Abstract
A soft actuator is an essential component in a soft robot that enables it to perform complex movements by combining different fundamental motion modes. One type of soft actuator that has received significant attention is the twisted and coiled polymer artificial muscle (TCP actuator). Despite many recent advancements in TCP actuator research, its use as an extensile actuator is less common in the literature. This works introduces the concept of using TCP actuators as thermal-driven extensile actuators for robotics applications. The low-profile actuator can be easily fabricated to offer two unique deformation capabilities. Results from the characterization indicate that extensile actuators, made with various rod diameters and under different load conditions, display remarkable elongation deformation. Additionally, a proof-of-concept soft-earthworm robot was developed to showcase the potential application of the extensile actuator and to demonstrate the benefits of combining different types of motion modes.
1. Introduction
Soft robotics is an emerging field of robotics that focuses on creating highly deformable, flexible robots. An essential component of soft robots is the soft actuator, which enables soft robots to perform intricate movements and interact with their surroundings. Soft actuators can produce a range of basic actuation responses such as contraction, expansion, rotation, and bending, allowing soft robots to achieve a variety of complex behaviors.
The specific type of motion generated by a soft actuator depends on its design and the materials used. For instance, shape memory alloy (SMA) contracts in response to heat, which has been leveraged by researchers to produce mechanical work [1,2]. Pneumatic artificial muscles (PAMs) and hydraulic actuators contract in response to changes in air or hydraulic pressure, respectively [3,4,5]. Torsional actuation originating from structural twist behavior can be found in twisted nano-/macrofiber yarns [6,7], twisted and coiled polymer artificial muscle [8,9,10,11], spider dragline silk [12], graphene oxide [13] and SMA fibers [14,15]. Bending motion can be found in ionic polymer–metal composites (IPMCs) [16,17], which use the movement of ions under the influence of an electric field. Dielectric elastomer actuators can also produce a bending motion in response to an applied electric field [18,19]. By conducting structural design and combining multiple basic actuation responses, complex motions such as twisting [20,21], curling [22,23], and folding [24,25] can also be achieved in the aforementioned actuators. However, the concept of deploying elongation as a driving force is less common in the literature. DEA artificial muscles with a certain degree of anisotropy can exhibit an expanding motion [26], forming antagonistic soft actuator systems to mimic biological systems [27,28]. However, the high operating voltage of dielectric elastomer actuators presents a significant barrier to their extensive adoption in soft robotics [29,30]. For pneumatic actuators, different jamming structures [31,32] and alterations in the braid angle of PAMs [33,34] can enable elongation motion. However, high noise levels and bulky forms may make them unsuitable for certain applications where a quiet operation or compact size is important.
In this work, we reported twisted and coiled polymer (TCP) muscle as an extensile actuator capable of performing mechanical work and demonstrated the possibility of creating soft robots for the first time. The research presented in this paper builds upon the work conducted by Beau in his thesis [35]. Recently, TCP actuators have attracted wide attention in various applications, including soft robots [36,37], soft grippers [38,39], robotic hand/prosthetic hands [40,41], orthotic devices [42,43], sensors [44,45], musculoskeletal systems [46], healing composites [47], and energy harvesters [48], due to their high strain and force generation, low weight and low-profile nature. These applications highlight that TCP actuators are mainly used as torsional or contractile actuators.
Despite many recent advancements in TCP actuator research, their use as extensile actuators is less common in the literature. This is the first study to use TCP muscle as an extensile actuator in soft robotics. The main contributions of this paper are three-fold. First, this work proposes a thermal-driven extensile actuator for soft robotics, which broadens the range of motion modes available for this type of actuator. It provides an additional novel solution for powering soft robots. Second, this work presents a detailed experimental characterization of TCP muscle as an extensile actuator, showing its potential to perform mechanical work. Finally, the paper demonstrates the feasibility of applying an extensile actuator in soft-earthworm robots, highlighting their potential for use in soft robotics applications.
The rest of this article is organized as follows. We first introduce the fabrication method for this type of heterochiral artificial muscles, followed by the characterization method in Section 2. In Section 3, the properties and performance of the actuator are tested, followed by a proof-of-concept demonstration in soft robotics. Finally, Section 4 concludes this article.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Heterochiral Artificial Muscle Fabrication
We first fabricated the heterochiral artificial muscle using a nylon 6 monofilament fishing line fiber (Eagle Claw monofilament 80 lb-test fishing line with a diameter of 0.8 mm). The fabrication process for this type of heterochiral actuator followed the four major steps that were reported in our previous work [46]: twist insertion (Figure 1c), resistance wire wrapping (Figure 1d), mandrel coiling (Figure 1e) and thermal annealing.
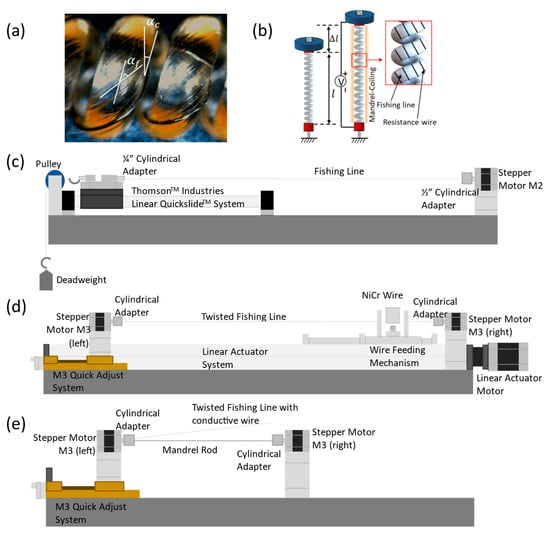
Figure 1.
(a) The extensile artificial muscle (heterochiral structure) with a fiber bias angle ( = 37°) and coil bias angle ( = 16°) measured from a microscope. (b) Schematic illustration of elongational deformation realized by heterochiral coiled artificial muscle. (c) Inserting twist into the pristine fishing line. (d) Incorporating the nickel-chromium wire (resistance wire) into the muscle by wrapping the resistance wire around the twisted fiber. (e) Forming the mandrel-coiling muscle from the twisted fiber with resistance wire as made in (d) by wrapping it around the rod via the rotation of the stepper motor.
To achieve twist insertion, we twisted the 0.8-mm diameter nylon 6 fiber in the Z direction (clockwise) using the setup in Figure 1c until the first coil formation was observed along the fiber. A 500-g deadweight was used to keep the fishing line fiber under tension during the twist insertion process. For resistance wire wrapping, we rapped a thin nickel-chromium wire with a diameter of 0.076 mm around the twisted fiber using the setup in Figure 1d. The conductive wire pool was placed on the pool holder. The pool holder was mounted to the linear actuator. The linear actuator traveled along the axis direction of the twisted fiber. Both stepper motors (M3) rotated in the opposite direction to prevent any additional twist from being added to the twisted fiber. With the combination of linear movement of the linear actuator and rotational movement of the stepper motors (M3), the conductive wire was woven around the twisted line. To ensure the conducting wire does not become bunched up within the feeding mechanism, we attached a small 10 g weight to keep the wire taut. Next, we performed mandrel coiling by wrapping the fishing line onto the rod in the S direction (counterclockwise). The major difference in this work from the previous work is that the actuator is oppositely twisted and coiled to form a heterochiral structure. The term “heterochiral” refers to the opposite chirality or handedness of the TCP muscles in their structure compared to the direction of their twisting or coiling. The final step was thermal annealing. We placed the coiled artificial muscle, with both ends tethered, in an oven (Memmert Universal Oven) where the temperature was set to 180 degrees Celsius for 90 min. The same annealing process was used for all the muscles used in this work. The thermal expansion induced untwist of the fiber produced the untwist of the helical structure which resulted in the muscle elongation [11].
Figure 1a shows a microscopic image of the heterochiral TCP actuator. The image was taken using a microscope (HAYEARTM HY-150X) and processed with the proprietary microscope image processing software to measure the fiber bias angle and coil bias angle . The fiber bias angle (an angle between the fiber axis and its initial orientation) resulted from the applied torque during the twist insertion step, where the disordered molecular chains became aligned. The initial coil bias angle (an angle between the fiber and the coil’s cross-section) resulted from the mandrel-coiling step. Figure 1b illustrates that upon receiving a thermal stimulus, the actuator can elongate along its axis direction to lift a deadweight and perform mechanical work. The displacement ratio (tensile actuation strain ) is expressed as a percentage and calculated as , where and are the muscle deformation displacement after actuation and its original lengths before actuation.
2.2. Characterization Method
The lengthwise elongation of the extensile TCP actuator upon heating with varying mandrel rod diameters and deadweights was characterized using an experimental setup, as depicted in Figure 2. A laser displacement sensor (Keyence IL-300) was used to measure the elongation displacement, while a power supply (BK Precision 9206) was used to program and define the power input waveforms. We intend to control the current instead of the voltage, as different lengths of muscle require different voltages. A deadweight was placed on top of a 3D-printed plate mounted to the low-friction linear ball slide, which could freely move up and down. It is very challenging to have an accurate and reliable measurement of temperature due to the small diameter of the fiber. In this study, we tried our best to use thermocouples for temperature measurement. Even though the temperature might not be accurate, we relied on this to monitor the trend of the muscles’ temperature to prevent overheating-induced damage. To be specific, two type-E thermocouples from Omega Engineering were used to monitor the muscle’s temperature. The data were acquired using a National Instrument DAQ.
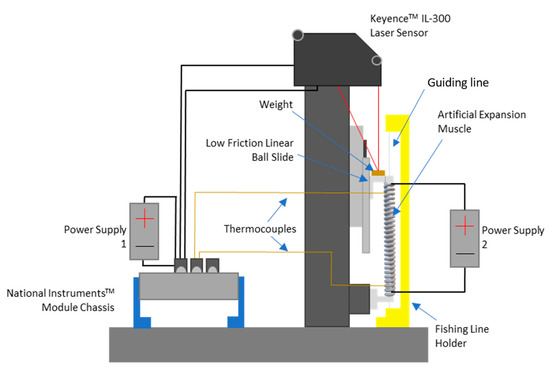
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the experimental setup to characterize the extensile TCP actuator.
Due to the tendency of the extensile TCP actuator to buckle, it is necessary to constrain the out-of-plane deflection during testing. A guiding line (a thin non-twisted fishing line) was run through the center of the muscle, which was fastened to the yellow fishing line holder. This guiding line kept the muscle upright while remaining electrically insulated to avoid interfering with the electrical current flowing through the muscle. Before each muscle was tested, it was trained via 10 cycles of heating and cooling to eliminate the lonely stroke while testing. Based on the results from the preliminary testing, a regulated constant current of 0.20 A and a 60-s period with a 25% duty cycle (15 s on vs. 45 s off) were used for the characterization test. This period was repeated five times for a total of 300 s. Data were acquired via a LabVIEW program and were plotted into graphs via a MATLAB program.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spring Index
We first investigated the effect of the spring index on the extensile actuator’s performance. The spring index is a ratio of the mean coil diameter to the fiber diameter, and it determines the final coil diameter. Due to the intrinsic structural nature of the coiled muscle, the mean coil diameter is determined by the diameter of the rod as well as the fiber diameter. The rod was used in the muscle fabrication to form a mandrel-coiled structure. In this study, the extensile actuators were fabricated with varying mandrel rod diameters of 0.035″, 0.041″, and 0.055″. The spring index is directly related to the mandrel coil diameter. The spring index of the muscle made from a 0.035″ rod diameter was 2.98; the spring index of the muscle made from a 0.041″ rod diameter was 3.23; and the spring index of the muscle made from a 0.055″ rod diameter was 3.63. A regulated constant current of 0.20 A was applied to each muscle, and no deadweight was applied for this experiment. The loaded lengths were 73.4 mm, 73.2 mm, and 68.3 mm, respectively.
Figure 3a,b show the fabricated actuators’ ability to deform in the direction of the axis. It is obvious when viewing Figure 3a,b that the muscle made from the 0.055″ rod diameter with the largest spring index produced the largest absolute displacement with a peak value of 35.3 mm as well as the largest displacement ratio reaching up to 54%. The larger spring index contributed to the actuator’s ability to deform along the axis, resulting in greater displacement under a given load. After completing the cooling cycle, the preliminary temperature results showed that the muscle temperature ranged from 42 °C to 47 °C. The experiment’s cooling time setting may have been insufficient for the muscle made from the 0.055″ rod diameter to fully return to its original position. Therefore, additional cooling time or the use of active cooling may be necessary to achieve complete recovery. Overall, the data indicate a distinct pattern where the increase in the diameter of the rod results in a larger spring index, which contributes to a greater deformation.
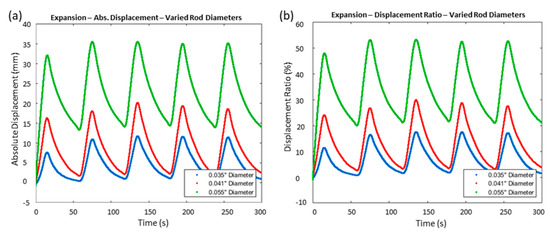
Figure 3.
The elongation performance of the muscles made from various rod diameters obtained at a regulated current of 0.2 A. The absolute displacement (a) and the displacement ratio (b) of an extensile actuator with different spring indexes made from different varying rod diameters.
3.2. Various Load Conditions
In addition to investigating the effect of the spring index, we also examined the deformation of the actuator under various load conditions using the muscle made from a 0.055″ rod diameter, which exhibited desirable deformation properties. To ensure accurate and consistent results, we performed a training phase for at least 10 cycles on each muscle by applying a regulated constant current of 0.20 A at various load conditions. Three deadweights of 20 g, 40 g, and 60 g were used, and the loaded lengths were 67.6 mm, 67.4 mm, and 67.3 mm, respectively.
Our findings, depicted in Figure 4a,b, show that the maximum peak absolute displacement decreased as the deadweight increased. Specifically, the muscle exhibited a maximum peak absolute displacement of 32.6 mm under a 20 g deadweight, while the deadweights of 40 g and 60 g resulted in a maximum absolute displacement of 26.1 mm and 14.6 mm, respectively. The maximum displacement ratio achieved for each weight was 48.2% for 20 g, 38.9% for 40 g, and 21.8% for 60 g. Based on the preliminary temperature results, the residual temperature was between 50 °C and 57 °C, which we believe may negatively impact the life cycle performance due to the accumulative effect of the temperature on the system over time. Therefore, for the endurance test, we reduced the test current to 0.18 A to extend its performance longevity. Furthermore, we observed that the greater the compressive load, the more it facilitated the muscle’s return motion, indicating the actuator’s resilience to external pressure. Overall, the results suggest that the extensile actuator has promising applications in load-bearing and deformation-sensitive tasks.
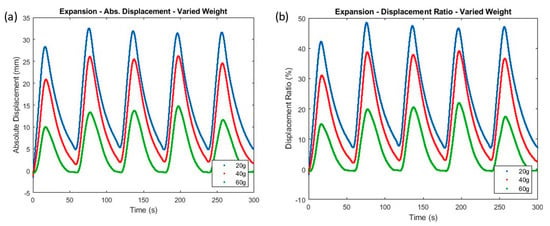
Figure 4.
The elongation performance of the muscles at various load conditions obtained at a regulated current of 0.2 A. The absolute displacement (a) and the displacement ratio (b) of the extensile actuator subjected to different deadweights.
3.3. Endurance Test
The endurance test was performed to determine how long the actuator can perform at an acceptable level without failure or degradation. A muscle made from a 0.055″ rod diameter with a loaded length of 45.1 mm was used with a 20 g deadweight. For the endurance test, we reduced the current to 0.18 A to extend its performance longevity. The muscle was tested at a duty cycle of 25% and a period of 60 s for 1000 cycles continuously in ambient air. Figure 5a shows that after around 80 cycles, the peak displacement ratio dropped from 20% and stabilized around 13% through the rest of the cycles. Figure 5b,c show a subtle visual color change in the muscle starting from cycle 0 until the end of the test. It was observed that the heating wire left some imprints or marks on the surface of the fishing line, which might contribute to the slight degradation of the actuator’s performance.
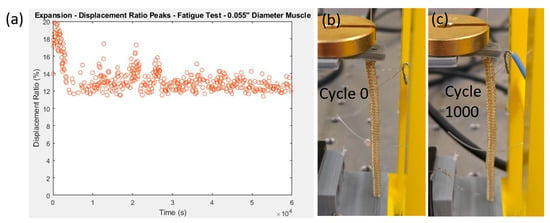
Figure 5.
(a) Endurance test of the muscle driven by a constant current (0.18 A, duty cycle 25% and a period of 60 s) under a constant 20 g load for 1000 cycles of actuation (total time 60,000 s). The pictures of the muscle at cycle 0 (b) and cycle 1000 (c) indicate a slight discoloration.
3.4. Application of The Extensile Actuator
To further illustrate the potential application of the extensile actuator and demonstrate the advantages of combining different types of motion modes, we developed a soft-earthworm robot that combines the contraction and elongation capabilities of artificial muscles. The earthworm robot moves by relying on frictional interaction with the surfaces of the vessel it is placed in [49]. The ability to adjust this frictional interaction is a crucial aspect of moving effectively. To showcase this capability, we designed the end caps of the robot with extensile artificial muscles that manipulate frictional forces to assist locomotion.
In this study, as depicted in Figure 6, the silicone shell was fabricated using a Hyrel modular 3D printer (Hydra 16 A). The shell was manufactured first by producing a hollow mold made of water-soluble PVA as shown in Figure 6a. The printer bed was covered with a layer of painter’s tape to allow for better adhesion of the print to the build plate as shown in Figure 6b. Figure 6c shows that after the PVA mold was finished, a static mixing head connected to two reservoir heads hosting silicone parts A and B, respectively, was then used to fill the mold with Smooth-On Ecoflex 00–30 silicone. The static mixing head permits the mixing in a 1:1 ratio between parts A and B. After the printing was finished, we waited for 4 h before taking the entire build-out of the printer and placing it into a Vevor 26–30 L Digital Ultrasonic Cleaner at 35 °C. Figure 6d shows the final fabricated silicone shell.
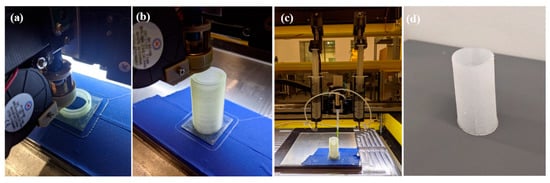
Figure 6.
(a) The first few layers of printing PVA mold. (b) The completed printing of PVA mold. (c) A static mixing head that dynamically mixes silicones at a 1:1 ratio dispenses silicone into a PVA mold (d) Finished silicone shell.
The end caps of the robot with extensile artificial muscles are mainly used for providing two friction modes to assist locomotion. Figure 7a shows the end cap in a high friction mode, with the U-shaped variable friction piece in the up position (actuators were not actuated); in Figure 7b, the actuated muscles pushed the U-shaped variable friction piece out of the end cap, reducing the contact area and minimizing friction with the surface. When reduced friction is no longer needed, the muscles naturally cool and retract, pulling the friction piece back up into the body of the end cap. Rubber tips were added at the base of the design to prevent slippage. Figure 7c shows the prototype of the earthworm, which uses a total of seven muscles. Due to the tendency of the extensile TCP actuator to buckle, it is very challenging to constrain the out-of-plane deflection during motion. Therefore, contractile muscles were used in the middle long section and extensile muscles were used in the end sections. Three contractile muscles were fabricated using the same method reported in our previous work [46]. These muscles were placed equidistant from each other in the middle section of the robot, and a long spring was included in the center of the robot to form an antagonist pair. When the contractile muscles in the middle section are activated, the length of the prototype shortens. However, the central spring enabled the robot to return to its original length when heat was no longer applied to the contraction muscles. Four extensile muscles were housed in both ends of the robot to alter frictional interaction. The contraction muscles were attached to the end caps with Loctite Instant Mix Epoxy. The silicone shell was attached to the end cap around the artificial muscles via the same epoxy.
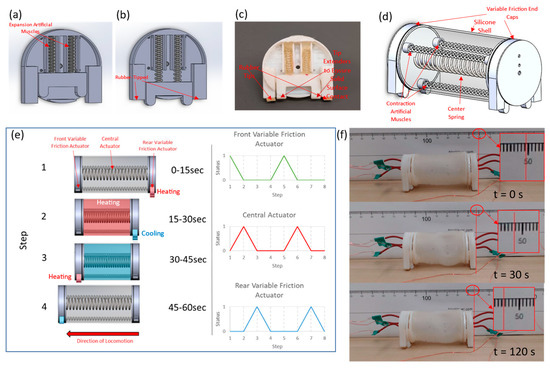
Figure 7.
A variable friction end cup powered by the extensile actuator in high-friction mode (a) and low-friction mode (b). (c) The prototype of the variable friction end cup. (d) The design concept of the earthworm robot. (e) The breakdown of the actuation sequence is in four steps. (f) Photographic sequence with time stamps showing the horizontal locomotion of the earthworm (magnified views of the scale reading are inset).
To move forward, the contraction muscles were periodically activated in conjunction with the extensile muscles located within the variable friction endcaps. This allowed the robot to move forward with only one segment, and the movement was broken into four repeating steps as shown in Figure 7e. In step 1 (0–15 s), the front variable friction actuators were powered on to create a smaller contact area in the rear. In step 2 (15–30 s), the central actuators were powered on to pull the rear-end cap forward. In step 3 (30–45 s), the front variable friction actuators were powered on to allow the front-end cap to be pushed forward. In step 4 (45–60 s), the front variable friction actuators were powered off to prepare for the next cycle of motion. The entire sequence of movement was programmed and controlled via a PLC (Triangle Research Fx2424 PLC, White Rock, BC, Canada), and the locomotion of the earthworm robot was recorded using a web camera.
Figure 7f shows the locomotion of the robot, with the central contraction muscle actuated at 0.36 A and the extensile muscle actuated at 0.20 A. The top picture in Figure 7f shows the initial state at 0 s; the middle picture shows that peak deformation occurred in the central actuator at 30 s; the bottom picture shows the final state at 120 s. The maximum axial move distance is 3.7 mm. One of the limitations of the thermal-driven actuator is the efficiency; the maximum energy conversion efficiency during contraction for homochiral artificial muscle that can contract is less than 1.08% [11]. Although the proposed soft robot has limitations in terms of movement speed and operation frequency, the combination of multiple motion modes shows the promising potential application of extensile actuators. To overcome these limitations, future work could focus on improving the design of the actuating system, incorporating active cooling for faster actuation, exploring cascading structures composed of multiple units for complex robotic systems, or designing new control strategies that enable faster and more precise movements.
4. Conclusions
This paper described the fabrication and characterization of a heterochiral extensile muscle that had a unique capability for elongation compared to other widely reported homochiral contractile muscles. Upon receiving Joule heat, the muscle’s fiber untwists due to thermal expansion, resulting in the untwisting of the helical structure and causing muscle elongation. The results show that the extensile actuator’s performance is affected by the spring index, which is directly related to the mandrel coil diameter. Increasing the mandrel rod’s diameter and hence the spring index leads to greater deformation and displacement of the actuator. However, additional cooling time or the use of active cooling may be necessary to achieve complete recovery.
In addition to characterizing the actuator, we also tested the deformation of the actuator under various load conditions. The actuator made from a 0.055″ diameter rod was tested under different deadweight conditions and found to be inversely related to the load applied to it. Additionally, the greater the compressive load, the more it facilitated the actuator’s return motion.
The study also explored the actuator’s potential as an earthworm soft robot drive system. The actuator can deliver not only contraction but also elongation motion, making it suitable for many robotic applications where elongation is desired. These actuators are expected to play a prominent role in tasks that require low-cost, silent operation, and high-performance and multi-motion modes. The combination of these basic actuation motion modes also offers the potential to produce other complex motions.
Author Contributions
B.R.: conceptualization, data acquisition, visualization, investigation, writing. L.W.: conceptualization, supervision, writing, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (lwu@georgiasouthern.edu) upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support by the Startup from Georgia Southern University. Most of the materials contained in the paper were previously published in Beau Ragland’s master thesis https://digitalcommons.georgiasouthern.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3539&context=etd (accessed on 27 March 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tadesse, Y.; Hong, D.; Priya, S. Twelve Degree of Freedom Baby Humanoid Head Using Shape Memory Alloy Actuators. J. Mech. Robot. 2011, 3, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kumar, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Nasab, A.M.; Ye, Z.; Shan, W.; Majidi, C. Highly Dynamic Shape Memory Alloy Actuator for Fast Moving Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, P.; Valle, L.; King, J.; Low, K.; Yi, J.; Atkeson, C.G.; Park, Y.-L. Design of a Lightweight Soft Robotic Arm Using Pneumatic Artificial Muscles and Inflatable Sleeves. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-G.; Rodrigue, H. Origami-Based Vacuum Pneumatic Artificial Muscles with Large Contraction Ratios. Soft Robot. 2018, 6, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska, J.; Kosucki, A.; Stawiński, Ł. Overview of Materials Used for the Basic Elements of Hydraulic Actuators and Sealing Systems and Their Surfaces Modification Methods. Materials 2021, 14, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; de Andrade, M.J.; Fang, S.; Oh, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Kozlov, M.E.; Haines, C.S.; Suh, D.; Foroughi, J.; et al. Electrically, Chemically, and Photonically Powered Torsional and Tensile Actuation of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube Yarn Muscles. Science 2012, 338, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; de Andrade, M.J.; Fang, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, E.; Li, N.; Kim, S.H.; Wang, H.; Hou, C.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Sheath-run artificial muscles. Science 2019, 365, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, D.; Irisawa, T.; Takagi, K.; Tahara, K.; Sakurai, D.; Watanabe, H.; Takarada, W.; Shioya, M. Mechanism for anisotropic thermal expansion of polyamide fibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Naficy, S.; Foroughi, J.; Brown, H.R.; Spinks, G.M. Controlled and scalable torsional actuation of twisted nylon 6 fiber. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Cho, K.H.; Jung, H.S.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.H.; Jang, H.; Nam, J.; Koo, J.C.; Moon, H.; et al. Double Helix Twisted and Coiled Soft Actuator from Spandex and Nylon. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.S.; Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; Spinks, G.M.; Foroughi, J.; Madden, J.D.W.; Kim, S.H.; Fang, S.; de Andrade, M.J.; Göktepe, F.; et al. Artificial Muscles from Fishing Line and Sewing Thread. Science 2014, 343, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tarakanova, A.; Hsu, C.C.; Yu, M.; Zheng, S.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Dunstan, D.J.; Buehler, M.J. Spider dragline silk as torsional actuator driven by humidity. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Moon, J.H.; Mun, T.J.; Park, T.G.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Kim, S.J. Thermally Responsive Torsional and Tensile Fiber Actuator Based on Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32760–32764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, K.; Seo, S.; Shin, D.; Park, J.H.; Gong, Y.J.; Choi, H.R. Hybrid Antagonistic System with Coiled Shape Memory Alloy and Twisted and Coiled Polymer Actuator for Lightweight Robotic Arm. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4496–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-E.; Quan, Y.-J.; Wang, W.D.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.-H.; Ahn, S.-H. A smart soft actuator using a single shape memory alloy for twisting actuation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, W.; Chen, H. Highly efficient structure design of bending stacking actuators based on IPMC with large output force. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 075033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, H.; Watanabe, H.; Sasaki, M. Bending direction change of IPMC by the electrode modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Bioinspired multimodal soft robot driven by a single dielectric elastomer actuator and two flexible electroadhesive feet. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2022, 53, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, M.; Ehrenhofer, A.; Lahiri, S.; Henke, E.-F.M.; Wallmersperger, T.; Richter, A. Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Driven Soft Robotic Structures with Bioinspired Skeletal and Muscular Reinforcement. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 510757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigue, H.; Bhandari, B.; Han, M.-W.; Ahn, S.-H. A shape memory alloy–based soft morphing actuator capable of pure twisting motion. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 26, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ji, C.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, M. Vacuum-Powered Soft Pneumatic Twisting Actuators to Empower New Capabilities for Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, S.; Ogura, K.; Suzumori, K.; Nishioka, Y. Miniature Soft Hand with Curling Rubber Pneumatic Actuators. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.J.; Jambon-Puillet, E.; Marthelot, J.; Brun, P.-T. Bubble casting soft robotics. Nature 2021, 599, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Jiao, Z. A Crawling Soft Robot Driven by Pneumatic Foldable Actuators Based on Miura-Ori. Actuators 2020, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ze, Q.; Zhang, R.; Hu, N.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, R. Symmetry-Breaking Actuation Mechanism for Soft Robotics and Active Metamaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41649–41658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Shi, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wang, T. Bioinspired bicipital muscle with fiber-constrained dielectric elastomer actuator. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2016, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yin, T.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Qu, S. Bistable rotating mechanism based on dielectric elastomer actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 29, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.T.K.; Ang, M.H.; Koh, S.J.A. Maximal Performance of an Antagonistically Coupled Dielectric Elastomer Actuator System. Soft Robot. 2020, 8, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Review of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators and Their Applications in Soft Robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zang, W.; Cao, P.; Tian, M.; Ning, N.; Zhang, L. Dielectric elastomer actuators for artificial muscles: A comprehensive review of soft robot explorations. Resour. Chem. Mater. 2022, 1, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracczak, L.; Nowak, M.; Koter, K. Flexible push pneumatic actuator with high elongation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 321, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, L.-J.; Zong, X.; Huang, J. Enhancing the Tensile-Shaping Stability of Soft Elongation Actuators for Grasping Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 8, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillsbury, E.T.; Wereley, N.M.; Guan, Q. Comparison of contractile and extensile pneumatic artificial muscles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, K.; Suzumori, K.; Wakimoto, S. Development of contraction and extension artificial muscles with different braid angles and their application to stiffness changeable bending rubber mechanism by their combination. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2011, 23, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, B. Design and Development of Soft Earthworm Robot Driven by Fibrous Artificial Muscles, in Department of Manufacturing Engineering. Master’s Thesis, Georgia Southern University, Statesboro, GA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://digitalcommons.georgiasouthern.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3539&context=etd (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, W. A Twisted and Coiled Polymer Artificial Muscles Driven Soft Crawling Robot Based on Enhanced Antagonistic Configuration. Machines 2022, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zuo, W.; Tang, X.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y. A multi-motion bionic soft hexapod robot driven by self-sensing controlled twisted artificial muscles. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2021, 16, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, R.; Bombara, D.; Swanbeck, S.; Zhang, J. Anthropomorphic Twisted String-Actuated Soft Robotic Gripper with Tendon-Based Stiffening. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 39, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tighe, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Twisted-and-Coiled Actuators with Free Strokes Enable Soft Robots with Programmable Motions. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, M.C.; Niemeyer, G. High-performance robotic muscles from conductive nylon sewing thread. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, T.; Seo, S.; Hudoklin, J.; Koo, J.C.; Choi, H.R.; Moon, H. Variable Stiffness Robotic Hand Driven by Twisted-Coiled Polymer Actuators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, L.; De Andrade, M.J.; Saleem, W.; Baughman, R.H.; Tadesse, Y. iGrab: Hand orthosis powered by twisted and coiled polymer muscles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsabedze, T.; Hartman, E.; Zhang, J. A compact, compliant, and biomimetic robotic assistive glove driven by twisted string actuators. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2021, 5, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weijde, J.; Smit, B.; Fritschi, M.; van de Kamp, C.; Vallery, H. Self-Sensing of Deflection, Force, and Temperature for Joule-Heated Twisted and Coiled Polymer Muscles via Electrical Impedance. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J. Differential Sensing Method for Multidimensional Soft Angle Measurement Using Coiled Conductive Polymer Fiber. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chauhan, I.; Tadesse, Y. A Novel Soft Actuator for the Musculoskeletal System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, G. Healing-on-demand composites based on polymer artificial muscle. Polymer 2015, 64, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lima, M.D.; Kozlov, M.E.; Haines, C.S.; Spinks, G.M.; Aziz, S.; Choi, C.; Sim, J.H.; Xuemin, W.; Hongbin, L.; et al. Harvesting temperature fluctuations as electrical energy using torsional and tensile polymer muscles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrouk, D.; Sharf, I.; Shoham, M. Analysis of worm-like robotic locomotion on compliant surfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).