Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
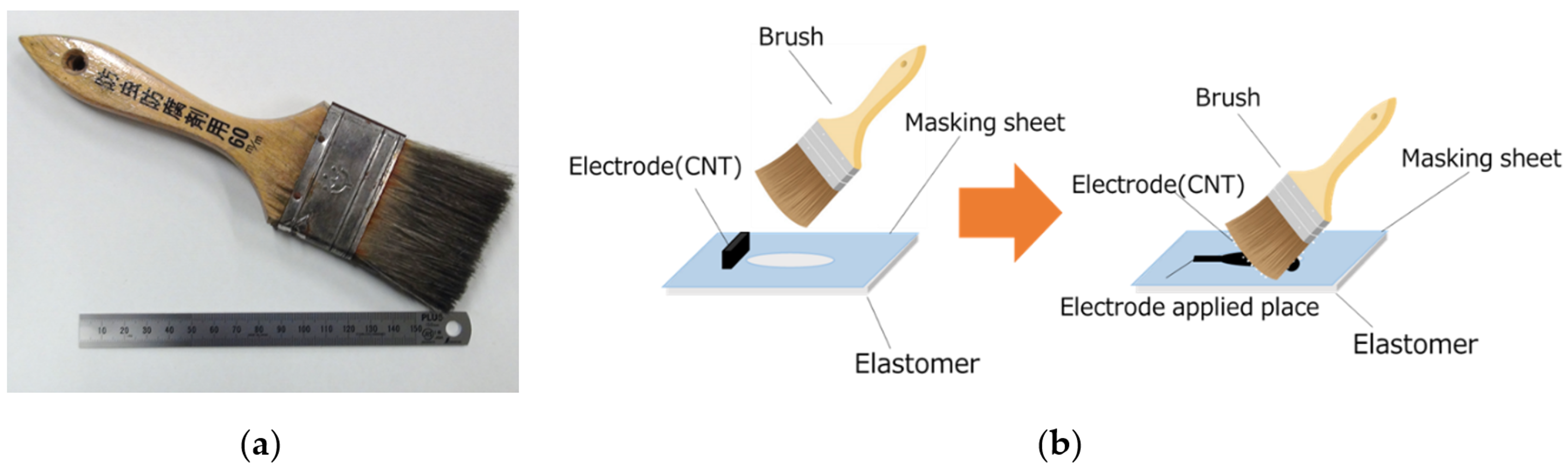
2.1. Observation Experiment
2.2. Performance Experiment
3. Results and Discussions
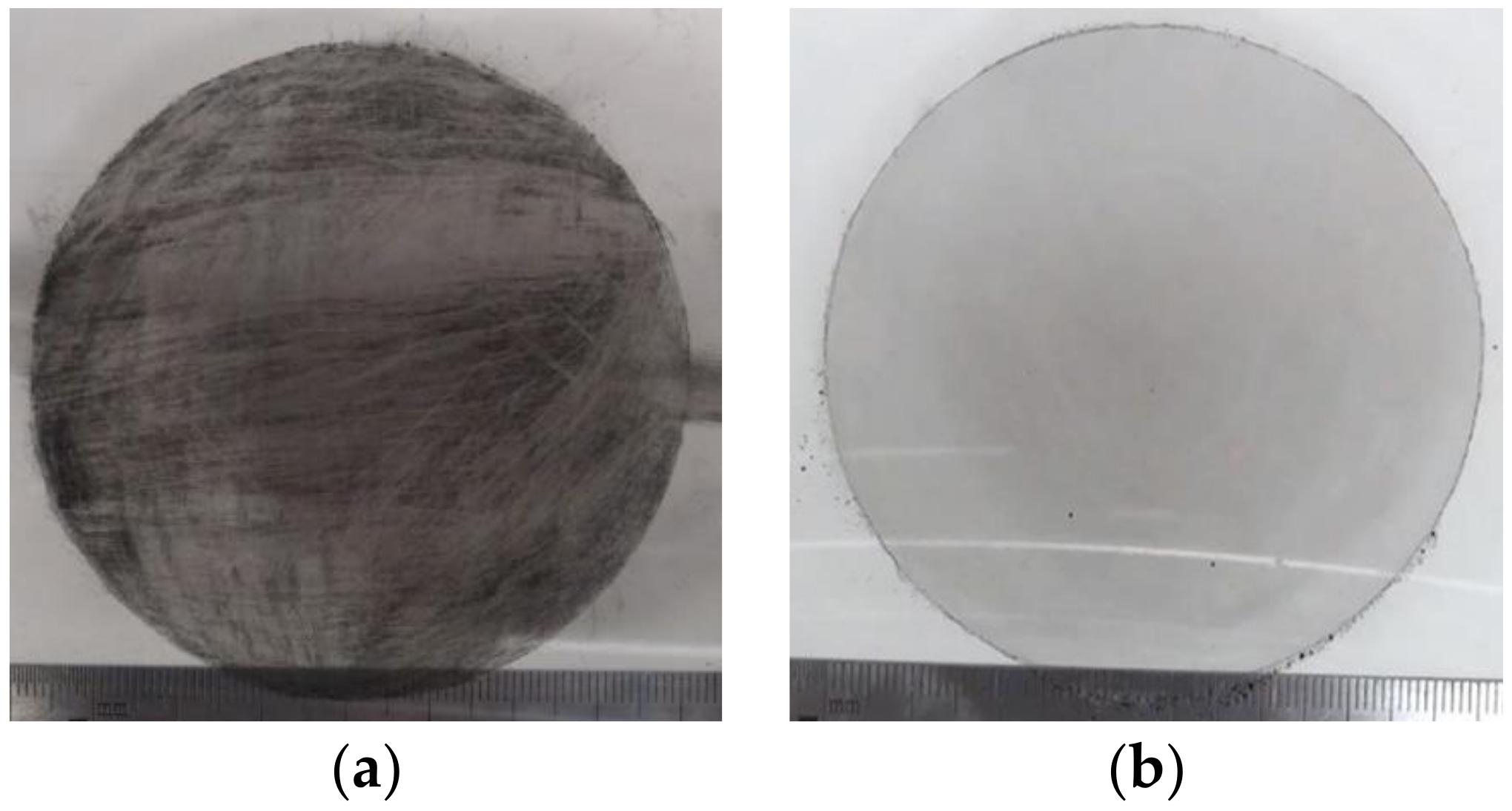
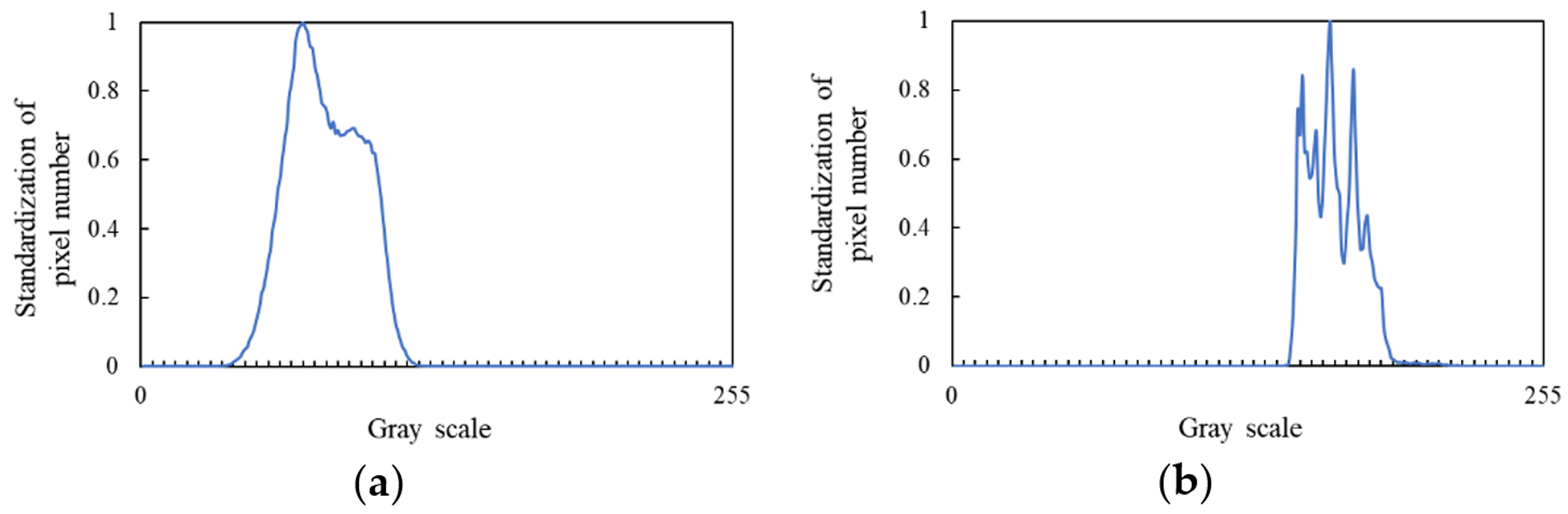
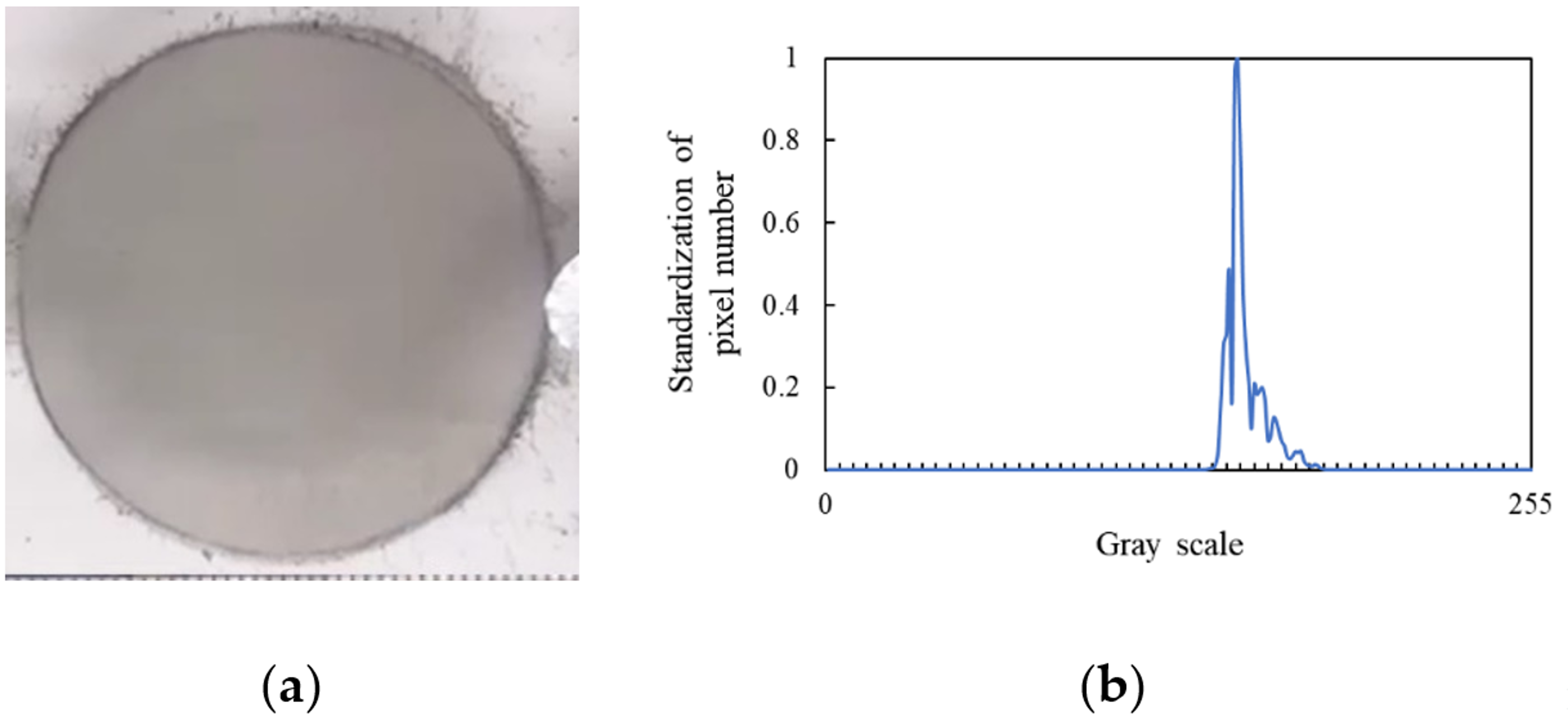
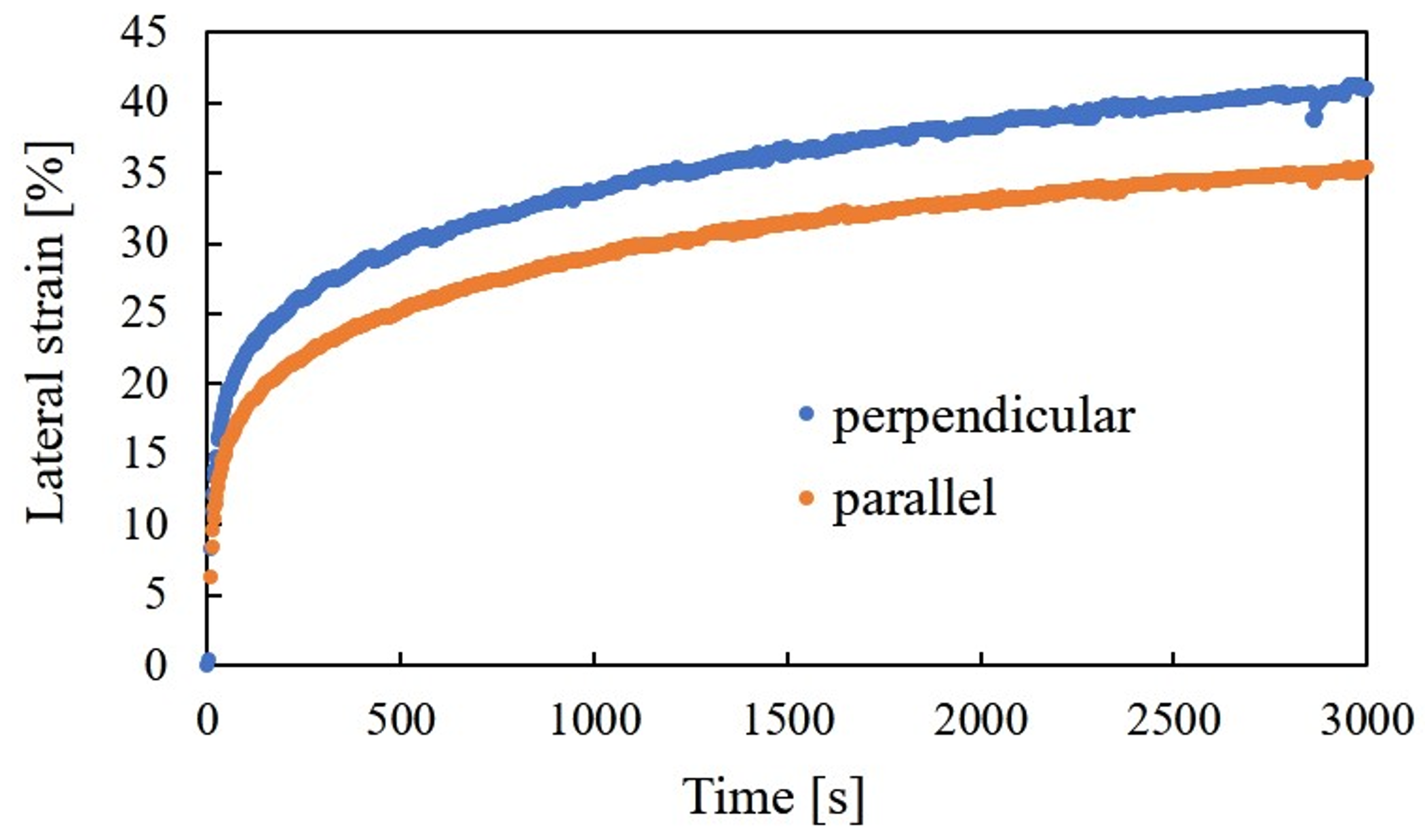
3.1. Observation Experiment
3.2. Performance Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzumori, K.; Iikura, S.; Tanaka, H. Applying a flexible microactuator to robotic mechanisms. IEEE Cont. Syst. 1992, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft robot arm inspired by the octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacucciolo, V.; Renda, F.; Poccia, E.; Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M. Modelling the nonlinear response of fibre-reinforced bending fluidic actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wehner, M.; Karpelson, M.; Wood, R.J.; Whitesides, G.M. A resilient, untethered soft robot. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.E.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Dielectric Elastomers As Electromechanical Transducers: Fundamentals, Materials, Devices, Models and Applications of an Emerging Electroactive Polymer Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 978-0-08-047488-5. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, Z. Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2010, 23, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, A.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Printing low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 244104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Self-walking gel. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3480–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Hara, Y.; Maeda, S.; Hashimoto, S. A pendulum-like motion of nanofiber gel actuator synchronized with external periodic pH oscillation. Polymers 2011, 3, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIELASTAR Research Project. Available online: https://www.festo.com/group/en/cms/10274.htm (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Hosoya, N.; Baba, S.; Maeda, S. Hemispherical breathing mode speaker using a dielectric elastomer actuator. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Joseph, J. Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 64, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Sun, J.Y.; Foo, C.C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Stretchable, transparent, ionic conductors. Science 2013, 341, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Joseph, J.; Heydt, R.; Pei, Q.; Chiba, S. High-field deformation of elastomeric dielectrics for actuators. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2000, 11, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochmatter, P.; Kovacs, G. Design and characterization of an active hinge segment based on soft dielectric EAPs. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; Araromi, O.A.; Schlatter, S.; Shea, H.R. Fabrication process of silicone-based dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozlar, M.; Punckt, C.; Korkut, S.; Zhu, J.; Chiang Foo, C.; Suo, Z.; Aksay, I.A. Dielectric elastomer actuators with elastomeric electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 091907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gao, W.; Xie, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, S.; Robinson, J.M.; Haroz, E.H.; Doorn, S.K.; Wang, W.; et al. Wafer-scale monodomain films of spontaneously aligned single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotech. 2016, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.Y.; Eun, K.; Choa, S.H.; Kim, H.K. Highly flexible and stretchable carbon nanotube network electrodes prepared by simple brush painting for cost-effective flexible organic solar cells. Carbon 2014, 66, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, E.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Song, J.S. Spray coated multi-wall carbon nanotube counter electrode for tri-iodide (I3-) reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobusa, Y.; Yomogida, Y.; Matsuzaki, S.; Yanagi, K.; Kataura, H.; Takenobu, T. Inkjet printing of single-walled carbon nanotube thin-film transistors patterned by surface modification. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 183106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemune, H.; Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Hosoya, N.; Hashimoto, S. Origami robot: A self-folding paper robot with an electrothermal actuator created by printing. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemune, H.; Maeda, S.; Cacucciolo, V.; Iwata, Y.; Iwase, E.; Hashimoto, S.; Sugano, S. Printed paper robot driven by electrostatic actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryokai, K.; Marti, S.; Ishii, H. I/O brush: Drawing with everyday objects as ink. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vienna, Austria, 24–29 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Enomae, T.; Han, Y.; Isogai, A. Nondestructive determination of fiber orientation distribution of paper surface by image analysis. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2006, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

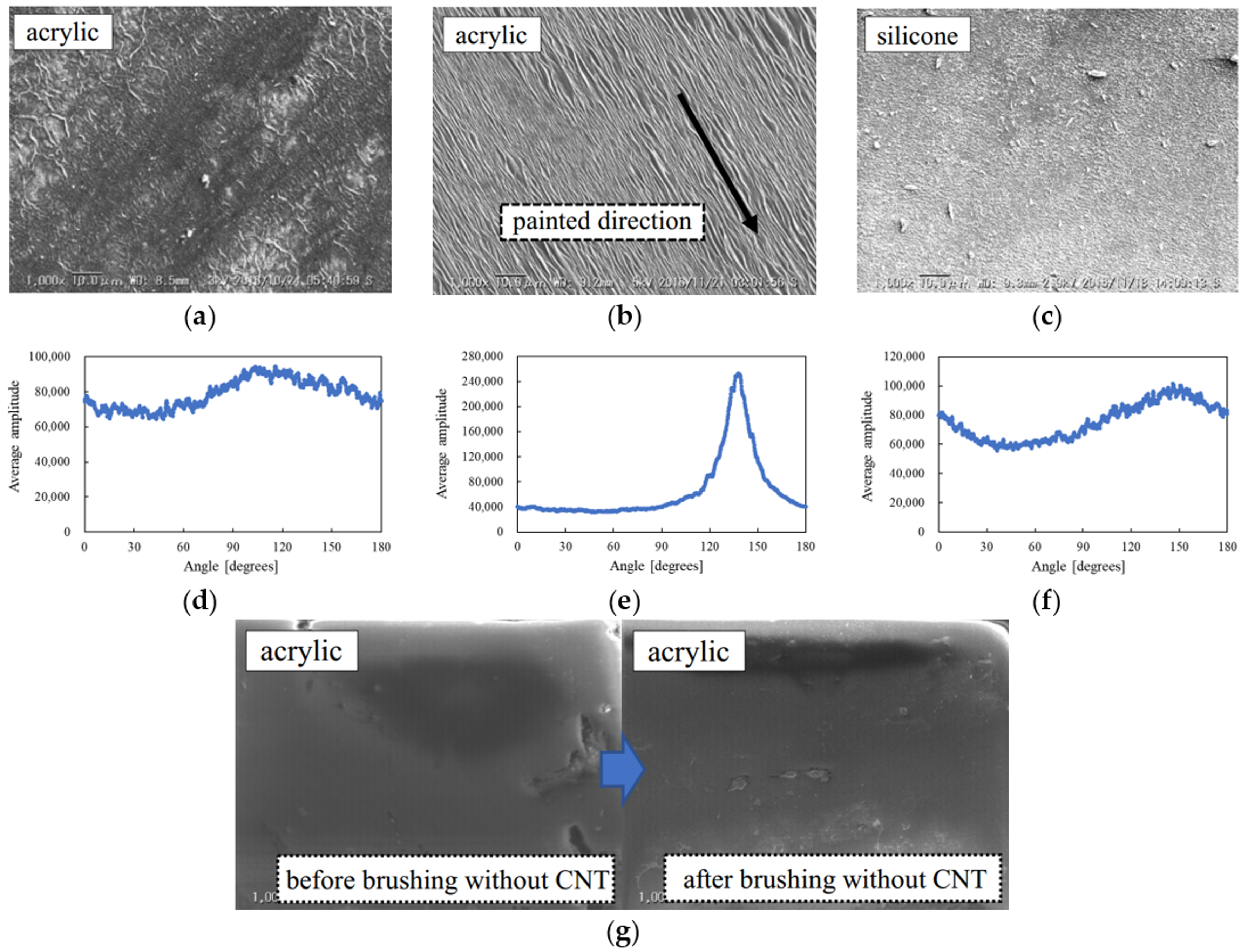
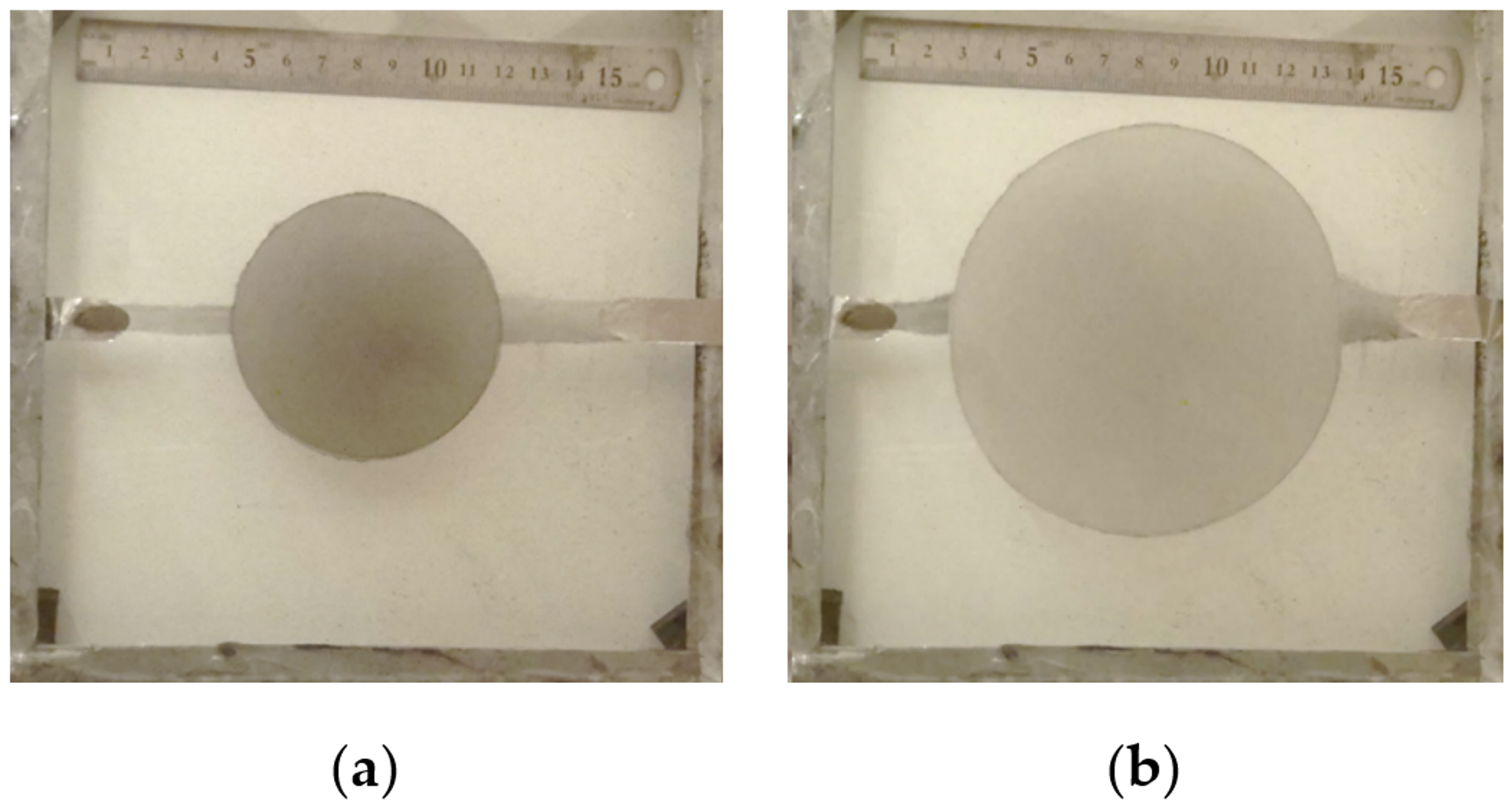

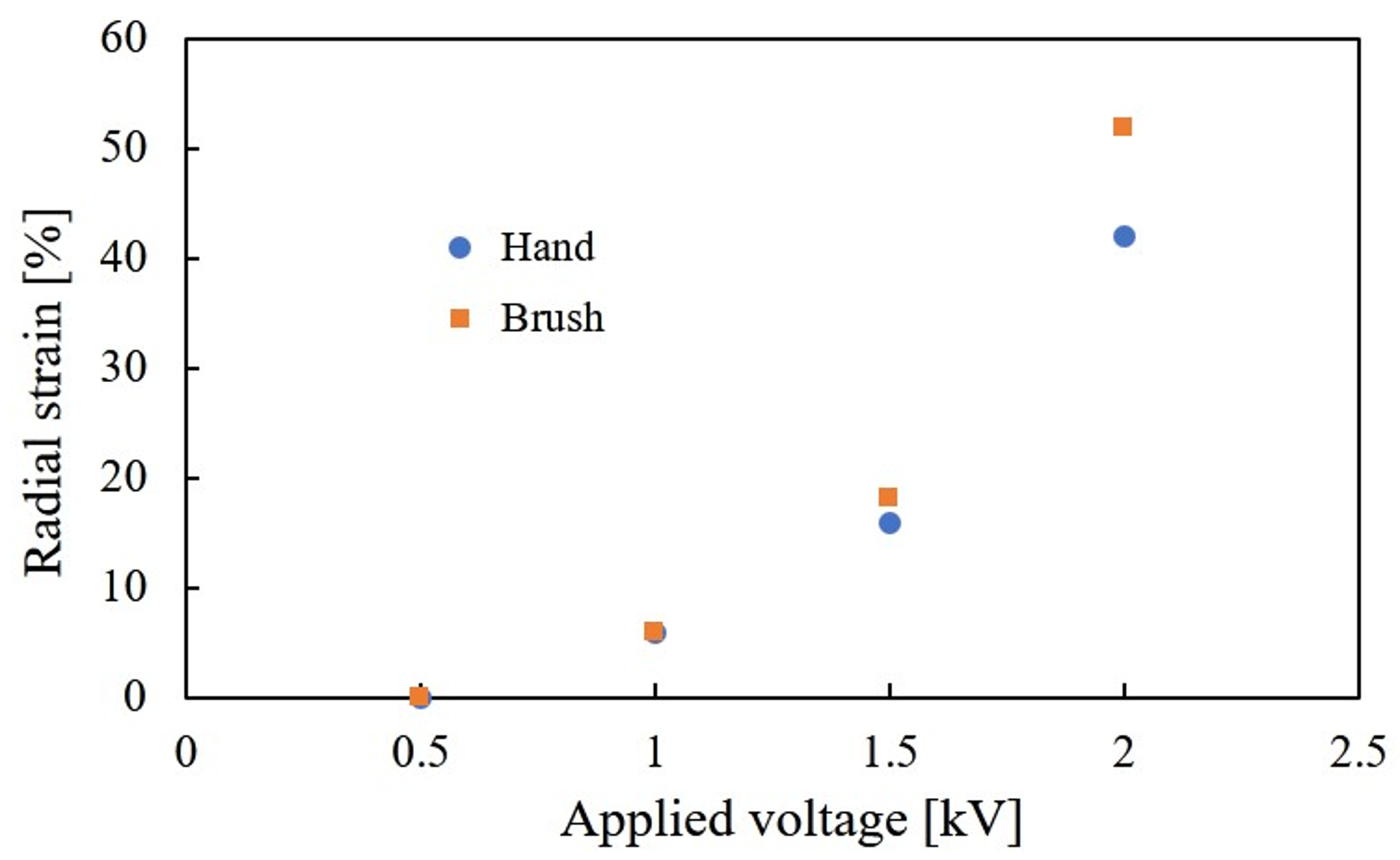
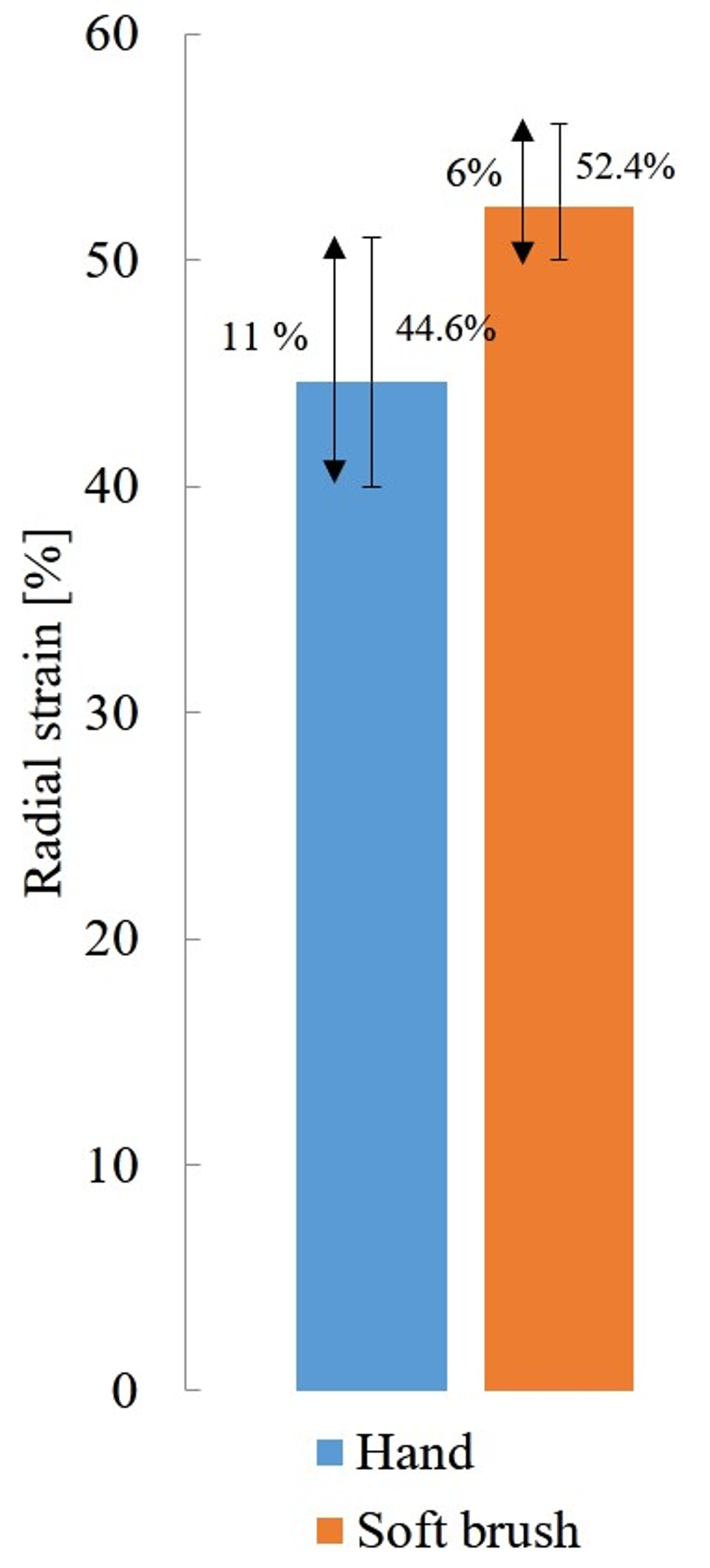
| DEA A | DEA B | DEA C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material of elastomer | Acrylic | Acrylic | Silicone |
| Model number (Supplier) | VHB Y-4905J (3M) | VHB Y-4905J (3M) | ELASTOSIL FILM 2030 SHEET (WACKER) |
| Painting tool | Hand | Brush | Brush |
| DEA A | DEA B | DEA C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max value | 122 | 217 | 179 |
| Minimum value | 33 | 56 | 137 |
| Mean value | 78.5 | 164 | 151 |
| Standard deviation | 15.3 | 11.1 | 6.65 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shigemune, H.; Sugano, S.; Nishitani, J.; Yamauchi, M.; Hosoya, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Maeda, S. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush. Actuators 2018, 7, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030051
Shigemune H, Sugano S, Nishitani J, Yamauchi M, Hosoya N, Hashimoto S, Maeda S. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush. Actuators. 2018; 7(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleShigemune, Hiroki, Shigeki Sugano, Jun Nishitani, Masayuki Yamauchi, Naoki Hosoya, Shuji Hashimoto, and Shingo Maeda. 2018. "Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush" Actuators 7, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030051
APA StyleShigemune, H., Sugano, S., Nishitani, J., Yamauchi, M., Hosoya, N., Hashimoto, S., & Maeda, S. (2018). Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush. Actuators, 7(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7030051





