Fast UOIS: Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Adaptive Clustering for Industrial Robotic Grasping
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a fast unseen object instance segmentation method and apply it to robotic grasping. Dual experiments on data sets and robots demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
- We propose a method for adaptive initialization of seed points to optimize the mean-shift clustering algorithm, which significantly improves the efficiency of the unseen object instance segmentation pipeline. Our method achieves competitive performance compared with benchmark methods.
2. Problem Statement
3. Method
3.1. Network Architecture
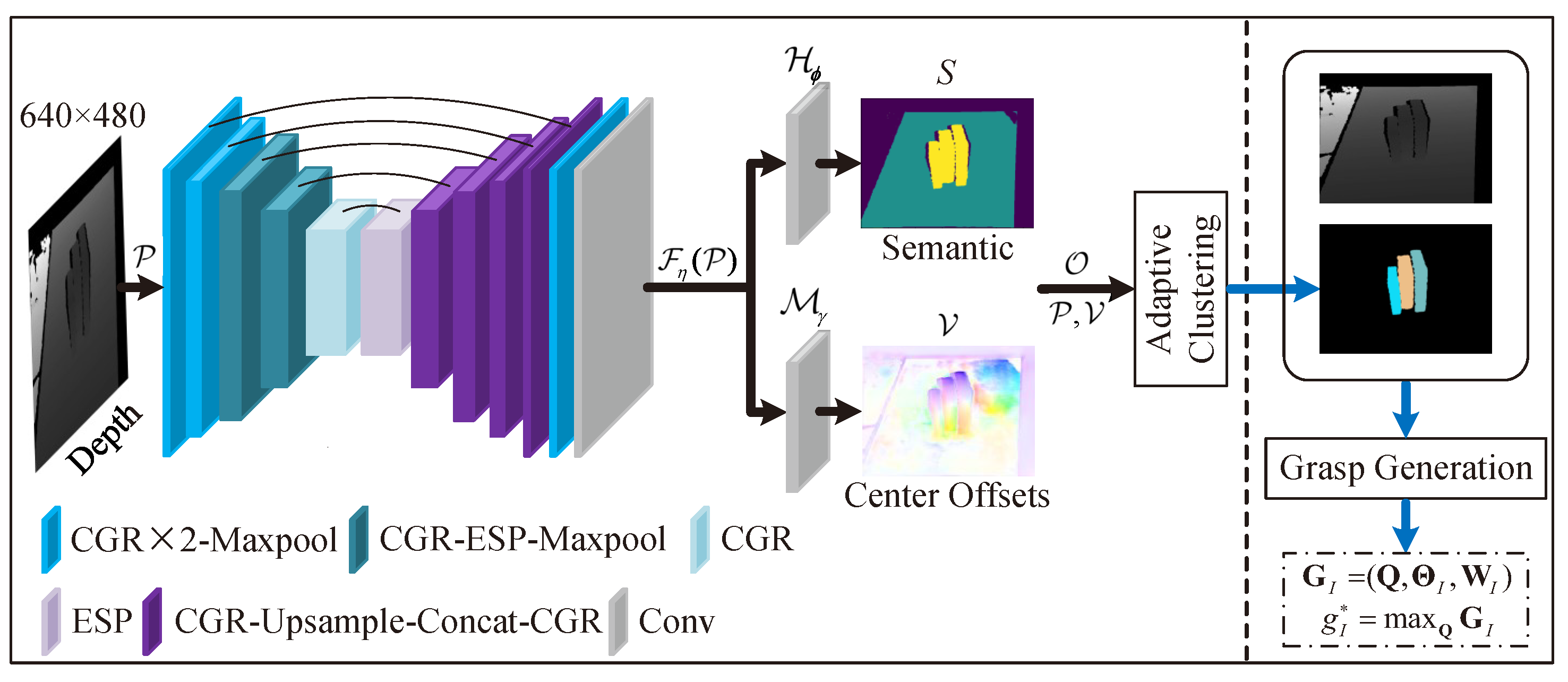
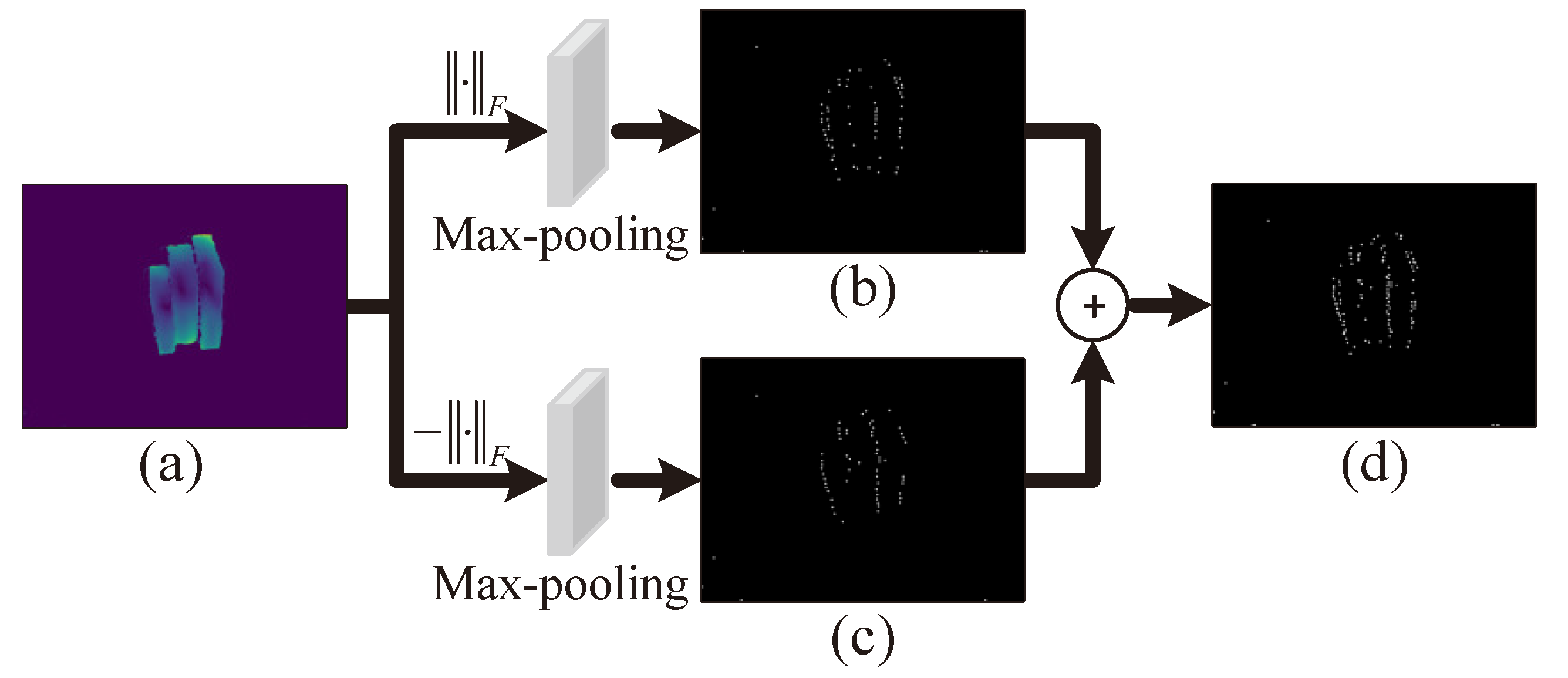
3.2. Adaptive Clustering
3.3. Loss Functions
4. Experiment
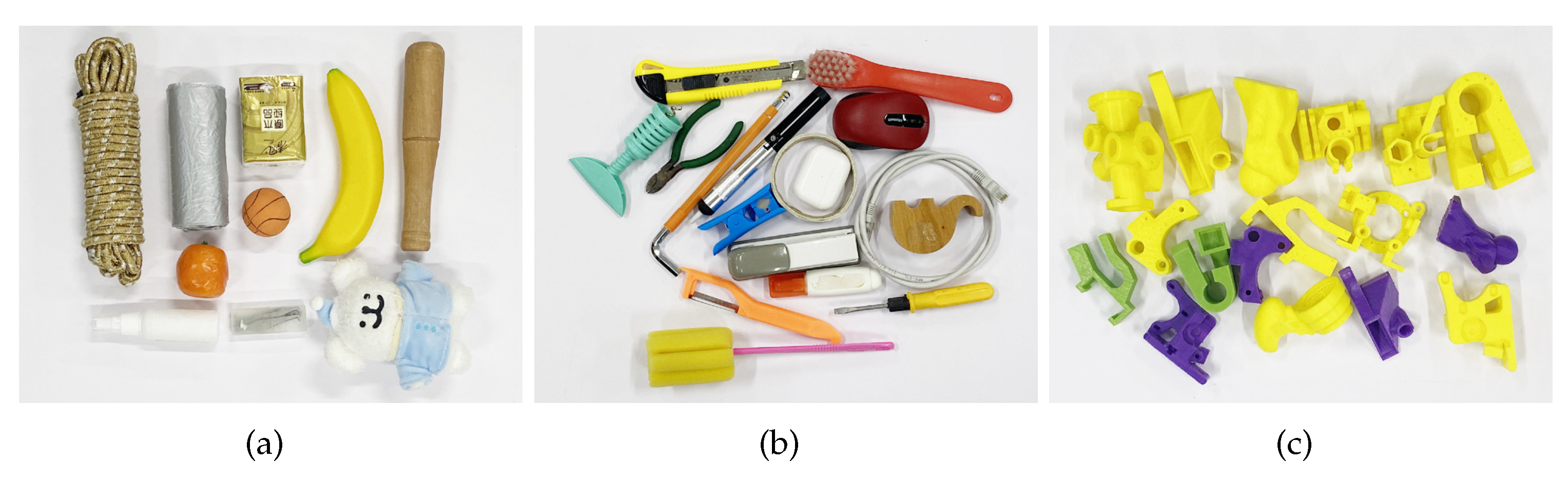
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Metrics
4.3. Details and Setups
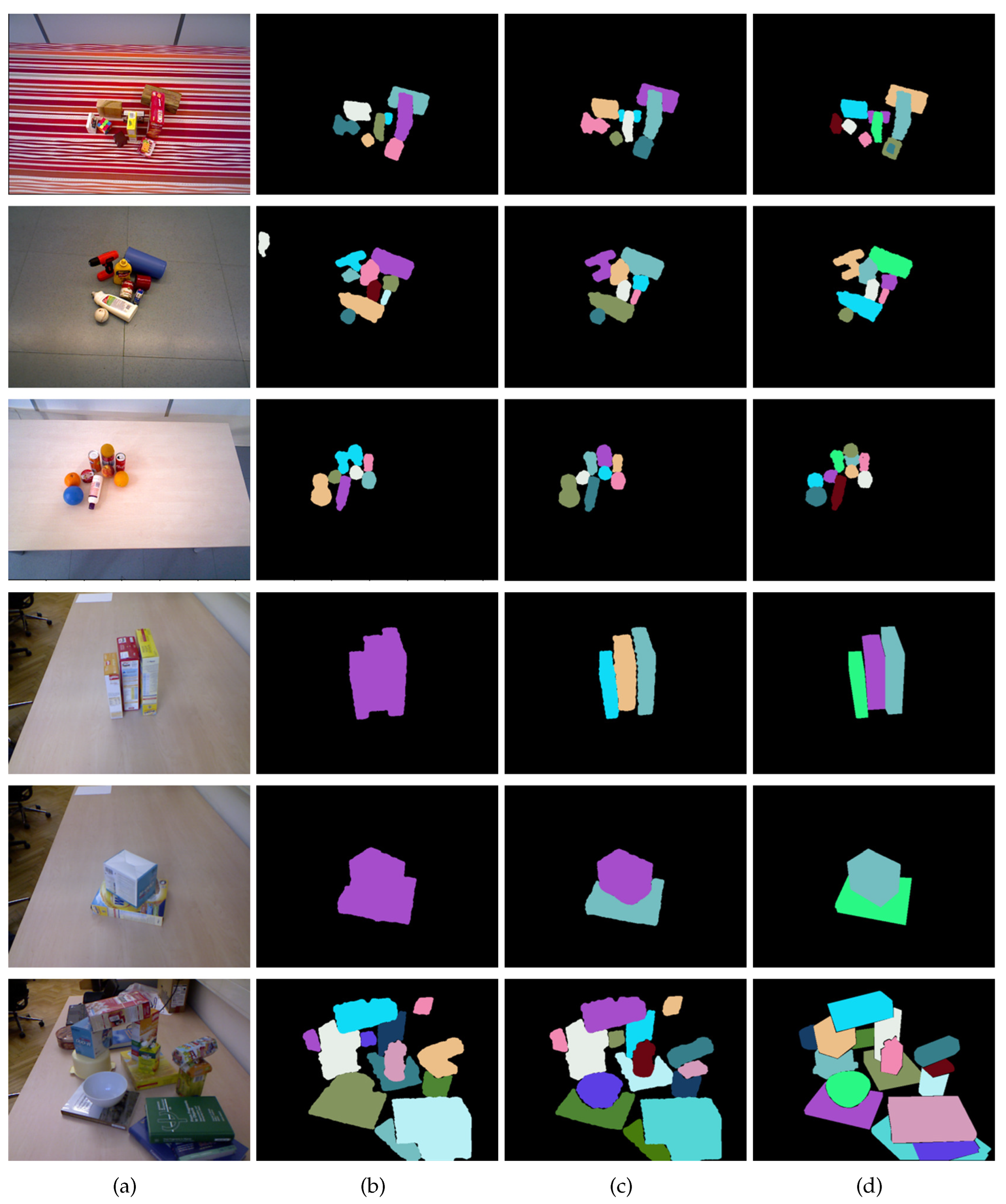
4.4. Experiments on Datasets
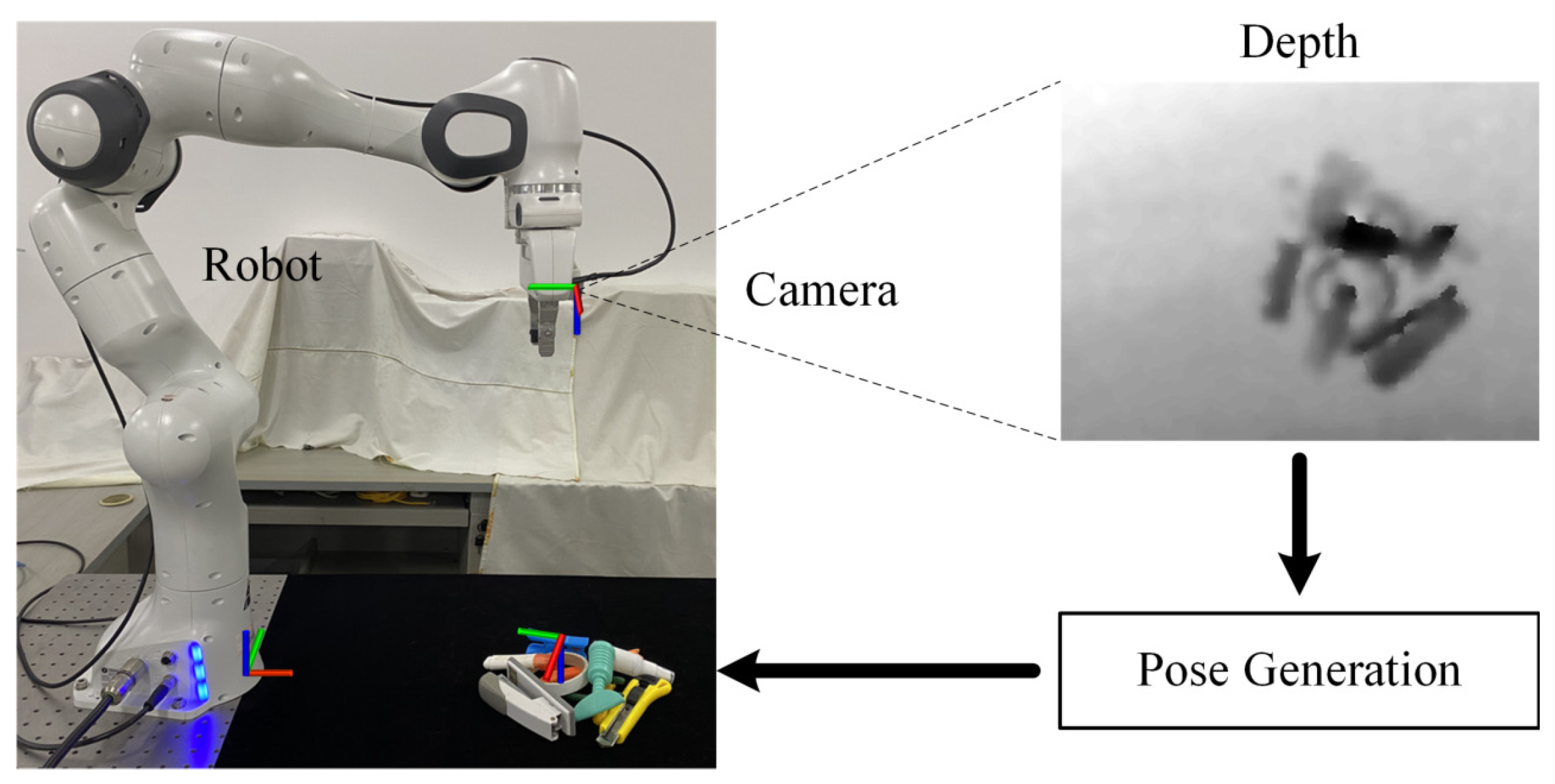
4.5. Robotic Grasping
4.6. Discussion of Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levine, S.; Pastor, P.; Krizhevsky, A.; Ibarz, J.; Quillen, D. Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with large-scale data collection. Int. J. Exp. Robot. Res. 2018, 37, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Song, S.; Yu, K.T.; Donlon, E.; Hogan, F.R.; Bauza, M.; Ma, D.; Taylor, O.; Liu, M.; Romo, E.; et al. Robotic pick-and-place of novel objects in clutter with multi-affordance grasping and cross-domain image matching. Int. J. Exp. Robot. Res. 2022, 41, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchi, A.; Vijay, K. Robotic grasping and contact: A review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Rubert, C.; Kappler, D.; Morales, A.; Schaal, S.; Bohg, J. On the relevance of grasp metrics for predicting grasp success. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Moseson, S.; Saxena, A. Efficient grasping from rgbd images: Learning using a new rectangle representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3304–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, I.; Lee, H.; Saxena, A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y. CGNet: Robotic grasp detection in heavily cluttered scenes. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2023, 28, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Yuan, L.; Du, Y.; Cong, M. Robotic objects detection and grasping in clutter based on cascaded deep convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N. Fully convolutional grasp detection network with oriented anchor box. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7223–7230. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Shen, W. A novel robotic grasp detection method based on region proposal networks. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 65, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Angelova, A. Real-time grasp detection using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1316–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Shang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Cong, S.; Li, Z. Robotic grasping of unknown objects using novel multilevel convolutional neural networks: From parallel gripper to dexterous hand. IEEE Trans. Automat. Sci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Learning robust, real-time, reactive robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumra, S.; Joshi, S.; Sahin, F. Antipodal robotic grasping using generative residual convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 9626–9633. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, M.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, C. VERGNet: Visual enhancement guided robotic grasp detection under low-light condition. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 2023, 8, 8541–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Song, K.; Li, S.; Ma, S.; Yan, Y. Lightweight pixel-wise generative robot grasping detection based on RGB-D dense fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 7, 5017912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, H.; Liao, J. SE-ResUNet: A novel robotic grasp detection method. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 2022, 7, 5238–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Lin, J.; Knoll, A. Efficient grasp detection network with gaussian-based grasp representation for robotic manipulation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2023, 28, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Dang, X. Light-weight convolutional neural networks for generative robotic grasping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 6696–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S. Information-theoretic exploration for adaptive robotic grasping in clutter based on real-time pixel-level grasp detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaei, H.; Kasaei, M. MVGrasp: Real-time multi-view 3D object grasping in highly cluttered environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2023, 160, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainetter, S.; Fraundorfer, F. End-to-end trainable deep neural network for robotic grasp detection and semantic segmentation from rgb. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Xi’an, China, 30 May 2021–5 June 2021; pp. 13452–13458. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Tong, L.; Song, K.; Tian, H.; Man, Y.; Yang, W. SISG-Net: Simultaneous instance segmentation and grasp detection for robot grasp in clutter. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 58, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xiang, Y.; Mousavian, A.; Fox, D. Unseen object instance segmentation for robotic environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xie, C.; Mousavian, A.; Fox, D. Learning rgb-d feature embeddings for unseen object instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Cambridge, MA, USA, 16–18 November 2020; pp. 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ruozzi, N.; Xiang, Y. Mean Shift Mask Transformer for Unseen Object Instance Segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11679. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Dang, X.; Zhang, Y. Taylor neural network for unseen object instance segmentation in hierarchical grasping. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. ESPnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 552–568. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira-Perpinan, M.A. A review of mean-shift algorithms for clustering. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.00687. [Google Scholar]
- Suchi, M.; Patten, T.; Vincze, M. EasyLabel: A semi-automatic pixelwise object annotation tool for creating robotic rgb-d datasets. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 6678–6684. [Google Scholar]
- Richtsfeld, A.; Mörwald, T.; Prankl, J.; Zillich, M.; Vincze, M. Segmentation of unknown objects in indoor environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 4791–4796. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Back, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.; Noh, S.; Kang, R.; Bak, S.; Lee, K. Unseen object amodal instance segmentation via hierarchical occlusion modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotic Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 5085–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, J.; Liang, J.; Niyaz, S.; Laskey, M.; Doan, R.; Liu, X.; Ojea, J.A.; Goldberg, K. Dex-net 2.0: Deep learning to plan robust grasps with synthetic point clouds and analytic grasp metrics. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09312. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Y. Real-time robotic multigrasp detection using anchor-free fully convolutional grasp detector. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13171–13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Chang, F.; Li, N.; Li, G. High-performance pixel-level grasp detection based on adaptive grasping and grasp-aware network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 11611–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
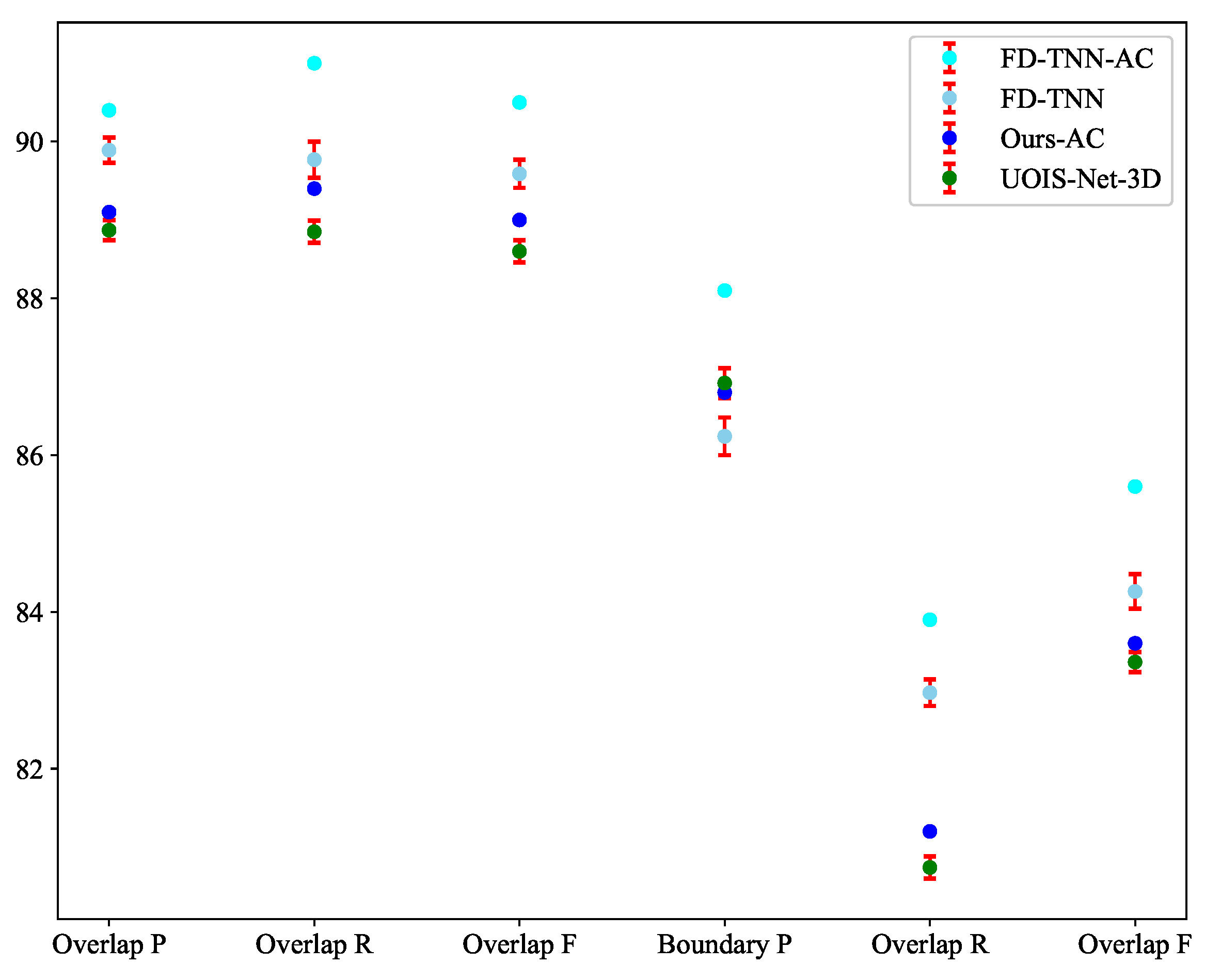


| Method | Time (s) | Parm (M) | OCID | OSD | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlap | Boundary | Overlap | Boundary | |||||||||||
| P | R | F | P | R | F | P | R | F | P | R | F | |||
| Mask R-CNN † [34] | - | - | 82.7 | 78.9 | 79.9 | 79.4 | 67.7 | 71.9 | 73.8 | 72.9 | 72.2 | 49.6 | 40.3 | 43.1 |
| UOIS-Net-3D [25] | 0.120 | 22.3 | 88.8 | 89.2 | 88.8 | 86.9 | 80.9 | 83.5 | 85.7 | 82.1 | 83.0 | 74.3 | 67.5 | 70.0 |
| UCN [26] | 0.250 ‡ | - | 83.1 | 90.7 | 86.4 | 77.7 | 74.3 | 75.6 | 78.7 | 83.8 | 81.0 | 52.6 | 50.0 | 50.9 |
| UOAIS-Net [35] | 0.074 | 77.4 | 89.9 | 90.9 | 89.8 | 86.7 | 84.1 | 84.7 | 84.9 | 86.4 | 85.5 | 68.2 | 66.2 | 66.9 |
| MSMFormer [27] | 0.278 | - | 88.4 | 90.2 | 88.5 | 84.7 | 83.1 | 83.0 | 79.5 | 86.4 | 82.8 | 53.5 | 71.0 | 60.6 |
| FD-TNN [28] | 0.123 | 27.2 | 90.0 | 89.9 | 89.7 | 86.4 | 83.1 | 84.4 | 88.0 | 87.4 | 87.7 | 74.3 | 72.8 | 73.4 |
| UOIS-Net-3D-AC | 0.065 | 22.3 | 88.8 | 88.7 | 88.5 | 86.7 | 80.5 | 83.1 | 86.3 | 82.6 | 83.7 | 74.7 | 68.1 | 70.6 |
| FD-TNN-AC | 0.068 | 27.2 | 90.4 | 91.0 | 90.5 | 88.1 | 83.9 | 85.6 | 88.2 | 87.2 | 87.7 | 75.0 | 72.9 | 73.7 |
| Ours-OC | 0.120 | 22.3 | 89.0 | 89.4 | 89.0 | 86.9 | 81.2 | 83.7 | 87.0 | 84.9 | 85.9 | 73.2 | 69.1 | 70.8 |
| Ours-AC | 0.065 | 22.3 | 89.1 | 89.4 | 89.0 | 86.8 | 81.2 | 83.6 | 87.5 | 85.3 | 86.2 | 73.8 | 69.7 | 71.4 |
| Method | Dataset | OCID | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlap | Boundary | ||||||
| P | R | F | P | R | F | ||
| FD-TNN-AC | OCID-F | 88.0 | 87.1 | 87.0 | 82.5 | 79.7 | 80.6 |
| FD-TNN-AC | OCID-FT | 89.5 | 90.2 | 89.5 | 87.4 | 82.2 | 84.4 |
| Ours-AC | OCID-F | 88.0 | 84.5 | 85.6 | 82.5 | 77.8 | 79.4 |
| Ours-AC | OCID-FT | 87.6 | 89.1 | 88.1 | 85.5 | 79.6 | 82.0 |
| OCID | OSD | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlap | Boundary | Overlap | Boundary | |||||||||
| P | R | F | P | R | F | P | R | F | P | R | F | |
| 89.06 | 89.44 | 89.02 | 86.85 | 81.21 | 83.60 | 87.53 | 85.36 | 86.22 | 73.88 | 69.74 | 71.46 | |
| 89.03 | 89.42 | 89.00 | 86.79 | 81.20 | 83.57 | 87.52 | 85.37 | 86.21 | 73.88 | 69.79 | 71.49 | |
| 89.00 | 89.40 | 88.98 | 86.74 | 81.20 | 83.55 | 87.52 | 85.37 | 86.21 | 73.88 | 69.79 | 71.49 | |
| 88.93 | 89.33 | 88.91 | 86.63 | 81.15 | 83.47 | 87.47 | 85.33 | 86.17 | 73.67 | 69.65 | 71.31 | |
| 88.90 | 89.30 | 88.87 | 86.58 | 81.12 | 83.43 | 87.46 | 85.33 | 86.17 | 73.69 | 69.67 | 71.33 | |
| Method | Gripper | GPU | Time (ms) | Grasp Success Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020/Morrison et al. [14] | Parallel-jaw | RTX3090 | 12 † | 87 |
| 2020/Kumra et al. [15] | Parallel-jaw | RTX3090 | 14 † | 93.5 |
| 2022/Wu et al. [37] | Parallel-jaw | RTX2080 | 26 | 83.3 |
| 2022/Wang et al. [38] | Parallel-jaw | RTX3090 | 142 † | 93.5 |
| 2022/Liu et al. [9] | Parallel-jaw | RTX2080Ti | 47 | 90.2 |
| 2023/Cao et al. [19] | Parallel-jaw | RTX2080Ti | - | 85.9 |
| 2023/Yu et al. [8] | Parallel-jaw | TITAN RTX | 40 | 91.7 |
| 2024/Fu et al. [28] | Parallel-jaw | RTX3090 | 137 | 97.0 |
| Ours | Parallel-jaw | RTX3090 | 77 | 93.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, K.; Dang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, J. Fast UOIS: Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Adaptive Clustering for Industrial Robotic Grasping. Actuators 2024, 13, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13080305
Fu K, Dang X, Zhang Q, Peng J. Fast UOIS: Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Adaptive Clustering for Industrial Robotic Grasping. Actuators. 2024; 13(8):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13080305
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Kui, Xuanju Dang, Qingyu Zhang, and Jiansheng Peng. 2024. "Fast UOIS: Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Adaptive Clustering for Industrial Robotic Grasping" Actuators 13, no. 8: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13080305
APA StyleFu, K., Dang, X., Zhang, Q., & Peng, J. (2024). Fast UOIS: Unseen Object Instance Segmentation with Adaptive Clustering for Industrial Robotic Grasping. Actuators, 13(8), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13080305





