Control of a Heavy-Lift Robotic Manipulator with Pneumatic Artificial Muscles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PAM-Actuated Robotic Manipulator
2.1. Design and Experimental Setup
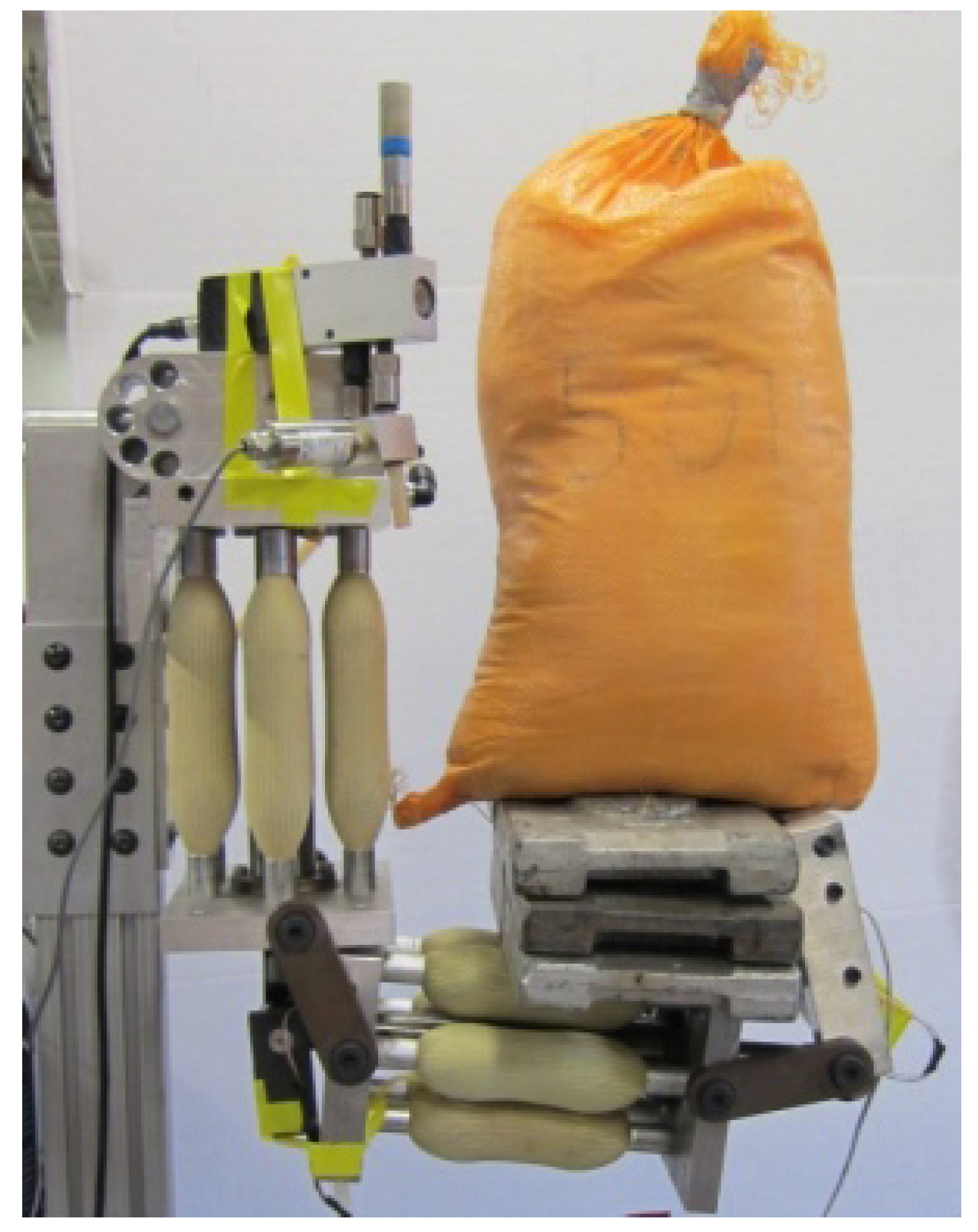
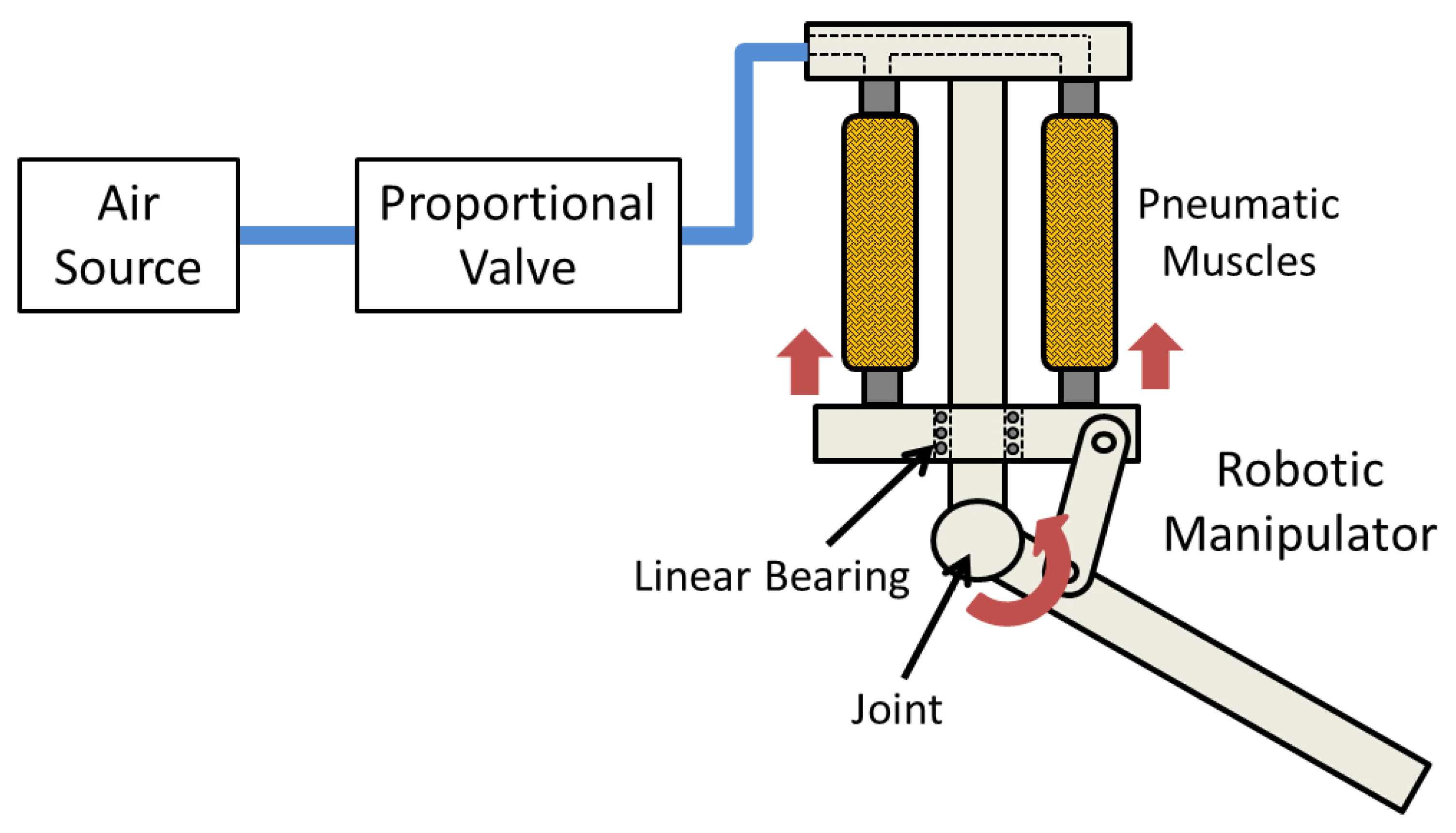

2.2. System Model
3. Control Strategies
3.1. Output Feedback Control
3.1.1. Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control
3.1.2. Fuzzy Control
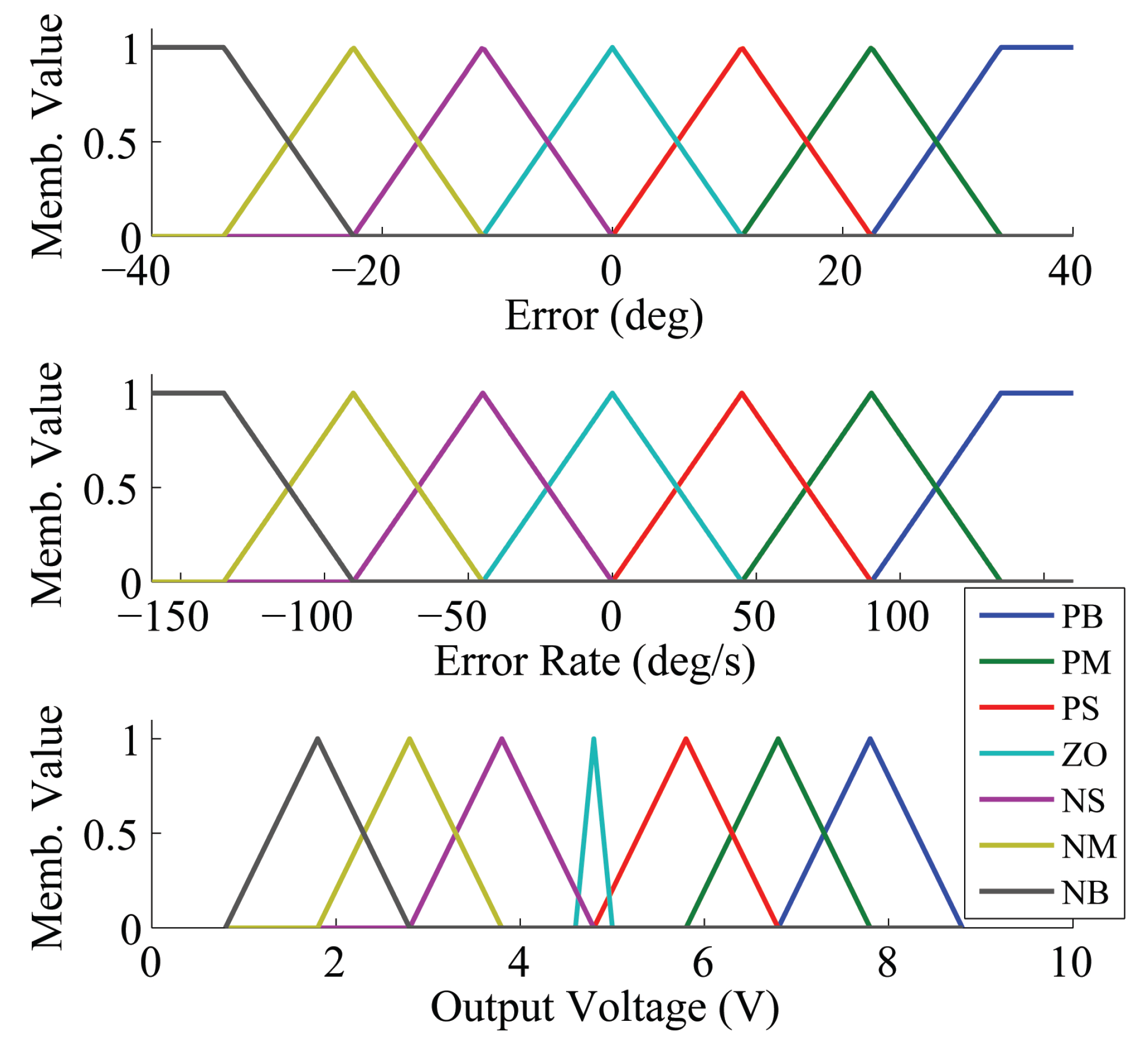
| Error | ||||||||
| Error Rate | NB | NM | NS | ZO | PS | PM | PB | |
| NB | PB | PB | PM | PS | ZO | ZO | NS | |
| NM | PB | PM | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | |
| NS | PB | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NB | |
| ZO | PB | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NB | |
| PS | PB | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NB | |
| PM | PM | PS | ZO | NS | NM | NM | NB | |
| PB | PS | ZO | ZO | NS | NM | NB | NB | |
3.2. Model-Based Feedforward Control
3.2.1. Model-Based Control without Feedback
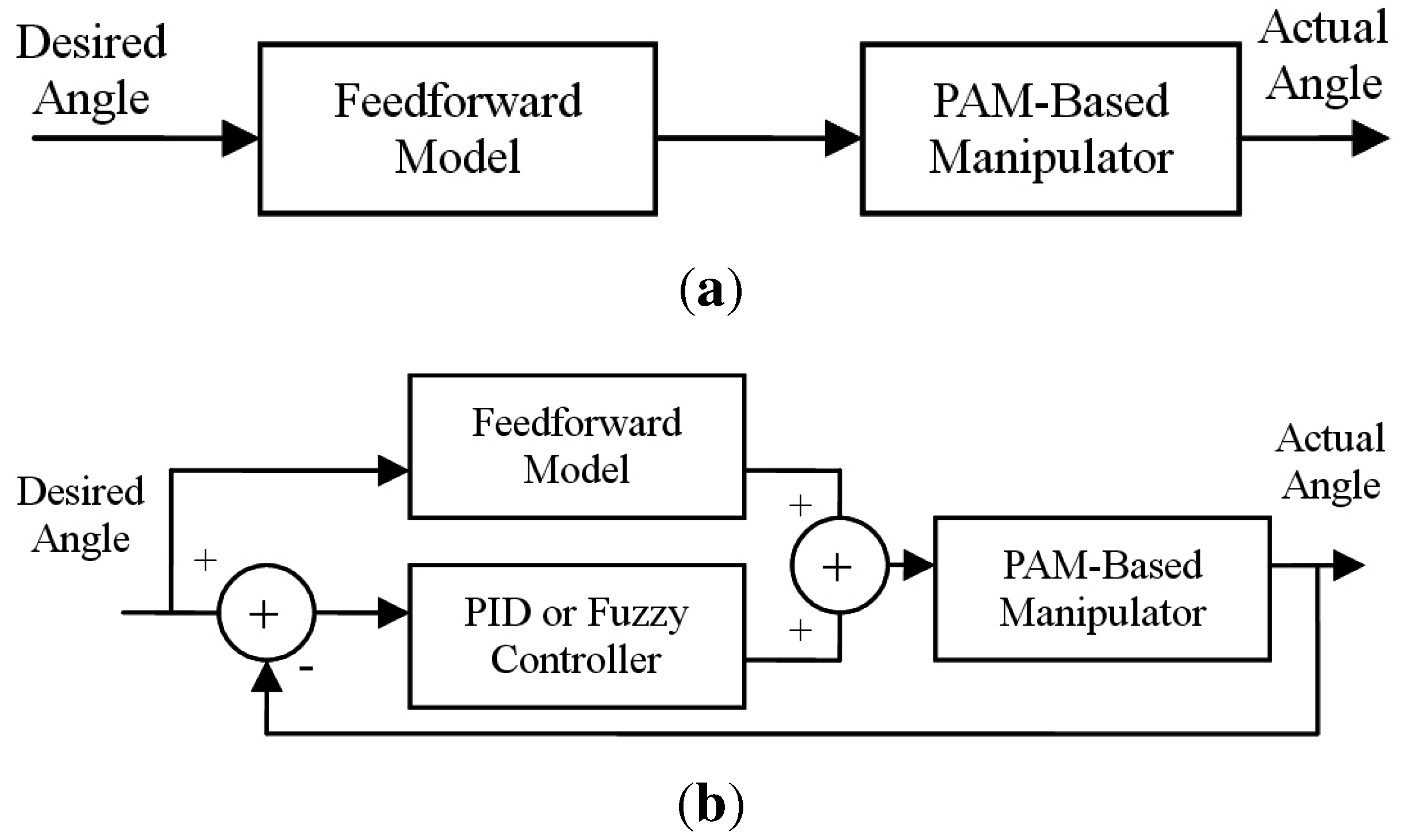
3.2.2. Model-Based Control Augmented with Output Feedback
4. Control Analysis via Simulation
4.1. PID and Fuzzy Control
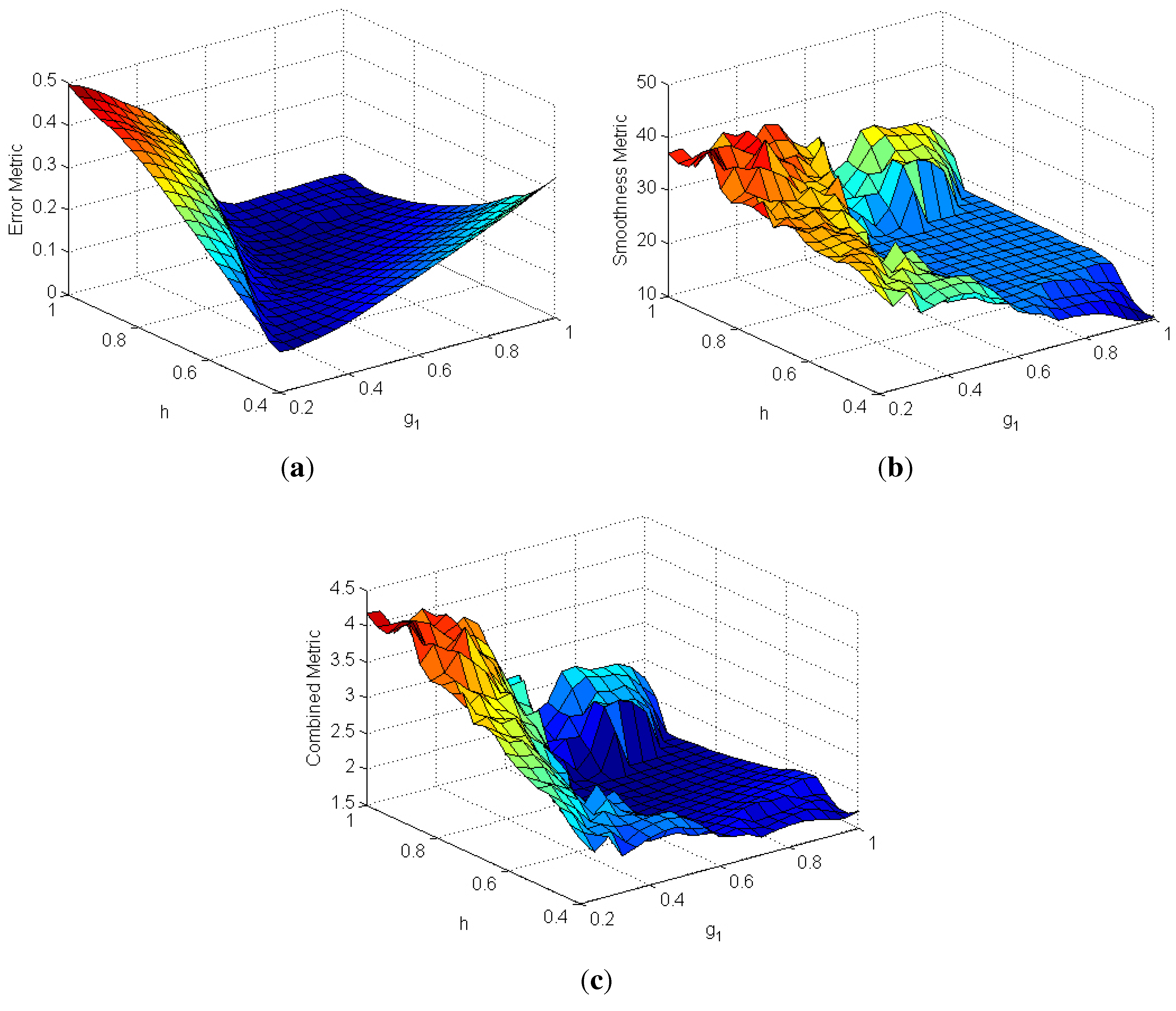
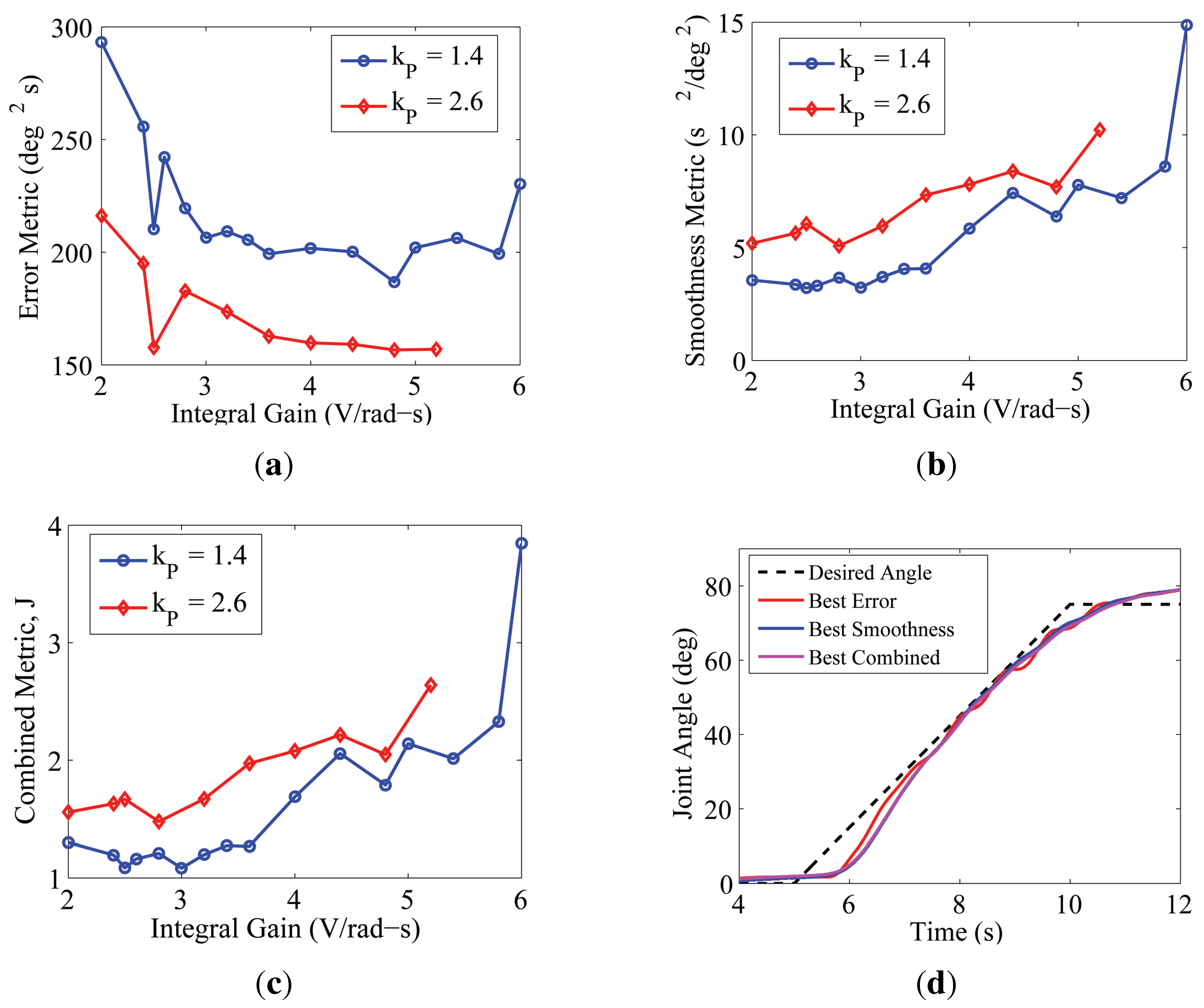
4.1.1. Gain Tuning Metrics
4.1.2. Simulated Trajectory Following
4.2. Model-Based Control with Output Feedback
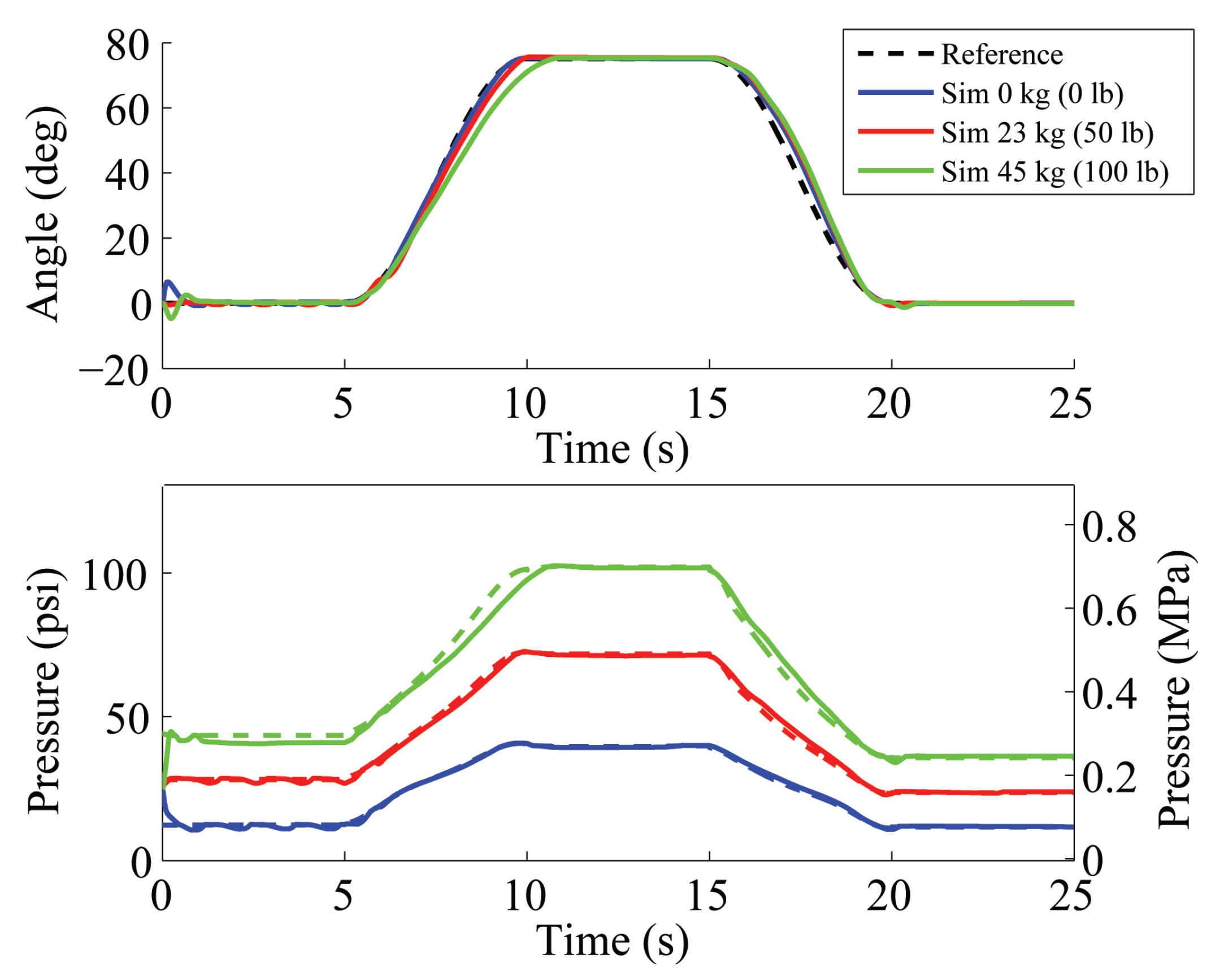
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. PID and Fuzzy Control
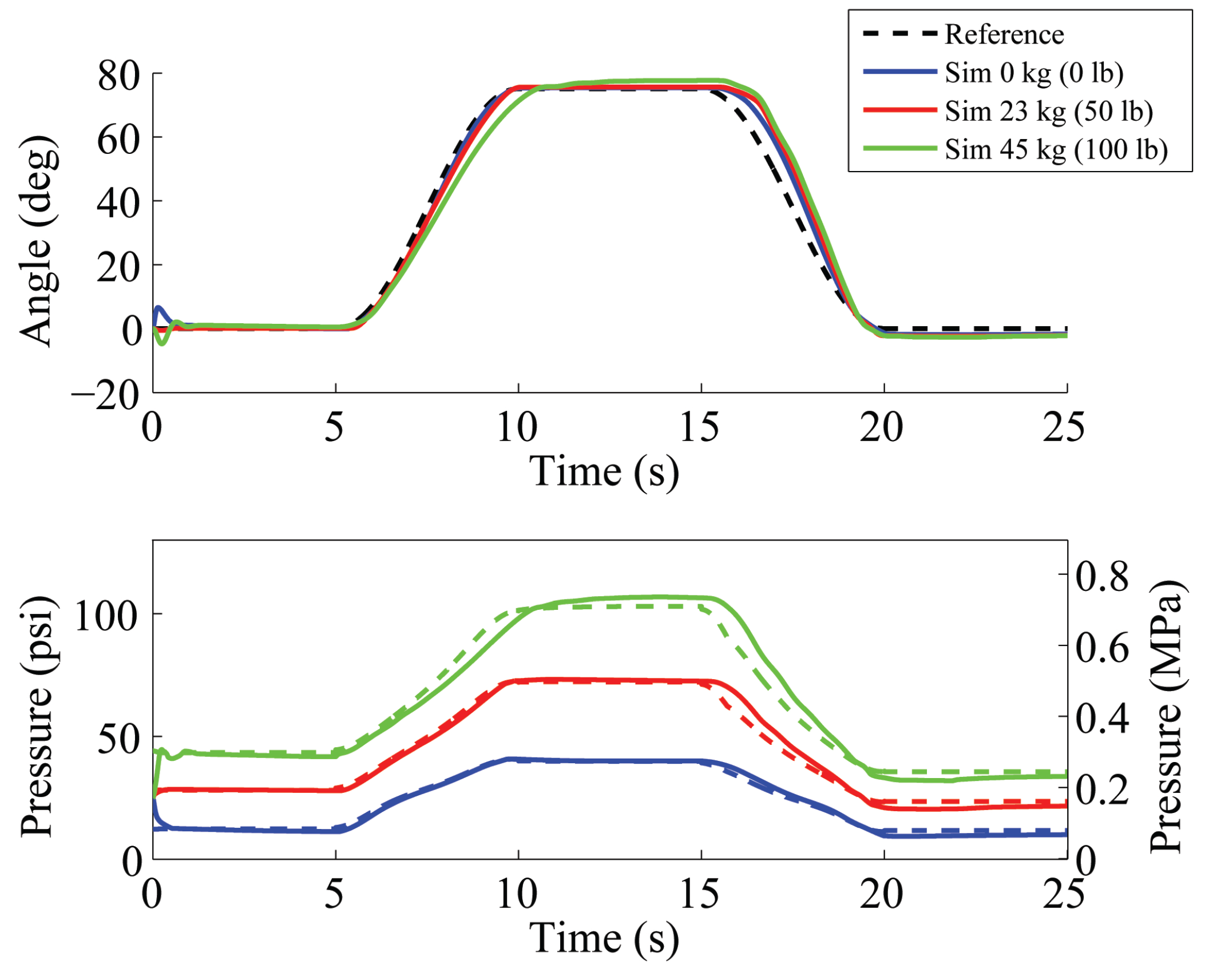
5.1.1. Experimental Validation
5.1.2. Experimental Gain Tuning
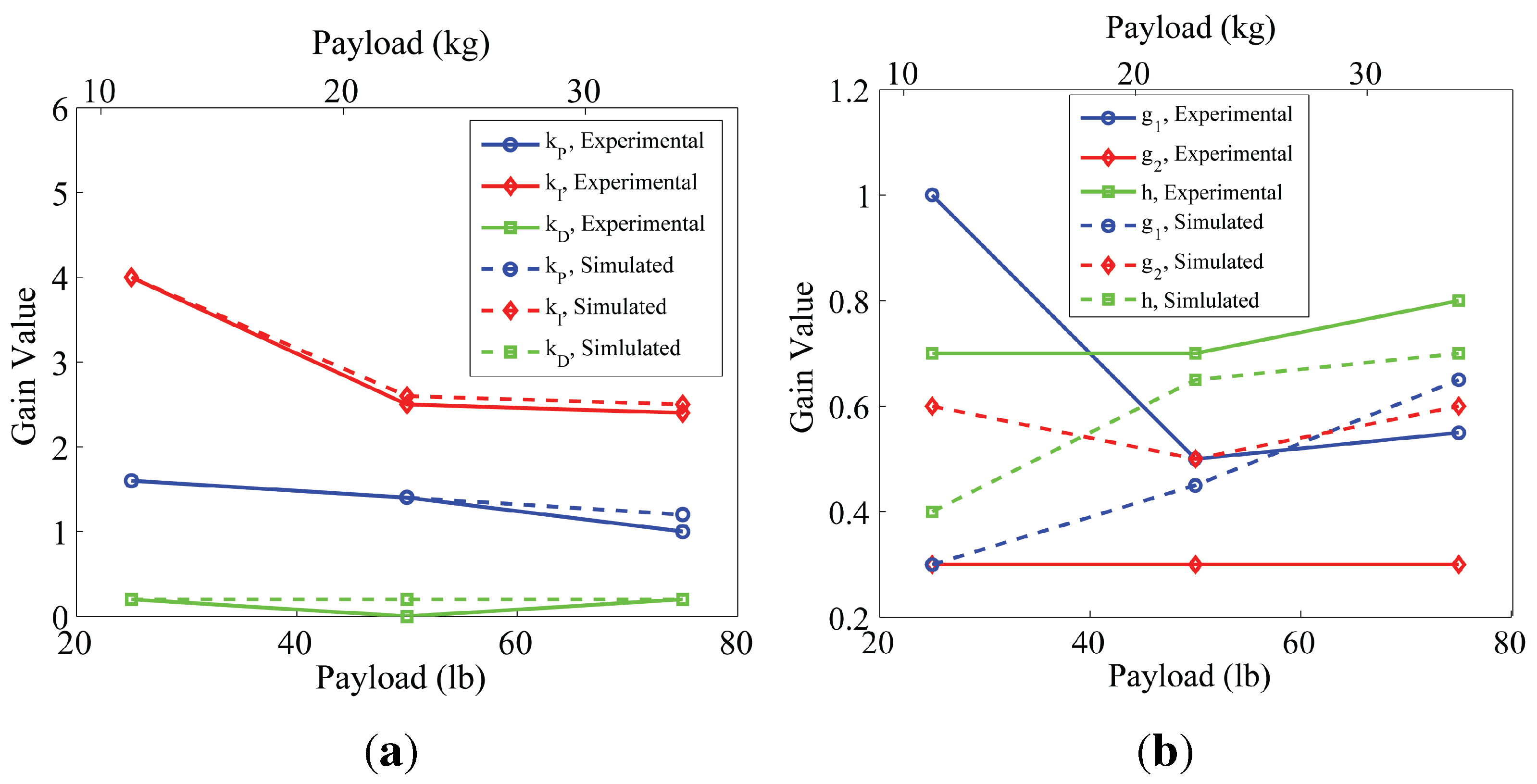
5.1.3. Comparison of Output Feedback Controllers
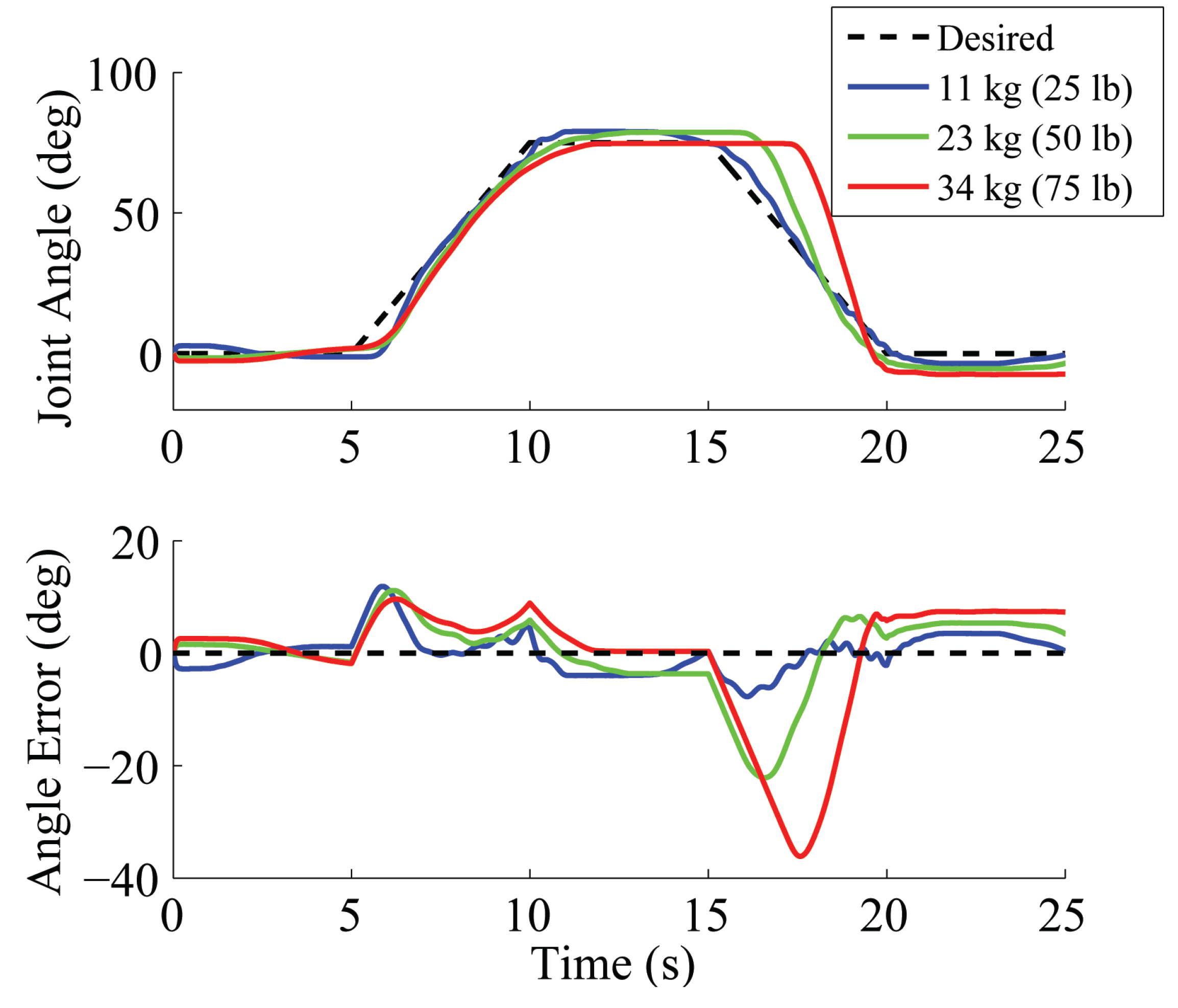
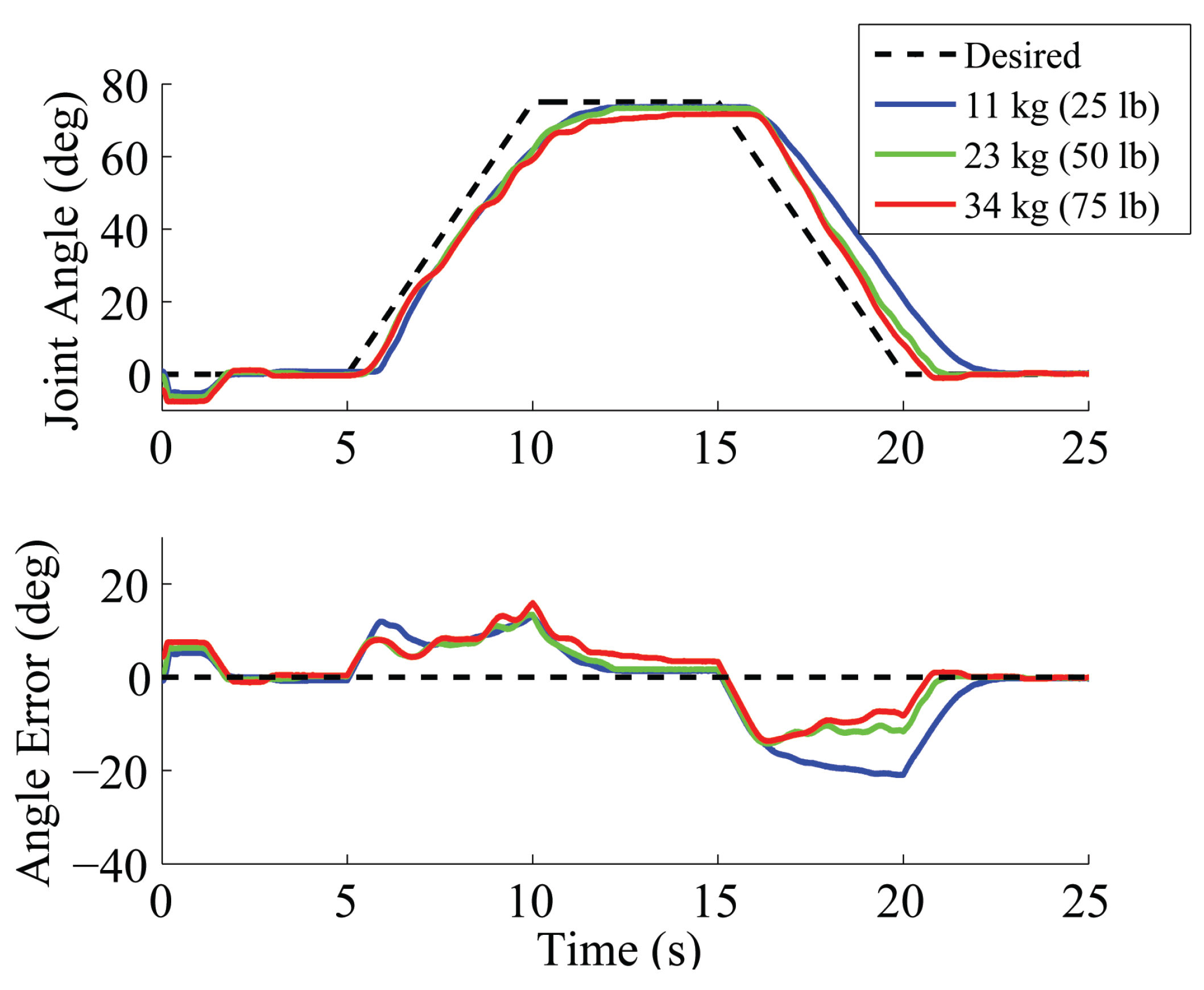
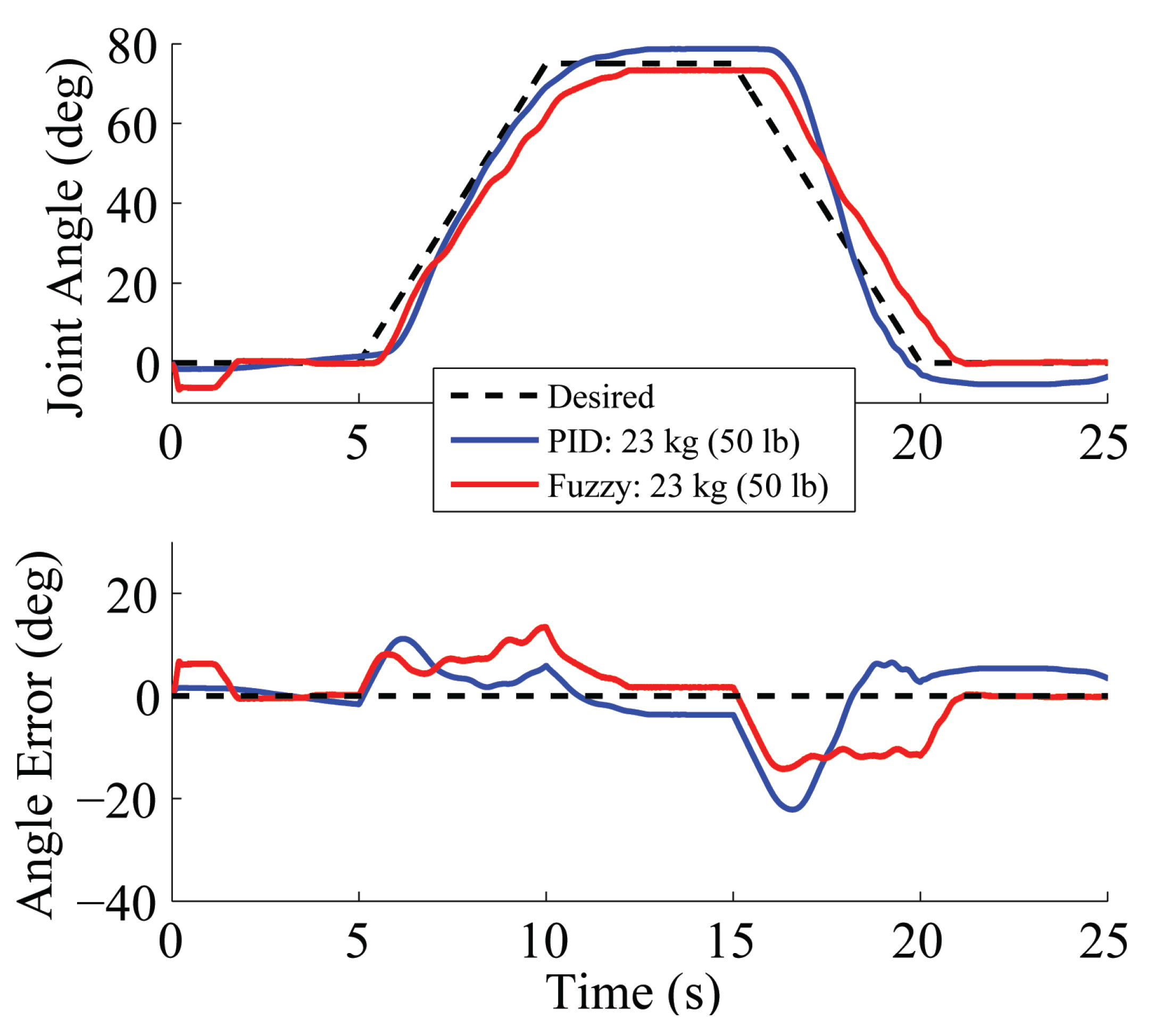
5.2. Model-Based Control with Output Feedback
5.2.1. Model Validation
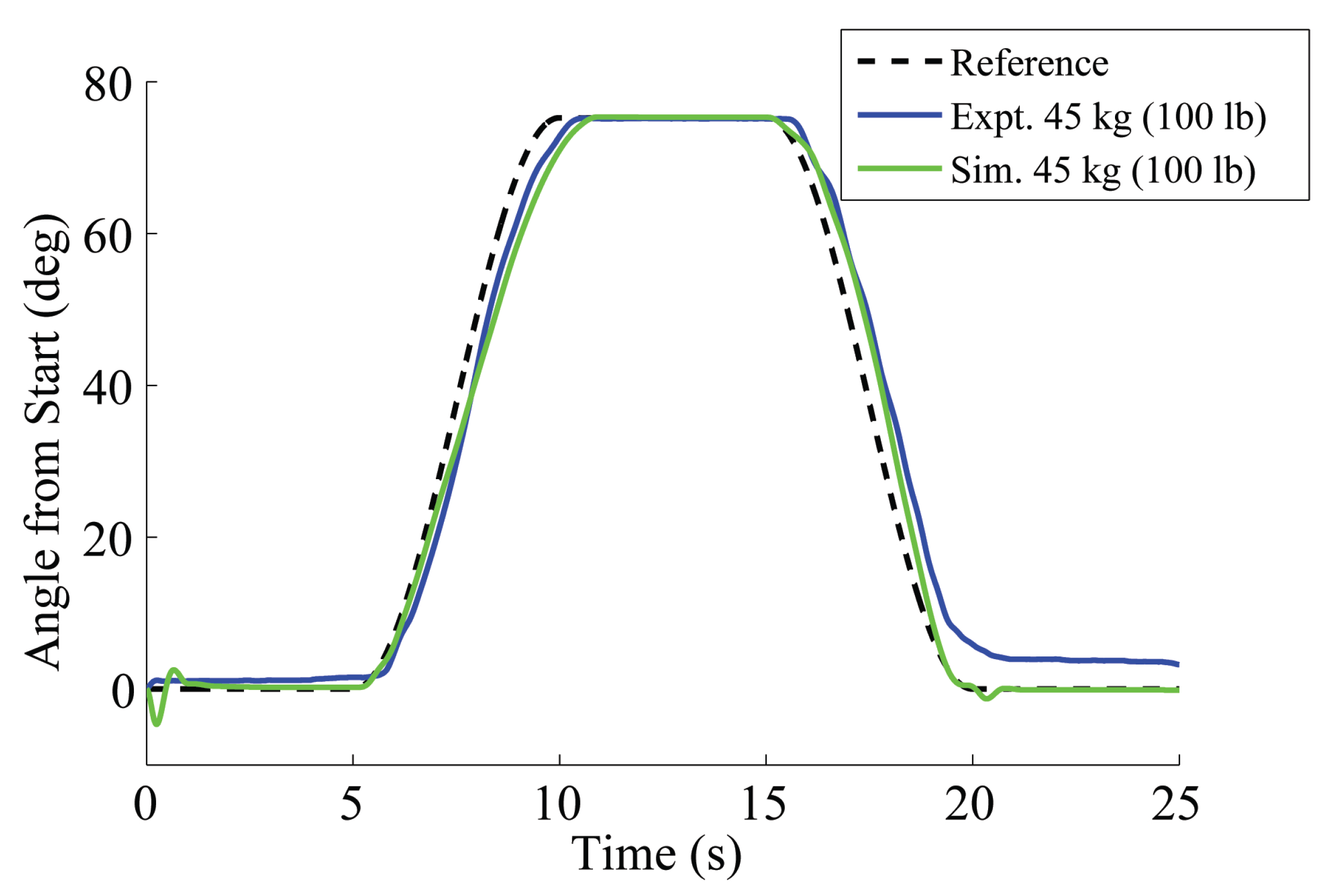
5.2.2. Experimental Analysis of Feedforward Gain
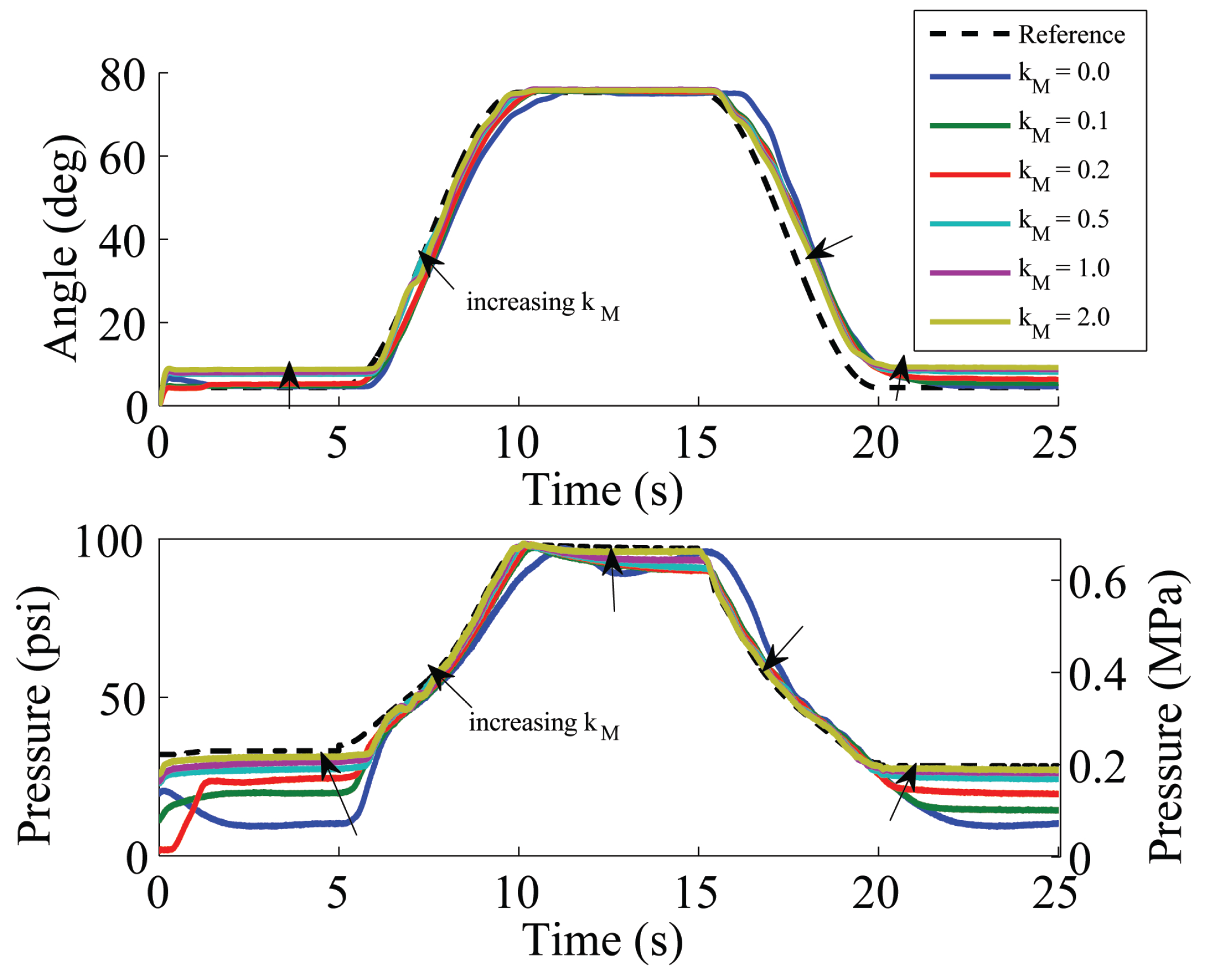
5.3. Discussion of Controllers
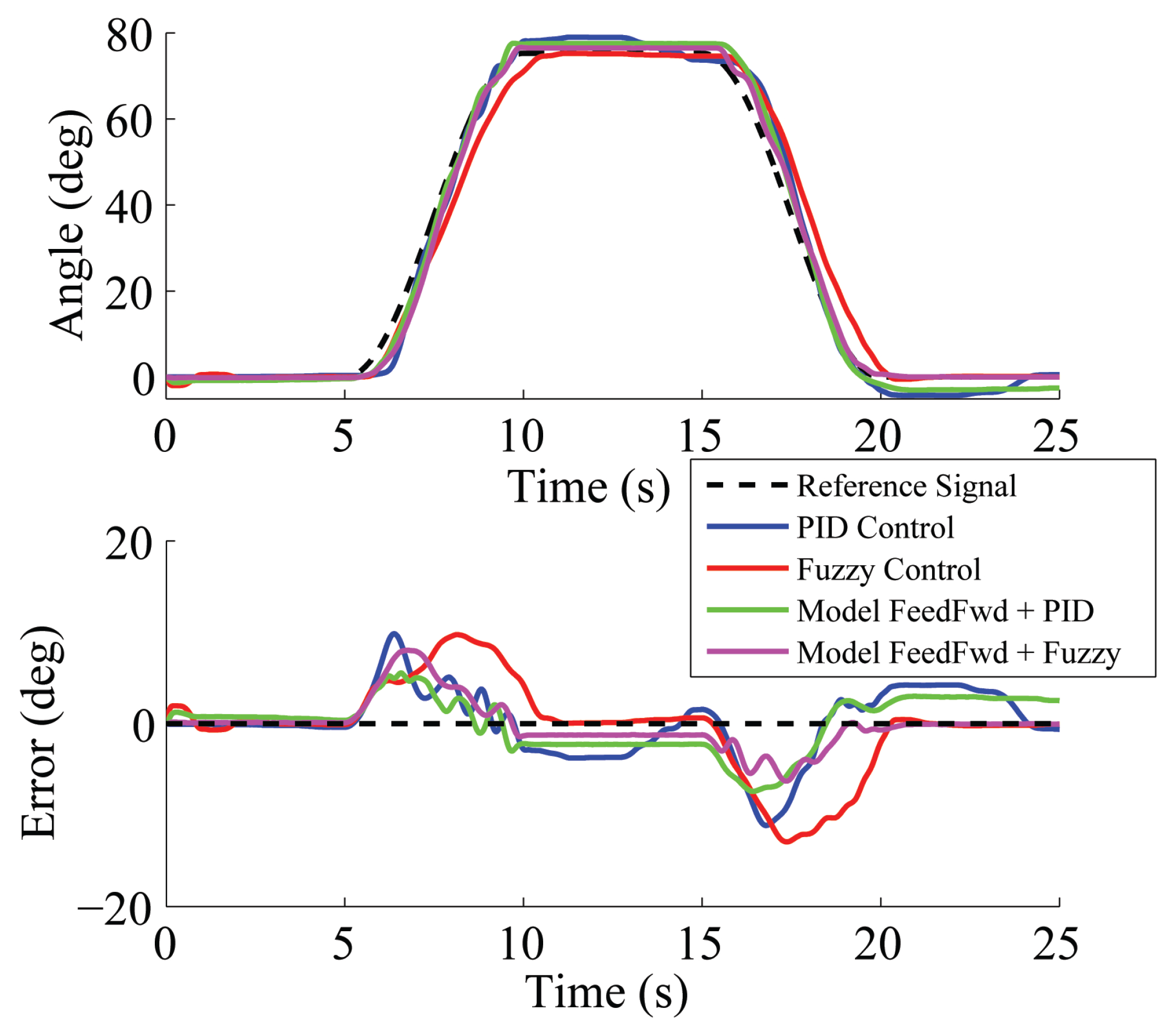
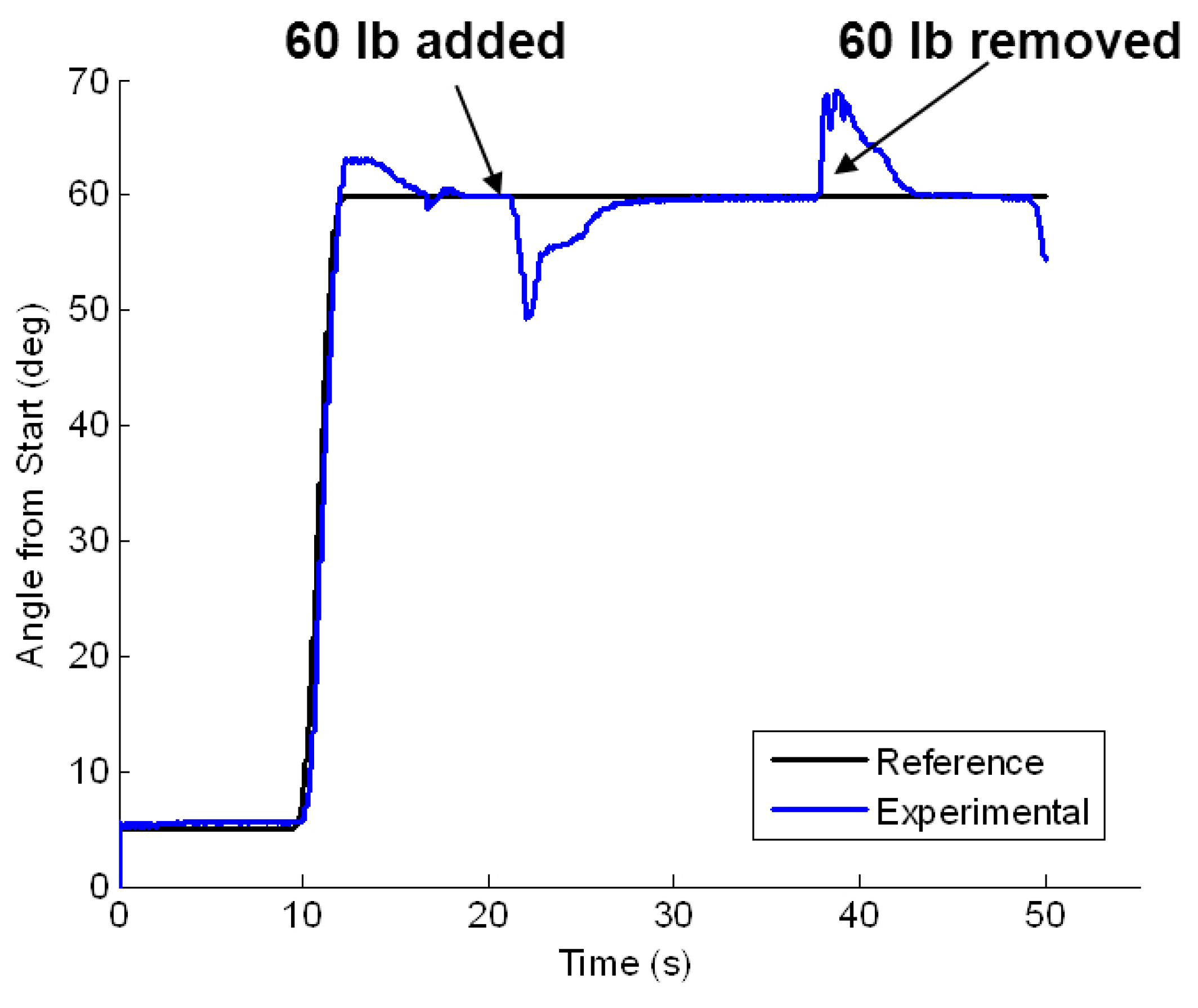
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Material
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, D.; Sardellitti, I.; Khatib, O. A hybrid actuation approach for human-friendly robot design. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1747–1752.
- Klute, G.K.; Czerniecki, J.M.; Hannaford, B. Artificial muscles: Actuators for biorobotic systems. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2002, 21, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, H. The Application of External Power in Prosthetics and Orthotics; Technical Report; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, D.G.; Tsagarakis, N. Biomimetic actuators in prosthetic and rehabilitation applications. Technol. Health Care 2002, 10, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knestel, M.; Hofer, E.P.; Barillas, S.K.; Rupp, R. The artificial muscle as an innovative actuator in rehabilitation robotics. In Proceedings of the 17th IFAC World Congress, Seoul, Korea, 6–11 July 2008; pp. 773–778.
- Li, X.; Xia, H.; Guan, T. Development of legs rehabilitation exercise system driven by pneumatic muscle actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008; pp. 1309–1311.
- Tondu, B.; Ippolito, S.; Guiochet, J.; Daidie, A. A seven-degrees-of-freedom robot-arm driven by pneumatic artificial muscles for humanoid robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2005, 24, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linde, R. Design, analysis, and control of a low power joint for walking robots, by phasic activation of McKibben muscles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1999, 15, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shen, X. Double-acting sleeve muscle actuator for bio-robotic systems. Actuators 2013, 2, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klute, G.K.; Hannaford, B. Accounting for elastic energy storage in McKibben artificial muscle actuators. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2000, 122, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraresi, C.; Franco, W.; Bertetto, A.M. Flexible pneumatic actuators: A comparison between the McKibben and the straight fibres muscles. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2001, 13, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Philen, M.P.; Bakis, C.E.; Wang, K.; Rahn, C.D. Nonlinear-elastic finite axisymmetric deformation of flexible matrix composite membranes under internal pressure and axial force. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Beyl, P.; Vanderborght, B.; Van Ham, R.; Vanderniepen, I.; Versluys, R.; Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. Modeling hysteresis in pleated pneumatic artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics, Chengdu, China, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 471–476.
- Davis, S.; Caldwell, D.G. Braid effects on contractile range and friction modeling in pneumatic muscle actuators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, D.; Medrano-Cerda, G.; Goodwin, M. Control of pneumatic muscle actuators. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1995, 15, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Nguyen, H. Intelligent switching control of a pneumatic muscle robot arm using learning vector quantization neural network. Mechatronics 2007, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xing, K.; Xu, Q. Fuzzy PID control of a wearable rehabilitation robotic hand driven by pneumatic muscles. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2009 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science, Nagoya, Japan, 9–11 November 2009; pp. 408–413.
- Yeh, T.J.; Wu, M.J.; Lu, T.J.; Wu, F.K.; Huang, C.R. Control of McKibben pneumatic muscles for a power-assist, lower-limb orthosis. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyl, P.; Van Damme, M.; Cherelle, P.; Lefeber, D. Safe and compliant guidance in robot-assisted gait rehabilitation using proxy-based sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 277–282.
- Sciavicco, L.; Sciliano, B. Modeling and Control of Robot Manipulators; Springer: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tao, G.; Yao, B.; Cao, J. Adaptive robust posture control of parallel manipulator driven by pneumatic muscles with redundancy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, S.; Garg, A.; Pasricha, A.; Dwivedy, S. Control of pneumatic artificial muscle system through experimental modelling. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nho, H.; Meckl, P. Intelligent feedforward control and payload estimation for a two-link robotic manipulator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2003, 8, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateh, M.M.; Izadbakhsh, A. Robust control of a high-speed manipulator in state space. Int. J. Aerosp. Mech. Eng. 2007, 1, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Utkin, V.; Ozguner, U. A control engineer’s guide to sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1999, 7, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotine, J.J.; Li, W. Applied Nonlinear Control; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Slotine, J.J. On the Adaptive Control of Robot Manipulators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1987, 6, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, P.; Jiang, Z.; Repperger, D. Nonlinear control of a pneumatic muscle actuator: backstepping vs. sliding-mode. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Mexico City, Mexico, 5–7 September 2001; Volume 2, pp. 167–172.
- Cai, D.; Dai, Y. A sliding mode controller for manipulator driven by artificial muscle actuator. Electron. Commun. Jpn. (Part III: Fundam. Electron. Sci.) 2003, 86, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, J.H. Adaptive tracking for pneumatic muscle actuators in bicep and tricep configurations. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, A.; Gauvert, C.; Tondu, B.; Lopez, P. Generalized variable structure model reference adaptive control of one-link artificial muscle manipulator in two operating modes. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Antonio, USA, 2–5 October 1994; Volume 2, pp. 1944–1950.
- Xing, K.; Xu, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Wu, J. Tracking control of pneumatic artificial muscle actuators based on sliding mode and non-linear disturbance observer. IET Control Theory Appl. 2010, 4, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X. Nonlinear model-based control of pneumatic artificial muscle servo systems. Control Eng. Pract. 2010, 18, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann, H.; Schindele, D. Sliding-mode control of a igh-speed linear axis driven by pneumatic muscle actuators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3855–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braikia, K.; Chettouh, M.; Tondu, B.; Acco, P.; Hamerlain, M. Improved control strategy of 2-sliding controls applied to a flexible robot arm. Adv. Robot. 2011, 25, 1515–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.M.; Kothera, C.S.; Woods, B.K.S.; Vocke, R.D.; Wereley, N.M. High specific power actuators for robotic manipulators. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonietti, G.; Schiavi, R.; Bicchi, A. Design and control of a variable stiffness actuator for safe and fast physical human/robot interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 526–531.
- Richer, E.; Hurmuzulu, Y. A high performance pneumatic force actuator system part 1—Nonlinear mathematical model. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2001, 122, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothera, C.S.; Jangid, M.; Sirohi, J.; Wereley, N.M. Experimental characterization and static modeling of McKibben actuators. ASME J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 091010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passino, K. Fuzzy Control; Addison Wesley Longman: Menlo Park, USA, 1998; pp. 1–492. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.M.; Wereley, N.M.; Kothera, C.S. Control of a heavy-lift robotic manipulator with pneumatic artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the AIAA Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 1–14.
- Van Damme, M.; Beyl, P.; Vanderborght, B.; Versluys, R.; Ham, R.; Vanderniepen, I.; Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. The safety of a robot actuated by pneumatic muscles—A case study. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2010, 2, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, S.; Albu-Schaffer, A.; Eiberger, O.; Hirzinger, G. New insights concerning intrinsic joint elasticity for safety. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 2181–2187.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Robinson, R.M.; Kothera, C.S.; Wereley, N.M. Control of a Heavy-Lift Robotic Manipulator with Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Actuators 2014, 3, 41-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020041
Robinson RM, Kothera CS, Wereley NM. Control of a Heavy-Lift Robotic Manipulator with Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Actuators. 2014; 3(2):41-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobinson, Ryan M., Curt S. Kothera, and Norman M. Wereley. 2014. "Control of a Heavy-Lift Robotic Manipulator with Pneumatic Artificial Muscles" Actuators 3, no. 2: 41-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020041
APA StyleRobinson, R. M., Kothera, C. S., & Wereley, N. M. (2014). Control of a Heavy-Lift Robotic Manipulator with Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Actuators, 3(2), 41-65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020041






