxicircle is possible through guided consensus assembly with nanopore sequencing reads, with as little coverage as with a mean of 3X. Such new CR sequences are similar in quality to those previously published from L. infantum, as they cluster together in a Leishmania–Trypanosoma phylogeny. Moreover, as shown in Figure 1, group typing is possible within the L. donovani–L. infantum complex with these reconstructed sequences. The CRs of MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033, and LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 isolates correspond to the classic JPC5-like group, which is very prevalent in the Iberian Peninsula and present in other Mediterranean areas. Interestingly, isolate MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 is placed within the non-JPC5 cluster as it possesses the same 17 SNPs described in Solana et al., 2022 [12], showing that the non-JPC5 L. infantum group was circulating at least two years prior than previously estimated with isolates MHOM/ES/2018/LLM-2404, MHOM/ES/2018/LLM-2406, MHOM/ES/2018/LLM-2408, MHOM/ES/2018/LLM-2409, and MHOM/ES/2018/LLM-2410, dated from 2018. Beyond establishing an earlier timeline, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 establishes the presence of a non-JPC5 L. infantum group out of the Iberian Peninsula (Mallorca, Balearic Islands).
4.2. Detection of Aneuploidy and Gene Copy Number Variation
Leishmania parasites mostly rely on aneuploidy and DNA CNVs to regulate the expression of stress response genes to, e.g., temperature, acidity, or drugs [7,34,35]. As presented in the Results section, direct uncorrected nanopore reads have been suitable to detect aneuploidy, including chromosome mosaicism, and previously described CNV related to genetic drug resistance biomarkers.
Notably, local CNVs of targeted chromosome regions were more common across chromosomes in all four samples than aneuploidy. These genome plasticity strategies are a good solution for transcript regulation for an organism that lacks promoter-dependent regulation [6]. However, with this approach, it is not possible to discern whether this local gene amplification is intrachromosomal, maintained as extrachromosomal (linear or circular) molecules [34], or an expansion of an entire chromosome. Therefore, further studies to conclude its physical conformation should be conducted.
Remarkably, when comparing the ploidy of the four samples, MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 has the smallest number of aneuploidies. Furthermore, it is the only sample where gene loss was quantified at the chromosomal level (sample is mosaic for a monoploidy of chromosome 13). It is noteworthy that MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033, despite being isolated from a dog, was propagated in hamsters (Cricetus aureus), in vivo, in contrast with the other three samples, which were only maintained as in vitro cultured promastigotes. MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 had the largest number of aneuploidies (n = 14), probably linked to its long propagation and culture history, as it was isolated in 1980. Such long culture history may have adapted that strain to culturing conditions, as it is known that parasite isolation and subsequent in vitro parasite maintenance are strong drivers for chromosome and gene copy number variation [36,37]. Moreover, according to Domagalska et al., aneuploidy was much lower in amastigotes (intracellular stage of the parasite) than in cultivated promastigotes (extracellular) [37]. Our results are consistent with previous studies, given that the closest diploid karyotype was found in the in vivo MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033. Otherwise, MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 showed the highest number of aneuploidies due to the in vitro effect on ploidy variation [37]. Considering changes in chromosome copy number as a highly common feature during experimental selection, the results support the importance of minimizing culture laboratory passaging or direct clinical samples when studying aneuploidy and CNV as genomic biomarkers.
Local detection of CNVs in the 22 genes studied revealed possible pharmacoresistance in our sample collection. A deletion in LdMT and/or ldRos3 (CN −1) is related with a 2- and 1.6-fold decrease in miltefosine sensitivity, respectively [32]. According to this genetic biomarker, samples MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1 and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 have the genetic potential to be pharmacoresistant to miltefosine. Additionally, the same samples have the genetic potential to have allopurinol pharmacoresistance as a deletion (CN −1) in the METK1 gene was quantified [10]. Regarding biomarkers for trivalent antimonial resistance, all four strains showed genetic potential for pharmacoresistance since an additional copy (CN +1) of the MRPA gene in the H locus is related to an increase in resistance [28]. MRPA CNVs ranged from +1 in MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033 to CN +5 in MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1. Finally, an extra copy of D-LDH and B-CAT genes is linked with a 4.87 and 4.08-fold increase in paromomycin resistance, respectively [30]. Potential genetic pharmacoresistance could be detected in MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101 and in LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102 since mosaic expansions (CN 0, +1) were found in B-CAT in both strains and D-LDH in the latter. A larger cohort of samples and phenotypic data (resistance) are required to validate the clinical relevance of these genetic pharmacoresistance profiles. A current limitation of this methodology is the elucidation of the physical conformation of aneuploidies and gene CNs (chromosomal or extrachromosomal). Despite not being relevant for possible genetic pharmacoresistance or virulence, this difference is relevant for the transmission of virulence, as described for Leishmania spp. Small extrachromosomal circles with virulence genes can be readily transmitted through vesicle transport to neighboring parasites [34]. Thus, an exhaustive analysis should be carried out in further studies to overcome this limitation.
5. Conclusions
Direct uncorrected nanopore reads were obtained from four samples of Leishmania infantum (MHOM/TN/80/IPT-1, MHOM/ES/2016/CATB101, LCAN/ES/2020/CATB102, and MCRI/ES/2006/CATB033). Those reads were successfully used to (i) identify the species in culture, (ii) type the parasite’s group, and (iii) identify potential biomarkers of pharmacoresistance or virulence, reducing the computational cost and time in comparison to other strategies (i.e., assembly). Additionally, the longer read lengths than other sequencing alternatives (i.e., Illumina sequencing) permitted a reconstruction of the conserved region of the maxicircle sequences with as little as 3X coverage. Likewise, direct uncorrected nanopore reads provided sufficient coverage to identify chromosomal aneuploidies. These findings supported the presence of intrastrain mosaicism and interstrain diversity in our samples. Moreover, this methodology was able to determine the CNV status of 22 genes (divided in 10 loci) related to pharmacoresistance and virulence with shallow coverage (>5X). The analysis of additional strains with available phenotype data will be needed to validate LeishGenApp and the methodology presented here. Furthermore, the analyses of aneuploidy and CNV directly from clinical samples, coupled with in vitro drug resistance and pathogenicity tests, would help decipher the selected regions’ suitability as biomarkers for L. infantum.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms10112256/s1, Figure S1: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the Leishmania–Trypanosoma group.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.-C., O.F., X.R. and L.F.; Methodology, J.M.-C., M.N.-J. and O.F.; Software, J.M.-C. and M.N.-J.; Validation, M.C. and M.G.-P.; Formal Analysis, J.M.-C., M.C. and M.G.-P.; Investigation, J.M.-C., M.C., M.G.-P., C.R. and R.F.; Resources, X.R., L.F. and O.F.; Data Curation, J.M.-C.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, J.M.-C., O.F., M.C. and M.G.-P.; Writing—Review and Editing, J.M.-C., O.F., M.C., M.G.-P., X.R., L.F., M.N.-J., C.R., R.F. and M.M.A.; Visualization, J.M.-C. and M.C.; Supervision, O.F.; Project Administration, O.F.; Funding Acquisition, X.R., L.F. and O.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This original work has been partially funded by the CDTI—NEOTEC project (SNEO-20211355) granted by the Spanish Science Ministry to develop innovative solutions to novel R&D companies, and by Elanco España SA.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequencing data for this experiment can be accessed at the NCBI-NIH SRA deposit SRR21601459—SRR21601462, BioSamples SAMN30884654—SAMN30884657, under BioProject (SUB12055562).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the technical advice provided by Daniel Pérez, as well as Marc Ibáñez and Roger Farrés Catalán for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
Nano1Health, SL is a for-profit contract research organization. J.M.-C., M.C., M.G.-P., and O.F. are currently employed by the company. M.N.-J., X.R., L.F., and O.F. own company stock. Nano1Health, SL has received travel awards from Oxford Nanopore Technologies to present part of this research in key conferences. Part of this research initiative was sponsored by Elanco España SA. The external funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hong, A.; Zampieri, R.A.; Shaw, J.J.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F. One Health Approach to Leishmaniases: Understanding the Disease Dynamics through Diagnostic Tools. Pathogens 2020, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Ferroglio, E.; Solano-Gallego, L. Role of Wildlife in the Epidemiology of Leishmania Infantum Infection in Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Solano, J.; González, G.; Osuna, A.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; Peracho, V.; Montalvo, T.; Fuentes, M.V. Molecular Detection of Leishmania Infantum in Rats and Sand Flies in the Urban Sewers of Barcelona, Spain. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Griensven, J.; Diro, E. Visceral Leishmaniasis. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2019, 33, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterkers, Y.; Lachaud, L.; Crobu, L.; Bastien, P.; Pagès, M. FISH Analysis Reveals Aneuploidy and Continual Generation of Chromosomal Mosaicism in Leishmania Major. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto Barja, P.; Pescher, P.; Bussotti, G.; Dumetz, F.; Imamura, H.; Kedra, D.; Domagalska, M.; Chaumeau, V.; Himmelbauer, H.; Pages, M.; et al. Haplotype Selection as an Adaptive Mechanism in the Protozoan Pathogen Leishmania Donovani. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, J.-M.; Raymond, F.; Mukherjee, A.; Plourde, M.; Gingras, H.; Roy, G.; Lapointe, A.; Leprohon, P.; Papadopoulou, B.; Corbeil, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Stochastic Adaptive DNA Amplification at Direct and Inverted DNA Repeats in the Parasite Leishmania. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussotti, G.; Gouzelou, E.; Côrtes Boité, M.; Kherachi, I.; Harrat, Z.; Eddaikra, N.; Mottram, J.C.; Antoniou, M.; Christodoulou, V.; Bali, A.; et al. Leishmania Genome Dynamics during Environmental Adaptation Reveal Strain-Specific Differences in Gene Copy Number Variation, Karyotype Instability, and Telomeric Amplification. mBio 2018, 9, e01399-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte-Sucre, A.; Gamarro, F.; Dujardin, J.-C.; Barrett, M.P.; López-Vélez, R.; García-Hernández, R.; Pountain, A.W.; Mwenechanya, R.; Papadopoulou, B. Drug Resistance and Treatment Failure in Leishmaniasis: A 21st Century Challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasur-Landau, D.; Jaffe, C.L.; David, L.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Baneth, G. Resistance of Leishmania Infantum to Allopurinol Is Associated with Chromosome and Gene Copy Number Variations Including Decrease in the S-Adenosylmethionine Synthetase (METK) Gene Copy Number. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufer, A.; Barratt, J.; Stark, D.; Ellis, J. The Complete Coding Region of the Maxicircle as a Superior Phylogenetic Marker for Exploring Evolutionary Relationships between Members of the Leishmaniinae. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 70, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, J.C.; Chicharro, C.; García, E.; Aguado, B.; Moreno, J.; Requena, J.M. Assembly of a Large Collection of Maxicircle Sequences and Their Usefulness for Leishmania Taxonomy and Strain Typing. Genes 2022, 13, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franssen, S.U.; Durrant, C.; Stark, O.; Moser, B.; Downing, T.; Imamura, H.; Dujardin, J.-C.; Sanders, M.J.; Mauricio, I.; Miles, M.A.; et al. Global Genome Diversity of the Leishmania Donovani Complex. eLife 2020, 9, e51243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.S.; Urban, A.E.; Mills, R.E. Structural Variation in the Sequencing Era. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, D.; Ross, M.G.; Chen, W.-S.; Danielsson, M.; Fennell, T.; Russ, C.; Jaffe, D.B.; Nusbaum, C.; Gnirke, A. Analyzing and Minimizing PCR Amplification Bias in Illumina Sequencing Libraries. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST plus: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-de la Fuente, S.; Peiró-Pastor, R.; Rastrojo, A.; Moreno, J.; Carrasco-Ramiro, F.; Requena, J.M.; Aguado, B. Resequencing of the Leishmania Infantum (Strain JPCM5) Genome and de Novo Assembly into 36 Contigs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A Statistical Framework for SNP Calling, Mutation Discovery, Association Mapping and Population Genetical Parameter Estimation from Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, E.; Rastrojo, A.; Sanchiz, Á.; González-de la Fuente, S.; Aguado, B.; Requena, J.M. Leishmania Mitochondrial Genomes: Maxicircle Structure and Heterogeneity of Minicircles. Genes 2019, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the Number of Nucleotide Substitutions in the Control Region of Mitochondrial DNA in Humans and Chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Chaisson, M.J.P. Lra: A Long Read Aligner for Sequences and Contigs. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talevich, E.; Shain, A.H.; Botton, T.; Bastian, B.C. CNVkit: Genome-Wide Copy Number Detection and Visualization from Targeted DNA Sequencing. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnielli, J.B.T.; Crouch, K.; Forrester, S.; Silva, V.C.; Carvalho, S.F.G.; Damasceno, J.D.; Brown, E.; Dickens, N.J.; Costa, D.L.; Costa, C.H.N.; et al. A Leishmania Infantum Genetic Marker Associated with Miltefosine Treatment Failure for Visceral Leishmaniasis. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fadili, K.; Messier, N.; Leprohon, P.; Roy, G.; Guimond, C.; Trudel, N.; Saravia, N.G.; Papadopoulou, B.; Légaré, D.; Ouellette, M. Role of the ABC Transporter MRPA (PGPA) in Antimony Resistance in Leishmania Infantum Axenic and Intracellular Amastigotes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.L.; Stetson, D.B.; Locksley, R.M. Leishmania Major LACK Antigen Is Required for Efficient Vertebrate Parasitization. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrojo, A.; García-Hernández, R.; Vargas, P.; Camacho, E.; Corvo, L.; Imamura, H.; Dujardin, J.-C.; Castanys, S.; Aguado, B.; Gamarro, F.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Alterations in Leishmania Donovani Lines Experimentally Resistant to Antileishmanial Drugs. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.; Baba, E.H.; Machado-de-Avila, R.A.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Demicheli, C.P.; Frézard, F.; Monte-Neto, R.L.; Murta, S.M.F. Silver and Nitrate Oppositely Modulate Antimony Susceptibility through Aquaglyceroporin 1 in Leishmania (Viannia) Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 4482–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Victoria, F.J.; Sánchez-Cañete, M.P.; Castanys, S.; Gamarro, F. Phospholipid Translocation and Miltefosine Potency Require Both L. Donovani Miltefosine Transporter and the New Protein LdRos3 in Leishmania Parasites. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23766–23775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, H.L.; Beverley, S.M. Heavy Metal Resistance: A New Role for P-Glycoproteins in Leishmania. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 18427–18430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douanne, N.; Dong, G.; Amin, A.; Bernardo, L.; Blanchette, M.; Langlais, D.; Olivier, M.; Fernandez-Prada, C. Leishmania Parasites Exchange Drug-Resistance Genes through Extracellular Vesicles. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprohon, P.; Legare, D.; Raymond, F.; Madore, E.; Hardiman, G.; Corbeil, J.; Ouellette, M. Gene Expression Modulation Is Associated with Gene Amplification, Supernumerary Chromosomes and Chromosome Loss in Antimony-Resistant Leishmania Infantum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagalska, M.A.; Imamura, H.; Sanders, M.; van den Broeck, F.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Vanaerschot, M.; Maes, I.; D’Haenens, E.; Rai, K.; Rijal, S.; et al. Genomes of Leishmania Parasites Directly Sequenced from Patients with Visceral Leishmaniasis in the Indian Subcontinent. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumetz, F.; Imamura, H.; Sanders, M.; Seblova, V.; Myskova, J.; Pescher, P.; Vanaerschot, M.; Meehan, C.J.; Cuypers, B.; de Muylder, G.; et al. Modulation of Aneuploidy in Leishmania Donovani during Adaptation to Different In Vitro and In Vivo Environments and Its Impact on Gene Expression. MBio 2017, 8, e00599-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).