1. Introduction
Lower-limb exoskeleton systems are wearable robotic devices designed to assist, augment, or rehabilitate the motion of the human legs by supporting joint movement at the hip, knee, and/or ankle. These systems typically consist of rigid or semi-rigid mechanical structures attached to the user’s lower limbs, actuators that generate motion (such as electric motors or pneumatic cylinders), sensors (e.g., joint encoders and inertial measurement units) to capture human movement or interaction forces, and an embedded controller to coordinate assistance or resistance [
1,
2].
The tracking control problem for lower-limb exoskeleton systems has attracted increasing attention in rehabilitation and assistive technology applications. Lower-limb exoskeleton systems are often corrupted by unknown disturbances, such as contact with the environment, friction, muscle irregularities, unknown dynamics, and interaction torques applied by the wearer [
3,
4]. Due to their several advantages, such as robustness against disturbances and finite-time convergence, sliding-mode control (SMC) and sliding-mode observer strategies have been applied in several applications (see, for instance, references [
1,
5,
6]) and in particular for lower-limb exoskeleton systems to ensure robust tracking control objectives despite the presence of unknown inputs. To further improve stability performance and robustness, researchers have focused on combining sliding-mode control with different types of nonlinear observers, especially sliding-mode observers, whose role is to join unmeasured states (angular velocities) and unknown disturbances corrupting the system dynamics by using partial measurements (joint angles) [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11], etc.
For example, in [
12,
13,
14], the authors developed different improved strategies to control active disturbance rejection of the robotic rehabilitation exoskeleton of the lower and upper extremities. In [
15], the authors presented a robust adaptive fractional-order nonsingular fast terminal sliding-mode control mechanism designed to address unknown external disturbances and uncertainties for a two-DOF lower-limb exoskeleton. Moreover, in [
7], a terminal super-twisting sliding-mode control method was proposed for a two-degree-of-freedom serial elastic actuator inspired by lower-limb systems. It utilizes a high-order sliding-mode observer to estimate unmeasured states and disturbances, enabling robust position tracking. In [
8], the authors proposed a linear extended state observer aimed at estimating unmeasured angular velocities and unknown uncertainties within a two-DOF lower-limb exoskeleton. The proposed observer was combined with a sliding-mode controller to ensure position tracking control despite the presence of human–exoskeleton impedance torque. Furthermore, in [
9], a nonlinear terminal sliding-mode tracking control strategy based on an extended state observer was designed for lower-extremity exoskeletons. The proposed observer allows one to reconstruct disturbances and uncertainties that may impinge on system performance. Furthermore, the authors of [
16] developed an output-feedback adaptive high-order sliding-mode control strategy specifically designed for a lower-limb exoskeleton characterized by nine degrees of freedom, with an emphasis on trajectory tracking. In the proposed control strategy, a high-order sliding-mode differentiator is used for the estimation of unmeasured states. Numerical simulations illustrate improved tracking efficacy accompanied by a diminished chattering amplitude. In [
10], the authors proposed a robust model-free terminal sliding-mode control strategy for a two-DOF exoskeleton upper-limb system with gravity compensation. In [
11], a composite position control method was proposed for a flexible lower-limb exoskeleton using second-order sliding-mode control and employing two finite-time state observers to estimate matched and unmatched disturbances to improve trajectory tracking performance in terms of robustness and reduce chattering phenomena. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed control scheme compared to classic PD and sliding-mode control techniques. In the same context, an adaptive neural network-based fixed-time tracking controller was designed in [
17] by combining a nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control approach with an adaptive neural network procedure for the upper-limb exoskeleton robotic system. More recently, a neural network-based adaptive control algorithm was proposed in [
18] for the Exoskeleton Motion Rehabilitation Robot system with disturbances and uncertain parameters.
In this context, we propose in this article an output-feedback sliding-mode control method based on a cascade super-twisting observer for a two-DOF lower-limb exoskeleton system. The proposed output-feedback strategy leverages a cascade super-twisting observer composed of a super-twisting differentiator (STD) using only joint angle sensors designed for unmeasured angular velocity estimation and a second-order adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO) to estimate unknown external torques using joint angle measurements and angular velocity estimations.
The main contributions of this paper are summarized and highlighted below:
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. The next section presents the model of the two-DOF exoskeleton system and the problem formulation. A super-twisting differentiator (STD) is developed with a stability analysis in
Section 3. A super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO), as well as its stability proof, is provided in
Section 4. In
Section 5, we introduce the sliding-mode tracking control and the stability demonstration. Numerical simulations through Matlab/Simulink assert the performance of the proposed output-feedback control scheme in
Section 6. Finally, the concluding remarks are summarized in
Section 7.
2. Problem Statement
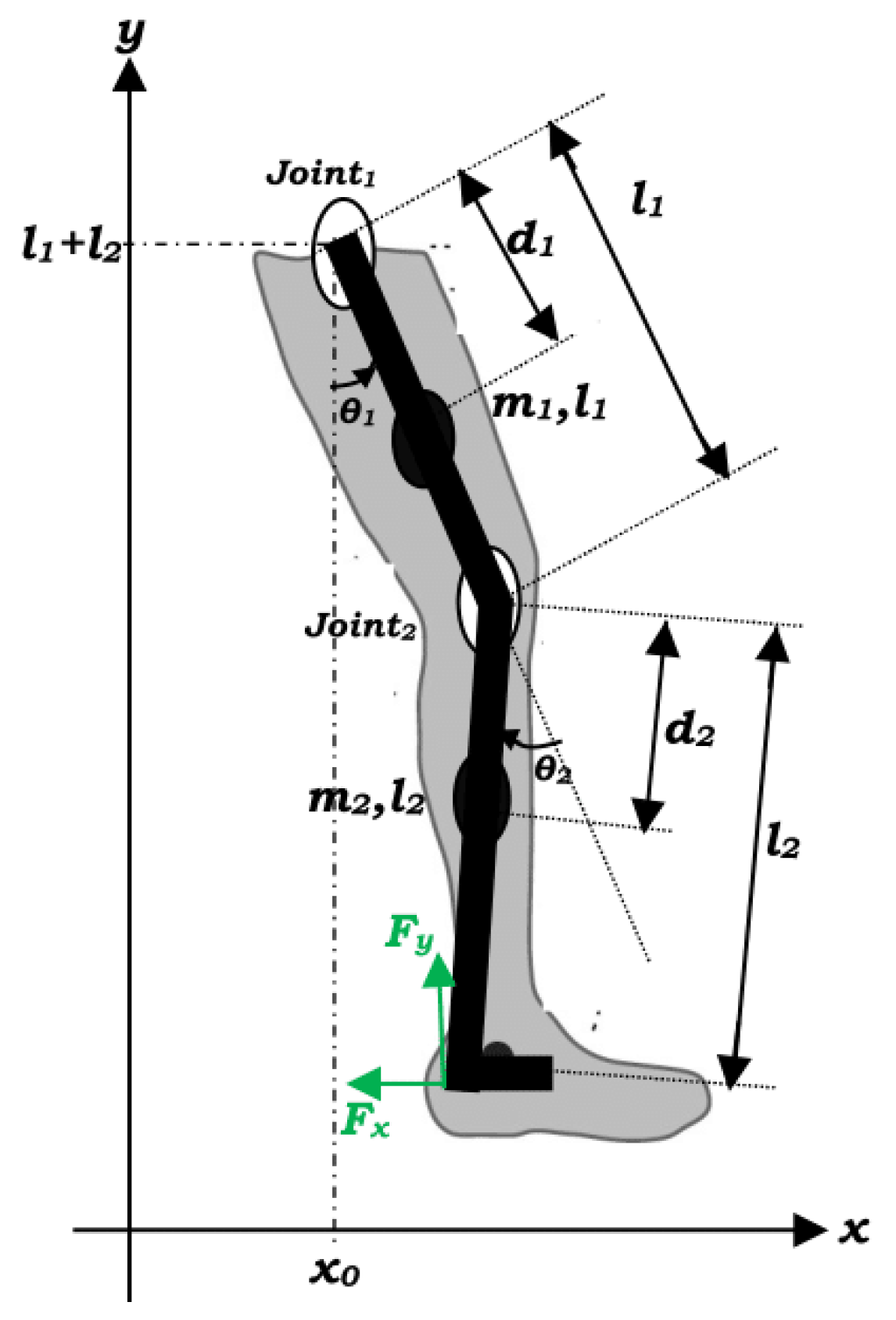
According to the dynamical modeling analysis developed in [
22], the state-space representation of a two-DOF lower-limb human exoskeleton system is described by
where
x represents the state of the system with
, where
,
are the joint angles and
and
are the respective angular velocities. The control input vector
represents the control input torques.
represents the disturbance vector, where
represents unmodeled dynamics and
denotes interaction torques.
where
,
,
, and
are the inertia functions;
and
are the Coriolis and centrifugal effects;
and
are the gravitational forces. Their respective expressions are provided by the following equations [
22]:
where
,
, and
(respectively
,
, and
) are the inertia, the mass, and the length of the thigh (respectively of the shank) regarding the distance between the mass center and joint,
and
.
The considered exoskeleton scheme is depicted in
Figure 1.
It should be noted that the latter state model is established based on the Euler–Lagrange equation of a two-DOF lower-limb human exoskeleton system governed by [
23]
with
and
In real-life applications, lower-limb exoskeletons may be corrupted by significant unknown inputs, including unmodeled dynamics and external load torques. In practice, not all states are available for measurement due to economic constraints, such as sensor cost, and technological constraints, such as noise sensitivity or hardware integration. Moreover, external disturbances, such as unexpected torques from the environment or interaction with a human user, can degrade control accuracy if not rejected or compensated.
In this context, let us now focus on the modeling of the disturbance torque.
The reference trajectories the exoskeleton depicted in
Figure 1 are provided by
where
is the initial state of the thigh joint.
The disturbance torque is provided by the following equation:
with
Using a Taylor development, we obtain the following approximation:
Achieving robust control objectives in the considered exoskeleton model requires the estimation of unmeasured states (angular velocities) and the reconstruction of unknown disturbances.
In this paper, the exoskeleton system dynamics are nonlinear and subject to unknown external torques. In fact, our cascade observer-based control design is fundamentally nonlinear, following established nonlinear control theory, and no linearization of the exoskeleton dynamics is performed in our design, maintaining the full nonlinear model. Moreover, only joint angles are assumed to be measured. The control method to be designed must ensure robust tracking control objectives based on partial measurements despite the presence of disturbances.
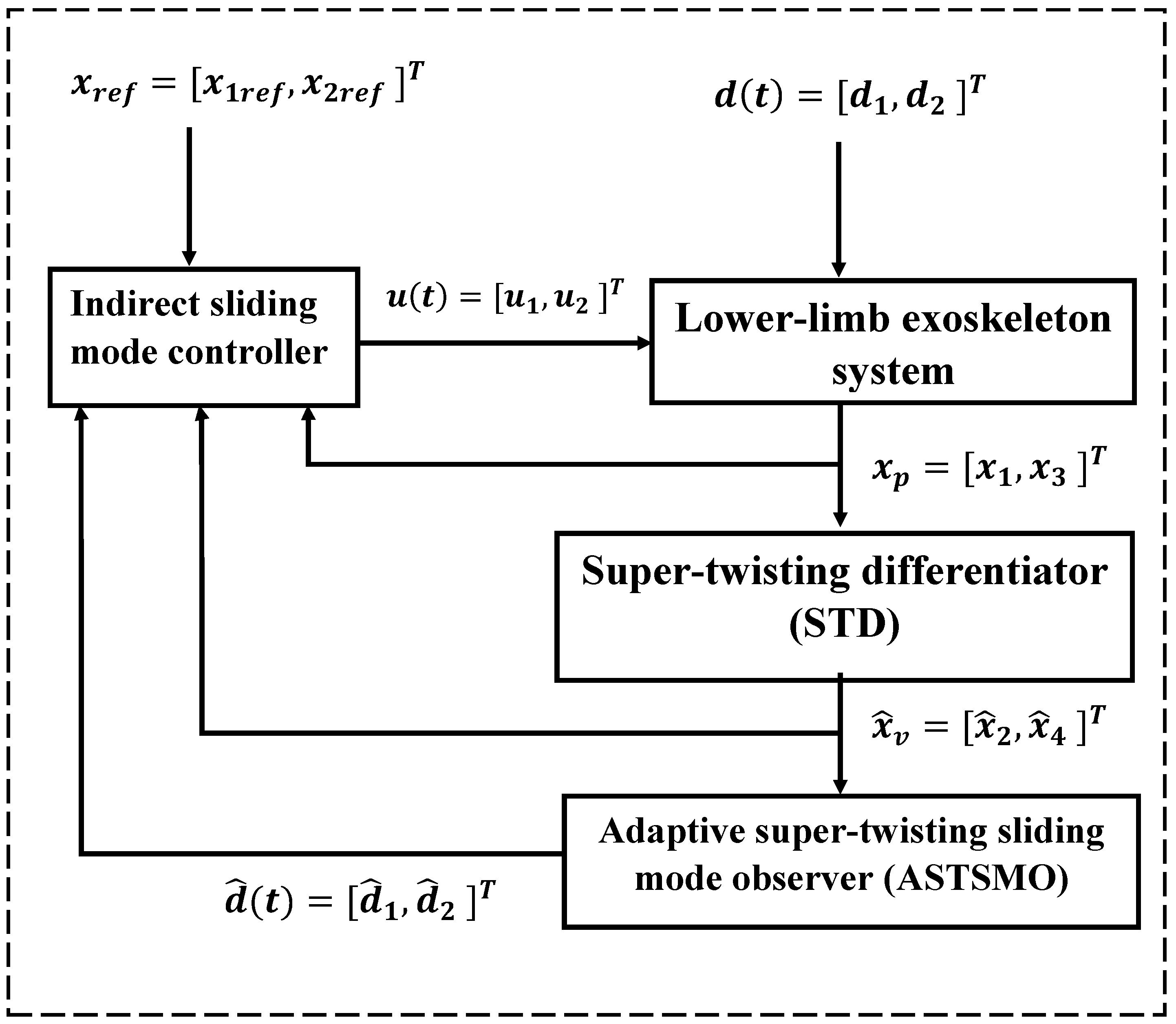
To address these challenges, a three-layer architecture is proposed in this paper. First, a super-twisting differentiator (STD) is synthesized to estimate unmeasured angular velocity states based on joint angle measurements. Second, an adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO) is designed to estimate the external load torques, modeled as unknown disturbances based on the estimated angular velocities from the super-twisting differentiator (STD).
Then, a sliding-mode controller (SMC) uses the reconstructed disturbances and the estimated states to compute the control input: A smooth sliding surface drives the tracking error to zero. The estimated disturbance is used to compensate for the unknown input (including load torques). A saturation-based discontinuous term ensures robustness without excessive chattering. The control approach is chosen for its robustness, low chattering, and compatibility with the proposed cascade super-twisting observer.
Figure 2 represents the proposed cascaded super-twisting observer-based sliding-mode control architecture for the considered exoskeleton, including external load torque perturbations.
3. Super-Twisting Differentiator for the Estimation of Unmeasured States (Angular Velocities)
We consider the estimation of the unmeasured joint velocities and , using only the available joint position measurement and .
To this end, we employ a second-order super-twisting differentiator, which provides finite-time estimation of and under mild assumptions.
The second-order super-twisting differentiator that we propose is composed of two parts (a first part for the joint 1 dynamics and a second part for joint 2 dynamics).
The differentiator dynamics (for joint 1) is provided by
where
such that
is the observer estimate of
, and
is the estimate of
.
,
are design parameters.
The differentiator dynamics (for joint 2) is provided by
where
such that
is the observer estimate of
, and
is the estimate of
.
,
are design parameters.
First, we present the Lyapunov-based convergence proof for the joint 1 part of the sliding-mode differentiator.
Define estimation errors:
Differentiating yields
where
, where
L is a known positive constant.
Consider the following Lyapunov function:
The time derivative of
V along the trajectories is
Using
and the fact that
, we have
If the gains are chosen such that
then
where
.
This proves finite-time convergence of the estimation errors to zero.
An identical proof of convergence is applied for the joint 2 part of the super-twisting differentiator for the estimation .
In fact, for joint 2, we define the estimation errors:
and we consider the Lyapunov function
Proceeding, as in the the convergence proof provided for the joint 1 part of the differentiator, and based on a similar Lyapunov analysis for the joint 2 part of the proposed super-twisting differentiator, we demonstrate the finite-time estimation of unmeasured joint velocity using the measured angle joint .
Consequently, we deduce that the proposed super-twisting differentiator provides finite-time estimation of unmeasured joint velocities ( and ) using only position measurements ( and ).
4. Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Observer Design for the Estimation of Disturbances
The nonlinear dynamic model of a two-DOF robotic leg exoskeleton may be rewritten in the form
where
,
,
and
denotes an unknown input function depending on the load torque disturbance
as follows:
We propose the following adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer, whose objective consists of reconstructing the state
and the unknown input function
(which enables deducing the reconstruction of the load torque disturbance
):
where
and
are the respective estimates of angular velocity states
and
provided after a finite time from the first super-twisting differentiator described by dynamics (
9) and (
11).
The proposed adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (
32) may be written in the following compact form:
Define
: the estimation error, with
the finite-time estimate of
provided from the first super-twisting differentiator described by dynamics (
9) and (
11) and
.
,
.
The error’s system may be written in the following form:
Using the previous proof of finite-time estimation of angular velocities provided by the first super-twisting differentiator described by dynamics (
9) and (
11), we assume that, after a finite time
,
and
, and, consequently, for
, we have
(hence,
) and
.
Then, for
, the error’s system may be written as
We consider the Lyapunov function
For
, the time derivative of
along the trajectories of the error’s system is provided by
Since
, the cross terms cancel:
Assuming
, where
are small positive design parameters introduced to guarantee finite-time convergence, with
, we deduce
Choosing appropriate positive parameters and sufficiently large values of , we obtain a decreasing Lyapunov function .
Using classical results of high-order sliding-mode observer stability, we deduce that
Finally, considering Equation (
30), highlighting the relation between
and
, the load torque disturbance
may be estimated as follows:
where
We conclude that the proposed adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer ensures robust convergence of estimation errors and enables asymptotic reconstruction of unknown input vector as well as the load torque disturbance in a two-DOF exoskeleton model.
5. Sliding-Mode Control Design
Robust tracking and disturbance rejection are crucial in robotic exoskeletons operating in uncertain environments. Sliding-mode control (SMC) is well known for its robustness, and, when combined with a robust observer such as the cascade super-twisting observer that we propose in this paper, it can ensure reliable performance with reduced chattering. In this context, we propose a sliding-mode control scheme using estimated disturbances from the designed cascade super-twisting observer.
We recall that the nonlinear dynamic model of a two-DOF robotic leg exoskeleton may be rewritten in the form (
28)
where
,
,
is the nonlinear function provided in Equation (
29), and
denotes the unknown input function depending on the load torque disturbance
, as described in Equation (
30).
We define the tracking errors as follows:
and propose the control law:
where
, with
is the estimated disturbance from the adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO).
if
, else
.
where
are positive parameters.
It is important to note here that, in addition to the use of the estimated disturbance
from the super-twisting sliding mode (ASTSMO) observer, the proposed sliding-mode controller also uses the estimated angular velocities
and
from the super-twisting differentiator (STD). However, for more simplicity and clarity, we assume that, after a finite time
,
and
, referring to the demonstration of finite-time estimation of angular velocities provided by the first super-twisting differentiator described by dynamics (
9) and (
11).
Furthermore, note that, by using the proposed sliding-mode control (SMC) structure (compensation via estimated disturbance and smooth saturation), we avoid direct discontinuous injection compared to standard first-order sliding-mode control, which suffers from high-frequency chattering, damaging actuators, and terminal or adaptive SMCs, which often still inject discontinuities and amplify noise.
For the control input design, we assume that the matrix is symmetric positive definite. The disturbance is bounded and differentiable.
We consider the candidate Lyapunov function:
Differentiating
V, we obtain the following result:
Exploiting the model form (
3) of exoskeleton system and substituting closed-loop dynamics, for
, we have
Consequently, we obtain
Let , with , and assume .
First, we consider the case where
:
Using
for any
:
Choose
, so
Now, we consider the case where
:
Since
:
In summary, in the region
for both
i:
where
Outside this region, .
Consequently, we conclude that all trajectories converge to the set
; i.e., the system is uniformly ultimately bounded:
If , then exponentially.
Note that the sliding surfaces are chosen as
, where
sets the convergence speed. Gains
are selected such that
>
, where
is the estimated upper bound of disturbances. The boundary layer width
is tuned empirically to balance precision and chattering suppression (see also chattering analysis in
Section 6).
6. Numerical Simulations
Numerical simulations are carried out using Matlab/Simulink software by applying the cascade-adaptive super-twisting observer-based output-feedback sliding-mode control to the dynamic model of the two-DOF exoskeleton described by Equation (
1), with nominal parameters provided in
Table 1.
Reference trajectories are defined as and The initial conditions for the two-link human–exoskeleton system are set as
The super-twisting differentiator parameters are provided as follows: , , , and . The initial conditions for the super-twisting differentiator are set as Initial values of the super-twisting differentiator are chosen close to zero to avoid bias and ensure finite-time convergence. The adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer parameters are provided as follows: , , , and . The initial conditions for the adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer are set as The sliding-mode controller parameters are provided as follows: , , , , and .
We assume that the exoskeleton system is corrupted by perturbations of two load torques and at time s.
Simulations were conducted with a sampling rate of 1 kHz (sampling time
ms) following typical exoskeleton control requirements [
21].
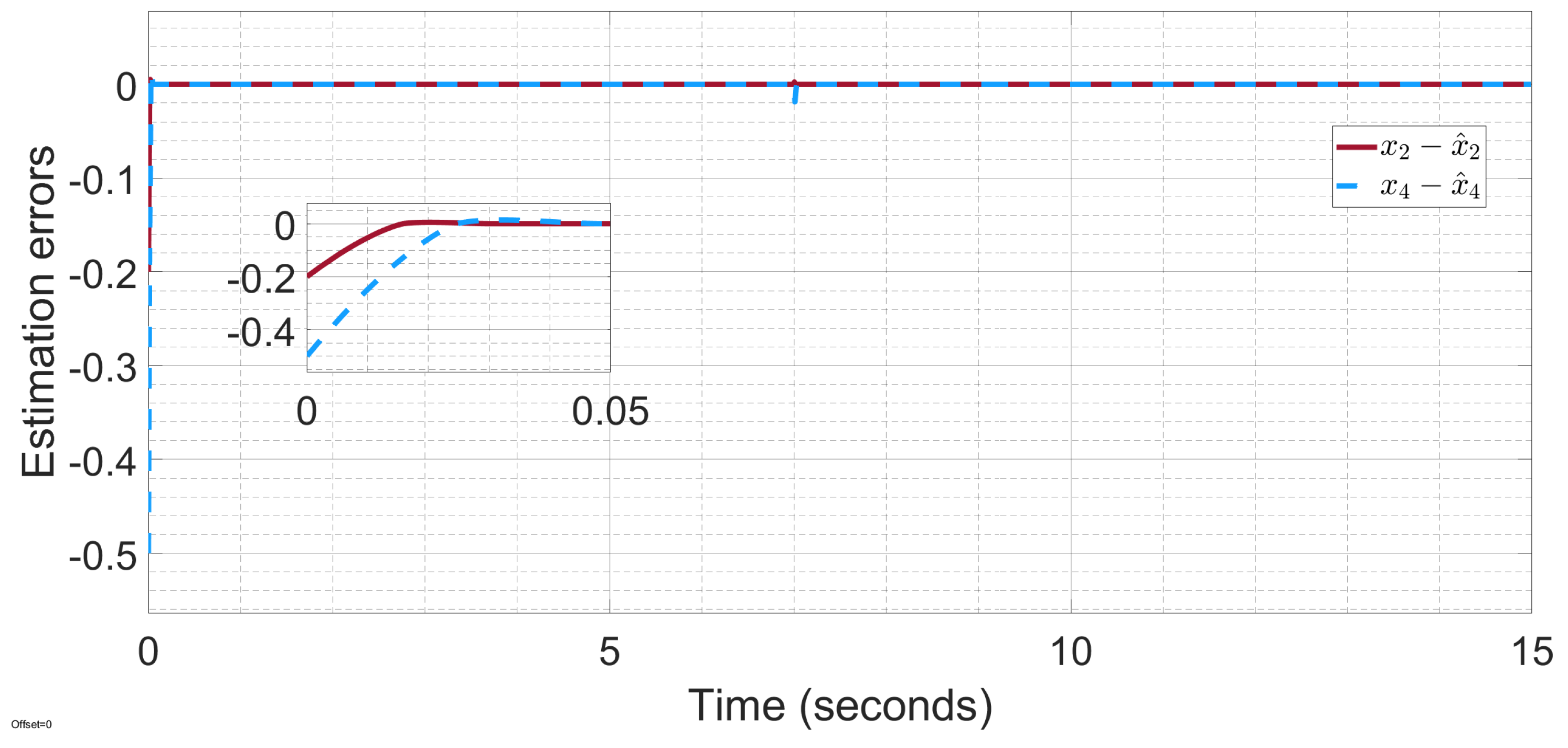
Figure 3 illustrates that the estimation errors of the angular velocity states converge to zero when time goes to infinity.
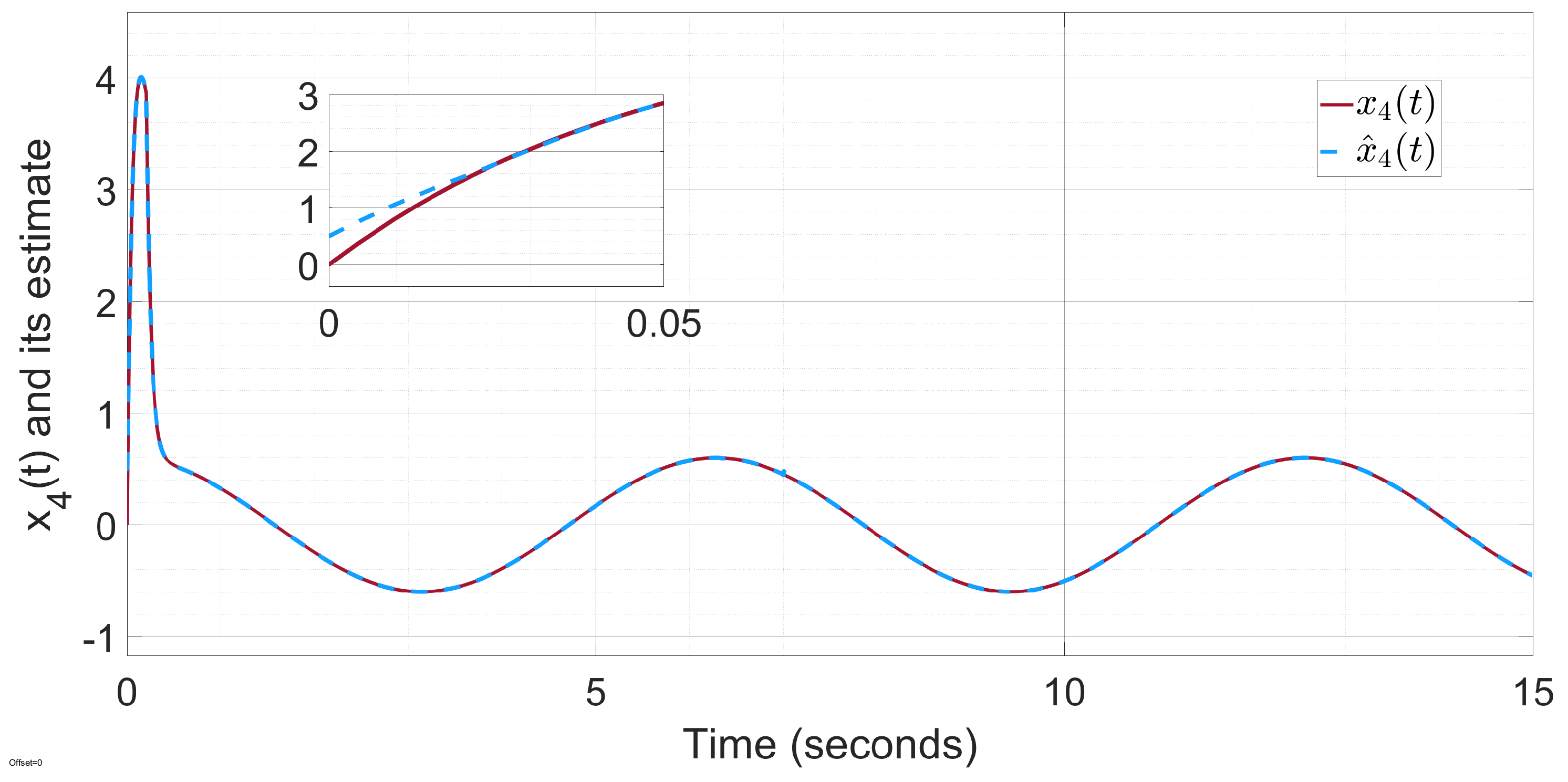
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 demonstrate that the unmeasured states
and
are well reconstructed by the proposed super-twisting differentiator.
Figure 6 and
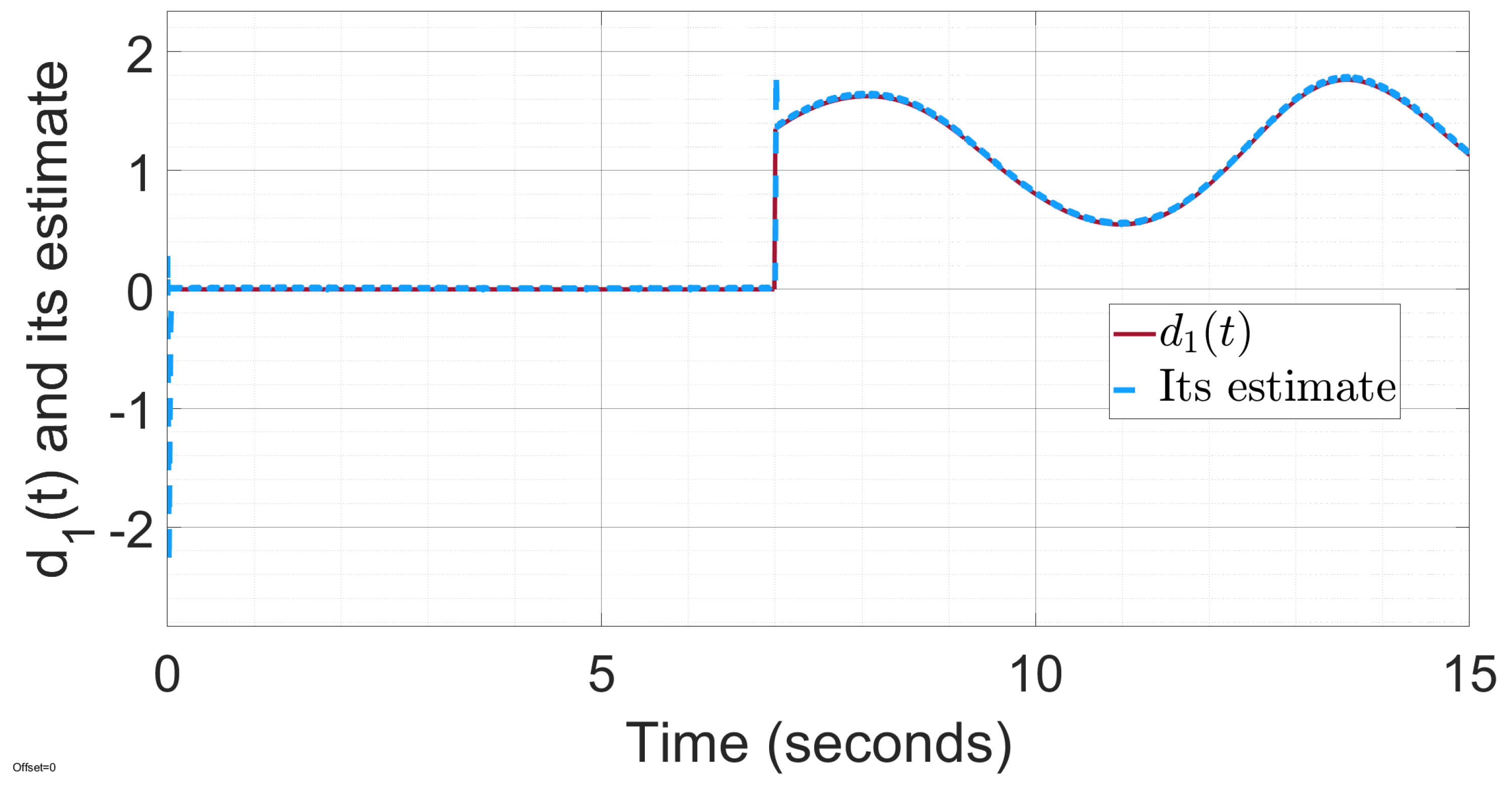
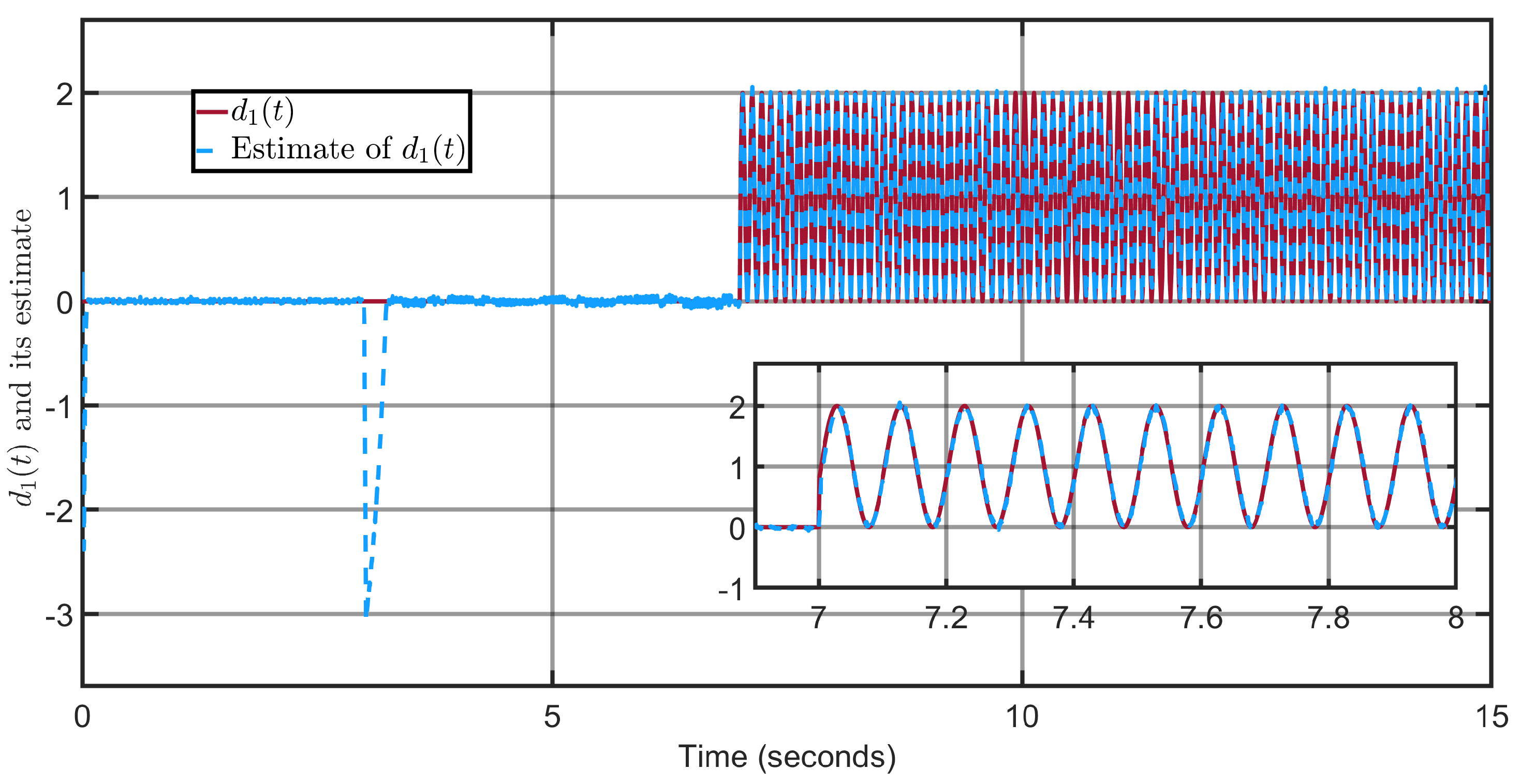
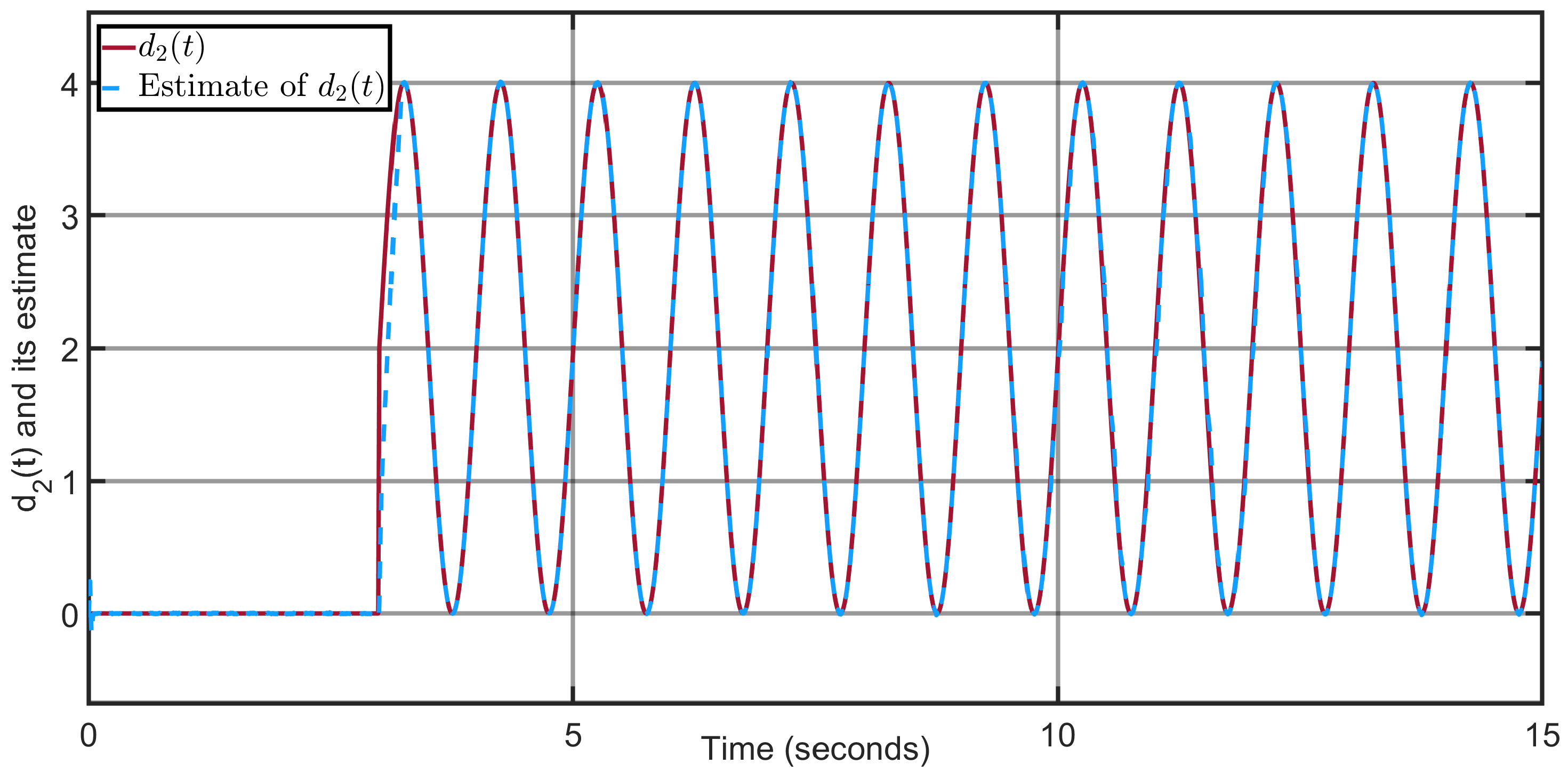
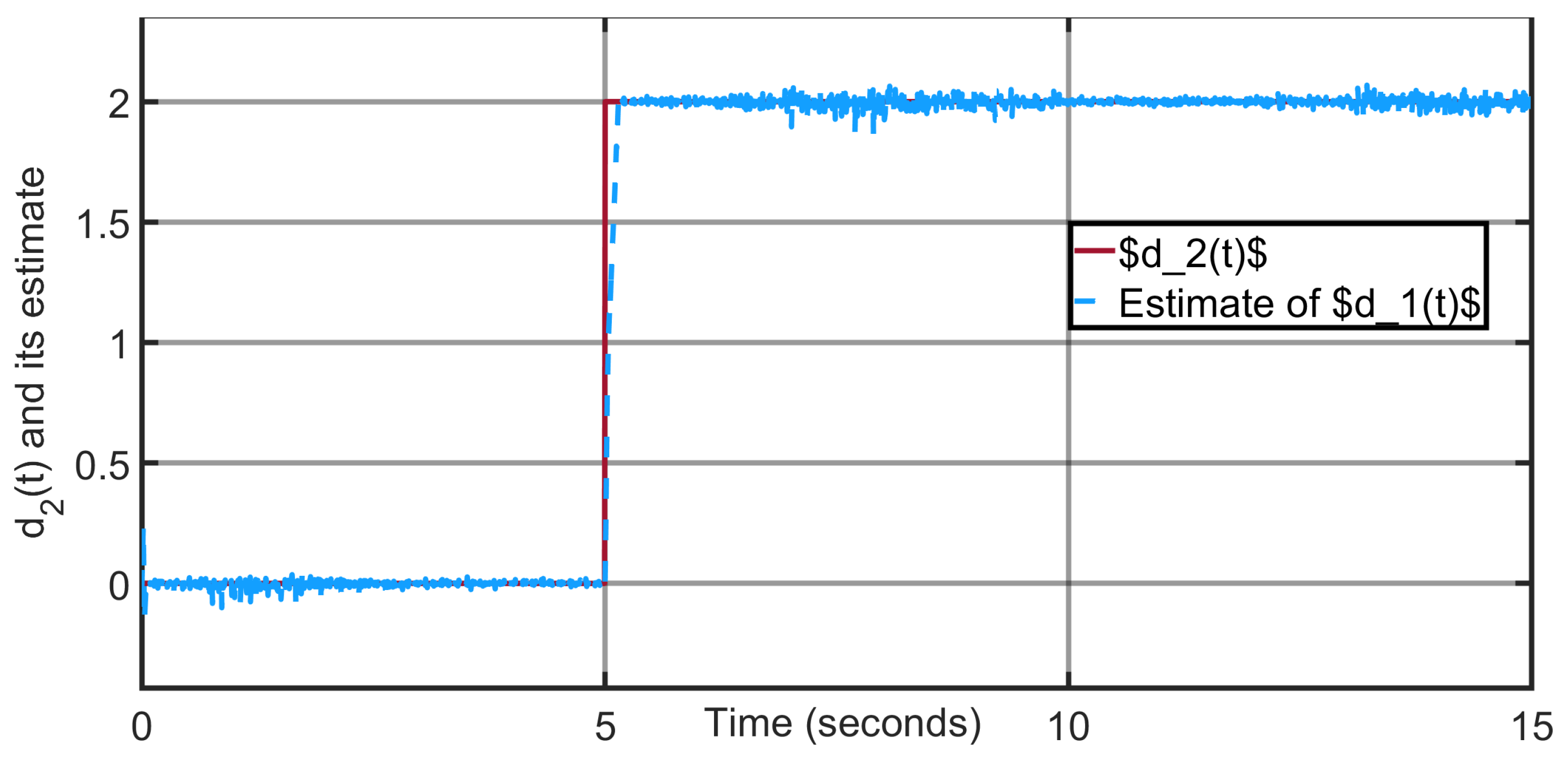
Figure 7 illustrate that the torque disturbances
and
are well reconstructed by the proposed adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO).
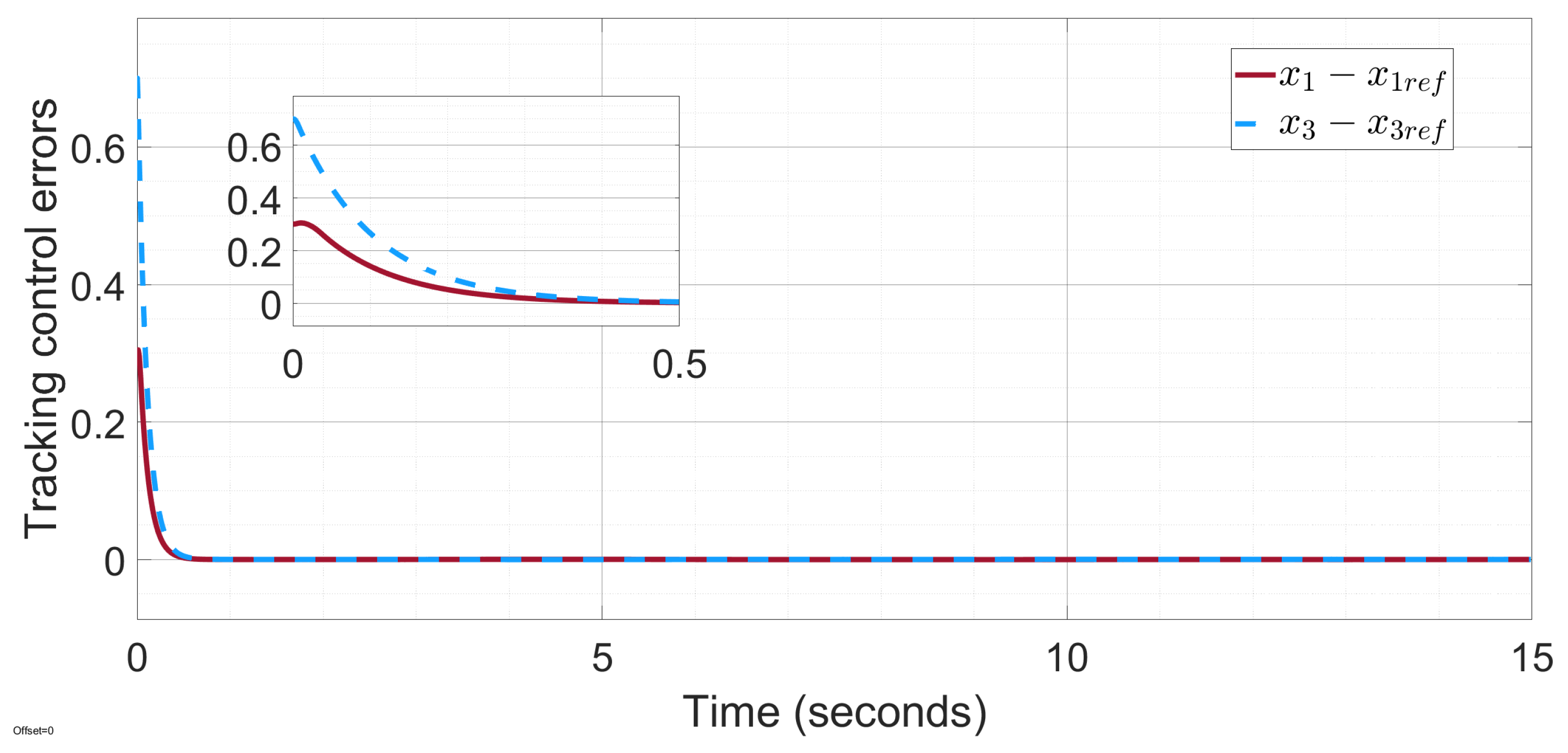
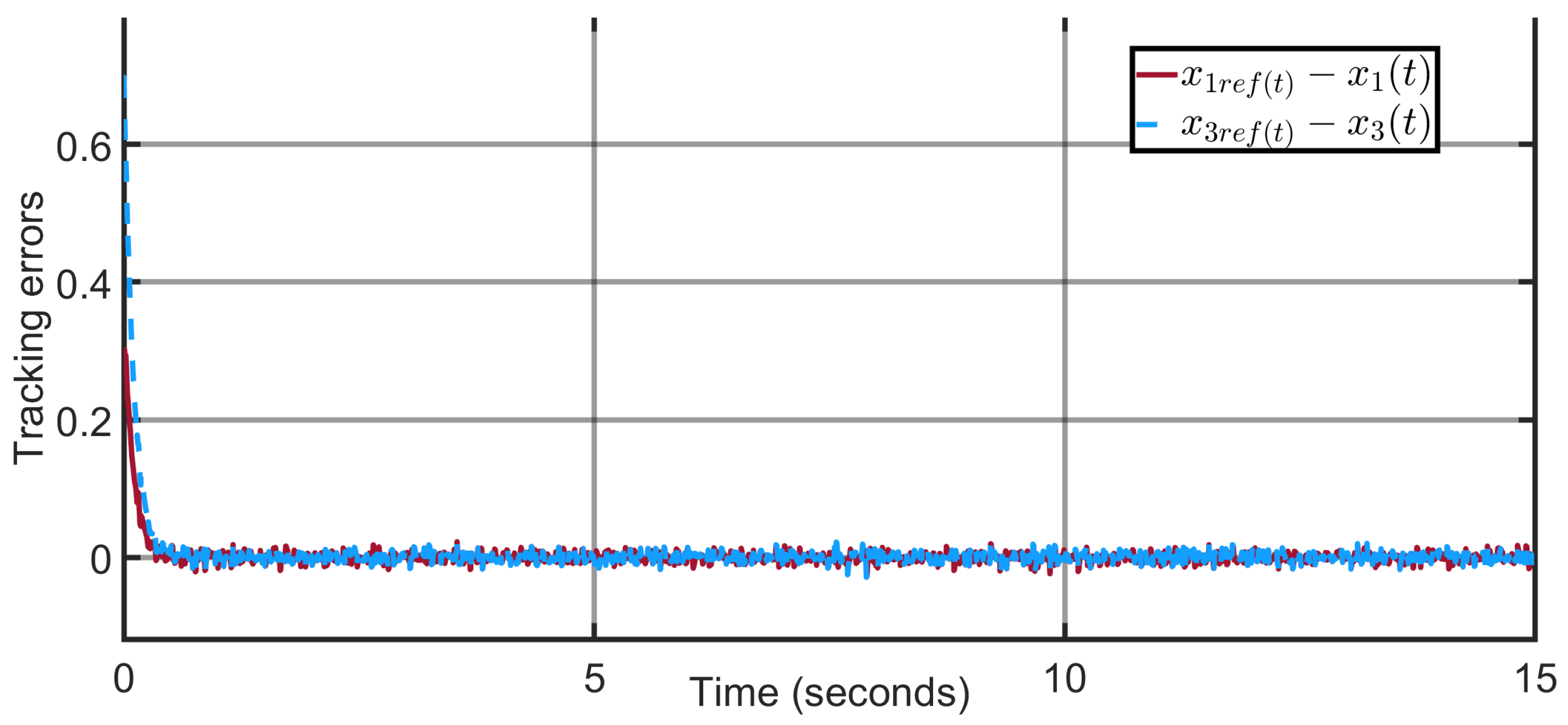
Figure 8 depicts that the tracking errors of the joint angle states converge to zero when time goes to infinity.
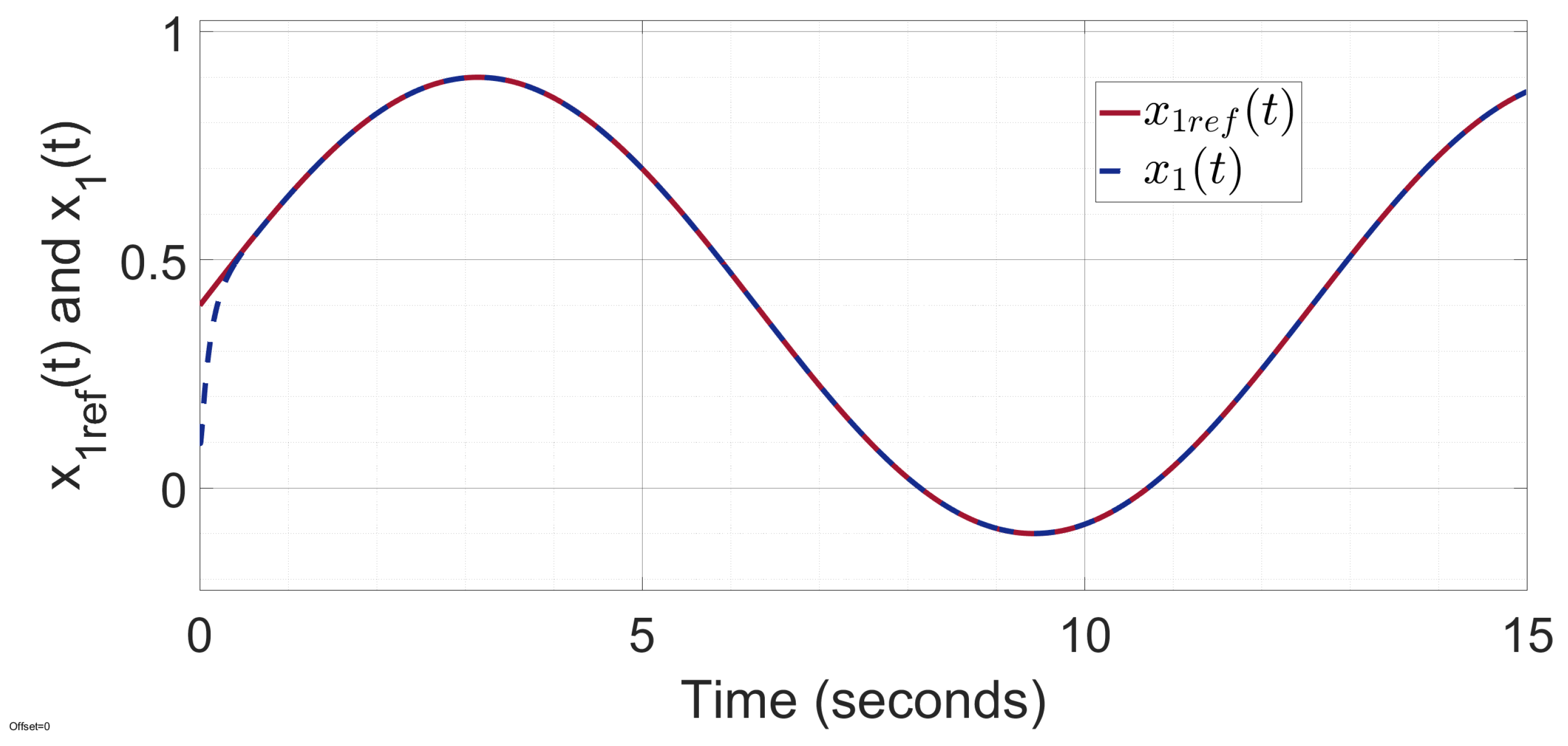
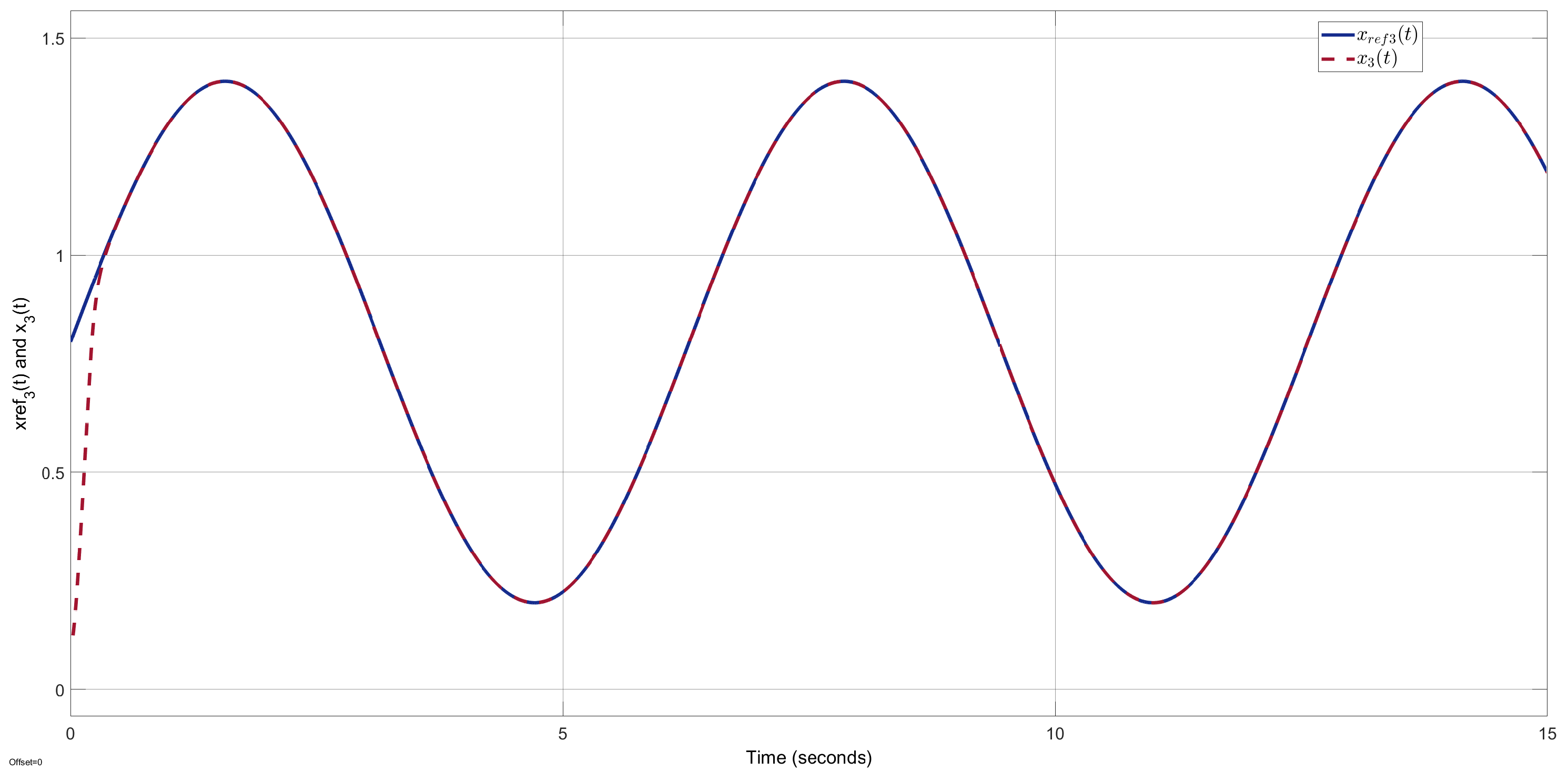
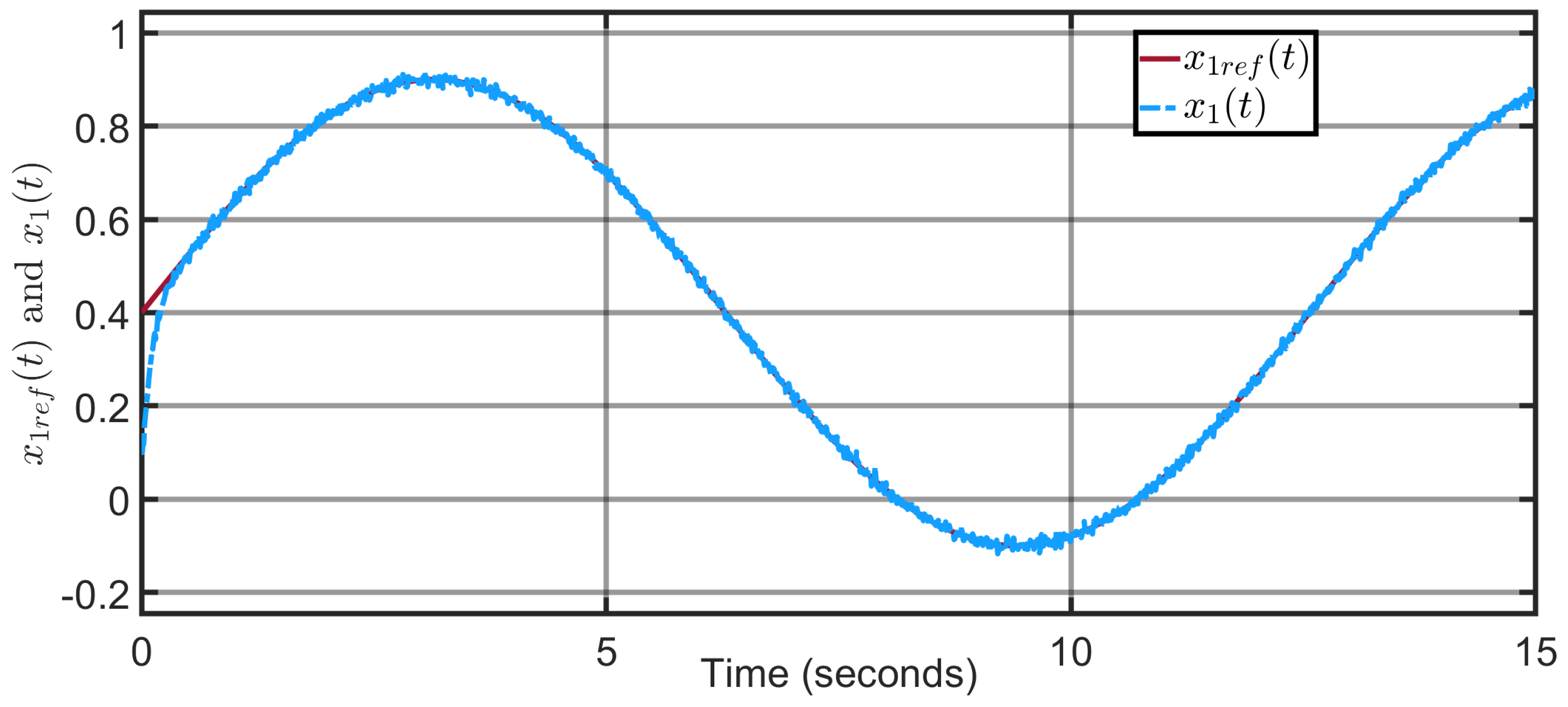
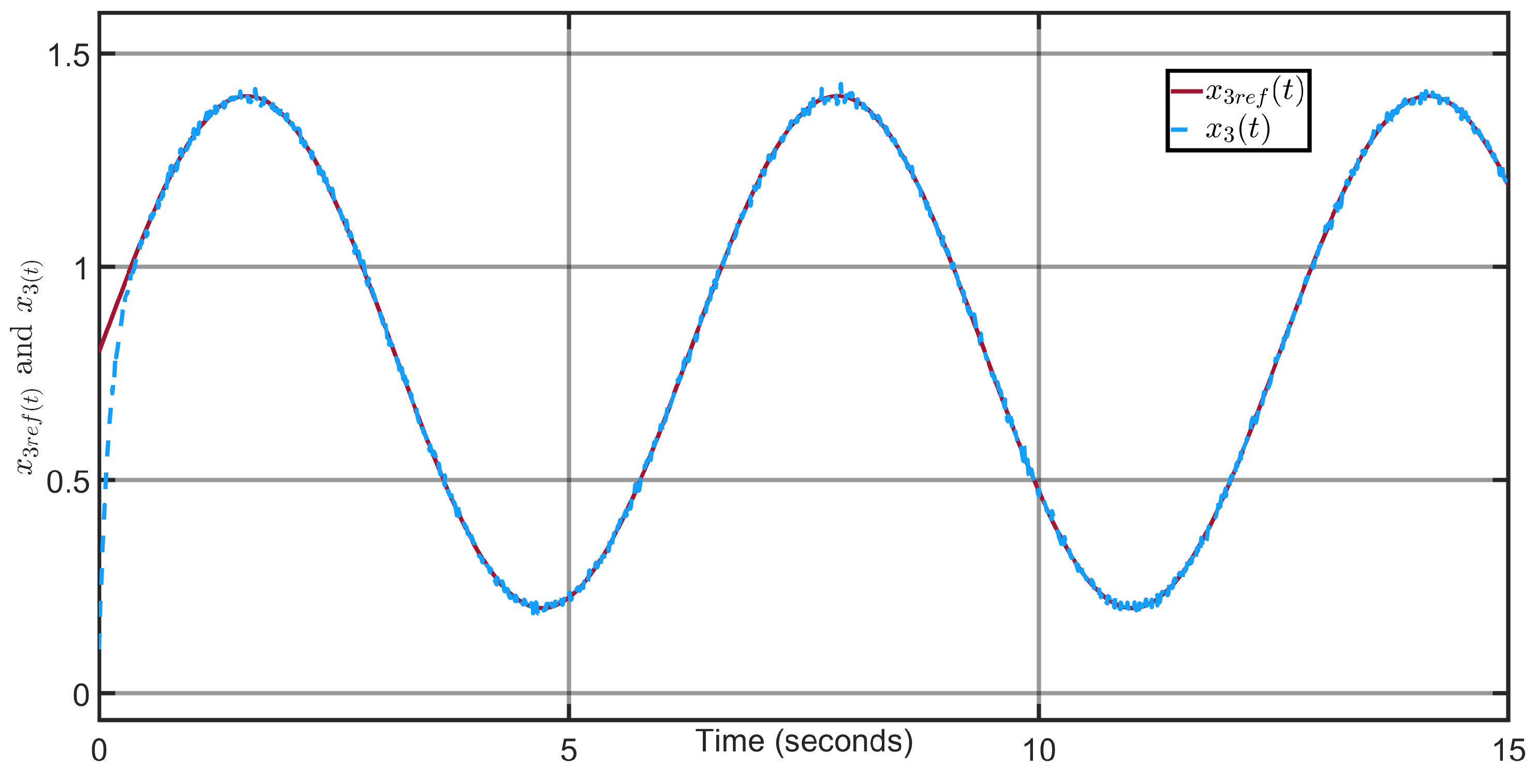
Figure 9 and
Figure 10 illustrate that the output states
and
perfectly follow the reference trajectories
and
. We deduce that the proposed super-twisting observer-based sliding-mode control scheme guarantees a very satisfactory reference tracking performance despite the presence of external load torque disturbances. Indeed, the effect of latter disturbances is perfectly compensated and canceled thanks to the use of their estimates provided by the proposed adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO).
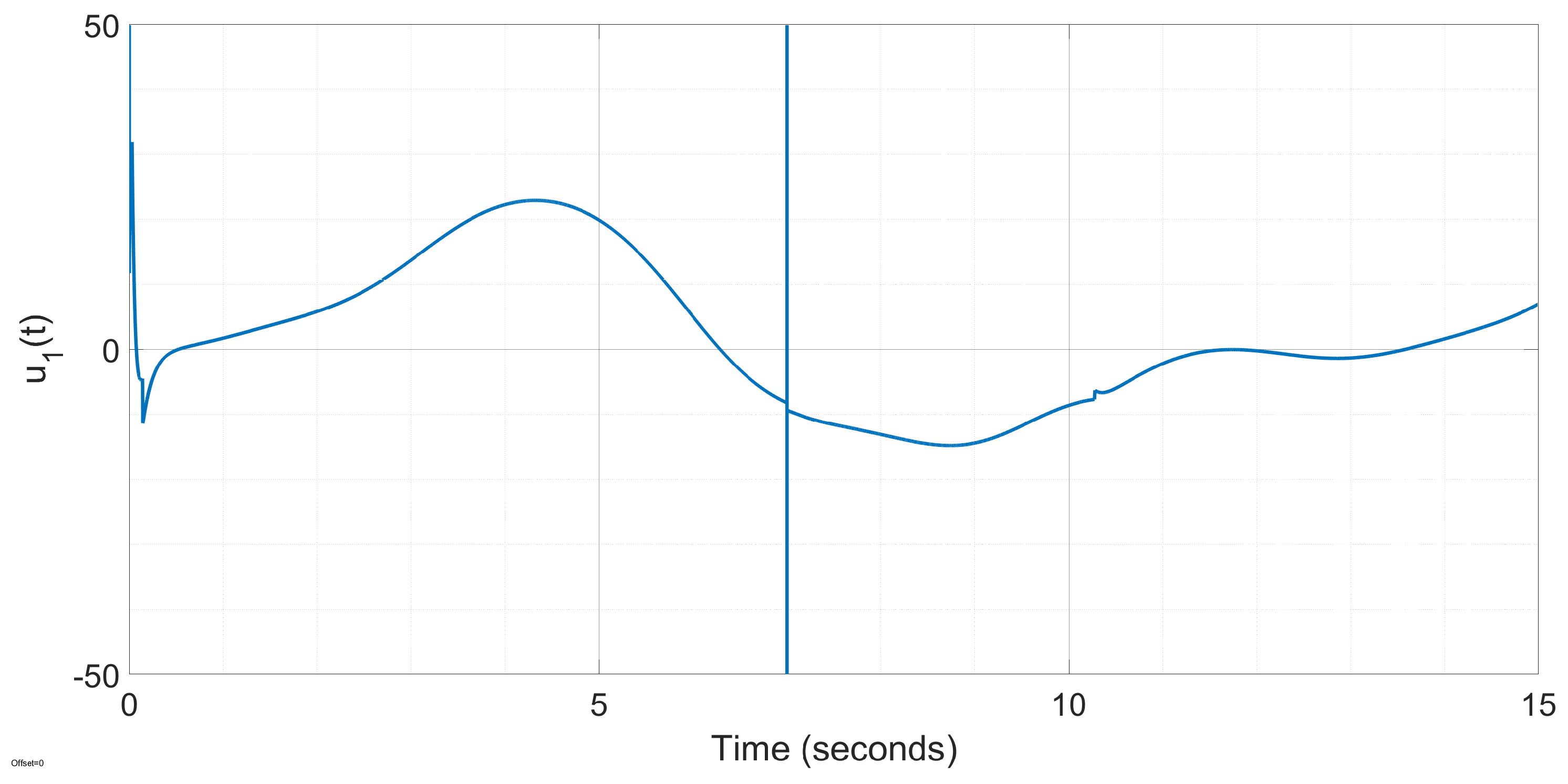
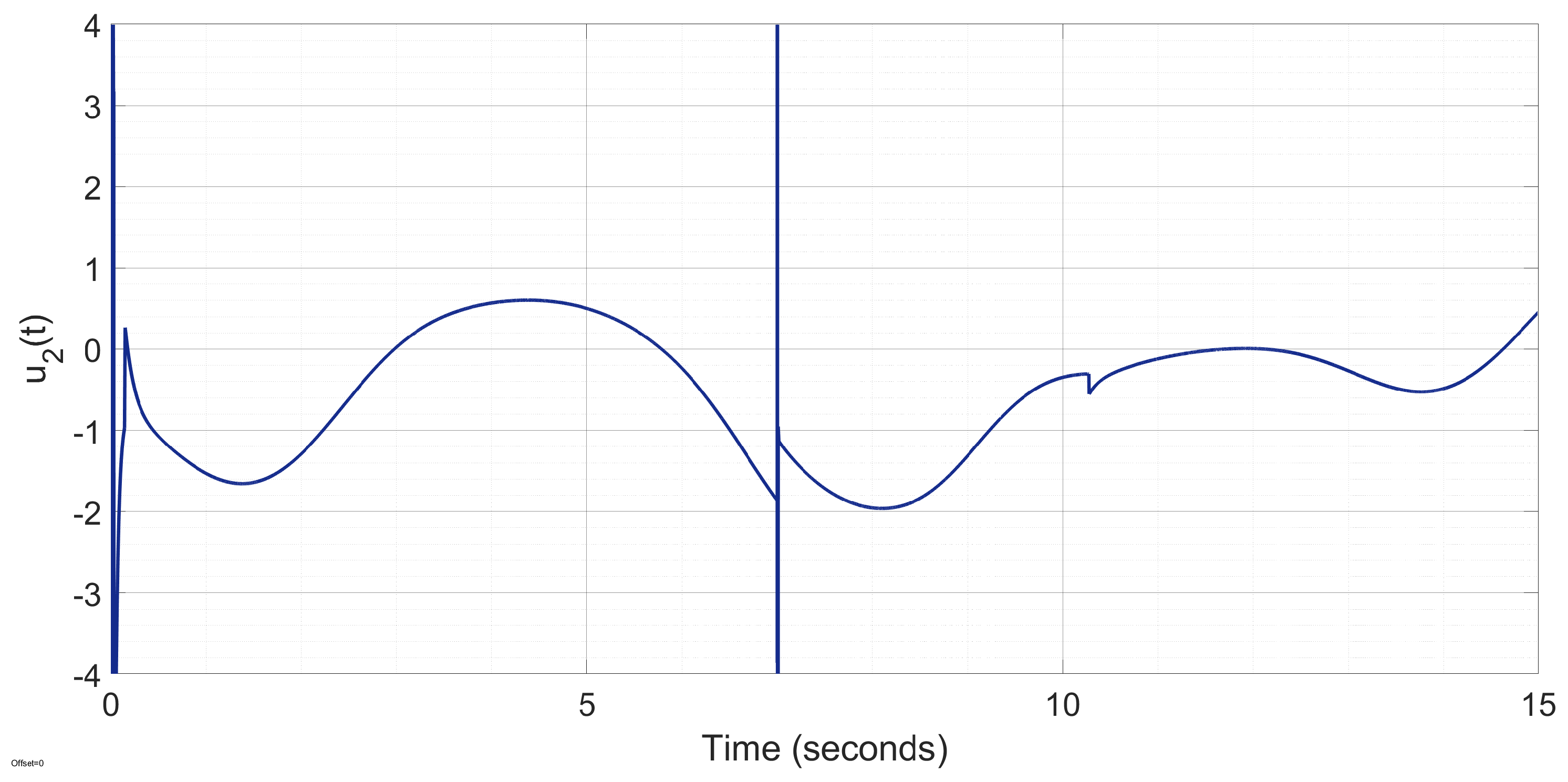
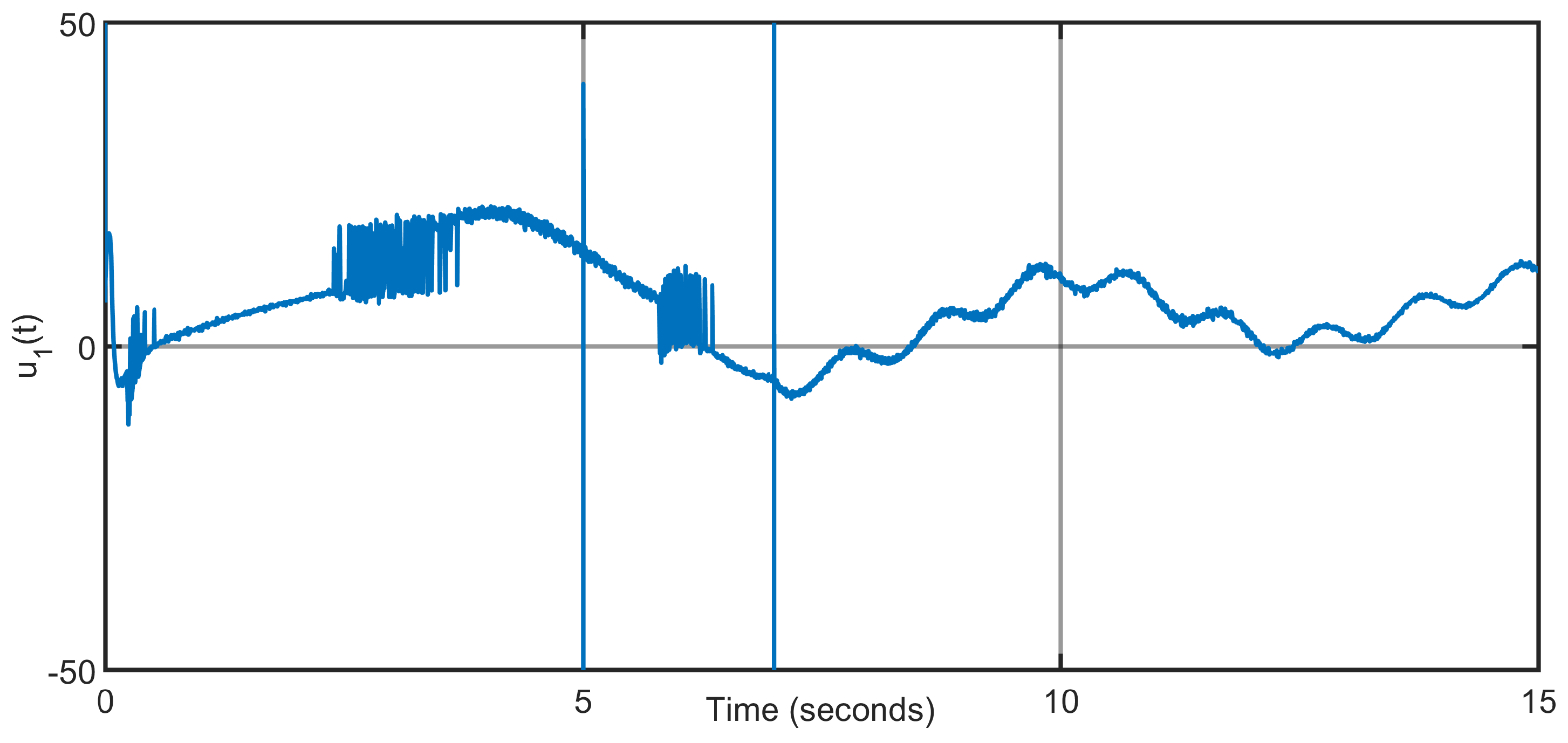
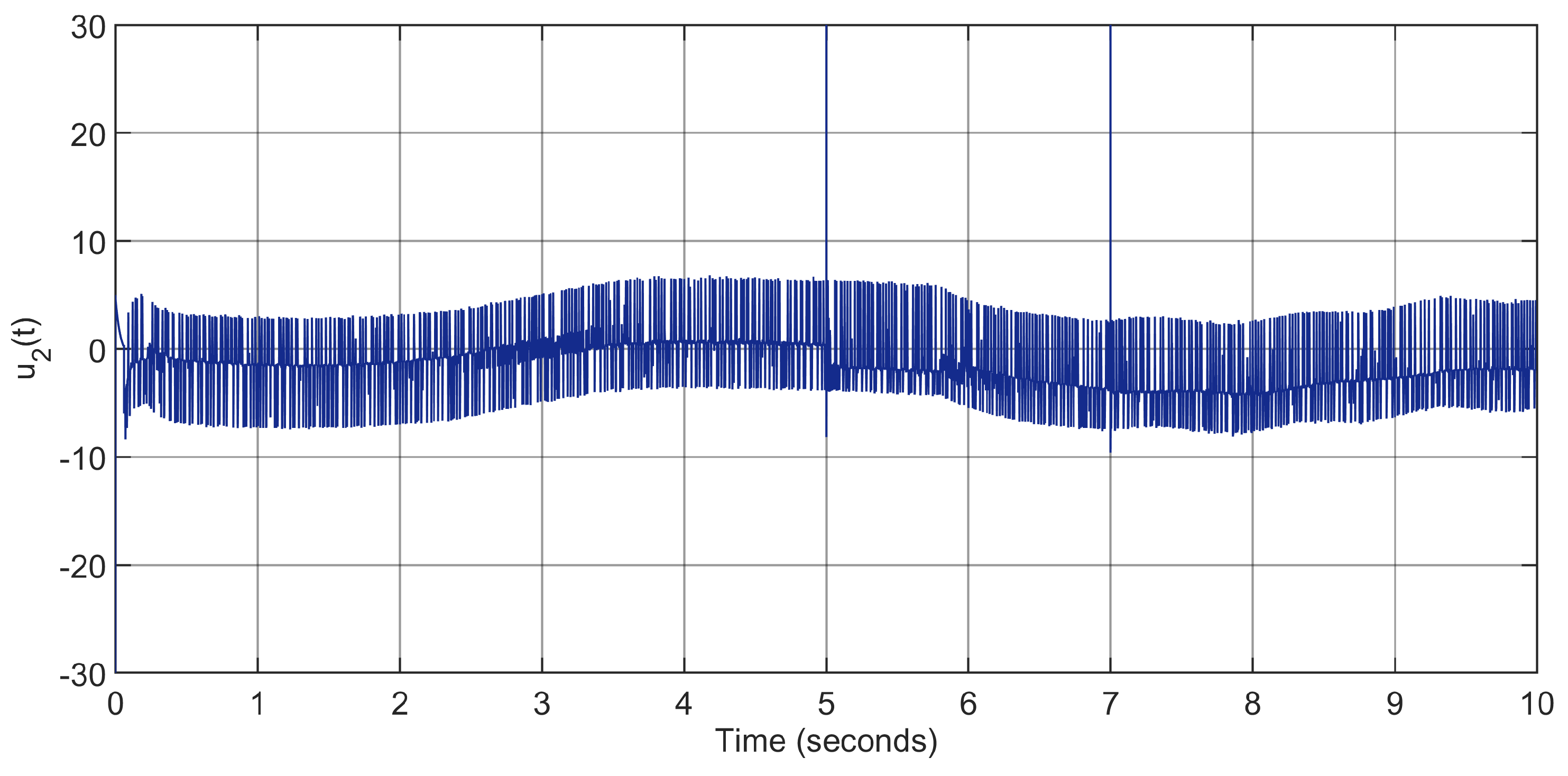
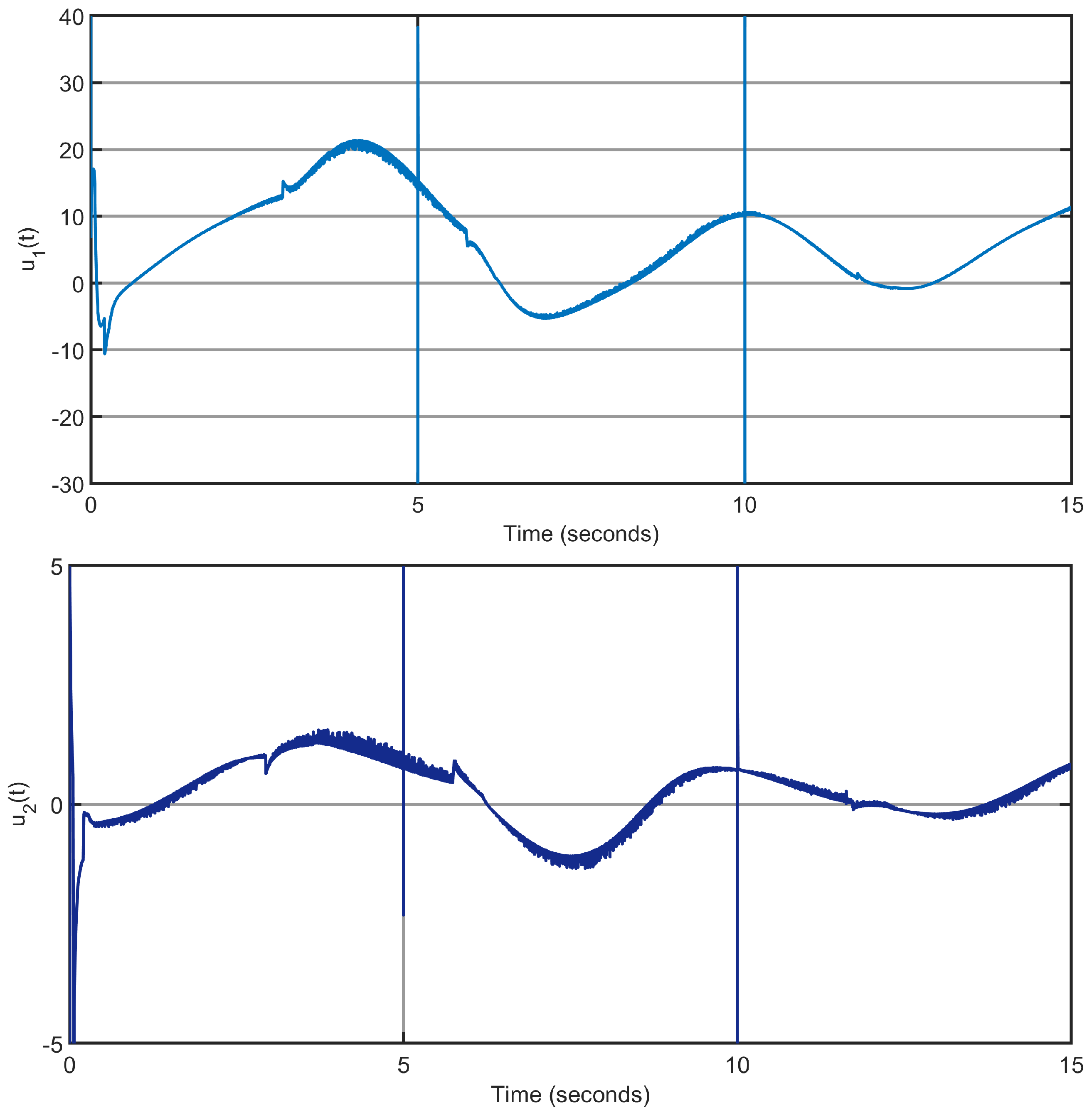
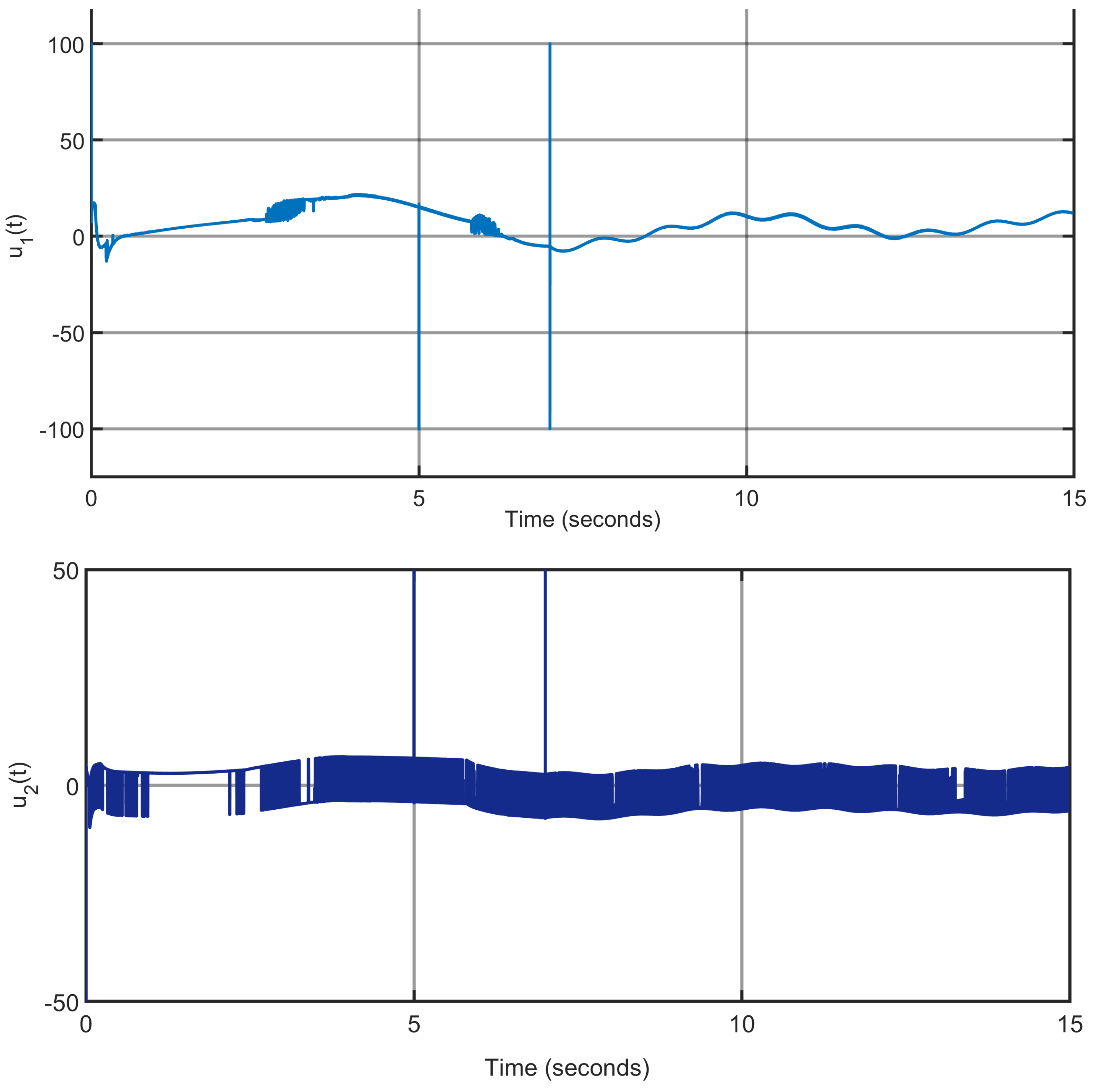
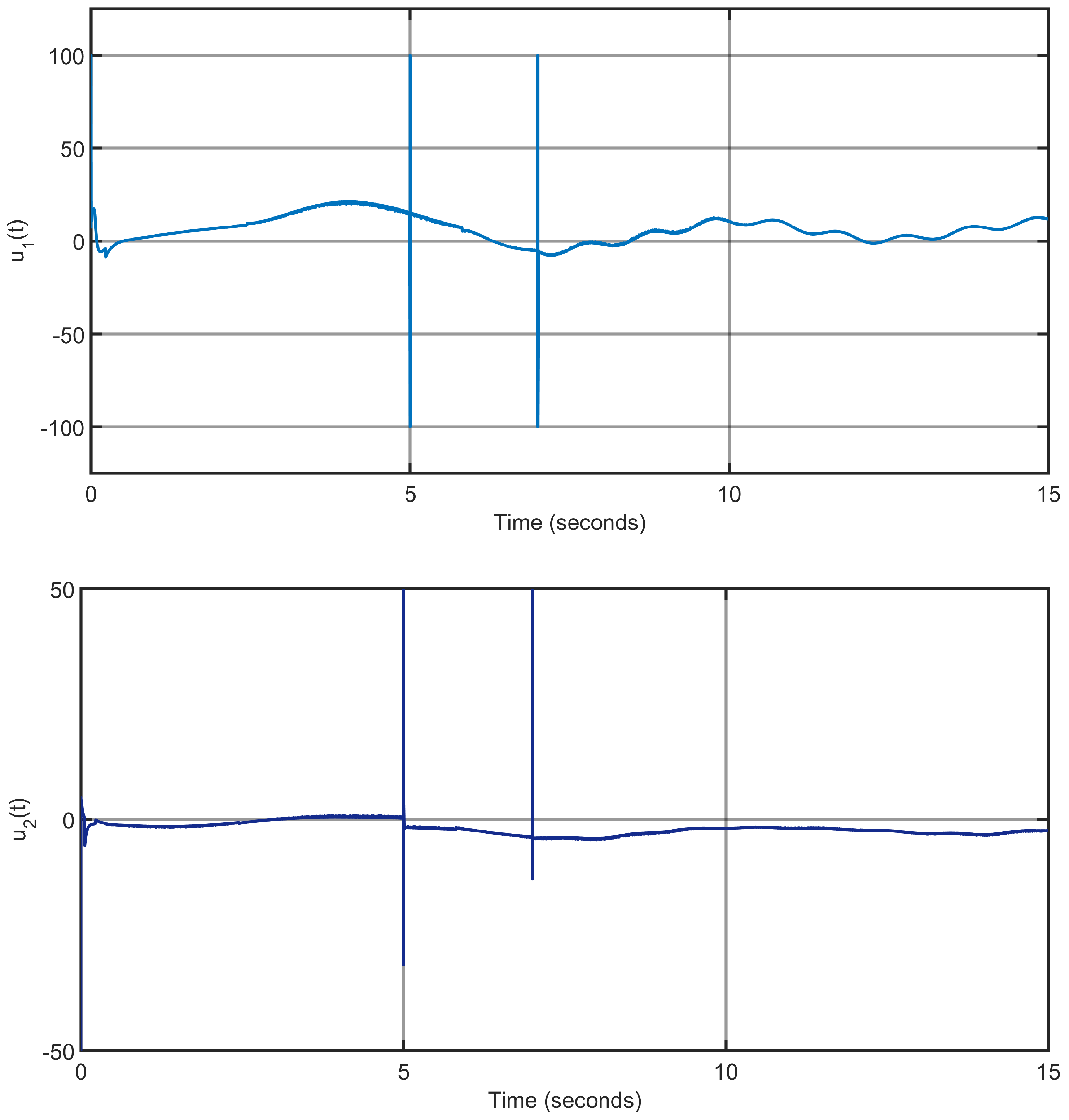
The control input torques, depicted in
Figure 11 and
Figure 12, exhibit greater adaptability to disturbance variations to preserve the tracking control performance.
6.1. Simulation Analysis Under Various Disturbances and Noise Effects
For more comprehensive analysis and richer testing, we have carried out additional new simulation scenarios following best practices in robust control evaluation.
Firstly, we test the robustness of our proposed observer-based control scheme in the case where the exoskeleton system is corrupted by two sinusoidal disturbances of different frequencies and amplitudes: the disturbance
occurring at the instant
s and
occurring at the instant
s.
Figure 13 and
Figure 14 illustrate the ability of the proposed cascade observer (STD+ASTSMO) to reconstruct time-varying disturbances of different frequencies and amplitudes with very good precision.
Moreover, to emulate sensor noise, an additive Gaussian noise of a power equal to
was added to the measured joint angles. The estimates of disturbances (
Figure 15 and
Figure 16), the tracking errors (
Figure 17), the joint trajectories (
Figure 18 and
Figure 19), and the control input signals (
Figure 20 and
Figure 21) show that the proposed cascade observer-based sliding-mode controller maintains good performance in terms of disturbance estimation and tracking accuracy despite the presence of Gaussian noise.
6.2. Simulation Analysis Under Various Loads
In practical rehabilitation scenarios, the effective load applied to an exoskeleton joint is not strictly constant but may change due to several factors, such as the patient carrying an additional object, variations in muscle activation, or sudden shifts in limb dynamics.
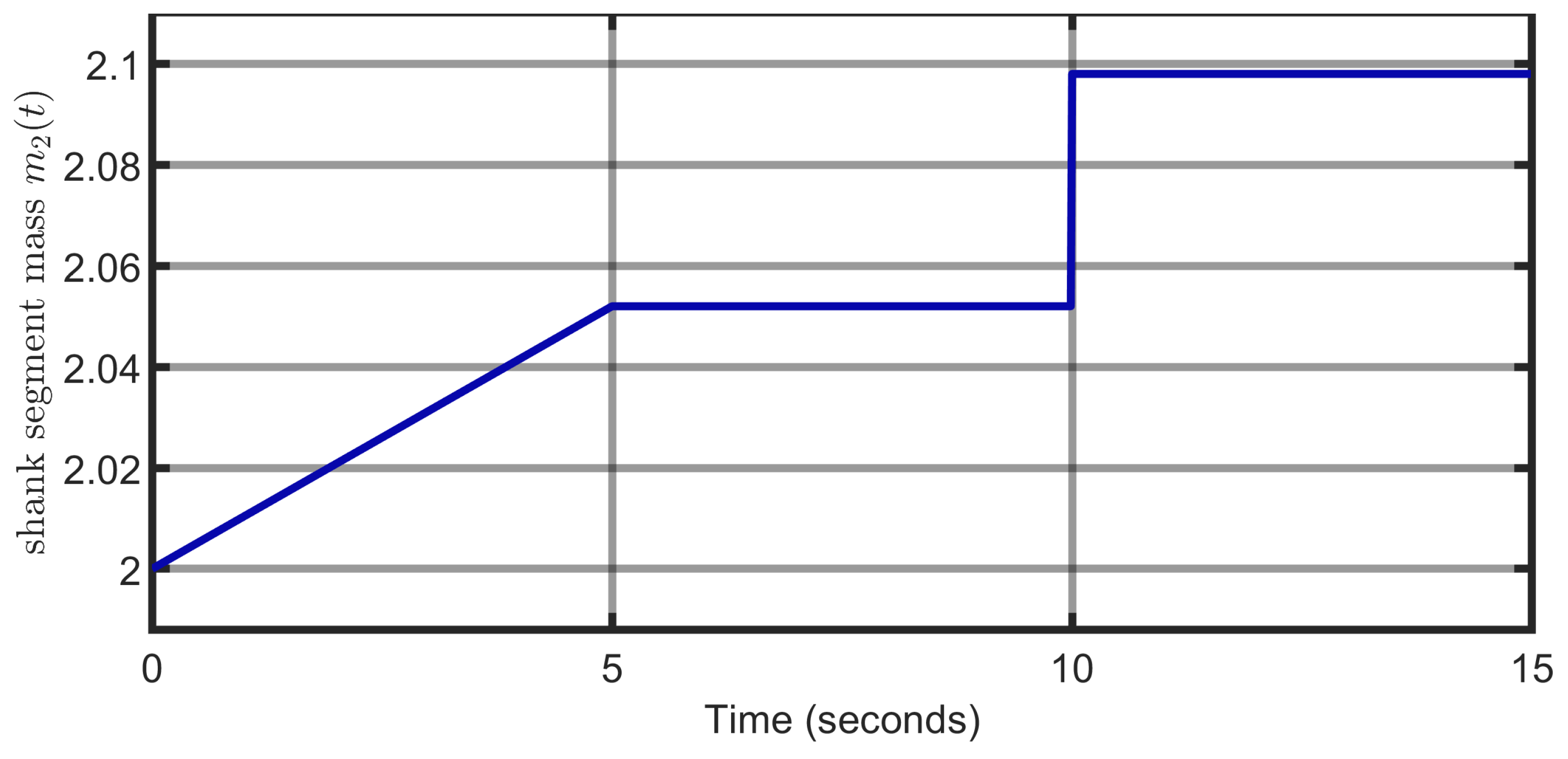
To further evaluate robustness, a disturbance scenario involving both progressive and sudden payload changes was simulated. Specifically, an additional mass of 0.1 kg was applied to the mass of shank segment
, which gradually increased in the time interval
s (progressive change), followed by sudden change at time 10 s (see
Figure 22).
Simulation results are depicted in
Figure 23 and
Figure 24. The results confirm that the proposed controller maintains accurate trajectory tracking and stable state estimation under these conditions, thereby demonstrating its capability to handle both instantaneous and gradual variations in load without compromising system stability.
6.3. Sampling Rate Sensitivity Analysis
Until this stage, simulations have been realized with a sampling rate equal to 1 Khz (
ms). In order to analyze the sampling rate sensitivity, we have realized a new set of simulations by showing the control torque input signals
and
for
Khz (
ms) and
Hz (
ms). We deduce from the obtained
Figure 25 and
Figure 26 that control input signals have better performance and are updated faster with the higher sampling rate (
Khz) compared to the case of lower sampling rate (
Hz), where we note a slight degradation in the curves of control torque input signal, which becomes less responsive.
6.4. Numerical Simulation and Quantitative Chattering Analysis
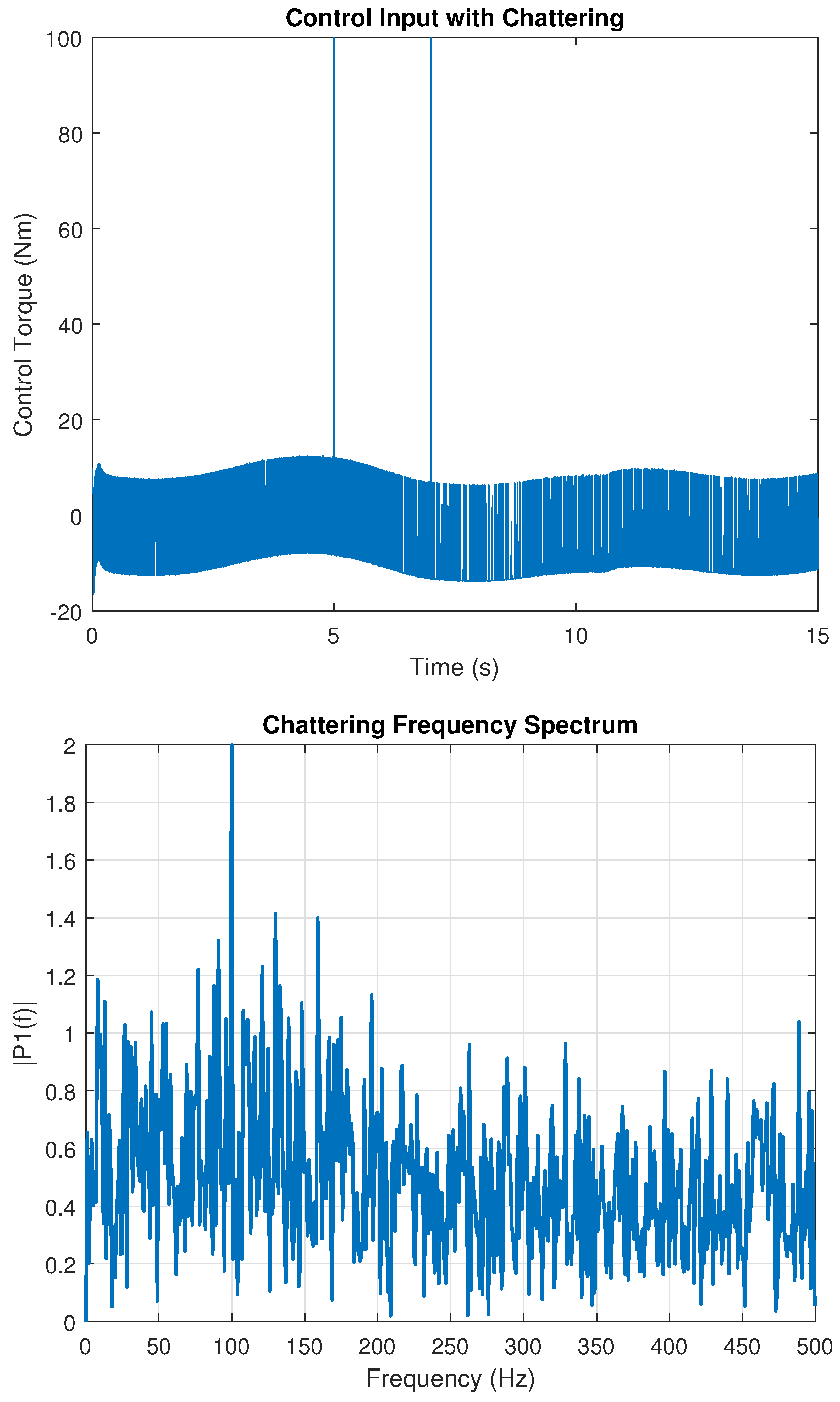
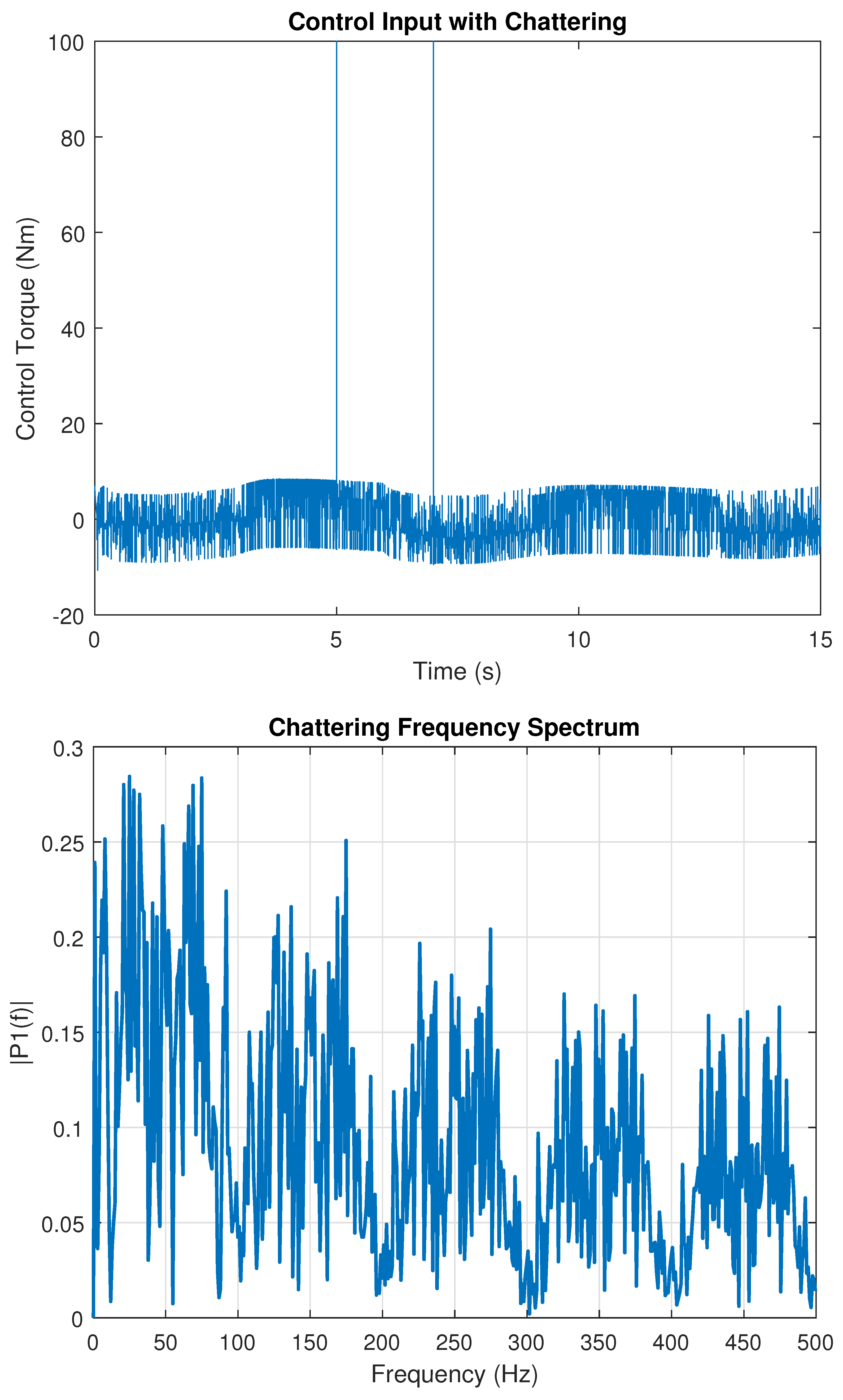
It is well known that the chattering phenomenon is the primary limitation of a sliding-mode control system that requires thorough analysis. To that end, we have developed a numerical simulation analysis of chattering in our proposed control system by showing the input torque (control signal ) as well as its high-frequency content under Gaussian measurement noise of a power equal to and step/sinusoidal disturbances.
To quantify the severity of chattering, we computed the (root mean square of the high-frequency component of the control torque). We compute also the dominant high frequency (dominant HF), which represents the main frequency component of the high-frequency part of the control input (after Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)).
Three tuning configurations (three simulation experiences) were tested:
- -
Experience 1 (control parameters , and ): The steady-state metrics (window [2 s –3 s]) are as follows: max total torque = 12.05 Nm, Nm, and dominant HF 118 Hz.
- -
Experience 2 (control parameters , and ): The steady-state metrics (window [2 s –3 s]) are as follows: max total torque = 12.05 Nm, Nm, and dominant HF 100 Hz.
- -
Experience 3 (control parameters , and ): The steady-state metrics (window [2 s –3 s]) are as follows: max total torque = 8.54 Nm, Nm, and dominant HF 65.9 Hz.
These results show that increasing the boundary layer and reducing the discontinuous gains substantially reduces the high-frequency content injected by the controller: Experience 3 reduces the HF by compared with Experiences 1 and 2 while also lowering the overall commanded torque.
In
Figure 27,
Figure 28 and
Figure 29, we show the control input
with chattering and the corresponding chattering frequency spectrum for each simulation experience and corresponding tuning configuration.
These results show that increasing the boundary layer (smoothing the discontinuous action) and reducing the discontinuous gains and (until a satisfactory trade-off between tracking transient and high-frequency content is obtained) substantially reduces the high-frequency content injected by the controller. A mild output filter may be also applied if necessary.
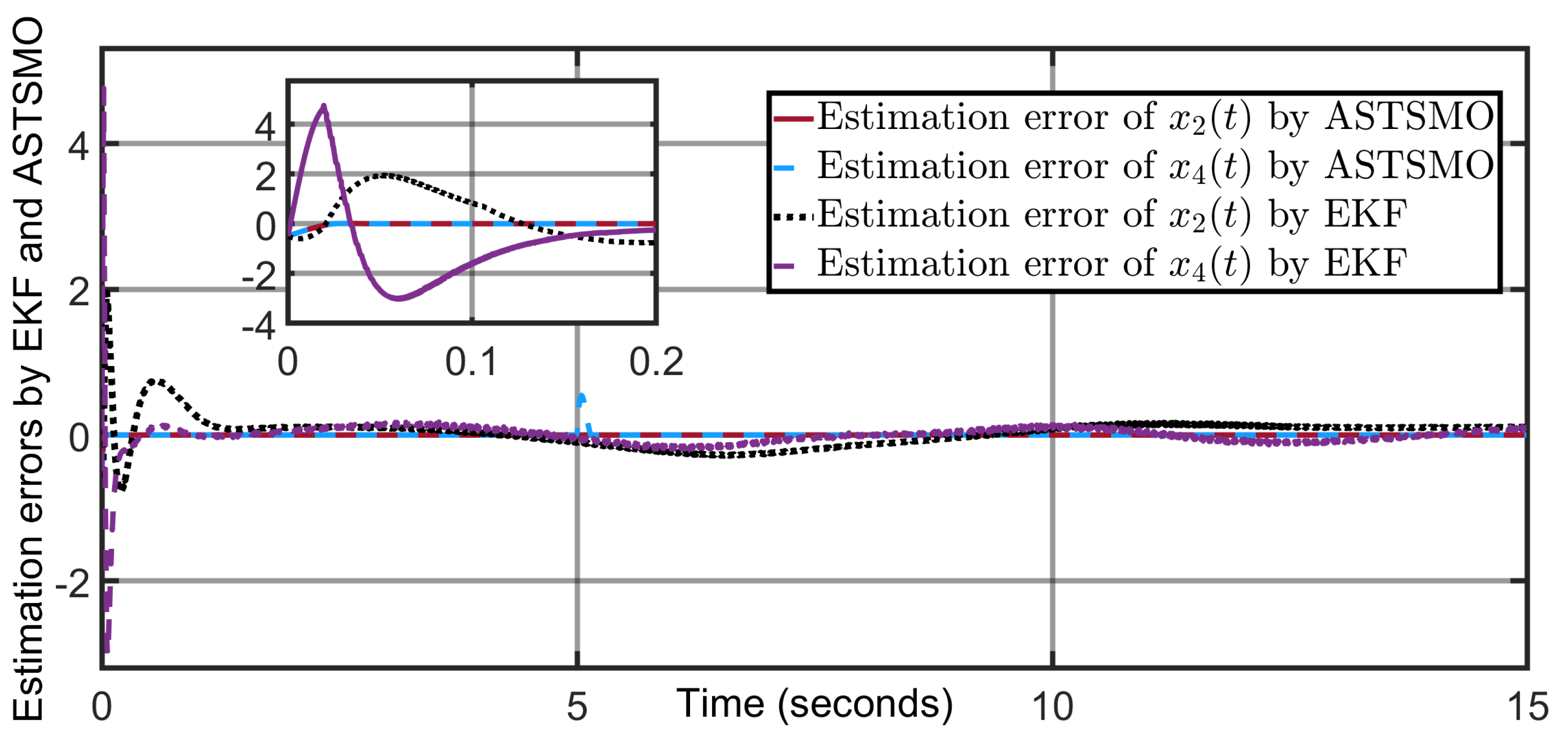
6.5. Comparative Study Between the Proposed Cascade-Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Observer (ASTSMO) and Standard Extended Kalman Filter (EKF)
In order to compare the performance of our proposed cascade-adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (STD+ASTSMO) to the standard Extended Kalman Filter (EKF), we have carried out new numerical simulation by implementing and simultaneously simulating our proposed cascade observer (STD+ASTSMO) and the standard EKF for state/disturbance estimation in the exoskeleton system under identical disturbance and noise conditions.
In fact, we implemented an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) with augmented state and augmented dynamics using the Control System Toolbox (Bloc Simulink “Extended Kalman Filter”) with a discrete sampling time of ms ( KHz) on the nonlinear two-DOF model. The measurements were sampled through a Zero-Order Hold and corrupted with Gaussian noise. Three scenarios were tested in the same disturbance and noise conditions (step and varying torque disturbances) and Gaussian measurement noise. The covariance matrices were conservatively tuned (, ).
The simulation results show a comparison in terms of state estimation performance (
Figure 30 and
Figure 31) and disturbance estimation (
Figure 32) between our proposed cascade-adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (STD+ASTSMO) and the standard Extended Kalman Filter (EKF).
The results show that, while the EKF is able to track the measured states, it struggles to reconstruct unknown disturbances. In contrast, the proposed cascade observer provides a robust finite-time estimation of disturbances with faster transient response. However, Kalman filters are efficient in appropriate applications such as linear or linearized systems.
6.6. Discussion and Perspectives on Real-Time Hardware Implementation
The present work focuses on the theoretical development and simulation validation of the proposed cascade-observer-based control algorithm. The experimental validation will be considered in our future works, where we will investigate the real-time implementation on embedded hardware such as field programmable gate array (FPGA) or microprocessor-based systems (such as microcontrollers).
Indeed, FPGA implementation of sliding-mode controllers and sliding-mode observers was successfully realized in several existing works in different applications, such as robotic systems [
24], electrical systems [
25,
26], etc. FPGA choice is relevant for Parallel Processing (the main characteristic in FPGAs): the cascade observer structure-based controller benefits from parallel computation of the STD, ASTSMO, and SMC controller. Moreover, FPGAs provide deterministic execution times that are crucial for real-time control and are able to handle high sampling rates (>1 kHz) required for smooth control [
24,
26].
Microprocessor-based systems such as microcontrollers are generally used for less demanding applications and may suffice for moderate control bandwidths; however, modern high-performance microprocessors could also implement this algorithm.
Experimental strategies and plans of validation will be addressed in our future works using a detailed analysis of the algorithm’s computational steps, execution time estimation, and suitability for real-time embedded platforms.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we have developed a new output-feedback tracking control scheme for a two-DOF lower-limb exoskeleton system. First, based on the joint angle measurements, a super-twisting differentiator (STD) was designed to estimate the angular velocity states. Second, the estimates of the latter observer were used by an adaptive super-twisting sliding-mode observer (ASTSMO), whose objective is to reconstruct the external load torque disturbance. Third, the estimated states and disturbances were integrated into a sliding-mode controller that was designed to ensure tracking control objectives despite the presence of unknown inputs. Numerical simulations realized with Matlab/Simulink software demonstrated the excellent estimation performance of the designed observers and that robust tracking control objectives are achieved with very good accuracy and fast convergence.