Evaluating the Reduction of Stress Intensity Factor in Center-Cracked Plates Using Piezoelectric Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
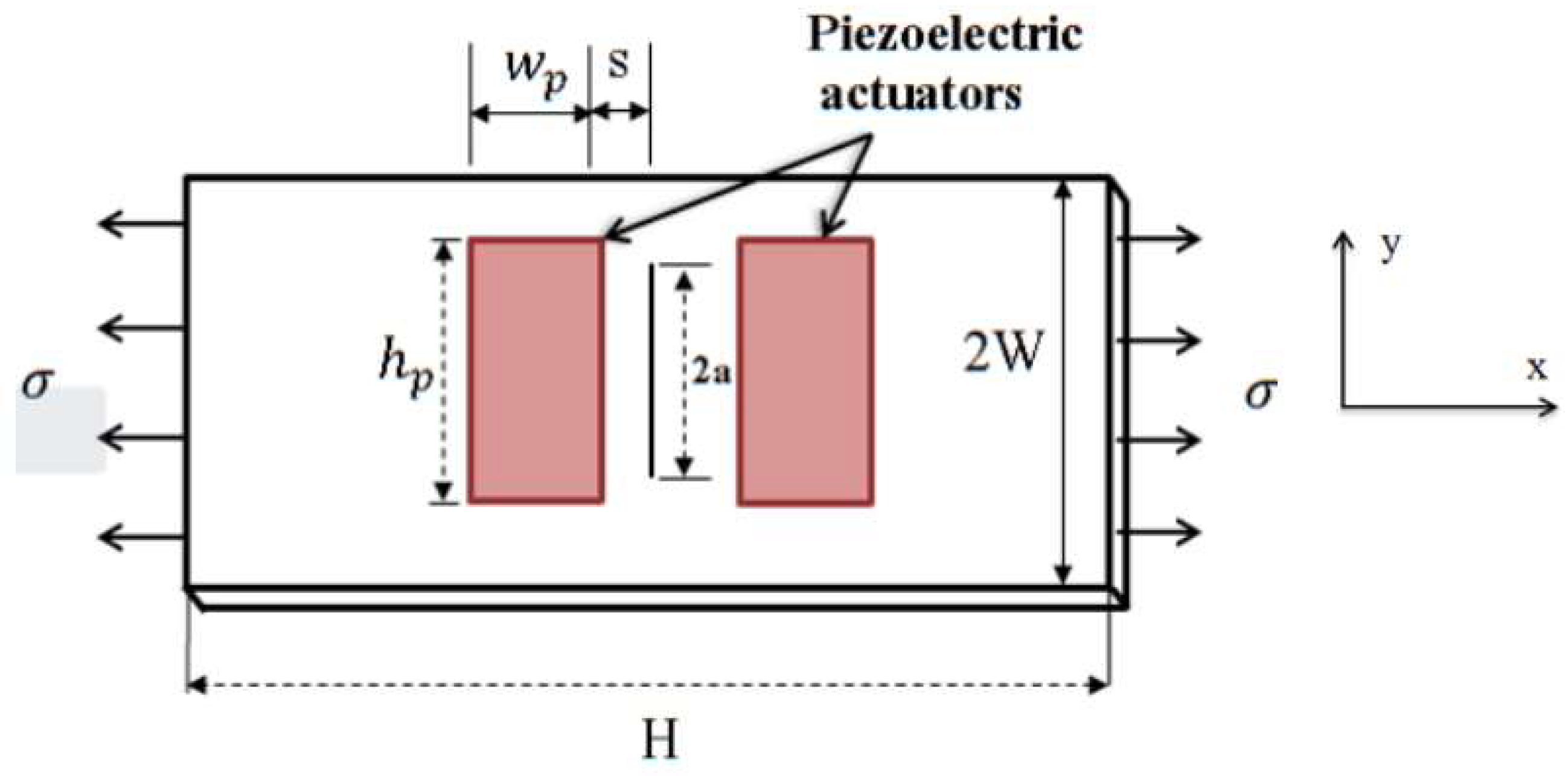
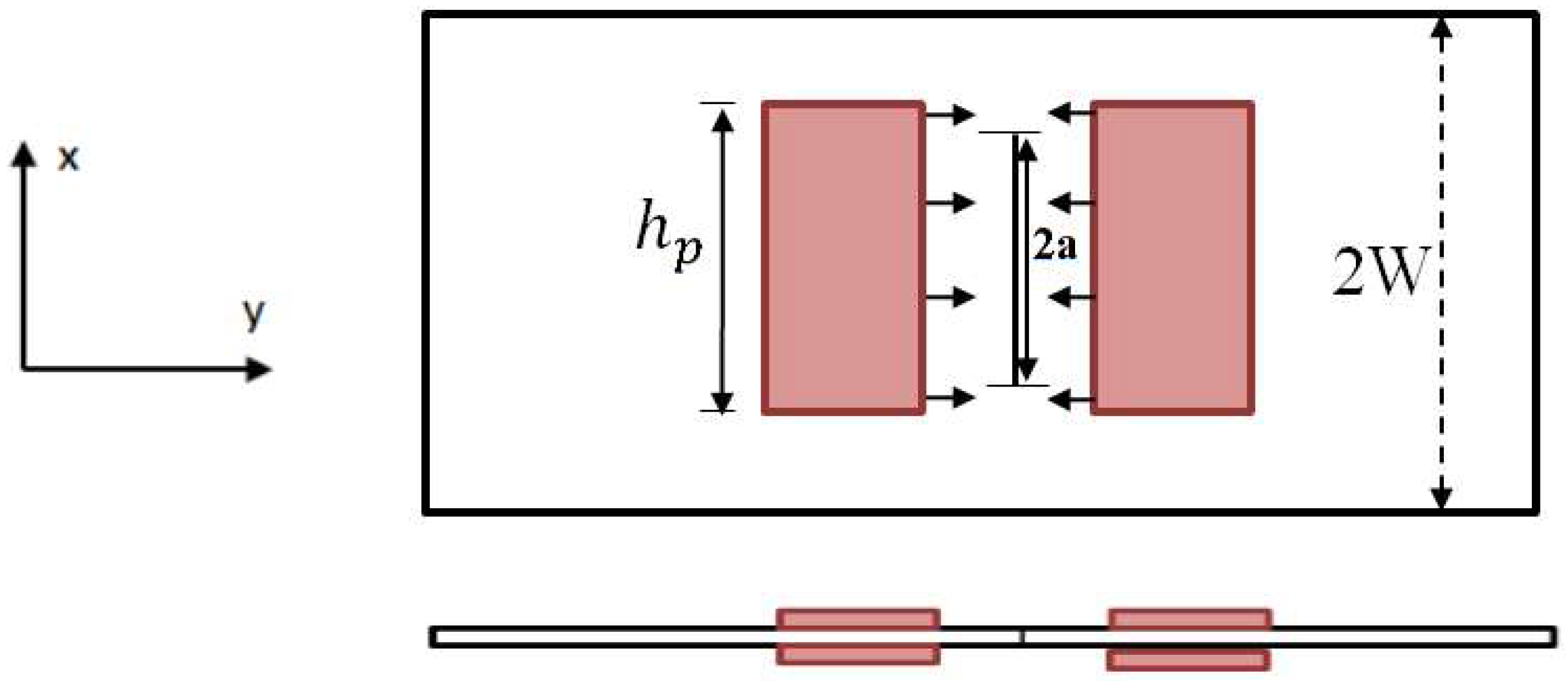
2.1. Modelling of the Active Repair of the Center-Cracked Plate with Integrated Piezoelectric Actuator
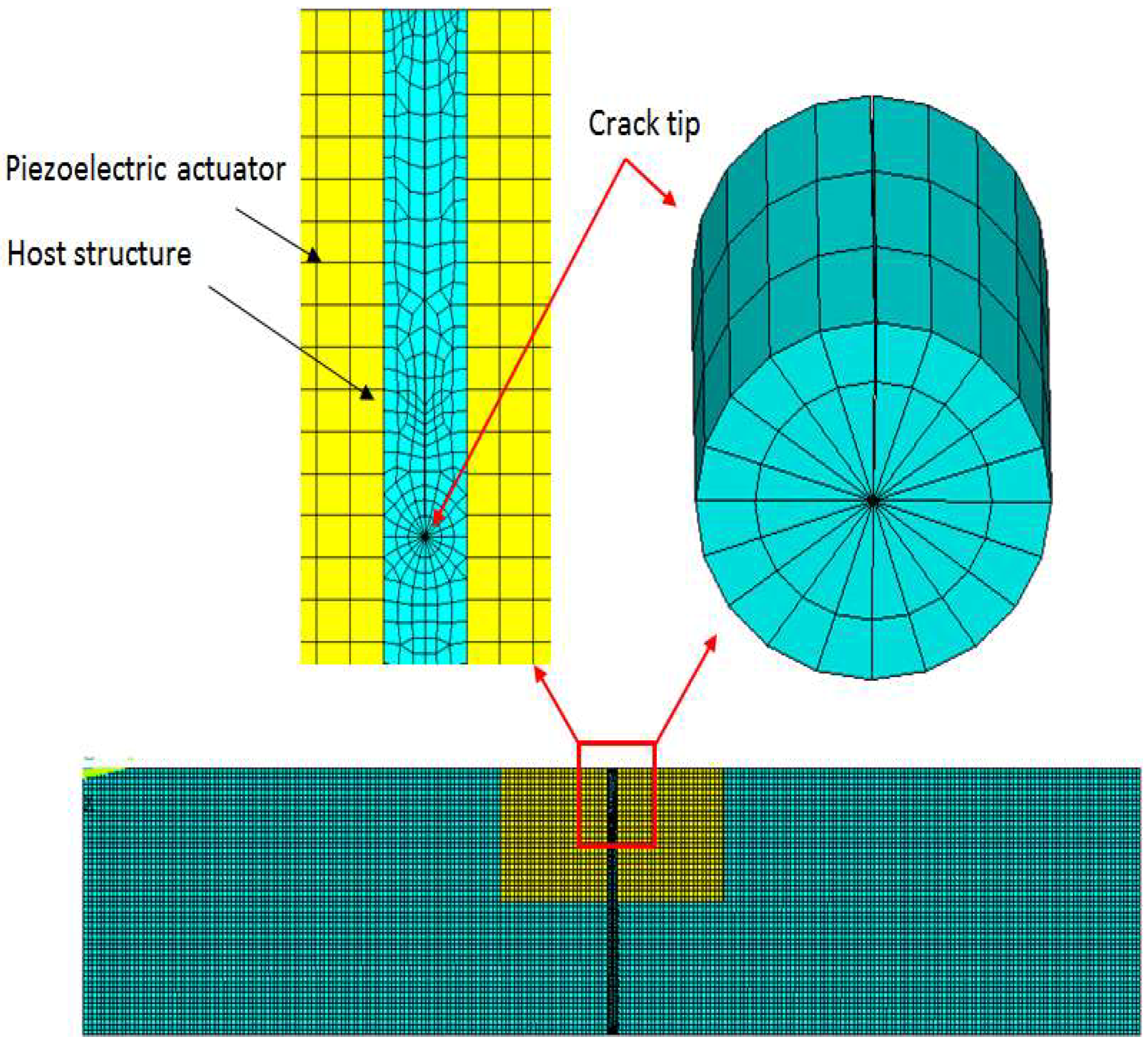
2.2. Geometrical and Finite Element Models
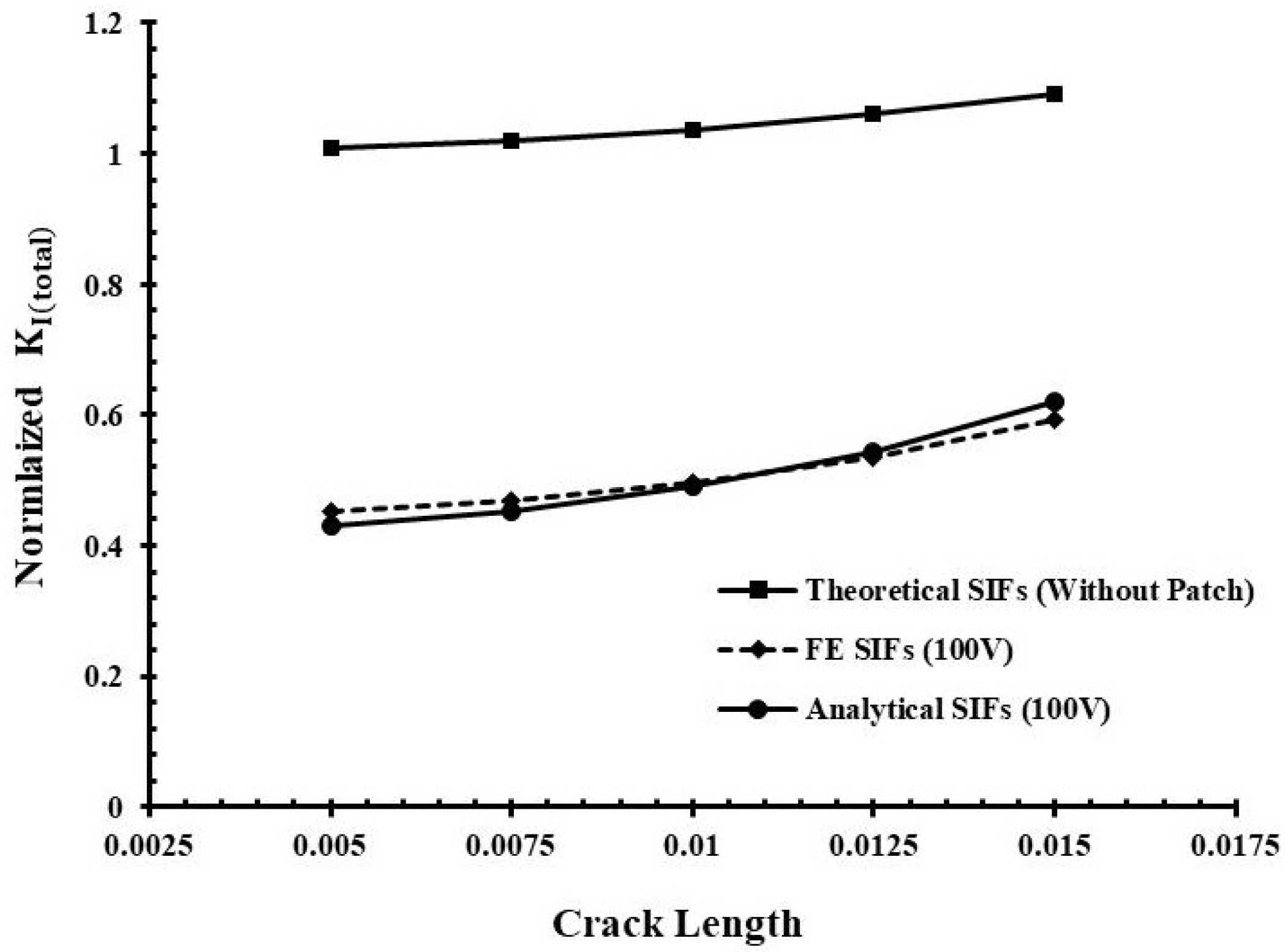
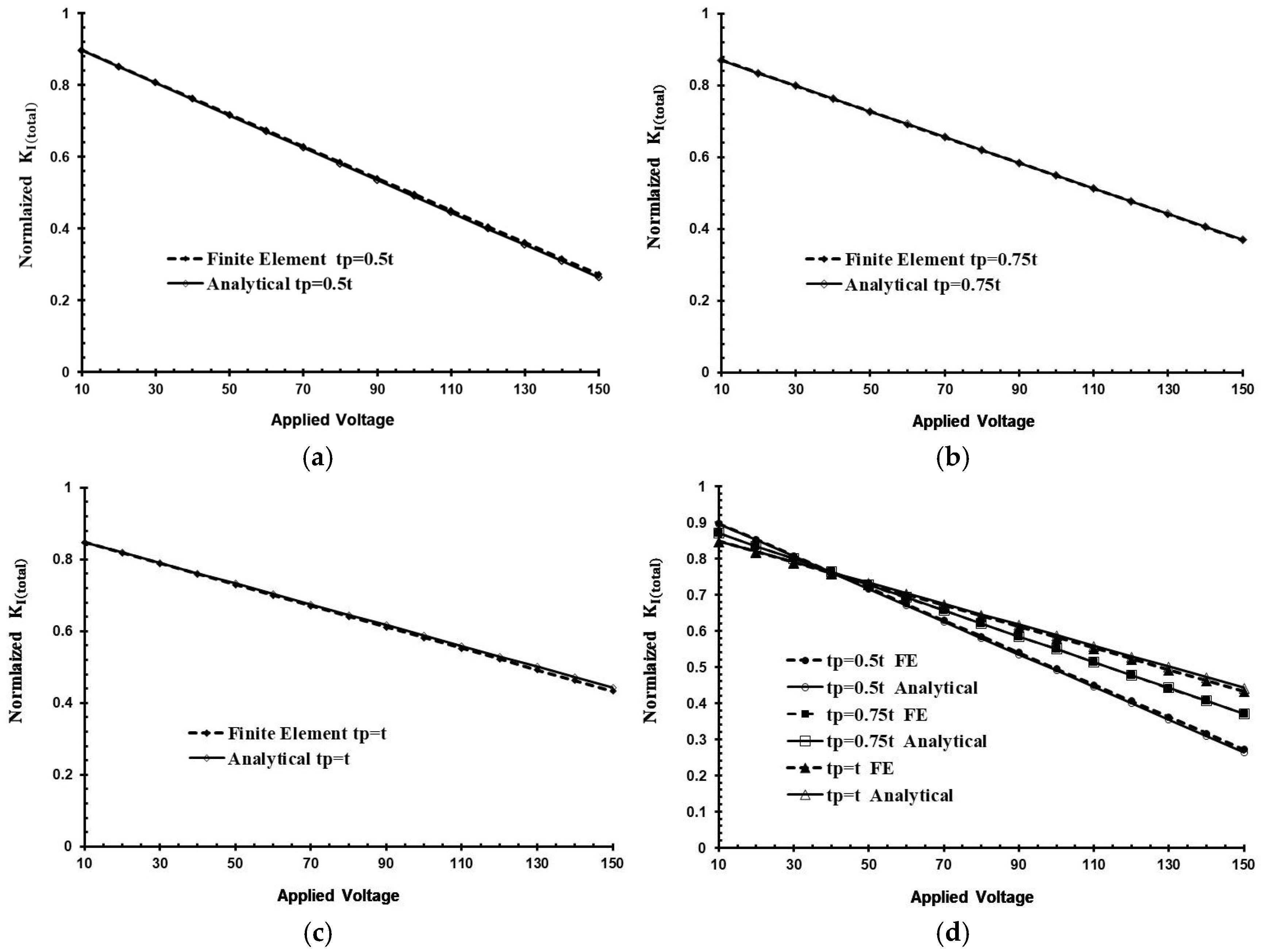
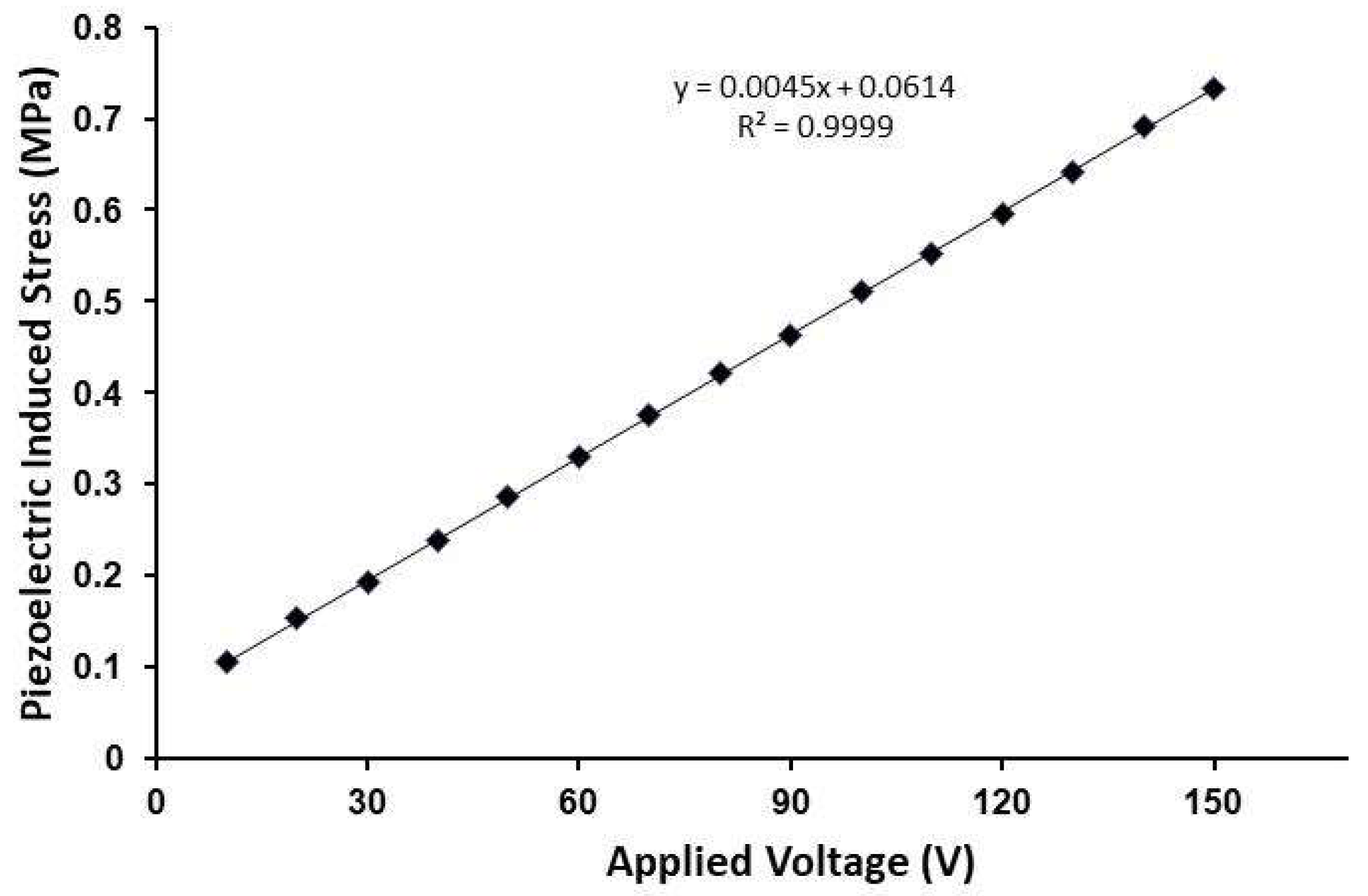
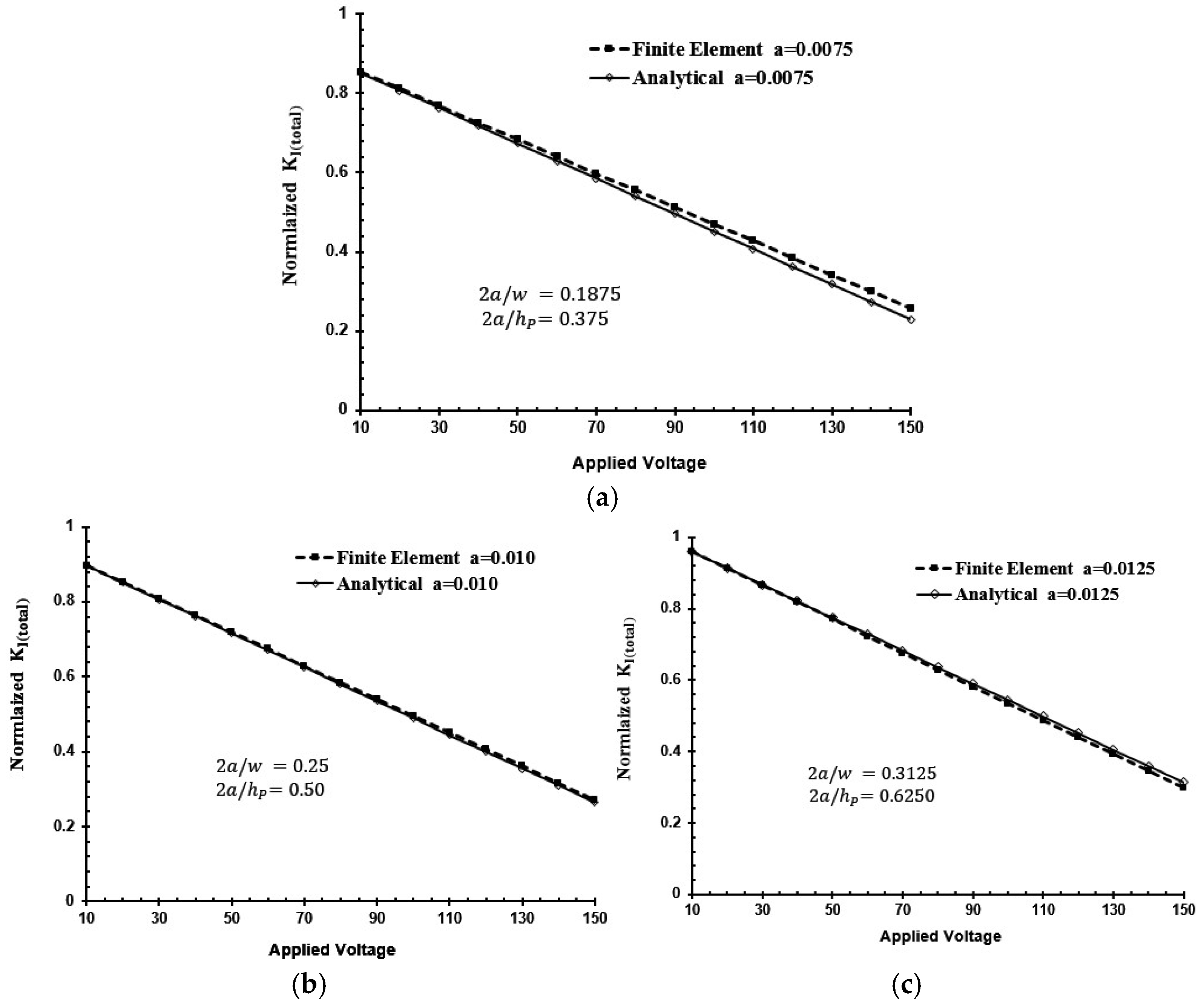
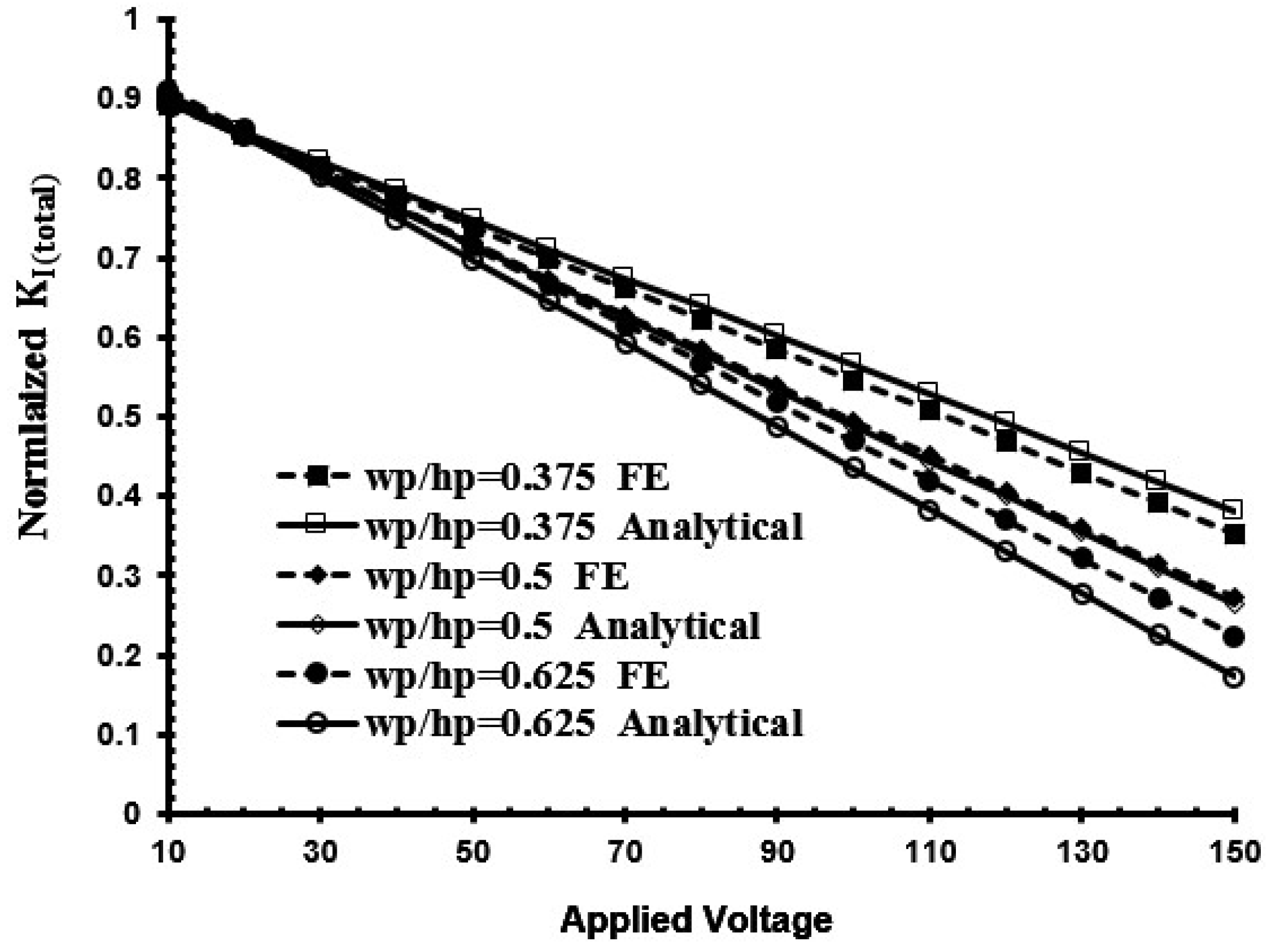
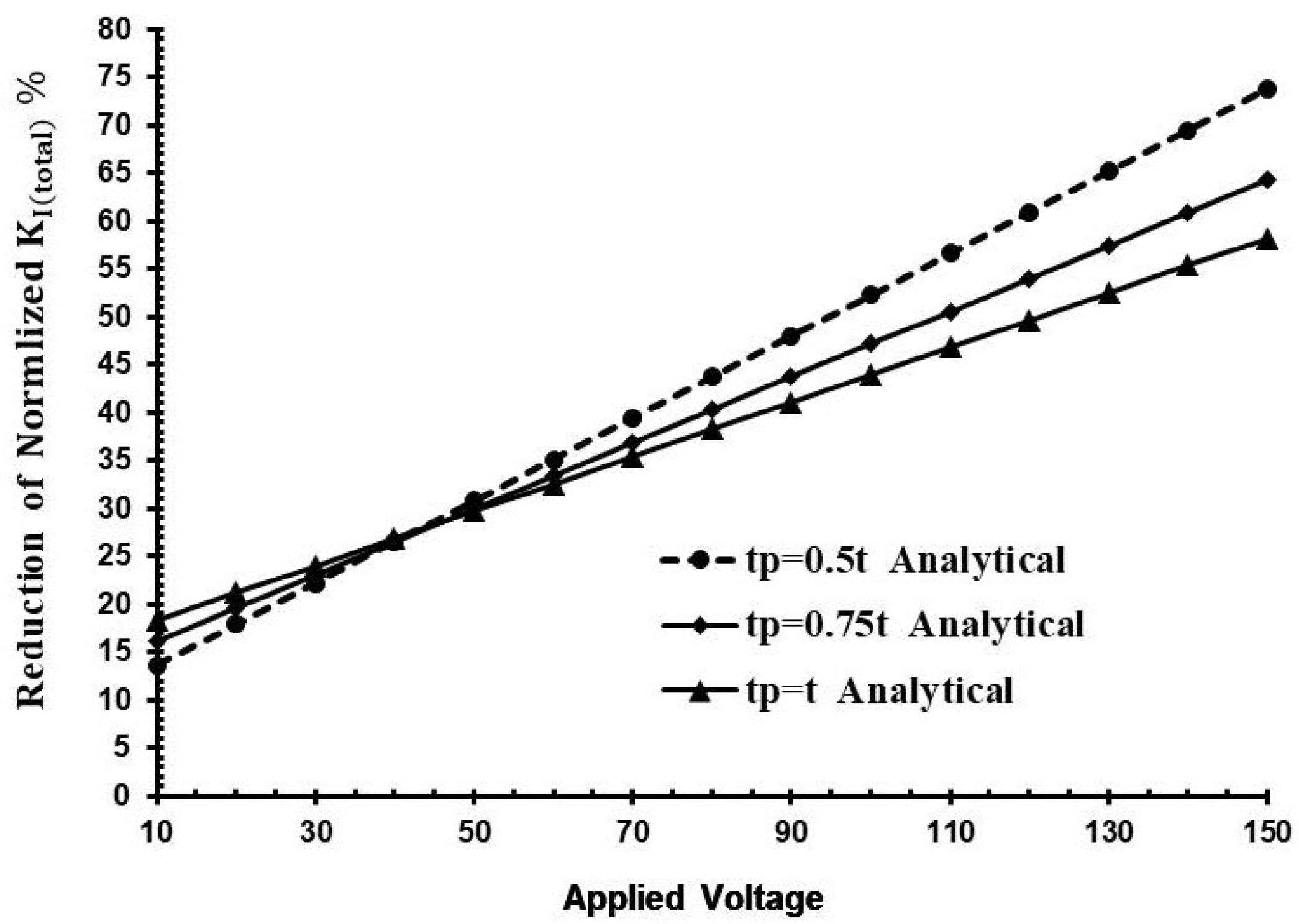
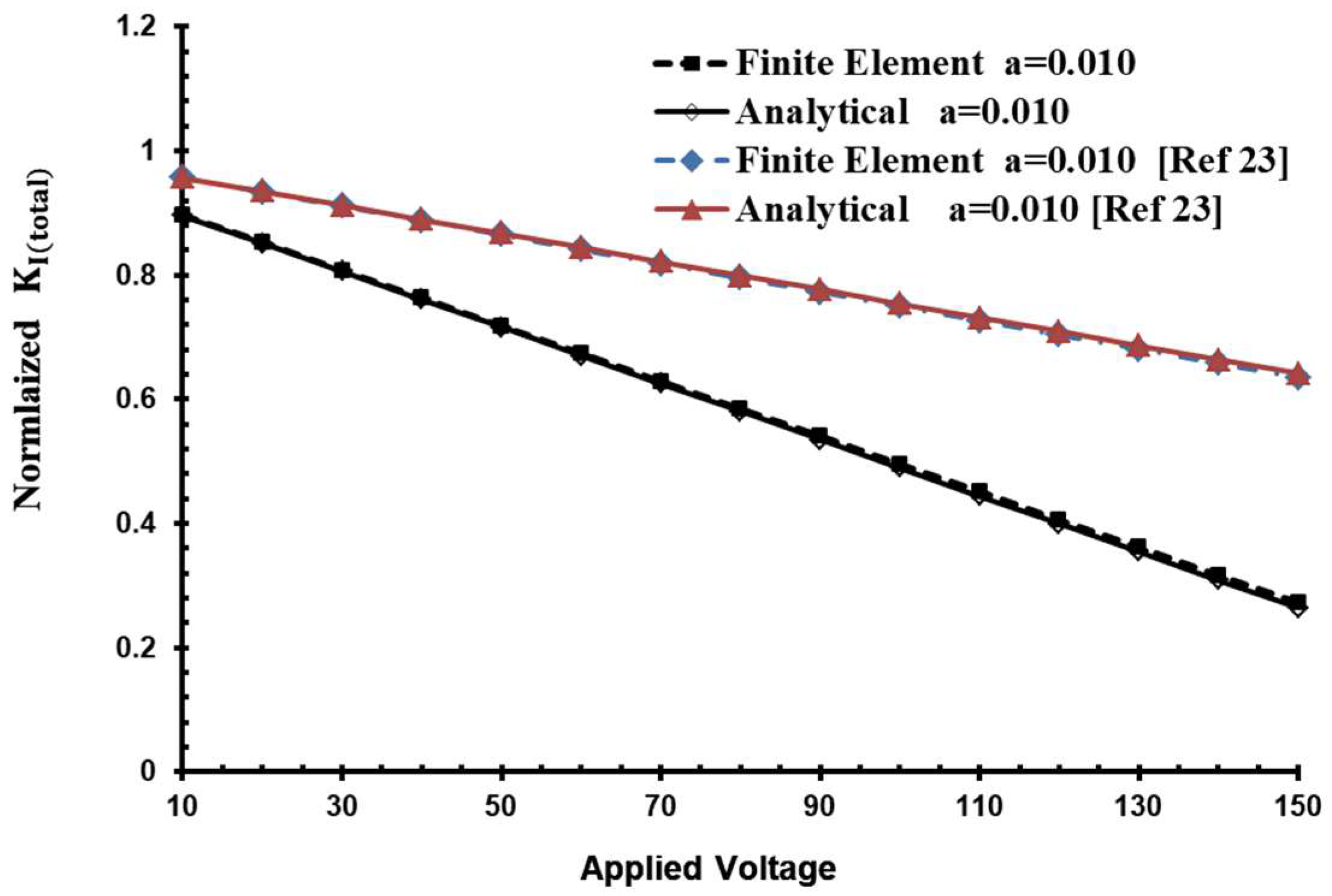
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- For very thin aluminum plates, the application of the stress produced by the piezoelectric actuator at the crack tip decreases the stress intensity factor.
- The piezoelectric actuator’s geometry plays an important role in effective repair of the center-cracked plate.
- To achieve the best result in reduction of the SIFs, it is a good idea to use thin actuators with relatively high voltage.
- An accurate result with less than 1.2% discrepancy can be found when the piezoelectric actuator’s width is double the crack length.
- The reductions of the SIF with an increase in the actuator’s thickness are not absolute and tend to be inverse to the application of high voltage.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Wu, N. A review on structural enhancement and repair using piezoelectric materials and shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.; Hrairi, M.; Dawood, M.S.I. Survey of Active Structural Control and Repair Using Piezoelectric Patches. Actuators 2015, 4, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, Q. An experimental study on the repair of a notched beam subjected to dynamic loading with piezoelectric patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, Q. Repair of vibrating delaminated beam structures using piezoelectric patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 035027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, Q. Repair of a delaminated plate under static loading with piezoelectric patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Quek, S.T.; Liew, K.M. On the repair of a cracked beam with a piezoelectric patch. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Quek, S.T. Repair of cracked column under axially compressive load via piezoelectric patch. Comput. Struct. 2005, 83, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Quek, S.T. Repair of delaminated beams via piezoelectric patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Duan, W.H.; Quek, S.T. Repair of notched beam under dynamic load using piezoelectric patch. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2004, 46, 1517–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaei, A.; Ziaei-Rad, S.; Ghayour, M. Repair of a cracked Timoshenko beam subjected to a moving mass using piezoelectric patches. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2010, 52, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, A.; Milazzo, A.; Orlando, C.; Messineo, A. Numerical analysis of piezoelectric active repair in the presence of frictional contact conditions. Sensors 2013, 13, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaimo, A.; Milazzo, A.; Orlando, C. On the dynamic behavior of piezoelectric active repair by the boundary element method. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platz, R.; Stapp, C.; Hanselka, H. Statistical approach to evaluating reduction of active crack propagation in aluminum panels with piezoelectric actuator patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 085009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.J.C. Crack repair performance of piezoelectric actuator estimated by slope continuity and fracture mechanics. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Diaz-Molina, A.; Ruiz, D.; Donoso, A.; Bellido, J.C.; Wistrela, E.; Kucera, M.; Schmid, U.; Hernando-García, J.; et al. Design and Characterization of In-Plane Piezoelectric Microactuators. Actuators 2017, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez Carazo, A.; Uchino, K. Novel Piezoelectric-Based Power Supply for Driving Piezoelectric Actuators Designed for Active Vibration Damping Applications. J. Electroceramics 2001, 7, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez Carazo, A. Piezoelectric Transformers: An Historical Review. Actuators 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Wang, F.; Ma, X. A new transformerless buck–boost converter with positive output voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C. Micro converter with a high step-up ratio to drive a piezoelectric bimorph actuator applied in mobile robots. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.J.C. Fracture mechanics and crack contact analyses of the active repair of multi-layered piezoelectric patches bonded on cracked structures. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2007, 47, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.; Hrairi, M.; Dawood, M.S.I. Mode I stress intensity factor for a cracked plate with an integrated piezoelectric actuator. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1115, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.; Dawood, M.S.I.; Hrairi, M. Effects of Adhesive Bond on Active Repair of Aluminium Plate Using Piezoelectric Patch. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 799–800, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.; Hrairi, M.; Dawood, M.S.I. Modeling approach to evaluating reduction in stress intensity factor in center-cracked plate with piezoelectric actuator patches. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki, J.J.; Golabi, S. Effect of stiffness ratio of piezoelectric patches and plate on stress concentration reduction in a plate with a hole. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2017, 24, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki, J.J.; Golabi, S. A novel method to specify pattern recognition of actuators for stress reduction based on Particle swarm optimization method. Smart Struct. Syst. 2016, 17, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, V.A.; Mohammadi, N. Buckling analysis of cracked functionally graded material column with piezoelectric patches. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Paris, P.C.; Irwin, G.R. The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, 3rd ed.; ASME Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0791801535. [Google Scholar]
- Bueckner, H. Novel principle for the computation of stress intensity factors. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1970, 50, 529–546. [Google Scholar]
- Fett, T.; Munz, D. Stress Intensity Factors and Weight Functions; Computational Mechanics Publications: Southampton, UK, 1997; ISBN 1853124974. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, J.R. Some remarks on elastic crack-tip stress fields. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1972, 8, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Anderson, T. Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 9781420058215. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, E.F.; De Luis, J. Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 1987, 25, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki, J.J.; Madani, S.G.; Golabi, S. Effect of stiffness and thickness ratio of host plate and piezoelectric patches on reduction of the stress concentration factor. Int. J. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2016, 8, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | S11 m2/N | S33 m2/N | d31 m/V | d32 m/V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 | 2395 |
| Crack Length (mm) | Theoretical NSIF (without Patch) | Finite Element NSIF | Analytical NSIF | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0050 | 1.0083 | 0.4537 | 0.4303 | −5.41 |
| 0.0075 | 1.0195 | 0.4698 | 0.4512 | −4.11 |
| 0.0100 | 1.0363 | 0.4950 | 0.4896 | −1.11 |
| 0.0125 | 1.0596 | 0.5348 | 0.5439 | 1.67 |
| 0.0150 | 1.0906 | 0.5935 | 0.6211 | 4.44 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuzaid, A.; Hrairi, M.; Dawood, M.S.I.B.S. Evaluating the Reduction of Stress Intensity Factor in Center-Cracked Plates Using Piezoelectric Actuators. Actuators 2018, 7, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7020025
Abuzaid A, Hrairi M, Dawood MSIBS. Evaluating the Reduction of Stress Intensity Factor in Center-Cracked Plates Using Piezoelectric Actuators. Actuators. 2018; 7(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuzaid, Ahmed, Meftah Hrairi, and Mohd Sultan Ibrahim Bin Shaik Dawood. 2018. "Evaluating the Reduction of Stress Intensity Factor in Center-Cracked Plates Using Piezoelectric Actuators" Actuators 7, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7020025
APA StyleAbuzaid, A., Hrairi, M., & Dawood, M. S. I. B. S. (2018). Evaluating the Reduction of Stress Intensity Factor in Center-Cracked Plates Using Piezoelectric Actuators. Actuators, 7(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7020025






