Prescribed-Performance-Based Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Actuator Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Description of the PEA System
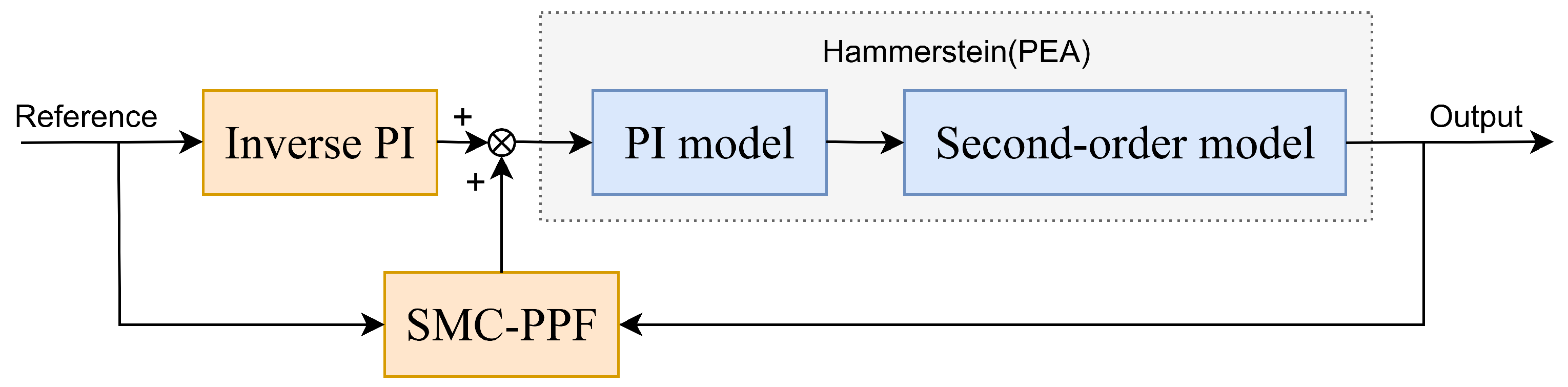
3. Design of Prescribed Performance Sliding Mode Controller
3.1. Definition of PPF
3.2. Constraint Conditions and Transformation Errors
3.3. Design of SMC
3.4. Stability Analysis
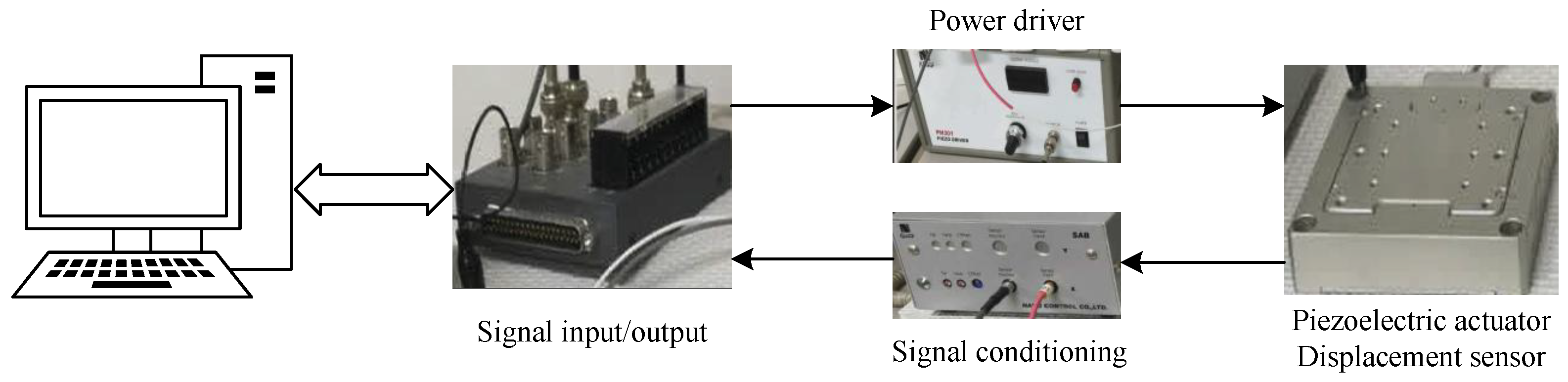
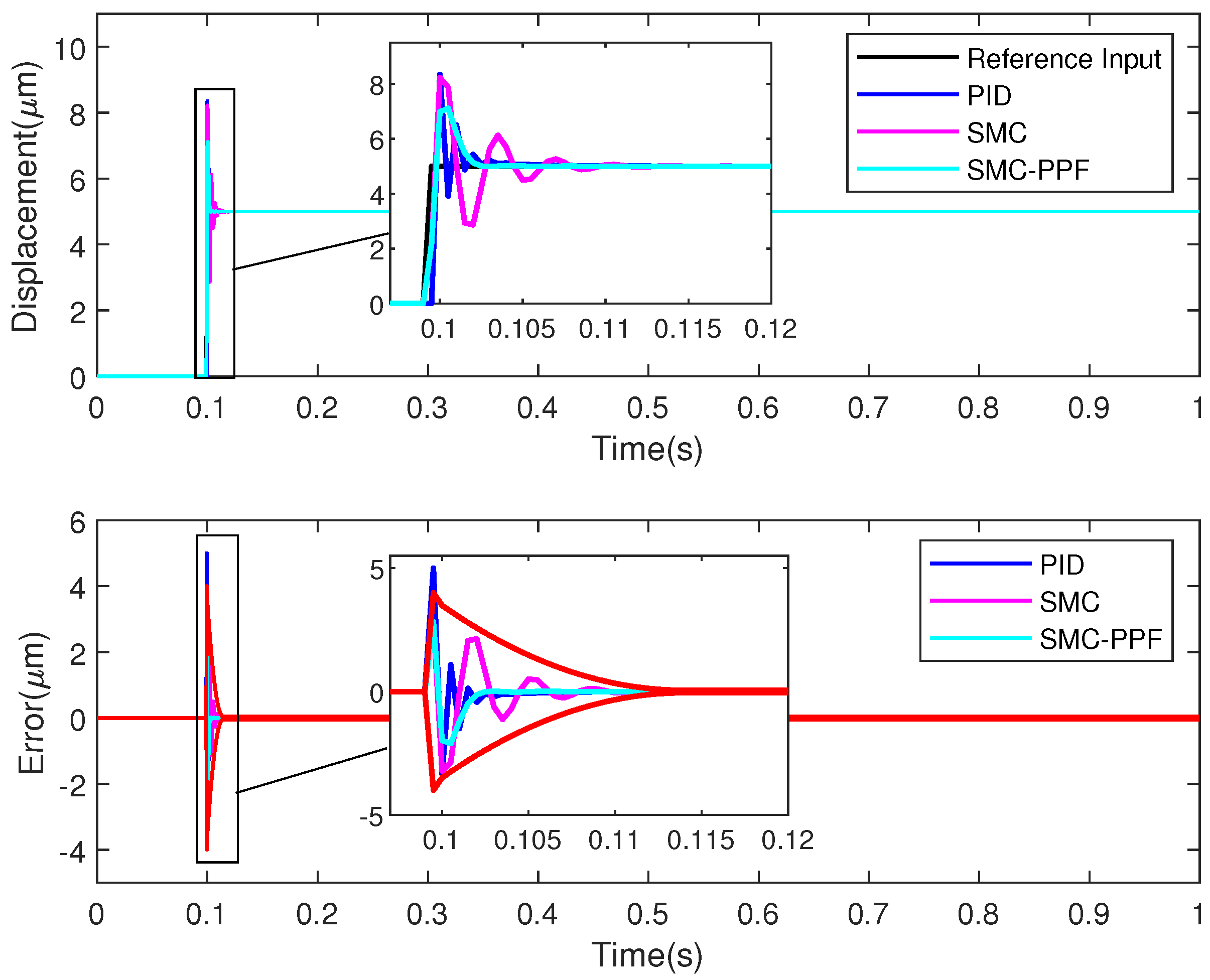
4. Experimental Verification
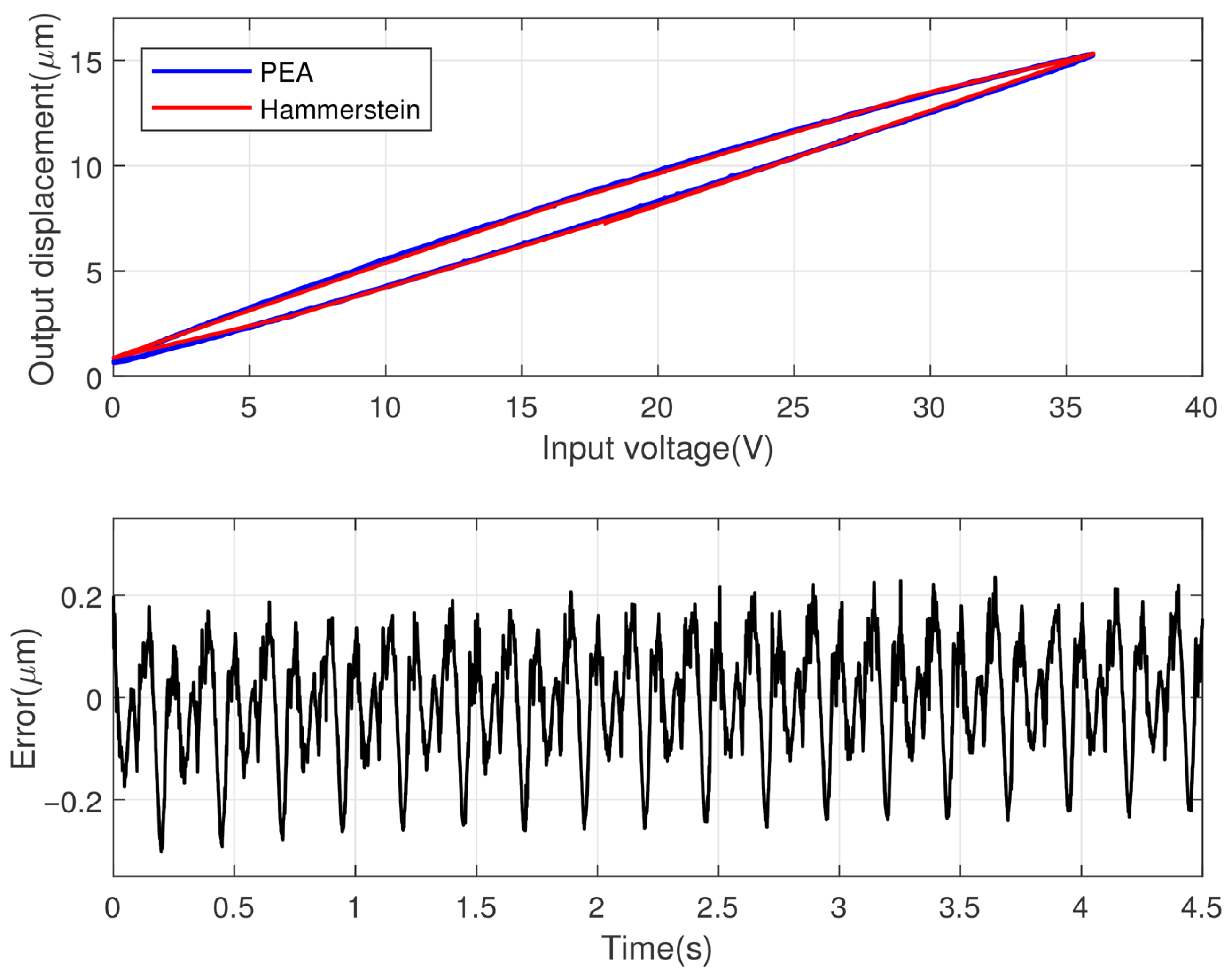
4.1. Model Identification
4.2. Experimental Results
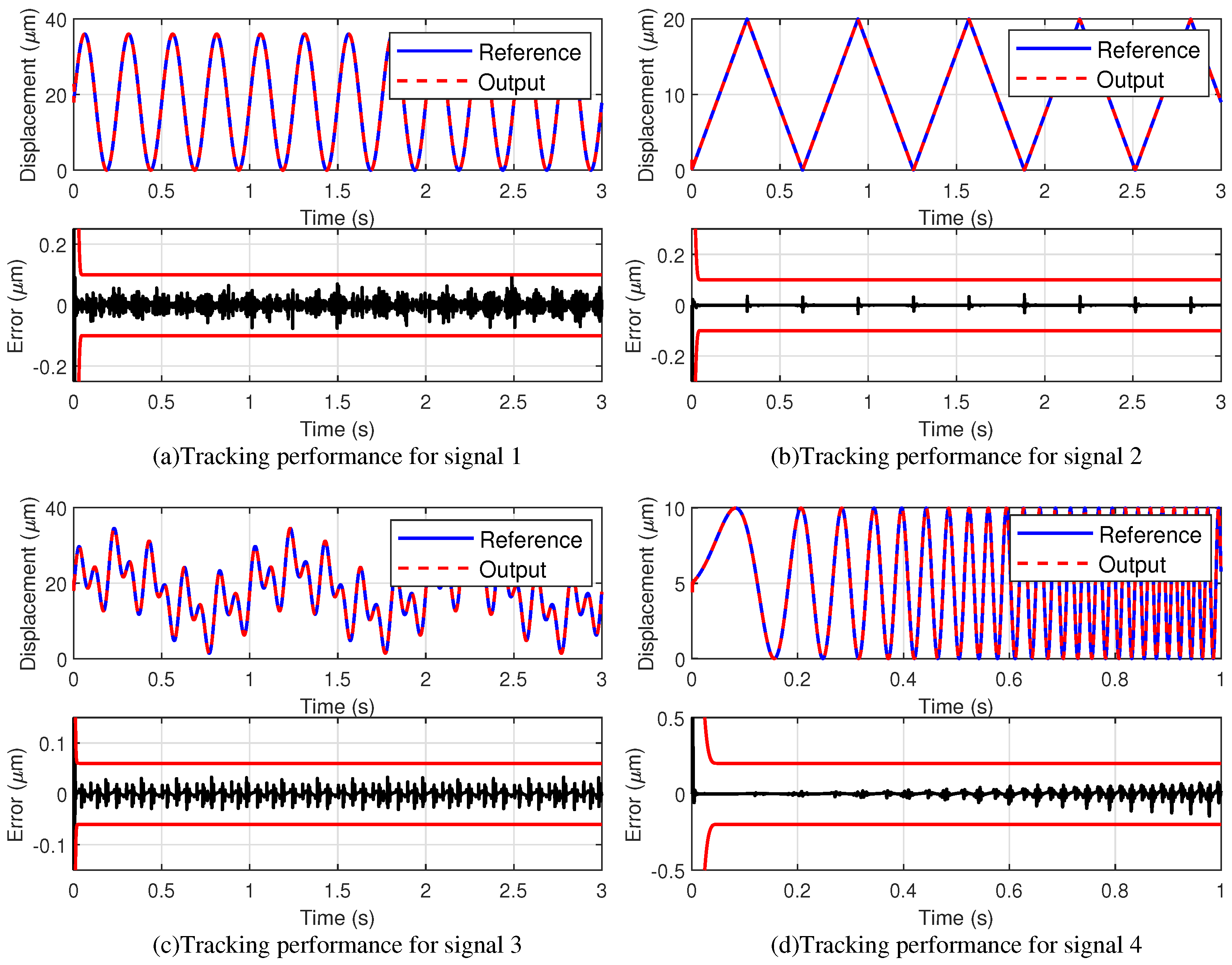
4.2.1. Reference Input Signals
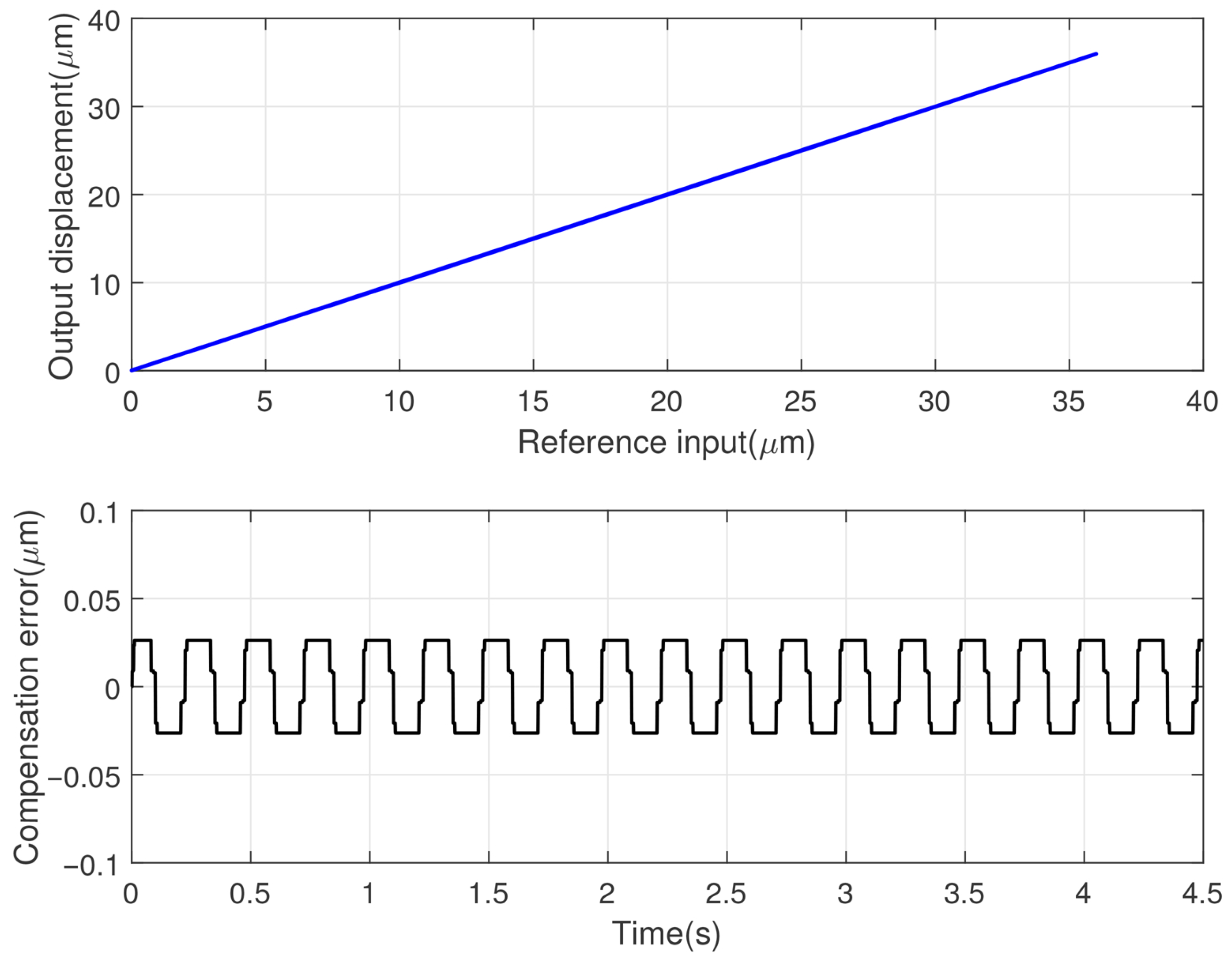
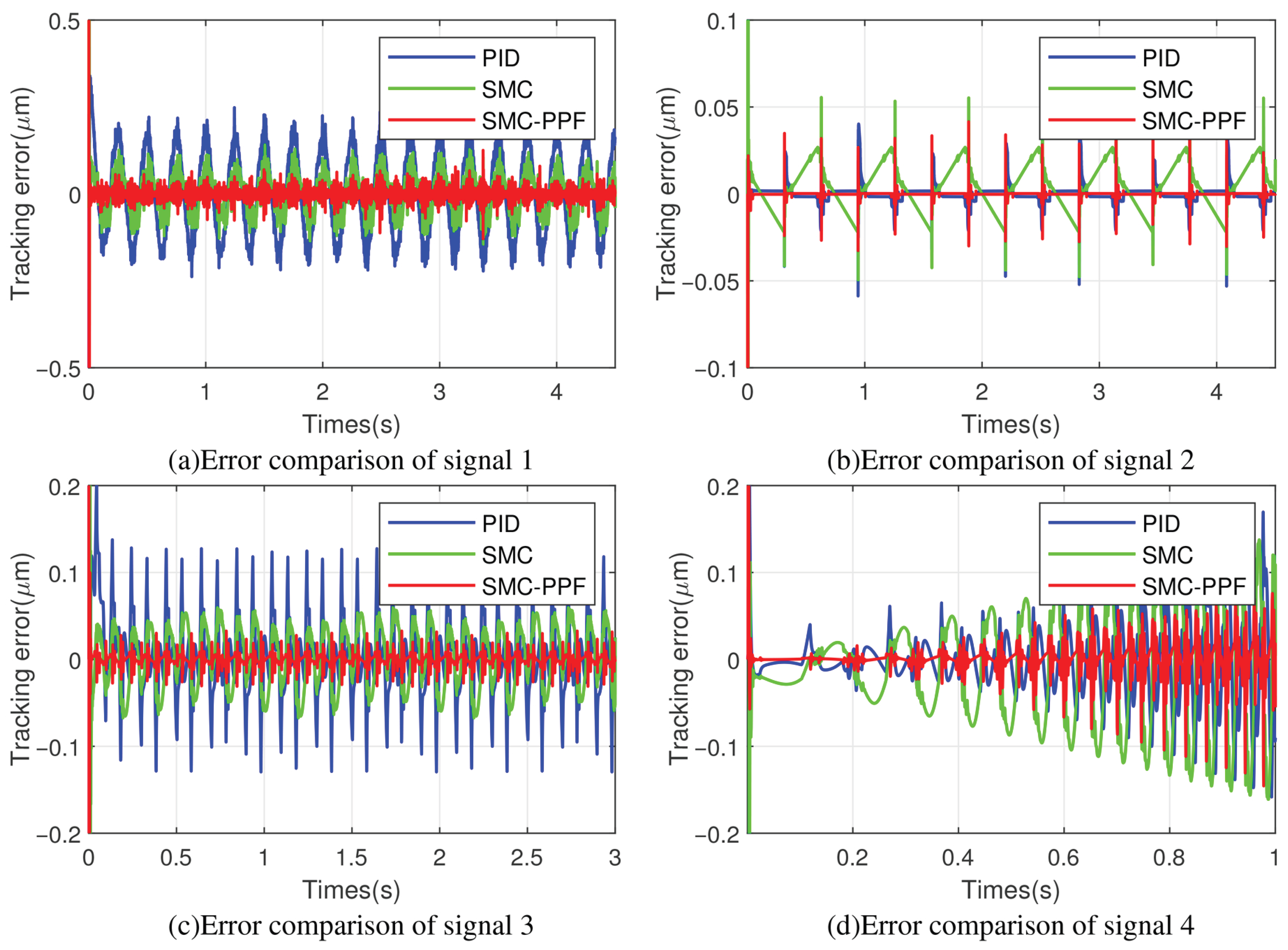
4.2.2. Tracking Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, D. Review on the Nonlinear Modeling of Hysteresis in Piezoelectric Ceramic Actuators. Actuators 2023, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Cho, K. Deep Learning and NLP-Based Trend Analysis in Actuators and Power Electronics. Actuators 2025, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, H.; Gao, H.; Cai, K. Ultrasonic Guided Wave Health Monitoring of High-Temperature Aircraft Structures Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Fuzzy Entropy. Actuators 2024, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, K.; Anton, R. Vibration Control of Satellite Antennas via NMPC and NARX Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 9406–9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, K.; Tian, F.; Xu, G. Frequency-Convertible Driving Principle of Low-Frequency Linear Actuation with Double Orthogonal Wafer Oscillators. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 7500611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Yang, W.; Dong, L.; Zhou, J. Investigation of Hysteresis Phenomena and Compensation in Piezoelectric Stacks for Active Rotor. Actuators 2025, 14, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qi, C.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, F. Actuation Force Modeling and Identification for Piezoelectric Actuator with Neural Network Compensator and Nonlinear Hysteresis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Nan, F.; Li, T.; Mo, C.; Su, J.; Wei, K.; Zhang, X. Integrating Strain Gauge Feedback with Adaptive Sliding Mode Motion Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage. Actuators 2025, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fei, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Memory-Enhanced Neural Network Control of Piezoelectric Actuators with a Rate-Amplitude-Dependent Hysteresis Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 14875–14885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Dynamic Surface Control Based on Observer for a Class of Nonlinear Systems With Prandtl-Ishlinskii Hysteresis. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2023, 237, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, M. A Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Model Reference Adaptive Control. Actuators 2024, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Adaptive Integral Terminal Third-Order Finite-Time Sliding-Mode Strategy for Robust Nanopositioning Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 7, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Gao, W.; Zhou, M. Neural Network Self-Tuning Control for a Piezoelectric Actuator. Sensors 2020, 20, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Qian, S.; Wang, D.; Wei, X.; Yu, X. Tracking Control with External Force Self-Sensing Ability Based on Position/Force Estimators and Non-Linear Hysteresis Compensation for a Backdrivable Cable-Pulley-Driven Surgical Robotic Manipulator. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 183, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napole, C.; Barambones, O.; Derbeli, M.; Calvo, I. Design and Experimental Validation of a Piezoelectric Actuator Tracking Control Based on Fuzzy Logic and Neural Compensation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2023, 464, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Su, C. Compound Estimation-Based Output-Feedback Hysteresis Compensation and Sensor Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy: Application to Piezoelectric Micropositioning Stage. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2025, 30, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y. Time-Frequency Analysis-Based Real-Time Iterative Compensation for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 4468–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xie, M.; Wu, H.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, H. Composite Proportional-Integral Sliding Mode Control with Feedforward Control for Cell Puncture Mechanism With Piezoelectric Actuation. ISA Trans. 2022, 124, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Online Hysteresis Identification and Compensation for Piezoelectric Actuators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5595–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T. Prescribed Performance Control for MIMO Stochastic Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems in a Strict-Feedback Form Using a Set of Noisy Measurements. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2022, 53, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. Adaptive Neural Indirect Inverse Control of Fractional-Order Rate-Dependent Hysteretic Nonlinear Systems and Its Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 8522–8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Q. Fuzzy-Based Adaptive Reliable Motion Control of a Piezoelectric Nanopositioning System. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 4413–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qi, X.; Shi, W.; Tan, J. Global Linearization Identification and Compensation of Nonresonant Dispersed Hysteresis for Piezoelectric Actuator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, F. Adaptive Backstepping Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control with Estimated Inverse Hysteresis Compensation for Piezoelectric Positioning Stages. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2024, 71, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qi, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, F. Development of a Neural Network-Based Compensatory Enhanced-Hammerstein Modeling Strategy for Piezoelectric System with Hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 9506712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X. Intelligent Tracking Error Prediction and Feedforward Compensation for Nanopositioning Stages with High-Bandwidth Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 6460–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Irfan, A.; Yasser, B.S. Experimental Analysis of Fuzzy Gain-Scheduled PID Controller with a Feedforward Compensator for an Ultra-Precise Piezoactuated Micropositioning Stage. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 25059–25073. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Tong, Y.; Li, C. Modeling and Control of a Linear Piezoelectric Actuators. Actuators 2024, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wen, S. Coupling Modeling and Adaptive Control for Piezoelectric-Actuated Positioning Stage. Model. Simul. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2534439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | |||||||||
| Value | 0.2085 | 0.1614 | 0.0614 | 0.0265 | 0.002 | −1.377 | 0.382 | 0.595 | 0.591 |
| Symbol | K | ||||||
| Value | 0.015 | 4 | 0.05 | 2 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J. Prescribed-Performance-Based Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Actuator Systems. Actuators 2025, 14, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110516
Wen S, Zhang S, Yu J. Prescribed-Performance-Based Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Actuator Systems. Actuators. 2025; 14(11):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110516
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Shengjun, Shixin Zhang, and Jun Yu. 2025. "Prescribed-Performance-Based Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Actuator Systems" Actuators 14, no. 11: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110516
APA StyleWen, S., Zhang, S., & Yu, J. (2025). Prescribed-Performance-Based Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Actuator Systems. Actuators, 14(11), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110516






