A Hybridization Grey Wolf Optimizer to Identify Parameters of Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A hybridization optimization algorithm is provided to optimize the system of complex nonlinear function.
- Using the hybridization optimization algorithm, an improved version of parameter identification algorithm for HHRA is presented.
2. Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Model Design
- (1)
- Flow continuity formula
- (2)
- Load balance formula
- (3)
- Rotational equilibrium formula
- (4)
- Flow equation of servo valve
- (5)
- Transfer function equation
2.3. Identification Model
3. Methodology
3.1. Preliminary
3.2. GWO Algorithm
- (1)
- Hunting siege
- (2)
- Hunting
- (3)
- Attacking
3.3. Modified Differential Evolution
- (1)
- Mutation
- (2)
- Crossover
- (3)
- Selection
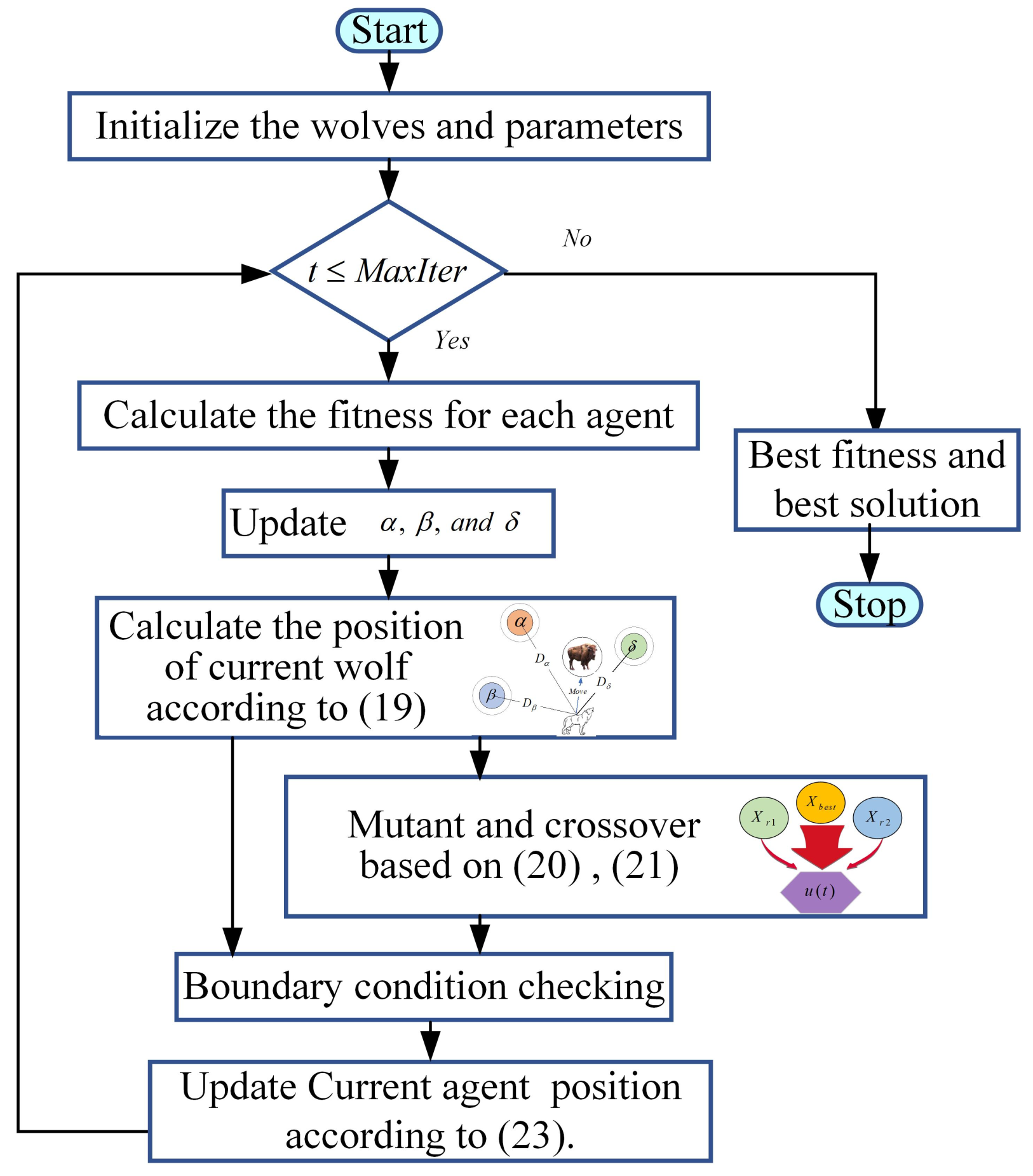
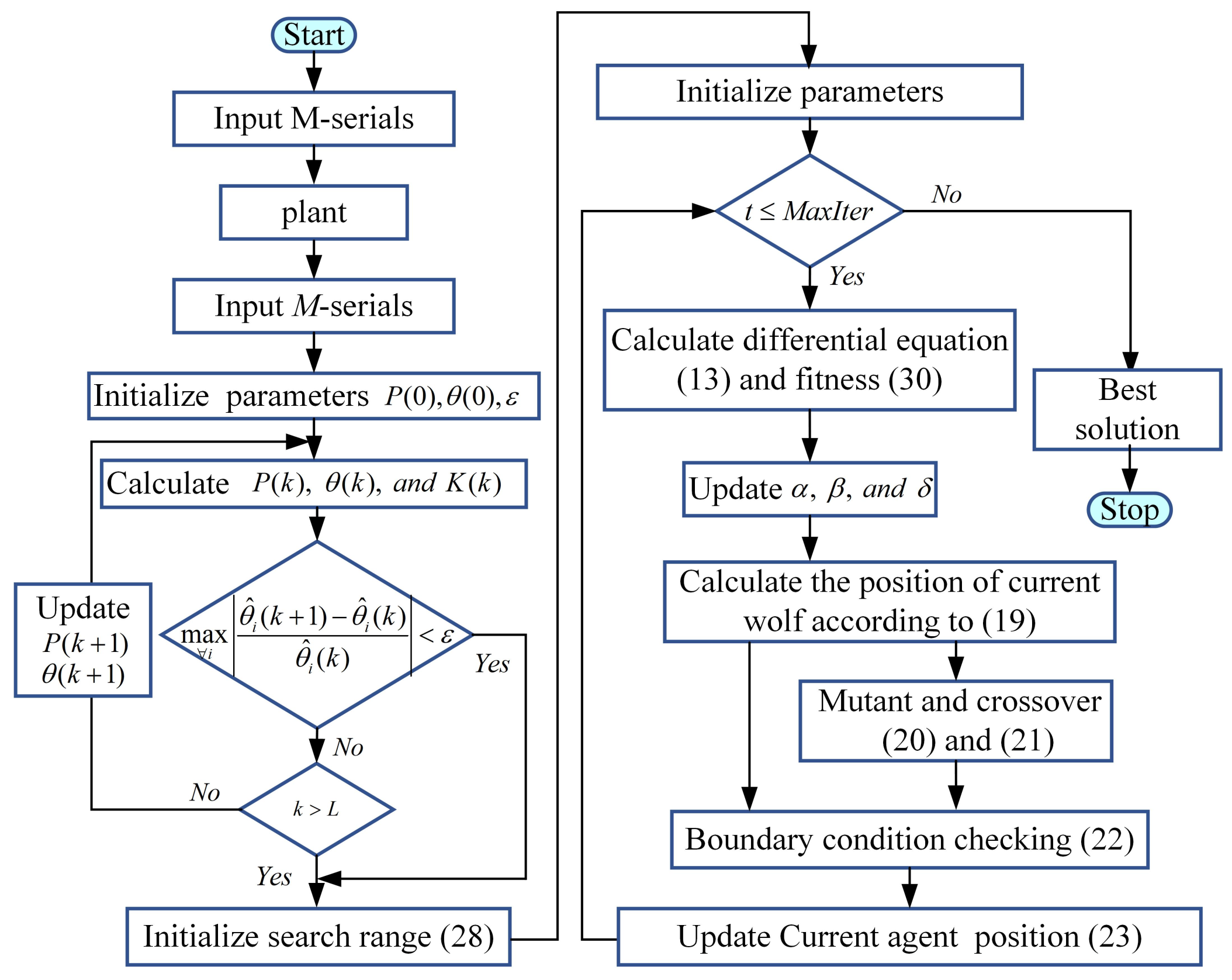
3.4. GWO with DE Hybrid Algorithm
- (1)
- Initialization scheme
- (2)
- Population diversification strategy
- Step 1.
- Initializing parameters and values of a, A, and C as well as the crossover rate , scaling factor F, and maximum number of iterations ;
- Step 2.
- Initializing a population of n agents position randomly according to Equation (27);
- Step 3.
- Calculating the fitness f for all individuals;
- Step 4.
- Updating , , and ;
- Step 5.
- Step 6.
- Calculating the position of the current wolf according to Equation (19);
- Step 7.
- Step 8.
- Checking and processing the boundary condition according to Equation (22);
- Step 9.
- Updating position of the current agent according to Equation (23);
- Step 10.
- Returning the Step 3 at stopping criteria , or otherwise going to next step;
- Step 11.
- Returning the best fitness and the best solution .
3.5. Verification and Discussion of H-GWO Algorithm
- (1)
- PSO:
- (2)
- GWO:
- (3)
- DE:
- (4)
- H-GWO:
- (1)
- Discussion on exploitation and exploration
- (2)
- Local minima avoidance
4. Application of H-GWO Algorithm for Parameter Identification
4.1. Parameter Identification Strategy
4.2. Accuracy Index
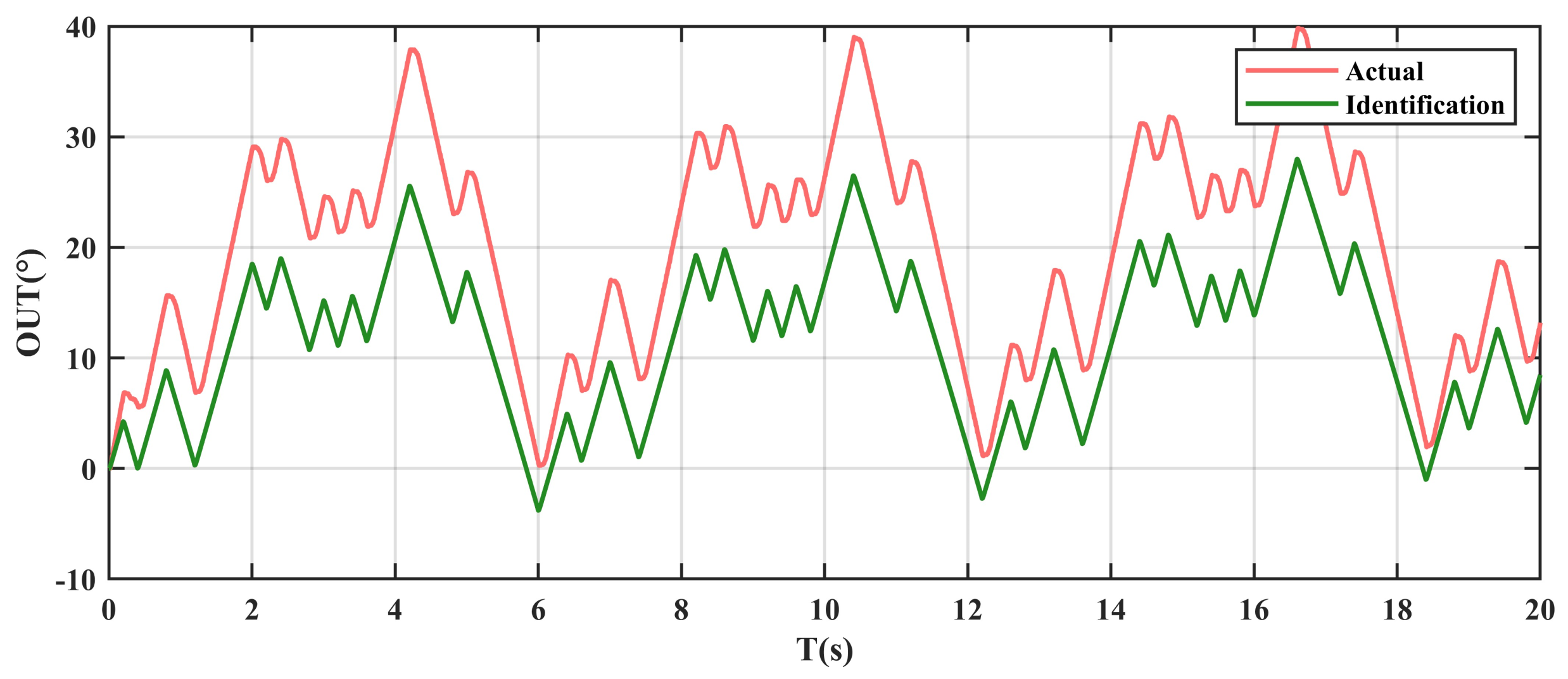
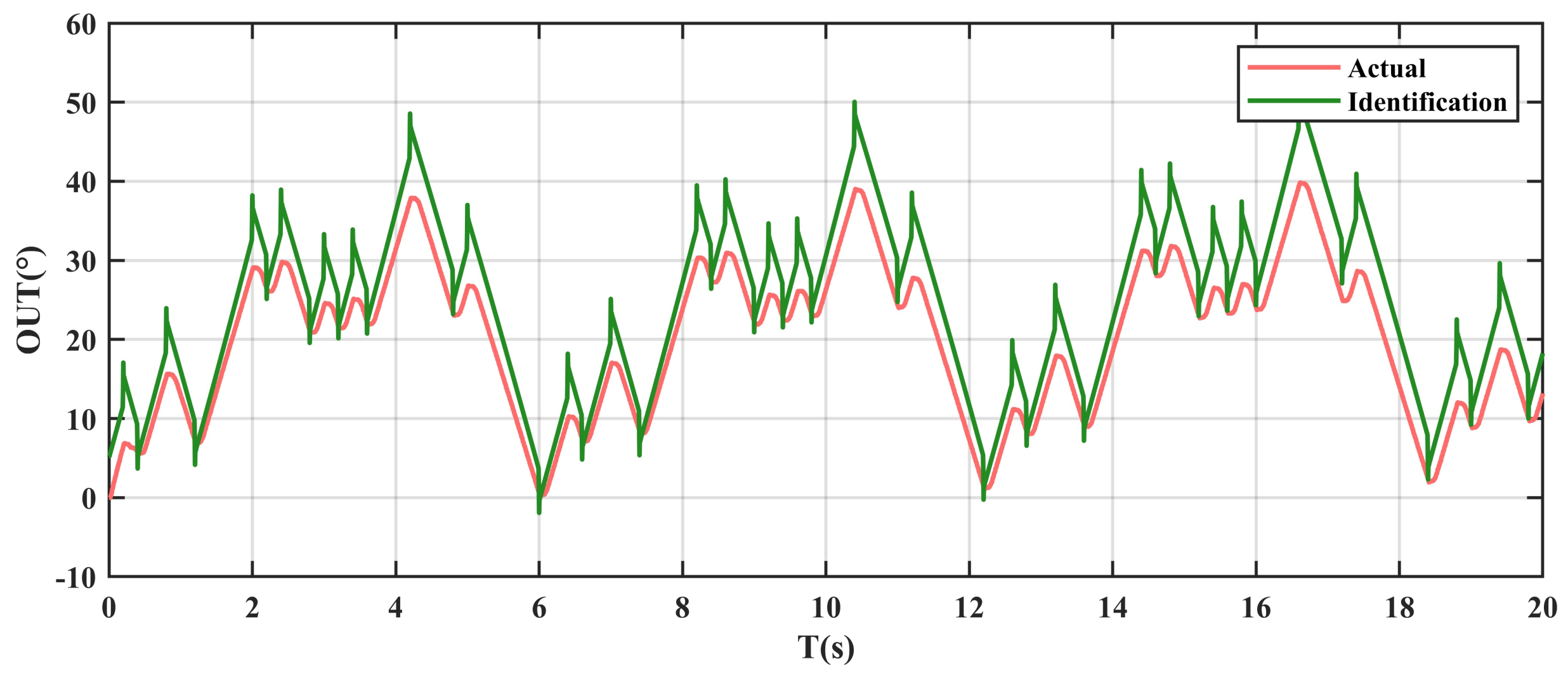
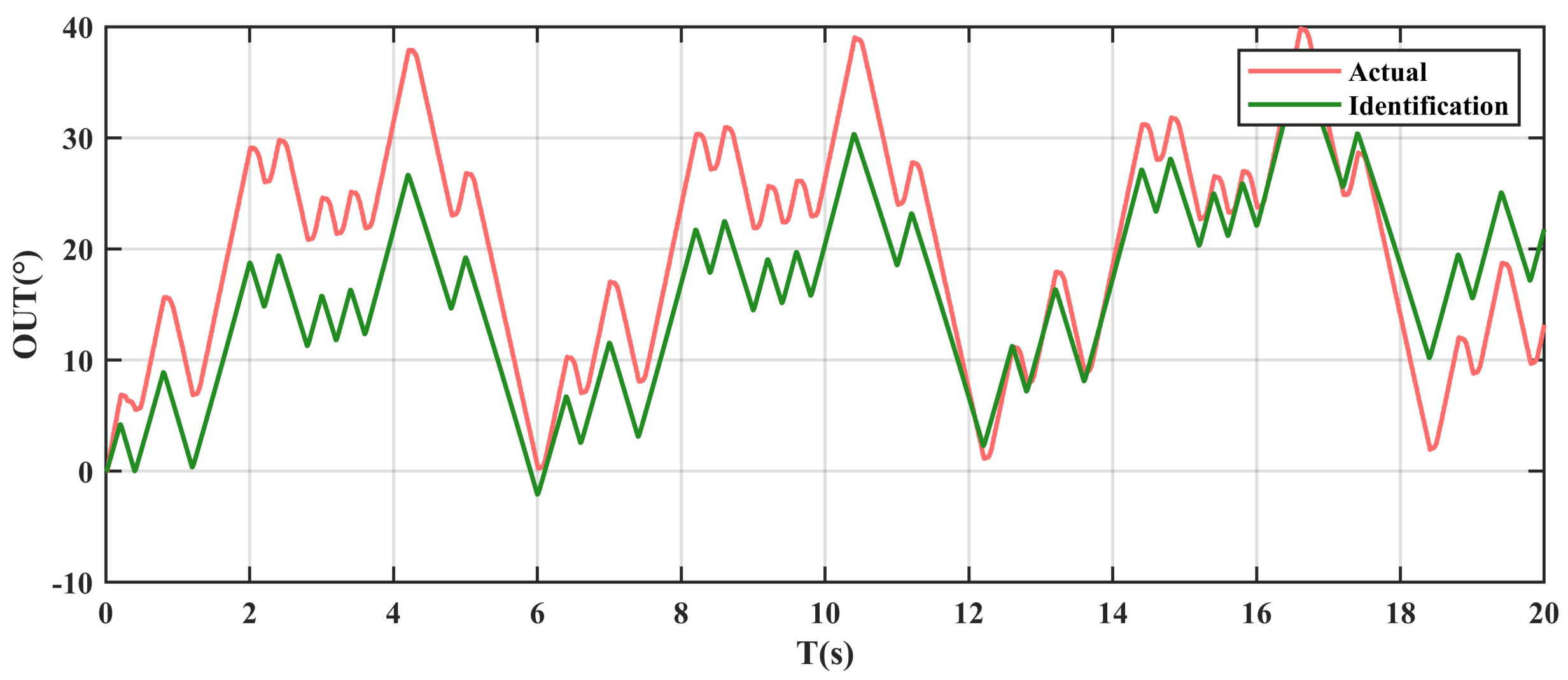
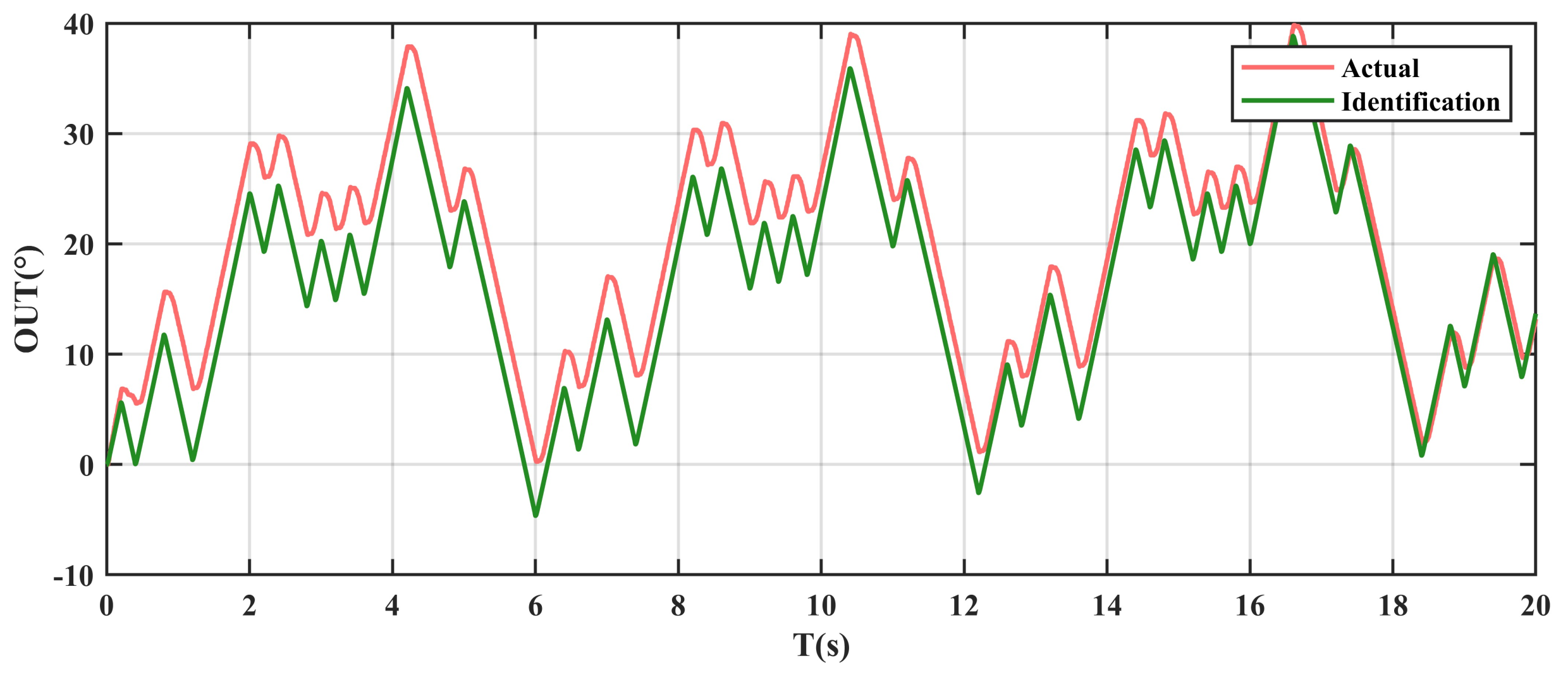
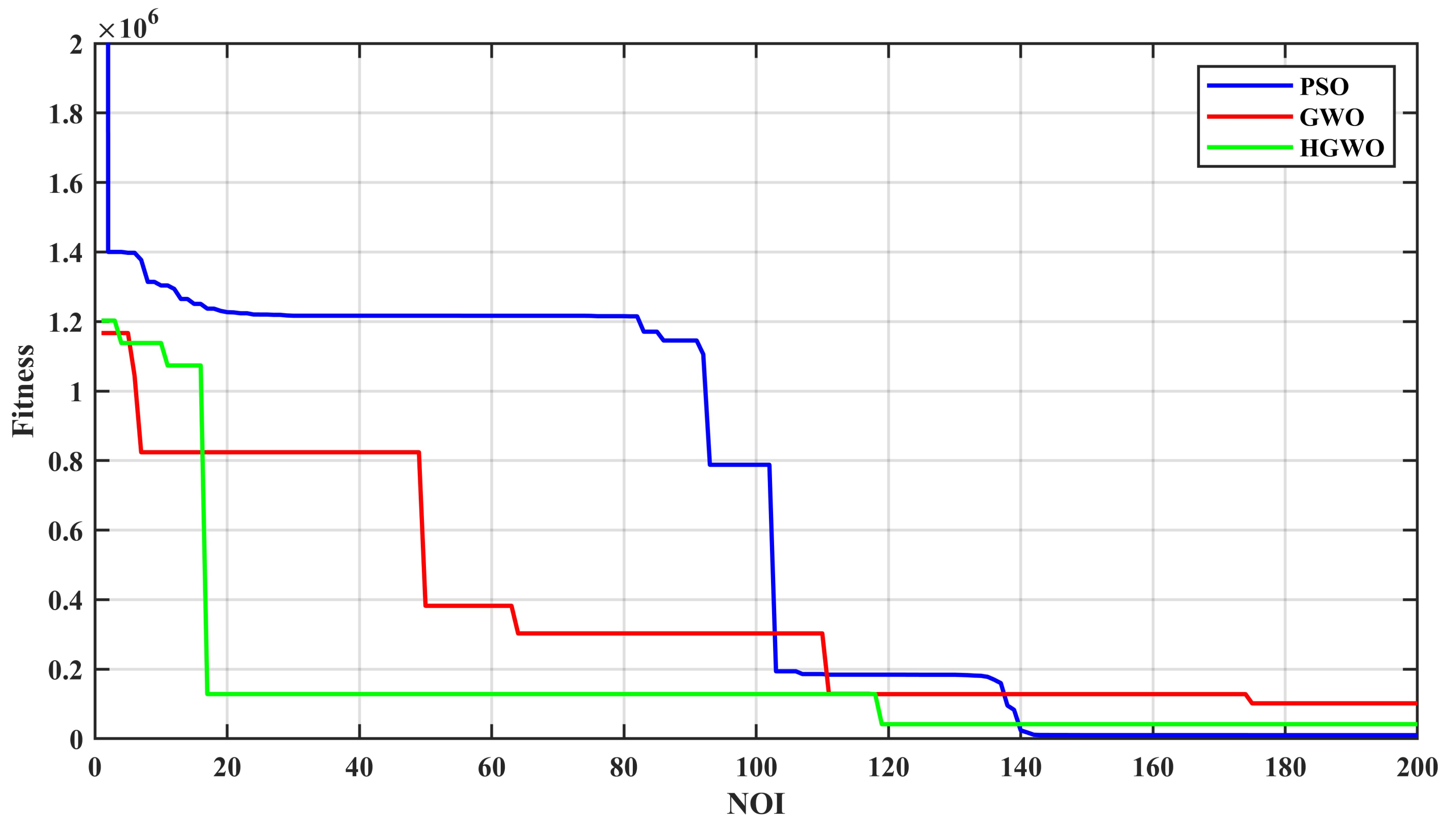
4.3. Results and Analysis
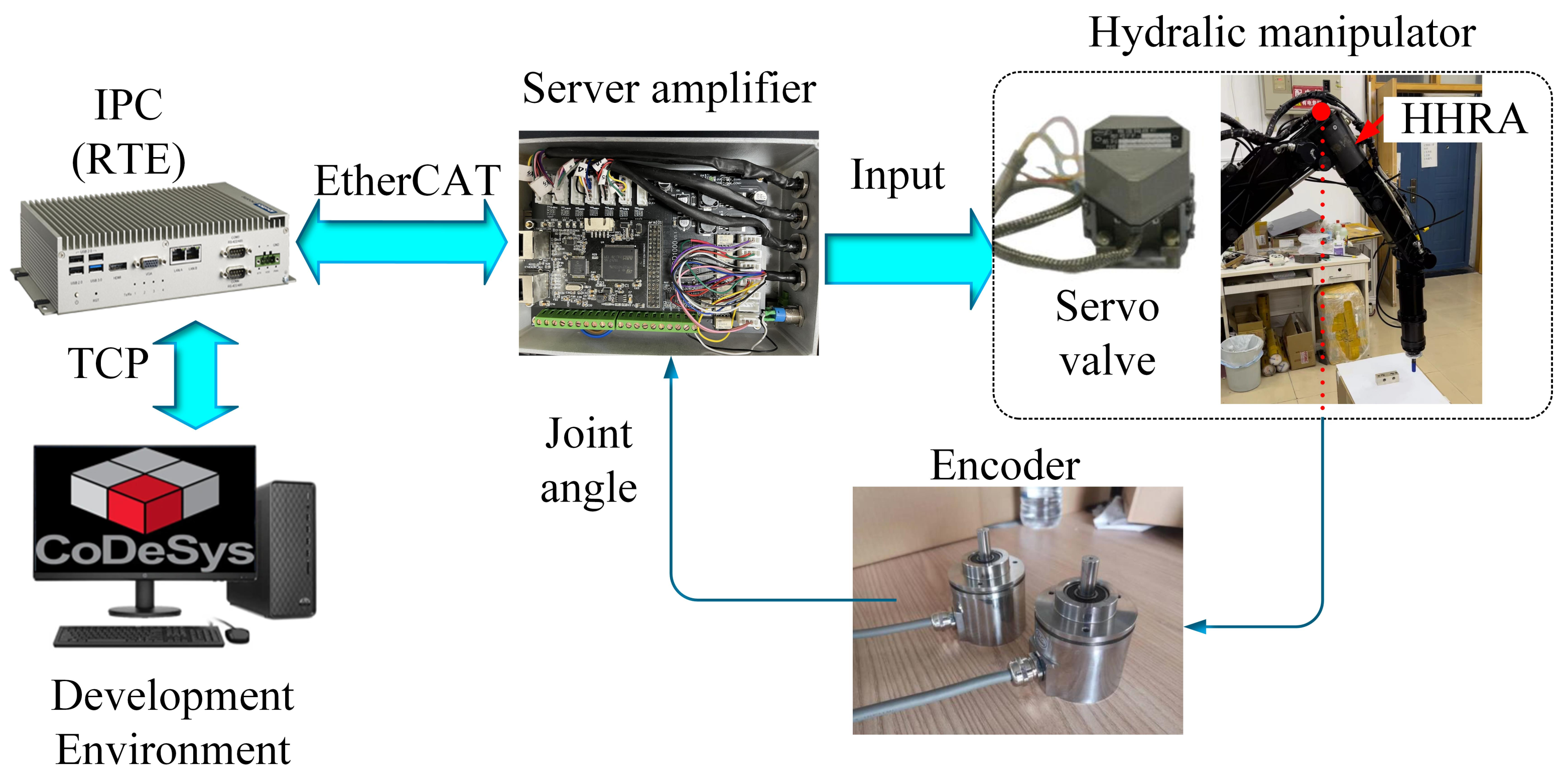
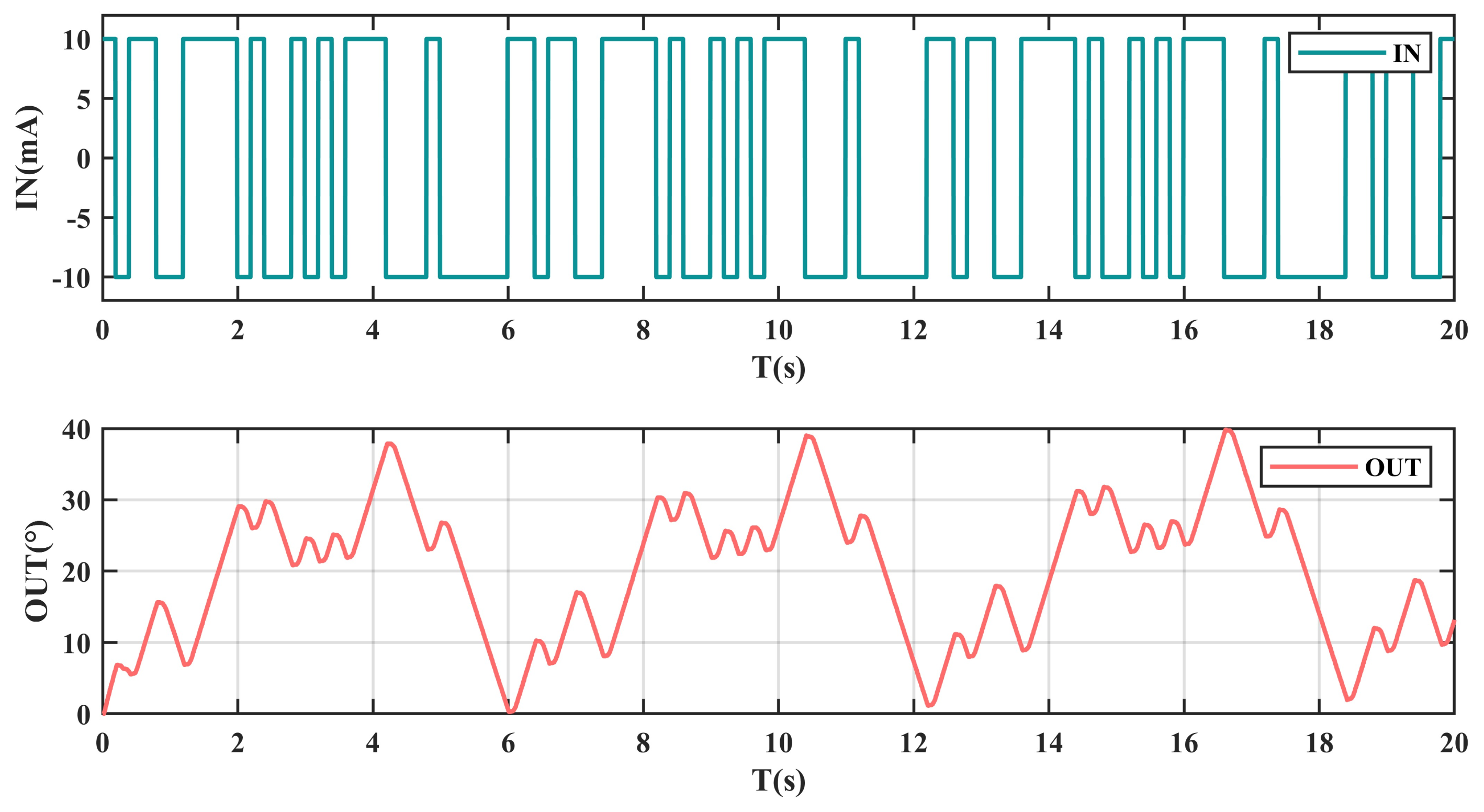
- Experiment setup
- B.
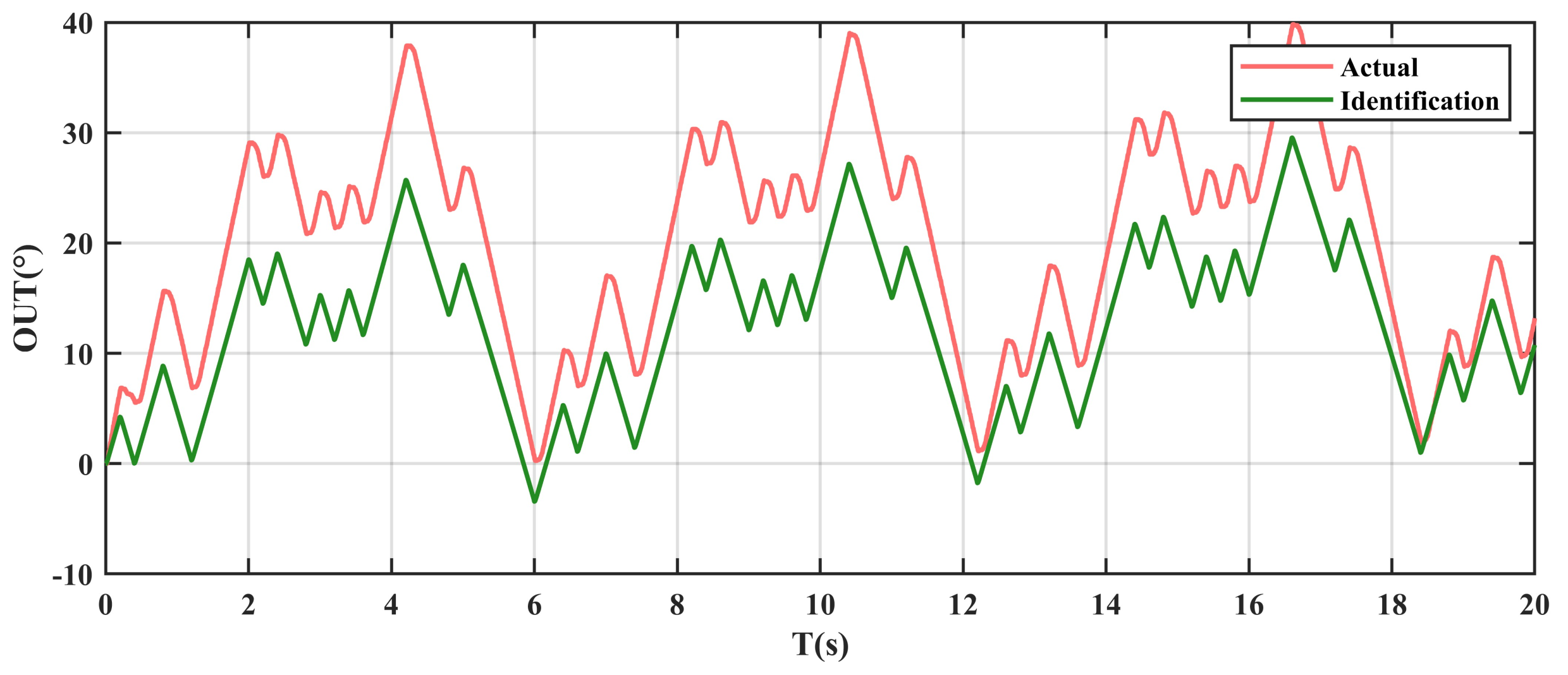
- Experimental Results
- (1)
- LS method:
- (2)
- RLS method
- (3)
- FFRLS method
- (4)
- PSO method
- (5)
- GWO method
- (6)
- FFRLS and H-GWO hybrid method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jelali, M.; Kroll, A. Hydraulic Servo-Systems: Modelling, Identification, and Control; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Gan, M.; Zong, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Xu, B. Modeling and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of Valve-Controlled Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator System. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, H. Design and tracking control of an electro-hydrostatic actuator for a disc cutter replacement manipulator. Autom. Constr. 2022, 142, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L. Mobile Machinery Cylinders-Aerial Work Platform Cylinder. Available online: https://www.henglihydraulics.com/en/application/ApplicationCenter (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Parker. Helac Products|Parker Cylinder Division. Available online: https://promo.parker.com/promotionsite/helac/us/en/products (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Schwenzer, M.; Ay, M.; Bergs, T.; Abel, D. Review on model predictive control: An engineering perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 1327–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Do, T.C.; Ahn, K.K. Extended high gain observer-based sliding mode control for an electro-hydraulic system with a variant payload. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, D. Extended-state-observer-based output feedback nonlinear robust control of hydraulic systems with backstepping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6285–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, D.; Yan, L. High-accuracy tracking control of hydraulic rotary actuators with modeling uncertainties. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 19, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghieh, A.; Sazgar, H.; Goodarzi, K.; Lucas, C. Identification and realtime position control of a servo-hydraulic rotary actuator by means of a neurobi-ologically motivated algorithm. ISA Trans. 2012, 51, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multi-Media Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO): A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Suganthan, P.N. Differential evolution: A survey of the state-of-the-art. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2010, 15, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Myung, H. Evolutionary programming techniques for constrained optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Q.; Coello, C.A.C.; Wong, K.C.; Chen, F. An adaptive immune-inspired multi-objective algorithm with multiple differential evolution strategies. Inf. Sci. 2018, 430, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, A.B. CIDE: Chaotically initialized differential evolution. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4632–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Isa, N.A.M.; Lim, W.H.; Ang, K.M. Differential evolution: A recent review based on state-of-the-art works. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3831–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Cai, Z. Differential evolution with ranking-based mutation operators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Ant Colony Optimization: Overview and Recent Advances; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abedinia, O.; Amjady, N.; Ghasemi, A. A new metaheuristic algorithm based on shark smell optimization. Complexity 2016, 21, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga, D.; Gorkemli, B.; Ozturk, C.; Karaboga, N. A comprehensive survey: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2014, 42, 21–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.M. Evolutionary population dynamics and grey wolf optimizer. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 26, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Coelho, L.D.S. Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: A novel algorithm for multicriterion optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 47, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; AlBetar, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Grey wolf optimizer: A review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.P.; She, C.; Bagal, H.A. Optimal parameter identification of SOFC model using modified gray wolf optimization algorithm. Energy 2022, 240, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Ding, H.F. Modeling and Parameter Identification of High Voltage Pulse Rock-breaking Discharge Circuit. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 58, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ladi, S.K.; Panda, G.K.; Dash, R.; Ladi, P.K.; Dhupar, R. A novel grey wolf optimisation based CNN classifier for hyper-spectral image classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 28207–28230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, J.S. Dynamic modeling of steam condenser and design of PI controller based on grey wolf optimizer. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 120975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achom, A.; Das, R.; Pakray, P. An improved Fuzzy based GWO algorithm for predicting the potential host receptor of COVID-19 infection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 151, 106050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Rashid, T. A novel hybrid GWO with WOA for global numerical optimization and solving pressure vessel design. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 14701–14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HKS. HKS—Products. Available online: https://www.hks-partner.com/en/products (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Song, B.L. Dynamic Characteristics Study of Screw Oscillating Hydraulic Cylinder; Central South University: Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.H. Research on Modeling and Control Method of Valve-Controlled Asymmetrical Cylinder System; Hefei University of Technology: Hefei, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K.; Moayedi, H.; Foong, L.K.; Assad, A.L. Sine cosine grey wolf optimizer to solve engineering design problems. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 3123–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Isa, N.A.M.; Lim, W.H.; Ang, K.M. Differential evolution with modified initialization scheme using chaotic oppositional based learning strategy. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 11835–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


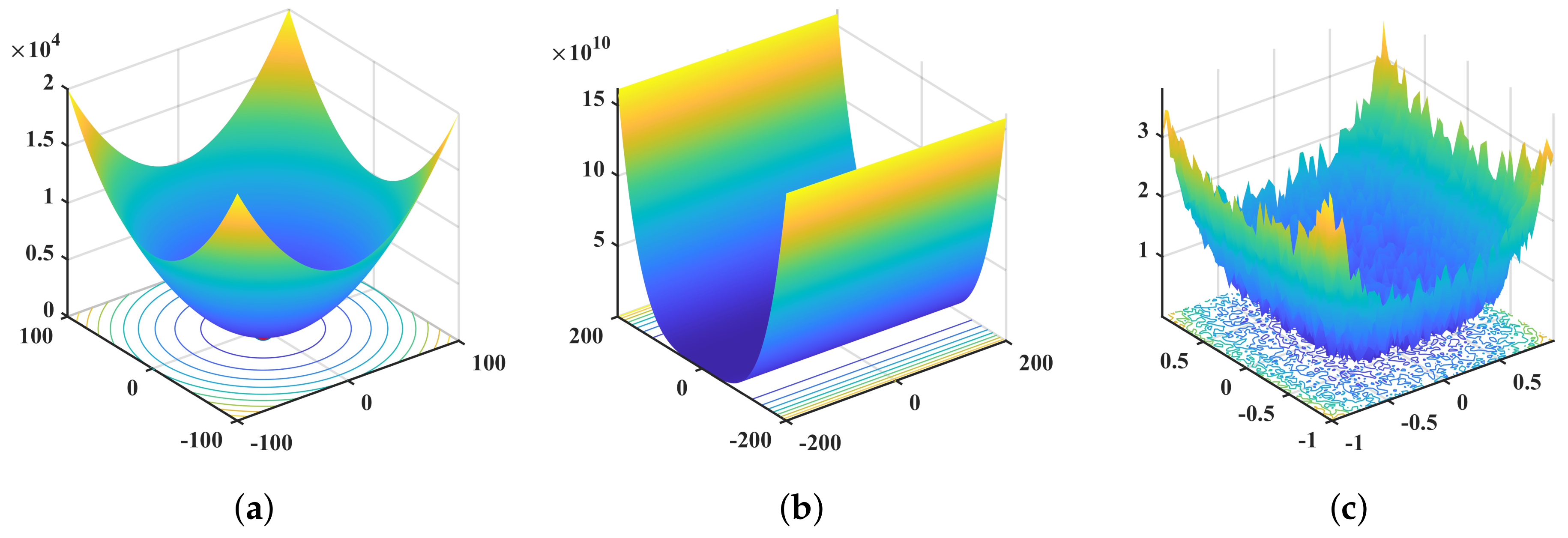
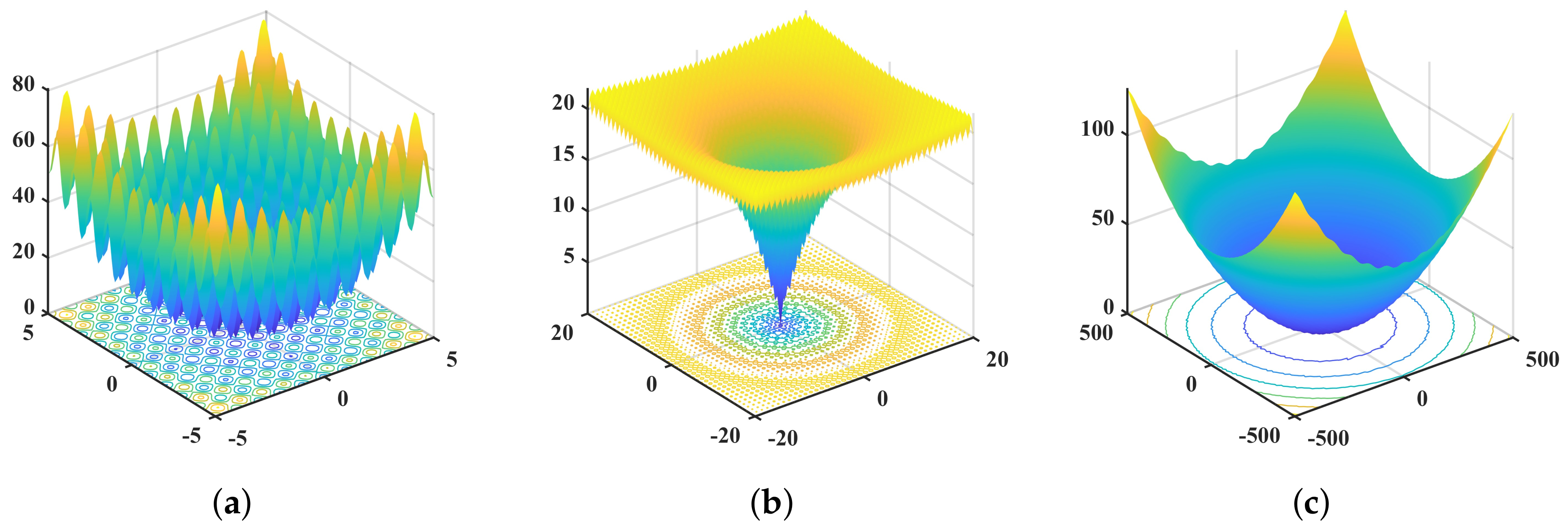
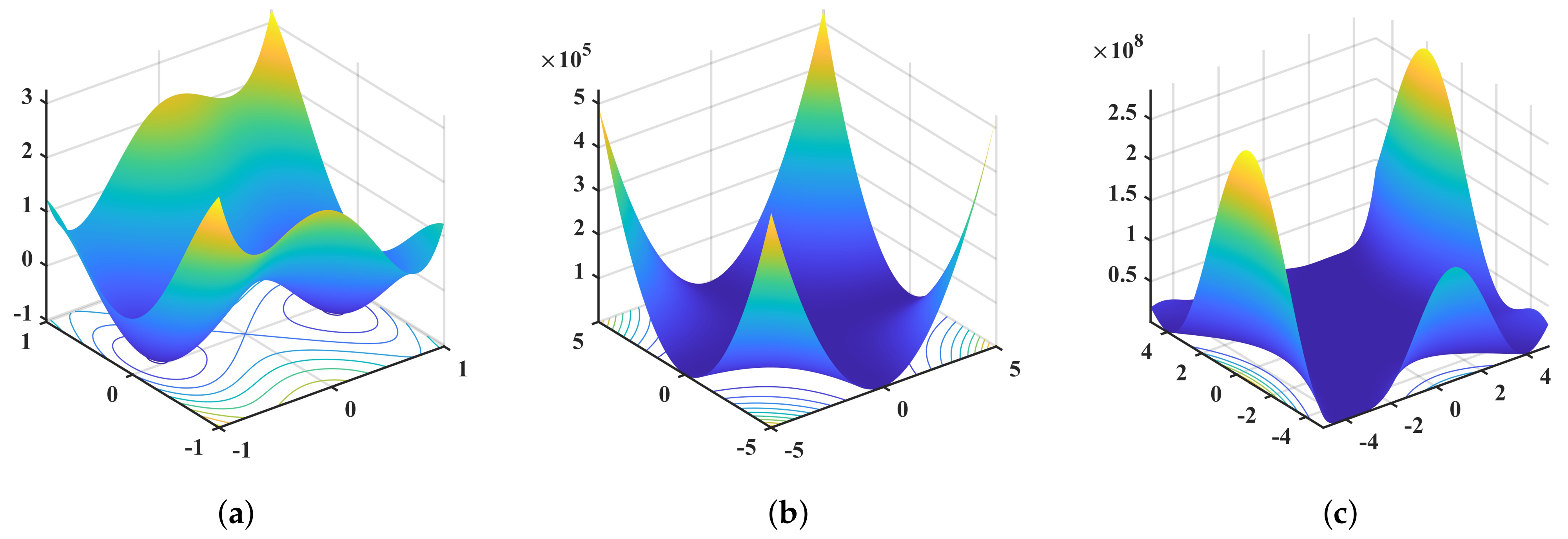

| Function | Dim | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unimodal benchmark functions | |||
| 30 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−30, 30] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−1.28, 1.28] | 0 | |
| Multimodal benchmark functions | |||
| 30 | [−5.12, 5.12] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−30, 30] | 0 | |
| 30 | [−600, 600] | 0 | |
| Fixed-dimension Multimodal benchmark functions | |||
| 2 | [−5, 5] | −1.0316 | |
| 4 | [−5, 5] | 0.0003 | |
| 2 | [−2, 2] | 3 |
| Function | PSO | GWO | DE | H-GWO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | St. dev | Average | St. dev | Average | St. dev | Average | St. dev | |
| 5.107963 | 2.045059 | 0.002765 | 1.3874 | 4.0215 | ||||
| 68.341611 | 39.848151 | 27.960574 | 0.00391 | 28.940232 | 0.02895 | 25.901103 | 0.671705 | |
| 8.714045 | 6.275347 | 0.003067 | 0.003762 | 0.030475 | 0.039981 | 0.001465 | ||
| 38.039407 | 31.421778 | 1.544107 | 35.973785 | 81.892454 | 17.961906 | 0.513119 | ||
| 3.080351 | 0.351753 | 0.004442 | 0.014036 | |||||
| 18.80006 | 5.574793 | 0.006625 | 0.020953 | |||||
| −1.031628 | −1.031628 | −1.028604 | 0.003393 | −1.031628 | ||||
| 0.001655 | 0.003372 | 0.002952 | 0.001598 | |||||
| 3.00001 | 3.000219 | 6.944784 | 4.913727 | 3.000008 | ||||
| Criterion | MSE | VAF (%) | NOI |
|---|---|---|---|
| LS | 95.31 | 61.52 | – |
| RLS | 89.98 | 65.73 | – |
| FFRLS | 77.47 | 91.28 | – |
| PSO | 13.94 | 93.21 | 142 |
| GWO | 40.68 | 71.24 | 175 |
| Proposed | 12.73 | 96.18 | 118 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, R.; Li, Y. A Hybridization Grey Wolf Optimizer to Identify Parameters of Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator. Actuators 2023, 12, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12060220
Zheng Y, Sun R, Liu Y, Wang Y, Song R, Li Y. A Hybridization Grey Wolf Optimizer to Identify Parameters of Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator. Actuators. 2023; 12(6):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12060220
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yukun, Ruyue Sun, Yixiang Liu, Yanhong Wang, Rui Song, and Yibin Li. 2023. "A Hybridization Grey Wolf Optimizer to Identify Parameters of Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator" Actuators 12, no. 6: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12060220
APA StyleZheng, Y., Sun, R., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Song, R., & Li, Y. (2023). A Hybridization Grey Wolf Optimizer to Identify Parameters of Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuator. Actuators, 12(6), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12060220






