Thermal Behavior of a Magnetically Levitated Spindle for Fatigue Testing of Fiber Reinforced Plastic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
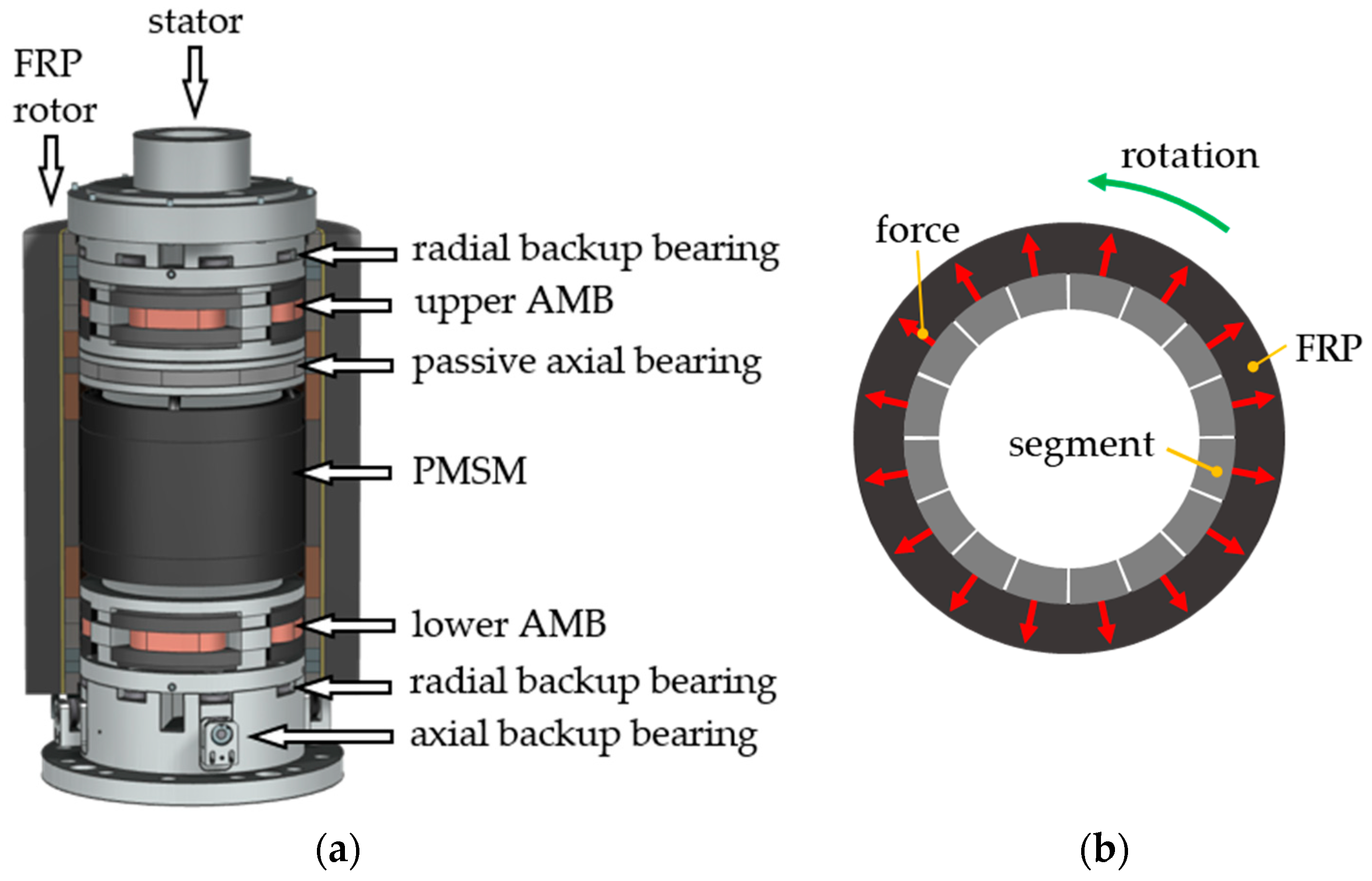
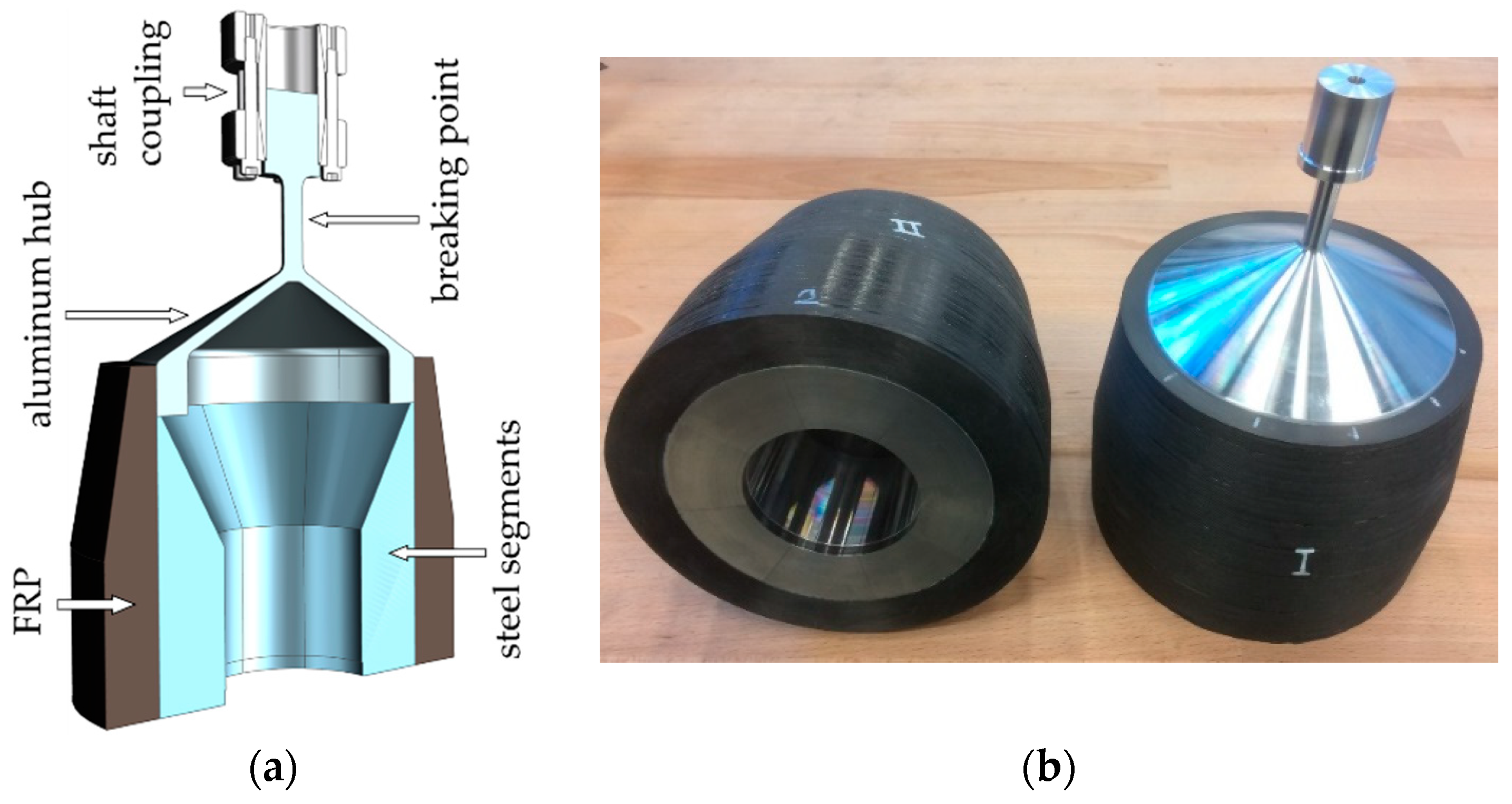
1.1. Outer-Rotor Fywheel Design
1.2. Testing Procedure
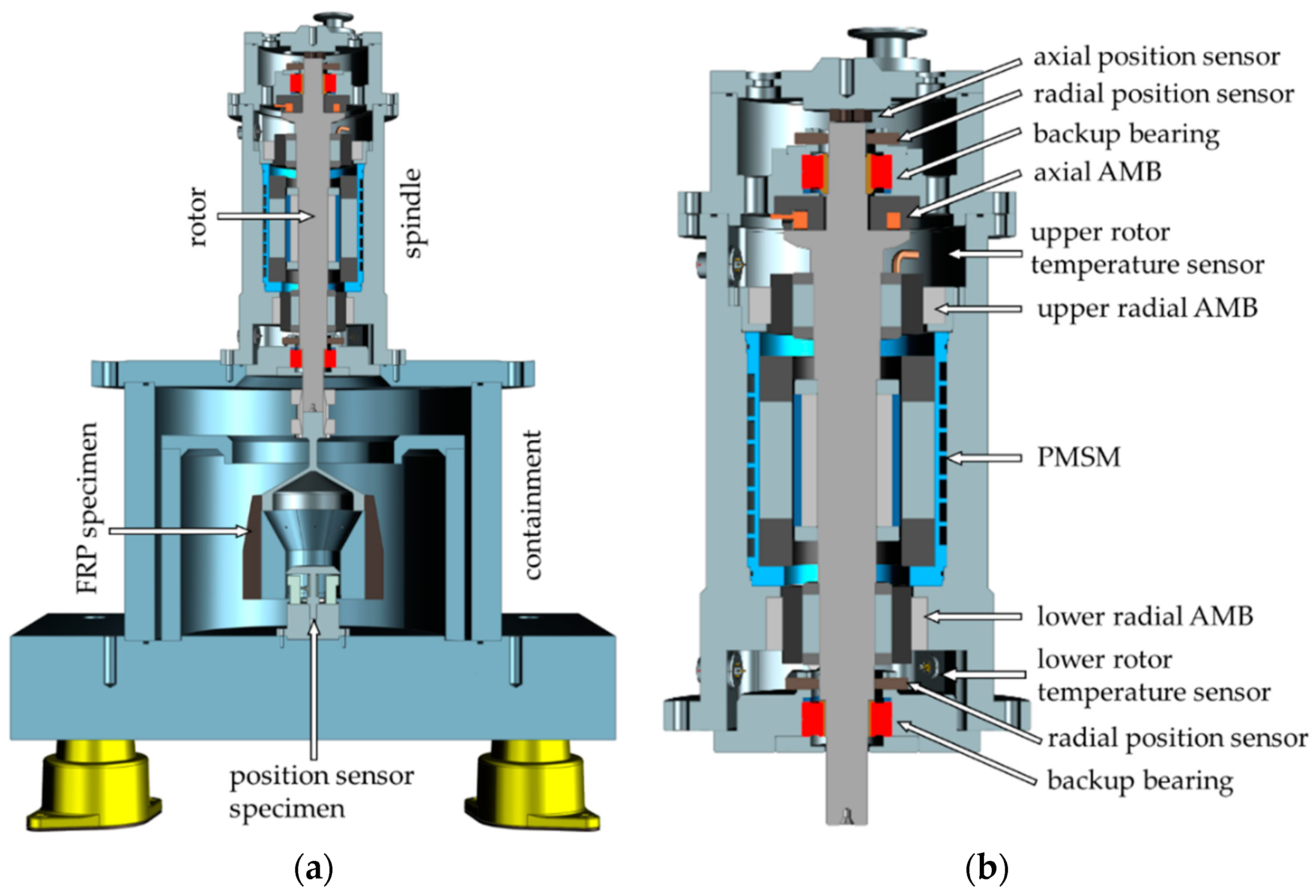
1.3. Test Rig Description
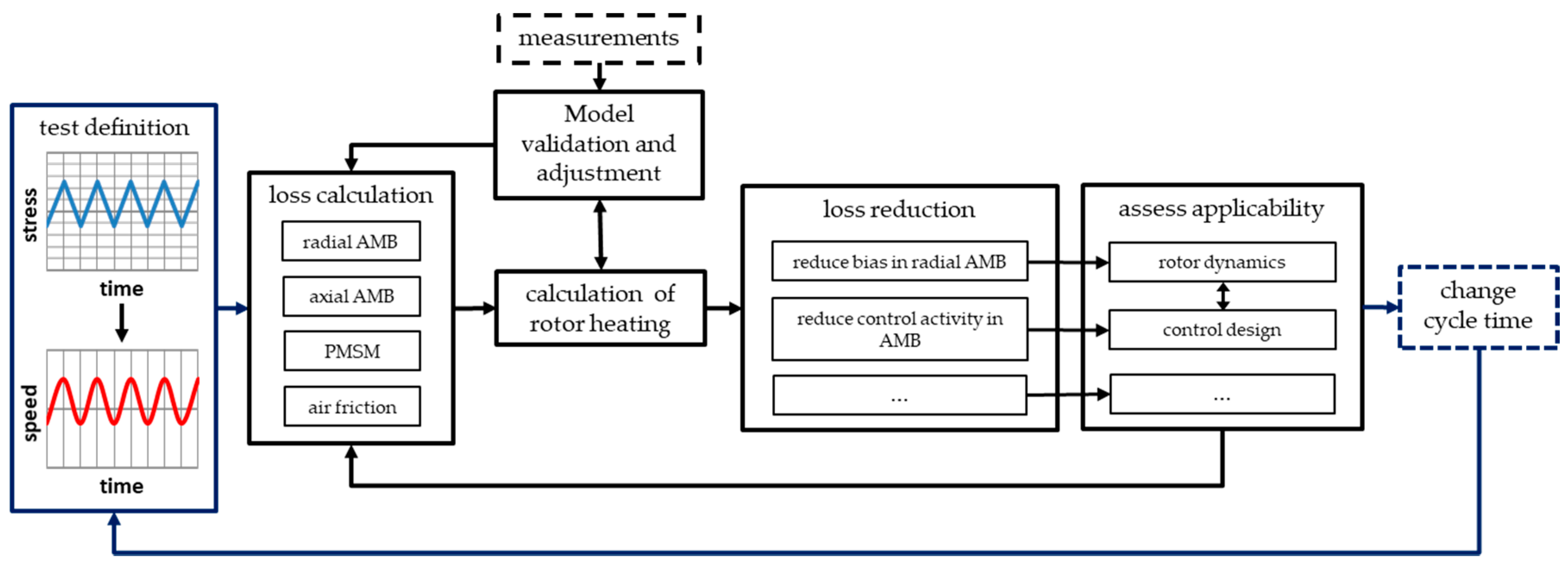
2. Method
3. Modeling of the Thermal Stability of the Rotor
3.1. Loss Calculation of the Radial Active Magnetic Bearings
3.2. Loss Calculation the of Axial Active Magnetic Bearing
3.3. Loss Calculation of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine
3.4. Air Friction Losses
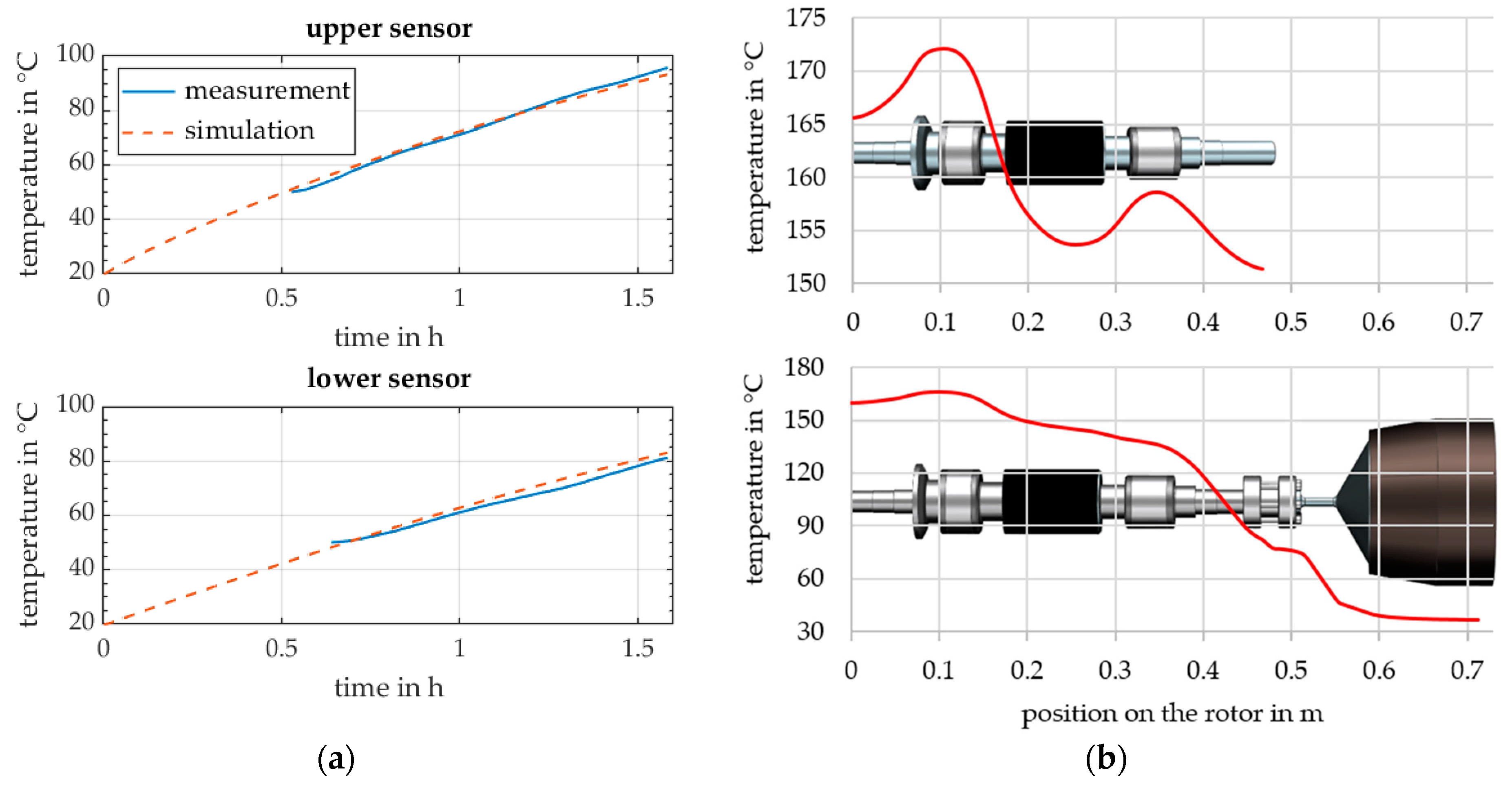
3.5. Simulation of Thermal Rotor Behavior
3.6. Temperature Measurements
4. Loss Reduction
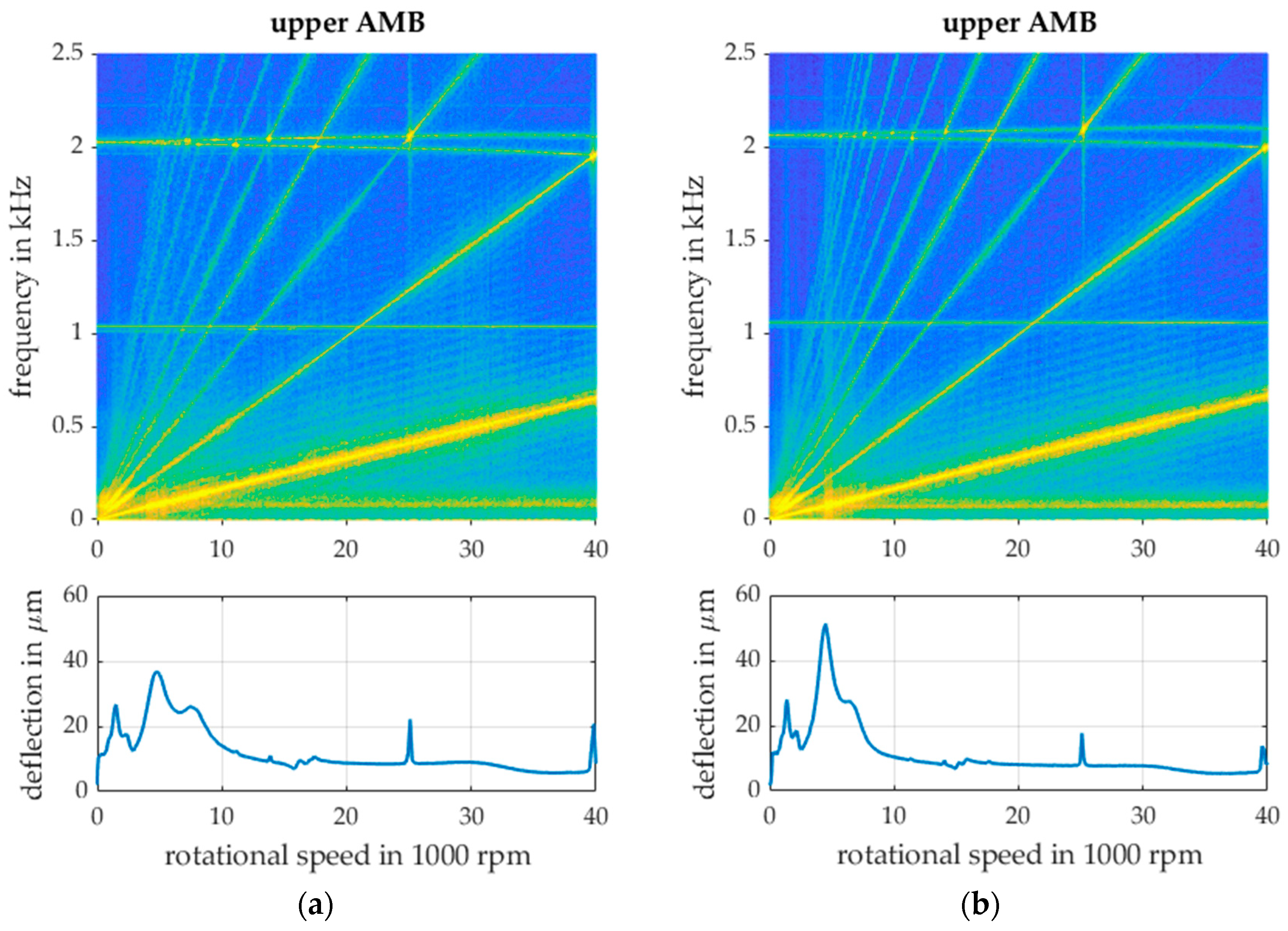
4.1. Reducing Losses in the Radial Bearings
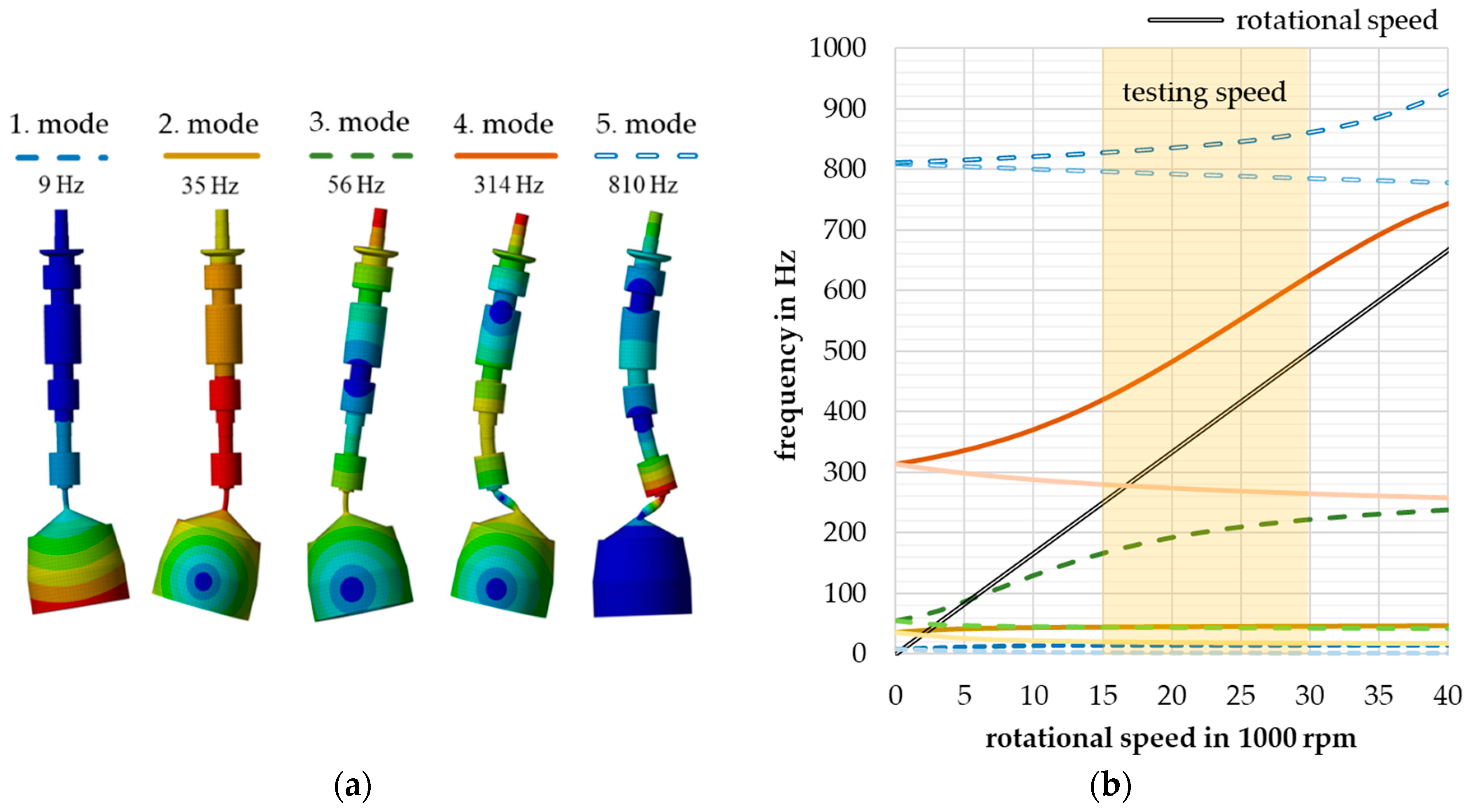
4.2. Rotor Dynamics
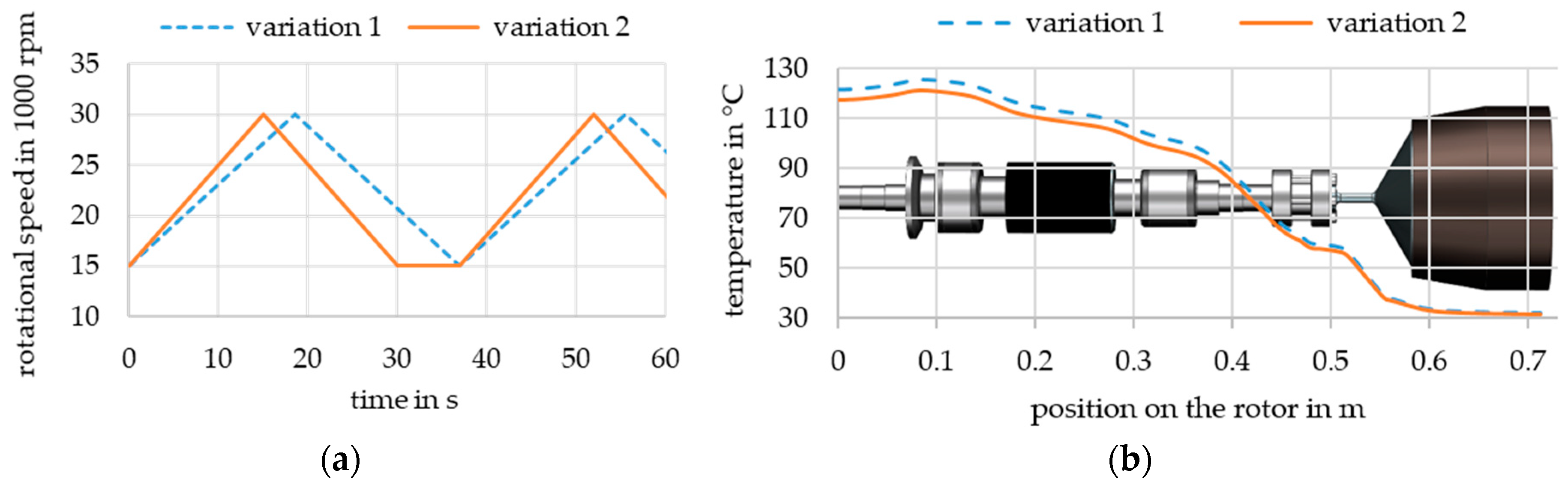
4.3. Increasing the Cycle Time
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Time in s | axial AMB | Time in s | Upper AMB | Lower AMB | Time in s | Motor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25.0 °C | 0 | 38.8 °C | 40.9 °C | 0 | 35.4 °C |
| 4500 | 23.1 °C | 2500 | 35.7 °C | 37.3 °C | 550 | 23.3 °C |
| 7600 | 22.5 °C | 7600 | 34.6 °C | 35.6 °C | 7600 | 22.3 °C |
| Time in s | Axial AMB | Time in s | Upper AMB | Lower AMB | Time in s | Motor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 18.6 °C | 0 | 18.9 °C | 18.9 °C | 0 | 20.7 °C |
| 1800 | 22.4 °C | 1600 | 43.0 °C | 45.3 °C | 800 | 35.2 °C |
| 5720 | 25.9 °C | 5720 | 51.1 °C | 53.3 °C | 5720 | 35.5 °C |
| Time in s | Axial AMB | Time in s | Upper AMB | Lower AMB | Time in s | Motor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 18.5 °C | 0 | 18.9 °C | 19.0 °C | 0 | 20.2 °C |
| 2800 | 23.0 °C | 1850 | 32.7 °C | 34.9 °C | 800 | 35.2 °C |
| 8000 | 25.0 °C | 8000 | 38.8 °C | 40.9 °C | 8000 | 35.4 °C |
References
- Sebastián, R.; Peña-Alzola, R. Flywheel energy storage systems: Review and simulation for an isolated wind power system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 6803–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryar, M.E.; Pullen, K.R. A Review of flywheel energy storage system technologies and their applications. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.; Howe, D.; Atallah, K. Soft Magnetic Composites in Active Magnetic Bearings. In Proceedings of the IEE Colloquium on New Magnetic Materials—Bonded Iron, Lamination Steels, Sintered Iron and Permanent Magnets, London, UK, 28 May 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichot, M.A.; Driga, M.D. Loss reduction strategies in design of magnetic bearing actuators for vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaede, H.; Richter, M.; Quurck, L.; Rinderknecht, S. Losses in an Outer-Rotor-Type Kinetic Energy Storage System in Active Magnetic Bearings. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings, Linz, Austria, 11–14 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Quurck, L.; Richter, M.; Schneider, M.; Franz, D.; Rinderknecht, S. Design and practical realization of an innovative flywheel concept for industrial applications. In Proceedings of the SIRM 2017–12 Internationale Tagung Schwingungen in Rotierenden Maschinen, Graz, Austria, 15–17 February 2017; pp. 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.M.; Saleeb, A.F.; Al-Zoubi, N.R. Deformation and life analysis of composite flywheel disk systems. Compos. Part B Eng. 2002, 33, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527-5, Plastics—Determination of Tensile properties—Part 5: Test Conditions for Unidirectional Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites. Available online: http://www.iso.org/standard/52991.html (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- ISO 14126, Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Compressive Properties in the in-Plane Direction. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/23638.html (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Knops, M. Analysis of Failure in Fiber Polymer Laminates; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, D.; Schneider, M.; Richter, M.; Rinderknecht, S. Magnetically levitated spindle for long term testing of fiber reinforced plastic. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings, Beijing, China, 13–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hagg, A.C.; Sankey, G.O. The containment of disk burst fragments by cylindrical shells. ASME J. Eng. Power 1974, 96, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsonneur, R. Design and Control of Active Magnetic Bearing Systems for High Speed Rotation. Doctoral dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zuerich, Zuerich, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoppa, A.; Delarbre, P. Soft magnetic powder composites and potential applications in modern electric machines and devices. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaechter, S.; Kameno, H.J. Application of zero-bias current active magnetic bearings to flywheel energy storage systems. Koyo Eng. J. 2004, 165, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, R.; Bühler, P.; Gähler, C.; Larsonneur, R. Unbalance compensation using generalized notch filters in the multivariable feedback of magnetic bearings. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1996, 4, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaraci, G.; Pesch, A.H.; Sawicki, J.T. Experimental investigations of minimum power consumption optimal control for variable speed AMB rotor. In Proceedings of the ASME 2010 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–18 November 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.; Maslen, E.H. Magnetic Bearings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, G. General properties of power losses in soft ferromagnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60404-2, Magnetic Materials—Part 2: Methods of Measurement of the Magnetic Properties of Electrical Steel Strip and Sheet by Means of an Epstein Frame. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/62746 (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Jousten, K. Handbook of Vacuum Technology, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R. Schwung-Energiespeicher-System mit Supraleitendem Magnetlager. Ph.D Thesis, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Baehr, D.B.; Stephan, K. Heat and Mass Transfer, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Vogt, K.; Ponick, B. Berechnung elektrischer Maschinen, 6th ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canders, W.R. Berechnung von Eisenverlusten—Physikalisch Basierter Ansatz Nach Bertottis Theorie. Annual report, Braunschweig, Germany. 2011. Available online: https://www.tu-braunschweig.de/Medien-DB/imab/09-Jahresberichte/2010-11/07_Canders_2010_11.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Lévine, J.; Lottin, J.; Ponsart, J.C. A nonlinear approach to the control of magnetic bearings. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1996, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.C.; Panagiotis, T.; Heck-Ferri, B. Experimental validation of control designs for low-loss active magnetic bearings. In Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference 2005, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 August 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochmal, T.R.; Lynch, A.F. Nonlinear control of an active magnetic bearing with bias currents: experimental study. In Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
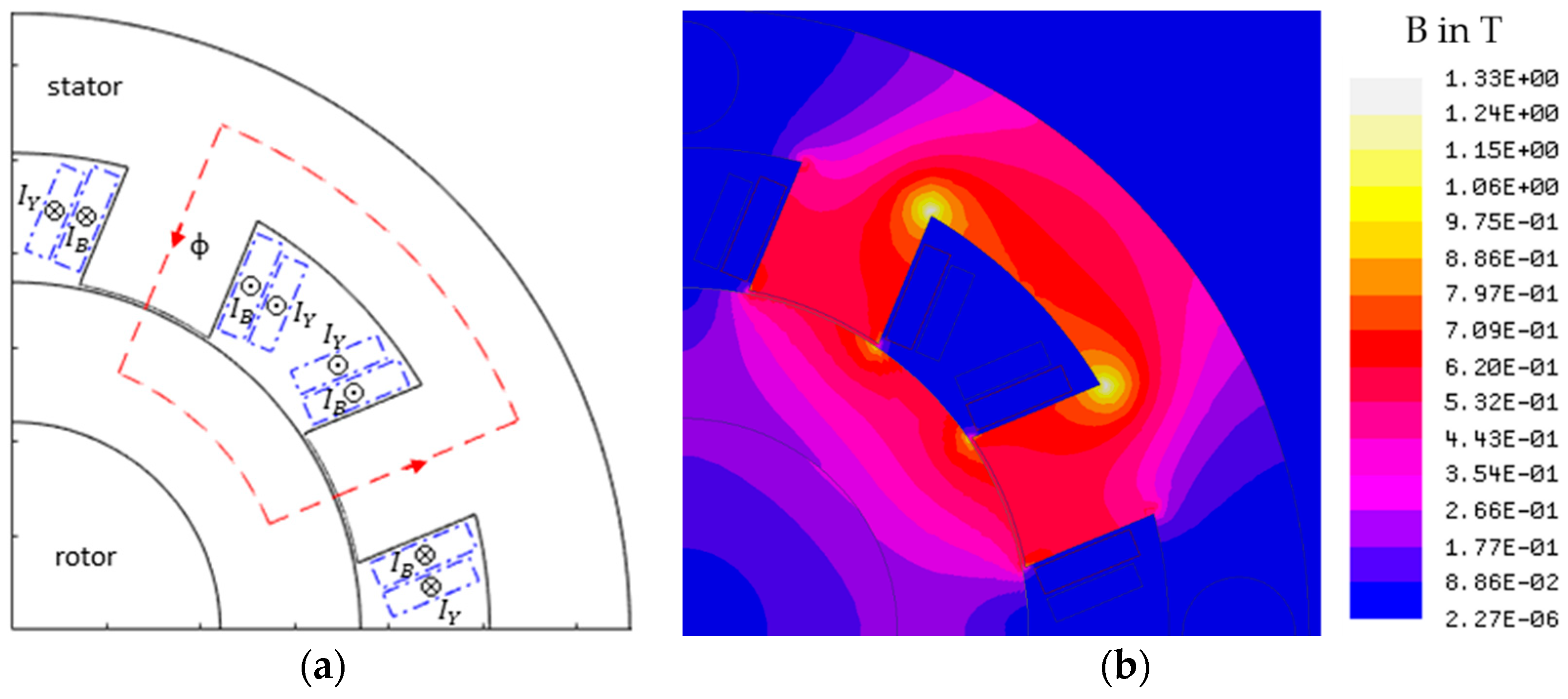
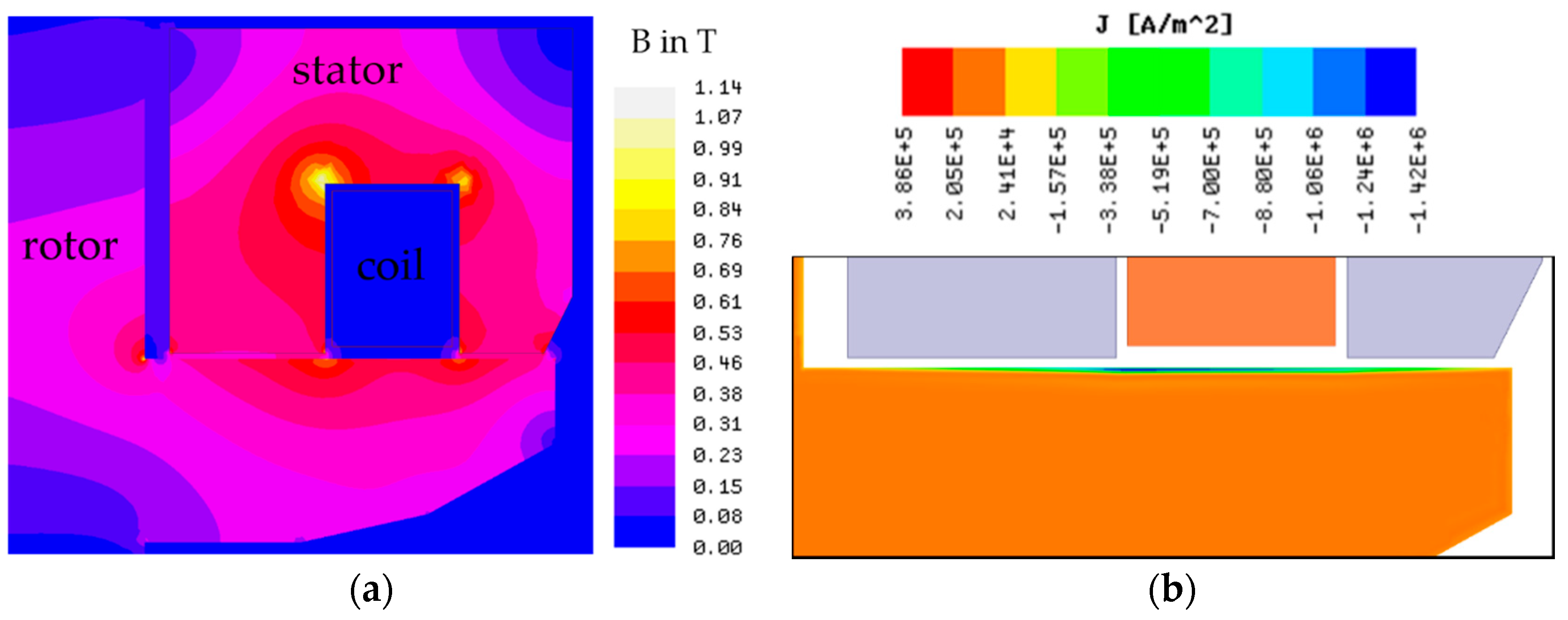
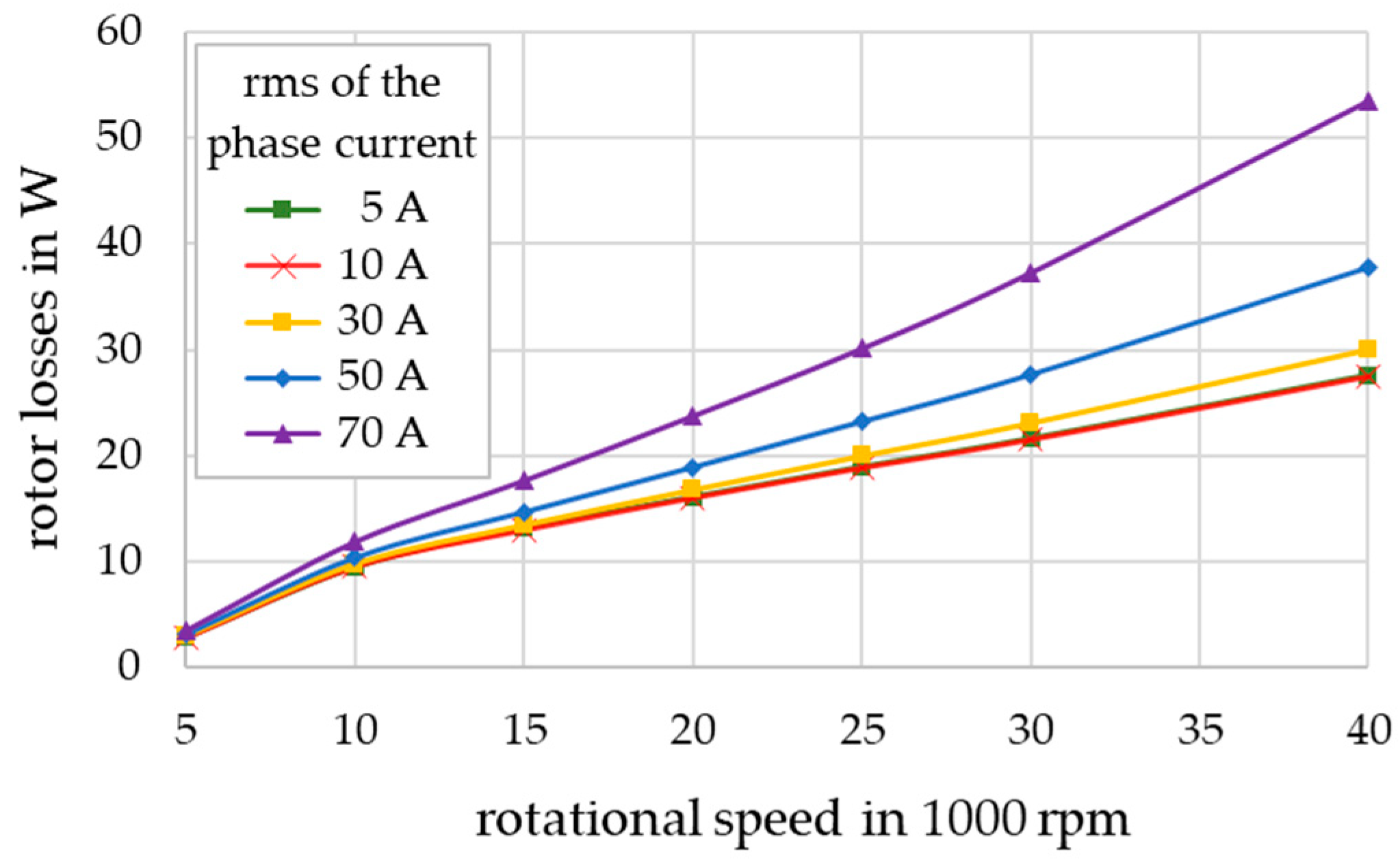
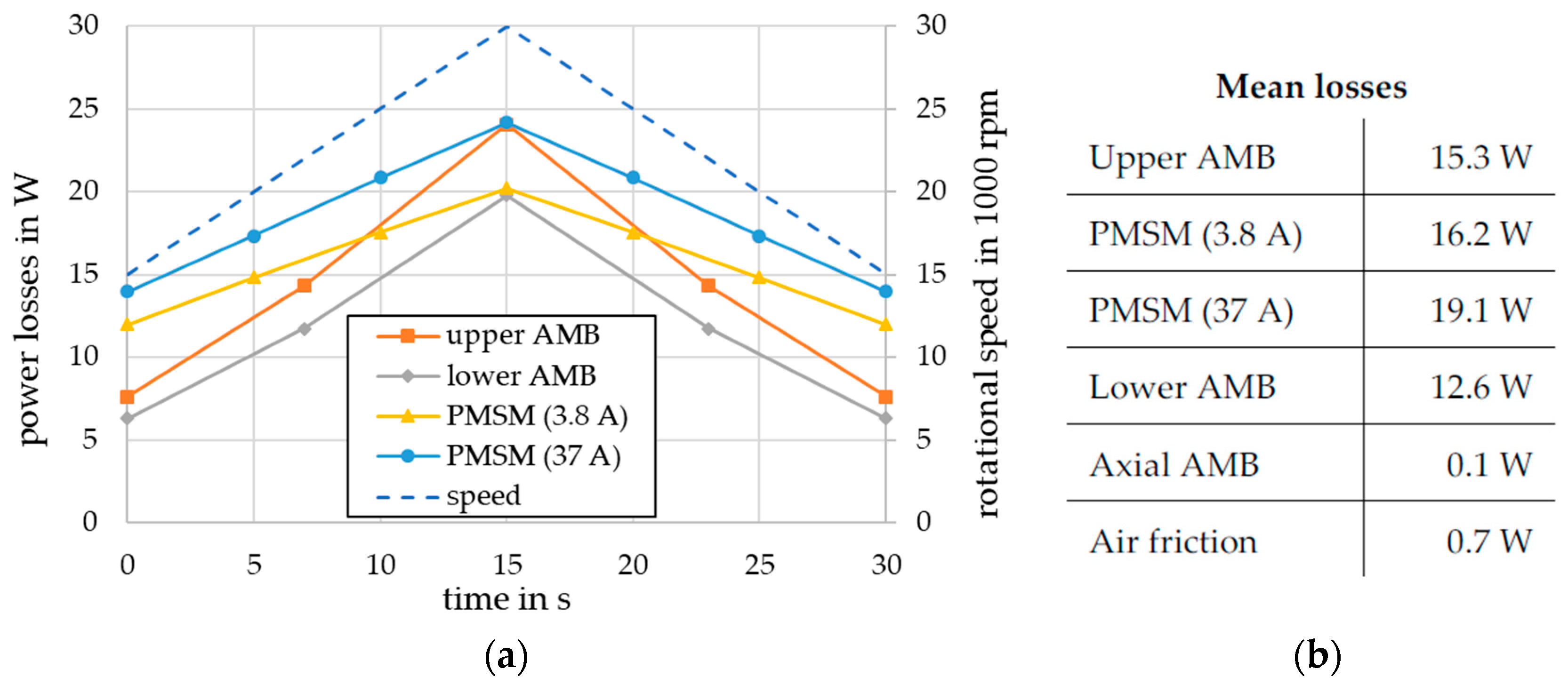


| 15,000 rpm | 22,000 rpm | 30,000 rpm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper AMB | 7.6 W | 14.3 W | 24.1 W |
| Lower AMB | 6.3 W | 11.8 W | 19.8 W |
| 15,000 rpm | 30,000 rpm | |
|---|---|---|
| rotor | 0.016 W | 0.066 W |
| specimen | 0.283 W | 1.131 W |
| Axial AMB | Upper AMB | Lower AMB |
|---|---|---|
| 8.1 W | 16.9 W | 13.8 W |
| Upper AMB | PMSM (30 A) | PMSM (37 A) | Lower AMB | Air Friction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variation 1 | 8.2 W | 17.4 W | - | 6.8 W | 0.70 W |
| Variation 2 | 7.5 W | - | 17.7 W | 6.2 W | 0.59 W |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franz, D.; Schneider, M.; Richter, M.; Rinderknecht, S. Thermal Behavior of a Magnetically Levitated Spindle for Fatigue Testing of Fiber Reinforced Plastic. Actuators 2019, 8, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020037
Franz D, Schneider M, Richter M, Rinderknecht S. Thermal Behavior of a Magnetically Levitated Spindle for Fatigue Testing of Fiber Reinforced Plastic. Actuators. 2019; 8(2):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020037
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranz, Daniel, Maximilian Schneider, Michael Richter, and Stephan Rinderknecht. 2019. "Thermal Behavior of a Magnetically Levitated Spindle for Fatigue Testing of Fiber Reinforced Plastic" Actuators 8, no. 2: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020037
APA StyleFranz, D., Schneider, M., Richter, M., & Rinderknecht, S. (2019). Thermal Behavior of a Magnetically Levitated Spindle for Fatigue Testing of Fiber Reinforced Plastic. Actuators, 8(2), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020037






