Effectiveness of Powered Hand Exoskeleton on Upper Extremity Function in People with Chronic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
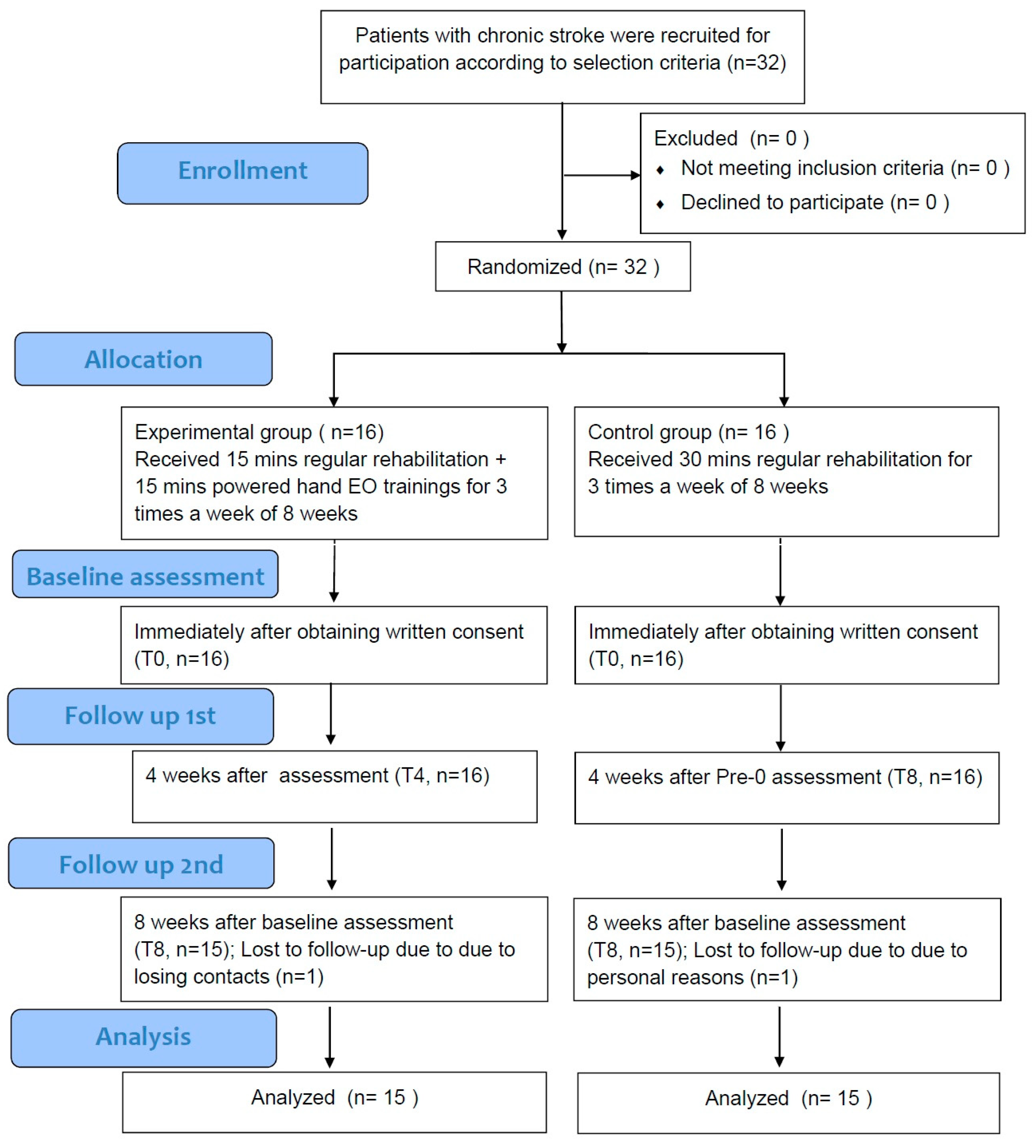
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Trial Participants
2.2. Intervention
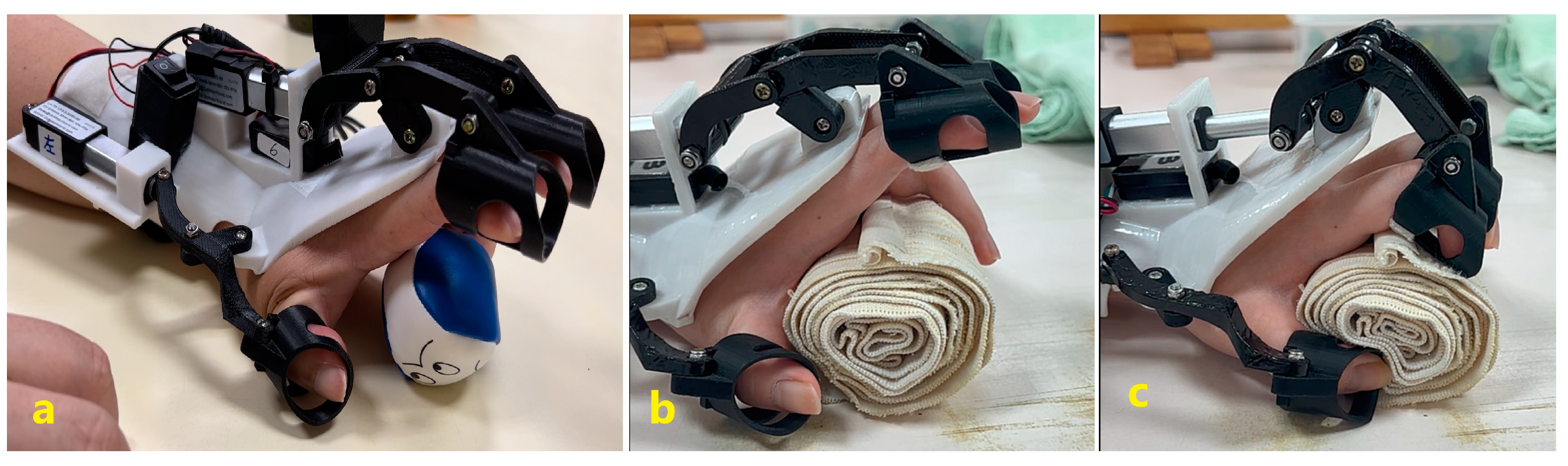
2.3. Powered Hand EO Design
2.4. Assessments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Participants
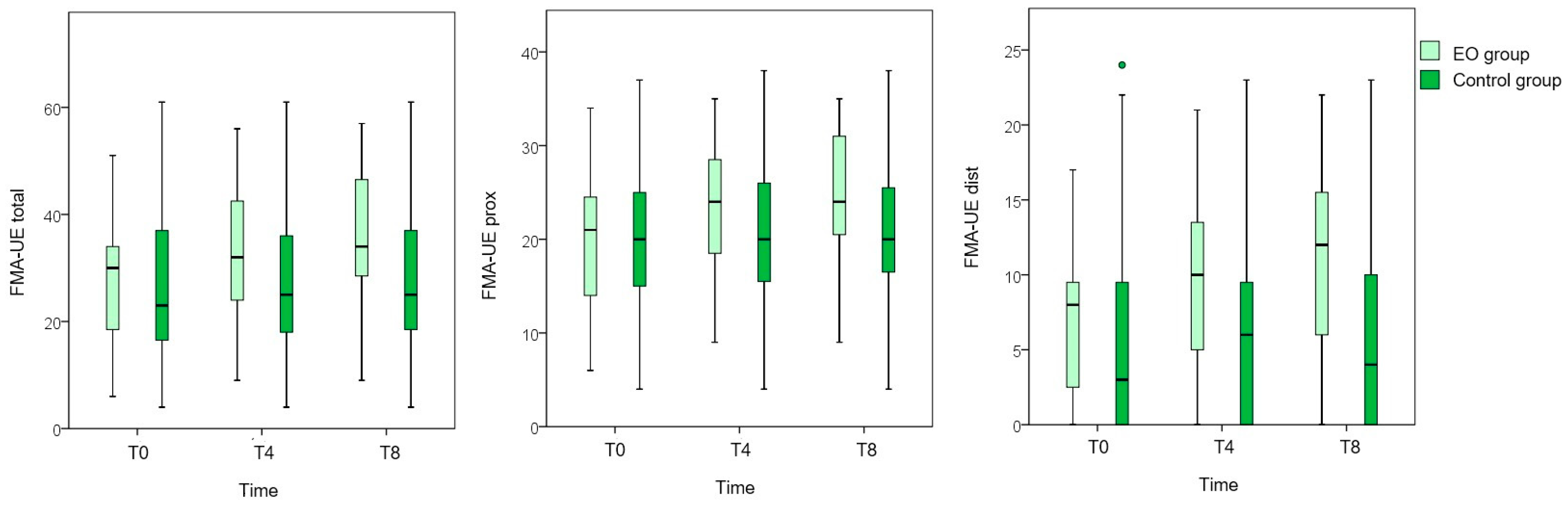
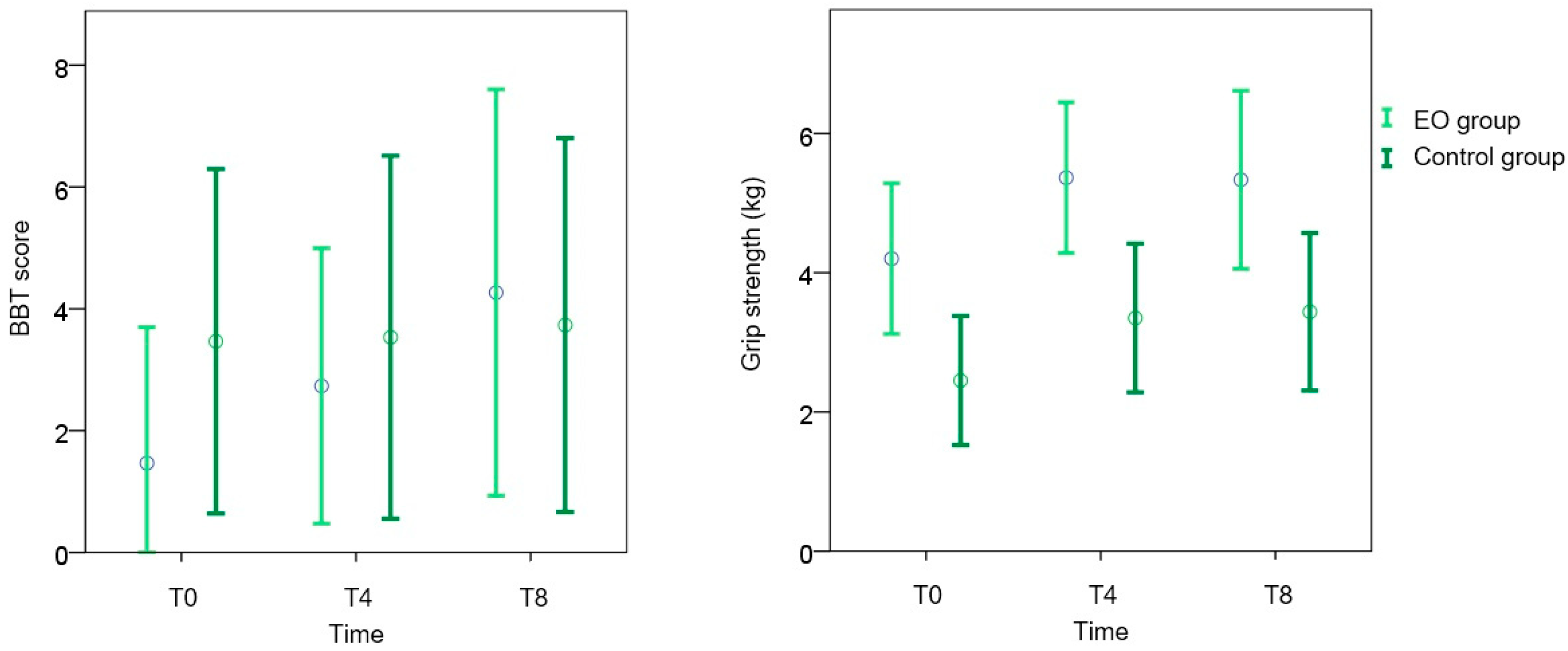
3.2. Primary Outcome Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.J.; Wagenaar, R.C. Therapy impact on functional recovery in stroke rehabilitation: A critical review of the literature. Physiotherapy 1999, 85, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Coupar, F.; Pollock, A. Motor recovery after stroke: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-H.; Hsu, S.-S.; Yip, P.-K.; Jeng, J.-S.; Wang, Y.-H. Early and intensive rehabilitation predicts good functional outcomes in patients admitted to the stroke intensive care unit. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijn, C.J.; Hankey, G.J. Management of acute ischaemic stroke: New guidelines from the American Stroke Association and European Stroke Initiative. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, E.; Hillier, S.; Cadilhac, D. When should physical rehabilitation commence after stroke: A systematic review. Int. J. Stroke 2014, 9, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, B.; Thomas, L.H.; Coupe, J.; McMahon, N.E.; Connell, L.; Harrison, J.; Sutton, C.J.; Tishkovskaya, S.; Watkins, C.L. Repetitive task training for improving functional ability after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD006073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Howe, T.-H. Effectiveness of Activity-Based Task-Oriented Training on Upper Extremity Recovery for Adults with Stroke: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2024, 78, 7802180070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozevink, S.G.; Hijmans, J.M.; Horstink, K.A.; van der Sluis, C.K. Effectiveness of task-specific training using assistive devices and task-specific usual care on upper limb performance after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2023, 18, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, K.N.; Pandian, S.; Verma, R.; Garg, R. Movement therapy induced neural reorganization and motor recovery in stroke: A review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2011, 15, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.L. Improving poststroke recovery: Neuroplasticity and task-oriented training. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 11, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Ballester, B.R.; Verschure, P.F. Principles of neurorehabilitation after stroke based on motor learning and brain plasticity mechanisms. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauraugh, J.H.; Summers, J.J. Neural plasticity and bilateral movements: A rehabilitation approach for chronic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 75, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.B. Brain plasticity and stroke rehabilitation: The Willis lecture. Stroke 2000, 31, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, J.H.; Shepherd, R.B. Neurological Rehabilitation: Optimizing Motor Performance; Elsevier Health Sciences: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.H.; Kim, Y.-H. Robot-assisted therapy in stroke rehabilitation. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basteris, A.; Nijenhuis, S.M.; Stienen, A.H.; Buurke, J.H.; Prange, G.B.; Amirabdollahian, F. Training modalities in robot-mediated upper limb rehabilitation in stroke: A framework for classification based on a systematic review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerbeek, J.M.; Langbroek-Amersfoort, A.C.; Van Wegen, E.E.; Meskers, C.G.; Kwakkel, G. Effects of robot-assisted therapy for the upper limb after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duret, C.; Grosmaire, A.-G.; Krebs, H.I. Robot-assisted therapy in upper extremity hemiparesis: Overview of an evidence-based approach. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejasz, P.; Eschweiler, J.; Gerlach-Hahn, K.; Jansen-Troy, A.; Leonhardt, S. A survey on robotic devices for upper limb rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteni, F.; Gasperini, G.; Cannaviello, G.; Guanziroli, E. Exoskeleton and end-effector robots for upper and lower limbs rehabilitation: Narrative review. PM&R 2018, 10, S174–S188. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, G.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-B.; Shin, J.-H. Comparisons between end-effector and exoskeleton rehabilitation robots regarding upper extremity function among chronic stroke patients with moderate-to-severe upper limb impairment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moggio, L.; De Sire, A.; Marotta, N.; Demeco, A.; Ammendolia, A. Exoskeleton versus end-effector robot-assisted therapy for finger-hand motor recovery in stroke survivors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2022, 29, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.; Chong, Y.; Tse, M.; Chien, C.; Cheng, H. Robot-assisted therapy for upper-limb rehabilitation in subacute stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaiasl, M.; Mahdioun, S.H.; Jaryani, P.; Yazdani, M. A review of technological and clinical aspects of robot-aided rehabilitation of upper-extremity after stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2016, 11, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Naghdy, F.; Naghdy, G.; Du, H.; Todd, C. Robot-assisted post-stroke motion rehabilitation in upper extremities: A survey. Int. J. Disabil. Hum. Dev. 2017, 16, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Hand rehabilitation robotics on poststroke motor recovery. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 3908135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarac, M.; Solazzi, M.; Frisoli, A. Design requirements of generic hand exoskeletons and survey of hand exoskeletons for rehabilitation, assistive, or haptic use. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2019, 12, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiboni, M.; Borboni, A.; Vérité, F.; Bregoli, C.; Amici, C. Sensors and actuation technologies in exoskeletons: A review. Sensors 2022, 22, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.C.; Moioli, R.C.; Brasil, F.L.; Vallejo, M.; Corne, D.W.; Vargas, P.A.; Stokes, A.A. Robotic devices and brain-machine interfaces for hand rehabilitation post-stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.D. Studies to Determine the Functional Requirements for Hand and Arm Prosthesis; Department of Engineering University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, K.; Cano, S.J.; Playford, E.D. Outcome measurement in stroke: A scale selection strategy. Stroke 2011, 42, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Lannin, N.A.; Borschmann, K.; English, C.; Ali, M.; Churilov, L.; Saposnik, G.; Winstein, C.; Van Wegen, E.E.; Wolf, S.L. Standardized measurement of sensorimotor recovery in stroke trials: Consensus-based core recommendations from the stroke recovery and rehabilitation roundtable. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.J.; Levine, P.; Hade, E. Psychometric properties and administration of the wrist/hand subscales of the Fugl-Meyer Assessment in minimally impaired upper extremity hemiparesis in stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 2373–2376.e2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, C.B.; Maribo, T. The Fugl–Meyer assessment of the upper extremity: Reliability, responsiveness and validity of the Danish version. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, E.D.; Galeano, C.P.; Barbosa, N.E.; Forero, S.M.; Nordin, Å.; Sunnerhagen, K.S.; Alt Murphy, M. Intra-and inter-rater reliability of Fugl-Meyer assessment of upper extremity in stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Chen, C.C.; Hsueh, I.-P.; Huang, S.-L.; Hsieh, C.-L. Test-retest reproducibility and smallest real difference of 5 hand function tests in patients with stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebers, A.; Öberg, U.; Skargren, E. The effect of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on spasticity and motor function of the affected arm in patients with chronic stroke. Physiother. Can. 2010, 62, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Qin, Q.; Suen, L.K.P.; Liang, G.; Qin, H.; Zhang, L. Effects of wearable device training on upper limb motor function in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2024, 52, 03000605241285858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Cai, S. Robot-assisted therapy for upper extremity motor impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys. Ther. 2021, 101, pzab010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, G.; Wang, A.; Cheng, L.J.; Lau, Y. Robot-assisted distal training improves upper limb dexterity and function after stroke: A systematic review and meta-regression. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1641–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shi, X.; Xue, X.; Deng, Z. Efficacy of robot-assisted training on rehabilitation of upper limb function in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 104, 1498–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-C.; Kuo, F.-L.; Lin, Y.-N.; Liou, T.-H.; Lin, J.-C.; Huang, S.-W. Effects of robot-assisted rehabilitation on hand function of people with stroke: A randomized, crossover-controlled, assessor-blinded study. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2021, 75, 7501205020p1–7501205020p11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela-Espina, F.; Roldán, G.F.; Sánchez-Villavicencio, I.; Palafox, L.; Leder, R.; Sucar, L.E.; Hernández-Franco, J. Robot training for hand motor recovery in subacute stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hand Ther. 2016, 29, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.; Tong, K.; Hu, X.; Fung, K.; Wei, X.; Rong, W.; Susanto, E. An EMG-driven exoskeleton hand robotic training device on chronic stroke subjects: Task training system for stroke rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, P.; Thomas, M.E.; Cisneros-Franco, J.M.; de Villers-Sidani, É. Dynamic brains and the changing rules of neuroplasticity: Implications for learning and recovery. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 274878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-L.; Tong, R.K.-y.; Ho, N.S.; Xue, J.-j.; Rong, W.; Li, L.S. Wrist rehabilitation assisted by an electromyography-driven neuromuscular electrical stimulation robot after stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Q.; Nam, C.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Ng, S.C.; Zheng, Y.; Poon, W. Distal versus proximal-an investigation on different supportive strategies by robots for upper limb rehabilitation after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Nam, C.; Li, W.; Rong, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Q.; Hu, X. A comparison of the rehabilitation effectiveness of neuromuscular electrical stimulation robotic hand training and pure robotic hand training after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 56, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, C.; Zhang, B.; Chow, T.; Ye, F.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, W.; Rong, W.; Hu, X.; Poon, W. Home-based self-help telerehabilitation of the upper limb assisted by an electromyography-driven wrist/hand exoneuromusculoskeleton after stroke. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2021, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, N.; Izumi, S.-I. Maladaptive plasticity for motor recovery after stroke: Mechanisms and approaches. Neural Plast. 2012, 2012, 359728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woytowicz, E.J.; Rietschel, J.C.; Goodman, R.N.; Conroy, S.S.; Sorkin, J.D.; Whitall, J.; Waller, S.M. Determining levels of upper extremity movement impairment by applying a cluster analysis to the Fugl-Meyer assessment of the upper extremity in chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographic Characteristics | EO Group (n = 15) | Control Group (n = 15) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (SD) | 50.8 (12.2) | 58.9 (9.5) | 0.06 |
| Sex, male (%) | 53.3% | 40.0% | 0.72 |
| Affected side, right (%) | 38.5% | 36.4% | 1.00 |
| Stroke type, hemorrhagic (%) | 38.5% | 36.4% | 1.00 |
| Mean months from onset (SD) | 34.8 (21.8) | 47.1 (32.9) | 0.39 |
| FMA-UE score (SD) | 26.8 (12.9) | 26.9 (17.5) | 0.98 |
| BBT-pcs (SD) | 1.5 (5.7) | 3.5 (7.2) | 0.41 |
| Grip strength—kg (SD) | 4.2 (2.8) | 2.5 (2.4) | 0.07 |
| EO Group (n = 15) | Control Group (n = 15) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 Mean (SD) | T4 Mean (SD) | T8 Mean (SD) | T0 Mean (SD) | T4 Mean (SD) | T8 Mean (SD) | |
| FMA-UE total | 26.8 (12.9) | 32.6 (13.4) ** | 35.3 (14.6) ** | 26.9 (17.5) | 27.9 (17.2) | 28.1 (17.6) * |
| FMA-UE prox | 19.7 (8.2) | 22.9 (7.6) ** | 24.5 (7.9) ** | 20.1 (10.0) | 20.8 (10.2) | 21.2 (10.4) * |
| FMA-UE dist | 7.1 (5.1) | 9.7 (6.2) ** | 10.8 (7.1) ** | 6.8 (8.3) | 7.1 (7.8) | 6.9 (7.9) |
| BBT | 1.5 (5.7) | 2.7 (5.8) ** | 4.3 (8.5) ** | 3.5 (7.2) | 3.5 (7.6) | 3.7 (7.8) |
| Grip strength | 4.2 (2.8) | 5.4 (2.8) ** | 5.3 (3.3) ** | 2.5 (2.4) | 3.3 (2.7) * | 3.4 (2.9) ** |
| EO Group (n = 15) | Control Group (n = 15) | Inter-Group p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔT4-T0 Mean (SD) | ΔT8-T0 Mean (SD) | ΔT4-T0 Mean (SD) | ΔT8-T0 Mean (SD) | ΔT4-T0 | ΔT8-T0 | |
| FMA-UE total | 5.8 (5.0) | 8.5 (7.1) | 1.0 (2.0) | 1.1 (1.7) | <0.01 ** | <0.01 ** |
| FMA-UE prox | 3.2 (3.1) | 4.8 (4.1) | 0.7 (1.2) | 1.0 (1.3) | <0.01 ** | <0.01 ** |
| FMA-UE dist | 2.6 (2.7) | 3.7 (4.2) | 0.3 (1.5) | 0.1 (1.0) | <0.01 ** | <0.01 ** |
| BBT | 1.3 (1.3) | 2.8 (3.7) | 0.1 (1.5) | 0.3 (1.0) | 0.03 * | 0.02 * |
| Grip strength | 1.2 (1.2) | 1.1 (1.0) | 0.9 (1.4) | 1.0 (1.2) | 0.57 | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, S.-J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Fang, W.-C.; Huang, S.-C.; Yang, Y.-S. Effectiveness of Powered Hand Exoskeleton on Upper Extremity Function in People with Chronic Stroke. Actuators 2025, 14, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14020067
Yeh S-J, Wang Y-C, Fang W-C, Huang S-C, Yang Y-S. Effectiveness of Powered Hand Exoskeleton on Upper Extremity Function in People with Chronic Stroke. Actuators. 2025; 14(2):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Shan-Ju, Yi-Chuan Wang, Wei-Chien Fang, Shyh-Chour Huang, and Yu-Sheng Yang. 2025. "Effectiveness of Powered Hand Exoskeleton on Upper Extremity Function in People with Chronic Stroke" Actuators 14, no. 2: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14020067
APA StyleYeh, S.-J., Wang, Y.-C., Fang, W.-C., Huang, S.-C., & Yang, Y.-S. (2025). Effectiveness of Powered Hand Exoskeleton on Upper Extremity Function in People with Chronic Stroke. Actuators, 14(2), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14020067








