Tracking and Vibration Control with a Parallel Structure Controller Based on a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LPV Model for a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System
3. Parallel Controller Structure
4. Tracking Controller Design Based on LQR
5. Structural Vibration Controller Design Based on Interpolating Gain-Scheduled μ Synthesis
5.1. μ-Synthesis Design
5.2. Interpolating Gain-Scheduled Controller Design via Youla Parameterization
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Experimental Setup
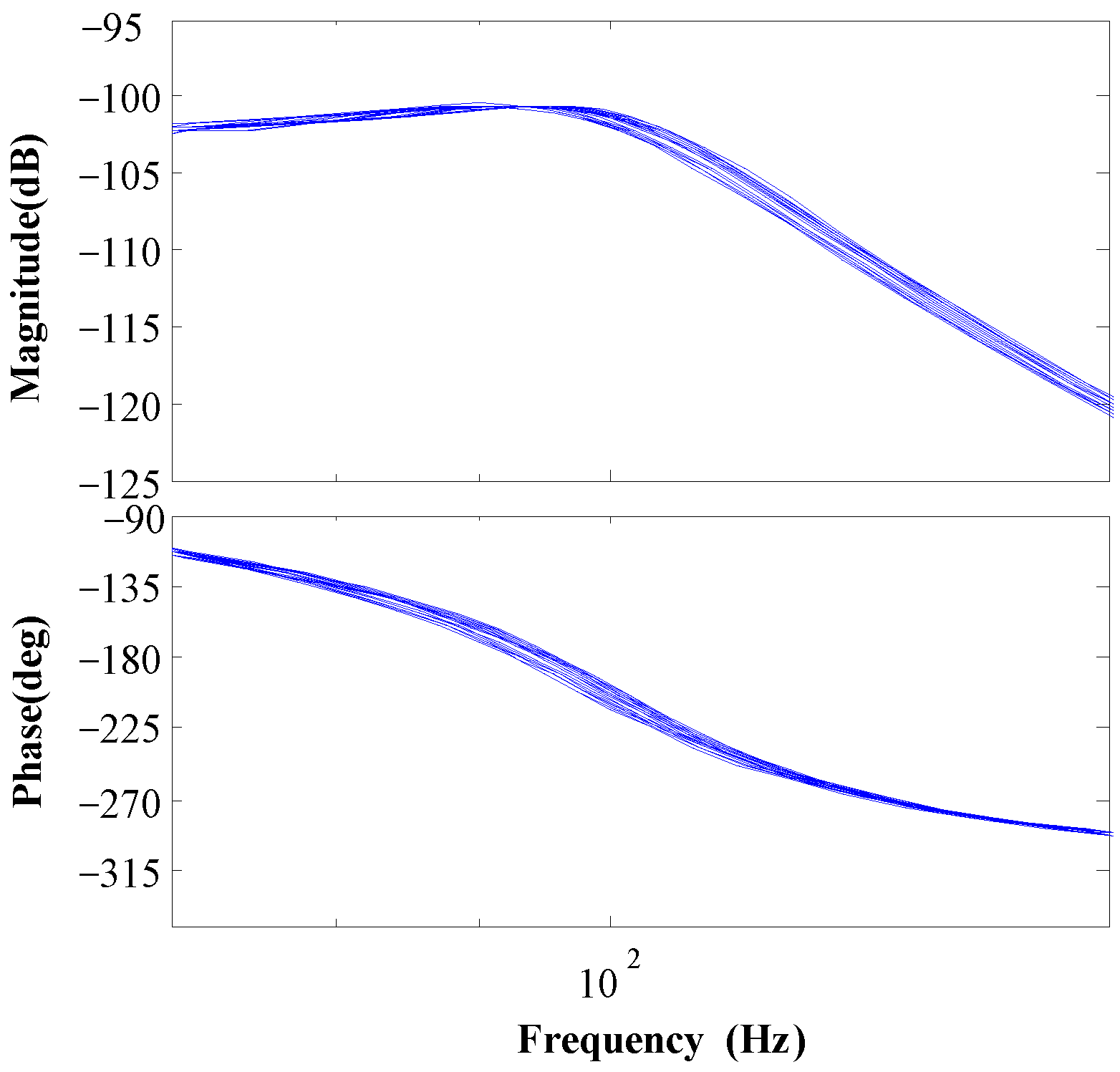
6.2. System Identification
6.3. Controller Design for Experimental Setup
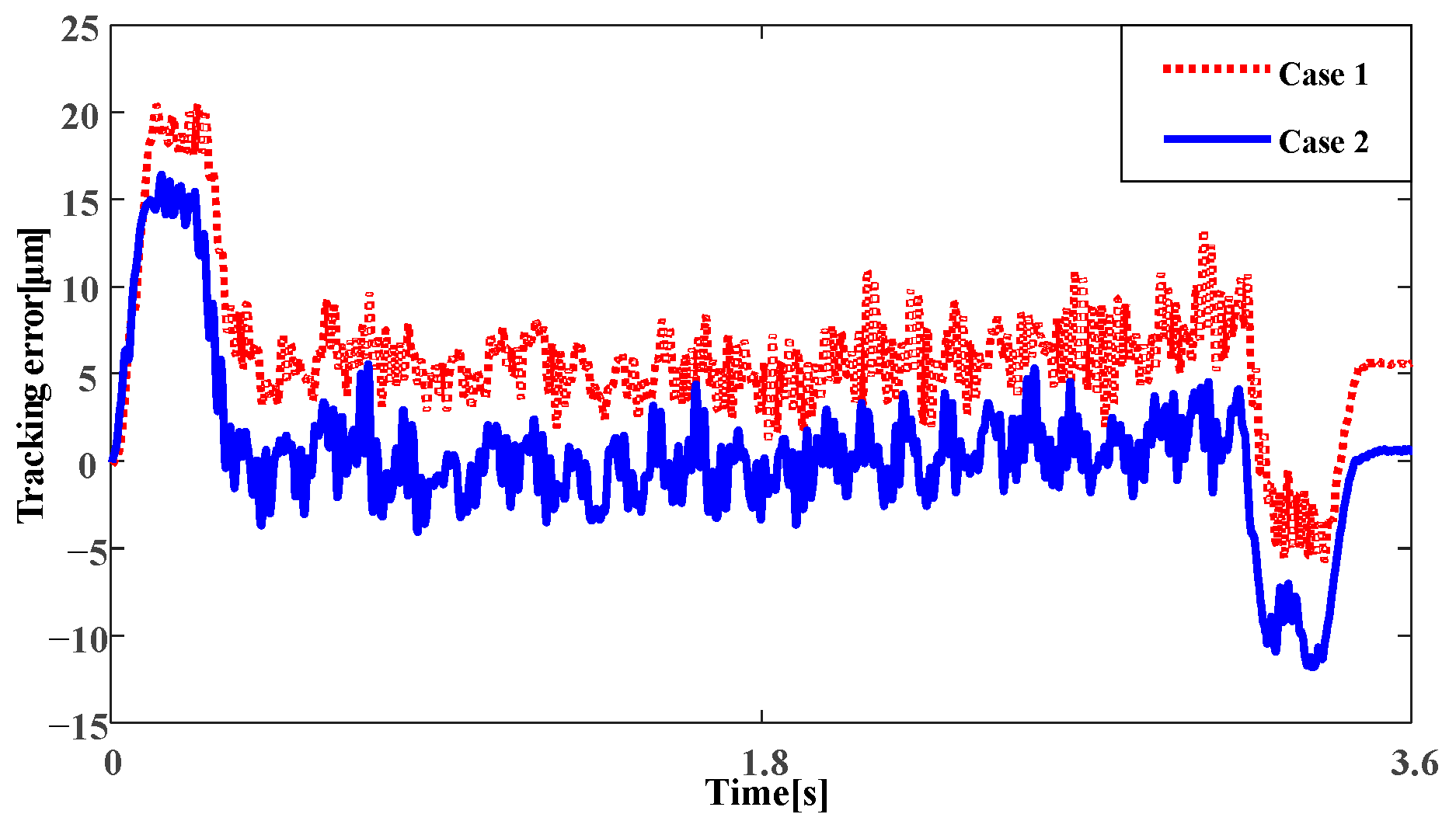
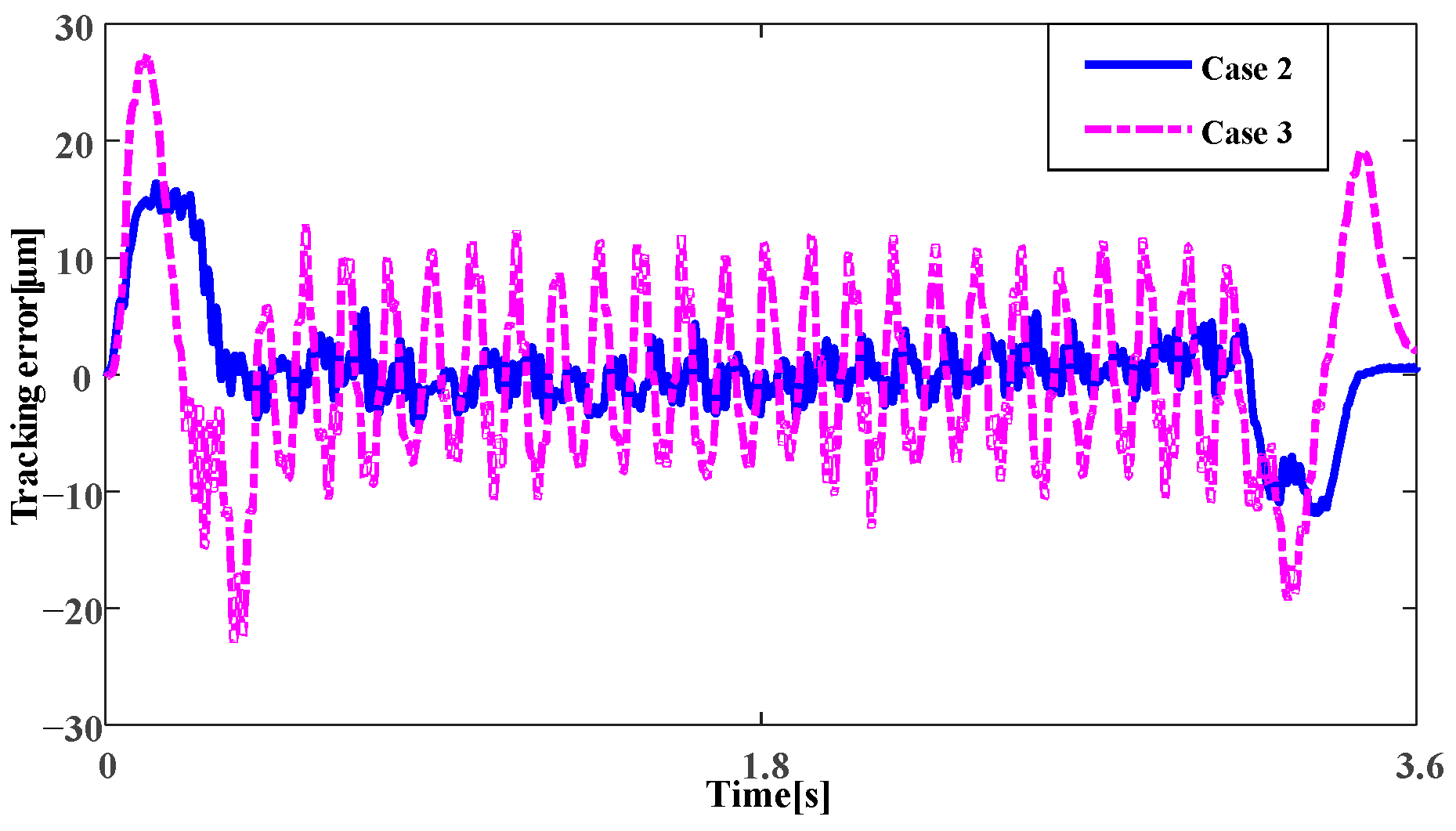
6.4. Tracking Performance Experiments
- Case 1: only a KTrack controller;
- Case 2: both a KTrack controller and a KVib controller;
- Case 3: a P-PI controller with velocity feedforward.
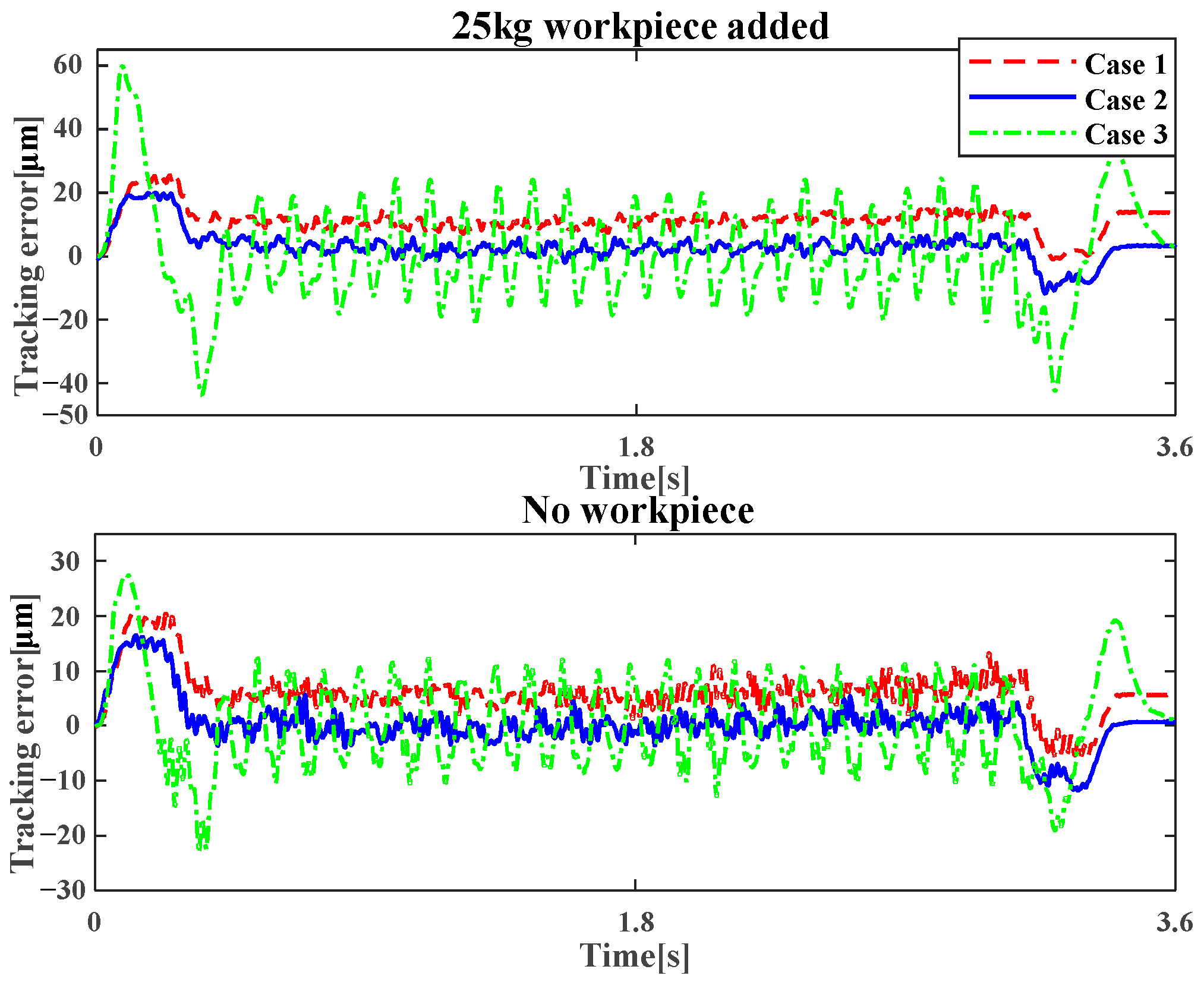
6.5. Robust Performance Experiments for Mass Variation
6.6. Vibration Suppression Performance Experiments
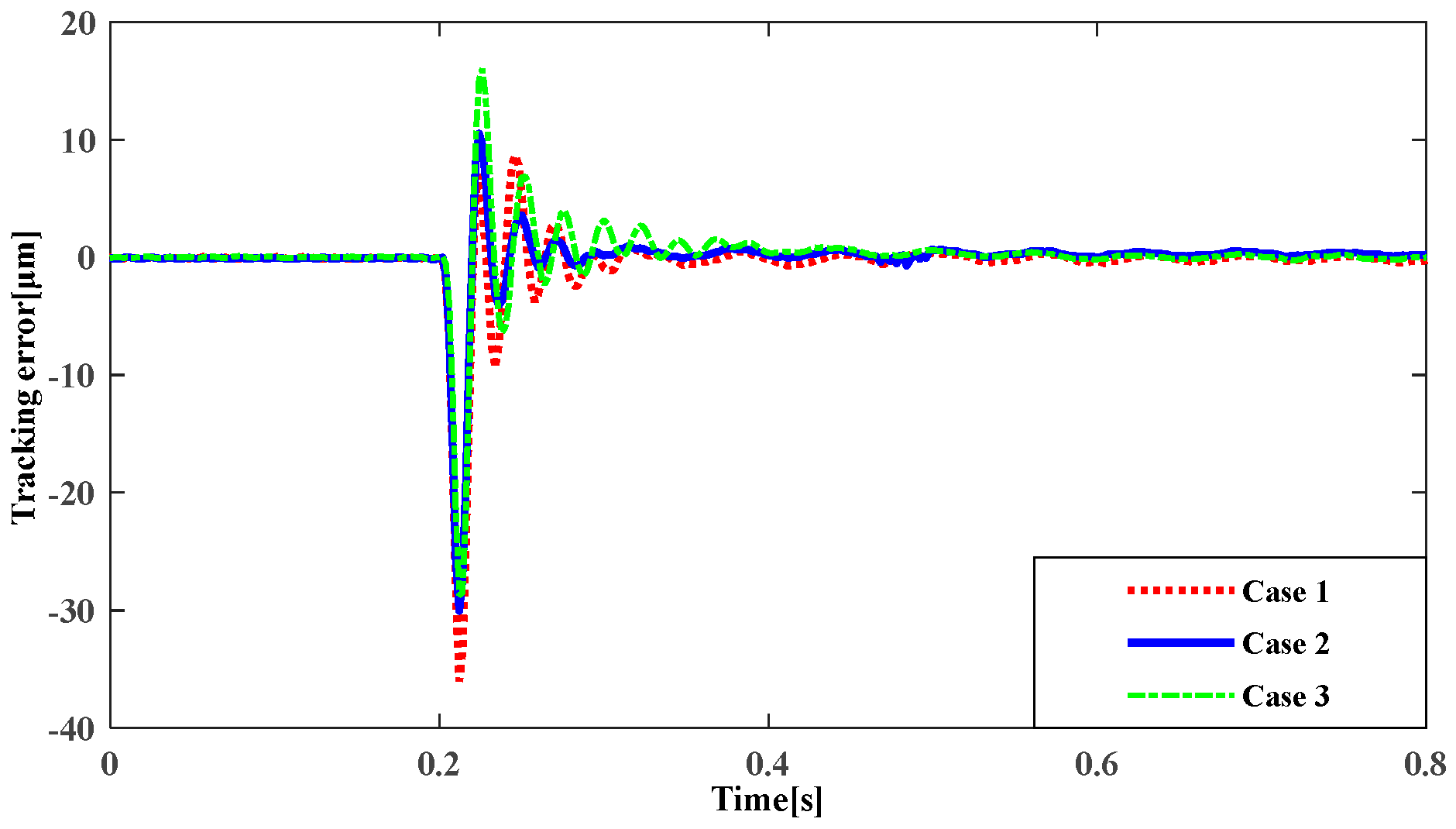
6.7. Disturbance-Rejection Performance Experiments
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Altintas, Y.; Verl, A.; Brecher, C.; Uriarte, L.; Pritschow, G. Machine tool feed drives. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Kilic, Z.M. Generalized dynamic model of metal cutting operations. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifzadegan, M.; Nagamune, R. Switching gain-scheduled control design for flexible ball-screw drives. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2014, 136, 014503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwudire, C.; Altintas, Y. Hybrid modeling of ball screw drives with coupled axial, torsional, and lateral dynamics. J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 071002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Tang, W.C. Hybrid modeling and analysis of structural dynamic of a ball screw feed drive system. Mechanics 2013, 19, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, K.K.; Nayfeh, S.A. The dynamics of lead-screw drives: Low-order modeling and experiments. Trans.-Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2004, 126, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y. Manufacturing Automation: Metal Cutting Mechanics, Machine Tool Vibrations, and CNC Design; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.U.; Le, Q.N.; Jeon, J.W. An FPGA-based multiple-axis motion control chip. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 856–870. [Google Scholar]
- Erkorkmaz, K.; Kamalzadeh, A. High bandwidth control of ball screw drives. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalzadeh, A.; Erkorkmaz, K. Compensation of axial vibrations in ball screw drives. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2007, 56, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwudire, C.; Altintas, Y. Minimum tracking error control of flexible ball screw drives using a discrete-time sliding mode controller. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2009, 131, 051006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Tang, W.C. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control of flexible ball screw drives with time-varying parametric uncertainties and disturbances. ISA Trans. 2014, 53, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.J.; Erkorkmaz, K. Accurate control of ball screw drives using pole-placement vibration damping and a novel trajectory prefilter. Precis. Eng. 2013, 7, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Khoshdarregi, M.R. Contour error control of CNC machine tools with vibration avoidance. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Takemura, T. High-precision control of ball-screw-driven stage based on repetitive control using n-times learning filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Yen, C.L.; Yau, H.T. Integration of an empirical mode decomposition algorithm with iterative learning control for high-precision machining. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Tracking Control of Ball Screw Drives Using ADRC and Equivalent-Error-Model-Based Feedforward Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7682–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, N.; Abolmasoumi, A.H.; Soleymani, M. Sliding mode trajectory tracking control of a ball-screw-driven shake table based on online state estimations using EKF/UKF. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Lee, J.M.; Han, S.I. Tracking error constrained terminal sliding mode control for ball-screw driven motion systems with state observer. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Pritschow, G.; Zahn, P.; Lechler, A. A novel cascade control principle for feed drives of machine tools. CIRP Ann. 2018, 67, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Isaoka, Y.; Terada, Y. Projection-based iterative learning control for ball-screw-driven stage with consideration of rolling friction compensation. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2020, 9, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Isaoka, Y.; Terada, Y. Negative quadrant glitch suppression control of ball-screw-driven stage for machine tool by friction compensation and initial value compensation. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2022, 215, e23402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencer, B.; Dumanli, A. Optimal control of flexible drives with load side feedback. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanli, A.; Sencer, B. Optimal high-bandwidth control of ball-screw drives with acceleration and jerk feedback. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ni, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, D. Vibration suppression and over-quadrant error mitigation methods for a ball-screw driven servo system with dual-position feedback. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 213758–213771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, H.K.; Hosseinkhani, Y.; Erkorkmaz, K. Suppression of harmonic positioning errors in ball-screw drives using Adaptive Feedforward Cancellation. Precis. Eng. 2021, 68, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symens, W.; Van Brussel, H.; Swevers, J. Gain-scheduling control of machine tools with varying structural flexibility. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2004, 53, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.; Brüls, O.; Swevers, J.; Desmet, W.; Van Brussel, H. Computer-aided integrated design for machines with varying dynamics. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 1733–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paijmans, B.; Symens, W.; Van Brussel, H.; Swevers, J. Identification of interpolating affine LPV models for mechatronic systems with one varying parameter. Eur. J. Control 2008, 14, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasi, D.; Nagamune, R.; Sassani, F. Tracking control of flexible ball screw drives with runout effect and mass variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Tang, W.C.; Bao, D.F. Interpolating gain-scheduled H∞ loop shaping design for high speed ball screw feed drives. ISA Trans. 2015, 55, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifzadegan, M.; Nagamune, R. Smooth switching LPV controller design for LPV systems. Automatica 2014, 50, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifzadegan, M.; Nagamune, R. Tracking and structural vibration control of flexible ball–screw drives with dynamic variations. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, C.; Yao, M.; Chen, F.; Zhang, C. Gain scheduling control of ball screw feed drives based on linear parameter varying model. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 124, 4493–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balini, H.; Witte, J.; Scherer, C.W. Synthesis and implementation of gain-scheduling and LPV controllers for an AMB system. Automatica 2012, 48, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, H.; Stoustrup, J.; Abrahamsen, R.B. Switching between multivariable controllers. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 2004, 25, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, B.P.; Chang, Y.J. Stable controller interpolation and controller switching for LPV systems. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2010, 132, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Postlethwaite, I.; Gu, D.W. μ-K iteration: A new algorithm for μ-synthesis. Automatica 1993, 29, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balini, H.; Scherer, C.W.; Witte, J. Performance Enhancement for AMB Systems Using Unstable Controllers. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hencey, B.M. Robust Controller Interpolation with Application to Gain-Scheduling; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ProQuest Dissertations Publishing: Champaign, IL, USA, 2008; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar]
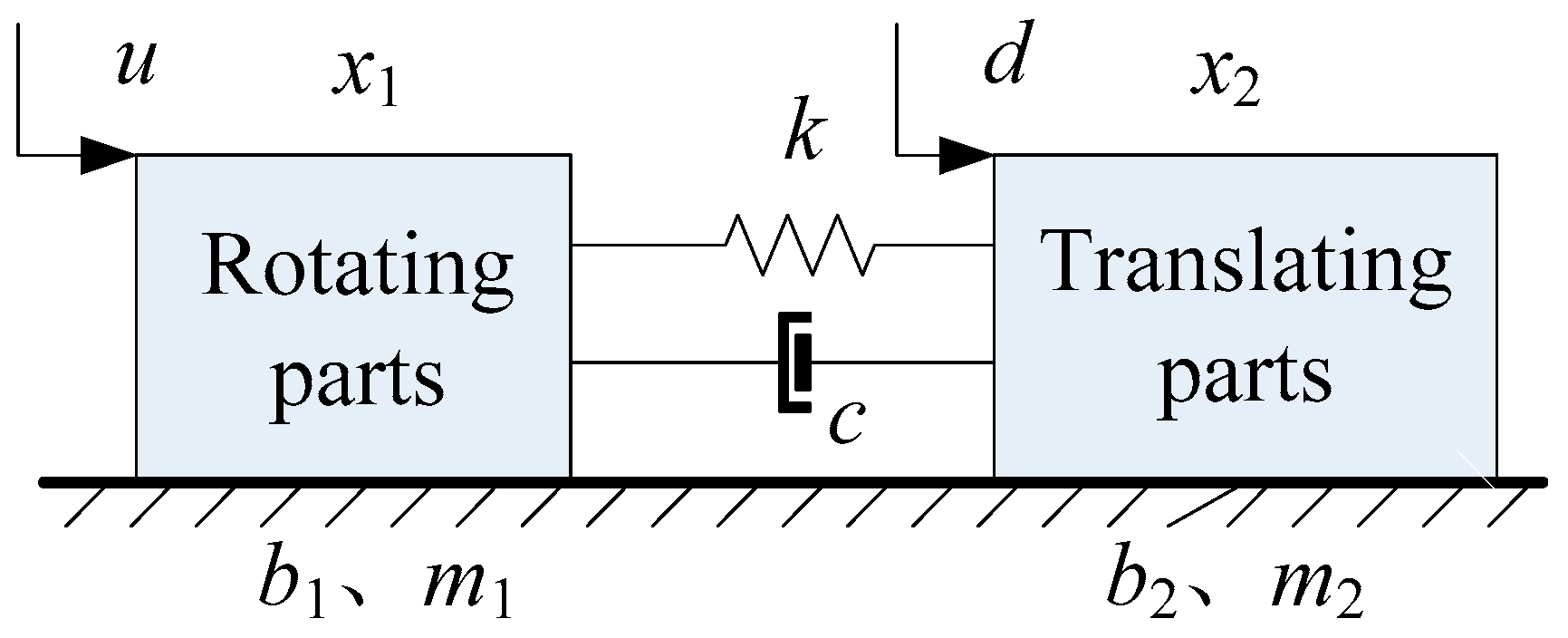



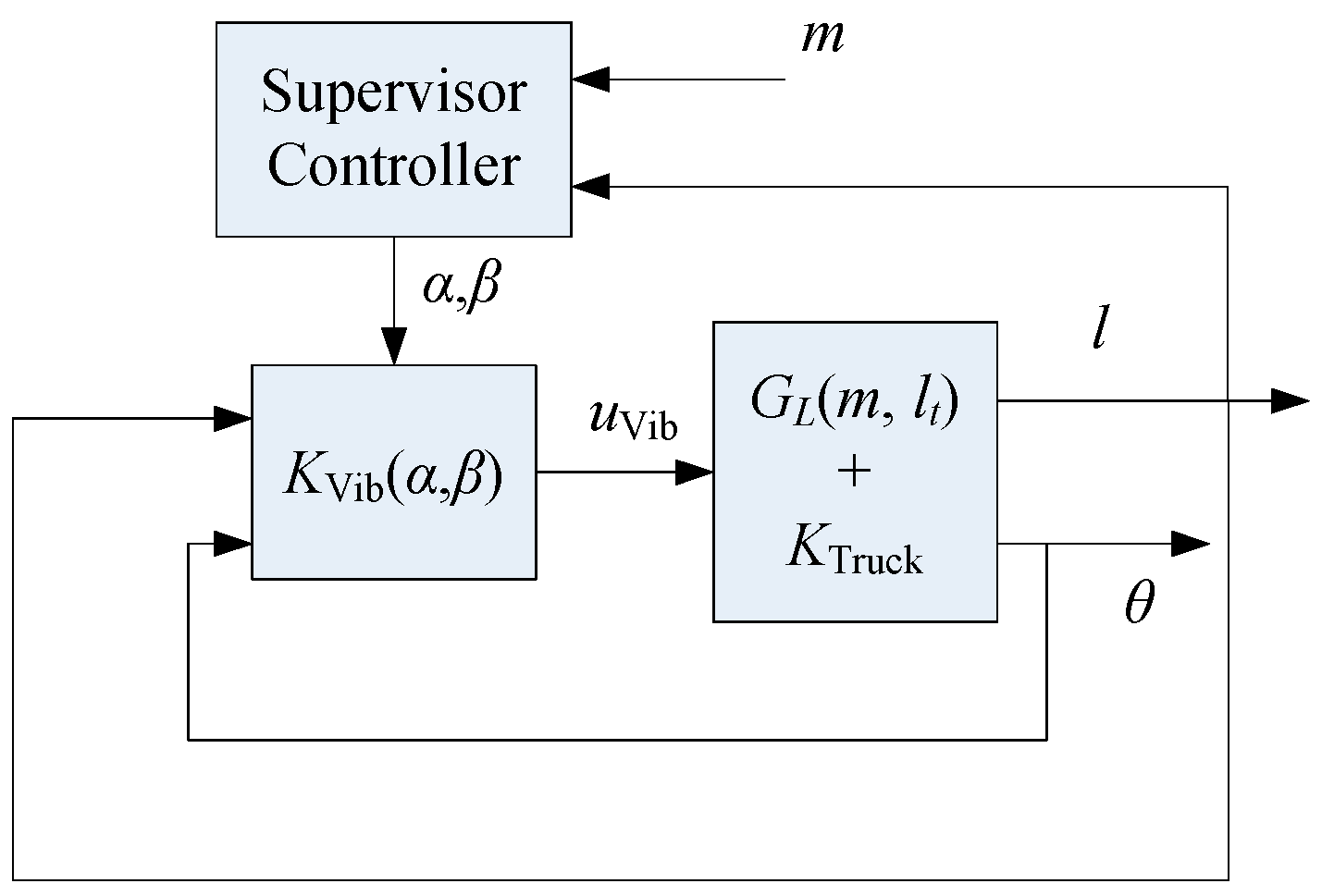
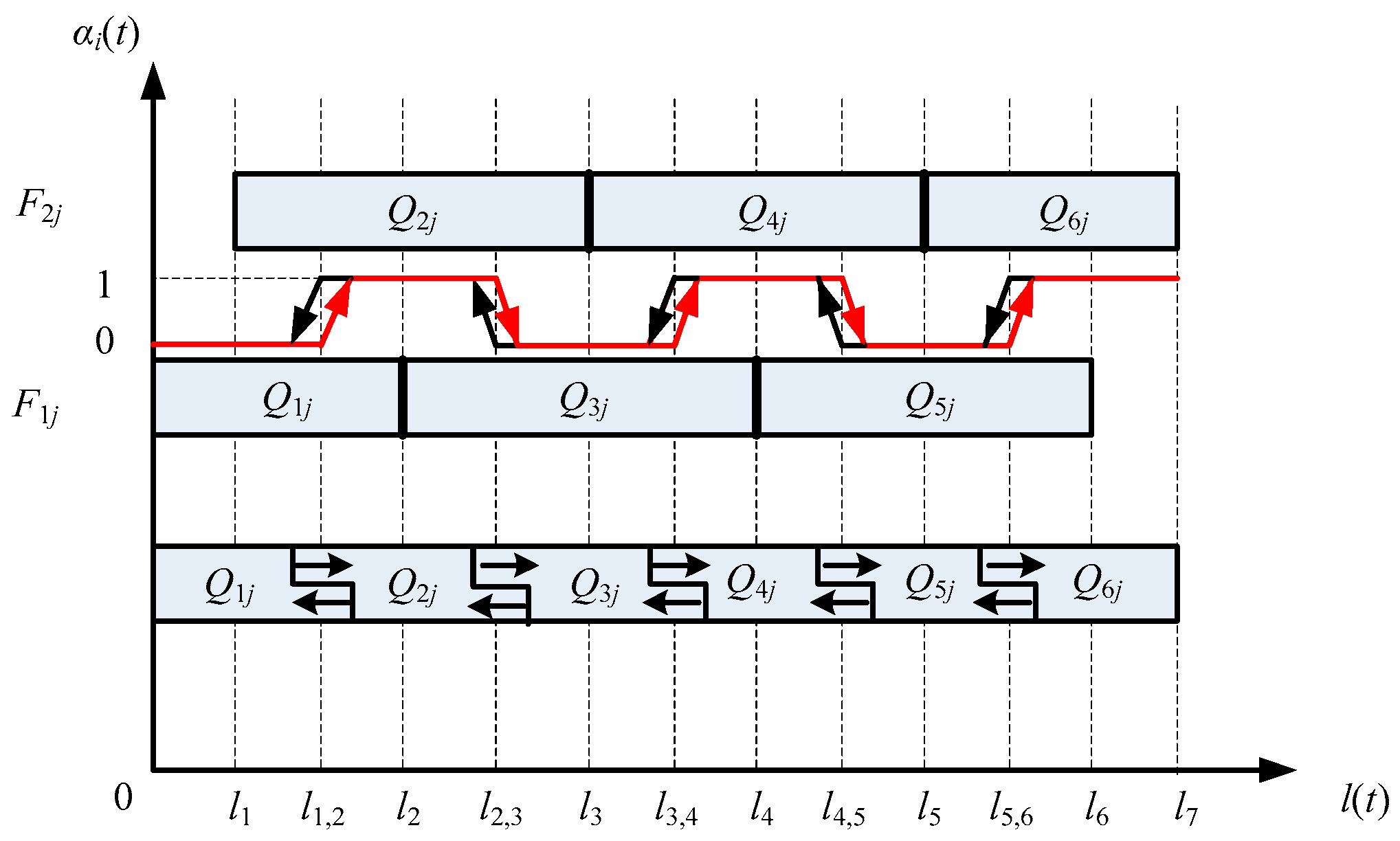
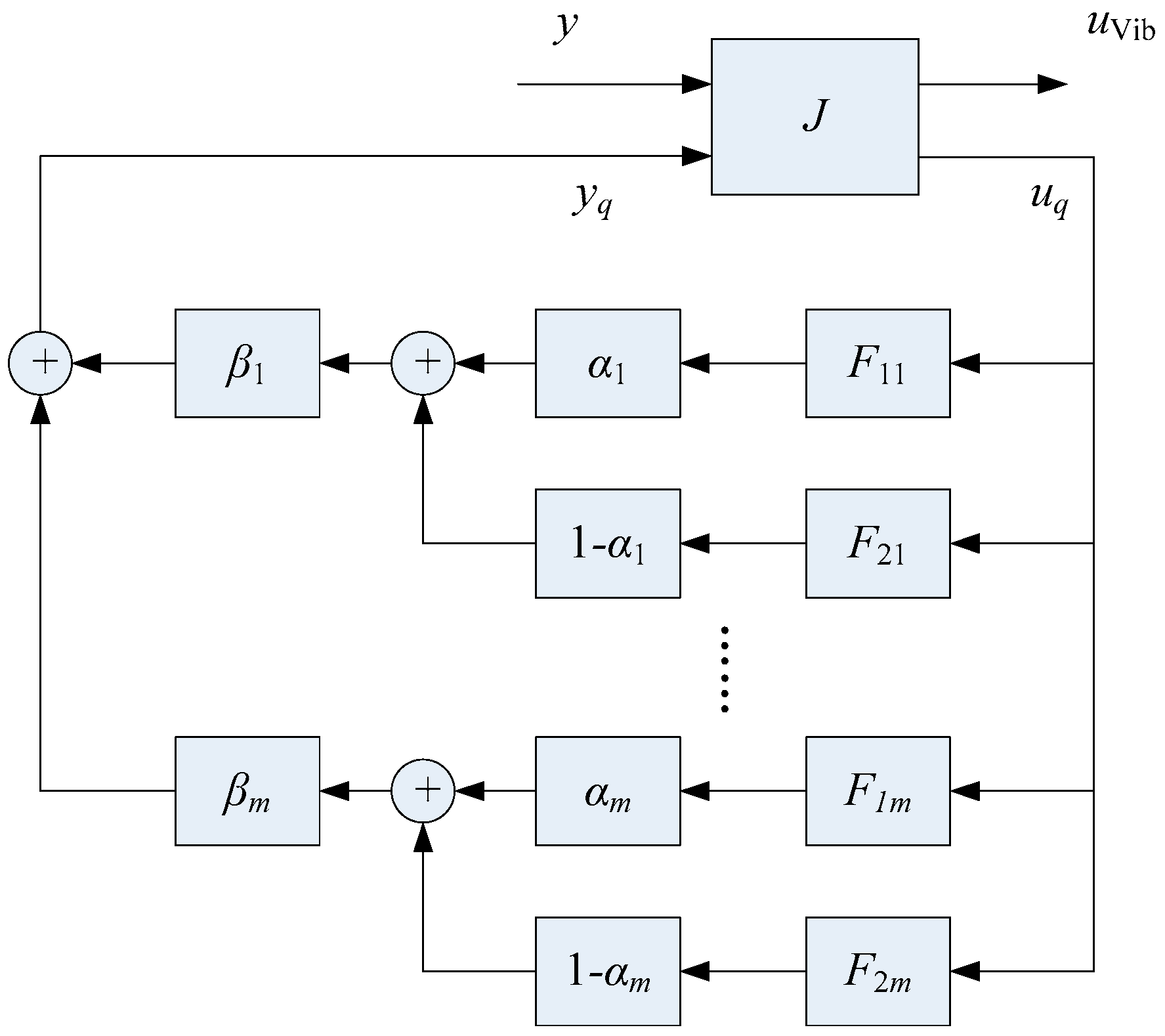
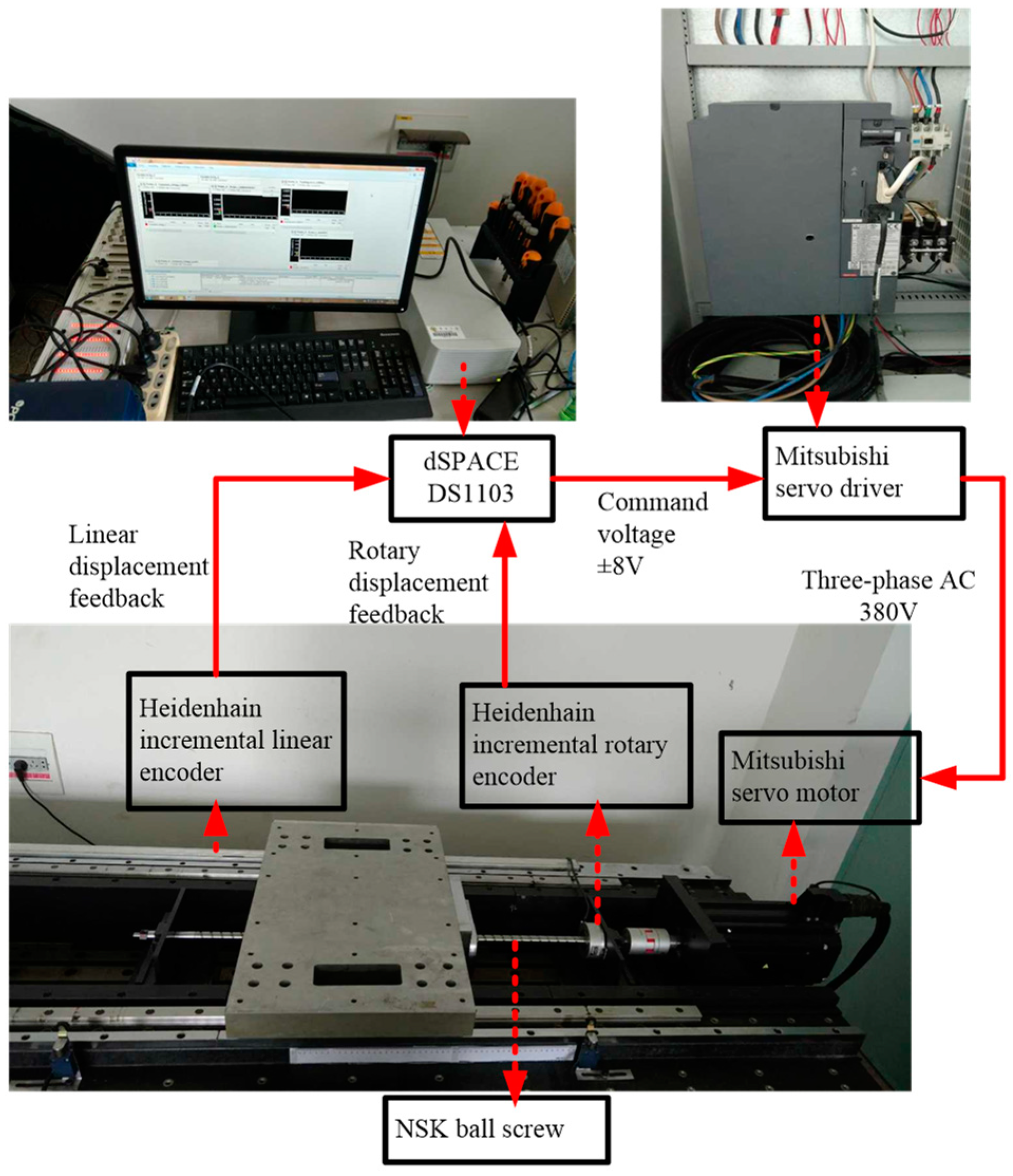




| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| m1 | 0.6512 | (V·s2·m−1) |
| m2 | 0.0771 | (V·s2·m−1) |
| b1 | 4.1571 × 10−4 | (V·s·m−1) |
| b2 | 0.8052 | (V·s·m−1) |
| k | 2.1153 × 10−4 | (V·m−1) |
| c | 2.6775 | (V·s·m−1) |
| Case | Max Abs. Error | RMS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tracking error with no workpiece (μm) | 1 | 20.44 | 7.30 |
| 2 | 16.45 | 4.51 | |
| 3 | 27.35 | 8.48 | |
| Tracking error with a 25 kg workpiece added (μm) | 1 | 25.38 | 10.86 |
| 2 | 19.9 | 5.31 | |
| 3 | 59.76 | 16.45 | |
| Tracking error with harmonic disturbance (μm) | 1 | 27.70 | 9.28 |
| 2 | 17.60 | 5.22 | |
| 3 | 41.15 | 10.96 | |
| Error between linear and rotary displacement (μm) | 1 | 8.00 | 2.76 |
| 2 | 7.79 | 2.66 | |
| 3 | 12.4 | 4.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Bao, D.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y. Tracking and Vibration Control with a Parallel Structure Controller Based on a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System. Actuators 2023, 12, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12080330
Zhu M, Bao D, Sun M, Liu Y. Tracking and Vibration Control with a Parallel Structure Controller Based on a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System. Actuators. 2023; 12(8):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12080330
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Muzhi, Dafei Bao, Mengxin Sun, and Yong Liu. 2023. "Tracking and Vibration Control with a Parallel Structure Controller Based on a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System" Actuators 12, no. 8: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12080330
APA StyleZhu, M., Bao, D., Sun, M., & Liu, Y. (2023). Tracking and Vibration Control with a Parallel Structure Controller Based on a Flexible Ball Screw Drive System. Actuators, 12(8), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12080330






