Abstract
Haptic technology that provides tactile sensation feedback by utilizing actuators to achieve the purpose of human–computer interaction is obtaining increasing applications in electronic devices. This review covers four kinds of electromechanical actuators useful for achieving haptic feedback: electromagnetic, electrostatic, piezoelectric, and electrostrictive actuators. The driving principles, working conditions, applicable scopes, and characteristics of the different actuators are fully compared. The designs and values of piezoelectric actuators to achieve sophisticated and high-definition haptic effect sensations are particularly highlighted. The current status and directions for future development of the different types of haptic actuators are discussed.
1. Introduction
Touch is one of the most important human senses for perceiving environmental information, and “tactile” is the term raised to describe the sense of touch. Haptics, also connected with touch sensing, refers to the ability to apply both tactile and kinesthetic sensations to human–computer interactions, which often relies on the largest active organ of the human body—skin, typically the skin on the fingers, as illustrated in Figure 1. The skin and underlying tissues can receive mechanical vibrating signals and deform subtlety, which will be detected by nerve fibers and transmitted to the perceptual system [1,2,3]. Haptic technology [4,5] is an emerging interdisciplinary scientific field that uses haptic devices such as sensors or actuators to combine the interaction between physical human touching and the virtual computer environment. It aims to reproduce the sense of touch through the force, vibration, and motion transmitted to the user.

Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of a vibrating surface as a haptic interface with finger touching.
The global haptic technology market size remains large and growing. The market reached USD 8.1 billion value in the year 2021 globally, and it is forecasted to progress at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.9% during the years 2022–2026 and will reach USD 17.7 billion by 2027, as shown in Figure 2. According to the different total market estimations, while the final value by 2027 may change from USD 17.7 billion to USD 41.42 billion, the CAGR of at least more than 10% during the forecast period is a consensus [6,7].
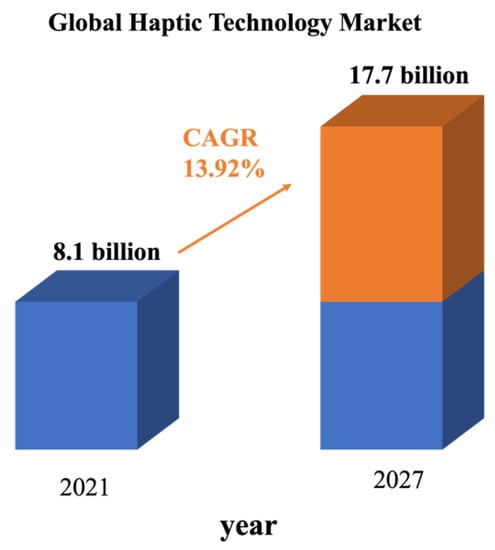
Figure 2.
Global haptic technology market size in years 2021 and 2027 [8].
For the most simple haptic technology, we only need short vibrations for notification or confirmation. For more advanced requirements, which would enhance user experience, high-definition haptic feedback mechanisms would be needed to communicate with the user’s sense of touch. These are the prime reasons that drive the haptic market growth [7].
The emergence of touch surfaces has led to its wide use in devices utilizing touch-sensitive displays (TSDs) which include mobile phones, smart watches, laptops, TVs, ATMs, vending machines, electronic kiosks, and car navigation systems [9]. At the same time, haptic applications in grounded, hand-held, and wearable devices such as game controllers, VR, joysticks, steering wheels, haptic teleoperation, underground exploration, and soft robots also promote the growth of the market [10,11,12]. Currently, due to the promotion of electronic devices, especially mobile phones, consumer electronic products have occupied the largest share of the haptic market. Potential needs in fields such as education, research, medical care, automotive, transportation, and engineering manufacturing also provide opportunities to boost the haptic industry.
As the core component to realizing haptic feedback, the actuators’ design [13] significantly influences the quality of the haptic impression. Therefore, in this review, we will summarize current research states, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and suitable applications of different electromechanical haptic actuators with the materials they use, especially highlighting the piezoelectric actuators, discussing current developments, and exploring their future direction.
2. Different Actuators in Haptic Feedback
2.1. Haptic Requirements
Basically, haptic actuators should meet the fundamental tactile sensation needs of humans. Skin perception varies widely in different parts of the human body [14,15]. Taking the human fingers used for sensory interaction as an example, although the frequency of human tactile sensing is verified from 5 Hz to 10 kHz, the maximum sensitive noticing is in the 200–300 Hz range, in which peak sensitivity is approximately 250 Hz [16,17]. The stimuli on the order of 10–100 mN and 10–100 μm are the typical perception thresholds in a static position; but if hand movement (dynamic condition) is permitted, 0.85 μm in the height of surface vertically could also be perceived [17,18,19,20]. When considering the friction perception in the horizontal direction, humans can detect the changes in tangential force and displacement at around 40–50 mN [21] and 0.2 μm [22,23] in the ultrasonic vibration range, such as in 20 kHz–40 kHz [24]. Further increased ultrasonic frequency may lead to degradation in spatial resolution and attenuation of sound pressure in the air.
Thus, in terms of haptic types, there are two important routes to provide surface haptic feedback: One is vibrotactile haptic, which only provides simple vibration prompts and can be perceived well when the frequency is below 1 kHz. The other is ultrasonic haptic, which provides more expressive tactile control and more complicated haptic effects by creating friction modulation when the fingers slide on the surface [9,25,26]. When the touch panels are excited and vibrated in ultrasonic frequency, standing Lamb waves are generated to produce the out-of-plane displacement which enables haptic interfaces [27,28]. This vibration traps a thin layer of air at the skin–surface interface, which is known as the squeeze film effect [21,29,30]. The friction between the air film and the surface is reduced by vibration (illustrated in Figure 3), and its degree of decline will depend on the vibration amplitude [31,32,33]. This frictional tactile impression can be transferred into fingers by “air smoothness” [29]. Therefore, the dynamic adjustment between the ultrasonic wave amplitude and frictional sensation makes it possible to provide complex tactile sensations [34,35].
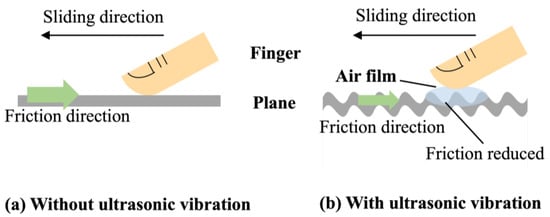
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of friction shift on a surface without and with ultrasonic wave.
Therefore, when further considering the ultrasonic vibrating surface, the commercial requirements change to a resonance frequency above 20 kHz, an out-of-plane displacement amplitude larger than 1 µm, and an in-plane half wavelength below 15 mm [36,37,38]. We summarize the requirements of two different haptic feedback methods in Table 1. In addition, a smaller driving voltage, lower power consumption, simpler device structure, and lower costs are also desired for realizing practical applications.

Table 1.
Requirements of actuators for haptic feedback.
2.2. Different Kinds of Haptic Actuators
Nowadays, several different types of actuators [39] are used to generate haptic vibrations, including electromagnetic actuators, electrostatic actuators, piezoelectric actuators, and electrostrictive actuators (shown in Figure 4), all of which have their respective strengths and weaknesses.
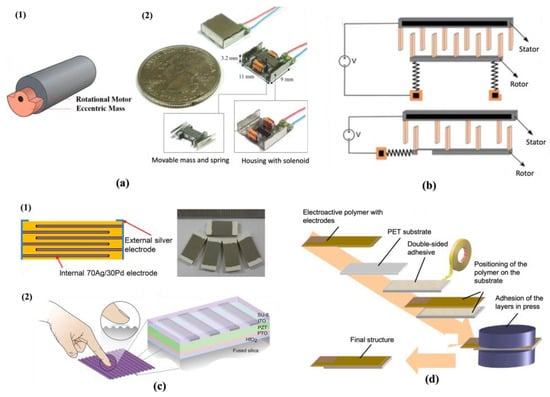
Figure 4.
Different types of actuators: (a) Electromagnetic actuators: (1) eccentric rotary mass (ERM) vibration motor. Reproduced with permission [40]. Copyright 2021, Springer Nature. (2) Linear resonant actuators (LRAs). Reproduced with permission [41]. Copyright 2015, Elsevier. (b) Electrostatic comb-drive actuators. Reproduced with permission [42]. Copyright 2017, Springer Nature. (c) Piezoelectric actuators based on ceramics: (1) multilayer cross-section structure and samples. Reproduced with permission [43]. Copyright 2016, John Wiley and Sons. (2) Transparent thin-film structure. Reproduced with permission [38]. Copyright 2021, John Wiley and Sons. (d) Electrostrictive actuators in the fabrication process based on electroactive polymers (EAPs). Reproduced with permission [44].
Electromagnetic actuators are based on electromagnetic field for electromechanical energy conversion. There are two common types of electromagnetic haptic actuators used in the market which are eccentric rotary mass (ERM) and linear resonant actuators (LRAs) [45,46,47,48]. The ERM actuators (with one sample shown in Figure 4(a1)) are direct current (DC) motors. After turning on the power, the vibrations will be activated by the rotating of eccentric mass inside, whose frequency and amplitude cannot be controlled independently [49,50]. When increasing the input voltage, the generated rotation becomes faster and the vibration frequency and the amplitude turn larger. Therefore, this type of actuator cannot achieve a random combination of frequencies and amplitudes, which extremely limits the diversity of vibration waveforms. Due to the time required to complete this rotation, the response speed of this design is relatively hysteretic, which will further be aggravated by the increase in device sizes. In general, ERM actuators are only available for simple vibration needs in small device parts [45,51]. In the LRAs (shown in Figure 4(a2)), alternating currents (ACs) pass through the voice coils enclosing one movable permanent magnet, and the forces generated by the electromagnet act on a small mass mounted on the springs to generate resonant frequency, thereby utilizing a small input to gain a large output vibration [52]. Even though the response speeds of these designs are faster than ERMs, they only work in a very narrow frequency range and have the problem of the residual vibration [53]. At the same time, the larger sizes also lead to slower response speeds and increased energy consumption. [41,54] Researchers [47,55,56,57,58] have tried to use liquid–metal coils to replace the copper wires or change the supporting hard shells with flexible polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrates, which allows LRAs to become better potential candidates for soft robotic and wearable devices. However, complex equipment designs, limited deformability, and insufficient durability are challenges that are needed to be overcome. Currently, there are various new types of electromagnetic actuators proposed to overcome the traditional weaknesses, such as impact actuators, seismic mass actuators, solenoid actuators, and so on [59,60].
Electrostatic actuators use the attractive forces of electrical charges between two capacitor plates, which is based on Coulomb’s law [61]. The most common structure in electrostatic actuators is the comb-drive structure with two comb sets of interdigitated fingers, as illustrated in Figure 4b. This simple design makes it possible to reduce the diameters to as small as 100 µm and beyond, which is particularly suitable for producing micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMSs) [62,63,64]. However, with the movable planes driven by the electrostatic force and the interactions between the mechanical and electrostatic forces, it is possible for pull-in instability, which is when the two plates collide with each other or even initiate collapse [65,66]. Most research studies on utilizing electrostatic actuators to provide haptic feedback focus on soft dielectric elastomers. Yong-Bok et al. [67] tried to excite two glass panels with input electric beats and created beat-patterned vibration to realize tactile sensing. There are also some film-type actuators with flexible and transparent cellulose acetate (CA) films showing promise for wearable device application [68,69,70]. However, the electrode surface areas in MEMSs are generally small, which results in weak outputs of electrostatic forces, vibration amplitudes, and sensory feedback. These non-linear outputs may contribute to a significant decline in performance at the end of the output range. Meanwhile, the electrostatic fields used by electro-vibration are dramatically affected by the external environment. Small changes in humidity or ambient gas contents will greatly impact the performance of the actuators and even cause electric shocks, which restricts the commercialization of electrostatic actuators [45,71].
Piezoelectric actuators (shown in Figure 4c) [72,73] utilize the piezoelectric effect in ferroelectric ceramics or polymers to convert input electrical signals into physical displacements or forces. The resonance frequencies of piezoelectric elements can conveniently reach tens of kHz, which enables piezoelectric actuators to work over a wide frequency range. At frequencies close to resonance, piezoelectric actuators can generate ultrasonic waves and weaken the surface frictions to supply complex tactile feedback. At low frequency range, such as about 250 Hz, which is far below the resonant frequency, piezoelectric actuators can provide maximum sensitive vibrational stimulations of human fingers. A variety of piezoelectric actuators using bulk, multilayer, and film piezoelectric materials are available, in which the most common commercialized material and structure for the piezoelectric actuator applications is the lead zirconate titanate (Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3, PZT)-based ceramic multilayers. Compared with the traditional ERMs and LRAs, piezoelectric actuators are more accurate with faster responses, higher acceleration rates, and forces and have more convenience for miniaturization, and most importantly, the unique ability to achieve high-definition tactile sensation [74,75,76,77,78]. Piezoelectric actuators are considered to be the most suitable for haptic feedback applications, whose specific materials and research studies will be discussed in the next section. The current problem with this type of haptic actuator is that they generate larger forces but with smaller displacements, which leads to high voltage input requirements. Furthermore, the fragility of some piezoelectric designs with ceramic materials is also problematic.
The device structures and characteristics of electrostrictive actuators are very similar to those of piezoelectric actuators, which is the reason why they are at times classified into one category [79]. Strictly speaking, the distinction is that electrostrictive actuators use electrostrictive relaxor ferroelectrics such as lead magnesium niobate (Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3, PMN) or some electrostrictive polymers [44] rather than piezoceramics. Compared with liner responses in piezoelectric actuators, the quadratic relationships between driven voltage and output stroke in electrostrictive actuators cause the hysteresis non-linearity and drift behavior, which make it more difficult to realize precise motion controls, impeding their commercial applications [80]. Using PMN ceramic as an example, they usually form piezoelectric solid solutions with lead titanate (PbTiO3, PT) as 0.65 Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.35 PbTiO3 turning into similar piezoelectric characteristics for usage [81,82,83]. Therefore, we will also group these materials with piezoelectric actuators for discussion. Nowadays, most electrostrictive haptic actuators are based on electroactive polymers (EAPs) [84] (shown in Figure 4d), in which a poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene-chlorofluoroethylene/chlorotrifluoro ethylene) P(VDF-TrFE-CFE/CTFE) fluorinated terpolymer is used. Differing from typical inorganic piezoelectric material, EAPs are light, flexible, lower cost, and easy to manufacture in a large area [85,86]. However, the displacement magnitude of EAPs is usually smaller than those of inorganic piezoelectric materials, which results in the requirement of an extremely high driving electric field to satisfy the tactile requirements. In previous studies, the property measurements of P(VDF–TrFE–CFE) are often conducted in the low-frequency range of around 100 mHz [87,88,89] because its electrostrictive coefficient will drop with the increasing frequency with deteriorating performance. At present, the utilization of this type of material in haptic devices is still under exploration, and its most promising actuation application may be in artificial muscles.
To sum up, the characteristics and current states of the four types of actuators for haptic applications as described above are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of four types of actuators for haptic feedback application.
3. Piezoelectric/Electrostrictive Actuators
For haptic feedback actuator applications, there are several requirements for the characteristics of the piezoelectric materials inside: Firstly, piezoelectric materials should have large piezoelectric strain constants (dij) or high electrostrictive strain coefficients Q33 to generate enough displacement. Secondly, materials are desired to have small dielectric permittivity, or dielectric constant εT33/εo values (preferably less than 2000) and low leakage, which correspond to a low power consumption [106]. Since the dielectric constant is proportional to capacitance, the increase in capacitance will result in an elevation of power consumption.
Piezoelectric actuators, based on the material classification, could be divided into piezoceramic actuators and piezopolymer actuators. Piezoceramic, PZT, which typically has the best cost-effective piezoelectric property, is most commonly used in haptic actuators and is commercialized. However, the release of the toxic element, lead, during their preparation and disposal is causing concerns for health and the environment. The same problem also exists in other lead-based piezoelectric and electrostrictive ceramics, such as PMN-PT [107]. The “Restriction of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment” (RoHS) rules of the European Union have raised prohibition for the use of lead in electrical and electronic products, but currently allowing a temporary exemption for piezoelectric devices before a replacement is made available [108,109]. Consequently, lead-free piezoelectric ceramics including potassium sodium niobate ((KxNa1−x)NbO3, KNN) and barium neodymium titanate ((BixNa1−x)TiO3, BNT) systems [110] have emerged for actuators applications. Compared with lead-based ceramics, the piezoelectric properties of lead-free piezoceramics are slightly inferior and lack stability in both properties and supply. At present, their application in haptic actuators is still in the exploration stages. Moreover, these perovskite structure ceramics, the wurtzite-structured AlN and ZnO piezoelectric materials, also can deform, but the much lower piezoelectric coefficients significantly reduce their competitiveness for displacement actuators [111,112,113]. In contrast to rigid ceramics, piezoelectric and electrostrictive polymers, typically PVDF and its various copolymers such as P(VDF-TrFE) and P(VDF-TrFE-CFE/CTFE) [114,115,116], are flexible and can be processed at much lower temperatures into films, fibers, or even textiles to perform as haptic actuators in wearable devices or soft robotics. However, the relatively low piezoelectric coefficient and low mechanical force of the piezoelectric and electrostrictive polymers need to be resolved for actuator applications.
According to the structural classification, piezoelectric actuators can be divided into four categories, including bulk, multilayer/stack, thick film, and thin film actuators. Bulk piezoelectric ceramic, mostly with single thicknesses in the mm range, is first used for producing haptic actuators since they are easy to fabricate. The bulk piezoelectric actuators based on PZT or PMN-PT ceramics working at frequencies in the kHz range typically require hundreds of volts to achieve displacement magnitude of tens of micrometers. This is the biggest obstacle for the practical application [117,118,119,120]. Consequently, these kinds of actuators are always manufactured in large sizes, which is not acceptable for miniaturized systems such as MEMSs.
Implementation of multilayer ceramics (MLCs) is a good way to reduce the high input voltage. Stacking and cofire process involving screen printing [121] or tape-casting [122] method are used to obtain the piezoelectric multilayer ceramics, in which solid solutions with lower sintering temperature could be a significant advantage for the co-firing approach [123]. As the most commonly used piezoceramic, PZT multilayers have been used as the core components to produce most of the commercial haptic actuators. An example is the PowerHap™ piezoelectric actuators from TDK Corporation, which can generate a displacement of 15–27 µm under 60 V [124]. Performance improvement is expected to be achieved with structural and dimensional optimization guided by numerical simulation [125], such as for working at the adjusted resonance frequency. Solid solutions with more complex compositions for larger piezoelectric outputs and lowered sintering temperature, including PZT-PZNN, PMW-PNN-PZT [126], or PNN-PZN-PMN-PZ-PT [43], are promising for haptic use. In-Tae Seo et al. [106] developed a piezoelectric haptic actuator composed of 3-layer 0.5CPZT-PZNN with a small εT33/εo of 1801 and a high d33 value of 659 pm/V under 110 V. These PZT-based actuators basically meet the characteristic requirements of tactile sensation with an operating frequency from one hundred to one thousand hertz, making them suitable for use as vibrotactile. Although the implementation of the multilayer structure could reduce the driving voltage from hundreds of volts for piezoelectric bulk ceramics to tens of volts, the relatively high driving voltage is still an issue in many applications for these piezoelectric ceramic actuators, in comparison with the commercialized ERM and LRA whose driving voltage is 1–5 V with the similar displacement magnitude for vibrotactile function. In some studies [127] and commercialized products [128,129], integrated boost converters are proposed to be packaged together with the piezoelectric ceramic actuators, for generating the voltages as required. This solution for solving the high voltage problem results in the expense of device miniaturization. Lead-free piezoelectric multilayers, for example, BF-BT [130] or CuO-KNN [131], are also emerging as a new type of material, which aim to resolve the toxicity of lead-based piezoelectric ceramics. However, they have weaknesses related to the lower piezoelectric coefficient and higher cost.
Compared with low-cost and easy-to-manufacture polycrystalline ceramics, the piezoelectric single-crystal stacks such as PMN-PT [132,133,134] fabricated using the solid-state crystal growth (SSCG) method and possessing a higher piezoelectric coefficient and electromechanical coupling factor could also be applied to produce actuators. For example, J.H. Kim et al. obtained a potential PMN-PT single crystal haptic actuator with 37 µm displacement and 0.25 g vibration acceleration at 200 Hz and 150 VPeak-to-Peak [135]. These relaxor ferroelectric single crystals could attain the characteristics of haptic actuators at a smaller size or lighter weight, but the high cost of fabrication makes them more suitable for high-end applications, such as in aerospace [136].
There are also multilayer piezoelectric or electrostrictive P(VDF-TrFE)-based polymer structures fabricated with successive solution depositions [137] or electrophoretic deposition [138], promising to be used for the development of actuators. P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE) multilayers, which exhibited deflection up to 213 µm at 320 Hz and 50 Vrms (root mean square) [103], achieved the displacement required for haptic actuators. However, the driving voltage was very high, especially for large-area applications.
With the rapid expansion of micromechanical systems (MEMSs) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMSs), thin film-type piezoelectric haptic actuators are becoming popular. Compared with bulk materials, the fabrication technologies of piezoelectric thin films by sputtering or sol-gel deposition methods [139] are scalable with mass production. Unlike the thickness expansion in bulk piezoceramics which produces a large out-of-plane force, the displacements of the piezoelectric thin films are dominated by bending, with a rather small out-of-plane force [140,141]. With the decrease in thicknesses and design of the bending structure, thin film actuators could reach the same displacements of tens to hundreds of microns at a lower voltage [142]. In the report by F. Casset et al. [143,144], 450 nm displacement was achieved using sol-gel PZT thin film deposited on silicon wafers under 4 V, which was estimated to be further raised to 1 µm under 10 V using Finite Element Method simulation. This indicated the probability of a lower driving voltage. Furthermore, PZT thin film can be transparent due to its high bandgap (3.5 eV) [145] and small thickness. This would be interesting for fully transparent tribo-modulated haptic optics based on piezoelectric films, which can be achieved using transparent glass substrates and transparent ITO/FTO electrodes. It has been demonstrated that high-quality PZT layers grown on a Si substrate could be moved to a glass substrate using a layer transfer method [146], but it is likely to damage the films and thus the yield needs to be improved for mass production. Sebastjan Glinsek’s study [38] demonstrated that standing Lamb waves could be induced by vibrating at 73 kHz in piezoelectric thin films, which allowed the friction–modulation haptic interface to achieve complex tactile sensation, as illustrated in Figure 4(c2). In 2022, Hui Hua et al. [36] improved the 2-µm thick sol-gel PZT thin film on glass within 75% transparency and obtained an out-of-plane displacement of 1 µm under 10 VPeak-to-Peak. This revealed the feasibility and potential value of piezoceramic thin films for transparent haptic actuators to be applied in display devices. Similar to bulk piezoelectric materials, considering the harm to the environment and health, research efforts and significant progresses have been made on lead-free piezoelectric films, including the KNN-based [147,148,149] and BNT-based [150] materials. The piezoelectric coefficients of these lead-free piezoceramics are close to PZT, and the longitudinal piezoelectric coefficient could be improved to 250 pm/V [151]. These are thus potential lead-free candidates to replace Pb-based thin films for haptic actuator applications.
The main disadvantages of the thin-film piezoelectric actuators include the small force, and the large power consumption caused by the large capacitance and leakage, especially when the haptic interaction area of display increases. For example, the power consumption of the entire haptic device based on the PZT thin film actuators by Hui Hua et al. [36] above reached 3.58 W, which is larger than multilayer ceramics [152,153]. In contrast to the small thickness of a couple of micrometers or below, piezoelectric thick films usually have a thickness of tens to hundreds of micrometers, and the preparation methods include screen printing, tape casting, thermal spray, and ink-jet printing. [142,154,155,156,157,158,159]. Longfei Song et al. [160] tested both 10 μm thick film and 0.5 μm thin film haptic devices with the PZT materials, showing that one thick-film actuator consumed 50 mW to obtain a 1 μm displacement compared with 750 mW to 0.4 μm deflection in one thin-film actuator at 24 Vrms. However, the production of cost-effective high-quality piezoelectric thick films for haptic actuators remains to be further explored. The thermal spray process [161,162] is one of the promising methods to produce large area lead-free thick films. KNN-based piezoelectric thick films with a thickness of 120 μm and effective d33 of 125 pm/V [158] have been demonstrated.
Comparisons among the four kinds of piezoelectric actuators with different material structures are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of different piezoelectric actuators for haptic feedback applications.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
We have reviewed the principles, performance properties, strengths, and weaknesses of the various types of electromechanical actuators for haptic feedback applications.
The electrostatic haptic actuators using micromachined structures or soft elastomers have low power consumption and fast response speed and are used in miniaturized and integrated soft devices such as VR, but their high sensitivity to environmental changes immensely impeded commercialization. Piezoelectric and electrostrictive haptic actuators based on electroactive polymers are flexible for wearable medical devices and close to simulating biological muscles, but their lower piezoelectric coefficients and requirements for high driving voltage need to be overcome. The eccentric rotating mass (ERM) actuators and linear resonance actuators (LRAs), both made of electromagnetic material are two traditional actuators for tactile stimulation in the market. They offer large vibration displacement with a low driving voltage. However, they are liable to noise impact, have slow response speed, high power consumption, and a limited vibration frequency, which restrict their haptic applications to simple vibration notification.
Piezoelectric actuators made of ceramics are suitable for touch surfaces driven at high frequency, they can achieve rapid and accurate responses and have the ability to turn almost any surface into touch control. The high input voltage is an important factor that hinders the commercial haptic application of piezoelectric ceramics. Multilayer structures can decrease the driving voltages from hundreds to tens of volts, and PZT-based piezoelectric multilayer ceramic materials have already realized commercialized haptic applications. With the increasing demand for MEMSs, piezoelectric thin film actuators are emerging in the haptic field. PZT-based thin film actuators have recently exhibited technical feasibility and commercial viability to achieve both haptic requirements and high transparency. Most importantly, the ultrasonic working frequency provides friction modulation, which makes high-definition tactile sensing become possible.
In the future, lead-based piezoelectric ceramics such as PZT will gradually be replaced with lead-free piezoelectric materials with high performances. Research and development of lead-free piezoelectric thick film and thin film ceramics including KNN and BNT systems will be one of the focuses of piezoelectric actuators for haptic applications.
In practical applications, how to achieve both small driving voltages and power consumption needs to be addressed. The ability to provide feedback on multiple tactile modes should also be another focus of future research. This will involve determining how to generate suitable ultrasonic waves with piezoelectric actuators to control the frictions and understand the fundamentals between friction modulation and tactile sensation, the outcome of which will bring significant innovation to the haptic field.
As the potential core element of the touch screen, high transparency is the key to achieving both visual and tactile feedback. Achieving good transparency in thin films using suitable synthesis methods is the first step. How to use a glass surface to replace the opaque metal substrate while retaining sufficient stability is becoming a challenge requiring attention. In this direction, the development and integration of transparent electrodes in piezoelectric actuator design need to be considered.
Realizing a large haptic surface area will be important for realizing scalable future industry application. The advent of piezoelectric coatings and haptic actuators has opened the opportunities for realizing various tactile surfaces, not only being limited to electronic devices, but also for any surrounding surfaces desired for touchable with feedback. How to overcome the manufacturing difficulties to produce high performance, environment friendly, and cost-effective piezoelectric films actuators and how to integrate them with huge numbers of sensors with minimized power consumption will be the key challenges.
In addition to current ultrasonic tactile display technology, emerging techniques such as midair tactile display that provides non-contact tactile stimulation through air and skin integration as haptic interface are expected to further improve the ultrasonic range of application frequency and enhance the sensitivity of tactile perception.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.Y., J.C. and E.H.T.T.; methodology, J.C. and K.Y.; investigation, J.C. and K.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C. and K.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.C., K.Y. and E.H.T.T.; supervision, E.H.T.T. and K.Y.; project administration, E.H.T.T. and K.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author from IMRE acknowledges partial supports by A*STAR, Singapore, RIE2020 Advanced Manufacturing and Engineering (AME) Programmatic Fund, (Grant No. A20G9b0135).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Logozzo, S.; Valigi, M.C.; Malvezzi, M. Modelling the Human Touch: A Basic Study for Haptic Technology. Tribol. Int. 2022, 166, 107352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaye, B.P.; Jarocka, E.; Barrea, A.; Thonnard, J.-L.; Edin, B.; Lefèvre, P. High-resolution Imaging of Skin Deformation Shows that Afferents from Human Fingertips Signal Slip Onset. eLife 2021, 10, e64679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kuilenburg, J.; Masen, M.A.; van der Heide, E. A Review of Fingerpad Contact Mechanics and Friction and How this Affects Tactile Perception. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J: J. Eng. Tribol. 2015, 229, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddik, A.E.; Orozco, M.; Eid, M.; Cha, J. Haptics: General Principles. In Haptics Technologies: Bringing Touch to Multimedia; El Saddik, A., Orozco, M., Eid, M., Cha, J., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Broström, C. Development of Tactile Actuators. Master of Science in Mechanical Engineering, Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden, 6 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Global Haptic Technology Market would Register a Healthy Growth USD 41.42 billion by 2027: Fior Markets. Financial Services Monitor Worldwide. 2022. Available online: https://remotexs.ntu.edu.sg/user/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/wire-feeds/global-haptic-technology-market-would-register/docview/2665531514/se-2 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Technavio Issues Report on the Haptics Market. Entertainment Close-up. 2020. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A624015449/ITOF?u=nantecun&sid=bookmark-ITOF&xid=1036ecd8 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Research and Markets Offers Report: Haptic Technology Market. Entertainment Close-up. 2021. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A652520028/ITOF?u=nantecun&sid=bookmark-ITOF&xid=18731156 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Basdogan, C.; Giraud, F.; Levesque, V.; Choi, S. A Review of Surface Haptics: Enabling Tactile Effects on Touch Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2020, 13, 450–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adilkhanov, A.; Rubagotti, M.; Kappassov, Z. Haptic Devices: Wearability-Based Taxonomy and Literature Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, P. A Review of Soft Actuator Motion: Actuation, Design, Manufacturing and Applications. Actuators 2022, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Kim, Y.; Youm, W.; Min, Y.; Seo, S.; Lim, C.; Hong, C.-H.; Kwon, S.; Park, G.; Park, S.; et al. Highly Pixelated, Untethered Tactile Interfaces for an Ultra-flexible On-skin Telehaptic System. npj Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, T.A. Engineering Haptic Devices: A Beginner’s Guide for Engineers; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jarocka, E.; Pruszynski, J.A.; Johansson, R.S. Human Touch Receptors Are Sensitive to Spatial Details on the Scale of Single Fingerprint Ridges. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, S.; Watanabe, J.; Nishida, S.y. Integration of Vibrotactile Frequency Information beyond the Mechanoreceptor Channel and Somatotopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.L. Telerobotic Response Requirements. In Proceedings of the 1990 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4–7 November 1990; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld, C. Haptics as an Interaction Modality. In Engineering Haptic Devices: A Beginner’s Guide; Hatzfeld, C., Kern, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 29–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Hinchet, R.; Shea, H.; Majidi, C. Wearable Soft Technologies for Haptic Sensing and Feedback. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontarinis, D.A. Tactile Displays for Dextrous Telemanipulation; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- De Fazio, R.; Mastronardi, V.M.; Petruzzi, M.; De Vittorio, M.; Visconti, P. Human–Machine Interaction through Advanced Haptic Sensors: A Piezoelectric Sensory Glove with Edge Machine Learning for Gesture and Object Recognition. Future Internet 2023, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueorguiev, D.; Vezzoli, E.; Mouraux, A.; Lemaire-Semail, B.; Thonnard, J.-L. The Tactile Perception of Transient Changes in Friction. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddik, A.E.; Orozco, M.; Eid, M.; Cha, J. Human Haptic Perception. In Haptics Technologies: Bringing Touch to Multimedia; El Saddik, A., Orozco, M., Eid, M., Cha, J., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D.A.; Pao, L.Y.; Dougherty, A.M.; Pavlou, Y.; Brown, S.W.; Wallace, S.A. Human Perception of Friction in Haptic Interfaces. In Proceedings of the ASME 1998 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Dynamic Systems and Control, Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–20 November 1998; pp. 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Korres, G.; Eid, M. Characterization of Ultrasound Tactile Display. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, EuroHaptics 2016: Haptics: Perception, Devices, Control, and Applications, London, UK, 4–7 July 2016; pp. 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nara, T.; Takasaki, M.; Maeda, T.; Higuchi, T.; Ando, S.; Tachi, S. Surface Acoustic Wave Tactile Display. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2001, 21, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullenbach, J.; Johnson, D.; Colgate, J.E.; Peshkin, M.A. ActivePaD Surface Haptic Device. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 March 2012; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Casset, F.; Danel, J.S.; Renaux, P.; Chappaz, C.; Bernard, F.; Sednaoui, T.; Basrour, S.; Desloges, B.; Fanget, S. 4-inch Transparent Plates Based on Thin-film AlN Actuators for Haptic Applications. Mechatronics (Oxford) 2016, 40, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.; Casset, F.; Danel, J.S.; Chappaz, C.; Basrour, S. Characterization of a Smartphone Size Haptic Rendering System Based on Thin-film AlN Actuators on Glass Substrates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 84007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Fukui, S. A Method for Controlling Tactile Sensation of Surface Roughness Using Ultrasonic Vibration. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nagoya, Japan, 21–27 May 1995; Volume 1131, pp. 1134–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Wiertlewski, M.; Friesen, R.F.; Colgate, J.E. Partial Squeeze Film Levitation Modulates Fingertip Friction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9210–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzoli, E.; Vidrih, Z.; Giamundo, V.; Lemaire-Semail, B.; Giraud, F.; Rodic, T.; Peric, D.; Adams, M. Friction Reduction through Ultrasonic Vibration Part 1: Modelling Intermittent Contact. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 10, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sednaoui, T.; Vezzoli, E.; Dzidek, B.; Lemaire-Semail, B.; Chappaz, C.; Adams, M. Friction Reduction through Ultrasonic Vibration Part 2: Experimental Evaluation of Intermittent Contact and Squeeze Film Levitation. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 10, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghenna, S.; Vezzoli, E.; Giraud-Audine, C.; Giraud, F.; Amberg, M.; Lemaire-Semail, B. Enhancing Variable Friction Tactile Display Using an Ultrasonic Travelling Wave. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2017, 10, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemet, L.; Kanzari, K.; Monnoyer, J.; Birznieks, I.; Wiertlewski, M. Initial Contact Shapes the Perception of Friction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emgin, S.E.; Aghakhani, A.; Sezgin, T.M.; Basdogan, C. HapTable: An Interactive Tabletop Providing Online Haptic Feedback for Touch Gestures. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 25, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qi, D.; Li, Y. A Highly Transparent Haptic Device with an Extremely Low Driving Voltage Based on Piezoelectric PZT Films on Glass. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2022, 335, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biet, M.; Giraud, F.; Lemaire-Semail, B. Squeeze Film Effect for the Eesign of an Ultrasonic Tactile Plate. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2007, 54, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinsek, S.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Rupin, M.; Schenk, T.; Godard, N.; Girod, S.; Chemin, J.B.; Leturcq, R.; Valle, N.; Klein, S.; et al. Fully Transparent Friction-Modulation Haptic Device Based on Piezoelectric Thin Film. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide to Haptic Actuators in Product Design—Haptic Actuators & Types. Available online: https://engineeringproductdesign.com/knowledge-base/haptic-actuators/ (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Gao, S.; Yan, S.; Zhao, H.; Nathan, A. Haptic Feedback. In Touch-Based Human-Machine Interaction: Principles and Applications; Gao, S., Yan, S., Zhao, H., Nathan, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pyo, D.; Yang, T.-H.; Ryu, S.; Kwon, D.-S. Novel Linear Impact-Resonant Actuator for Mobile Applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Q. A Review on Actuation and Sensing Techniques for MEMS-based Microgrippers. J. Micro-Bio Robot. 2017, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.K.I.; Sharifzadeh Mirshekarloo, M.; Lai, S.C.; Zhang, L.; Yao, K. PNN-PZN-PMN-PZ-PT Multilayer Piezoelectric Ceramic with Low Sintering Temperature. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2016, 13, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Schiava, N.; Thetpraphi, K.; Le, M.-Q.; Lermusiaux, P.; Millon, A.; Capsal, J.-F.; Cottinet, P.-J. Enhanced Figures of Merit for a High-Performing Actuator in Electrostrictive Materials. Polymers 2018, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.-H.; Schuster, J.M.; Tantiyartyanontha, T.; Kim, Y.-M.; Yang, T.-H. Enhanced Haptic Sensations Using a Novel Electrostatic Vibration Actuator With Frequency Beating Phenomenon. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyraz, G.G.; Tamer, O. Different Haptic Senses with Multiple Vibration Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 28–30 November 2019; pp. 870–874. [Google Scholar]
- Doerger, S.R.; Harnett, C.K. Force-Amplified Soft Electromagnetic Actuators. Actuators 2018, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding ERM Vibration Motor Characteristics. Available online: https://www.precisionmicrodrives.com/ab-004 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Rantala, J.; Majaranta, P.; Kangas, J.; Isokoski, P.; Akkil, D.; Špakov, O.; Raisamo, R. Gaze Interaction With Vibrotactile Feedback: Review and Design Guidelines. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 35, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourishetti, R.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Evaluation of Vibrotactile Output From a Rotating Motor Actuator. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2022, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Vibrotactile Display: Perception, Technology, and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanian, R.; Riedel, M.; Yeganeh, N. Numerical Investigation on the Acceleration Vibration Response of Linear Actuator. Open Access Library J. 2022, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Son, B.; Lee, Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, W.; Park, J. A Two-DOF Impact Actuator for Haptic Interaction. In Haptic Interaction: Perception, Devices and Algorithms; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.J. Efficient Magnetic Microactuator with an Enclosed Magnetic Core. J. Micro/Nanopatterning Mater. Metrol. 2002, 1. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/journals/Journal-of-MicroNanolithography-MEMS-and-MOEMS/volume-1/issue-2/0000/Efficient-magnetic-microactuator-with-an-enclosed-magnetic-core/10.1117/1.1484161.short?SSO=1 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Guo, W.; Hu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wu, H. On-Skin Stimulation Devices for Haptic Feedback and Human–Machine Interfaces. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Kim, S.; Cha, Y. Soft Electromagnetic Actuator for Assembly Robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 67001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Drack, M.; Karami-Mosammam, M.; Wirthl, D.; Stockinger, T.; Schwödiauer, R.; Kaltenbrunner, M. Soft Electromagnetic Actuators. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc0251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.N.; Phan, H.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Visell, Y. Miniature Soft Electromagnetic Actuators for Robotic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, S.; Ogura, S.; Shimazu, A.; Kawamura, A. Basic Study on 1D Array Actuator Using Solenoid Actuators for 2D Haptic Display Realization. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), Tokyo, Japan, 9–11 March 2018; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, T.-H. Miniature Impact Actuator for Haptic Interaction with Mobile Devices. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2014, 12, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, N.; Williams, K. Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Boston, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.C.; Nguyen, T.-C.H.; Judy, M.W.; Howe, R.T. Electrostatic-comb Drive of Lateral Polysilicon Resonators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1990, 21, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyssens, F.; Sadeghpour, S.; Fujita, H.; Puers, R. Actuators: Accomplishments, Opportunities and Challenges. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 295, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, H.; Kaiser, B.; Gaudet, M.; Langa, S.; Stolz, M.; Uhlig, S.; Schimmanz, K.; Schenk, H. A Novel Electrostatic Actuator Class. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshenety, A.; El-Kholy, E.E.; Abdou, A.F.; Soliman, M.; Elhagry, M.M. A Flexible Model for Studying Fringe Field Effect on Parallel Plate Actuators. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2020, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algamili, A.S.; Khir, M.H.M.; Dennis, J.O.; Ahmed, A.Y.; Alabsi, S.S.; Ba Hashwan, S.S.; Junaid, M.M. A Review of Actuation and Sensing Mechanisms in MEMS-Based Sensor Devices. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.-B.; Shin, E.-J.; Heo, Y.; Park, W.-H.; Yang, T.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Development of an Electrostatic Beat Module for Various Tactile Sensations in Touch Screen Devices. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-g.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, K.-B.; Kim, J. A Film-type Haptic Actuator for Mobile Devices. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8344, 83440V. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.-y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Jang, S.-D.; Kim, D.-G.; Kim, J. Haptic Device Development Based on Electro Static Force of Cellulose Electro Active Paper. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2011; p. 797617. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Yun, G.-Y.; Kim, K.-B.; Kang, B.-W.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Film-type Haptic Actuator Made with Cellulose Acetate Layers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 25, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, B.; Friend, J.; Yeo, L. Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Micro/Milli-scale Actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 152, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Devices. In Ferroelectric Devices & Piezoelectric Actuators - Research Misconceptions and Rectifications; DEStech Publications: Lancaster, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Ferroelectric Devices, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Miniaturized Piezo Actuators With Haptic Feedback. ECN. 2017. Available online: https://remotexs.ntu.edu.sg/user/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/trade-journals/miniaturized-piezo-actuators-with-haptic-feedback/docview/2006921579/se-2 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Actuators 2006. J. Electroceram. 2008, 20, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupyrev, I.; Rekimoto, J.; Maruyama, S. TouchEngine: A Tactile Display for Handheld Devices. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 20–25 April 2002; pp. 644–645. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Roosen, A.; Oostra, H.; Hoppener, R.; De, M.M. Novel Low Voltage Piezoactuators for High Displacements. J. Electroceram. 2005, 14, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-S.; Yang, T.-H.; Cho, J. Trend & Prospects of Haptic Technology in Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 3778–3783. [Google Scholar]
- Damjanovic, D.; Newnham, R.E. Electrostrictive and Piezoelectric Materials for Actuator Applications. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1992, 3, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Du, H.; Ling, S.-F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y. Motion control of an Electrostrictive Actuator. Mechatronics (Oxford) 2004, 14, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngernchuklin, P. PMN-PT Piezoelectric-Electrostrictive Bi-Layer Composite Actuators; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, A.; Allahverdi, M.; Akdogan, E.K.; Safari, A. Piezoelectric/Electrostrictive Multimaterial PMN-PT Monomorph Actuators. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. Glory of Piezoelectric Perovskites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 046001–046016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. Electroactive Polymers as Actuators. In Advanced Piezoelectric Materials—Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 319–352. [Google Scholar]
- Guyomar, D.; Cottinet, P.-J.; Lebrun, L.; Sebald, G. Characterization of an Electroactive Polymer Simultaneously Driven by an Electrical Field and a Mechanical Excitation: An Easy Means of Measuring the Dielectric Constant, the Young Modulus and the Electrostrictive Coefficients. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 375, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganet, F.; Le, M.Q.; Capsal, J.F.; Gérard, J.F.; Pruvost, S.; Duchet, J.; Livi, S.; Lermusiaux, P.; Millon, A.; Cottinet, P.J. Haptic Feedback Using an All-organic Electroactive Polymer Composite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capsal, J.-F.; Lallart, M.; Galineau, J.; Cottinet, P.-J.; Sebald, G.; Guyomar, D. Evaluation of Macroscopic Polarization and Actuation Abilities of Electrostrictive Dipolar Polymers Using the Microscopic Debye/Langevin Formalism. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 205401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capsal, J.-F.; Galineau, J.; Lallart, M.; Cottinet, P.-J.; Guyomar, D. Plasticized Relaxor Fferroelectric Terpolymer: Toward Giant Electrostriction, High Mechanical Energy and Low Electric Field Actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 207, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thetpraphi, K.; Le, M.Q.; Houachtia, A.; Cottinet, P.J.; Petit, L.; Audigier, D.; Kuhn, J.; Moretto, G.; Capsal, J.F. Surface Correction Control Based on Plasticized Multilayer P(VDF-TrFE-CFE) Actuator—Live Mirror. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1900210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozioko, O.; Navaraj, W.; Hersh, M.; Dahiya, R. Tacsac: A Wearable Haptic Device with Capacitive Touch-Sensing Capability for Tactile Display. Sensors 2020, 20, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, H.; Schenk, H.; Kaiser, B.; Langa, S.; Gaudet, M.; Schimmanz, K.; Stolz, M.; Lenz, M. A Small-gap Electrostatic Micro-Actuator for Large Deflections. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yao, K. Crystallization Mechanism and Piezoelectric Properties of Solution-derived Ferroelectric Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Thin Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, C.-S.; Yun, S.-R. Cellulose Based Electro-active Papers: Performance and Environmental Effects. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haptic Energy Consumption. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/an/sloa194a/sloa194a.pdf?ts=1675427849728&ref_url=https%253A%252F%252Fwww.google.com%252F (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Boréas Technologies’ Ultra-Low-Power Haptic Chip Solves Power Problem with HD Touch. NASDAQ OMX’s News Release Distribution Channel. 2018. Available online: https://remotexs.ntu.edu.sg/user/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/wire-feeds/boréas-technologies-ultra-low-power-haptic-chip/docview/2117114145/se-2 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Heo, Y.H.; Choi, D.-S.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, S.-Y. Flexible Vibrotactile Actuator Based on Dielectric Elastomer for Smart Handheld Devices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trase, I.; Tan, H.Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.X.J. Wearable Haptic Array of Flexible Electrostatic Transducers. In Proceedings of the Human Interface and the Management of Information. Information Presentation and Visualization: Thematic Area, HIMI 2021, Held as Part of the 23rd HCI International Conference, HCII 2021, Virtual Event, 24–29 July 2021; pp. 369–385. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Li, C.; Tong, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhong, W. Design of a Low-Frequency Harmonic Rotary Piezoelectric Actuator. Actuators 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhong, J.; Jiang, T.; Li, Z.; Yao, M.; Shao, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Liang, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; et al. A Low Voltage-Powered Soft Electromechanical Stimulation Patch for Haptics Feedback in Human-machine Interfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Hinchet, R.; Shea, H. Multimode Hydraulically Amplified Electrostatic Actuators for Wearable Haptics. Adv. Mater. (Weinheim) 2020, 32, 2002564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yao, K.; Tang, X.; He, X.; Shannigrahi, S.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Okada, K. A Piezoelectric Micro-actuator with a Three-dimensional Structure and its Micro-fabrication. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 130, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.-Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Fabrication and Testing of Cellulose EAPap Actuators for Haptic Application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 164, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.C.; Werner, J.M.; Weissbach, T.; Strutwolf, J.; Eland, R.; Drossel, W.-G.; Hübler, A.C. Printed Multilayer Piezoelectric Transducers on Paper for Haptic Feedback and Dual Touch-Sound Sensation. Sensors 2022, 22, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosobata, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Higuchi, T. Transparent Synchronous Electrostatic Actuator for Long-Stroke Planar Motion. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron 2015, 20, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wallace, M.; Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Jackson, T.N. Piezoelectric Thin Films on Polyimide Substrates for Flexible Piezoelectric Devices. In Proceedings of the 2017 75th Annual Device Research Conference (DRC), South Bend, IN, USA, 25–28 June 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, I.-T.; Lee, T.-G.; Kim, D.-H.; Hur, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Nahm, S.; Ryu, J.; Choi, B.-Y. Multilayer Piezoelectric Haptic Actuator with CuO-modified PZT-PZNN Ceramics. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2016, 238, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Perovskite Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 190901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish State Gazette: S.I. No. 23 of 2020. European Union (Restriction of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment) (Amendment) Regulations 2020. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A614274864/ITOF?u=nantecun&sid=bookmark-ITOF&xid=90358b5f (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Council of the European Union:Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council amending Directive 2011/65/EU on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment ST 5708 2017 INIT. European Union News, 28 December 2017.
- Uchino, K. Lead Zirconate Titanate-Based Piezoceramics. In Advanced Piezoelectric Materials—Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Schlögl, M.; Schneider, M.; Schmid, U. Piezoelectricity in Y0.09Al0.91N Thin Films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2022, 276, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, B.; Casset, F.; Millet, A.; Agache, V.; Verplanck, N.; Boizot, F.; Fanget, S. Development of a MEMS Plate Based on Thin-Film Piezoelectric AlN Actuators for Biological Applications. Proceedings 2017, 1, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, C. Ultrathin Flexible Linear-piezoelectric ZnO Thin Film Actuators: Tuning the Piezoelectric Responses by In-plane Epitaxial Strain. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 599, 153969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Composition Dependence of Microstructures and Ferroelectric Properties in Poly(vinylidene fluoride-ter-trifluoroethylene-ter-chlorodifluoroethylene) Terpolymers. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, Z. Models for 31-Mode PVDF Energy Harvester for Wearable Applications. Sci. World 2014, 2014, 893496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Cohen, Y.; Zhang, Q. Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Sensors. MRS Bull. 2008, 33, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccabi, N.; Grinberg, I.; Kassie, A.; Shmulevich, S.; Elata, D. Bulk PZT Actuator for Parallel out-of-plane motion: The Superiority of Torsion Deformation over Bending Deformation. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Gonnard, P. Industrial Design of a Centimetric “TWILA” Ultrasonic Motor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 120, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciubotariu, D.A.; Ivan, I.A.; Clevy, C.; Lutz, P. Size-dependent Analysis and Experiments of Bulk PMN-PT [001] Piezoelectric Actuator for MOEMS Micro-mirrors. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Besacon, France, 8–11 July 2014; pp. 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Benouhiba, A.; Belharet, D.; Bienaimé, A.; Chalvet, V.; Rakotondrabe, M.; Clévy, C. Development and Characterization of Thinned PZT bulk Technology Based Actuators Devoted to a 6-DOF Micropositioning Platform. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 197, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zhu, W.; Uchino, E.; Zhang, Z.; Lim, L.C. Design and Fabrication of a High Performance Multilayer Piezoelectric Actuator with Bending Deformation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1999, 46, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.-J.; Jeong, S.-J.; Seo, C.-E.; Cho, K.-H.; Koh, J.-H. Multi-layered Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters Based on PZT Ceramic Actuators. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, S686–S690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Kelnberger, A.; Yang, G.Y.; Eitel, R.E.; Shrout, T.R. High Strain Piezoelectric Multilayer Actuators - A Material Science and Engineering Challenge. J. Electroceram. 2005, 14, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TDK Extends Portfolio of Mini PowerHap Haptic Feedback Actuators. ECN. 2019. Available online: https://remotexs.ntu.edu.sg/user/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/trade-journals/tdk-extends-portfolio-mini-powerhap-haptic/docview/2259525014/se-2 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Yoo, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Jeong, Y.-H. Displacement Distribution Properties of Force Feedback Multilayer Piezoelectric Actuator. Ferroelectrics 2020, 554, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Im, J.; Yu, I. Physical Properties of Pb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3-Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 Ceramics Doped with Tungsten Oxide for Haptic Display Actuator. Ferroelectrics Lett. Section 2021, 48, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.; Nam, H.; Lee, H.; Ahn, Y.; Roh, J. An 80-V Integrated Boost Converter for Piezoelectric Actuators in Smartphones. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2013, 75, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piezo Haptic Driver Features Integrated Boost Converter. Product News Network. 2011. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A262559849/ITOF?u=nantecun&sid=bookmark-ITOF&xid=c5f3588b (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- TI Introduces Industry’s Most Highly Integrated Piezo Haptic Driver. 2011, p. 179. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A263531433/STND?u=nantecun&sid=bookmark-STND&xid=87221a4b (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Yuan, H.; Li, L.; Hong, H.; Ying, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wen, F.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, G. Low Sintering Temperature, Large Strain and Reduced Strain Hysteresis of BiFeO3–BaTiO3 Ceramics for Piezoelectric Multilayer Actuator Applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 31349–31356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Seo, I.-T.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Ryu, J.; Han, S.H.; Jang, B.-y.; Nahm, S. Large Strain in CuO-added (Na0.2K0.8)NbO3 Ceramic for Use in Piezoelectric Multilayer Actuators. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-B.; Tolliver, L.; Jiang, X.; Su, J. A Single Crystal Lead Magnesium Niobate-lead Titanate Multilayer-Stacked Cryogenic Flextensional Actuator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 42906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Park, S.; Huh, J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Choi, J.-J.; Min, Y.; Yoon, W.-H. Design, Fabrication, and Characterization of Piezoelectric Single Crystal Stack Actuators Based on PMN-PT. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 342, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.S.; Phan, H.V.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.C. Blocking Force of a Piezoelectric Stack Actuator Made of Single Crystal Layers (PMN-29PT). Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 95038–95045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Lim, K.J. Haptic Actuator Design Using PMN-PT Ceramic. Ferroelectrics 2014, 469, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-B. Review on PMN-PT Relaxor Piezoelectric Single Crystal Materials for Cryogenic Actuators. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum, San Diego, CA USA & Virtual, 3–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Oh, S.R.; Wong, T.C.; Tan, C.Y.; Yao, K. Piezoelectric polymer multilayer on flexible substrate for energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, W.H.; Ke, Q.; Tan, C.Y.; Chen, S.; Yao, K. Ultrasonic Transducer From Piezoelectric Polymer Multilayer Through Electrophoretic Deposition for Photoacoustic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Kweon, S.-H.; Hida, H.; Mukouyama, Y.; Kanno, I. Transparent Piezoelectric Thin-Film Devices: Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 Thin Films on Glass Substrates. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 327, 112786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Muralt, P. Thin Film Piezoelectrics for MEMS. J. Electroceramics 2004, 12, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Yang, J.I.; Stitt, J.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. Quantitative and High Spatial Resolution d33 Measurement of Piezoelectric Bulk and Thin Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 174104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienaimé, A.; Chalvet, V.; Clévy, C.; Gauthier-Manuel, L.; Baron, T.; Rakotondrabe, M. Static/Dynamic Trade-off Performance of PZT Thick film Micro-Actuators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 75017–75018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casset, F.; Danel, J.S.; Chappaz, C.; Civet, Y.; Amberg, M.; Gorisse, M.; Dieppedale, C.; Le Rhun, G.; Basrour, S.; Renaux, P.; et al. Low Voltage Actuated Plate for Haptic Applications with PZT Thin-film. In Proceedings of the 2013 Transducers & Eurosensors XXVII: The 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXVII), Barcelona, Spain, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 2733–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casset, F.; Danel, J.; Renaux, P.; Chappaz, C.; Le Rhun, G.; Dieppedale, C.; Gorisse, M.; Basrour, S.; Fanget, S.; Ancey, P.; et al. Characterization and Post Simulation of Thin-film PZT Actuated Plates for Haptic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 15th International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Mulit-Physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems (EuroSimE), Ghent, Belgium, 7–9 April 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Lai, Z.Q.; Hu, Z.G. Low-temperature Preparation and Characterization of the PZT ferroelectric Thin Films Sputtered on FTO Glass Substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, G.; Dieppedale, C.; Wagué, B.; Querne, C.; Enyedi, G.; Perreau, P.; Montméat, P.; Licitra, C.; Fanget, S. Transparent PZT MIM Capacitors on Glass for Piezoelectric Transducer Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXXIII), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1800–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, P.C.; Yao, K.; Chen, Z. Lead-free Piezoelectric (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 Thin Films Derived from Chemical Solution Modified with Stabilizing Agents. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, K.; Qin, X.; Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Liu, X.; Tay, F.E.H. High Piezoelectric Performance and Phase Transition in Stressed Lead-Free (1-x)(K, Na)(Sb, Nb)O3-x(Bi, Na, K)ZrO3 Thin Films. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1700033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin Goh, P.; Yao, K.; Chen, Z. Lithium Diffusion in (Li, K, Na)NbO3 Piezoeletric Thin Films and the Resulting Approach for Enhanced Performance Properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 092902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Niu, G.; Ren, W.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, K.; Quan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Cai, H.; et al. Giant Strain Responses and Relaxor Characteristics in Lead-free (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-BaZrO3 Ferroelectric Thin Films. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. Opt. Electron. Devices 2022, 10, 7449–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Qin, X.; Yao, K.; Pennycook, S.J.; Tay, F.E.H. Outstanding Piezoelectric Performance in Lead-Free 0.95(K,Na)(Sb,Nb)O3-0.05(Bi,Na,K)ZrO3 Thick Films with Oriented Nanophase Coexistence. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-B.; Siochi, E.J.; Kang, J.H.; Zuo, L.; Zhou, W.; Tang, X.; Jiang, X. Energy Harvesting Using a PZT Ceramic Multilayer Stack. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Seo, I.-T.; Nahm, S. Enhanced Energy Harvesting Using Multilayer Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 6964–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, D.; Bramlage, B.; Gebhardt, S.E.; Schönecker, A.J. High Performance PZT Thick Film Actuators Using in Plane Polarisation. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2015, 114, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalvet, V.; Habineza, D.; Rakotondrabe, M.; Clévy, C. Presentation and Characterization of Novel Thick-film PZT Microactuators. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2016, 486, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zhu, W. Improved Preparation Procedure and Properties for a Multilayer Piezoelectric Thick-Film Actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 71, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; He, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M. Screen-printed Piezoelectric Ceramic Thick Films with Sintering Additives Introduced through a Liquid-Phase Approach. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 118, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tan, C.K.I.; Tan, S.Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, K. Potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramic coatings on steel structure by thermal spray method. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 5524–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinsek, S.; Song, L.; Kovacova, V.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Godard, N.; Girod, S.; Biagi, J.L.; Quintana, R.; Schleeh, T.; Guedra, M.; et al. Inkjet-Printed Piezoelectric Thin Films for Transparent Haptics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2200147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Glinsek, S.; Drnovsek, S.; Kovacova, V.; Malic, B.; Defay, E. Piezoelectric Thick Film for Power-efficient Haptic Actuator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2022, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tan, C.K.I.; Yao, K. Potassium-Sodium Niobate-Based Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramic Coatings by Thermal Spray Process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Chen, S.; Guo, K.; Tan, C.K.I.; Mirshekarloo, M.S.; Tay, F.E.H. Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramic Coatings Fabricated by Thermal Spray Process. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2017, 64, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).