A Two-Degree of Freedom Variable Stiffness Actuator Based on the MACCEPA Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Human-Inspired Actuation
1.2. MACCEPA
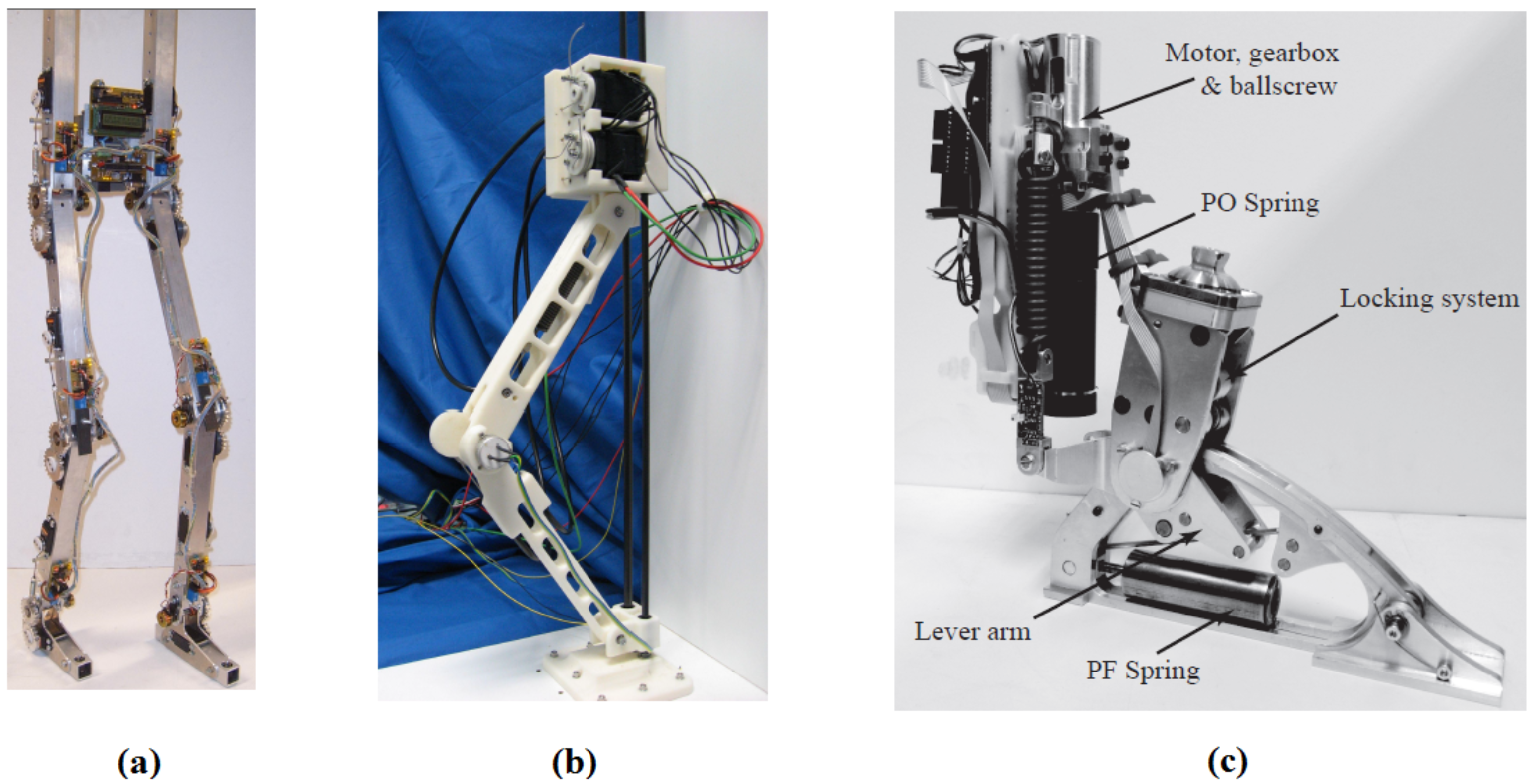
1.3. Outline
2. Design
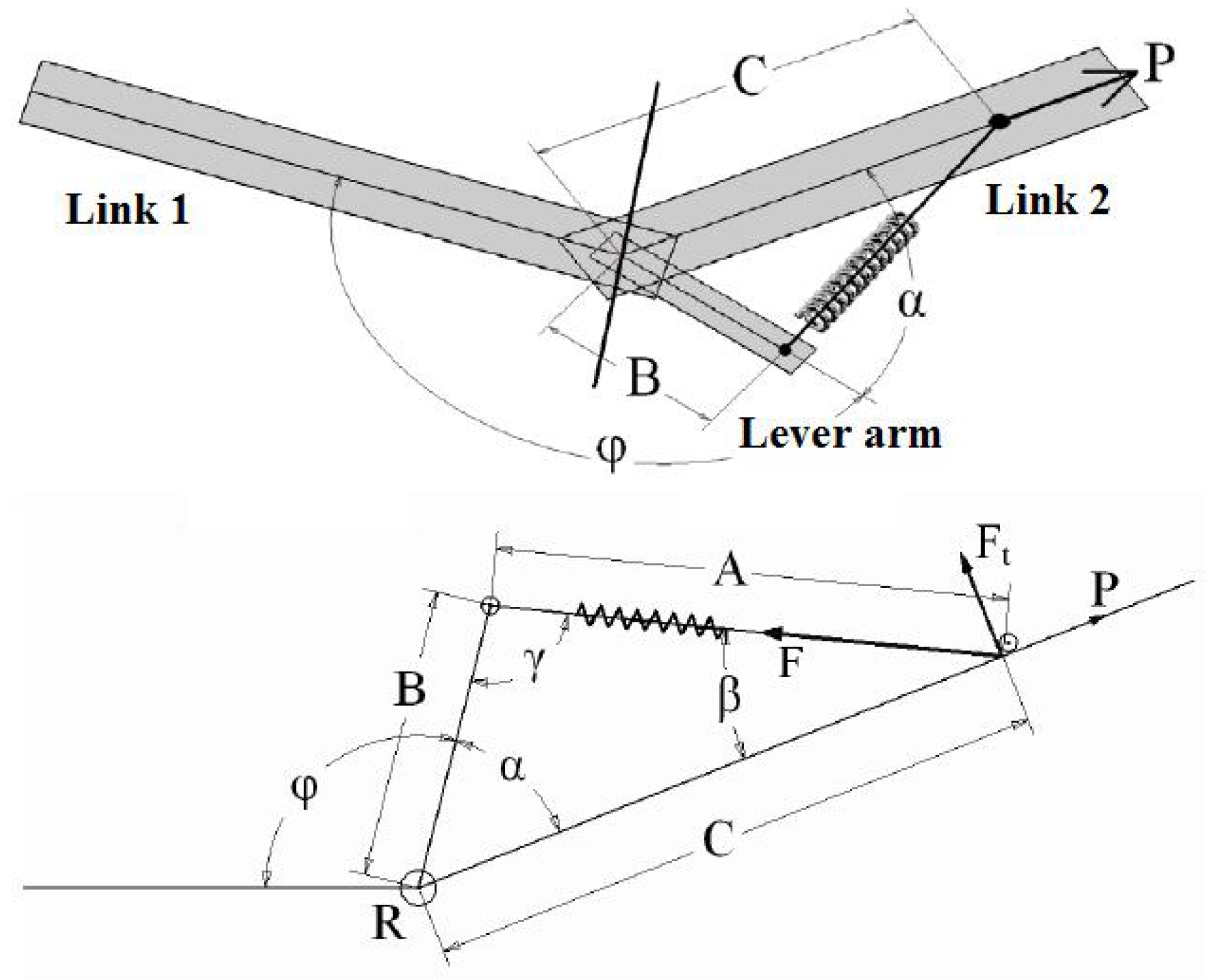
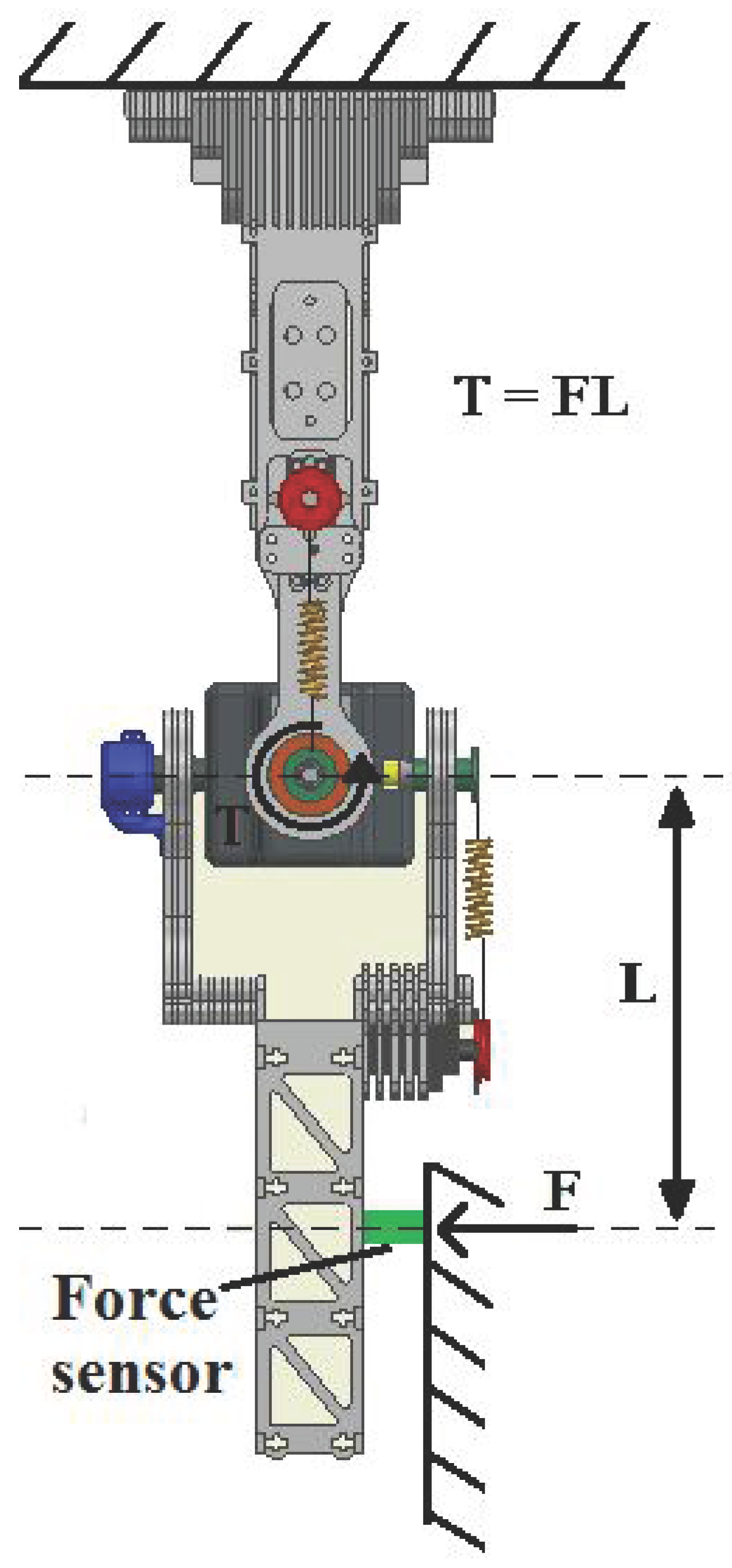
2.1. Concept
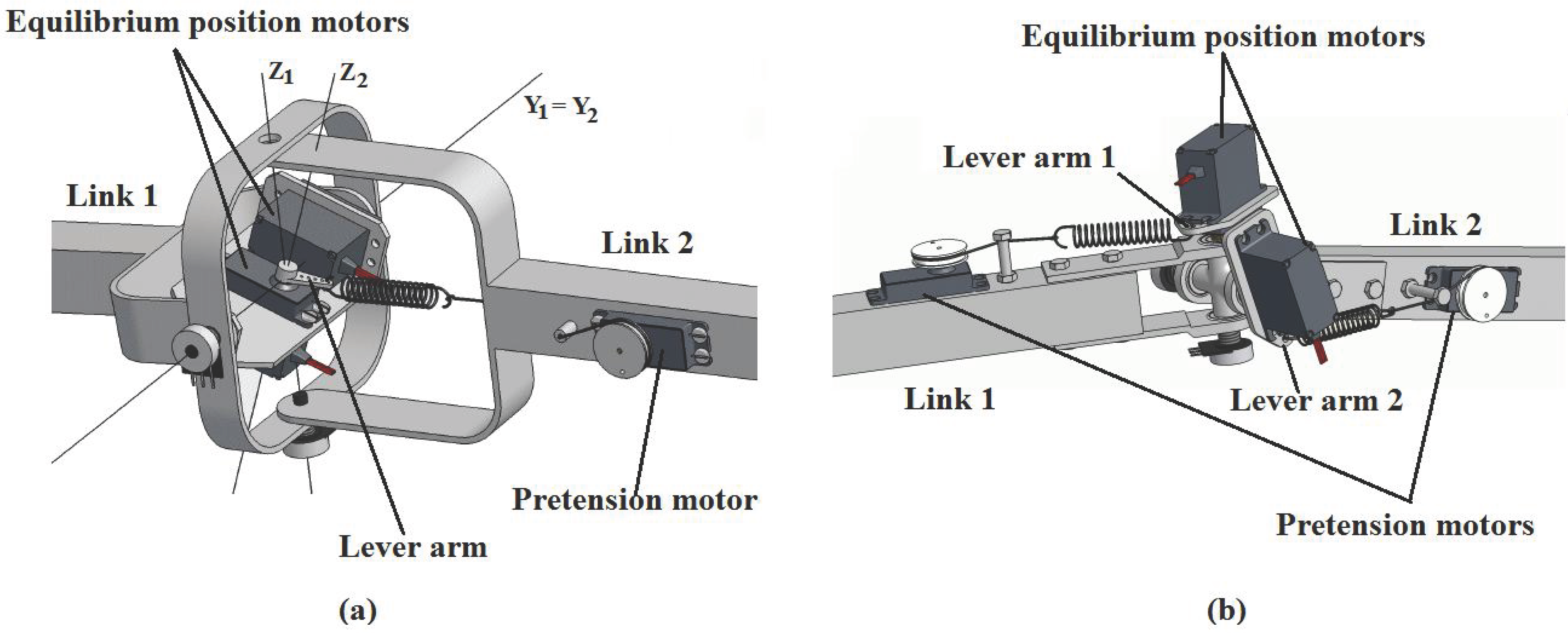
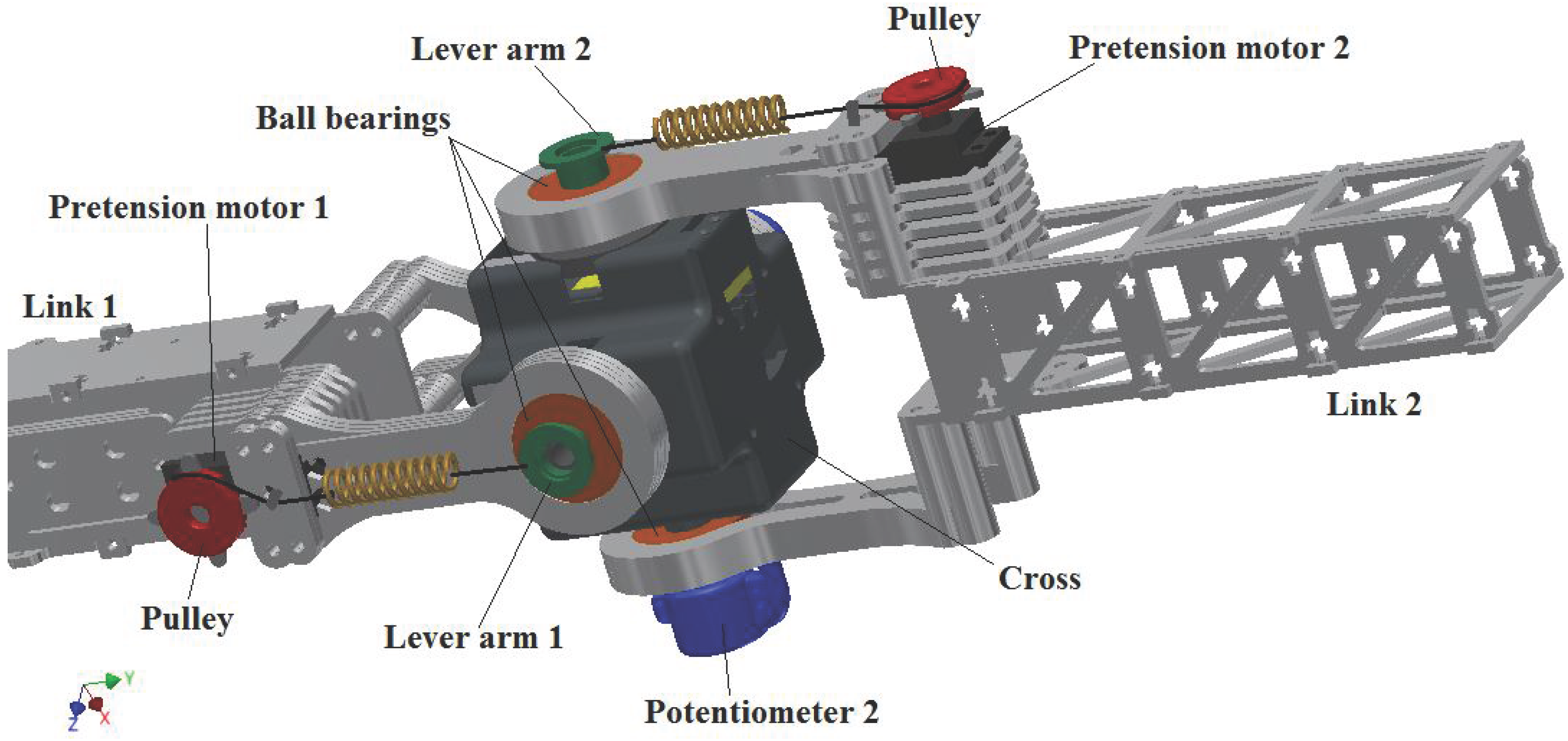
2.2. Mechanical Design
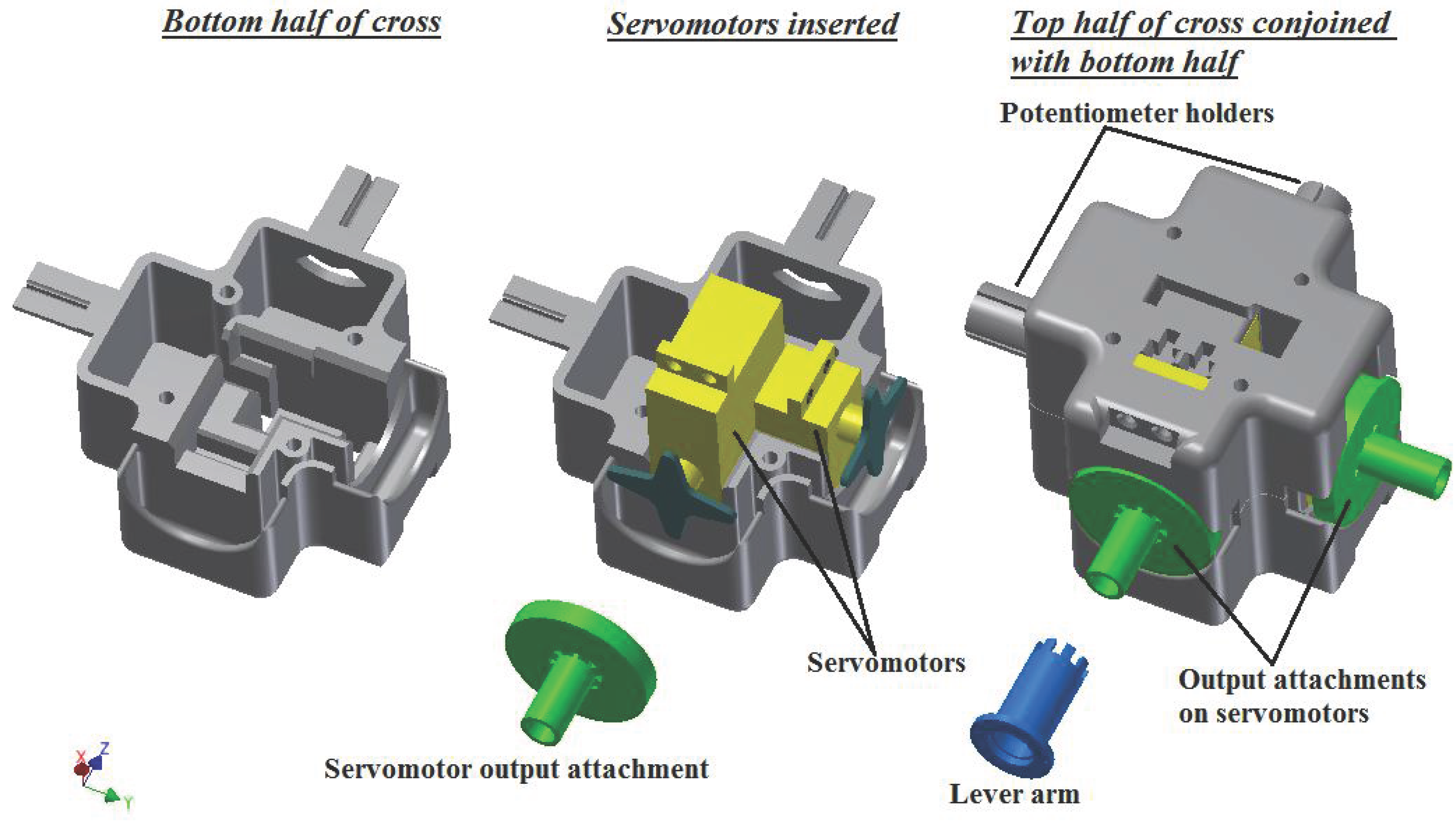
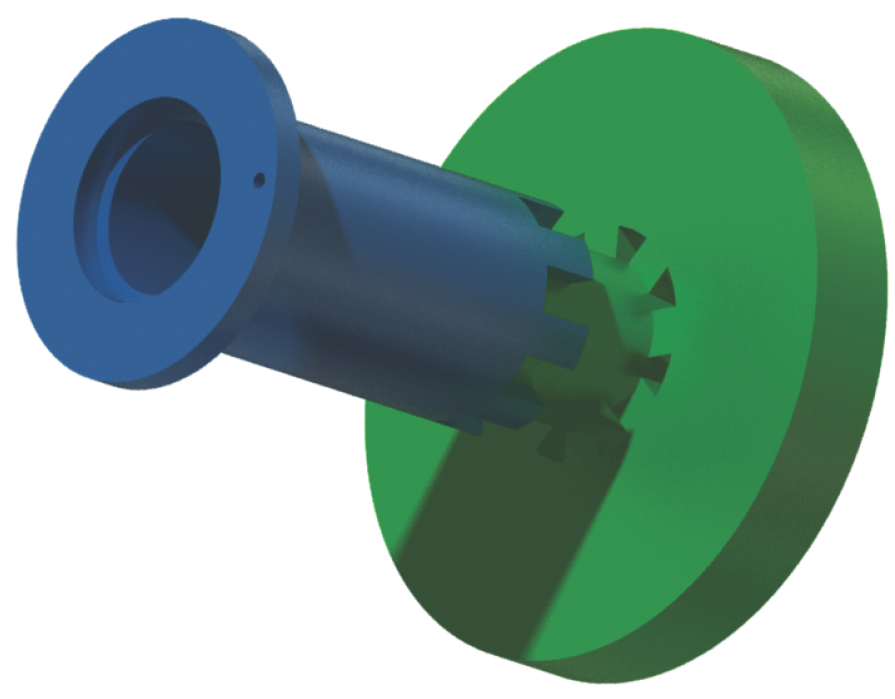
2.3. MACCEPA Characteristics
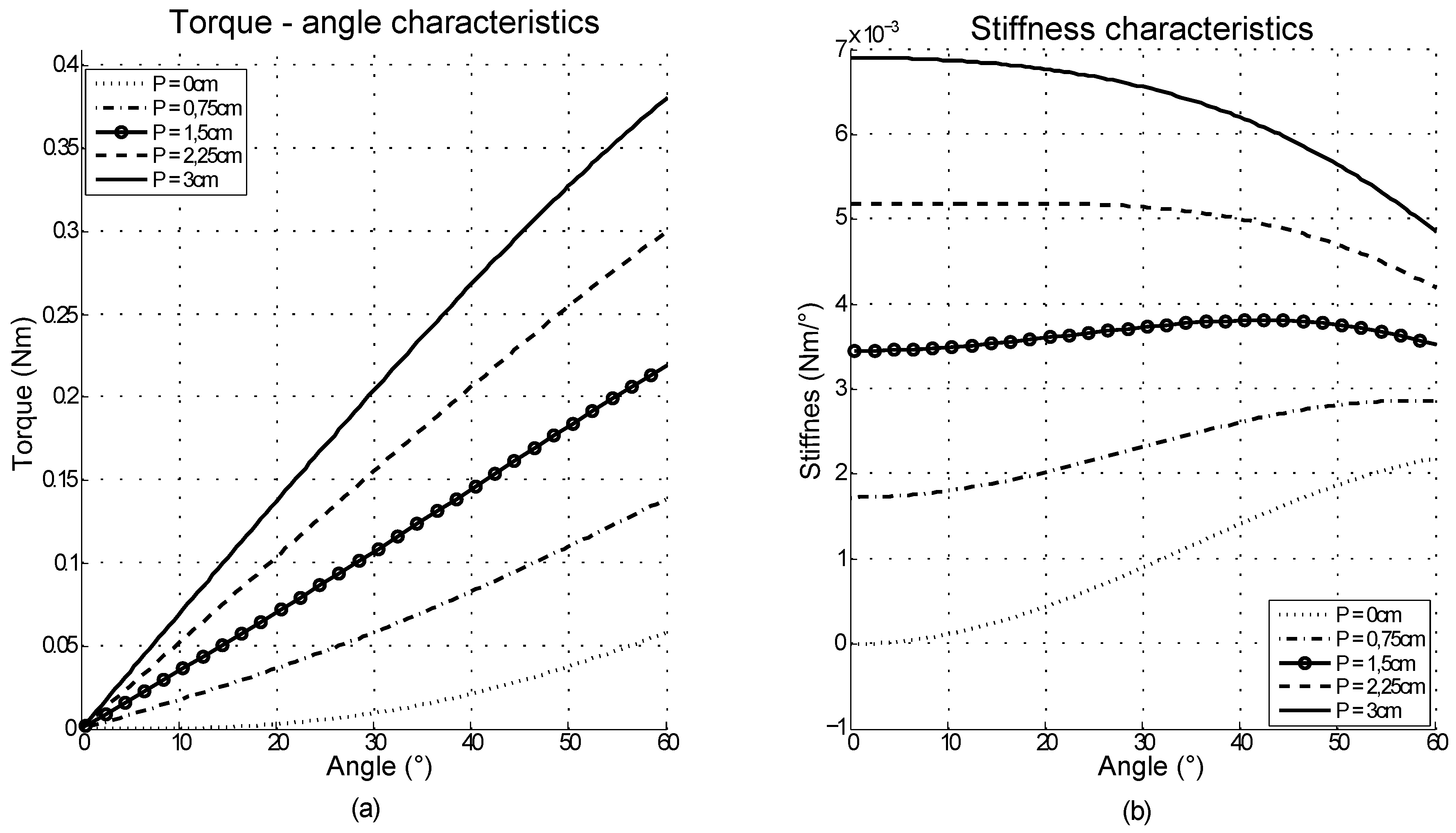
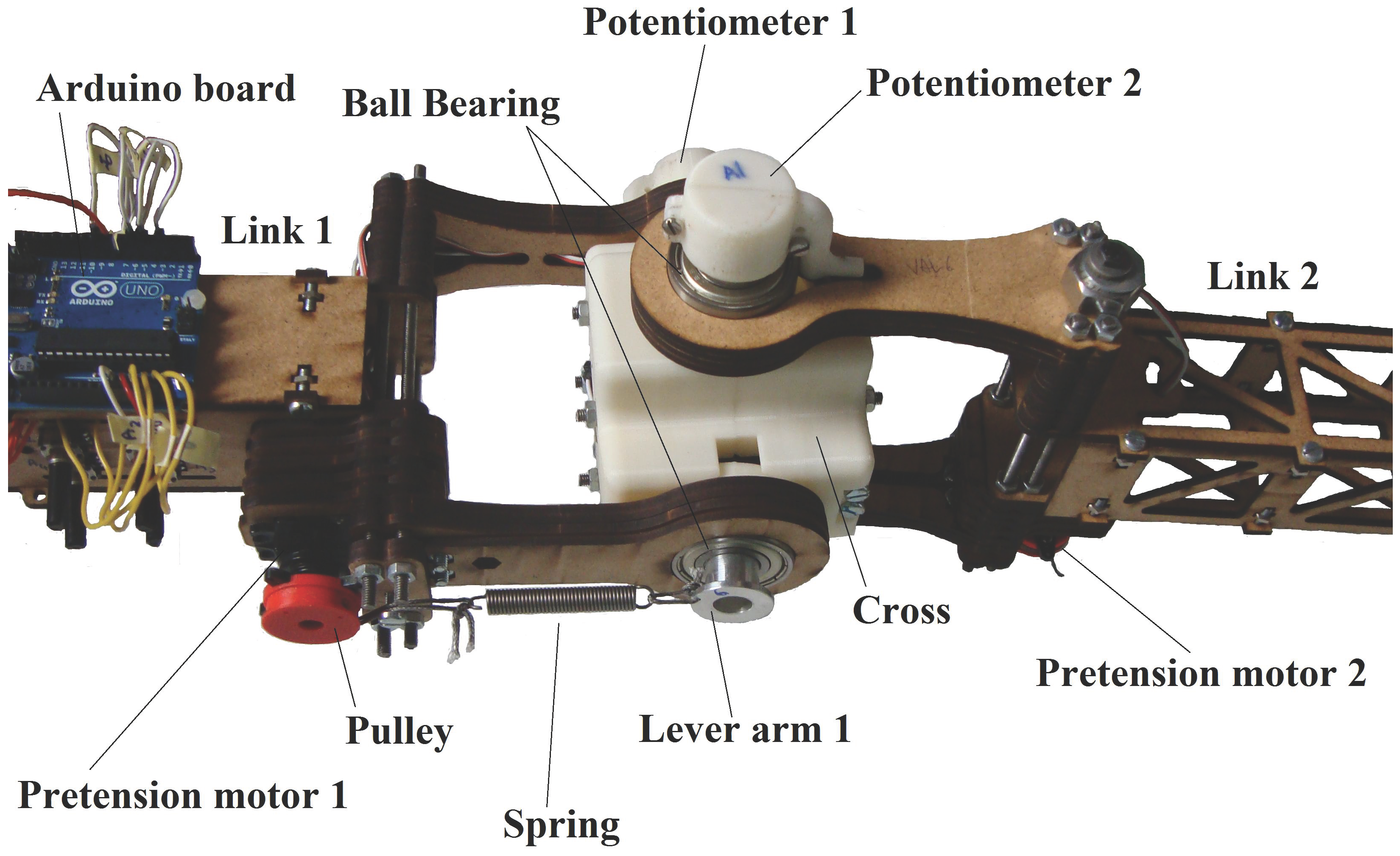
2.4. Electronics
3. Experiments
3.1. Experimental Torque-Angle Characteristics
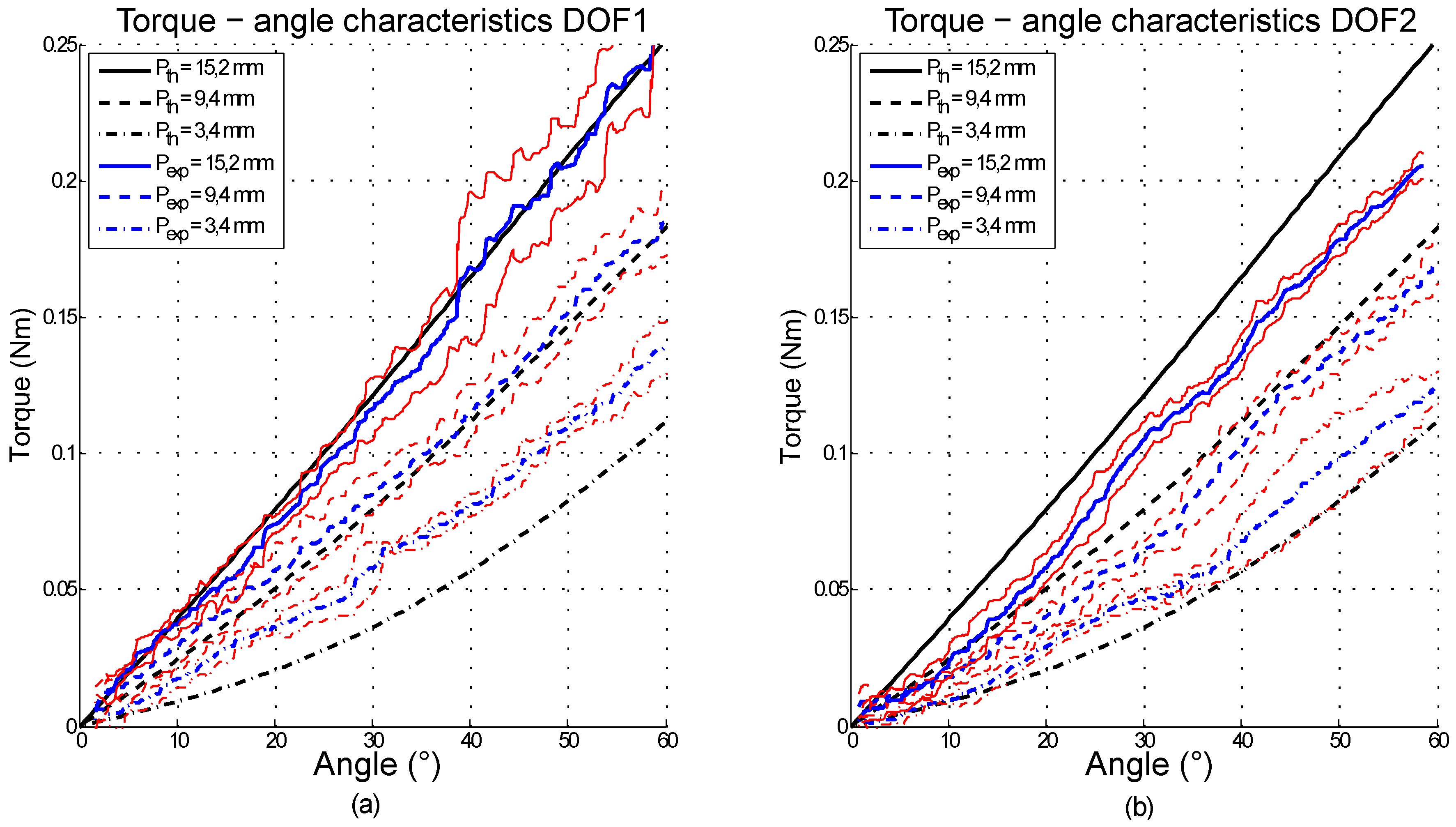
3.2. Independent Equilibrium Position and Stiffness
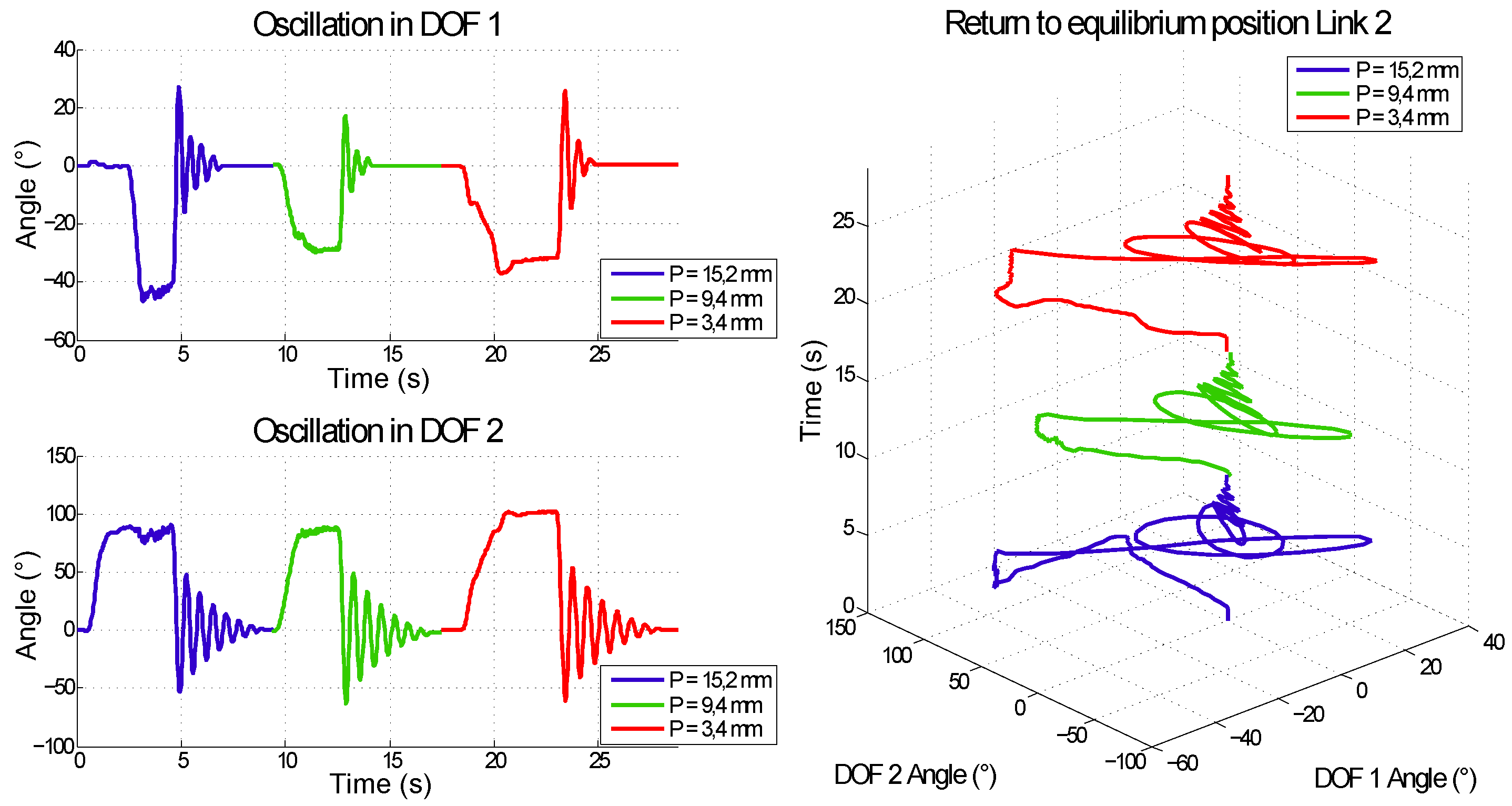
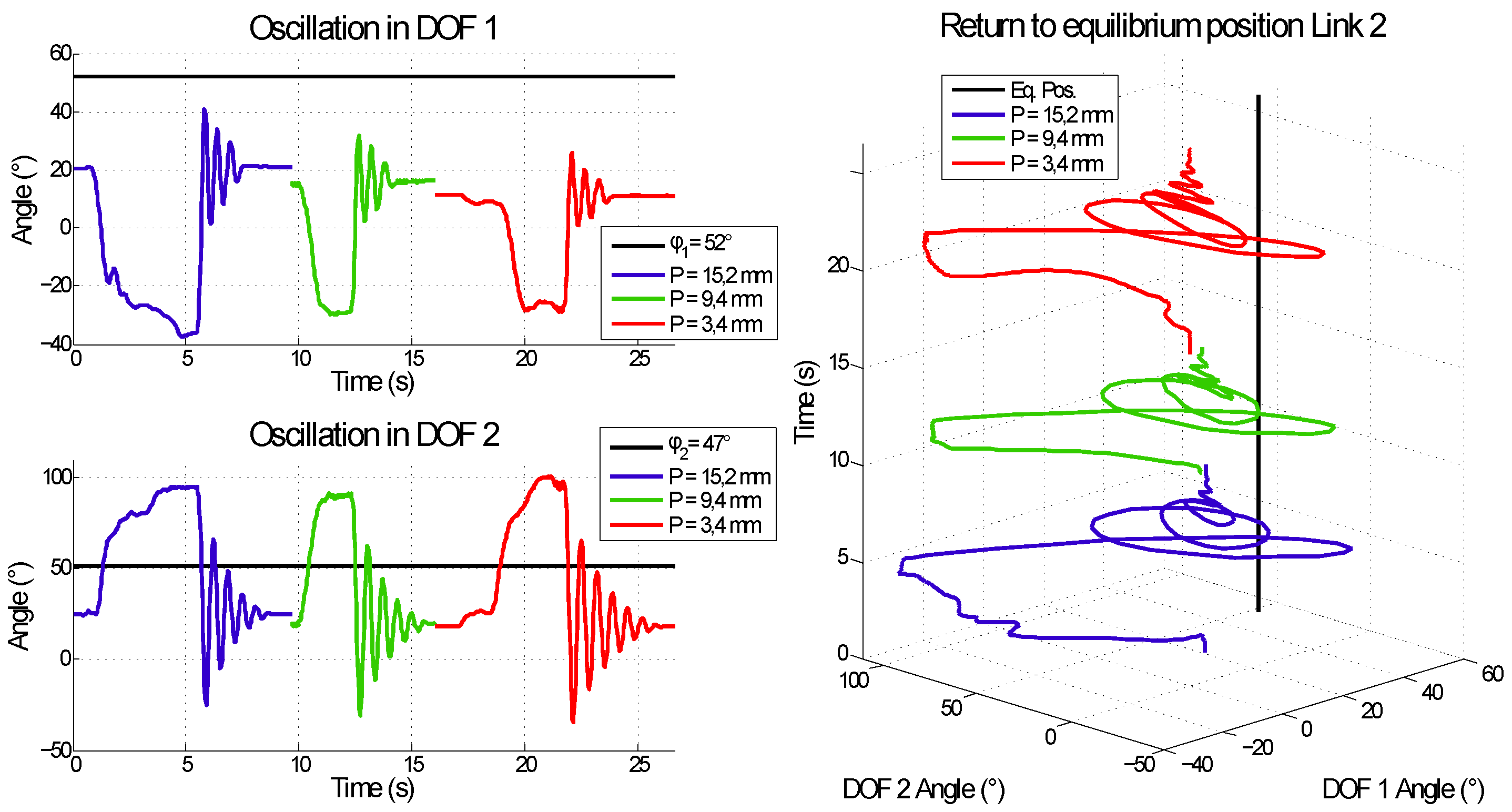
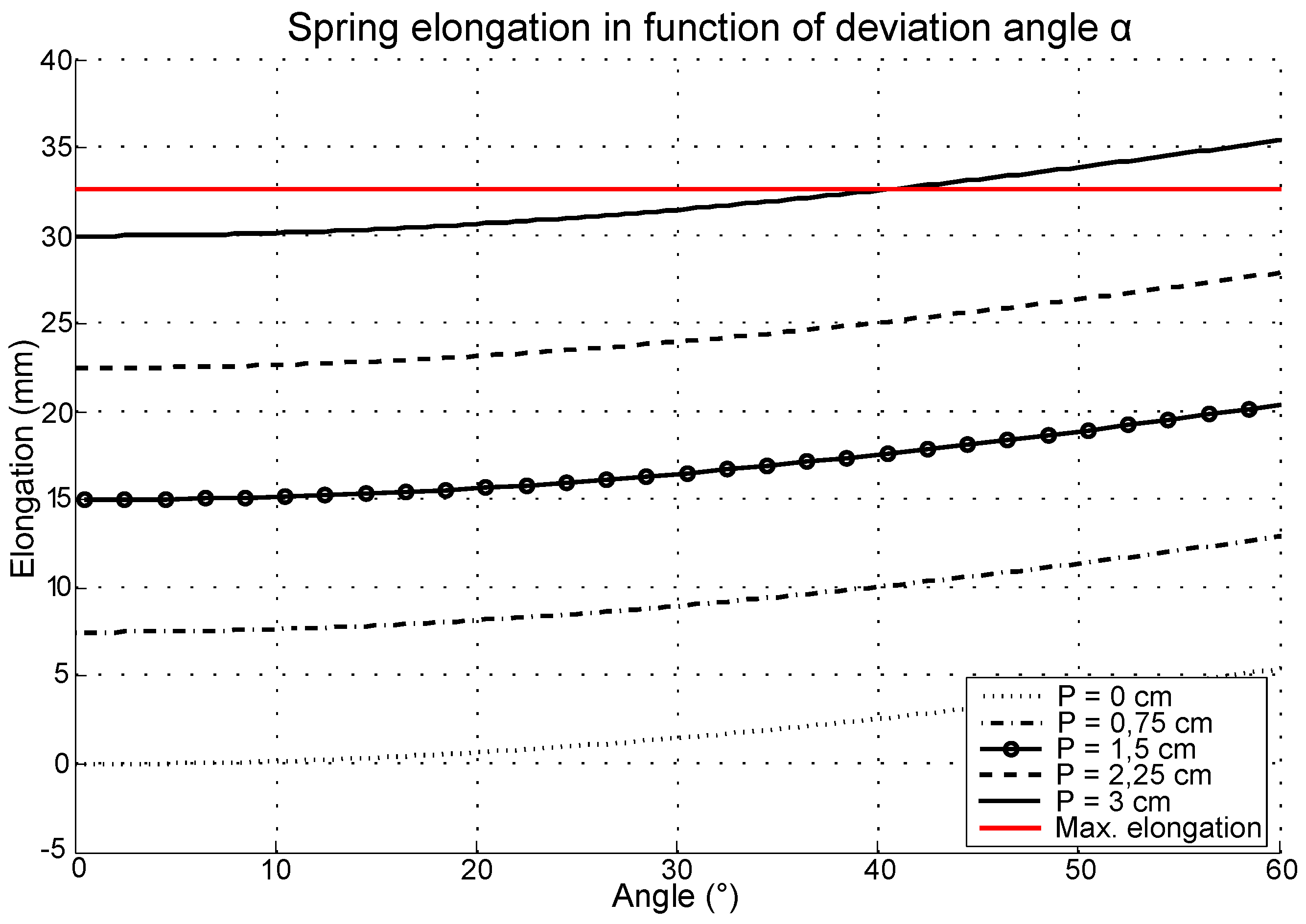
3.3. The Stiffness Ellipse Experimentally Composed
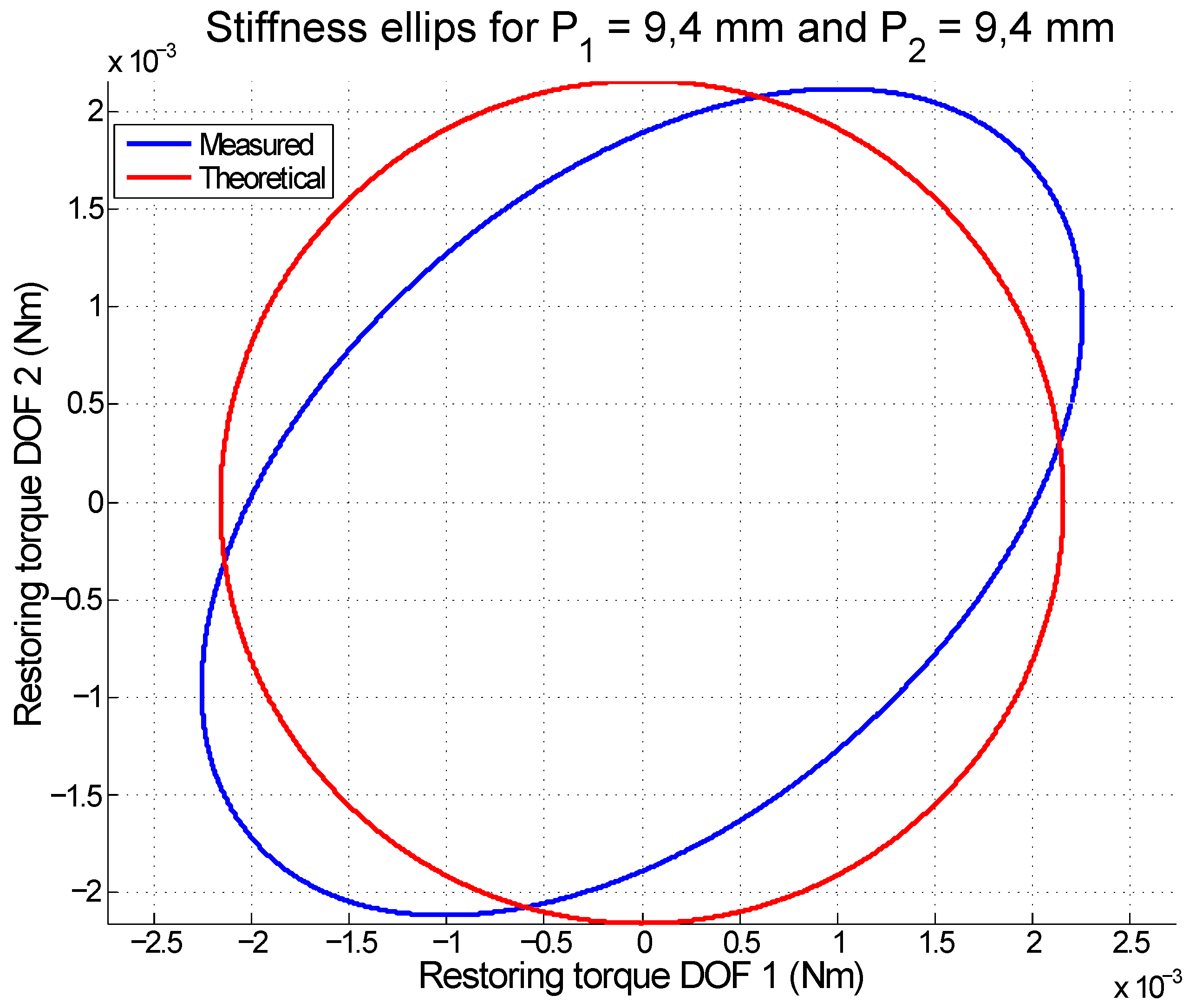
| (Nm/) | (Nm/) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0022 | 0.0005 | 0.0022 | 0 |
| 0.0005 | 0.0021 | 0 | 0.0022 |
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seyoung, K.; Sukyung, P. Leg stiffness increases with speed to modulate gait frequency and propulsion energy. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, C.; Gonzalez, O. Leg stiffness and stride frequency in human running. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.; Louie, M.; Farley, C. Running in the real world: Adjusting leg stiffness for different surfaces. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, London, United Kingdom, 1998; Volume 265, pp. 989–994.
- Vanderborght, B.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Bicchi, A.; Caldwell, D.; Tsagarakis, N.; van Damme, M.; Lefeber, D.; van Ham, R.; Jafari, A.; Burdet, E.; et al. Variable impedance actuators: A review. Rob. Autonom. Syst. 2013, 61, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; van Ham, R.; Verrelst, B.; van Damme, M.; Lefeber, D. Overview of the lucy project: Dynamic stabilization of a biped powered by pneumatic artificial muscles. Adv. Rob. 2008, 22, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Takuma, T.; Nakamoto, A. Design and control of 2D biped that can walk and run with pneumatic artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2006 6th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, 2006; pp. 284–289.
- Niiyama, R.; Nagakubo, A.; Kuniyoshi, Y. Mowgli: A bipedal jumping and landing robot with an artificial musculoskeletal system. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; 2007; pp. 2546–2551. [Google Scholar]
- Hettich, G.; Fennell, L.; Mergner, T. Double inverted pendulum model of reactive human stance control. Multibody Dyn. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ham, R.; Sugar, T.; Vanderborght, B.; Hollander, K.; Lefeber, D. Compliant actuator designs. IEEE Rob. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M.M. Series elastic actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Human Robot Interaction and Cooperative Robots, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 399–406.
- English, C.; Russell, D. Mechanics and stiffness limitations of a variable stiffness actuator for use in prosthetic limbs. Mech. Mach. Theory 1999, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, B.S.; Song, J.B. Compliant actuation of parallel-type variable stiffness actuator based on antagonistic actuation. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganezawa, K.; Nakazawa, T.; Inaba, T. Antagonistic control of multi-DOF joint by using the actuator with non-linear elasticity. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 15-19 May 2006; pp. 2201–2207.
- Migliore, S.; Brown, E.; deWeerth, S. Biologically inspired joint stiffness control. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 18-22 April 2005; pp. 4508–4513.
- Tonietti, G.; Schiavi, R.; Bicchi, A. Design and control of a variable stiffness actuator for safe and fast physical human/robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); 2005; pp. 526–531. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, J.; Chestnutt, J.E.; Rizzi, A.A. The Actuator With Mechanically Adjustable Series Compliance. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2010, 26, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Kuan, J.Y.; Huang, H.P. Design of a new variable stiffness actuator and application for assistive exercise control. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 25-30 September 2011; pp. 372–377.
- Martínez, J.L.; Blanco, J.; Vallejo, D.G.; Torres, J.; Fernández, A.G. AVASTT: A New Variable Stiffness Actuator with Torque Threshold. ROBOT2013: First Iberian Robotics Conference. Springer 2014, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, A.; Tsagarakis, N.; Sardellitti, I.; Caldwell, D. A new actuator with adjustable stiffness based on a variable ratio lever mechanism. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Hirzinger, G. A new variable stiffness design: Matching requirements of the next robot generation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 19-23 May 2008; pp. 1741–1746.
- Van Ham, R.; vanderborght, B.; van Damme, M.; Verrelst, B.; Lefeber, D. MACCEPA, the mechanically adjustable compliance and controllable equilibrium position actuator: Design and implementation in a biped robot. Rob. Autonom. Syst. 2007, 55, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.; Winter, D. Kinetic analysis of the lower limbs during walking: what information can be gained from a three-dimensional model? J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, C.; Winter, D. Control of whole body balance in the frontal plane during human walking. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodworth, A.; Peterka, R. Influence of stance width on frontal plane postural dynamics and coordination in human balance control. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 2, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manz, H.; lord, S.; Fitzpatrick, R. Acceleration pattern of the head and pelvis when walking on level and irregular surfaces. Gait Post. 2003, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.; Grioli, G.; Garabini, M.; Bonomo, F.; Mancinit, M.; Tsagarakis, N.; Bicchi, A. VSA-CubeBot: A modular variable stiffness platform for multiple degrees of freedom robots. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 9-13 May 2011; pp. 5090–5095.
- Hobbelen, D.; de Boer, T.; Wisse, M. System overview of bipedal robots flame and tulip: Tailor-made for limit cycle walking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 22-26 September 2008; pp. 2486–2491.
- Gallego, J.; Forner-Cordero, A.; Moreno, J.; Montellano, A.; Turewska, E.; Pons, J. Continuous assesment of gait stability in limit cycle walkers. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd IEEE/RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechanics (BioRob), 26-29 September 2010; pp. 734–739.
- Van Ham, R.; van Damme, M.; Verrelst, B.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. MACCEPA, the mechanically adjustable compliance and controllable equilibrium position actuator: A 3 DOF joint with two independent compliances. Int. Appl. Mech. 2007, 43, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Furusho, J. Development of high-performance actuators using ER fluids. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfarth, A.; Geyer, H.; Blickhan, S.; Lipfert, S.; Rummel, J.; Minekawa, Y.; Iida, F. Running and Walking With Compliant Legs. In Fast Motions in Biomechanics and Robotics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 383–401. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderborght, B.; Tsagarakis, N.; van Ham, R.; Thorson, I.; Caldwell, D. MACCEPA 2.0: Compliant actuator used for energy efficient hopping robot chobino 1D. Autonom. Rob. 2011, 31, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Vanderborght, B.; van Ham, R.; Wang, Q.; van Damme, M.; Guangming, X.; Lefeber, D. Step length and velocity control of dynamic bipedal walking robot with adaptable compliant joints. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, P.; Li, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z. A reinforcement learning based dynamic walking control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 10-14 April 2007; pp. 3609–3614.
- Cherelle, P.; Grosu, V.; Matthys, A.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. Design and validation of the ankle mimicing prosthetic (AMP-) foot 2.0. IEEE Trans. Neur. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 22, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mussa-Ivaldi, F.; Hogan, N.; Bizzi, E. Neural, mechanical, and geometric factors subserving arm posture in humans. J. Neurosci. 1985, 5, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Weckx, M.; Mathijssen, G.; Si Mhand Benali, I.; Furnemont, R.; Van Ham, R.; Lefeber, D.; Vanderborght, B. A Two-Degree of Freedom Variable Stiffness Actuator Based on the MACCEPA Concept. Actuators 2014, 3, 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020020
Weckx M, Mathijssen G, Si Mhand Benali I, Furnemont R, Van Ham R, Lefeber D, Vanderborght B. A Two-Degree of Freedom Variable Stiffness Actuator Based on the MACCEPA Concept. Actuators. 2014; 3(2):20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeckx, Maarten, Glenn Mathijssen, Idris Si Mhand Benali, Raphaël Furnemont, Ronald Van Ham, Dirk Lefeber, and Bram Vanderborght. 2014. "A Two-Degree of Freedom Variable Stiffness Actuator Based on the MACCEPA Concept" Actuators 3, no. 2: 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020020
APA StyleWeckx, M., Mathijssen, G., Si Mhand Benali, I., Furnemont, R., Van Ham, R., Lefeber, D., & Vanderborght, B. (2014). A Two-Degree of Freedom Variable Stiffness Actuator Based on the MACCEPA Concept. Actuators, 3(2), 20-40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020020