Genomic Insights into the Radiation-Resistant Capability of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis S5-59T and Sphingomonas glaciei S8-45T, Two Novel Bacteria from the North Slope of Mount Everest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria Isolation and Growth Conditions
2.2. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Chemotaxonomic Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, Annotation, and Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.6. The Radiation Resistance Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
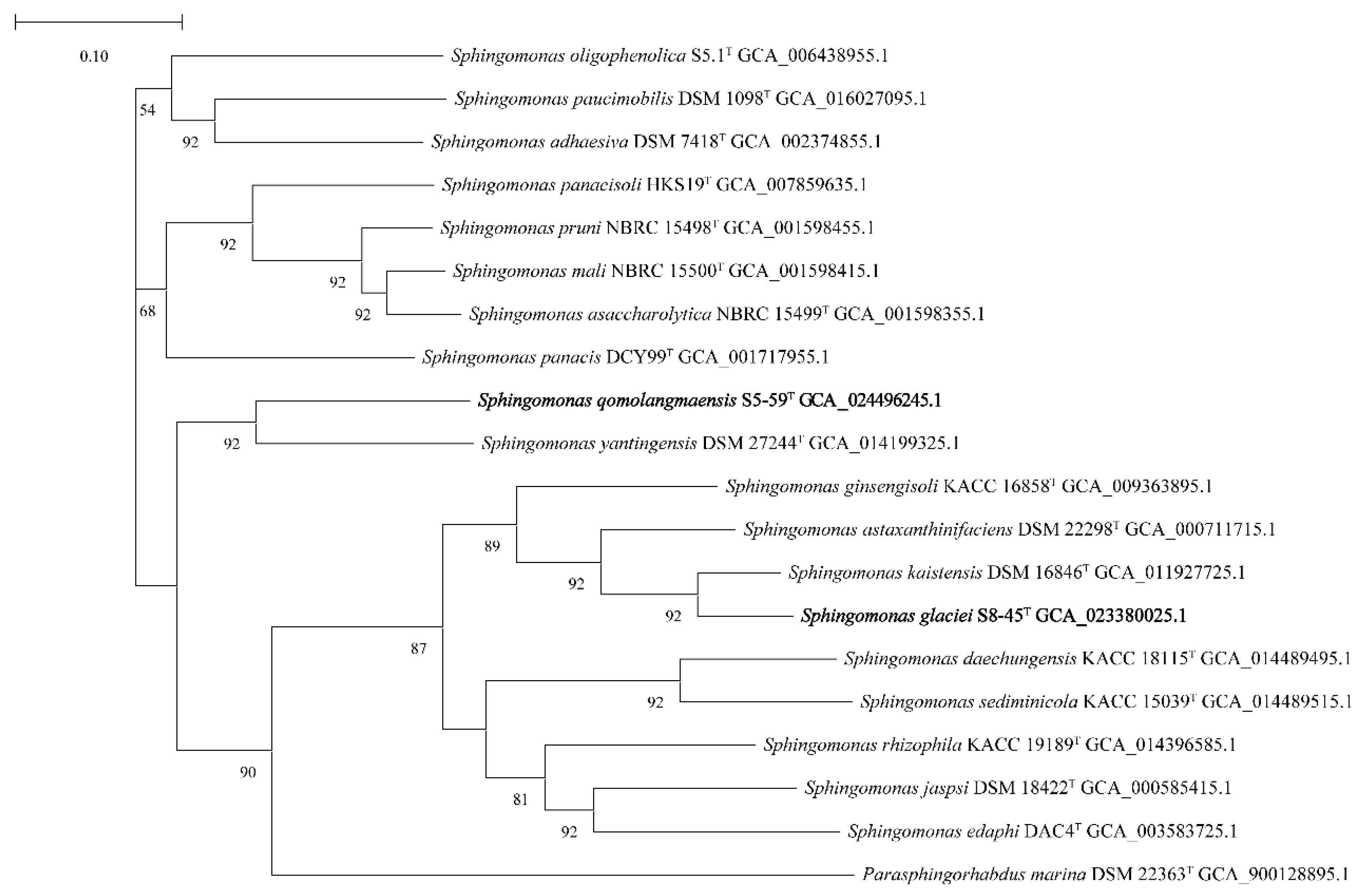
3.1. The Phylogenetic Characterization Based on 16S rRNA Gene and UBCG Set
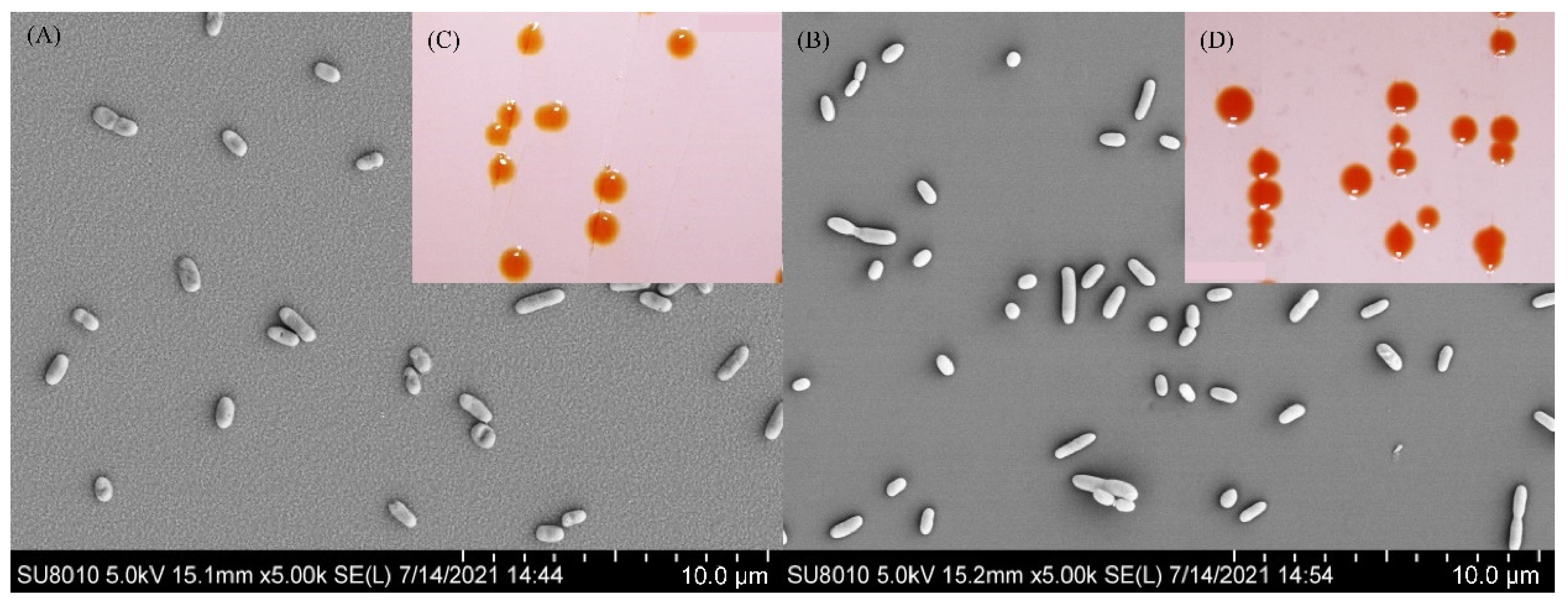
3.2. The Phenotypic Characterization of Strains S5-59T and S8-45T
3.3. Chemotaxonomic Characteristics of Strains S5-59T and S8-45T
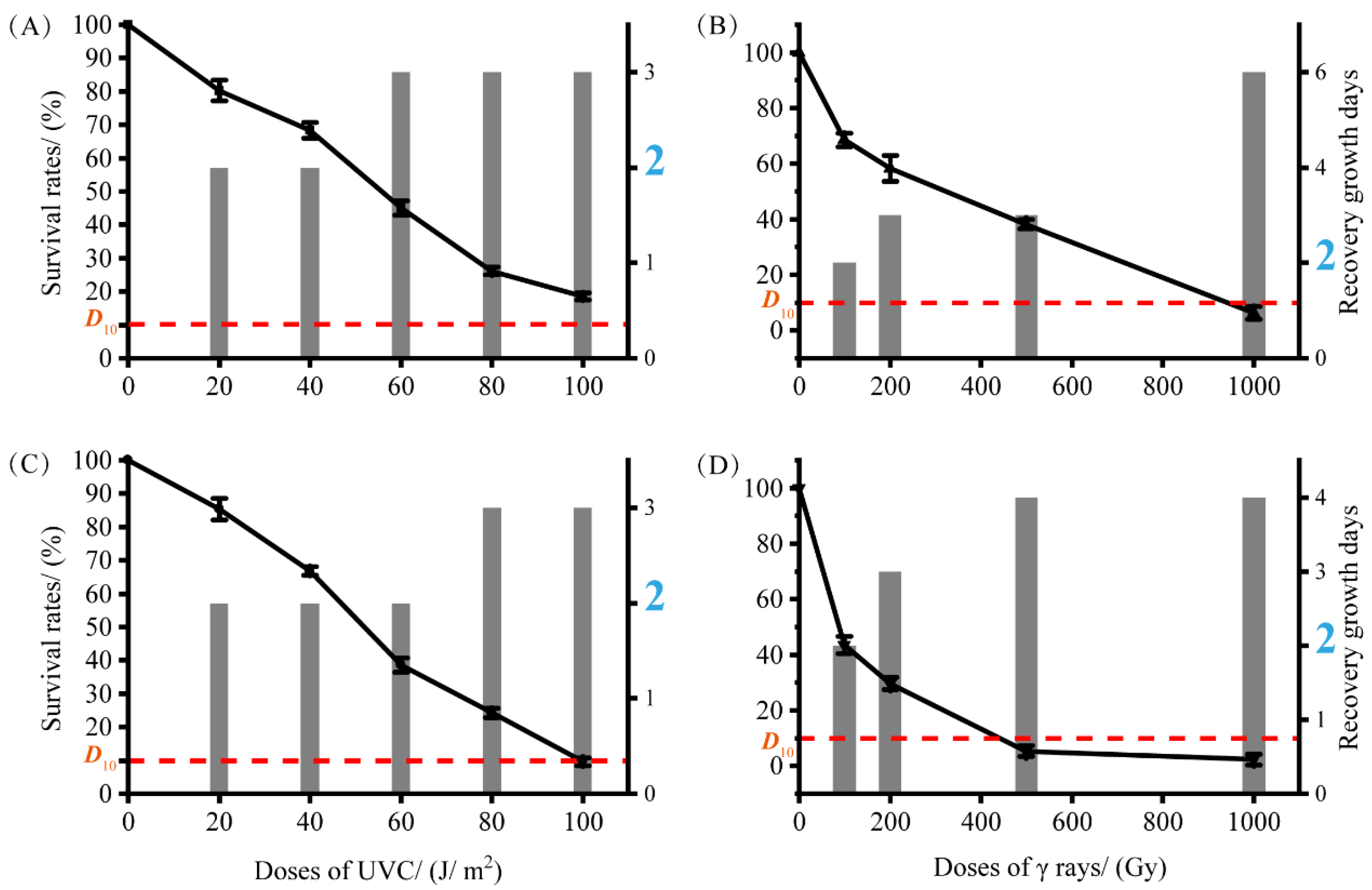
3.4. The Radiation-Resistant Ability of S5-59T and S8-45T
3.5. The Genome Analysis of Strains S5-59T and S8-45T
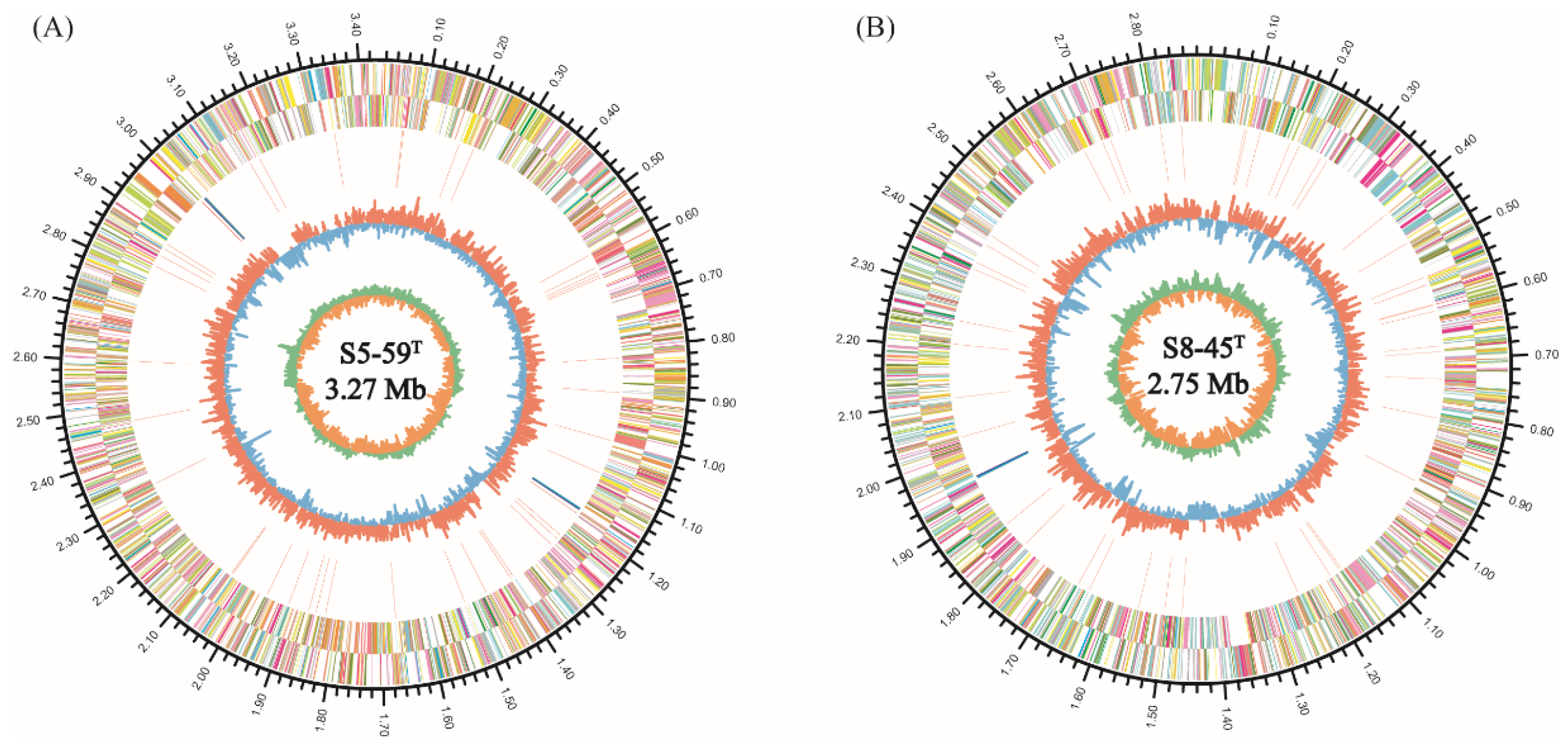
3.5.1. General Genome Features
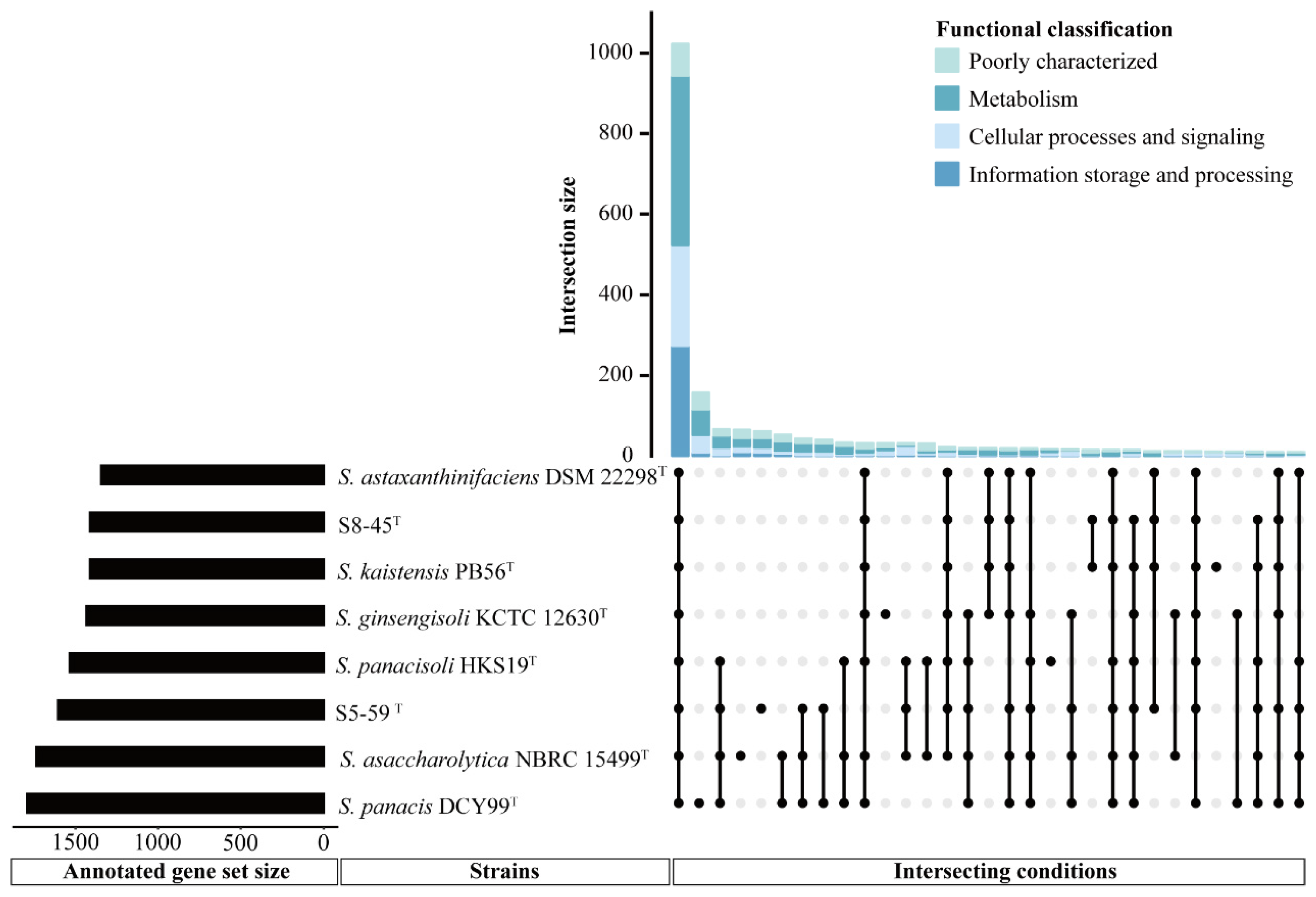
3.5.2. General COG Analysis
3.5.3. Pan-Genome Analysis Related to Radiation Resistance
3.5.4. Horizontal Gene Transfers Analysis Related to the Ability of Radiation Resistance
3.6. Genomic Insights into Two Novel Species Related to Radiation Resistance
4. Conclusions
4.1. Description of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis sp. nov.
4.2. Description of Sphingomonas glaciei sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lieberman, P.; Morey, A.; Hochstadt, J.; Larson, M.; Mather, S. Mount Everest: A space analogue for speech monitoring of cognitive deficits and stress. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2005, 76, B198-207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.W.; Semple, J.L. The impact of global warming on Mount Everest. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2009, 10, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, U.; Dhingra, G.G.; Anand, S.; Hira, P.; Kumar, R.; Kaur, J.; Verma, M.; Singhvi, N.; Lal, S.; Rawat, C.D.; et al. Microbial Journey: Mount Everest to Mars. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Kong, W.; Jia, H.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, B.C.; Malard, L.; Liang, C.; Xue, K.; et al. Polar soils exhibit distinct patterns in microbial diversity and dominant phylotypes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, T.; Liu, G. Genomic insights revealed the environmental adaptability of Planococcus halotolerans Y50 isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Gene 2022, 823, 146368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Y. Lentzea tibetensis sp. nov., a novel Actinobacterium with antimicrobial activity isolated from soil of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Pu, J.; Lai, X.H.; Jin, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Microbacterium wangchenii sp. nov., isolated from faeces of Tibetan gazelles (Procapra picticaudata) on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, S.; Yang, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; Dyson, P. Streptomyces dangxiongensis sp. nov., isolated from soil of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2729–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Niu, F.; Busse, H.J.; Ma, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, M.; Feng, H.; An, L.; Cheng, G. Hymenobacter psychrotolerans sp. nov., isolated from the Qinghai--Tibet Plateau permafrost region. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Ji, Z.; Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Tripathee, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Warming and thawing in the Mt. Everest region: A review of climate and environmental changes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 225, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Cui, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, G. Sphingomonas radiodurans sp. nov., a novel radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from the north slope of Mount Everest. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, T.; Liu, G. Characteristics of Planococcus antioxidans sp. nov., an antioxidant-producing strain isolated from the desert soil in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press USA: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.W.; Lim, S.; Bahn, Y.S. Microbial radiation-resistance mechanisms. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, D.M.; Nelson, W.H.; Bernhard, W.A. DNA damage by the direct effect of ionizing radiation: Products produced by two sequential one-electron oxidations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 12608–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madian, A.G.; Regnier, F.E. Proteomic identification of carbonylated proteins and their oxidation sites. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3766–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, E.I.; Jay-Gerin, J.P.; Pain, D. Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged cell injury. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruskov, V.I.; Karp, O.E.; Garmash, S.A.; Shtarkman, I.N.; Chernikov, A.V.; Gudkov, S.V. Prolongation of oxidative stress by long-lived reactive protein species induced by X-ray radiation and their genotoxic action. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranawat, P.; Rawat, S. Radiation resistance in thermophiles: Mechanisms and applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhang, W.; Dai, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tao, T.; Chen, M.; Lin, M. Deinococcus gobiensis sp. nov., an extremely radiation-resistant bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Liao, R.; Chou, B.; Contreras, L.M. Transcriptional analysis of Deinococcus radiodurans reveals novel small RNAs that are differentially expressed under ionizing radiation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.H.; Kang, M.S.; Joo, E.S.; Kim, E.B.; Lim, S.; Jeong, S.W.; Jung, H.Y.; Srinivasan, S.; Kim, M.K. Deinococcus persicinus sp. nov., a radiation-resistant bacterium from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5077–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.J.; Minton, K.W. Resistance to radiation. Science 1995, 270, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Wu, M.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. High Proportions of Radiation-Resistant Strains in Culturable Bacteria from the Taklimakan Desert. Biology 2022, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, E.; Yano, I.; Oyaizu, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ezaki, T.; Yamamoto, H. Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol. Immunol. 1990, 34, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.M.; Zhang, R.G.; Chen, H.Y.; Feng, Q.Q.; Lv, J. Sphingomonas floccifaciens sp. nov., isolated from subterranean sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, S.; Lian, W.H.; Wei, Q.C.; Mohamad, O.A.A.; Hozzein, W.N.; Ahmed, I.; Li, W.J. Sphingomonas arenae sp. nov., isolated from desert soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.C.; Busse, H.J.; Liu, H.C.; Zhou, Y.G.; Schinner, F.; Margesin, R. Sphingomonas glacialis sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asker, D.; Awad, T.S.; Beppu, T.; Ueda, K. Purification and Identification of Astaxanthin and Its Novel Derivative Produced by Radio-tolerant Sphingomonas astaxanthinifaciens. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1852, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reasoner, D.J.; Geldreich, E.E. A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirling, E.B.; Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species1. Microbiol. Soc. 1966, 16, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Wellington, E.M.; Sneath, P.H.; Sackin, M.J. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1983, 129, 1743–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurup, P.V.; Schmitt, J.A. Numerical taxonomy of Nocardia. Can. J. Microbiol. 1973, 19, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D.; Pirouz, T.; Goodfellow, M.; Minnikin, D.E. Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1977, 100, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechevalier, H.A.; Lechevalier, M.P.; Gerber, N.N. Chemical Composition as a Criterion in the Classification of Actinomycetes. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Perlman, D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; Volume 14, pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Staneck, J.L.; Roberts, G.D. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. MIDI technical note 101. In Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids; MIDI Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 1990; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimaki, T.; Sato, K. An Extension of the Kimura Two-Parameter Model to the Natural Evolutionary Process. J. Mol. Evol. 2019, 87, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.I.; Kim, Y.O.; Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Baek, I.; Chun, J. UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Rooney, A.P.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.W.; De Meyer, S.; et al. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.J.M.M. Bypassing Cultivation to Identify Bacterial Species: Culture-independent genomic approaches identify credibly distinct clusters, avoid cultivation bias, and provide true insights into microbial species. Microbe 2014, 9, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Z.; Zhongqiang, C.; Caiyun, J.; Yanan, L.; Jianhua, W.; Liang, L. Circular RNA detection methods: A minireview. Talanta 2022, 238, 123066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D.; et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein family’s database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Dutta, C. BPGA- an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultzhaus, Z.; Chen, A.; Kim, S.; Shuryak, I.; Chang, M.; Wang, Z. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the relationship of melanization to growth and resistance to gamma radiation in Cryptococcus neoformans. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2613–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Menor, E.; Gimeno-Valero, H.; Pascual, J.; Peretó, J.; Porcar, M. High Culturable Bacterial Diversity from a European Desert: The Tabernas Desert. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 583120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.S.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, L.G. International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology: Announcement of the report of the ad hoc Committee on Reconciliation of Approaches to Bacterial Systematics. Zentralblatt fur Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie, und Hygiene. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. Ser. A 1988, 268, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Natale, D.A.; Garkavtsev, I.V.; Tatusova, T.A.; Shankavaram, U.T.; Rao, B.S.; Kiryutin, B.; Galperin, M.Y.; Fedorova, N.D.; Koonin, E.V. The COG database: New developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.F.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Zandkarimi, F.; Harken, A.D.; Kinslow, C.J.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Dovas, A.; Higgins, D.M.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Radiation-Induced Lipid Peroxidation Triggers Ferroptosis and Synergizes with Ferroptosis Inducers. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwu, M.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Dong, K.; Ramasamy, D.; Waldman, B.; Adams, J.M. Community Ecology of Deinococcus in Irradiated Soil. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 855–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalziel, K.; Egan, R.R. The binding of oxidized coenzymes by glutamate dehydrogenase and the effects of glutarate and purine nucleotides. Biochem. J. 1972, 126, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veech, R.L.; Todd King, M.; Pawlosky, R.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Bradshaw, P.C.; Curtis, W. The "great" controlling nucleotide coenzymes. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettelin, H.; Riley, D.; Cattuto, C.; Medini, D. Comparative genomics: The bacterial pan-genome. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Hu, Q.; Cui, L.; Zhu, B.; Fu, X.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z.; Yang, S. Characterization of Sulfurimonas hydrogeniphila sp. nov., a Novel Bacterium Predominant in Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents and Comparative Genomic Analyses of the Genus Sulfurimonas. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 626705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres Manno, M.A.; Pizarro, M.D.; Prunello, M.; Magni, C.; Daurelio, L.D.; Espariz, M. GeM-Pro: A tool for genome functional mining and microbial profiling. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancic, T.; Jamnik, P.; Stopar, D. Cold shock CspA and CspB protein production during periodic temperature cycling in Escherichia coli. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiem, O.R.; Parijat, P.; Tripathi, P.; Batra, J.K. Mechanism of HrcA function in heat shock regulation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochimie 2020, 168, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohoshi, F.; Munakata, N. Multiple species of Bacillus subtilis DNA alkyltransferase involved in the adaptive response to simple alkylating agents. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, J.L.; Goedken, E.R.; Marqusee, S. Activation/attenuation model for RNase H. A one-metal mechanism with second-metal inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 34128–34133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, O.N.; Vanevski, F.; Khil, P.P.; Camerini-Otero, R.D. Characterization of the DNA damage-inducible helicase DinG from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28284–28293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciszewska, L.K.; Sherratt, D.J. Xer site-specific recombination in vitro. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barre, F.X.; Søballe, B.; Michel, B.; Aroyo, M.; Robertson, M.; Sherratt, D. Circles: The replication-recombination-chromosome segregation connection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8189–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, K.; Yeturu, K.; Chandra, N. targetTB: A target identification pipeline for Mycobacterium tuberculosis through an interactome, reactome and genome-scale structural analysis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2008, 2, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Martins, A.; Bongiorno, P.; Glickman, M.; Shuman, S. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the four DNA ligases of mycobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20594–20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeiser, B.; Pepper, E.D.; Goodman, M.F.; Finkel, S.E. SOS-induced DNA polymerases enhance long-term survival and evolutionary fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8737–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y. Comparing SSB-PriA Functional and Physical Interactions in Gram-Positive and -Negative Bacteria. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2281, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, D.; Radman, M. Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2011, 75, 133–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, C.S.; Smoczynski, R.; Tretyn, A. Sequencing technologies and genome sequencing. J. Appl. Genet. 2011, 52, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M.; Mackay, I.; Balding, D. Using Genetic Distance to Infer the Accuracy of Genomic Prediction. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Touma, B.; Holzenthal, R.W.; Rázuri-Gonzales, E.; Heckenhauer, J.; Pauls, S.U.; Storer, C.G.; Frandsen, P.B. De Novo Genome Assembly and Annotation of an Andean Caddisfly, Atopsyche davidsoni Sykora, 1991, a Model for Genome Research of High-Elevation Adaptations. Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, evab286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohan, F.M.; Perry, E.B. A systematics for discovering the fundamental units of bacterial diversity. Curr. Biol. CB 2007, 17, R373–R386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T. Superoxide Dismutase as an Intervention for Radiation Therapy-Associated Toxicities: Review and Profile of Avasopasem Manganese as a Treatment Option for Radiation-Induced Mucositis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.F.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.N.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.G.; Chen, R.Q.; Cao, J.C.; Wang, F.S. Effect of heparin-superoxide dismutase on γ-radiation induced DNA damage in vitro and in vivo. Drug Discov. Ther. 2010, 4, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kıvrak, E.G.; Yurt, K.K.; Kaplan, A.A.; Alkan, I.; Altun, G. Effects of electromagnetic fields exposure on the antioxidant defense system. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, D.J. Role of RecA in DNA damage repair in Deinococcus radiodurans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 274, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Modrich, P. Mutation detection with MutH, MutL, and MutS mismatch repair proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4374–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghout, P.; Bootsma, H.J.; Kloosterman, T.G.; Bijlsma, J.J.; de Jongh, C.E.; Kuipers, O.P.; Hermans, P.W. Search for genes essential for pneumococcal transformation: The RADA DNA repair protein plays a role in genomic recombination of donor DNA. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6540–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveson, C.J.; Lovett, S.T. Tandem repeat recombination induced by replication fork defects in Escherichia coli requires a novel factor, RadC. Genetics 1999, 152, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciello, I.; Zahradka, D.; Zahradka, K.; Ivanković, S.; Puc, N.; Đermić, D. RecF, UvrD, RecX and RecN proteins suppress DNA degradation at DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli. Biochimie 2018, 148, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, O.; Ha, T. Single-Molecule Studies of ssDNA-Binding Proteins Exchange. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 600, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, D.J.; Boubriak, I.; Berquist, B.R.; Clark, M.; Richard, E.; Sullivan, L.; DasSarma, S.; McCready, S. The uvrA, uvrB and uvrC genes are required for repair of ultraviolet light induced DNA photoproducts in Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. Saline Syst. 2006, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Norais, C.A.; Chitteni-Pattu, S.; Wood, E.A.; Inman, R.B.; Cox, M.M. DdrB protein, an alternative Deinococcus radiodurans SSB induced by ionizing radiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21402–21411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahradka, K.; Slade, D.; Bailone, A.; Sommer, S.; Averbeck, D.; Petranovic, M.; Lindner, A.B.; Radman, M. Reassembly of shattered chromosomes in Deinococcus radiodurans. Nature 2006, 443, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repar, J.; Cvjetan, S.; Slade, D.; Radman, M.; Zahradka, D.; Zahradka, K. RecA protein assures fidelity of DNA repair and genome stability in Deinococcus radiodurans. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicanò, G.; Al Mamun, M.; Jurado-Santiago, D.; Villa-Hernández, S.; Yin, X.; Giannattasio, M.; Lanz, M.C.; Smolka, M.B.; Yeeles, J.; Shirahige, K.; et al. Checkpoint-mediated DNA polymerase ε exonuclease activity curbing counteracts resection-driven fork collapse. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 2778–2792.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Narumi, I.; Funayama, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Watanabe, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Nikaido, O.; Yamamoto, K. Characterization of Pathways Dependent on the uvsE, uvrA1, or uvrA2 Gene Product for UV Resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3693–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.; Serrano, E.; Kawamura, R.; Carrasco, B.; Yan, J.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis RecA with DprA-SsbA antagonizes RecX function during natural transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 8873–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.A.; Filman, D.J.; Finkel, S.E.; Kolter, R.; Hogle, J.M. The crystal structure of Dps, a ferritin homolog that binds and protects DNA. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Murni, L.; Han, T.W.; Arfiati, D.; Shih, H.T.; Hu, S.Y. Molecular Characterization and Heterologous Production of the Bacteriocin Peocin, a DNA Starvation/Stationary Phase Protection Protein, from Paenibacillus ehimensis NPUST1. Molecules 2019, 24, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyk, T.K.; DeRose, E.J.; Gonye, G.E. LuxArray, a high-density, genomewide transcription analysis of Escherichia coli using bioluminescent reporter strains. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5496–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinski, J.; Feder, M.; Bujnicki, J.M. The PD-(D/E) XK superfamily revisited: Identification of new members among proteins involved in DNA metabolism and functional predictions for domains of (hitherto) unknown function. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makharashvili, N.; Koroleva, O.; Bera, S.; Grandgenett, D.P.; Korolev, S. A Novel Structure of DNA Repair Protein RecO from Deinococcus radiodurans. Structure 2004, 12, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanawong, K.; Koiso, N.; Toda, E.; Kinoshita, A.; Tanaka, M.; Tsuji, H.; Okamoto, T. Regulatory functions of ROS dynamics via glutathione metabolism and glutathione peroxidase activity in developing rice zygote. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 108, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsy, G.; Galiba, G.; Brunold, C. Role of glutathione in adaptation and signalling during chilling and cold acclimation in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2001, 113, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.J. A new perspective on radiation resistance based on Deinococcus radiodurans. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tian, B.; Sun, Z.; Lin, J.; Hua, Y. Identification and functional analysis of a phytoene desaturase gene from the extremely radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, O.K.; Deriabin, D.G.; El’-Registan, G.I. Influence of chemical analogues of microbial autoregulators on the sensitivity of DNA to UV radiation. Mikrobiologiia 2006, 75, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation source | Moraine | Soil | Plants | Rusty ginseng | Moraine | Soil | Misasa | Soil |
| Colony color | Orange | Yellow | Light yellow | Light yellow | Light red | Pink-red | Deep red | Deep orange |
| Growth temperature (°C) Range (optimum) | 10–35 (30) | 10–35 (30) | 10–35 (30) | 10–35 (30) | 10–35 (30) | 20–35 (30) | 40–45 (28) | 15–35 (30) |
| pH range (optimum) | 8–9 (8) | 6–9 (7) | 5–10 (8) | 5–7 (6) | 5–10 (7) | 5–8 (7) | 6–8 (7) | 6–7 (7) |
| NaCl tolerance range (%, w/v) (optimum) | 0–2 (0) | 0–1 (0) | 0–2 (0) | 0–1 (0) | 0–2 (0) | 0–4 (1) | 0–3 (1) | 0–1 (0) |
| Oxidase activity | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Hydrolysis of: | ||||||||
| Tween 20 | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − |
| Gelatin | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + |
| Starch | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| Utilization as carbon sources | ||||||||
| L-Arabinose | + | + | W | + | + | − | + | − |
| D-Fructose | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | − |
| D-Glucose | W | − | − | + | + | + | − | + |
| D-Lactose | W | − | − | + | + | W | − | − |
| D-Galactose | + | − | − | + | + | W | − | − |
| D-Mannitol | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| D-Raffinose | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| D-Rhamnose | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | − |
| Sucrose | + | + | − | + | W | − | − | − |
| D-xylose | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| Utilization as nitrogen sources | ||||||||
| L-Alanine | − | − | + | − | W | − | + | − |
| L-Aspartate | + | − | + | + | − | W | − | + |
| L-Histidine | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | + |
| L-Tyrosine | − | − | + | − | − | − | W | + |
| L-Cysteine | − | − | + | − | W | − | + | − |
| Enzymatic activity | ||||||||
| Alkaline phosphatase | + | − | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| Esterase (C4) | + | − | + | W | + | + | + | + |
| Acid phosphatase | + | − | + | + | − | + | W | + |
| N-acetyl-β-glucosaminase | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| naphtholAS-BI-phosphohydrolase | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Motility | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| GenBank ID of S5-59T | Gene Symbol | Description | GenBank ID of S8-45T | Gene Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UUL83393 | mutL | DNA mismatch repair endonuclease MutL | UUR08469 | mutL | DNA mismatch repair endonuclease MutL |
| UUL84211 | mutS | DNA mismatch repair protein MutS | UUR07385 | mutS | DNA mismatch repair protein MutS |
| UUL81296 | radA | DNA repair protein RadA | UUR08271 | radA | DNA repair protein RadA |
| UUL82802 | radC | DNA repair protein RadC | UUR08766 | radC | DNA repair protein RadC |
| UUL81325 | recN | DNA repair protein RecN | UUR06914 | recN | DNA repair protein RecN |
| UUL82320 | recF | DNA replication/repair protein RecF | UUR09455 | recF | DNA replication/repair protein RecF |
| UUL84186 | addA | Double-strand break repair helicase AddA | UUR08512 | addA | Double-strand break repair helicase AddA |
| UUL83610 | addB | Double-strand break repair protein AddB | UUR08510 | addB | Double-strand break repair protein AddB |
| UUL82209 | ssb | Single-stranded DNA-binding protein | UUR07233 | ssb | Single-stranded DNA-binding protein |
| UUL82624 | - | Ligase-associated DNA damage response exonuclease | UUR07010 | - | Ligase-associated DNA damage response exonuclease |
| UUL82626 | - | Ligase-associated DNA damage response DEXH box helicase | UUR07012 | - | Ligase-associated DNA damage response DEXH box helicase |
| UUL81513 | - | DNA repair protein | UUR07773 | - | DNA repair protein |
| UUL84288 | dinB | DNA polymerase IV | UUR07654 | - | putative DNA modification/repair radical SAM protein |
| UUL83514 | rumC | DNA recombination protein RmuC | UUR07413 | uvsE | UV DNA damage repair endonuclease UvsE |
| UUL82817 | recO | DNA repair protein RecO | UUR09226 | - | UvrD-helicase domain-containing protein |
| UUL82877 | - | RecX family transcriptional regulator | |||
| UUL81945 | - | MmcB family DNA repair protein | |||
| UUL82955 | - | DNA starvation/stationary phase protection protein Dps | |||
| UUL83357 | - | UvrB/UvrC motif-containing protein |
| Type Strain | BGCs Predicted by antiSMASH | Type | Predicted Compounds | Predicted Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S5-59T | C1 | Terpene | Zeaxanthin | Antioxidant |
| C5 | Saccharide | lipopolysaccharide | Antioxidant | |
| S8-45T | C1 | Terpene | Carotenoid | Antioxidant |
| C2 | Polyketide | Alkylresorcinol | UV-resistance | |
| Predicted structures |  | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Cui, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Genomic Insights into the Radiation-Resistant Capability of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis S5-59T and Sphingomonas glaciei S8-45T, Two Novel Bacteria from the North Slope of Mount Everest. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102037
Liu Y, Cui X, Yang R, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Liu G, Zhang B, Wang J, Wang X, Zhang W, et al. Genomic Insights into the Radiation-Resistant Capability of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis S5-59T and Sphingomonas glaciei S8-45T, Two Novel Bacteria from the North Slope of Mount Everest. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Xiaowen Cui, Ruiqi Yang, Yiyang Zhang, Yeteng Xu, Guangxiu Liu, Binglin Zhang, Jinxiu Wang, Xinyue Wang, Wei Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Genomic Insights into the Radiation-Resistant Capability of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis S5-59T and Sphingomonas glaciei S8-45T, Two Novel Bacteria from the North Slope of Mount Everest" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102037
APA StyleLiu, Y., Cui, X., Yang, R., Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Liu, G., Zhang, B., Wang, J., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Chen, T., & Zhang, G. (2022). Genomic Insights into the Radiation-Resistant Capability of Sphingomonas qomolangmaensis S5-59T and Sphingomonas glaciei S8-45T, Two Novel Bacteria from the North Slope of Mount Everest. Microorganisms, 10(10), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102037





