Evaluating Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators as Soft Motor Units for Forming Artificial Muscles in Biomimetic Rehabilitation Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
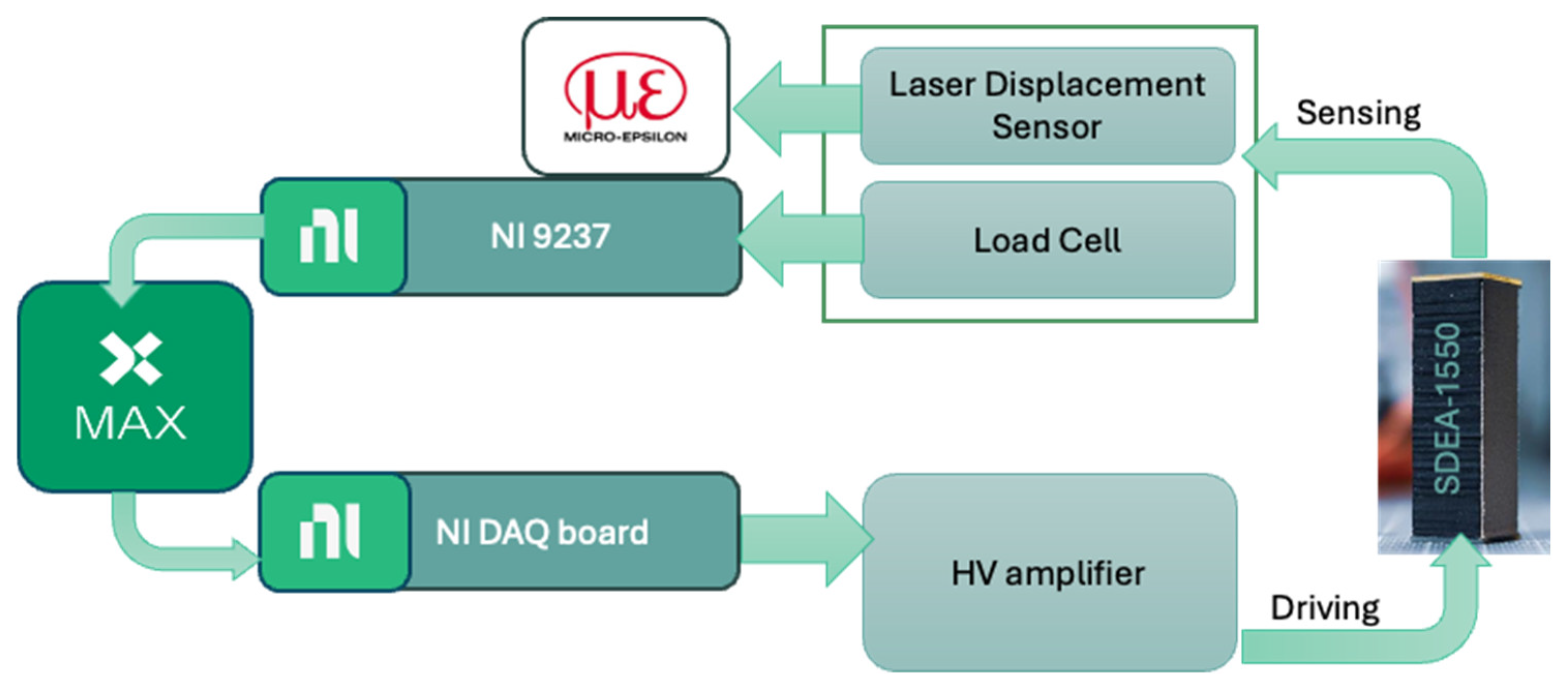
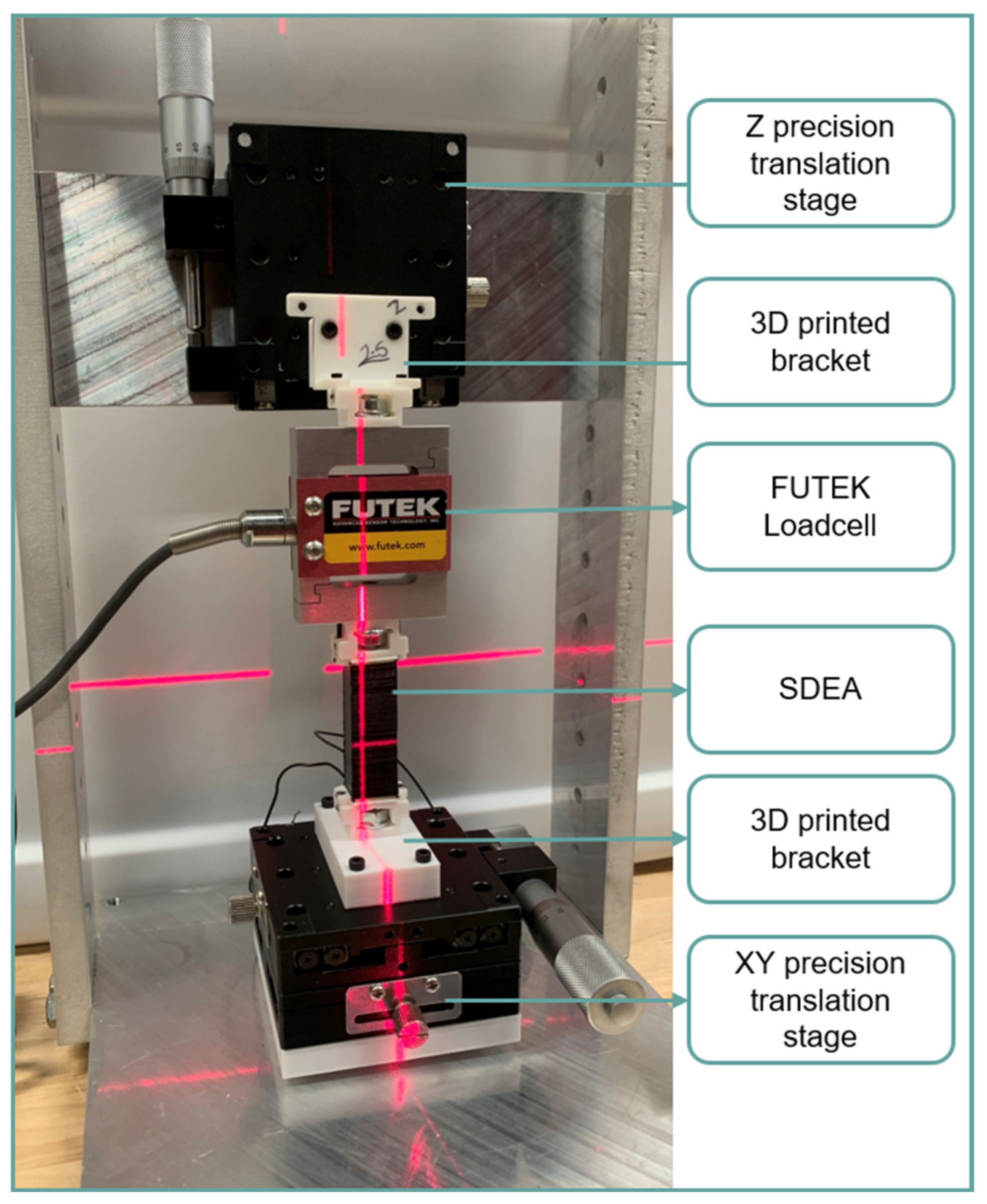
2. Methods
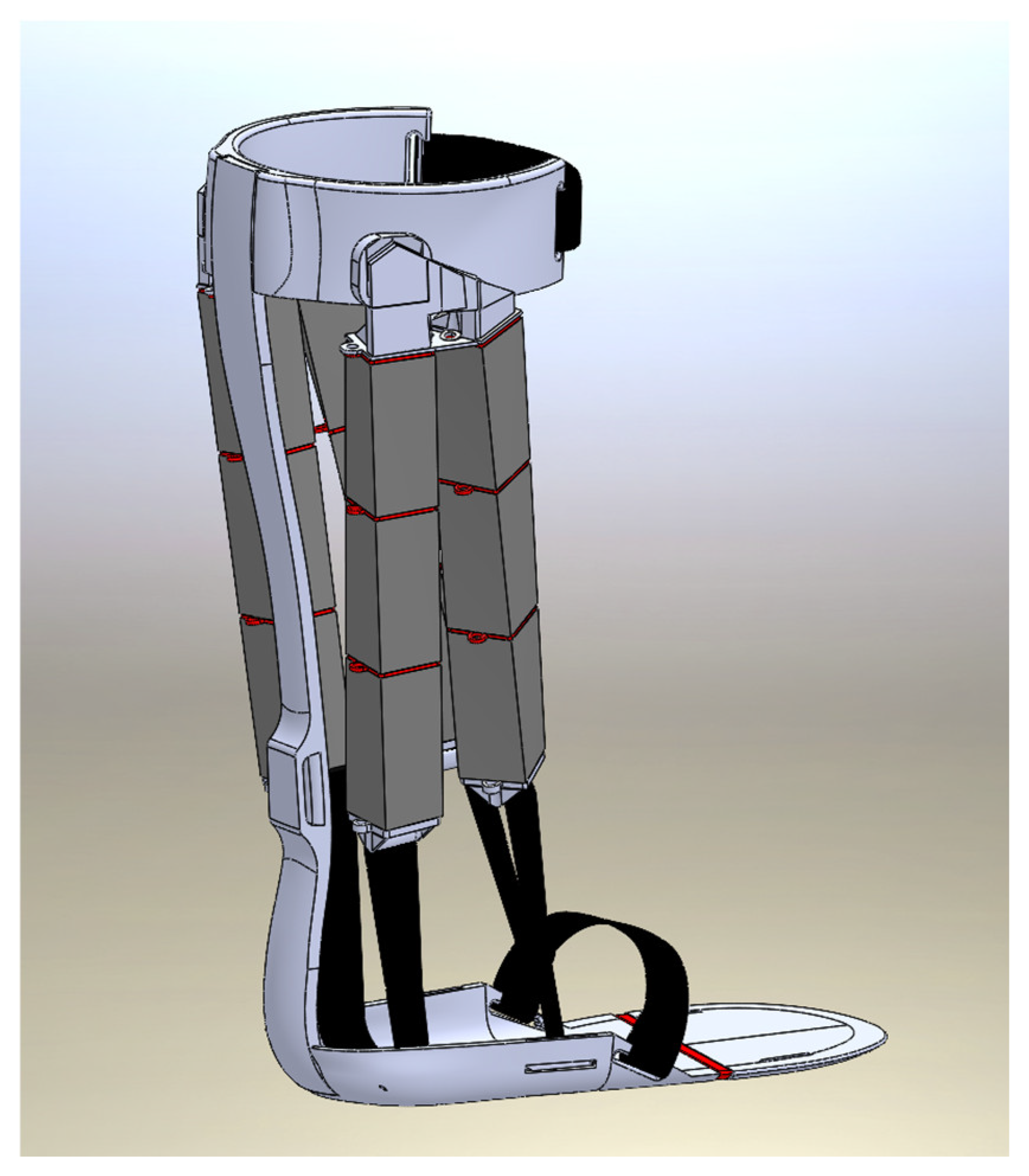
2.1. Testing Procedure
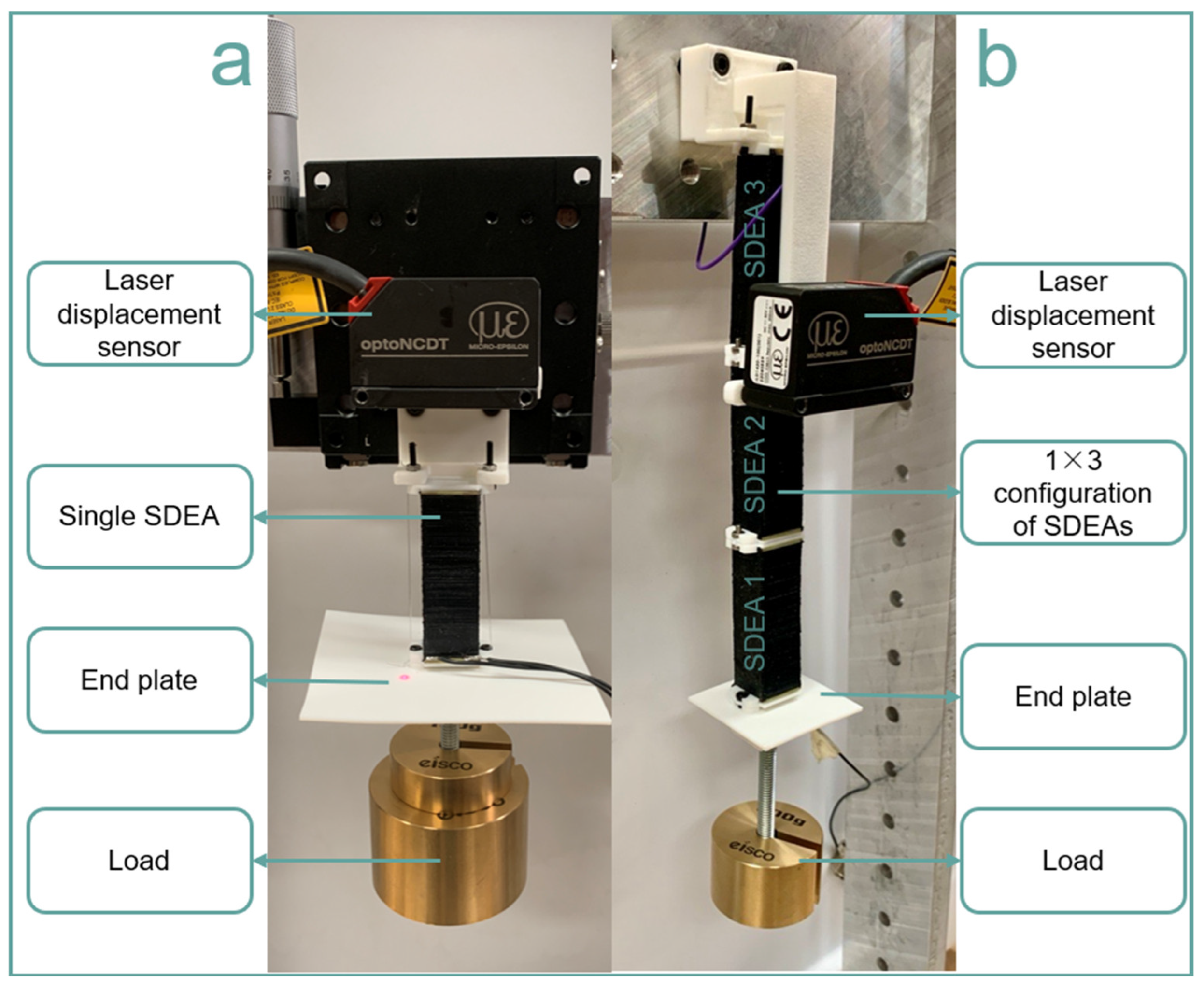
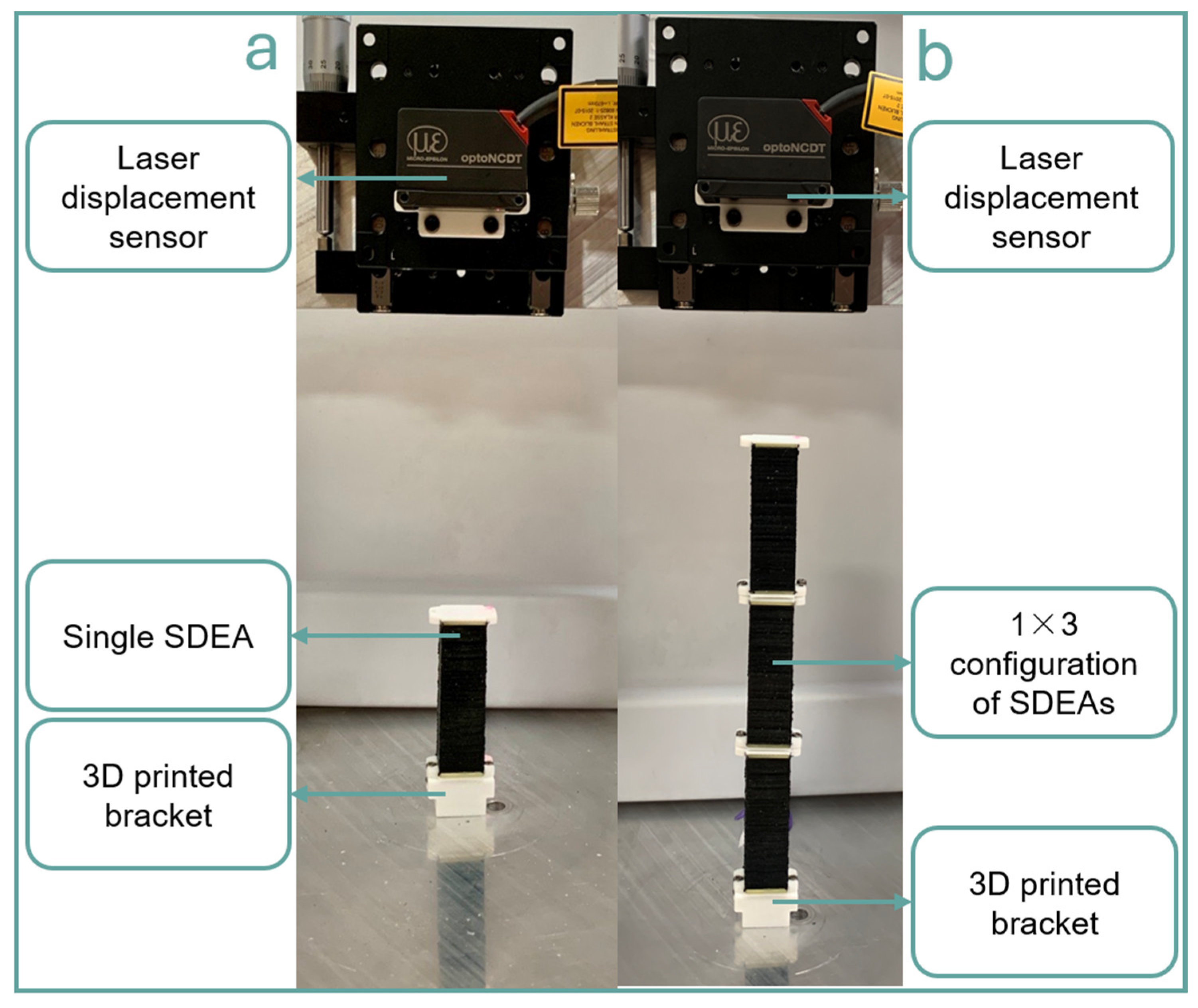
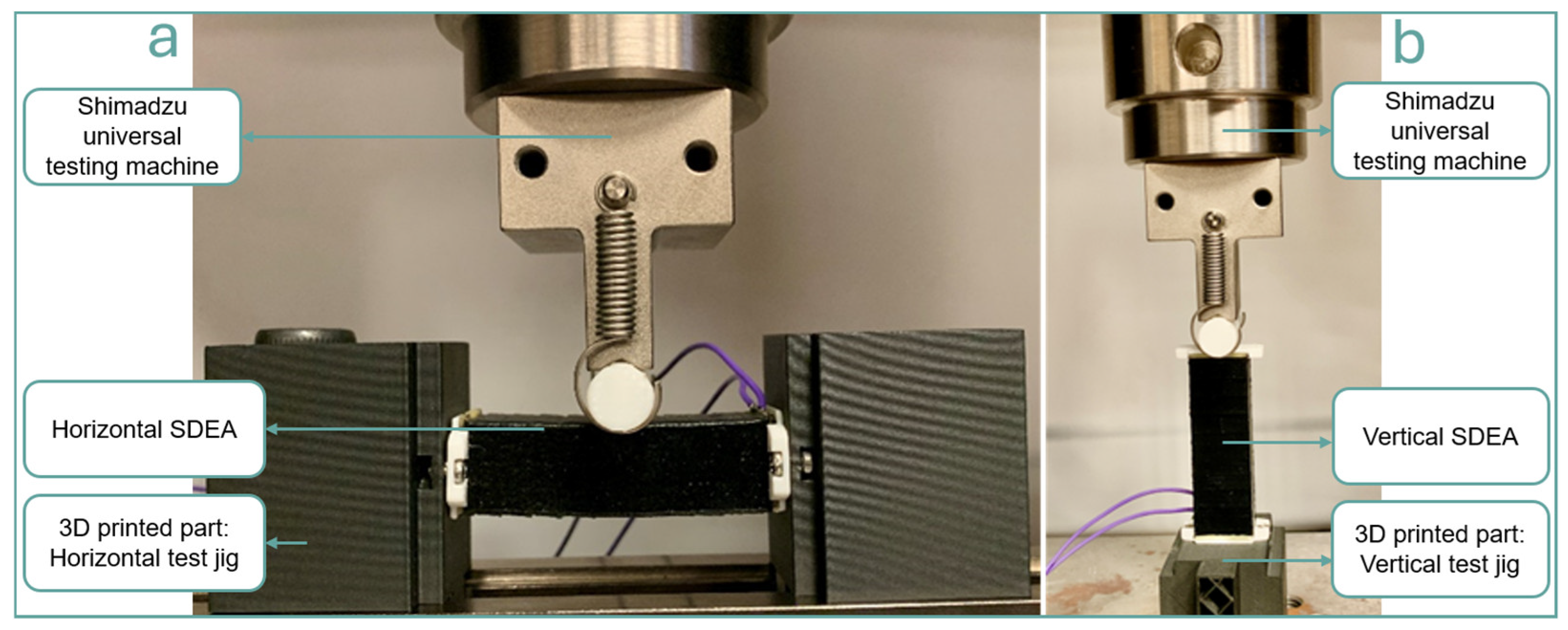
2.2. Strain-Stress Testing Setup
2.3. Isometric Condition
2.4. Isotonic Condition
2.5. Free-Standing Condition
2.6. Stiffness
3. Results
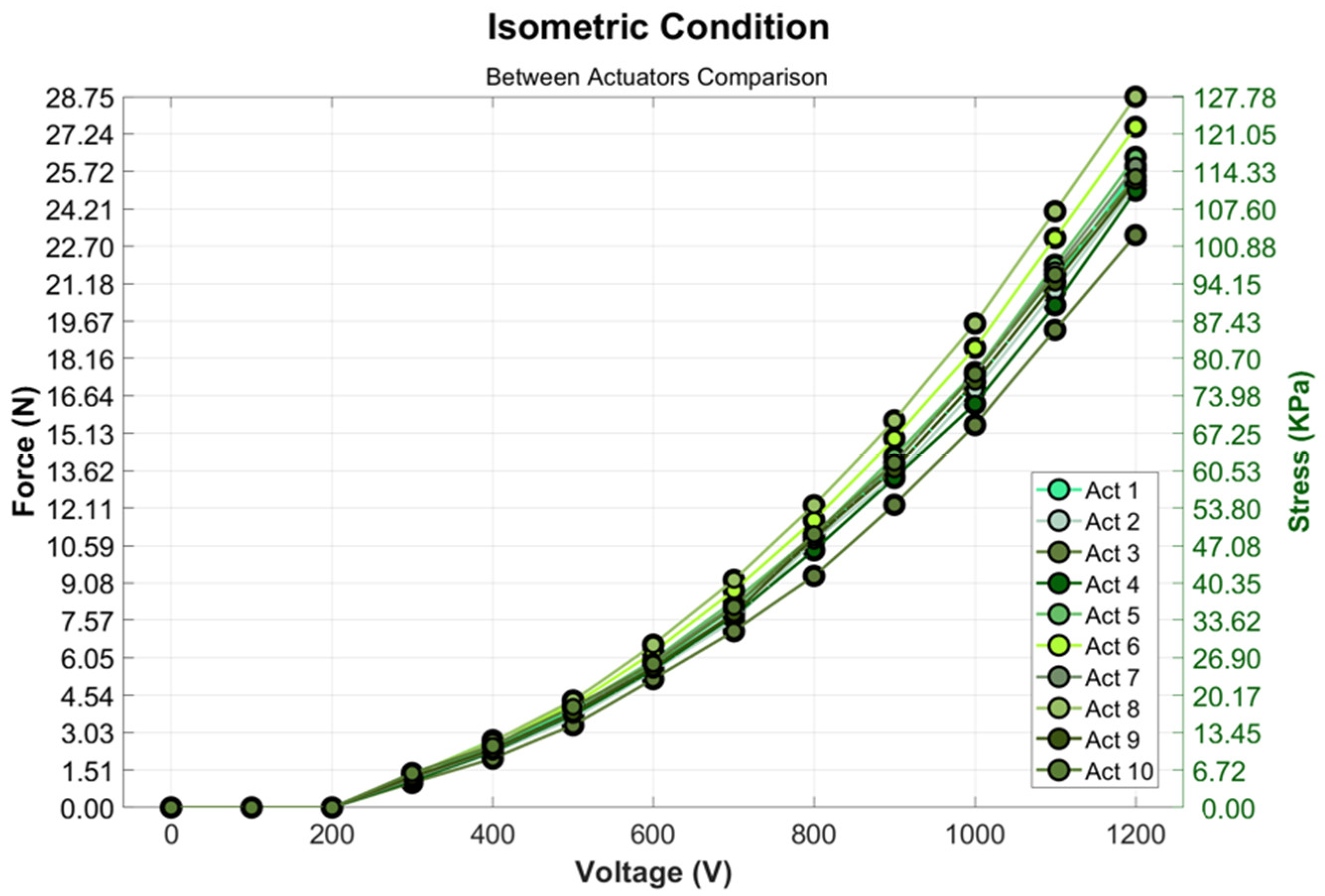
3.1. Isometric Condition
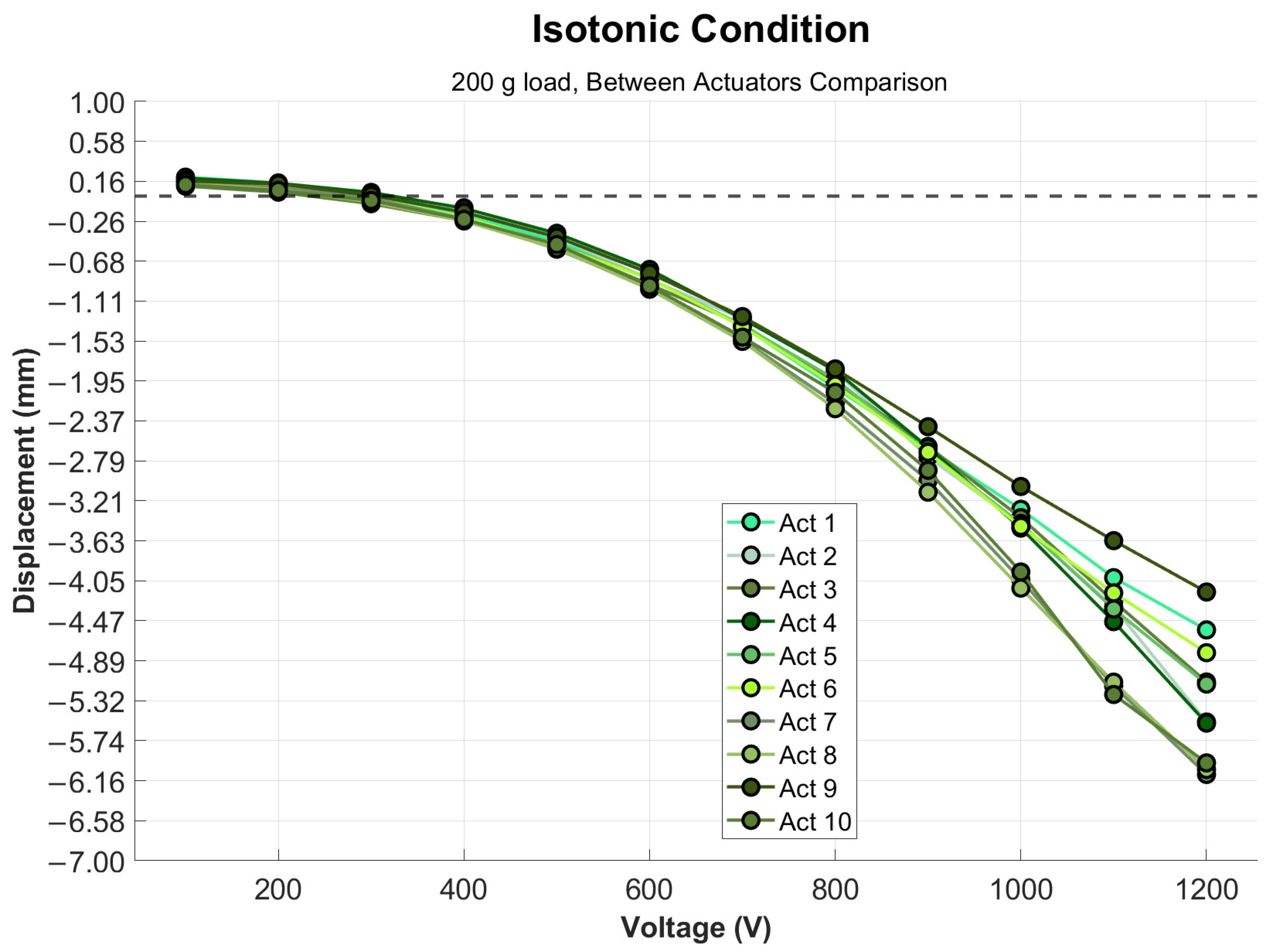
3.2. Isotonic Condition
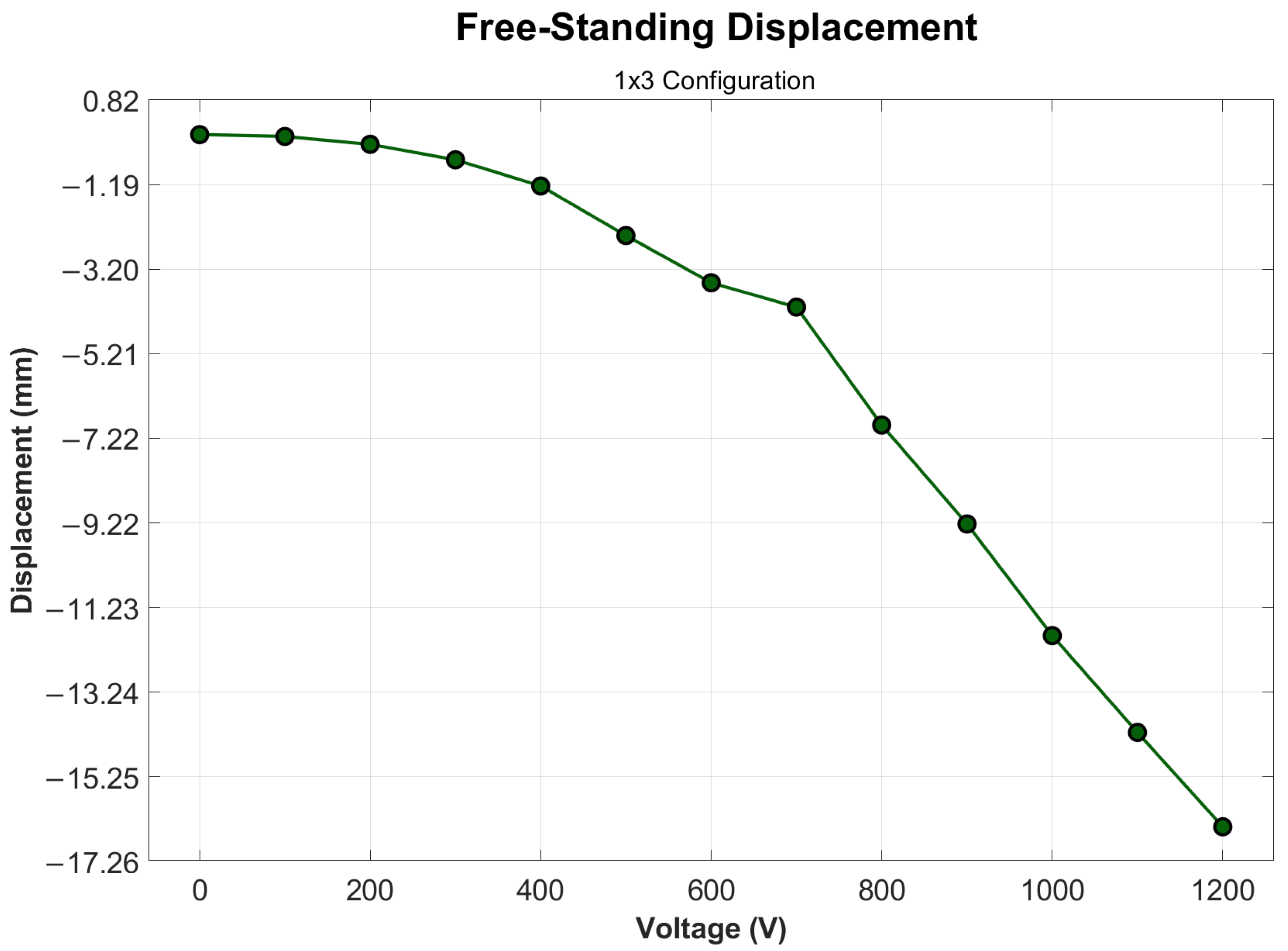
3.3. Free-Standing Condition
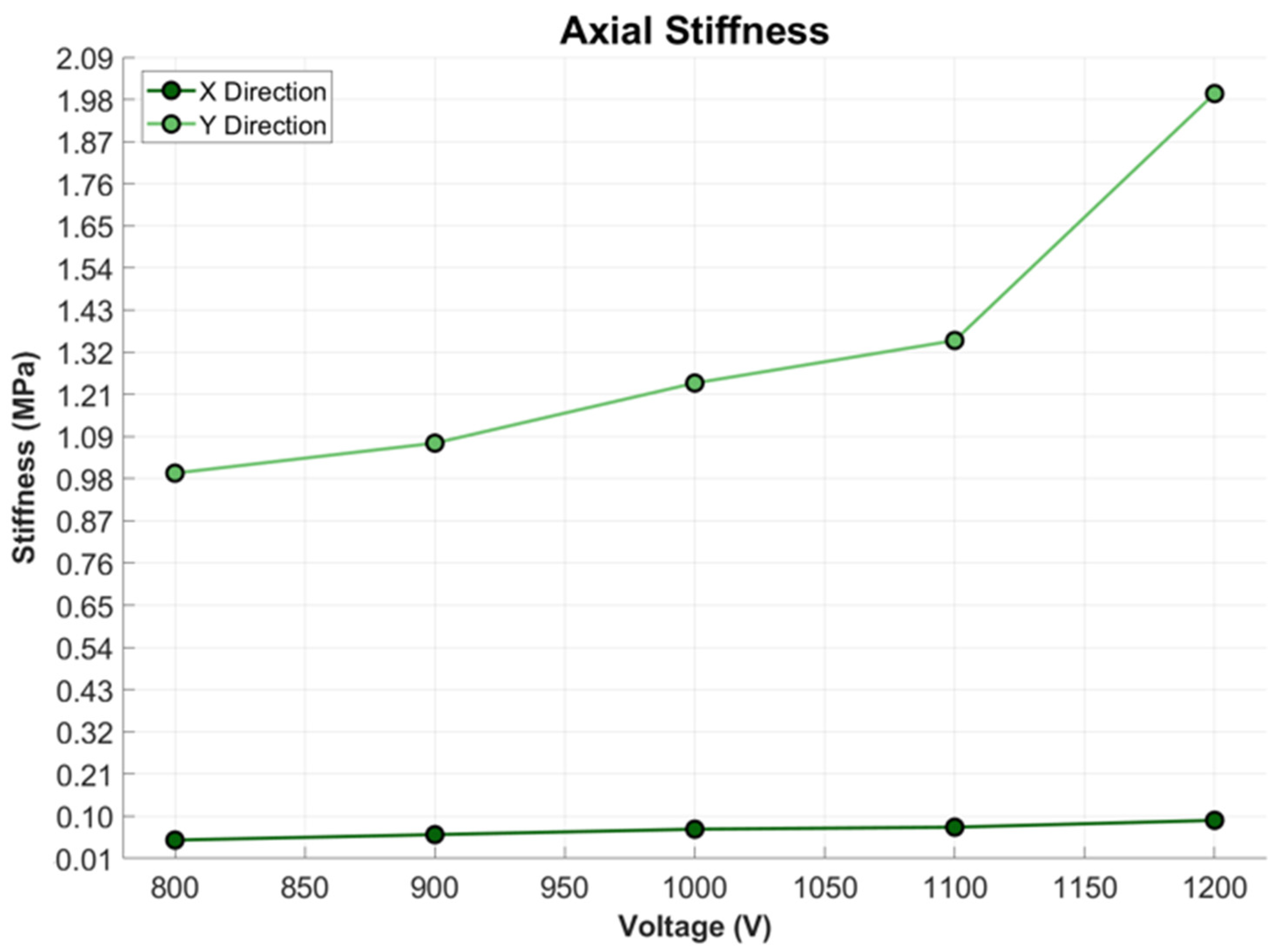
3.4. Stiffness
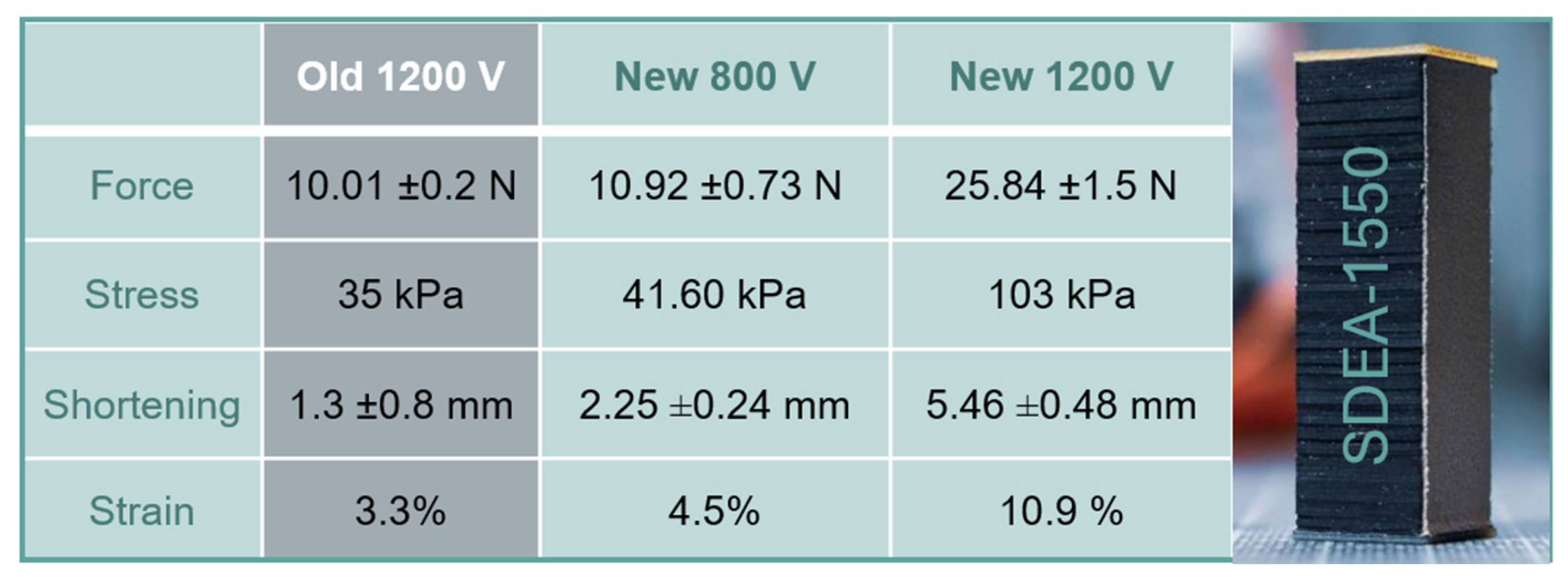
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verl, A.; Albu-Schäffer, A.; Brock, O.; Raatz, A. (Eds.) Soft Robotics: Transferring Theory to Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-662-44506-8 (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Miriyev, A.; Stack, K.; Lipson, H. Soft material for soft actuators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, I.S.; Reitelshöfer, S.; Landgraf, M.; Franke, J. Artificial Muscles, Made of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators—A Promising Solution for Inherently Compliant Future Robots. In Soft Robotics; Verl, A., Albu-Schäffer, A., Brock, O., Raatz, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 33–41. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-662-44506-8_4 (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.E.; Sommer-Larsen, P. (Eds.) Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstadt, T.; Griese, M.; Maas, J. Online identification algorithms for integrated dielectric electroactive polymer sensors and self-sensing concepts. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kunz, A.; Lochmatter, P.; Kovacs, G. Dielectric Elastomer Spring Roll Actuators for a Portable Force Feedback Device. In Proceedings of the 2006 14th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Alexandria, VA, USA, 25–26 March 2006; IEEE: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 347–353. Available online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1627137/ (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- IEC. 60479-2: 2007 Effects of Current on Human Beings and Livestock. Part. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/en/publication/63392 (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; Gerboni, C.; Gemignani, J.; De Rossi, D. Enabling variable-stiffness hand rehabilitation orthoses with dielectric elastomer transducers. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, V.; Tajdani, M.; Masaei, M.; Mohammadi Ghalehney, S.; Lee, S.C.K.; Behboodi, A. DE-AFO: A Robotic Ankle Foot Orthosis for Children with Cerebral Palsy Powered by Dielectric Elastomer Artificial Muscle. Sensors 2024, 24, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.P.; Little, R.; Laube, J.; Warren, J.; Voit, W.; Gregg, R.D. Towards an ankle-foot orthosis powered by a dielectric elastomer actuator. Mechatronics 2021, 76, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarban, R.; Jones, R.W.; Mace, B.R.; Rustighi, E. A tubular dielectric elastomer actuator: Fabrication, characterization and active vibration isolation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 2879–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Migliore, A.; Serra, G.; Rossi, D.D. Helical dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Salaris, C.; Rossi, D.D. Folded dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, S300–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Düring, L.; Michel, S.; Terrasi, G. Stacked dielectric elastomer actuator for tensile force transmission. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 155, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, J.; Prechtl, J.; Bruch, D.; Nalbach, S.; Motzki, P.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Design and fabrication of silicone-based dielectric elastomer rolled actuators for soft robotic applications. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) XXII; Bar-Cohen, Y., Anderson, I.A., Shea, H.R., Eds.; Online Only; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; p. 80. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/11375/2558444/Design-and-fabrication-of-silicone-based-dielectric-elastomer-rolled-actuators/10.1117/12.2558444.full (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Gabor Kovacs, L.D. CTSystem Swiss Compliant Transducer. 2016. Available online: http://www.ct-systems.ch/ (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Behboodi, A.; Lee, S.C.K. Benchmarking of a Commercially Available Stacked Dielectric Elastomer as an Alternative Actuator for Rehabilitation Robotic Exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; IEEE: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019; pp. 499–505. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8779378/ (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Pappas, G.P.; Asakawa, D.S.; Delp, S.L.; Zajac, F.E.; Drace, J.E. Nonuniform shortening in the biceps brachii during elbow flexion. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 2381–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboodi, A.; Zahradka, N.; Wright, H.; Alesi, J.; Lee, S.C.K. Real-Time Detection of Seven Phases of Gait in Children with Cerebral Palsy Using Two Gyroscopes. Sensors 2019, 19, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Du, Q.; Xie, L. Flexible Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robot for Rehabilitation Training of Children with Cerebral Palsy. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, L.N.; Kudzia, P.; Revi, D.A.; Ellis, T.D.; Walsh, C.J. Walking Faster and Farther with a Soft Robotic Exosuit: Implications for Post-Stroke Gait Assistance and Rehabilitation. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2020, 1, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, H.; Kargar Nigjeh, M.; Umbaugh, S.E. Unsupervised white matter lesion identification in multiple sclerosis (MS) using MRI segmentation and pattern classification: A novel approach with CVIPtools. In Applications of Digital Image Processing XLVI; Tescher, A.G., Ebrahimi, T., Eds.; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2023; p. 59. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/12674/2688268/Unsupervised-white-matter-lesion-identification-in-multiple-sclerosis-MS-using/10.1117/12.2688268.full (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Maciejasz, P.; Eschweiler, J.; Gerlach-Hahn, K.; Jansen-Troy, A.; Leonhardt, S. A survey on robotic devices for upper limb rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 3. Available online: https://jneuroengrehab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1743-0003-11-3 (accessed on 16 September 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, V.; Shahbad, R.; Hosseini, M.; Gholampour, M.H.; Shiry Ghidary, S.; Najafi, F.; Behboodi, A. Development of a Two-Finger Haptic Robotic Hand with Novel Stiffness Detection and Impedance Control. Sensors 2024, 24, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behboodi, A.; DeSantis, C.; Lubsen, J.; Lee, S.C.K. A Mechanized Pediatric Elbow Joint Powered by a De-Based Artificial Skeletal Muscle. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; IEEE: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2020; pp. 4930–4935. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9176332/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
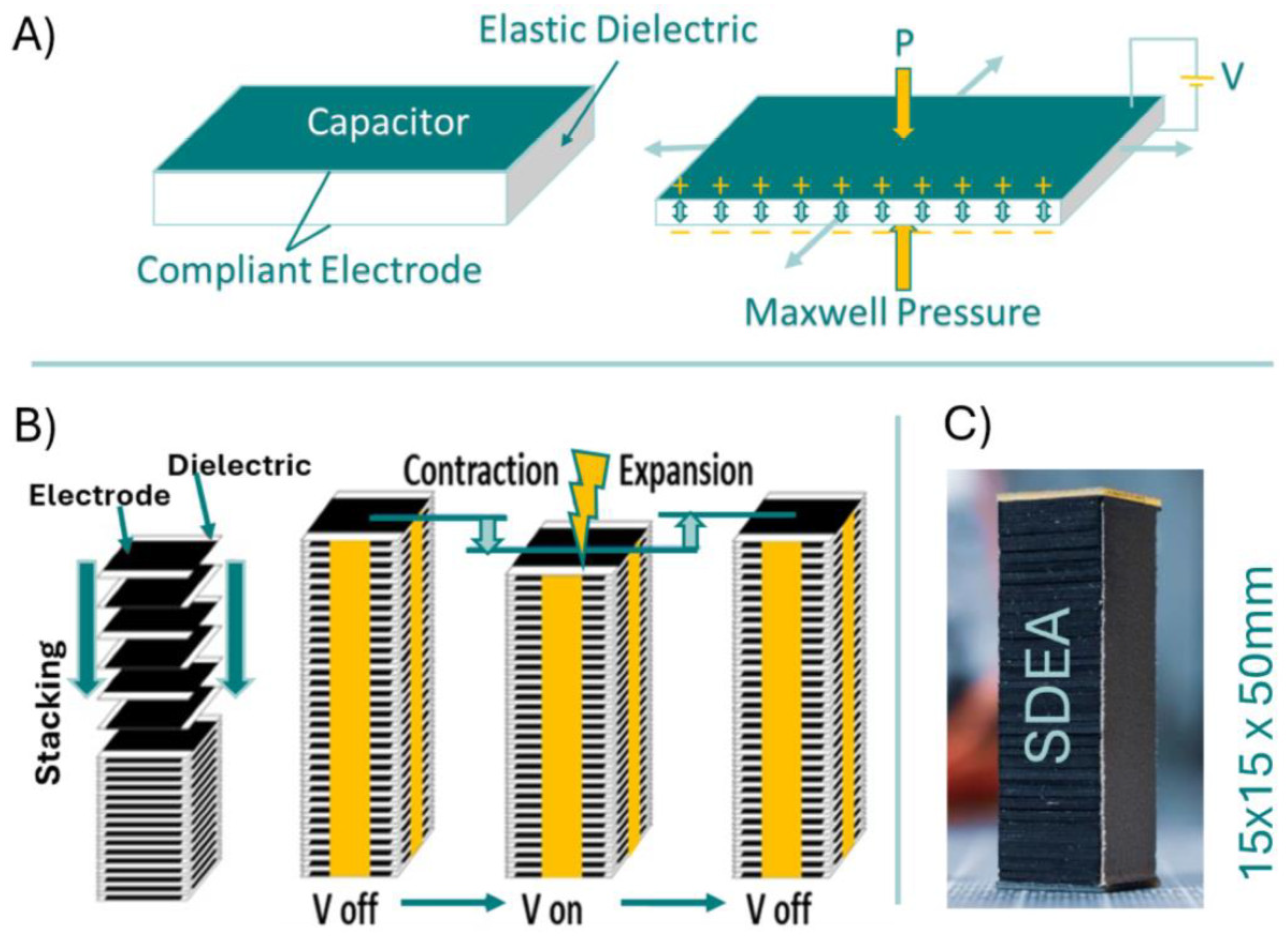
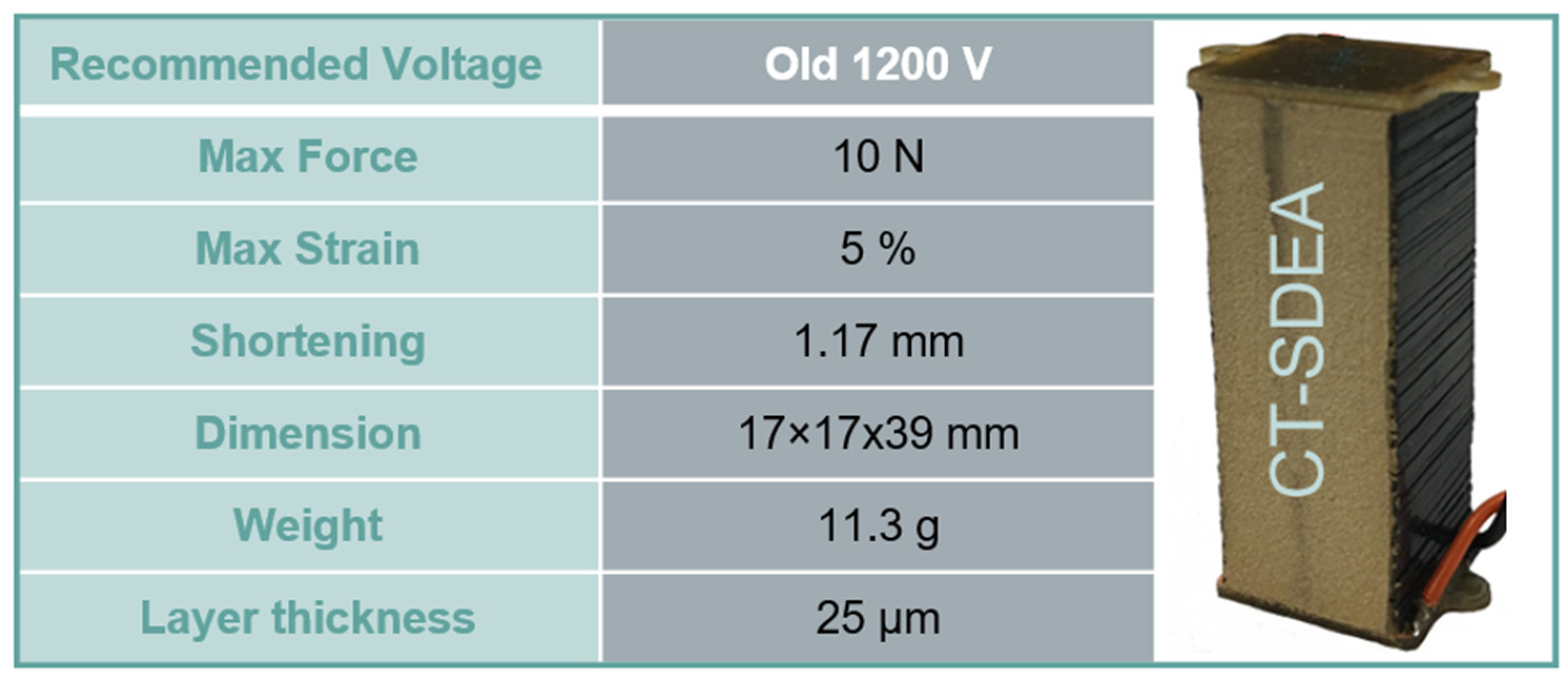



| Configuration | Strain | Force | Dimension (mm) | Voltage | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular [12] | 3% | 100 (60 active) | 2700 V | 105 g | |
| Helical [13] | 8% | ~0.65 N | 80 × 13 | ~1200 V | |
| Folded [14] | 5% | ~3 N | 85 × 25 | ~1000 V | |
| Stacked [15] | 18% | 32 N | 25 × 20 | 4200 V | 4 g |
| Rolled [16] | 2.5% | 0.18 N | 60 × 4 | 3000 V |
| Isometric (N) | Isotonic (mm) | Free−Standing (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD |
| 100 | −0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| 200 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.08 ± 0.00 |
| 300 | 1.20 ± 0.12 | −0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.02 |
| 400 | 2.40 ± 0.24 | −0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
| 500 | 3.88 ± 0.29 | −0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.65 ± 0.07 |
| 600 | 5.81 ± 0.38 | −0.89 ± 0.07 | 1.05 ± 0.09 |
| 700 | 8.09 ± 0.60 | −1.38 ± 0.10 | 1.55 ± 0.14 |
| 800 | 10.92 ± 0.74 | −1.99 ± 0.14 | 2.15 ± 0.19 |
| 900 | 13.90 ± 0.92 | −2.75 ± 0.20 | 2.88 ± 0.26 |
| 1000 | 17.39 ± 1.13 | −3.58 ± 0.35 | 3.79 ± 0.32 |
| 1100 | 21.54 ± 1.34 | −4.48 ± 0.54 | 4.69 ± 0.46 |
| 1200 | 25.85 ± 1.50 | −5.30 ± 0.65 | 5.43 ± 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammadi, V.; Mohammadi Ghalehney, S.; Tajdani, M.; Lee, S.C.K.; Behboodi, A. Evaluating Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators as Soft Motor Units for Forming Artificial Muscles in Biomimetic Rehabilitation Robots. Actuators 2024, 13, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13100381
Mohammadi V, Mohammadi Ghalehney S, Tajdani M, Lee SCK, Behboodi A. Evaluating Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators as Soft Motor Units for Forming Artificial Muscles in Biomimetic Rehabilitation Robots. Actuators. 2024; 13(10):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13100381
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammadi, Vahid, Sahel Mohammadi Ghalehney, Mohammad Tajdani, Samuel C. K. Lee, and Ahad Behboodi. 2024. "Evaluating Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators as Soft Motor Units for Forming Artificial Muscles in Biomimetic Rehabilitation Robots" Actuators 13, no. 10: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13100381
APA StyleMohammadi, V., Mohammadi Ghalehney, S., Tajdani, M., Lee, S. C. K., & Behboodi, A. (2024). Evaluating Stacked Dielectric Elastomer Actuators as Soft Motor Units for Forming Artificial Muscles in Biomimetic Rehabilitation Robots. Actuators, 13(10), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13100381










