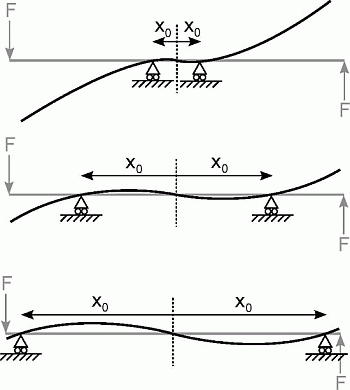
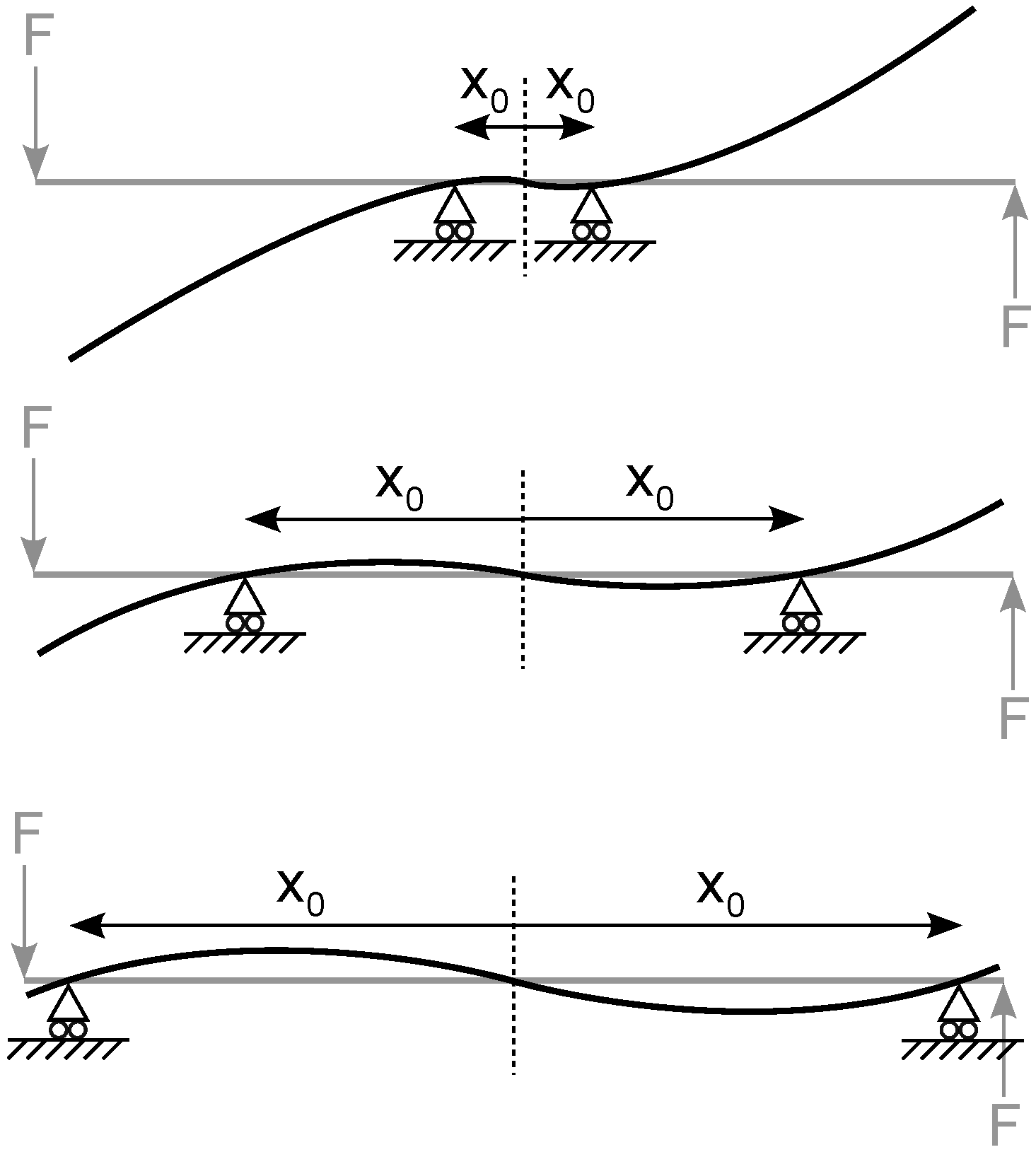
A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Design
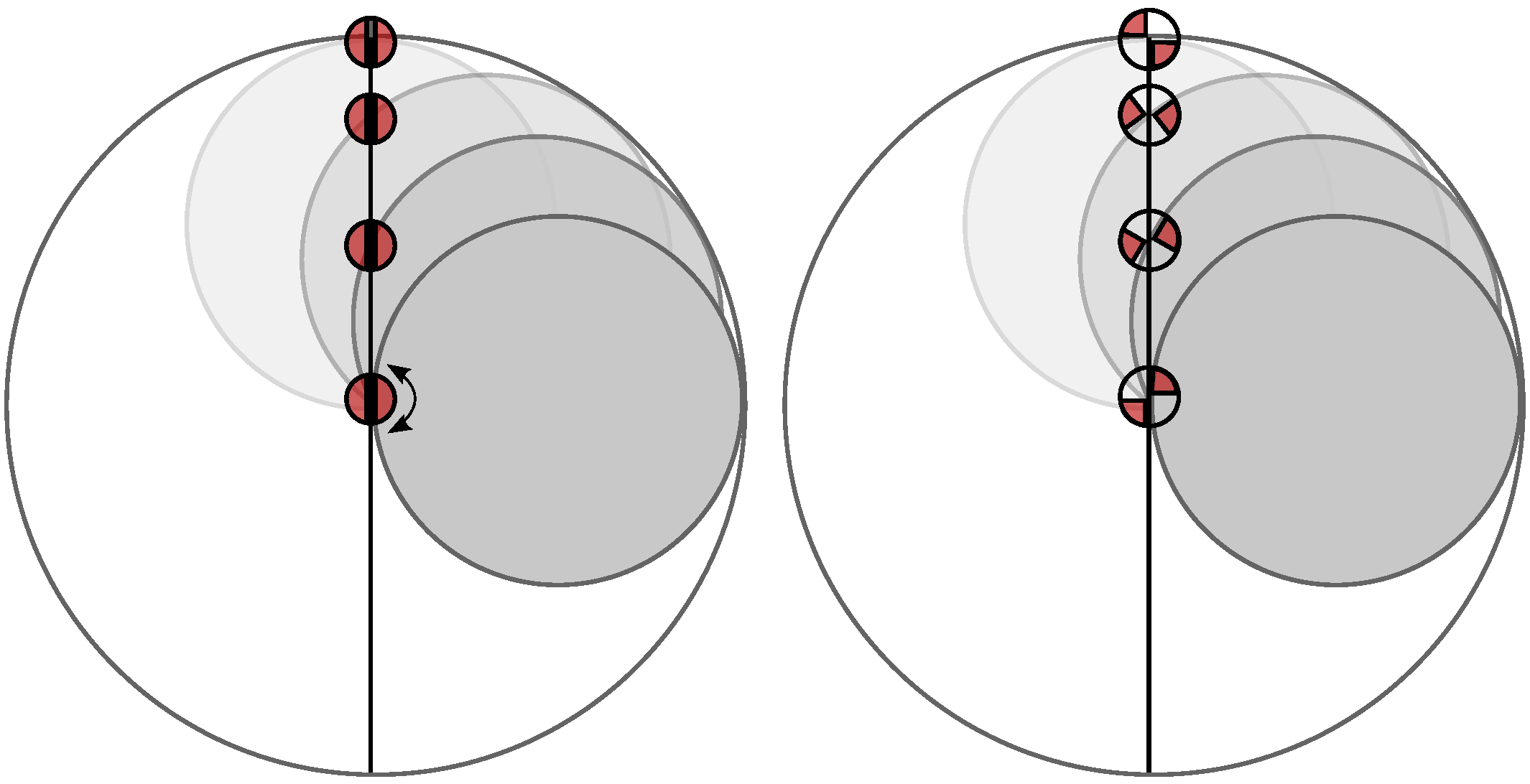
2.1. The Variable Stiffness Mechanism and Its Working Principle
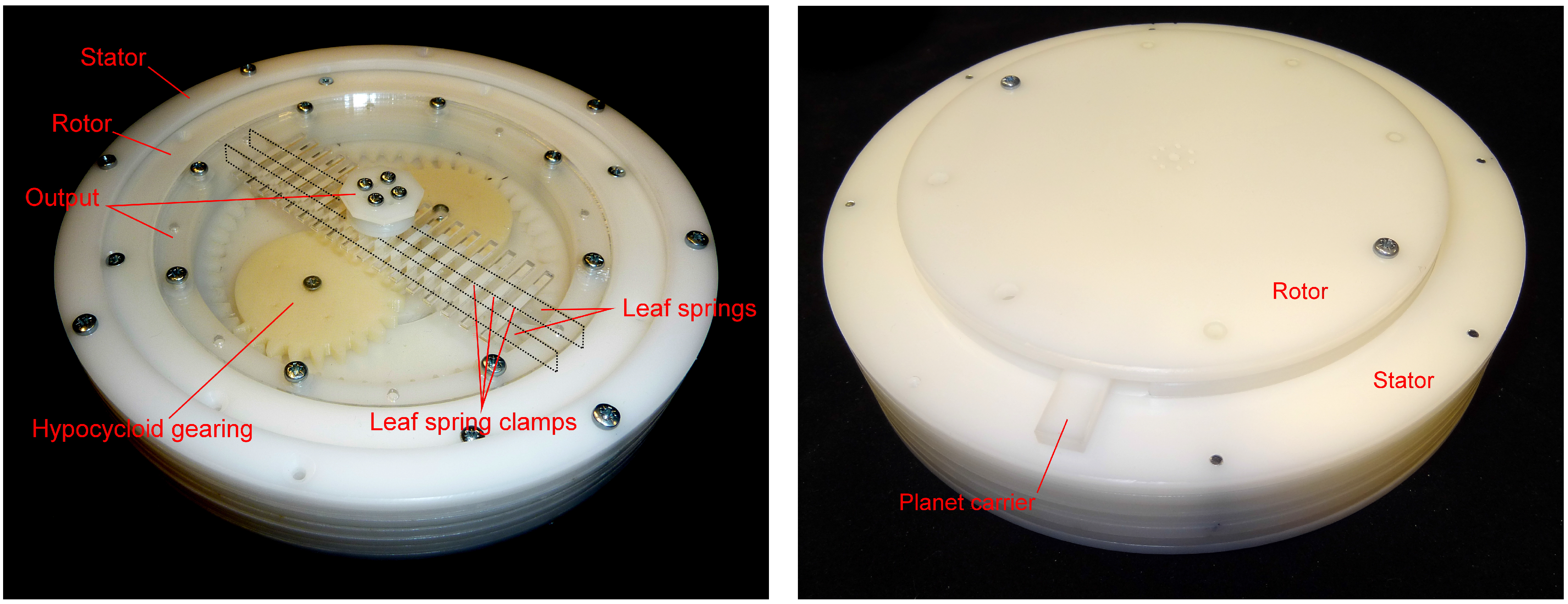
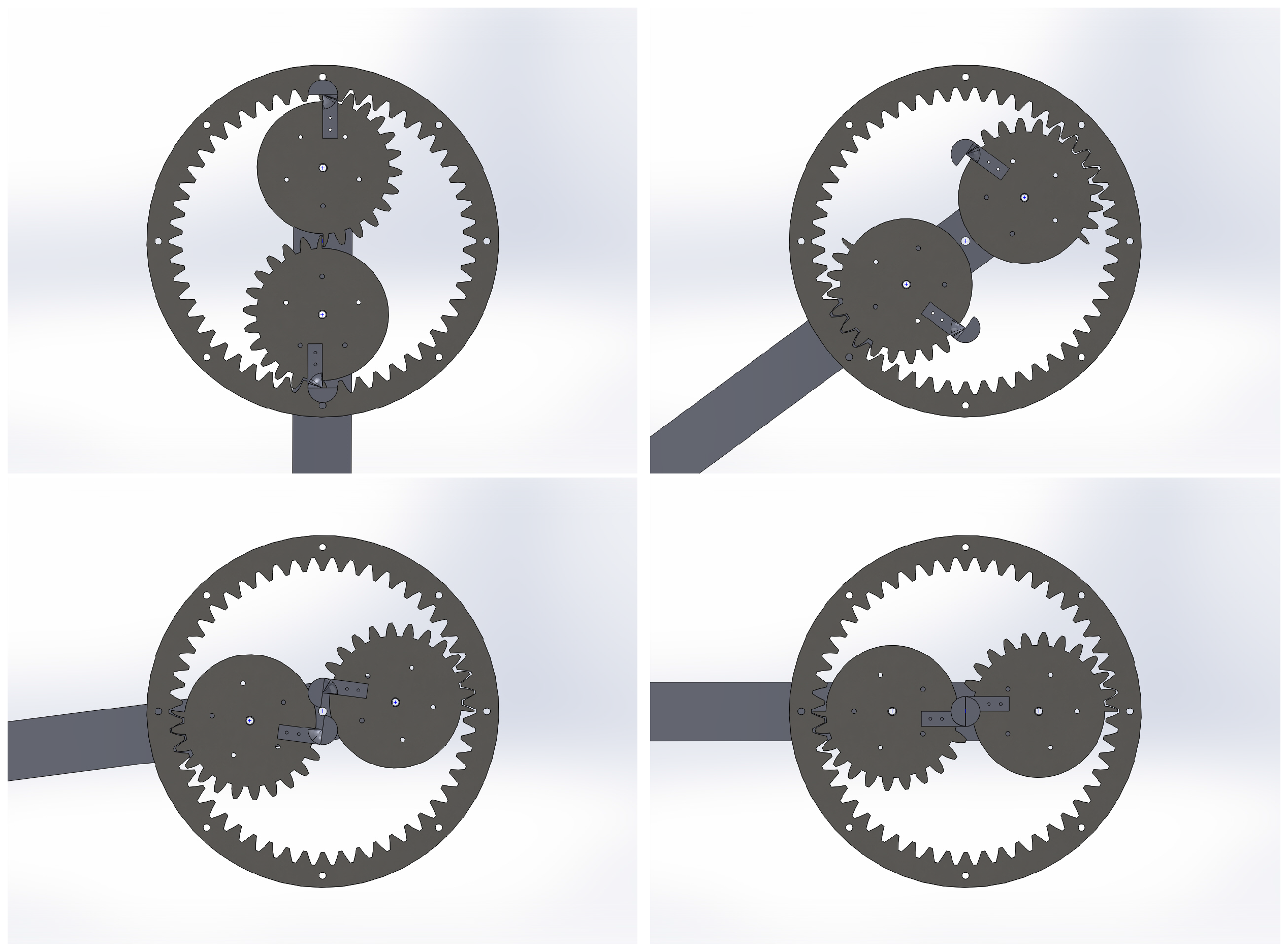
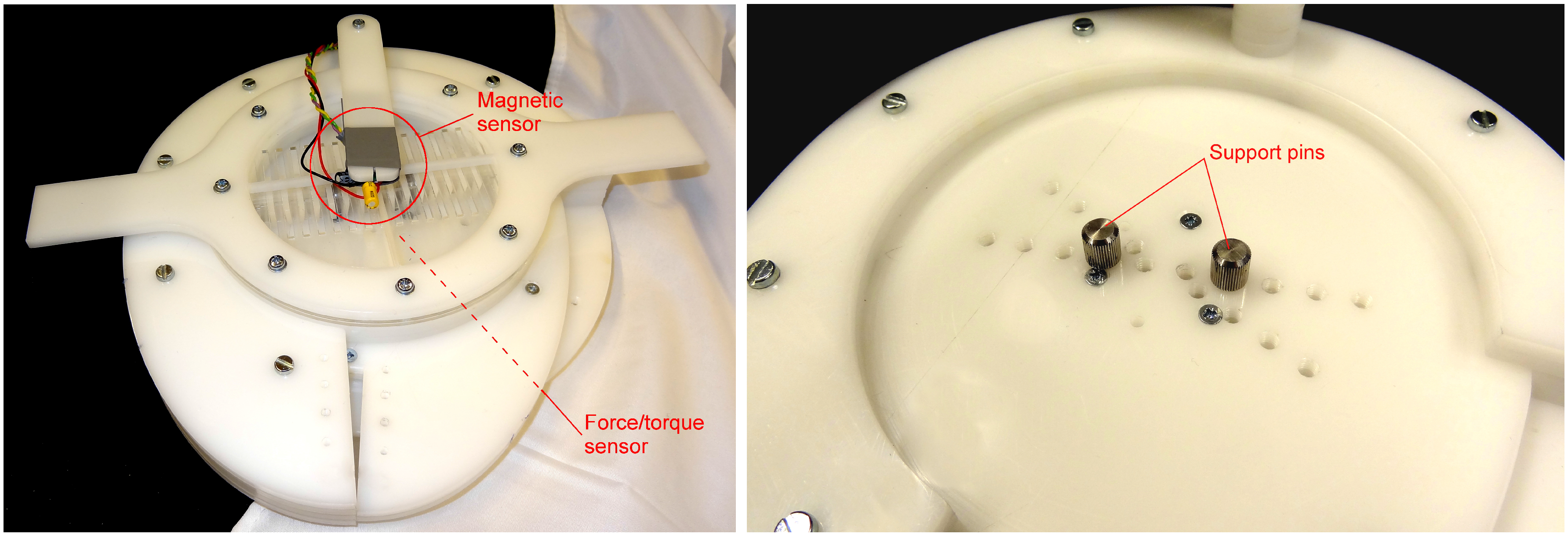
2.2. Support Pins
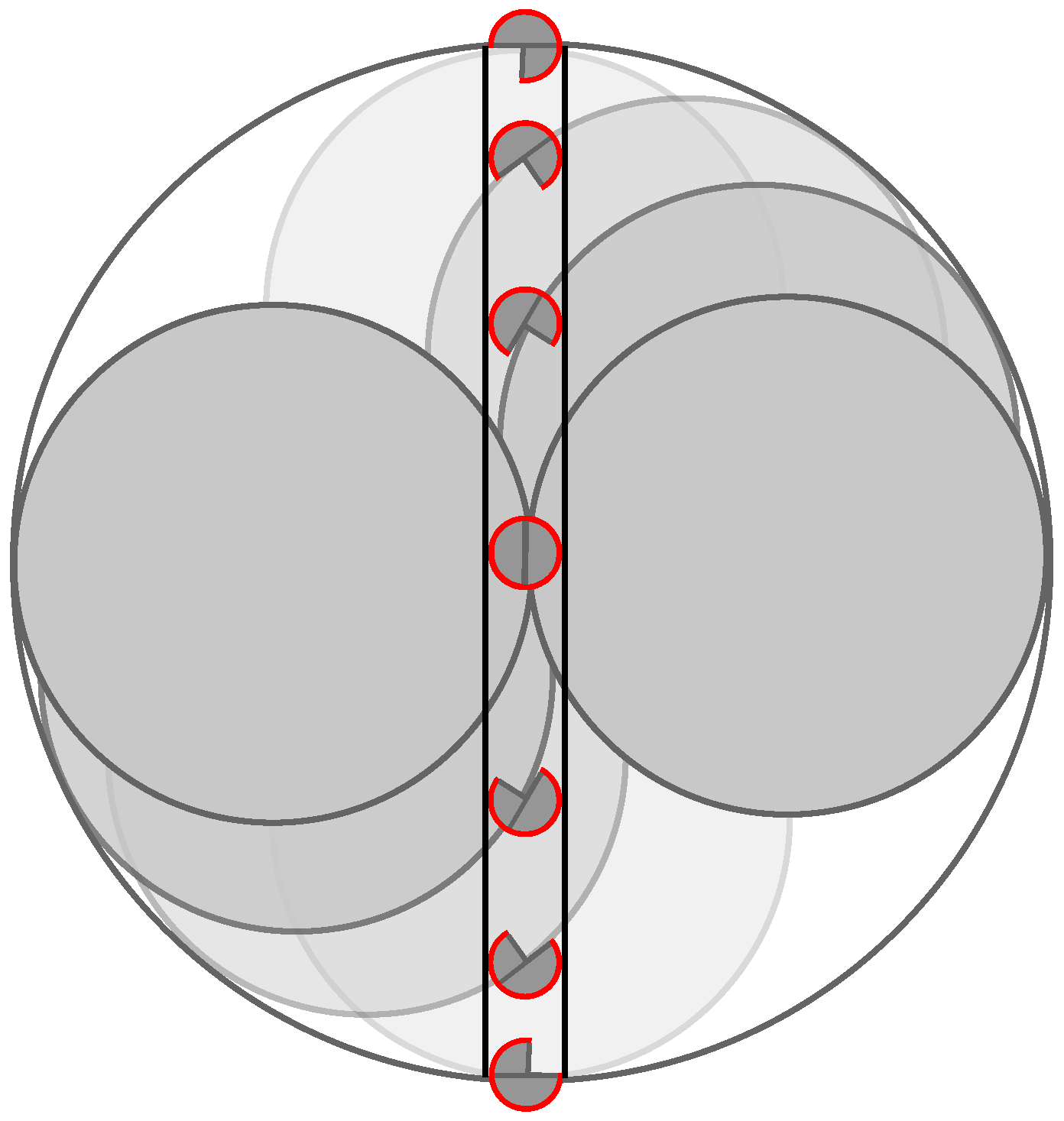
2.3. Hypocycloid Gearing Mechanism
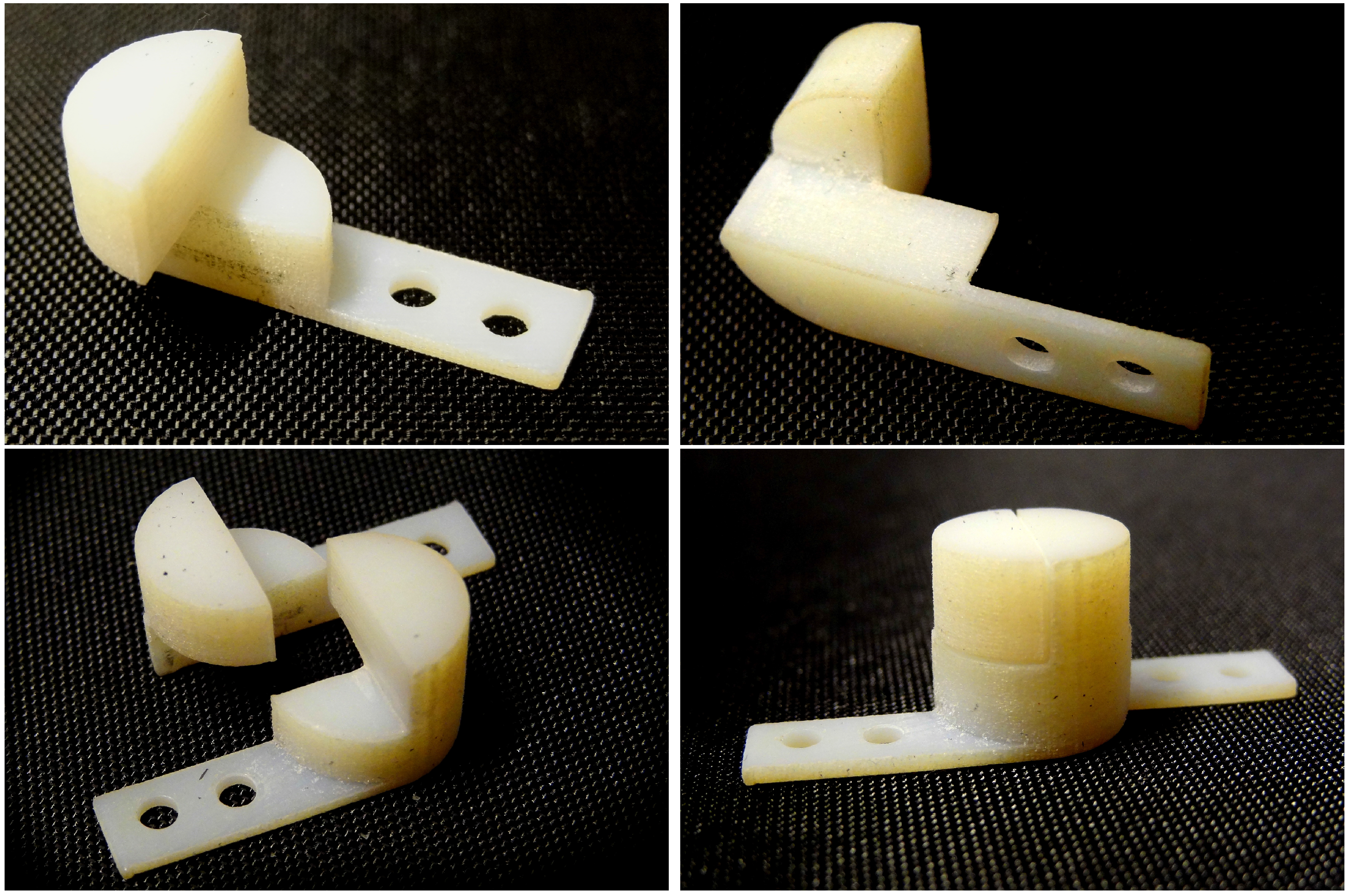
3. Modeling
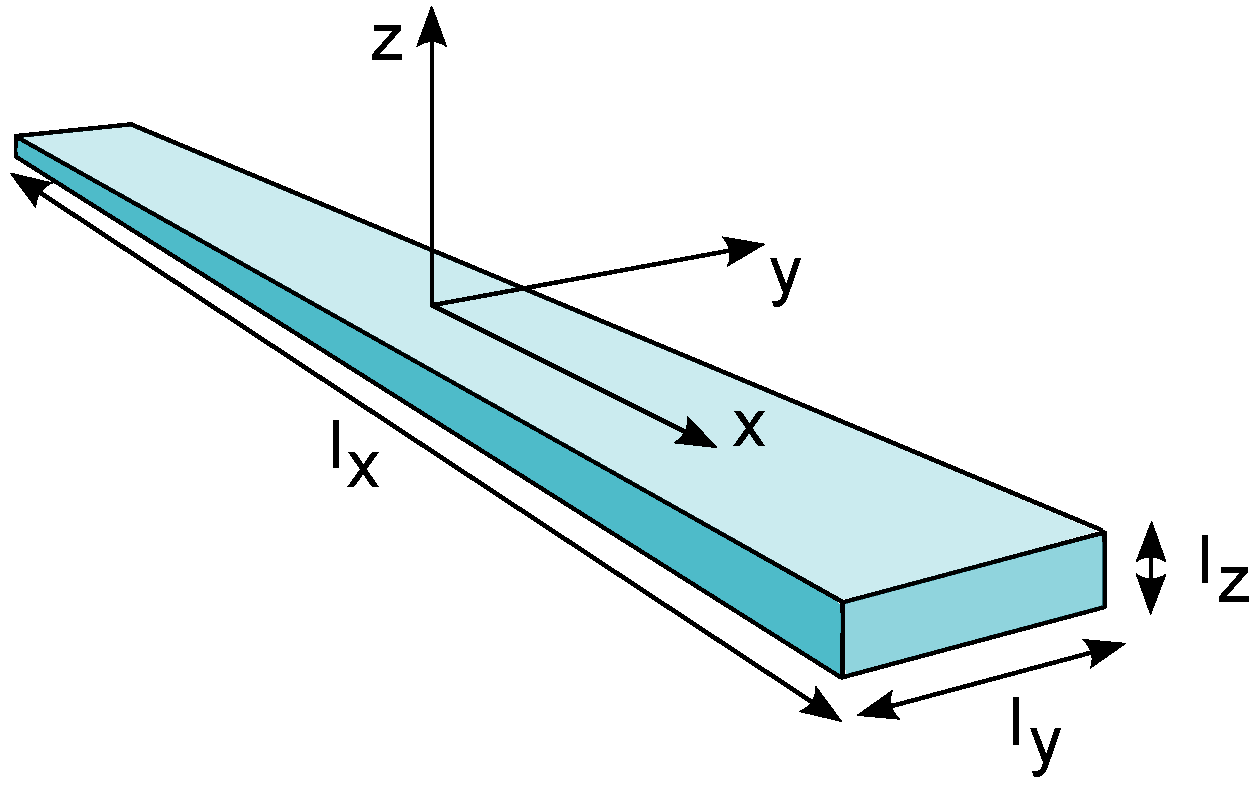
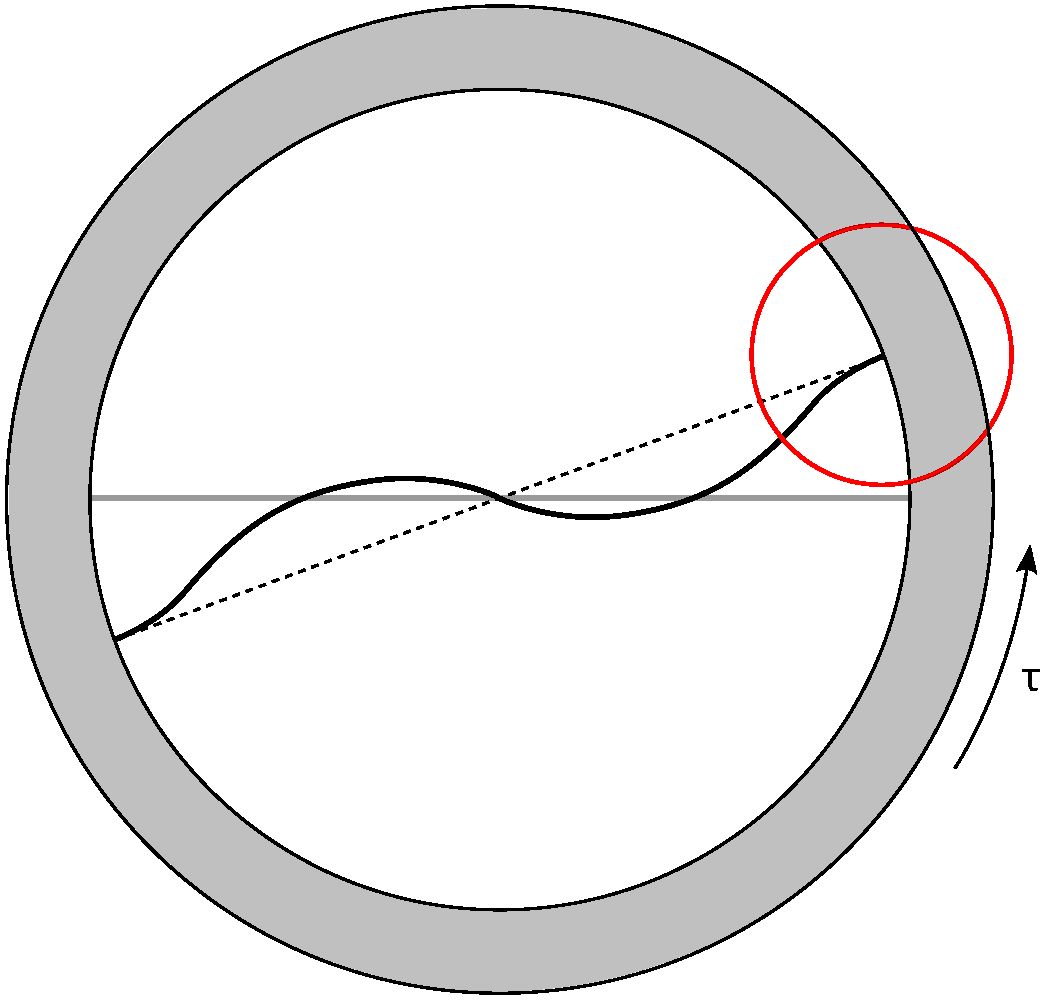
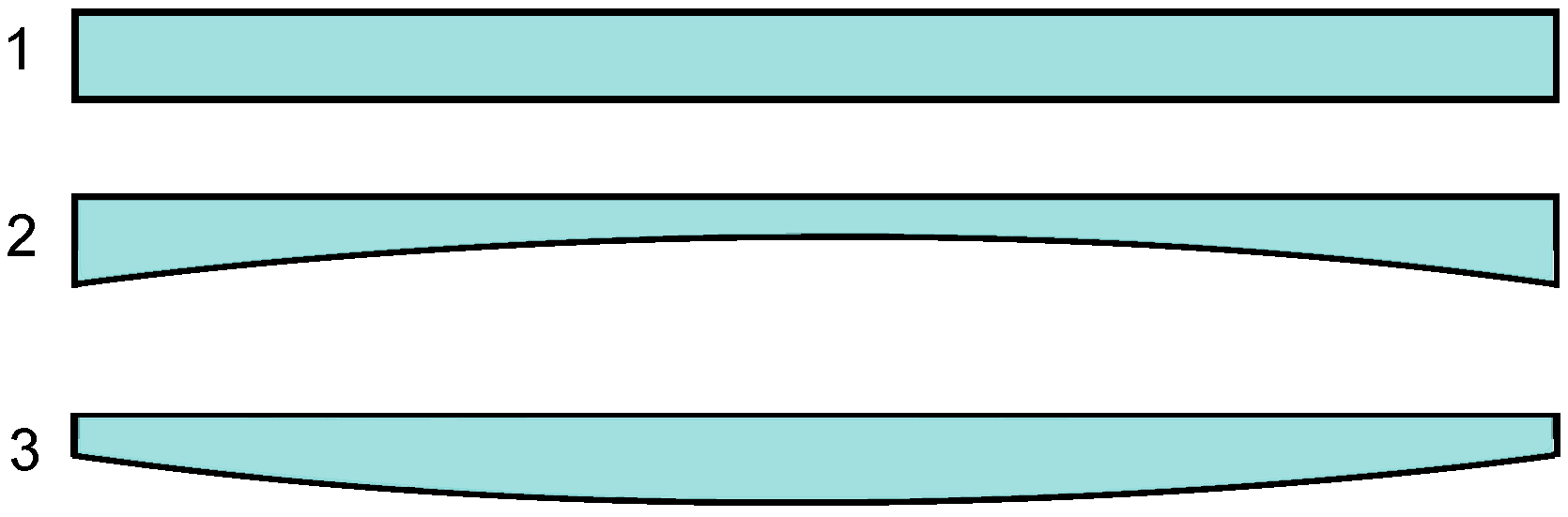
3.1. Leaf Spring
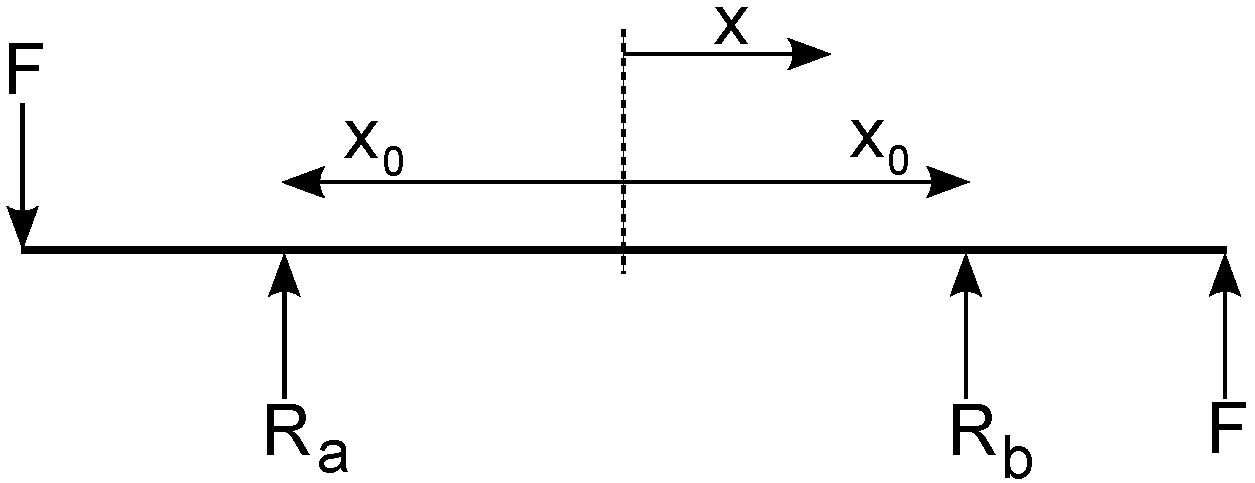
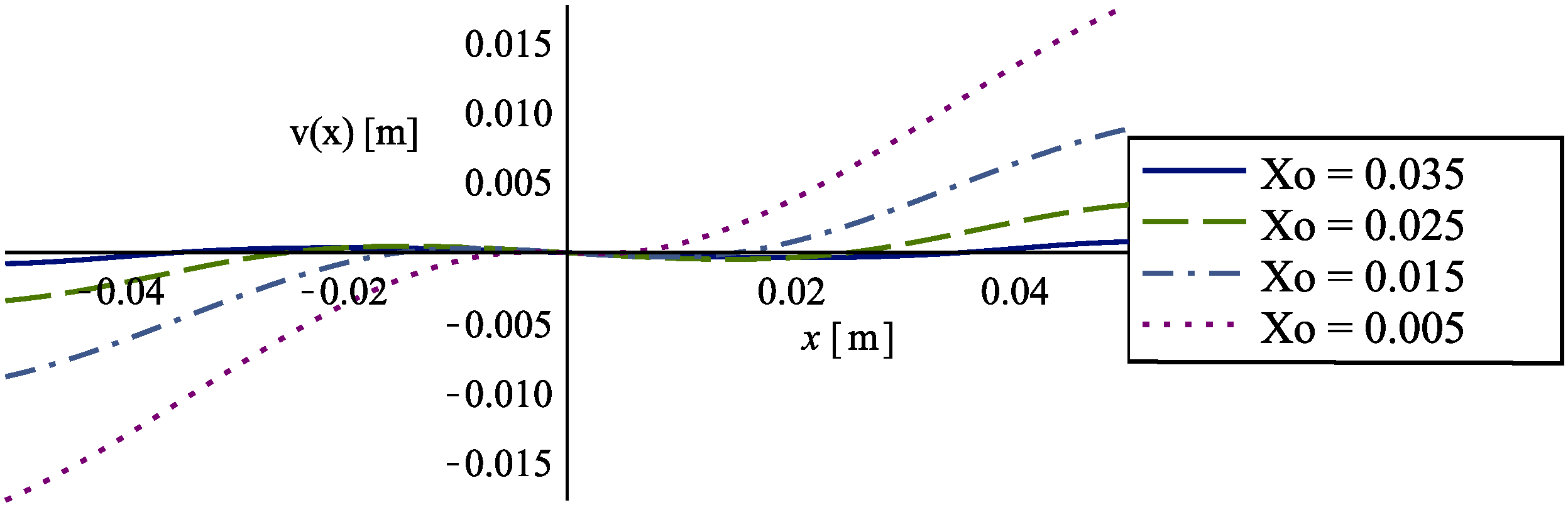
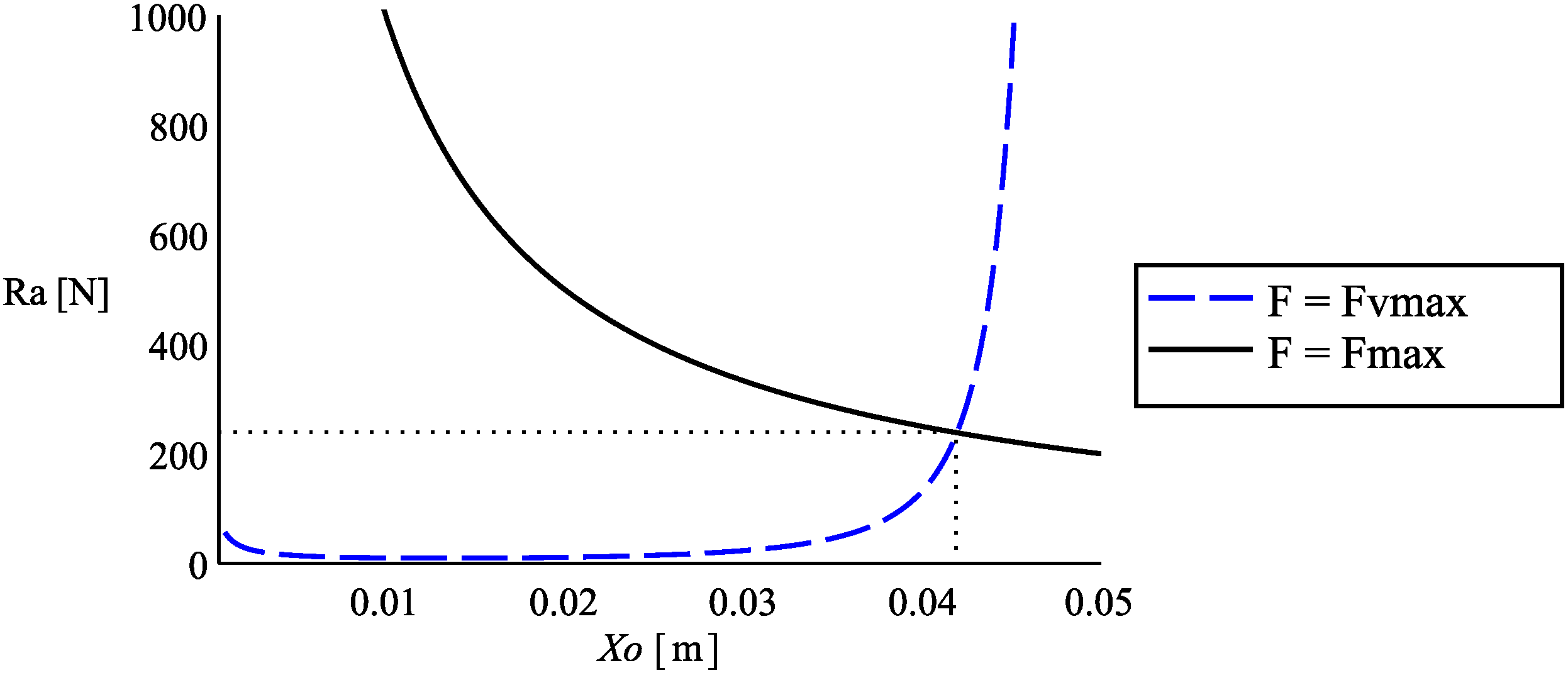
3.2. Support Pins
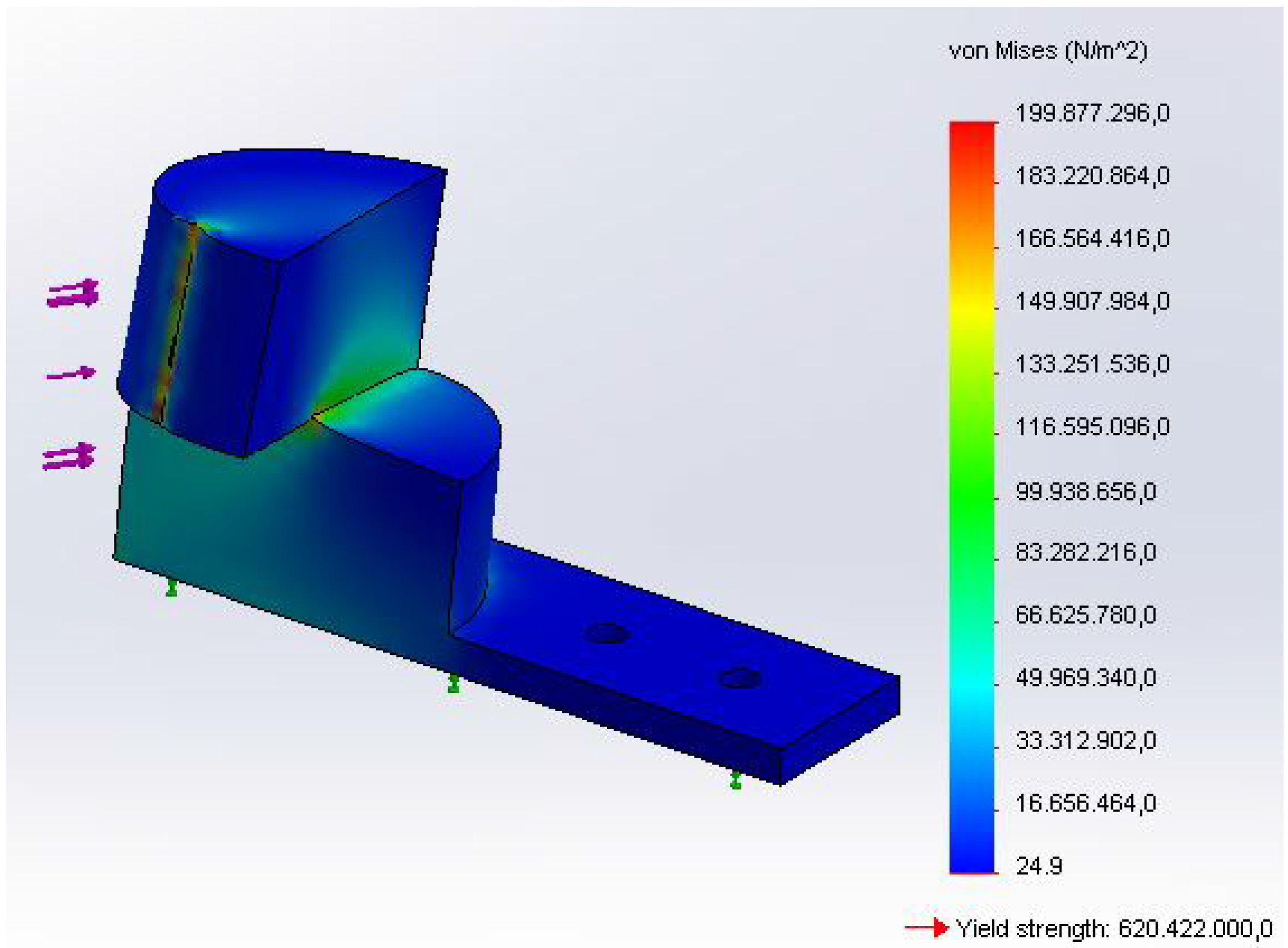
3.3. Hypocycloid Gearing Mechanism
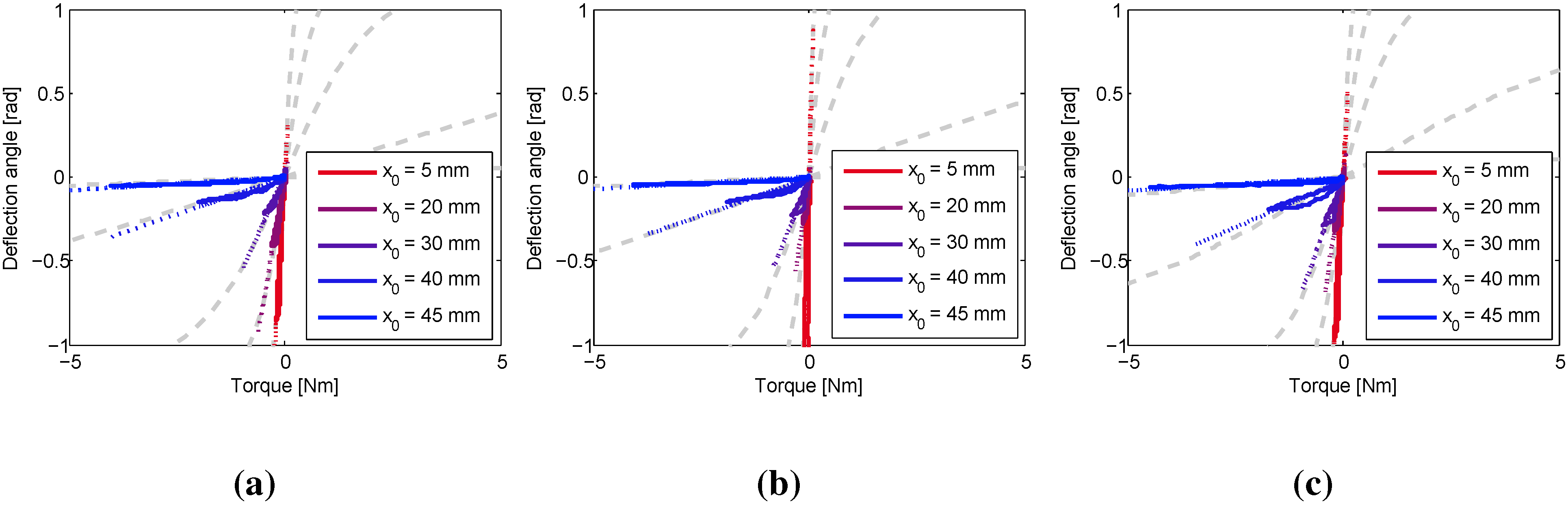
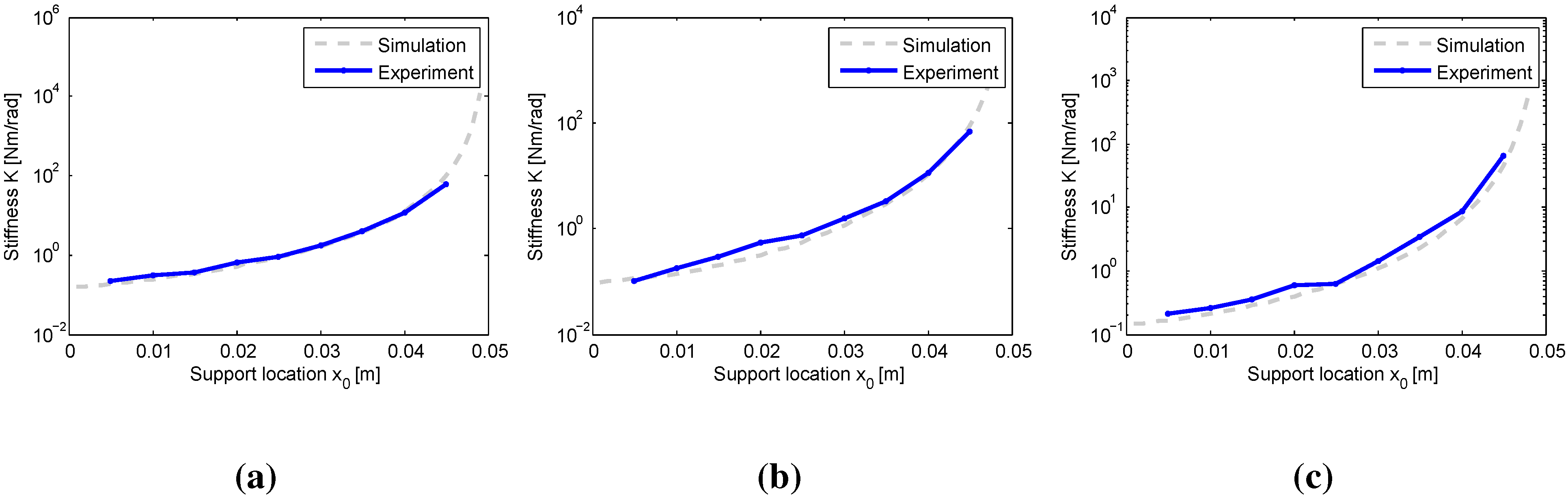
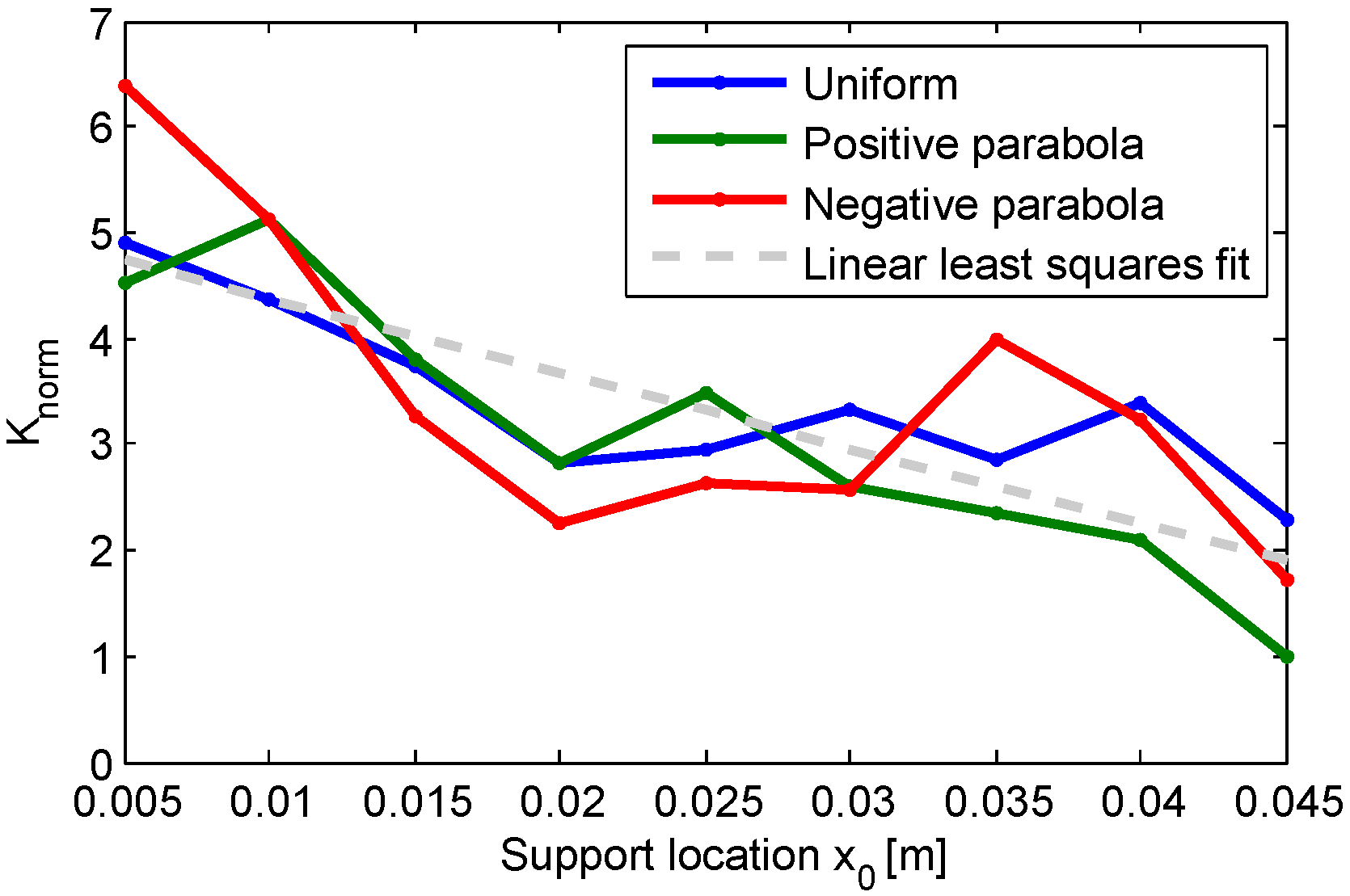
4. Experiments

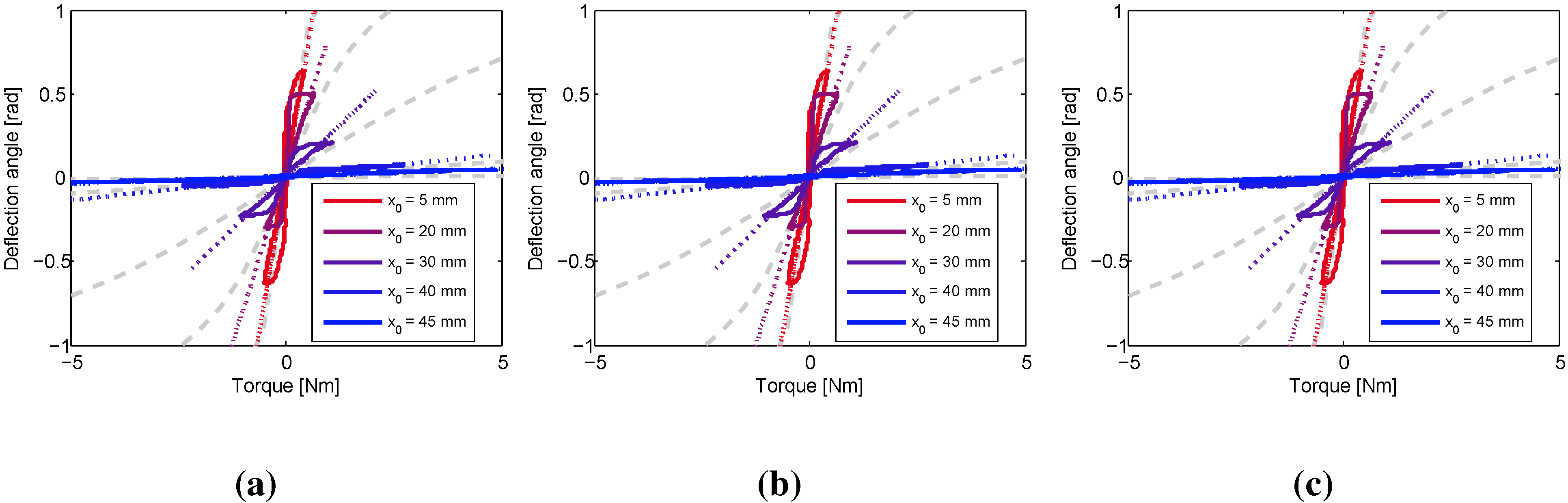

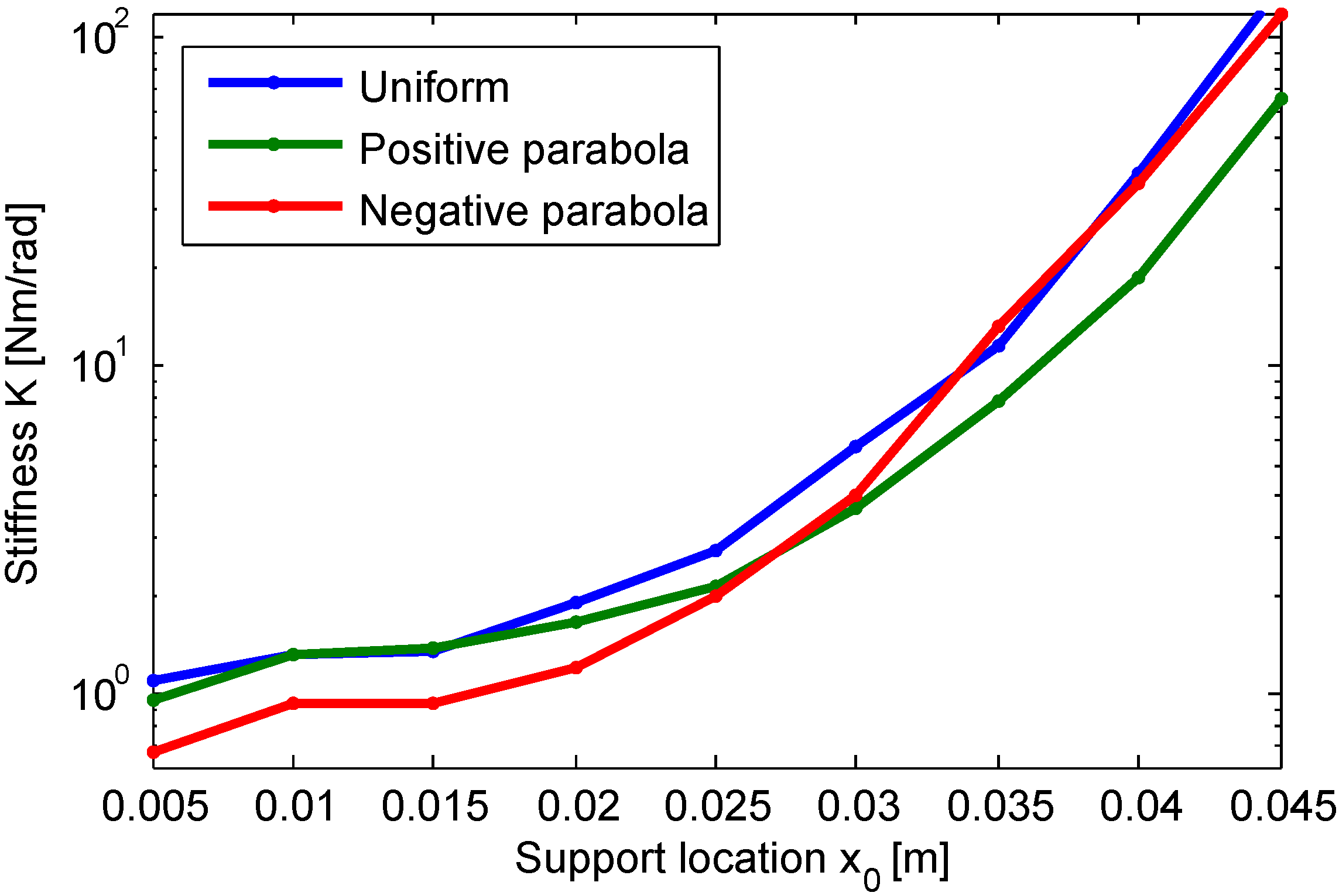
5. Conclusions
6. Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogan, N. Impedance control: An approach to manipulation: Part I, part II, part III. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1985, 107, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M. Series Elastic Actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–9 August 1995.
- Vanderborght, B.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Bicchi, A.; Burdet, E.; Caldwell, D.; Carloni, R.; Catalano, M.; Eiberger, O.; Friedl, W.; Ganesh, G.; et al. Variable impedance actuators: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M.; Kawamura, S. Resonance-based motion control method for multi-joint robot through combining stiffness adaptation and iterative learning control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 1543–1548.
- Groothuis, S.; Stramigioli, S.; Carloni, R. Lending a helping hand: Towards novel assistive robotic arms. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2013, 20, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; Tsagarakis, N.; Semini, C.; van Ham, R.; Caldwell, D. MACCEPA 2.0: Adjustable compliant actuator with stiffening characteristic for energy efficient hopping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009.
- Schiavi, R.; Grioli, G.; Sen, S.; Bicchi, A. VSA-II: A novel prototype of variable stiffness actuator for safe and performing robots interacting with humans. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008.
- Wolf, S.; Hirzinger, G. A new variable stiffness design: Matching requirements of the next robot generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008.
- Kim, B.S.; Song, J.B. Hybrid dual actuator unit: A design of a variable stiffness actuator based on an adjustable moment arm mechanism. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010.
- Tsagarakis, N.G.; Sardellitti, I.; Caldwell, D.G. A new variable stiffness actuator (CompAct-VSA): Design and modelling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011.
- Jafari, A.; Tsagarakis, N.; Vanderborght, B.; Caldwell, D. A novel actuator with adjustable stiffness (AwAS). In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010.
- Jafari, A.; Tsagarakis, N.; Vanderborght, B.; Caldwell, D. AwAS-II: A new actuator with adjustable stiffness based on the novel principle of adaptable pivot point and variable lever ratio. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011.
- Visser, L.C.; Carloni, R.; Stramigioli, S. Energy efficient variable stiffness actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groothuis, S.; Rusticelli, G.; Zucchelli, A.; Stramigioli, S.; Carloni, R. The variable stiffness actuator vsaUT-II: Mechanical design, modeling and identification. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 19, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Sugano, S. Development of an anthropomorphic force-controlled manipulator WAM-10. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advances Robotics, Monterey, CA, USA, 7–9 July 1997.
- Choi, J.; Hong, S.; Lee, W.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. A robot joint with variable stiffness using leaf springs. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, K.; Sugar, T.; Herring, D. Adjustable Robotics Tendon using a “Jack Spring”™. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005.
- Carloni, R.; Visser, L.; Stramigioli, S. Variable stiffness actuators: A port-based power-flow analysis. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Groothuis, S.; Carloni, R.; Stramigioli, S. A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion. Actuators 2014, 3, 107-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020107
Groothuis S, Carloni R, Stramigioli S. A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion. Actuators. 2014; 3(2):107-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleGroothuis, Stefan, Raffaella Carloni, and Stefano Stramigioli. 2014. "A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion" Actuators 3, no. 2: 107-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020107
APA StyleGroothuis, S., Carloni, R., & Stramigioli, S. (2014). A Novel Variable Stiffness Mechanism Capable of an Infinite Stiffness Range and Unlimited Decoupled Output Motion. Actuators, 3(2), 107-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/act3020107