An Adaptive BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearing in Aerospace Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Attention Mechanism in Bearing Remaining Life Prediction
2.2. Handcrafted Features in Bearing Remaining Life Prediction
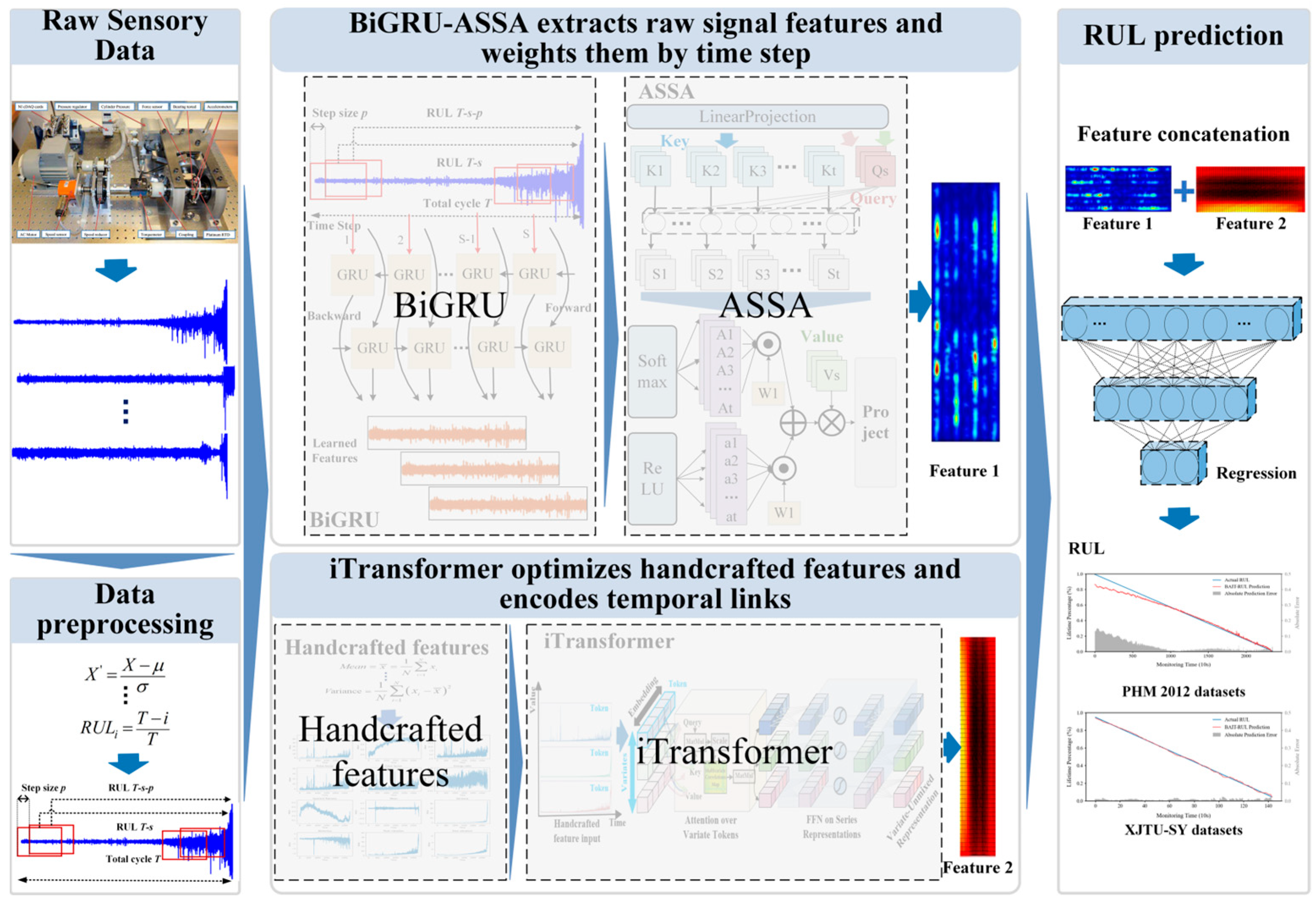
3. Methods
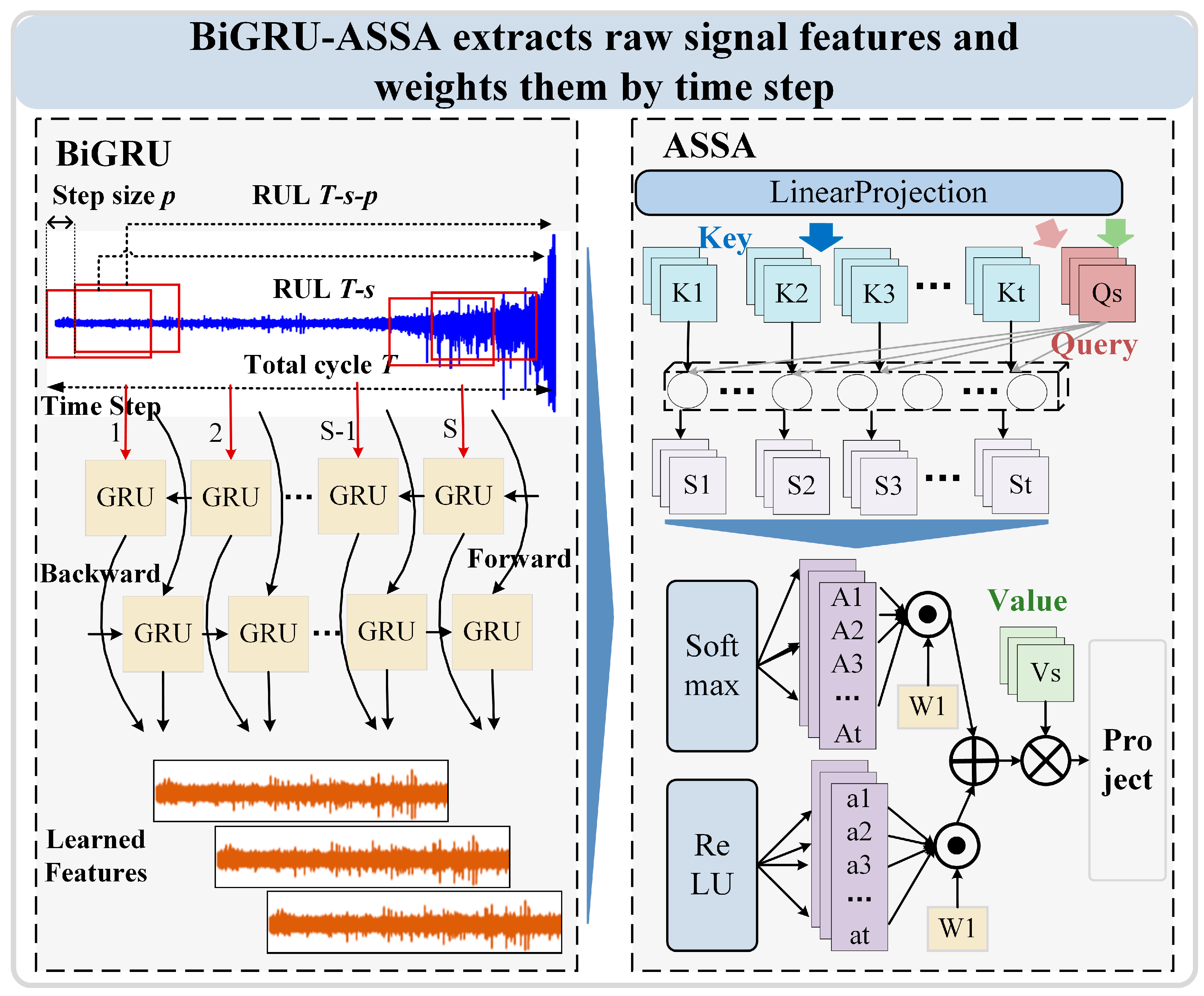
3.1. BiGRU-ASSA Module
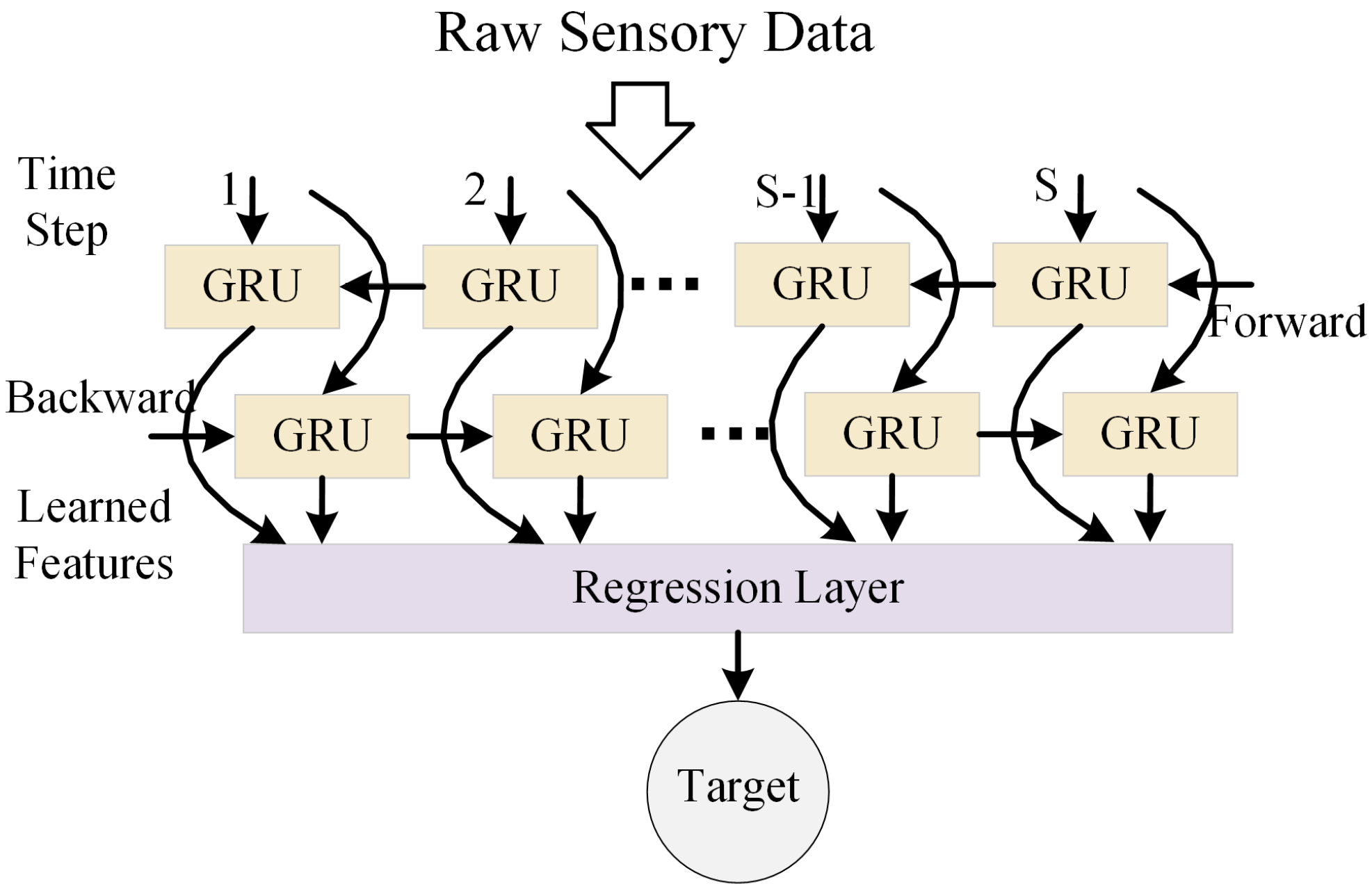
3.1.1. Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit
3.1.2. Adaptive Sparse Self-Attention
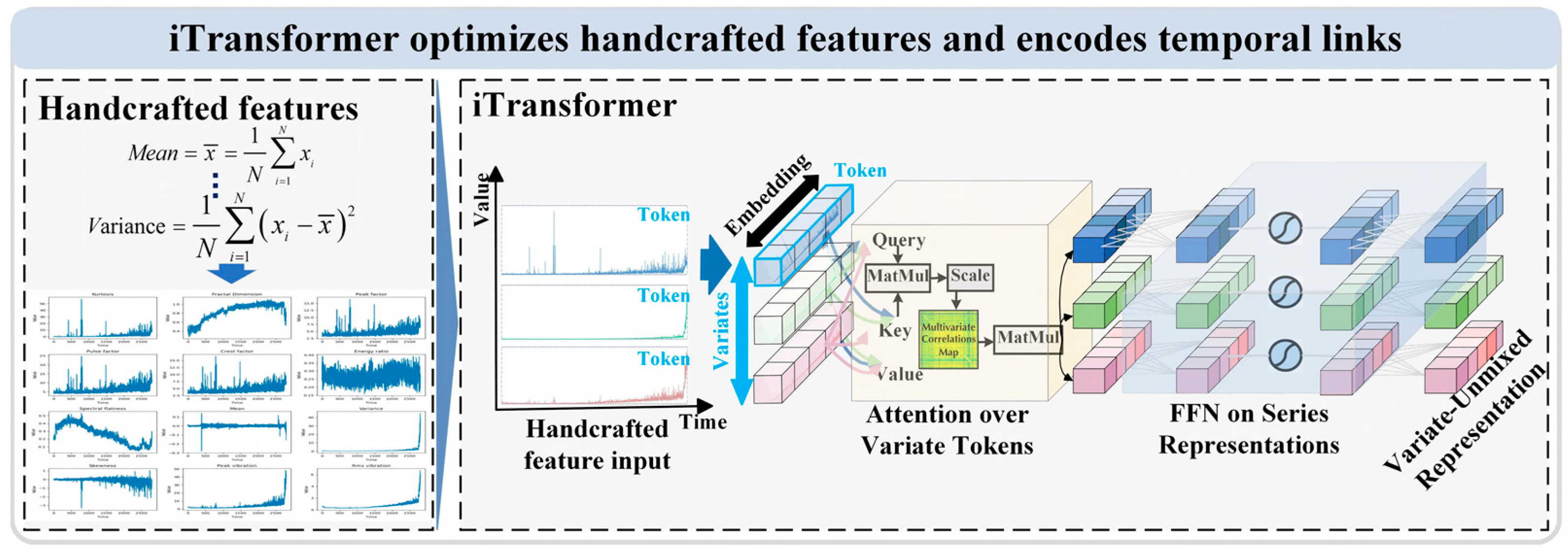
3.2. iTransformer Module
3.2.1. Handcrafted Features
3.2.2. iTransformer
- Feature embedding (Embedding)
- 2.
- Inter-feature interaction modeling (Self-Attention)
- 3.
- Time-dependent modeling (FFN)
3.3. Experimental Setup
3.3.1. Bearing Datasets
- PRONOSTIA Dataset
- 2.
- XJTU-SY Dataset
3.3.2. Data Preprocessing
- (1)
- Data Normalization
- (2)
- Sliding Window Division
- (3)
- RUL Label Calculation
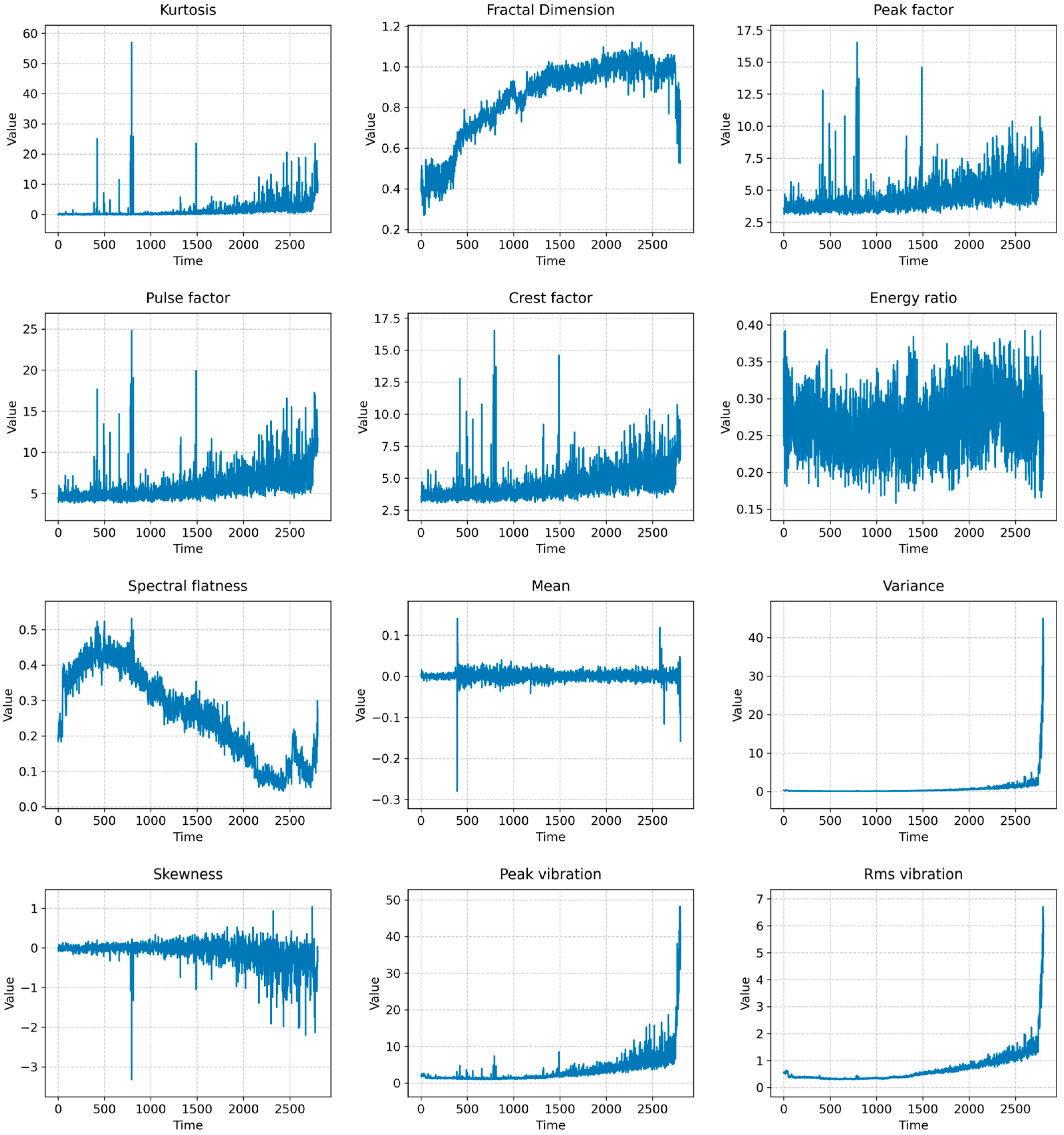
3.3.3. Handcrafted Features Calculation
3.3.4. Evaluation Metrics
- Root mean square error (RMSE):
- 2.
- Mean absolute error (MAE):
3.3.5. Model Parameters
4. Results
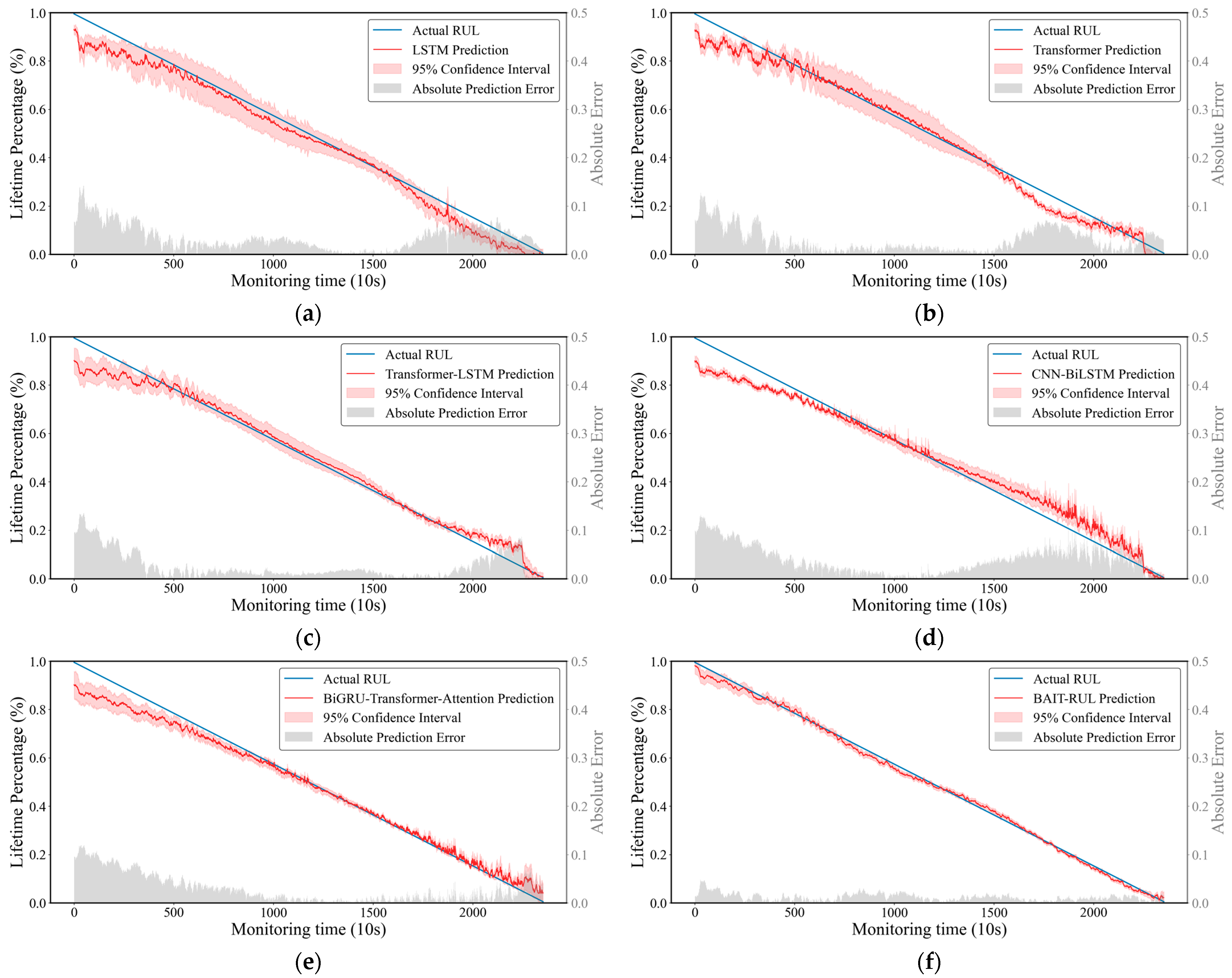
4.1. Experimental Results
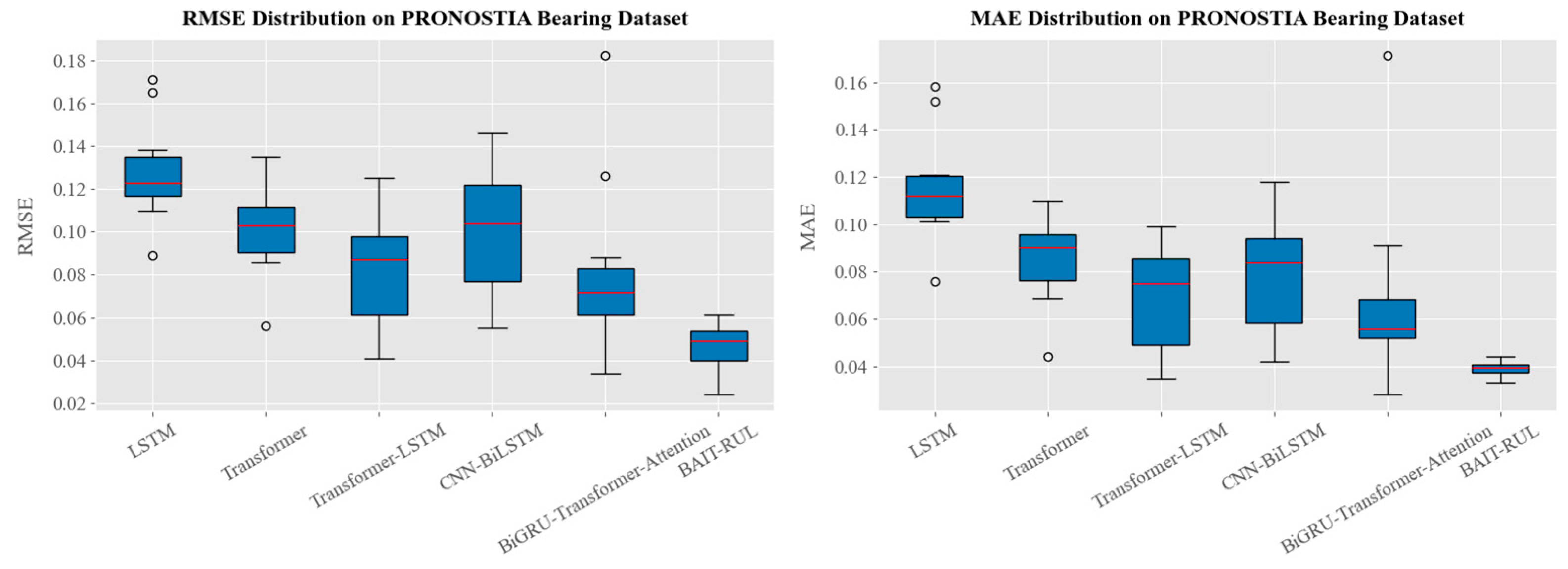
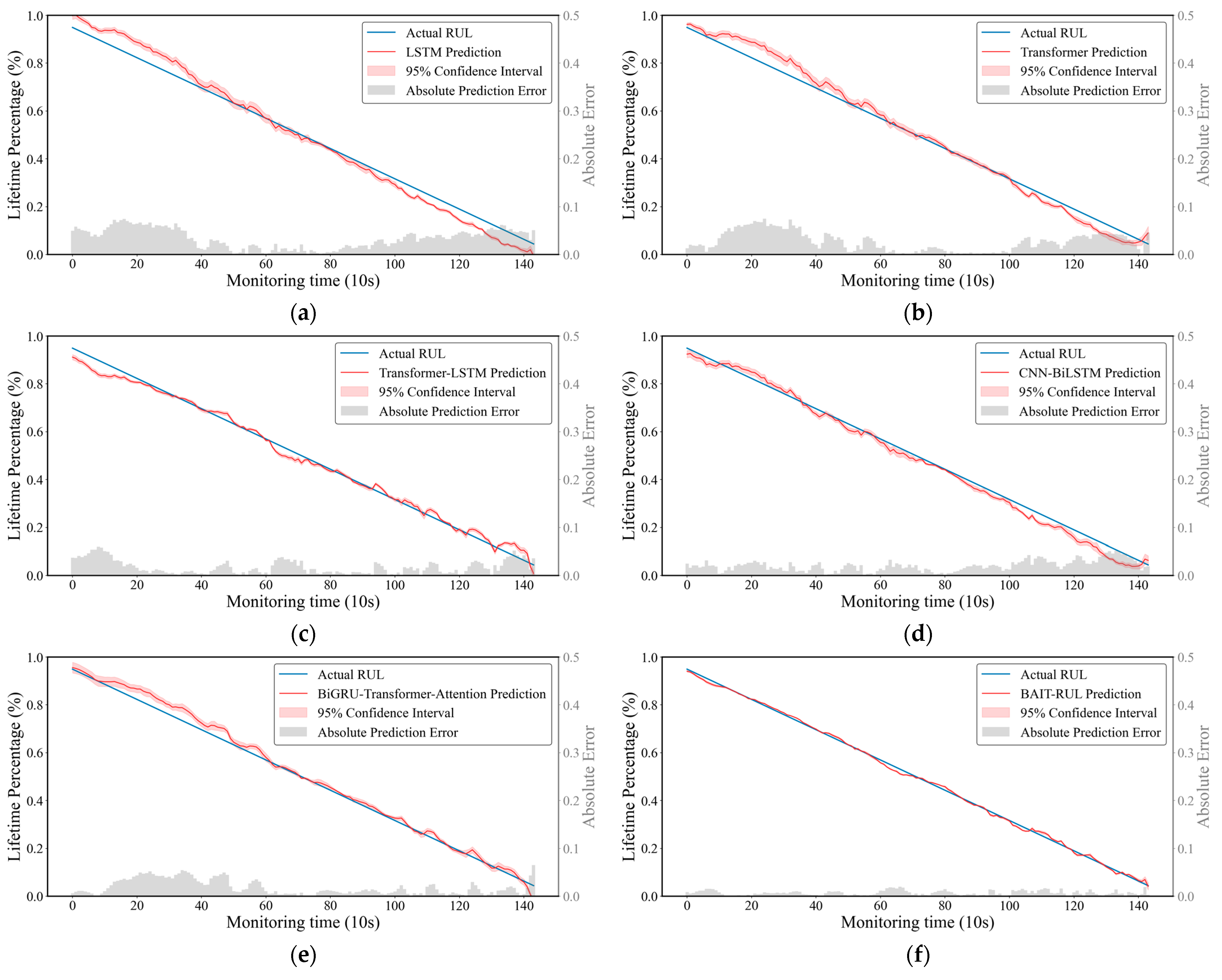
4.1.1. PRONOSTIA Bearing Dataset
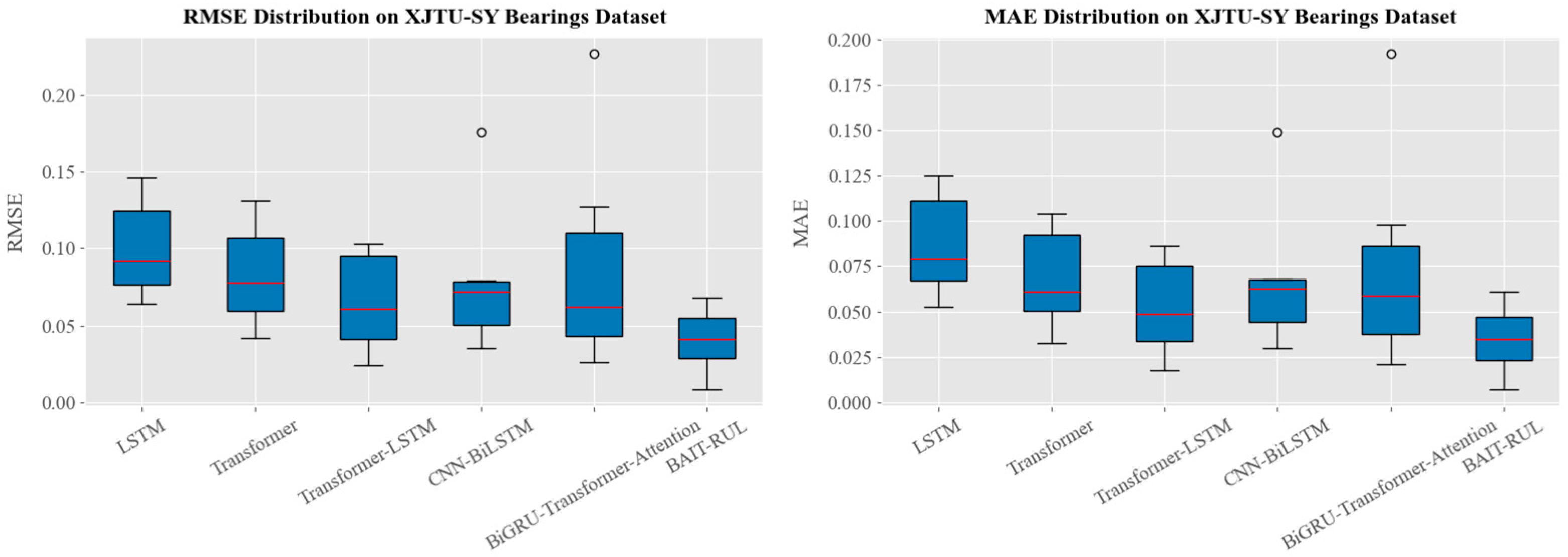
4.1.2. XJTU-SY Bearing Dataset
5. Discussion
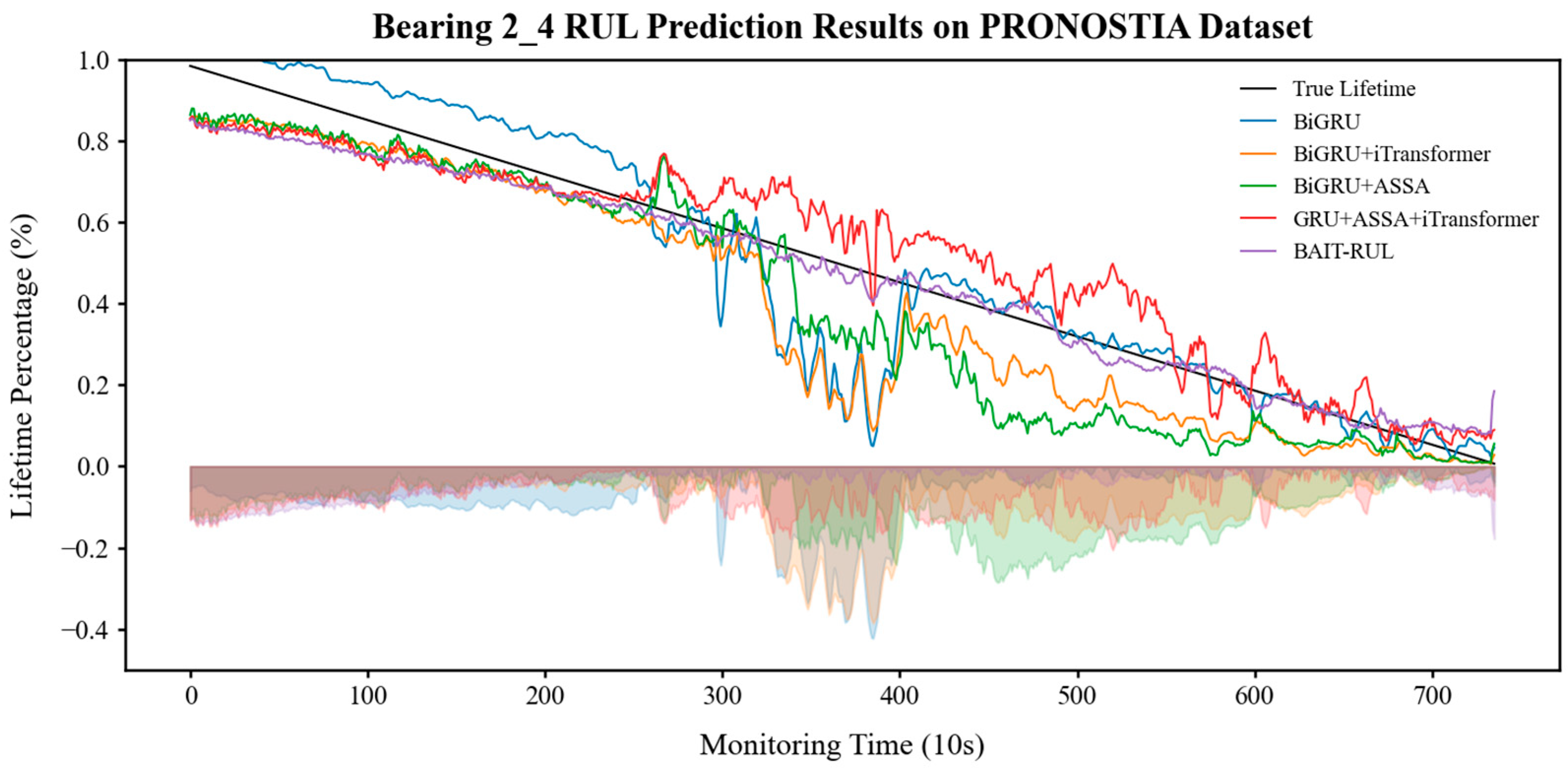
5.1. Ablation Experiment
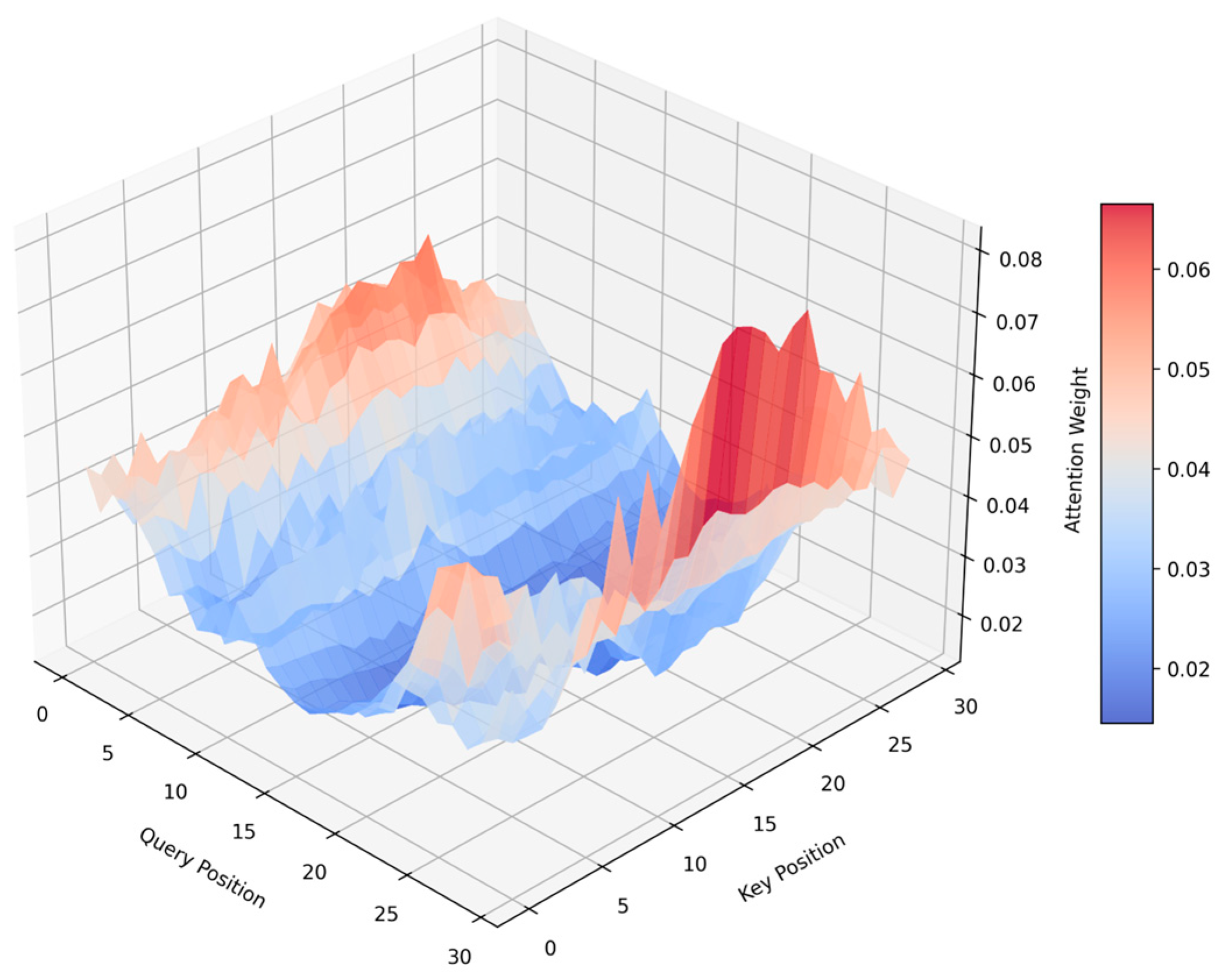
5.2. Impact of ASSA on Feature Weighting in RUL Prediction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RUL | Remaining useful life |
| BiGRU | Bidirectional gated recurrent unit |
| ASSA | Adaptive sparse self-attention |
| BAIT-RUL | BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer for remaining useful life prediction |
| GRU | Gated recurrent unit |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory network |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
References
- Yang, G.; Tan, Q.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, K.; Lu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, P. Integrated Optimization of Process Planning and Scheduling for Aerospace Complex Component Based on Honey-Bee Mating Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulou, E.; Daskalakis, E. Applications and Technologies of Big Data in the Aerospace Domain. Electronics 2023, 12, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, W. Optimization Method of Spindle Speed with the Consideration of Chatter and Forced Vibration for Five-Axis Flank Milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yin, M.; Cao, L.; Xie, L.-F.; Wang, X.-J.; Yin, G.-F. Study on the Thermally Induced Spindle Angular Errors of a Five-Axis CNC Machine Tool. Adv. Manuf. 2023, 11, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, T.; Su, Z. Prediction of Five-Axis Machining-Induced Residual Stress Based on Cutting Parameter Identification. J. Manuf. Processes 2023, 103, 320–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Liu, Y.; Ding, L.; Safian, A.; Liang, X. A New Structured Domain Adversarial Neural Network for Transfer Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearings under Different Working Conditions. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3509013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ma, B.; Fan, Y.; Ding, X. ATPRINPM: A Single-Source Domain Generalization Method for the Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Unknown Bearings. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the Era of Artificial Intelligence (ICSMD), Harbin, China, 30 November–2 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Chen, Z.; Mao, W.; Li, W. Transfer Learning Algorithms for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction: A Comprehensive Review from an Industrial Application Perspective. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 193, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Hei, X.; Shangguan, A. An Improved Nonlinear Health Index CRRMS for the Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings. Actuators 2025, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Prediction of Remaining Service Life of Rolling Bearings Based on Convolutional and Bidirectional Long- and Short-Term Memory Neural Networks. Lubricants 2022, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhao, R.; Guretno, F.; Yan, R.; Li, X. Machine Remaining Useful Life Prediction via an Attention-Based Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2521–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, D.; Pan, J.; Shi, J.; Yang, J. Adapt or Perish: Adaptive Sparse Transformer with Attentive Feature Refinement for Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16 June 2024; pp. 2952–2963. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Long, M. iTransformer: Inverted Transformers Are Effective for Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.06625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, H.; Jin, M.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Mu, Y.; Hong, Z. RUL Prediction of Rolling Bearings Based on Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm Optimized CNN-LSTM Neural Network. Lubricants 2025, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutin, D.; Bondarenko, M.; Polyakov, R.; Stebakov, I.; Savin, L. Method for On-Line Remaining Useful Life and Wear Prediction for Adjustable Journal Bearings Utilizing a Combination of Physics-Based and Data-Driven Models: A Numerical Investigation. Lubricants 2023, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, D.; Terpenny, J. Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction Using Self-Adaptive Graph Convolutional Networks with Self-Attention Mechanism. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 188, 110010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.S.; Harsha, S.P. An Attention-Based Stacked BiLSTM Framework for Predicting Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Bearings. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 131, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-I.; Song, J.W.; Kang, S.-J. Pseudo-Label-Vector-Guided Parallel Attention Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2023, 19, 5602–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L. Multi-Head Attention Network with Adaptive Feature Selection for RUL Predictions of Gradually Degrading Equipment. Actuators 2023, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Jiang, B.; Mao, Z.; Liu, S. Local Enhancing Transformer with Temporal Convolutional Attention Mechanism for Bearings Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3522312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Fan, P.; Mbeka, E. The Effect of the Head Number for Multi-Head Self-Attention in Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearing and Interpretability. Neurocomputing 2025, 616, 128946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Chen, X. Information Guided Attention Network for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction Adaptive to Working Conditions and Fault Modes. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 147, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Ming, W.; Chen, M. Long-Term Temporal Attention Neural Network with Adaptive Stage Division for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 251, 110218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. LSTM Networks Based on Attention Ordered Neurons for Gear Remaining Life Prediction. ISA Trans. 2020, 106, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Tang, J. A Wavelet Neural Network Informed by Time-Domain Signal Preprocessing for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Appl. Math. Modell. 2023, 122, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, J.; Duan, Y.; Guo, X. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearing Based on Multi-Domain Mixed Features and Temporal Convolutional Networks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, S.G.; Huang, T.; Zhou, H.; Bai, S.; Huang, H.-Z. Multi-Scale Time Series Analysis Using TT-ConvLSTM Technique for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 206, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, T. A Novel Based-Performance Degradation Indicator RUL Prediction Model and Its Application in Rolling Bearing. ISA Trans. 2022, 121, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Han, H. Digital Twin-Driven Graph Domain Adaptation Neural Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Rolling Bearing. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 245, 109991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bashir, M.; Liu, Q.; Miao, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ekere, N. A Novel Health Indicator for Intelligent Prediction of Rolling Bearing Remaining Useful Life Based on Unsupervised Learning Model. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 176, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Su, S.; Li, X.; Ding, W.; Feng, K. GRU-AE-Wiener: A Generative Adversarial Network Assisted Hybrid Gated Recurrent Unit with Wiener Model for Bearing Remaining Useful Life Estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 220, 111663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y. The Application of a BiGRU Model with Transformer-Based Error Correction in Deformation Prediction for Bridge SHM. Buildings 2025, 15, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; He, S.; Song, J. A Hybrid Algorithm for Predicting the Remaining Service Life of Hybrid Bearings Based on Bidirectional Feature Extraction. Measurement 2025, 242, 116152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Deep Transfer Network Based on Dual-Task Learning for Predicting the Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Bearings. Available online: https://colab.ws/articles/10.1088%2F1361-6501%2Fadafd2 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Nectoux, P.; Gouriveau, R.; Medjaher, K.; Ramasso, E.; Chebel-Morello, B.; Zerhouni, N.; Varnier, C. PRONOSTIA: An Experimental Platform for Bearings Accelerated Degradation Tests. In Proceedings of the Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, IEEE Catalog Number: CPF12PHM-CDR. Denver, CO, USA, 18–21 June 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Han, T.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Yan, T.; Yang, J. XJTU-SY Rolling Element Bearing Accelerated Life Test Datasets: A Tutorial. Researchgate 2019, 16, 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Li, N. A Hybrid Prognostics Approach for Estimating Remaining Useful Life of Rolling Element Bearings. IEEE Trans. Rel. 2020, 69, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Ma, S.; Cao, W.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Fan, F.; Wang, X. A Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method of Rolling Bearings by RSA-BAFT Combined with Copula Entropy Feature Selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 275, 127100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Luo, L. A Stage-Related Online Incremental Transfer Learning-Based Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method of Bearings. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 169, 112491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Mao, Z. Deep-Convolution-Based LSTM Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2021, 17, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seo, Y.-H.; Park, J. Transformer-Based Novel Framework for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lubricant in Operational Rolling Bearings. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 251, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Zhai, X.; Yin, D.; Qiao, F. A Method of Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Multi-Source Signals Aero-Engine Based on RF-Transformer-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; pp. 2502–2507. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Yan Yang, Y.Y.; Junyu Guo, J.G.; Le Dai, L.D. A Hybrid CNN-BiLSTM and Wiener Process-Based Prediction Approach of Remaining Useful Life for Rolling Bearings. Comput. Res. Prog. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Hao, J. Residual Life Prediction of Rolling Bearings Based on Transformer-BiGRU-Attention Model with Improved Sparrow Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the TEPEN International Workshop on Fault Diagnostic and Prognostic, Qingdao, China, 8–11 May 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 23–33. [Google Scholar]
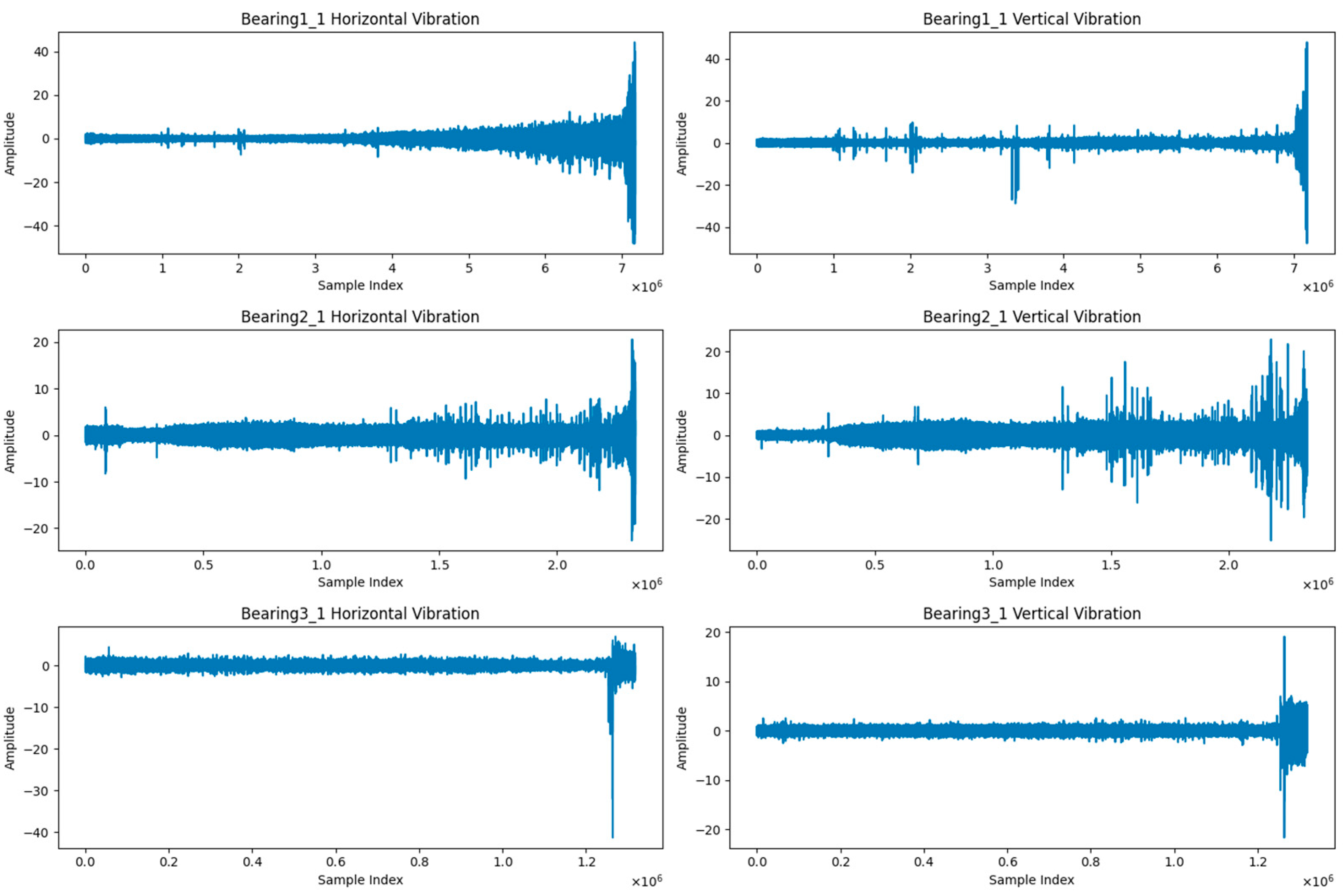
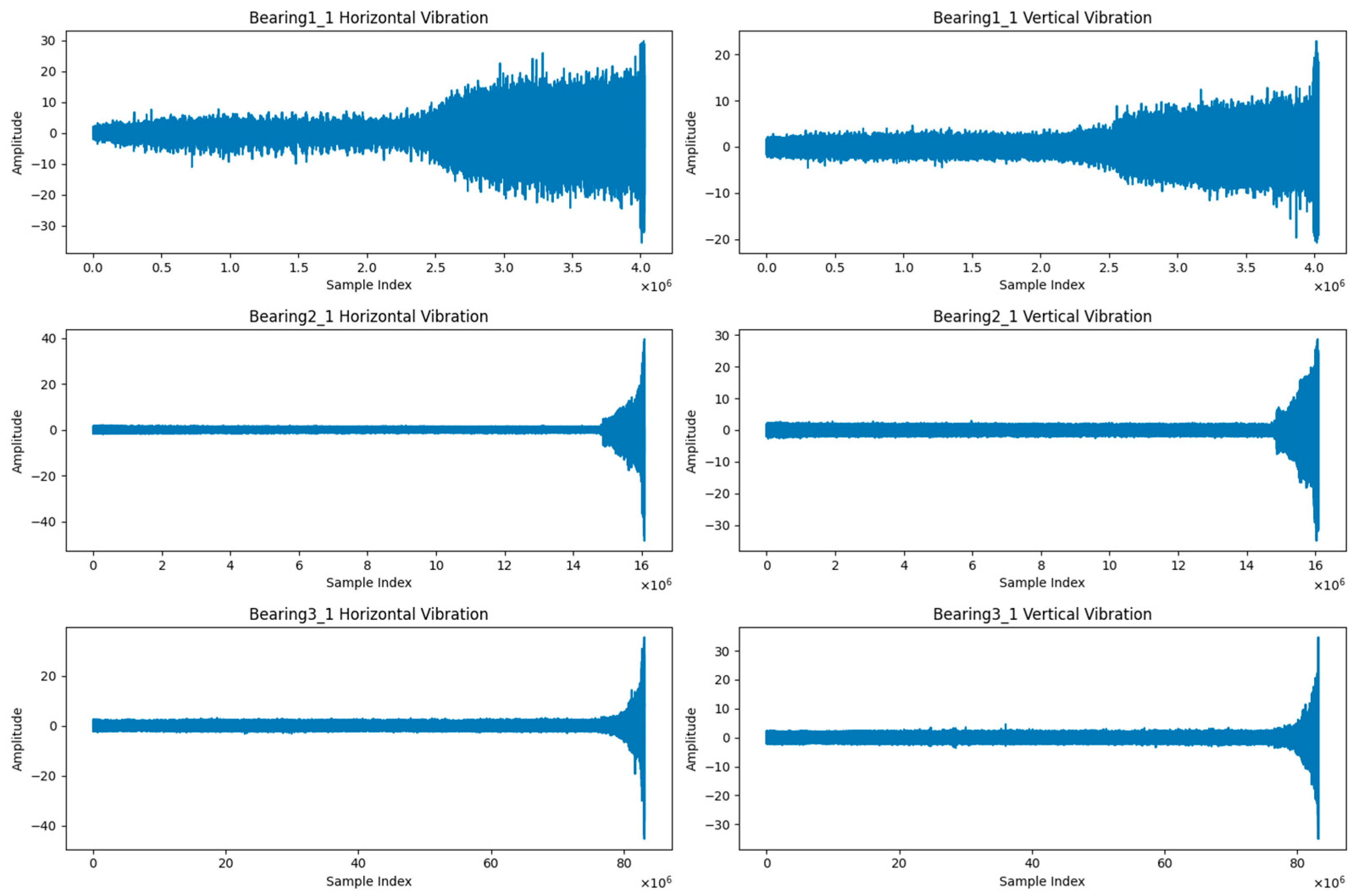
| Datasets | Operating Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions 1 | Conditions 2 | Conditions 3 | |
| Learning set | Bearing1_1 | Bearing2_1 | Bearing3_1 |
| Bearing1_2 | Bearing2_2 | Bearing3_2 | |
| Test set | Bearing1_3 | Bearing2_3 | Bearing3_3 |
| Bearing1_4 | Bearing2_4 | ||
| Bearing1_5 | Bearing2_5 | ||
| Bearing1_6 | Bearing2_6 | ||
| Bearing1_7 | Bearing2_7 | ||
| Datasets | Operating Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions 1 | Conditions 2 | Conditions 3 | |
| Learning set | Bearing1_1 Bearing1_2 | Bearing2_1 | Bearing3_1 |
| Bearing2_2 | Bearing3_2 | ||
| Bearing2_3 | Bearing3_3 | ||
| Test set | Bearing1_3 | Bearing2_4 Bearing2_5 | Bearing3_4 Bearing3_5 |
| Bearing1_4 | |||
| Bearing1_5 | |||
| Condition | Dataset | Sample Size | Work Time | Fault Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bearing1_1 | 123 | 2 h 3 min | Outer race fault |
| Bearing1_2 | 161 | 2 h 41 min | Outer race fault | |
| Bearing1_3 | 158 | 2 h 38 min | Outer race fault | |
| Bearing1_4 | 122 | 2 h 2 min | Cage fault | |
| Bearing1_5 | 52 | 52 min | Inner race fault | |
| 2 | Bearing2_1 | 491 | 8 h 11 min | Inner race fault |
| Bearing2_2 | 161 | 2 h 41 min | Outer race fault | |
| Bearing2_3 | 533 | 8 h 53 min | Cage fault | |
| Bearing2_4 | 42 | 42 min | Outer race fault | |
| Bearing2_5 | 339 | 5 h 39 min | Outer race fault | |
| 3 | Bearing3_1 | 2538 | 42 h 18 min | Outer race fault |
| Bearing3_2 | 2496 | 41 h 18 min | Compound fault | |
| Bearing3_3 | 371 | 6 h 11 min | Inner race fault | |
| Bearing3_4 | 1515 | 25 h 15 min | Inner race fault | |
| Bearing3_5 | 114 | 1 h 54 min | Outer race fault |
| Test Bearing | LSTM | Transformer | Transformer-LSTM | CNN-BiLSTM | BiGRU-Transformer-Attention | BAIT-RUL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |
| Bearing1_3 | 0.110 | 0.102 | 0.086 | 0.069 | 0.054 | 0.050 | 0.081 | 0.063 | 0.052 | 0.035 | 0.038 | 0.033 |
| Bearing1_4 | 0.116 | 0.104 | 0.090 | 0.071 | 0.063 | 0.045 | 0.095 | 0.078 | 0.034 | 0.028 | 0.046 | 0.036 |
| Bearing1_5 | 0.123 | 0.112 | 0.091 | 0.082 | 0.080 | 0.067 | 0.058 | 0.042 | 0.068 | 0.056 | 0.024 | 0.016 |
| Bearing1_6 | 0.118 | 0.101 | 0.103 | 0.091 | 0.101 | 0.085 | 0.073 | 0.054 | 0.074 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.044 |
| Bearing1_7 | 0.132 | 0.121 | 0.106 | 0.090 | 0.059 | 0.048 | 0.104 | 0.091 | 0.063 | 0.054 | 0.048 | 0.042 |
| Bearing2_3 | 0.138 | 0.120 | 0.123 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 0.088 | 0.124 | 0.097 | 0.072 | 0.054 | 0.061 | 0.039 |
| Bearing2_4 | 0.171 | 0.158 | 0.135 | 0.110 | 0.125 | 0.099 | 0.121 | 0.097 | 0.088 | 0.076 | 0.054 | 0.040 |
| Bearing2_5 | 0.165 | 0.152 | 0.117 | 0.104 | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.146 | 0.118 | 0.126 | 0.091 | 0.082 | 0.062 |
| Bearing2_6 | 0.123 | 0.112 | 0.098 | 0.082 | 0.090 | 0.075 | 0.120 | 0.090 | 0.078 | 0.061 | 0.054 | 0.038 |
| Bearing2_7 | 0.131 | 0.109 | 0.105 | 0.090 | 0.097 | 0.086 | 0.123 | 0.084 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.040 |
| Bearing3_3 | 0.089 | 0.076 | 0.056 | 0.044 | 0.041 | 0.035 | 0.055 | 0.042 | 0.182 | 0.171 | 0.029 | 0.021 |
| Test Bearing | LSTM | Transformer | Transformer-LSTM | CNN-BiLSTM | BiGRU-Transformer-Attention | BAIT-RUL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |
| Bearing1_3 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.042 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.024 | 0.035 | 0.030 | 0.026 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.007 |
| Bearing1_4 | 0.129 | 0.108 | 0.102 | 0.086 | 0.091 | 0.072 | 0.078 | 0.063 | 0.093 | 0.074 | 0.034 | 0.026 |
| Bearing1_5 | 0.087 | 0.076 | 0.068 | 0.055 | 0.052 | 0.044 | 0.072 | 0.067 | 0.062 | 0.059 | 0.046 | 0.042 |
| Bearing2_4 | 0.066 | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.046 | 0.024 | 0.018 | 0.056 | 0.052 | 0.052 | 0.047 | 0.041 | 0.035 |
| Bearing2_5 | 0.120 | 0.114 | 0.112 | 0.104 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 0.176 | 0.149 | 0.227 | 0.192 | 0.068 | 0.061 |
| Bearing3_4 | 0.092 | 0.079 | 0.078 | 0.061 | 0.061 | 0.049 | 0.045 | 0.037 | 0.034 | 0.029 | 0.023 | 0.021 |
| Bearing3_5 | 0.146 | 0.125 | 0.131 | 0.098 | 0.099 | 0.086 | 0.079 | 0.068 | 0.127 | 0.098 | 0.064 | 0.053 |
| Test Bearing | BiGRU | BiGRU + iTransformer | BiGRU + ASSA | GRU + ASSA + iTransformer | BAIT-RUL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | ||
| PRONOSTIA | Bearing1_3 | 0.098 | 0.090 | 0.067 | 0.058 | 0.048 | 0.034 | 0.076 | 0.061 | 0.038 | 0.033 |
| Bearing2_4 | 0.119 | 0.090 | 0.066 | 0.058 | 0.069 | 0.054 | 0.071 | 0.048 | 0.054 | 0.040 | |
| XJTU-SY | Bearing1_3 | 0.068 | 0.055 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.020 | 0.018 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.007 |
| Bearing2_5 | 0.199 | 0.168 | 0.071 | 0.063 | 0.150 | 0.130 | 0.187 | 0.156 | 0.068 | 0.061 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, J. An Adaptive BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearing in Aerospace Manufacturing. Actuators 2025, 14, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14050238
Lyu Y, Qiu Q, Chu Y, Zhang J. An Adaptive BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearing in Aerospace Manufacturing. Actuators. 2025; 14(5):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14050238
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Youlong, Qingpeng Qiu, Ying Chu, and Jie Zhang. 2025. "An Adaptive BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearing in Aerospace Manufacturing" Actuators 14, no. 5: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14050238
APA StyleLyu, Y., Qiu, Q., Chu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). An Adaptive BiGRU-ASSA-iTransformer Method for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Bearing in Aerospace Manufacturing. Actuators, 14(5), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14050238






