Abstract
Electroactive polymer actuators such as polypyrrole (PPy) are exciting candidates to drive autonomous devices that require low weight and low power. A simple PPy tri-layer bending type cantilever which operates in the air has been demonstrated previously, but the environmental effect on this actuator is still unknown. The major obstacle in the development of the PPy tri-layer actuator is to create proper packaging that reduces oxidation of the electrolyte and maintains constant displacement. Here, we report the variation in the displacement as well as the charge transfer at the different environmental condition. PPy trilayer actuators were fabricated by depositing polypyrrole on gold-coated porous poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) using the electro-synthesis method. It has been demonstrated that the charge transfer of tri-layer actuators is more in an inert environment than in open air. In addition, tri-layer actuators show constant deflection and enhancement of life due to the negligible oxidation rate of the electrolyte in an inert environment.
1. Introduction
Electroactive polymer (EAP) is suitable for low voltage electromechanical actuators, that are useful for a range of potential applications and may be appropriate replacements for high voltage low strain piezoelectric actuators [1]. In the last decade, a range of actuator materials has been reported, such as carbon nanotubes [2] and conducting polymer [3], which work in different environmental media [4,5]. Polypyrrole (PPy) EAP is one of the known materials used in the actuators regime which exhibits all properties of lifelike robots, artificial limbs and other bio-mimetic devices [6,7,8]. It is very suitable for autonomous electromechanical biologic systems because of its light weight, low potential (1–3 V), and the fact that it can be fabricated at microscale [9,10,11]. Furthermore, the scaling down of these PPy actuators improves their actuation properties, which are useful for numerous applications such as micromanipulation of cells [12], bioanalytical nano-systems [13], data storage [14], microvalves [15], Labs on chip [16], cantilever light modulators [17], and micro-optical instrumentation [18], etc. However, their limited structural strength, lifetime and low resistance electrical contacts still remain challenges to be addressed [19,20].
The mechanism for the volume change in PPy actuators involves the electrochemical transport of ions due to redox reactions [21,22,23,24]. While most PPy actuators work in a liquid electrolyte, multi-layer PPy consists of two active (PPy) thin films separated by an insulating porous medium (PVDF) which hold the electrolyte within the internal pores [17]. This type of structure operates in wet as well as dry media that become electrochemically oxidized and reduced in a continuous and reversible way, leading to a bending movement [25]. Although several investigations have been reported to enhance the performance in tri-layer actuators through miniaturization [26], thinning the porous medium [27], and adding a thin film of gold electrode to increase the strain [28], the system studied to date had never consider the environmental effect on actuators.
It has been found that the electrolyte degrades very easily in the presence of oxygen, humidity and other gases in the environment which slow down the ion diffusion and hence reduce the lifetime of an actuator [29]. In general, the overall increase in impedance of the system under an electric field leads to deviation in the bending displacement of the actuator [30]. Furthermore, oxidation of Pt and Au electrodes under certain environmental conditions after the operation of PPy actuators leads towards the delamination of the PPy film from its contacts and increases the system contact resistance [31].
In this paper, we present the environmental effect on the mechanism of tri-layer PPy actuators. The influence of oxidation on the electrolyte and metal electrode is shown in terms of displacement of the actuator. The redox reaction of the tri-layer actuator is performed in both the environmental and inert media.
2. Experimental Section
The tri-layer actuator consists of two outer PPy layers on a thin film of gold (Au) as an active component and an inner porous separator of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) which holds the electrolyte of lithium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide (Li+TFSI−) salt in the solvent of propylene carbonate (PC), as shown in Figure 1a. When the potential difference is applied between active layers of the actuator, one PPy layer is oxidized and the other is reduced. In the oxidation side, big anions are attracted towards the PPy layer and it thus expands, while in the reduction side, anions leave the PPy layer and it contracts, as shown in Figure 1b. The whole structure is like a cantilever beam in which one end is fixed and the other is free standing; the bending of the cantilever is towards the negative electrode i.e., the reduction side. The volume change in the PPy tri-layer actuator is due to the movement of charges i.e., the movement of anions and cations through the porous dielectric layer. The displacement of the actuator depends upon the area, thickness of the active layer and separator, ionic concentration of salt, type of salt and magnitude of applied potential difference [32,33].
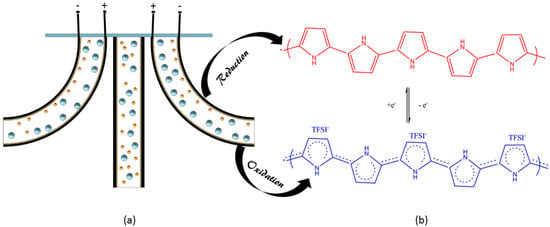
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the tri-layer actuator during oxidation and reduction; (b) Variation in molecular chain of the polypyrrole (PPy) during applied potential difference.
2.1. Materials and Methods
PPy monomers were acquired from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and stored at −16 °C prior to polymerization. Bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide lithium salt (LiTFSI) and Propylene carbonate (PC) (Sigma-Aldrich) were used as received. The separator material of porous poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) filter membrane films used are from Millipore, Immobilon-P, with a 0.45-μm pore size, and a thickness of 110 μm.
2.2. Electropolymerization of Pyrrole
Polypyrrole is synthesized by the electro oxidation of pyrrole monomers at a suitable anode (Au). When positive potential is applied to the electrodes, insoluble conducting polymeric material is deposited at the anode. As shown in Figure 2a, 5 nm Au is sputtered by CVC 601 sputter deposition on both side of the PVDF membrane as it received from the Millipore Immobilon-P roll. After coating Au on both sides, PPy is electro-synthesized by using the chronopotentiometry method at the current density of 0.2 mA/cm2 in an electrolyte solution consisting of 0.1 M LiTFSi in PC with 1% of DI water using Bio-Logic SP200 potentiostat. At −16 °C, PPy is synthesized with a two-electrode setup, in which both sides of the Au-sputtered PVDF act as working electrodes whereas counter and reference electrodes connected with stainless steel mesh. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were recorded at a scan rate of 0.03°·s−1 on a Rigaku Miniflex II (X-ray diffractometer) using a Cu Kα source. Raman studies were carried out on a Triax 550 (Horiba JobinYvon, Edison, NJ, USA) with 514 nm laser excitation. For electromechanical and electrochemical measurements of the tri-layer actuator, the potential difference is applied through a Bio-Logic SP200 potentiostat with related software that records voltage and current. The deflection of the actuator is recorded by using a SONY HD AVCHD handycam. UNIlab Glove box is used for the inert environment measurements.
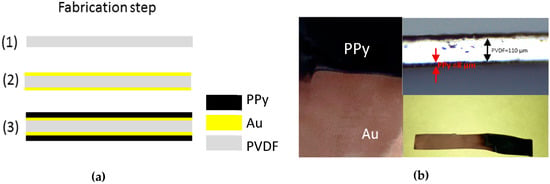
Figure 2.
Illustration of the process steps for the tri-layer actuator; fabrication steps and images after polymerization. (a) (1) A 5 cm × 5 cm piece of commercial PVDF membrane is cut from the roll; (2) Sputter deposition of 5 nm Au on both sides of the PVDF; (3) Electrochemical synthesis of PPy on gold electrode. (b) The final actuator with the dimensions of 5 cm × 5 cm, optical image of cross section and cut out from the membrane.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PPy
The conductive polymer film and cross-sectional area of the tri-layers actuator, as shown in Figure 2b. PPy film is deposited on the PVDF/Au electrode by constant current technique called chronopotentiometry. This constant current technique usually results in more uniform growth than other electrodeposition methods of polypyrrole. The thickness (8 µm) as well as particle size of the PPy film depends upon the interval of time, physical structure of the working electrode, and current density. The physical structure of the electrode plays an important role in deciding the morphology and conductivity of the film. Figure 3 shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Raman characteristics of polypyrrole tri-layer actuator. As can be seen in the SEM depicted in Figure 3b, a nodules-type structure is formed, which is made up of an aggregation of small particles on the porous PVDF/Au membrane. This type of structure is often referred to as a cauliflower structure [34]. The size of the cauliflower morphology increases in conjunction with the increase of polymerization time, which makes the polymer into crystalline domains. This porous membrane and partially crystalline structure of the polymer helps to enhance the conductivity of the polymer sheet, resulting in better actuation as well as improved response time [35]. The porous membrane helps to hold the liquid electrolyte, whereas the partially crystalline nature of the PPy film improves the conductivity, thus enhancing the lifetime and actuation stability of the actuator [36,37].
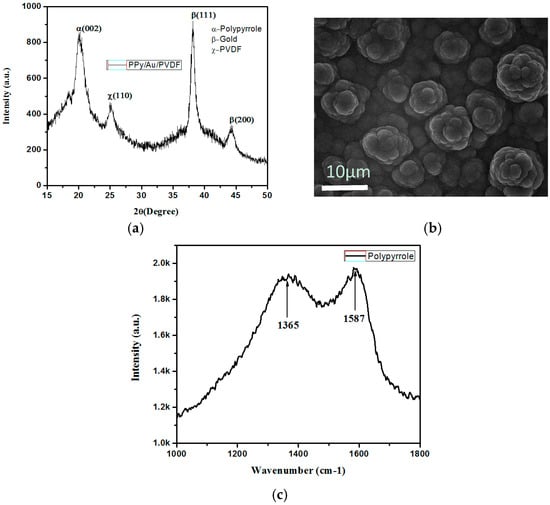
Figure 3.
(a) X-ray Diffraction (XRD) spectra of PPy doped with LiTFSi at −16 °C; (b) SEM images of electrodeposited polypyrrole (PPy) from pyrrole monomers; (c) Raman spectra of PPy on Gold and poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF).
As shown in Figure 3a, X-ray diffraction studies show that the PPy film is crystalline in nature, with a sharp diffraction peak observed at about 2θ = 23°. The sharp peak is characteristic of crystalline PPy [38], and is due to the scattering from PPy chains at the interplanar spacing [39,40]. Figure 3c illustrates the Raman spectrum of PPy/Au/PVDF, the characteristic bands of which appear at 1587 and 1365 cm−1, which were assigned to the C-C backbone stretching and the ring stretching vibration of PPy, respectively [41].
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the Tri-layer Actuator
The mechanical performance of the bending actuators was calculated by measuring their electromechanical and electrochemical responses. The samples for this calculation were prepared by cutting rectangular shaped strips, 15 mm × 5 mm in dimension, using scissors to avoid electrical contact between the two active layers. The tip displacement was recorded at different input frequencies by using graph paper at a step voltage with an amplitude of ±1.5 V square wave. The tip displacements as a function of ±1.5 V voltages were recorded for different environment conditions. The time period of the square wave was 5 s (frequency 0.2 Hz). To achieve the best possible results, some preliminary testing needed to be done. The first strip (strip 1) was tested for voltage tolerance. It was found that a voltage of ±5 V caused the strip to burn out within a few cycles. When the potential is too high, it creates high resistance at the contact of metal and the thin film actuator, generating heat which leads towards a short circuit. In general, because of the high temperature at the contact of the actuator, the electrolyte starts to decompose and burn the actuator at the point of the Kelvin clip. For strip 2, the voltage was set at ±2.5 V and the time was set to 10 s per side, which caused some instability in deflection of the actuator. This is because when the applied potential is too positive, over-oxidation of the polymer takes place. This over-oxidation of polypyrrole polymer has inferior mechanical and electrical properties. On other hand, when the potential is too negative, hydrogen evolution and subsequent deterioration of the polymer occurs, which further reduces the mechanical displacement of the actuator [42,43]. Finally, strip 3 was set at ±1.5 V with a 5-s time period per side, which displayed better actuation as well as stability. Initially the test was set up for 1000 cycles, and it was then changes to 2000 cycles to better understand the actuation deflection over time. It is important to note that the electrolyte used is created inside the environmental chamber with the same composition; the difference is that one of them is brought outside to use in the experiment of PPy actuation in open air. Both PPy strips were cut with the dimensions of 15 mm × 5 mm, and 30 µL of electrolyte was applied at a time. They were saturated properly before the testing began, since in the preliminary tests it was seen that improperly saturated PPy strips did not show adequate actuation. In order to apply the potential, the actuator with dimensions 15 mm × 5 mm was first clamped using Kelvin clip to measure the charge transfer in the film as well as the deflection at the point of electrical contact in the glove box (inert environment) and open air conditions.
Measurements in the air and glove box were performed, and three frames were captured in each case, as depicted in Figure 4, showing the full extent of deflection with ±1.5 V applied at 0.2 Hz. The PPy strip inside the glove box showed excessive bending, whereas the strip tested outside did not bend as much. The maximum deflection was 1.26 cm (negative x-axis) + 1.24 cm (positive x-axis) = 2.5 cm, and this occurred when the strip was completely horizontal to the x-axis, as shown in Figure 4d,e,f. The excessive bending upwards (above 180°) becomes noticeable towards end of the 1000 cycle test. This enhancement in the tri-layer actuator could be due to slow oxidation of the electrolyte inside the environment chamber, which leads towards better conductivity as well as an increase in the kinetics of the switching. These developments of the tri-layer actuator inside the environmental chamber give improved displacement, better response time, and an increased overall lifetime, which is helpful in certain applications.
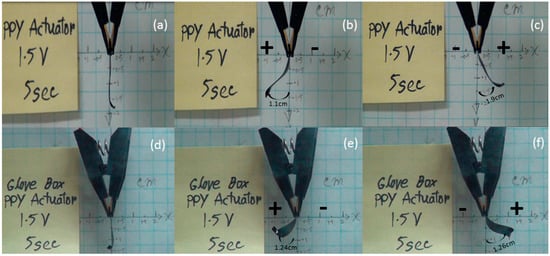
Figure 4.
Images of different frame grabs showing actuation of a PPy tri-layer actuator in open air and the glove box. (a–c) show the actuation at ±1.5 V in open air, while (d–f) show the actuation inside the glove box, i.e., inert environment.
In Figure 5, the difference in actuation behavior is observed in the two different conditions of PPy tri-layer actuator. These differences in both conditions are attributed to the mass transfer rates and strain of the actuator. It was found that tip displacements in the glove box (argon environment) were much larger than in open air. However, for the PPy actuator situated outside the glove box, the graph shows a steady decrease in deflection as time elapses, as shown in Figure 5b. When compared with the result from the PPy actuator situated inside glove box, we see that there are some minor decreases in deflection up to 44th minute, and then the deflection stays constant until the end of the 1000th cycle. The lower strains in the PPy actuator in the open air may be due to the oxidation of the electrolyte. The efficiency of the charge transfer is decreased in the electrolyte solution when it comes in contact with oxygen and the moisture present in the open air environment [44]. Figure 5a illustrates that the charge transfer outside the glove box is much lower than that inside, which reflects that the conversion efficiency of electrical energy to mechanical energy in the glove box is higher than that outside. In general, the stress generated in a bending actuator is directly proportional to the charge passed [27,45]. Comparing the data given in Figure 5a,b, the relationships between the force exerted by the actuator and the charge were found to be approximately linear, as depicted. These results show that there approximately twice as much charge transfer observed in the inert environment.
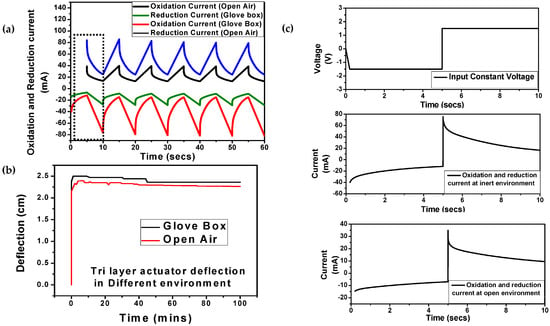
Figure 5.
(a) Oxidation and reduction currents of the PPy tri-layer actuator in the glove box and open air at ±1.5 V with the same dimensions; (b) Displacement of the polypyrrole actuator contacted by the Kelvin clip in the glove box and open air; (c) Step input voltage and output current in the inert and open environments.
The electrochemical bending of the tri-layer actuator under a frequency of 0.2 Hz and ±1.5 V square wave voltage was investigated in Figure 5c. The fast and slow response of the actuation in the actuator was attributed to the quick insertion and extraction of ions (ionic conductivity) and the diffusion of ions at the electrode-electrolyte interface [46]. As seen in Figure 5c, the flow of ions (oxidation and reduction current) is higher in an inert environment, which illustrate the better diffusion at the electrode-electrolyte interface, higher conductivity, and fast ion movement (electrodynamics). In addition, Figure 6a,b illustrate the charge transfer with respective time (two cycles) under similar input conditions. In an inert atmosphere, the magnitude of the charge is higher than in the open air, which displayed a large bending displacement. The stability of displacement or charge transfer over time shows better performance without any deterioration due to negligible oxidation of the electrolyte (Supplementary Materials Figure S5). Figure 6c illustrates the time-dependent charge vs. displacement plot, bending motion is shown with average displacement of 1.26 + 1.24 = 2.5 cm which shows constant deflection for several hours, compared to the open air where average displacement was 1.3 + 1.0 = 2.3 cm.
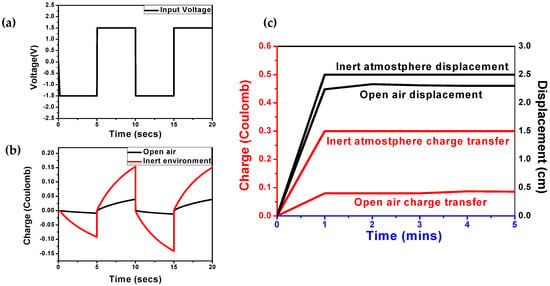
Figure 6.
(a) Input voltage of ±1.5 V square wave; (b) Charge transfer in as inert environment and open air; (c) Displacement vs. charge plot with respective time of the polypyrrole actuator contacted by Kelvin clip in the glove box and in open air.
4. Conclusions
Results of the PPy actuator confirms that mass and charge transfer in the film is higher in an inert environment than under real, open air conditions. The role of electrolyte in the PPy actuator is considered more important because it determines the conductivity and response time. The response time (switching on and off) of the actuator is also enhanced, because the electrodynamic properties of ions are not affected inside the glove box. The above results confirm that the mechanical properties of a PPy actuator widely varies in different conditions. Fully understanding the mechanical properties of a PPy actuator for different applications is important. In order for PPy actuators to be fully and confidently used in service applications, issues that must be addressed include the effect of temperature, different strain rates, cyclic loads and the effects of various liquid or gaseous media under the influence of an applied electric field.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2076-0825/6/2/17/s1, Figure S1: The galvanostatic polymerization of PPy on the gold-coated PVDF film, Figure S2: Laminated structure of a polymer and its equivalent cross-section as per equivalent width technique. The mechanical properties of the single material are equivalent to other multi-structure materials, Figure S3: FTIR characteristics of PVDF in four places, Figure S4: Lifetime test of the PPy tri-layer actuator, Figure S5: Actuator performance at different frequencies, Table S1: Displacement and current in inert/open air with respective time.
Acknowledgments
Leela Mohana Reddy Arava acknowledges the support from Wayne State University startup funds.
Author Contributions
Nirul Masurkar. and Leela Mohana Reddy Arava conceived and designed the experiments; Nirul Masurkar and Kawsar Jamil performed the experiments; Nirul Msaurkar. and Leela Mohana Reddy Arava analyzed the data; Leela Mohana Reddy Arava contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Nirul Masurkar and Leela Mohana Reddy Arava wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Spinks, G.M.; Liu, L.; Wallace, G.G.; Zhou, D. Strain response from polypyrrole actuators under load. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Cui, C.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Barisci, J.N.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Mazzoldi, A.; de Rossi, D.; Rinzler, A.G.; Jaschinski, O.; et al. Carbon nanotube actuators. Science 1999, 284, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R. Conducting polymer artificial muscles. Synth. Metals 1996, 78, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Inganäs, O. Electrochemical applications of the bending beam method. 1. Mass transport and volume changes in polypyrrole during redox. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 10507–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fadeev, A.G.; Qi, A.; Smela, E.; Mattes, B.R.; Ding, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Zhou, D.; Wallace, G.G.; et al. Use of ionic liquids for π-conjugated polymer electrochemical devices. Science 2002, 297, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, J.D.; Cush, R.A.; Kanigan, T.S.; Brenan, C.J.; Hunter, I.W. Encapsulated polypyrrole actuators. Synth. Metals 1999, 105, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhao, L.; Bai, H.; Zhao, H.; Xing, X.; Shi, G. Polypyrrole actuator with a bioadhesive surface for accumulating bacteria from physiological media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.M.; Li, C.; Chen, F.E.; Shi, G.Q. Polypyrrole microtubule actuators for seizing and transferring microparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, E.W.; Smela, E.; Inganäs, O. Microfabricating conjugated polymer actuators. Science 2000, 290, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, E.W.; Masurkar, N.; Nworah, N.F.; Gaihre, B.; Alici, G.; Spinks, G.M. Patterning and electrical interfacing of individually controllable conducting polymer microactuators. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, E.; Masurkar, N.; Nworah, N.F.; Gaihre, B.; Alici, G.; Spinks, G.M. Individually controlled conducting polymer tri-layer microactuators. In Proceedings of the 2013 Transducers & Eurosensors XXVII: The 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers & Eurosensors XXVII), Barcelona, Spain, 16–20 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alici, G.; Metz, P.; Spinks, G.M. A methodology towards geometry optimization of high performance polypyrrole (PPy) actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloju, S.; Wallace, G. Conducting polymers and the bioanalytical sciences: New tools for biomolecular communications. A review. Analyst 1996, 121, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snook, G.A.; Chen, G.Z.; Fray, D.J.; Hughes, M.; Shaffer, M. Studies of deposition of and charge storage in polypyrrole–chloride and polypyrrole–carbon nanotube composites with an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 568, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lau, K.T.; Shepherd, R.; Wu, Y.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Performance characteristics of a polypyrrole modified polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membrane based microfluidic pump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 148, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Crapez, E.; Livache, T.; Marchand, J.; Grenier, J. K-ras mutation detection by hybridization to a polypyrrole DNA chip. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alici, G.; Devaud, V.; Renaud, P.; Spinks, G. Conducting polymer microactuators operating in air. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Tong, L. Polymer single-nanowire optical sensors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2757–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naficy, S.; Stoboi, N.; Whitten, P.G.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G. Evaluation of encapsulating coatings on the performance of polypyrrole actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cot, A.; Chikhaoui, M.T.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Rougeot, P.; Andreff, N. Synthesis, encapsulation, and performance analysis of large deformation tri-layer polypyrrole actuator. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Banff, AB, Canada, 12–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, T.F.; Cortes, M.T. A sensing muscle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 96, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhou, D.; Spinks, G.; Wallace, G.; Forsyth, S.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D. Use of ionic liquids as electrolytes in electromechanical actuator systems based on inherently conducting polymers. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, L.; Jacobsen, T.; Skaarup, S.; West, K. Mechanism of actuation in conducting polymers: Osmotic expansion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 8492–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.; Masurkar, N.; Al Salem, H.; Arava, L.M.R. Transition metal dichalcogenide atomic layers for lithium polysulfides electrocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansinena, J.; Olazabal, V.; Otero, T.F.; Da Fonseca, C.P.; De Paoli, M.A. A solid state artificial muscle based on polypyrrole and a solid polymeric electrolyte working in air. Chem. Commun. 1997, 22, 2217–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Alici, G.; Madden, J.D.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G. Soft mechanical sensors through reverse actuation in polypyrrole. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3216–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaihre, B.; Alici, G.; Spinks, G.M.; Cairney, J.M. Synthesis and performance evaluation of thin film PPy-PVDF multilayer electroactive polymer actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, L.; West, K.; Sommer-Larsen, P.; Skaarup, S.; Benslimane, M. A conducting polymer artificial muscle with 12% linear strain. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jones, J.J.; Burford, R.P.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Conductivity and anisotropy of electrochemically prepared conducting polypyrrole films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 136, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, J.D.; Cush, R.A.; Kanigan, T.S.; Hunter, I.W. Fast contracting polypyrrole actuators. Synth. Metals 2000, 113, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.E.; Kornbluh, R.D.; Joseph, J.P. Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 64, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Kornbluh, R.; Sommer-Larsen, P.; Alici, G. Electroactive polymer actuators as artificial muscles: Are they ready for bioinspired applications? Bioinspiration Biomim. 2011, 6, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alici, G.; Huynh, N.N. Predicting force output of trilayer polymer actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 132, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetko, B.F.; Brungs, M.P.; Burford, R.P.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Structure, strength and electrical performance of conducting polypyrroles. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.G.; Teasdale, P.R.; Spinks, G.M.; Kane-Maguire, L.A. Conductive Electroactive Polymers: Intelligent Polymer Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, C.O.; Sung, H.K.; Kim, J.H.; Barsoukov, E.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H. The effect of low-temperature conditions on the electrochemical polymerization of polypyrrole films with high density, high electrical conductivity and high stability. Synth. Metals 1999, 99, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.; Kim, J.; Yun, S.-R. Studies on conducting polymer electroactive paper actuators: Effect of humidity and electrode thickness. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partch, R.; Gangolli, S.G.; Matijević, E.; Cal, W.; Arajs, S. Conducting polymer composites: I. Surface-induced polymerization of pyrrole on iron (III) and cerium (IV) oxide particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 144, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madakbaş, S.; Çakmakçı, E.; Kahraman, M.; Esmer, K. Preparation, characterisation, and dielectric properties of polypyrrole-clay composites. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. In situ ZnO nanowire growth to promote the PVDF piezo phase and the ZnO–PVDF hybrid self-rectified nanogenerator as a touch sensor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5475–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivel, P.; Kanagaraj, S.; Balamurugan, A.; Ponpandian, N.; Mangalaraj, D.; Viswanathan, C. Rheological behavior and electrical properties of polypyrrole/thermally reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 441, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Barsch, U.; Michaelis, R. Corrosion of conducting polymers in aqueous media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1993, 351, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenoff, J.B.; Xu, H. Evolution of physical and electrochemical properties of polypyrrole during extended oxidation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 2397–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, T.J.; Gonzalez, E.R. Effect of membrane characteristics and humidification conditions on the impedance response of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 503, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, T.; Martinez, J.; Arias-Pardilla, J. Biomimetic electrochemistry from conducting polymers. A review: Artificial muscles, smart membranes, smart drug delivery and computer/neuron interfaces. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Whoehling, V.; Plesse, C.; Nguyen, G.T.M.; Vidal, F.; Chen, W. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet electrode-based high-performance ionic actuator. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).