Identification and Compensation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Errors for Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscopes in Whole-Angle Mode
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A nonlinear error model of HRG including the detection gain asymmetry error and its coupling error is built by the average method.
- A comprehensive study of the influence mechanism of the parameter mismatch coupling error is conducted based on the established HRG error equation.
- A novel identification and compensation method for detection gain asymmetry error is proposed by taking advantage of the fact that the standing wave angle position is fixed when HRG works in FTR mode.
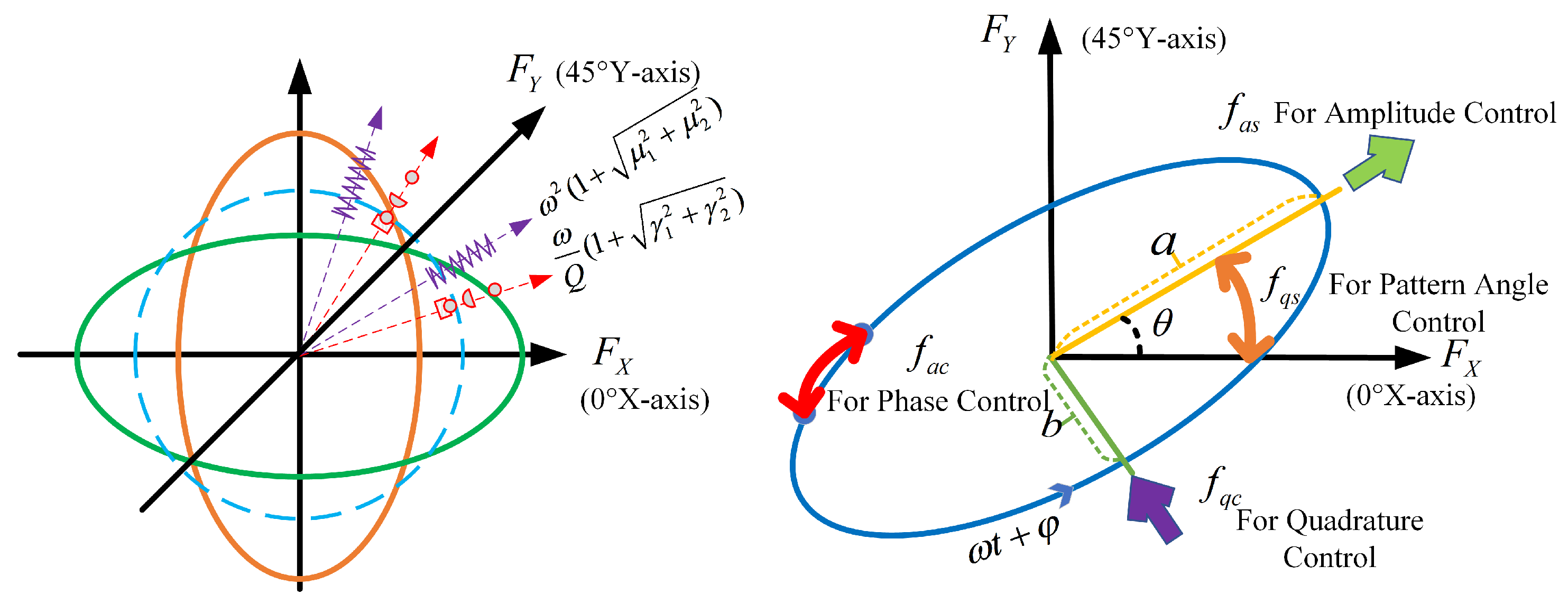
2. Error Model of HRG with Various Parameter Asymmetry
2.1. Equations of Motion
2.2. Detection Electrode Errors for HRG
- Gain of capacitance changes by the displacement .
- Gain of the front-end analog amplifier circuit .
- ADC and digital signal through the filter digital filter gain .
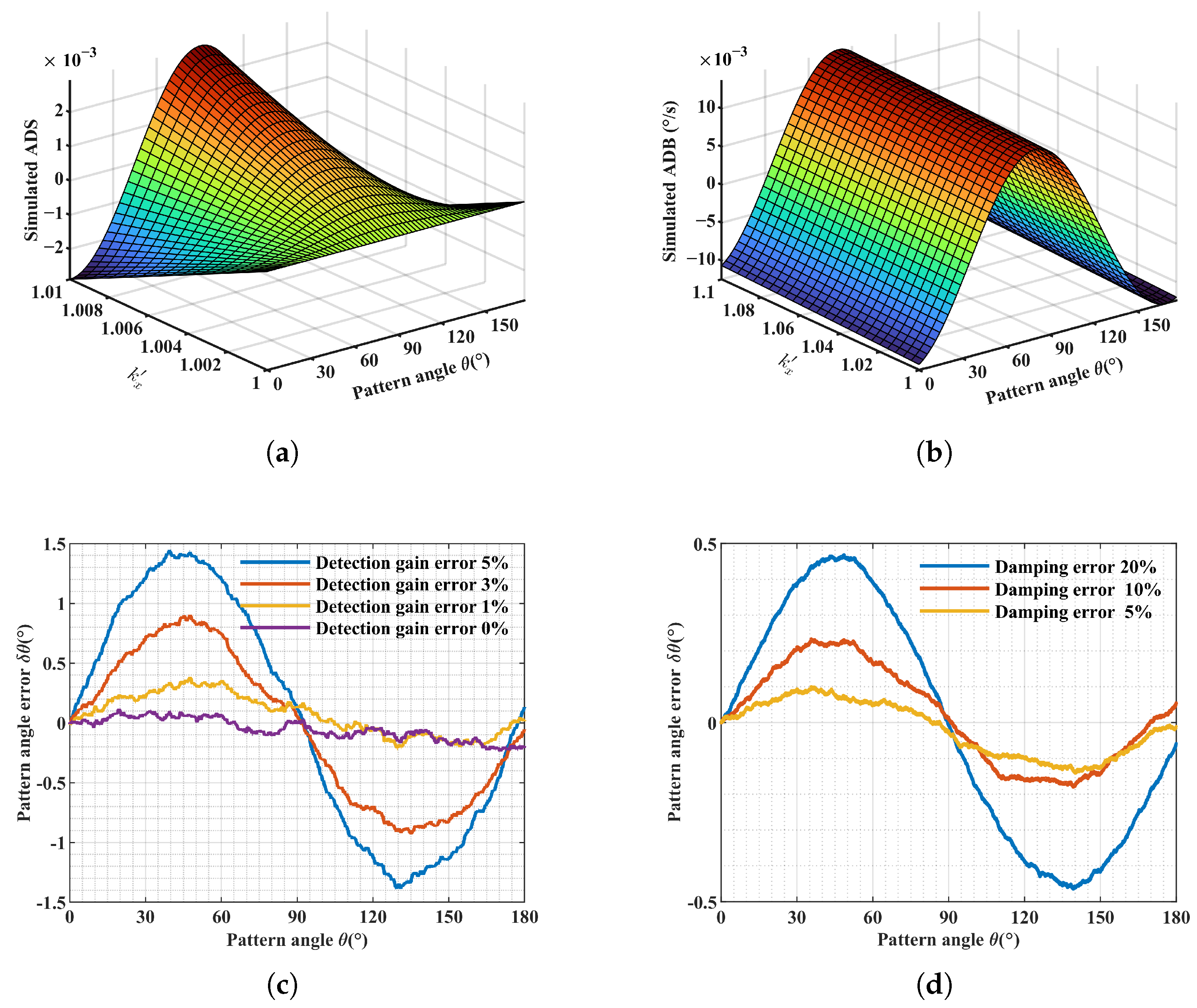
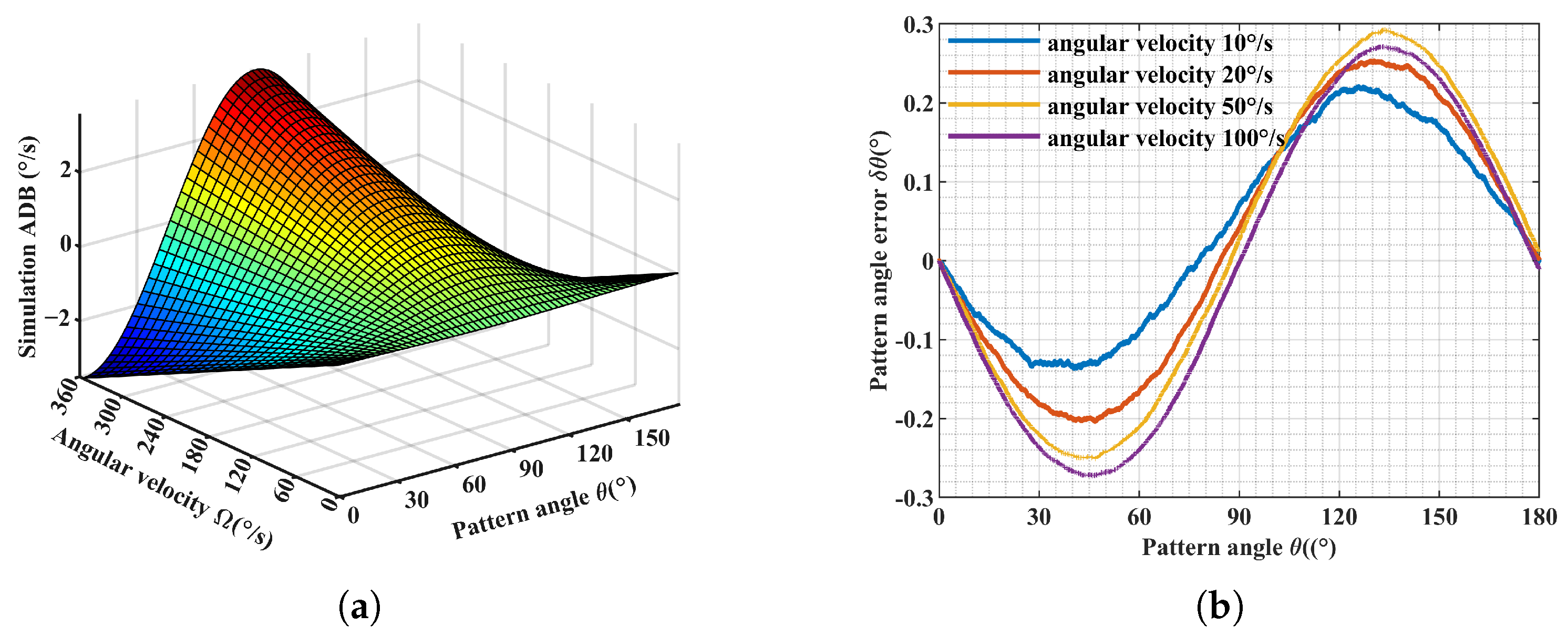
2.3. Numerical Simulation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Error for HRG in WA Mode
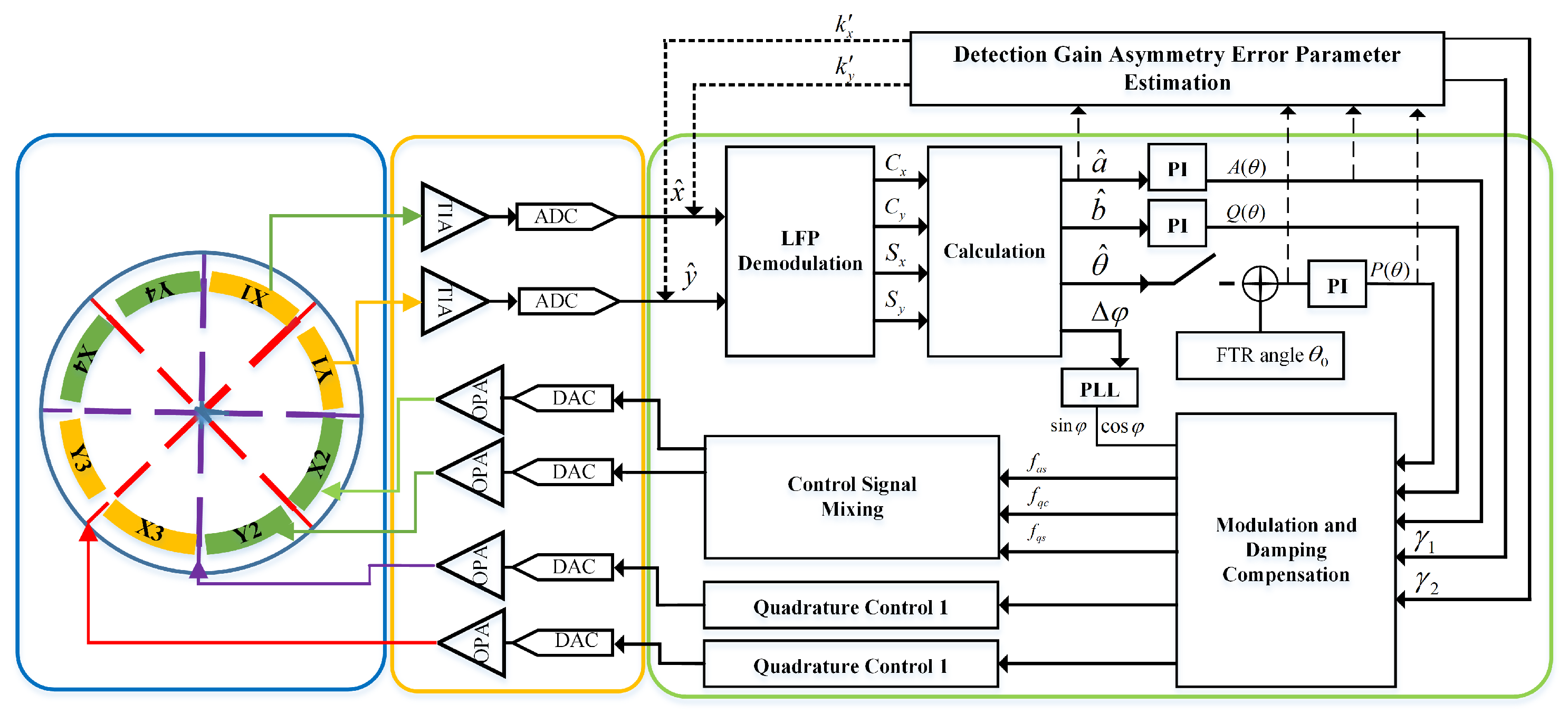
3. Novel Identification and Compensation Method of Detection Gain Asymmetry Error
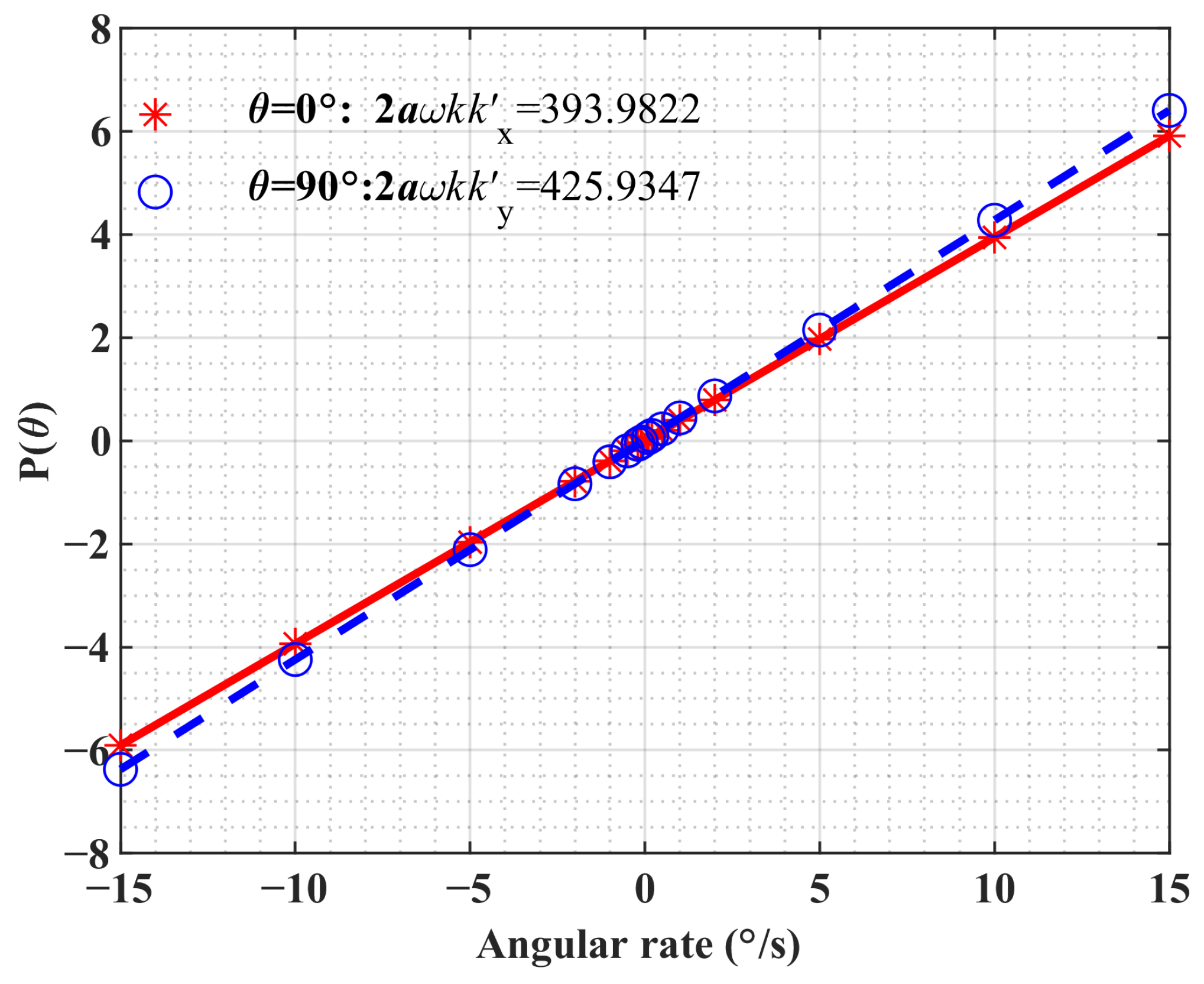
3.1. FTR-Mode-Based Error Observation and Identification Framework
3.2. Comparison with Existing Methods
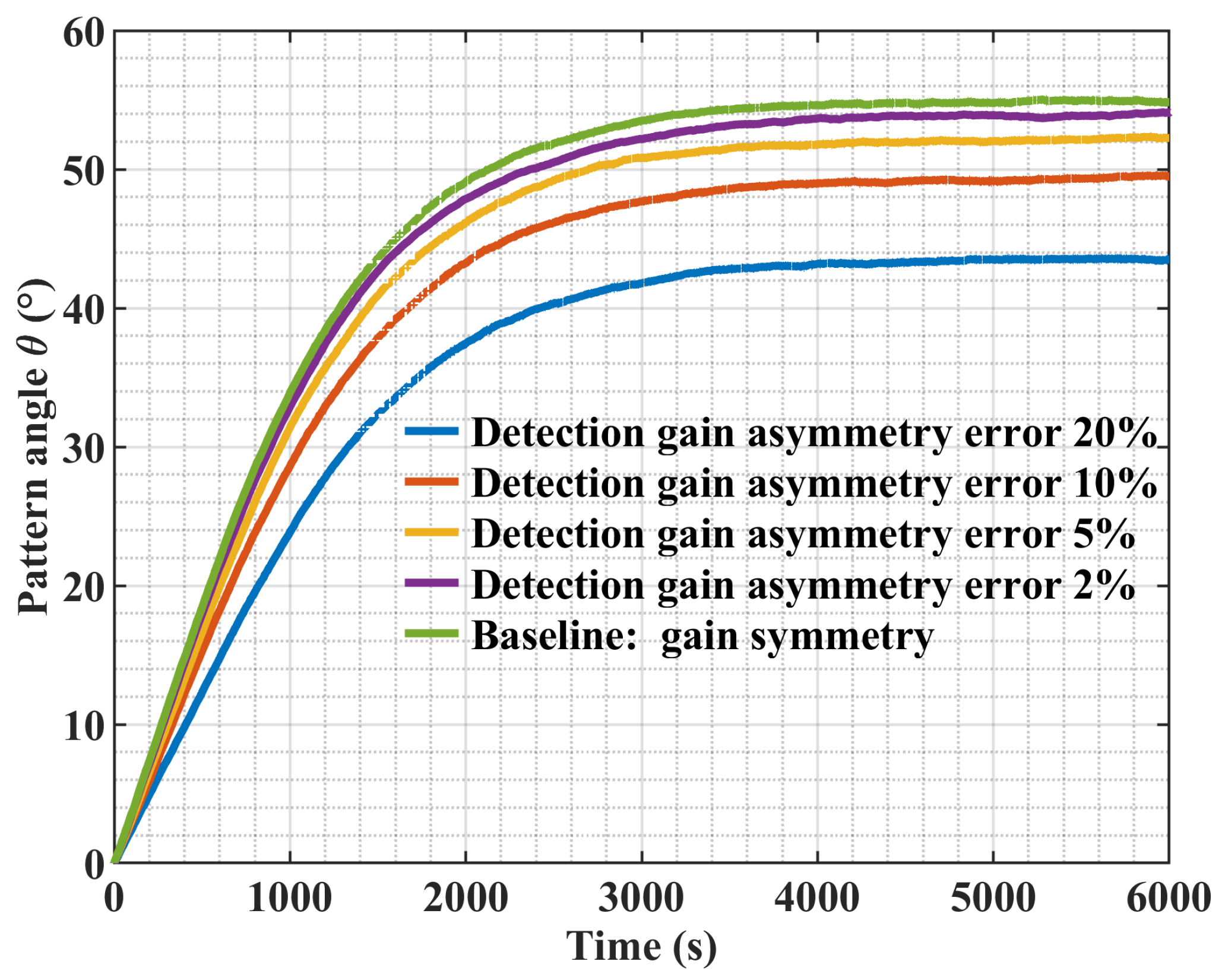
4. Experimental Validation and Results
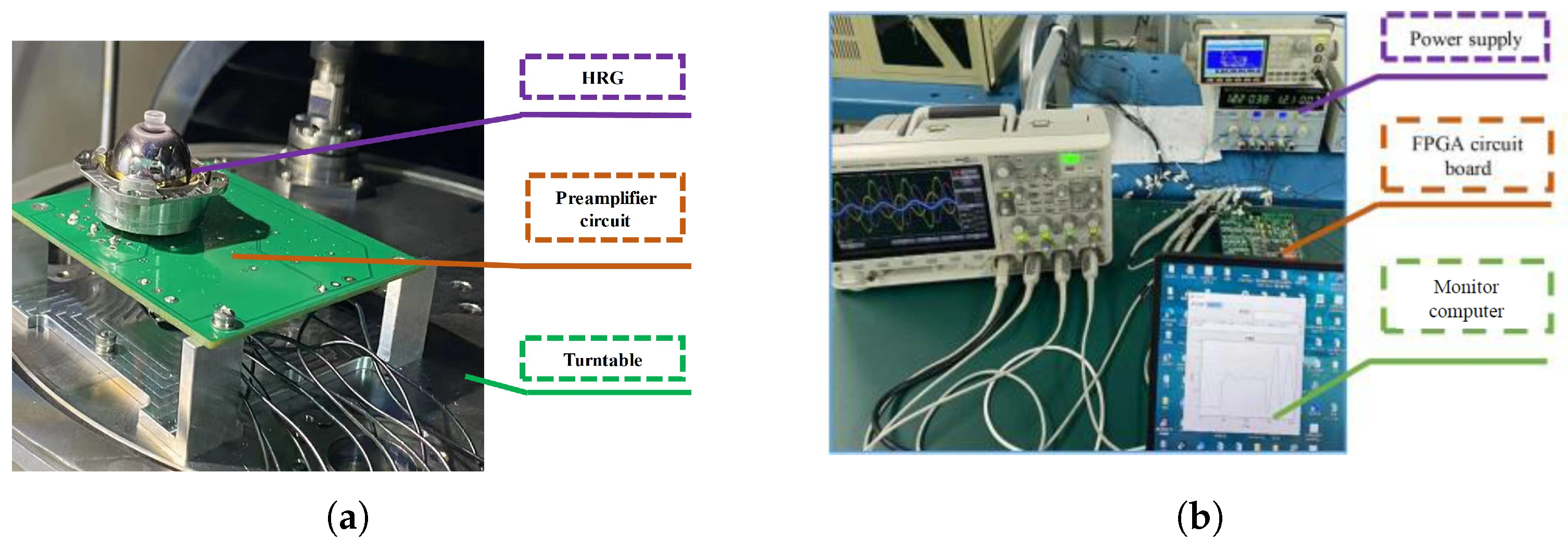
4.1. Experimental Environment
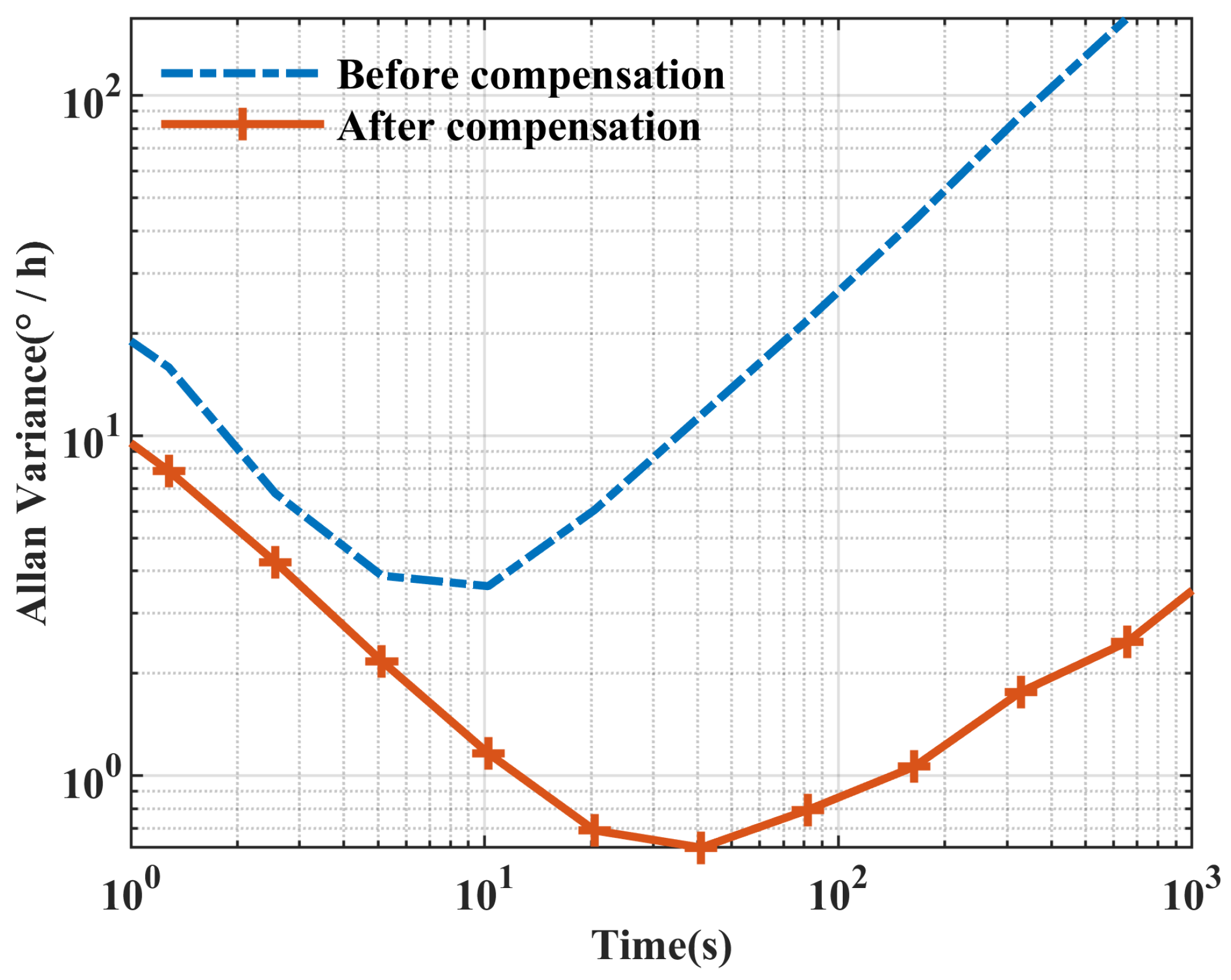
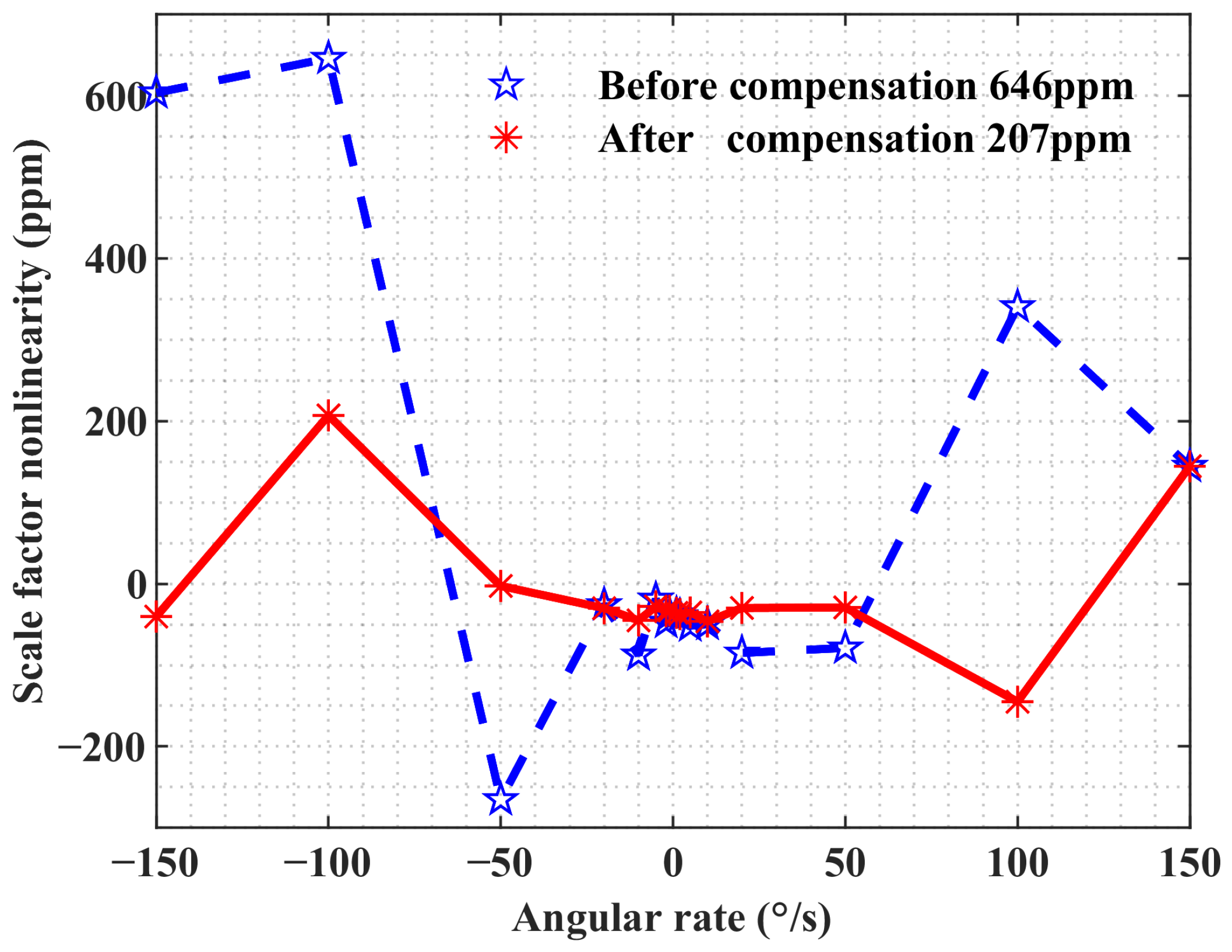
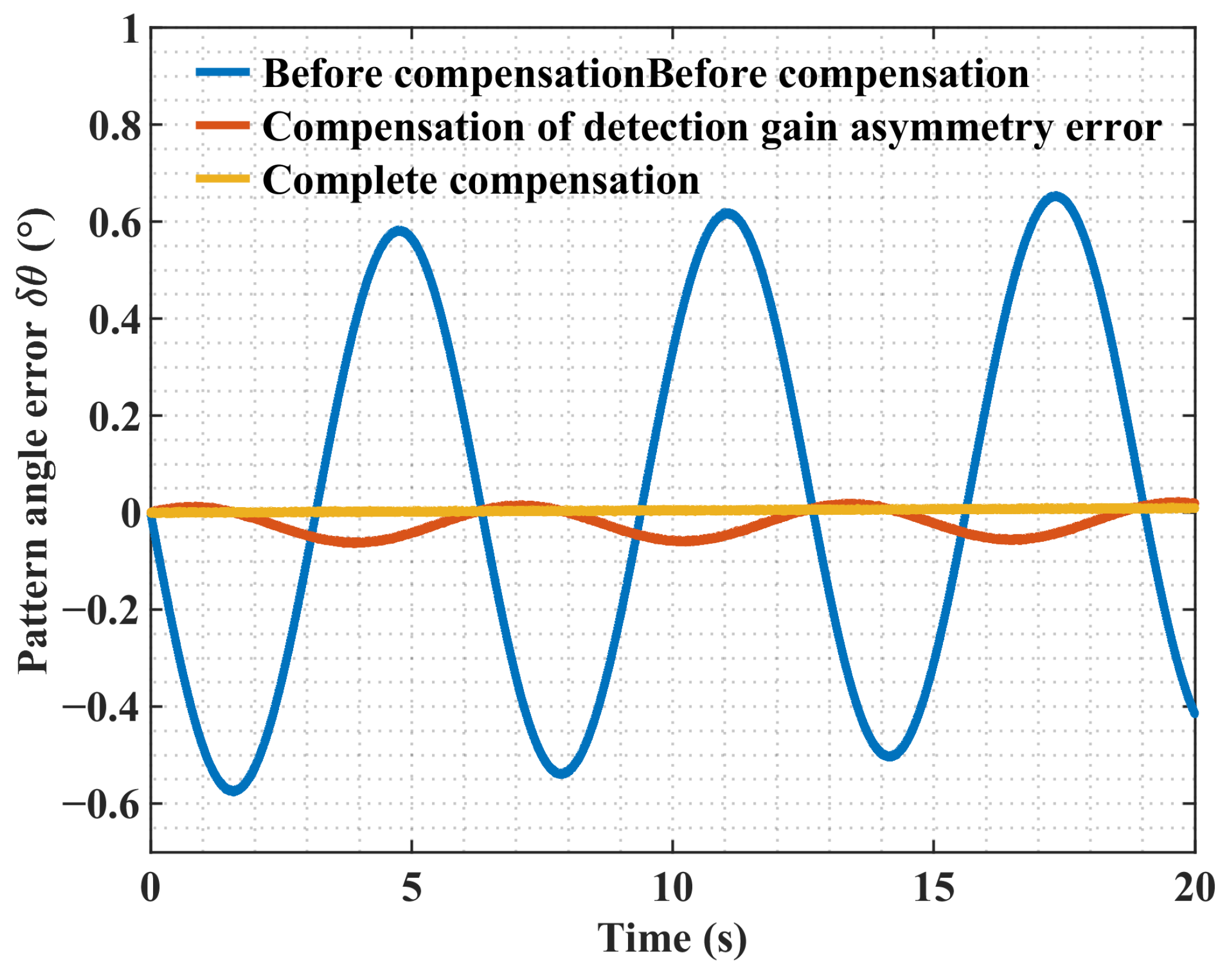
4.2. Experimental Verification and Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyer, A.; Rozelle, D.; Trusov, A.; Sakaida, D. Milli-HRG inertial sensor assembly—A reality. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 23–26 April 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Deleaux, B.; Lenoir, Y. The world smallest, most accurate and reliable pure inertial navigator: ONYX™. In Proceedings of the 2018 DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISS), Braunschweig, Germany, 11–12 September 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Delhaye, F.; Leprevier, C.D. SkyNaute by Safran–How the HRG technological breakthrough benefits to a disruptive IRS (Inertial Reference System) for commercial aircraft. In Proceedings of the 2019 DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISS), Braunschweig, Germany, 10–11 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Yang, G.; Cai, Q.; Wang, L.; Yin, H. Dynamical analysis and experimental verification of deviation angles caused by rubber dampers deformation in high precision mechanically dithered RLG dual-axis RINS. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 126, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Yang, G.; Cai, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X. Optimal design of SINS’s Stewart platform bumper for restoration accuracy based on genetic algorithm. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 124, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D. Coriolis vibratory gyros. In Proceedings of the Symposium Gyro Technology, Stuttgart, Germany, 15–16 September 1998; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vladislav, A. Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes: Theory and Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Zaman, M.F.; Sharma, A.; Ayazi, F. Energy loss mechanisms in a bulk-micromachined tuning fork gyroscope. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–25 October 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1333–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B.J. Effects of nonlinearity on the angular drift error of an electrostatic MEMS rate integrating gyroscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10271–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S.; Vengallatore, S. Theory of thermoelastic damping in micromechanical resonators with two-dimensional heat conduction. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, Y.; Wu, X. Investigation of cylindrical resonators’ damping asymmetry via analyzing q factor circumferential distribution. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B. Control and damping imperfection compensation for a rate integrating MEMS gyroscope. In Proceedings of the 2015 DGON Inertial Sensors and Systems Symposium (ISS), Karlsruhe, Germany, 22–23 September 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Natural frequency split estimation for inextensional vibration of imperfect hemispherical shell. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 2094–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallacher, B.J.; Hedley, J.; Burdess, J.S.; Harris, A.J.; Rickard, A.; King, D.O. Electrostatic correction of structural imperfections present in a microring gyroscope. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Bang, H. Imperfection parameter observer and drift compensation controller design of hemispherical resonator gyros. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2013, 14, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlyab, M.; Pedram, M.Z.; Salarieh, H.; Alasty, A. Parameter estimation and interval type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control of a z-axis MEMS gyroscope. ISA Trans. 2013, 52, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Král, L. Parameter estimation of MEMS gyroscope using local state estimation methods. IFAC-Pap. 2015, 48, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Wu, X. Adaptive compensation of damping asymmetry in whole-angle hemispherical resonator gyroscope. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gallacher, B. Extended Kalman filtering based parameter estimation and drift compensation for a MEMS rate integrating gyroscope. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 250, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lu, K.; Xi, X.; Wu, X.; Xiao, D. Characterization and compensation of detection electrode errors for whole-angle micro-shell resonator gyroscope. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2021, 31, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanparvar, D.; Shkel, A.M. Identification of gain mismatches in control electronics of rate integrating CVGs. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Kailua-Kona, HI, USA, 22–25 March 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Lin, C.; Su, Y. Rate-integration gyroscope (RIG) with gain self calibration. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Gao, Z.; Nan, F.; Zhang, Y. Single-channel control for hemispherical resonator gyro based on time division multiplexing and demultiplexing. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 21342–21348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D. Vibratory Gyro Analysis by the Method of Averaging. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Gyroscopic Technology and Navigation, St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–25 May 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri-Tehrani, P.; Challoner, A.D.; Izyumin, O.; Boser, B.; Horsley, D. A new electronic feedback compensation method for rate integrating gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems, Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 February 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, D.D. MRIG frequency mismatch and quadrature control. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (ISISS), Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 25–26 February 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Luo, B.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q. Force to rebalance control of HRG and suppression of its errors on the basis of FPGA. Sensors 2011, 11, 11761–11773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, P. Full digital control of hemispherical resonator gyro under force-to-rebalance mode. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri-Tehrani, P.; Challoner, A.D.; Horsley, D.A. Micromechanical rate integrating gyroscope with angle-dependent bias compensation using a self-precession method. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3533–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, R.; Yang, G.; Cai, Q.; Yi, X.; Tu, Y. Identification and Compensation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Errors for Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscopes in Whole-Angle Mode. Actuators 2025, 14, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060275
Cheng R, Yang G, Cai Q, Yi X, Tu Y. Identification and Compensation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Errors for Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscopes in Whole-Angle Mode. Actuators. 2025; 14(6):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060275
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ruizhao, Gongliu Yang, Qingzhong Cai, Xiaodi Yi, and Yongqiang Tu. 2025. "Identification and Compensation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Errors for Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscopes in Whole-Angle Mode" Actuators 14, no. 6: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060275
APA StyleCheng, R., Yang, G., Cai, Q., Yi, X., & Tu, Y. (2025). Identification and Compensation of Detection Gain Asymmetry Errors for Hemispherical Resonant Gyroscopes in Whole-Angle Mode. Actuators, 14(6), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060275





