Position Tracking for Multi-Channel Double-Crystal Monochromator Scanning Based on Iterative Learning Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
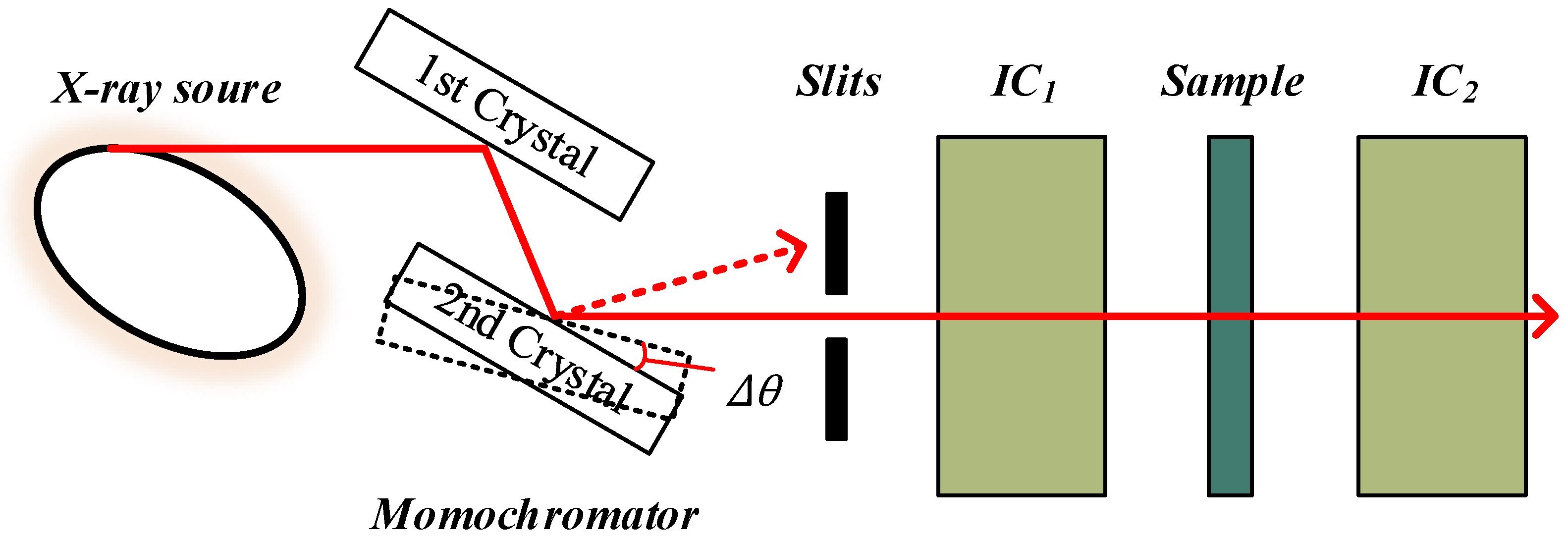
2. System Description
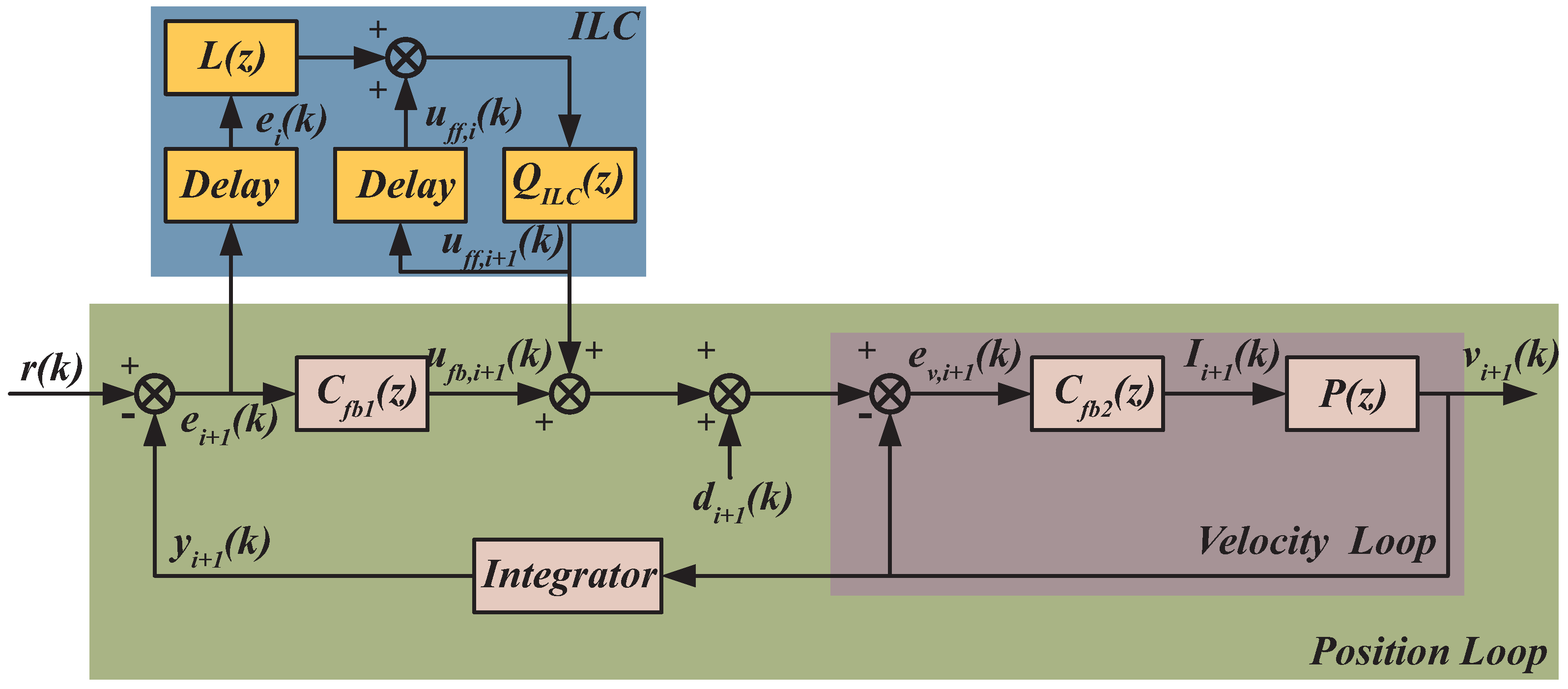
3. Controller Design
3.1. Iterative Learning Control
3.2. Learning Function
4. Experiment Results and Analysis
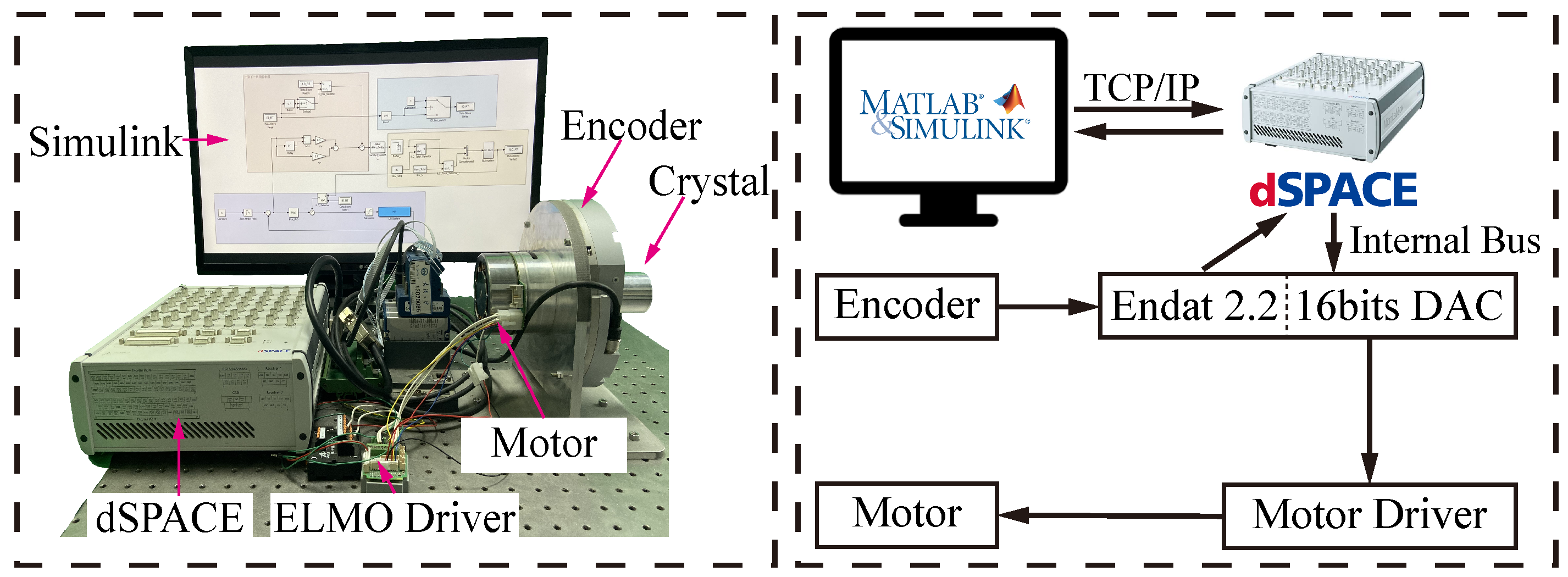
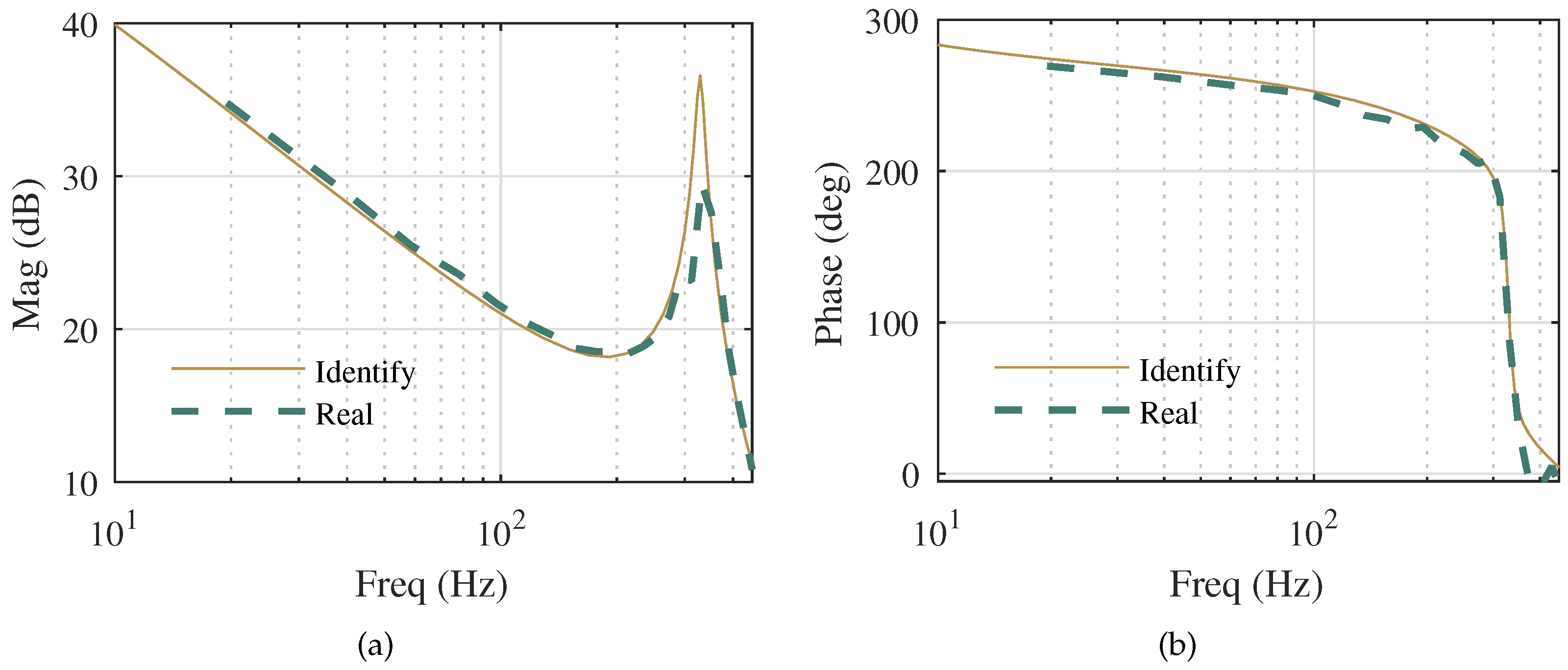
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Tracking Results
- (1)
- : feedback controller PID;
- (2)
- : model-based feedforward controller ZMETC;
- (3)
- : ILC which is illustrated in Figure 3.
4.2.1. Tracking Triangular Wave
4.2.2. Tracking Fourth-Order Motion Reference Trajectory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunz, C. Synchrotron radiation: Third generation sources. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2001, 13, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabashi, M.; Tanaka, H. The next ten years of X-ray science. Nat. Photon. 2017, 11, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerra, T.A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.C.; Nogales, A.; Müller, A.J. Introduction to the special issue on “Applications of synchrotron radiation in polymers science”. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frahm, R.; Richwin, M.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D. Recent advances and new applications of time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Scr. 2005, 2005, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O. Hard X-ray Synchrotron Beamline Instrumentation for Millisecond Quick Extended X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Mathematik und Naturwissenschaften, Universität Wuppertal, Wuppertal, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, H.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Tsuboki, I.; Ikeya, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Miura, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Senba, Y.; et al. Challenges toward 50 nrad-stability of X-rays for a next generation light source by refinements of SPring-8 standard monochromator with cryo-cooled Si crystals. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2054, 60018. [Google Scholar]
- Richwin, M.; Zaeper, R.; Lützenkirchen-Hecht, D.; Frahm, R. Piezo-XAFS-time-resolved x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2002, 73, 1668–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergueev, I.; Döhrmann, R.; Horbach, J.; Heuer, J. Angular vibrations of cryogenically cooled double-crystal monochromators. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2016, 23, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, A.I.; Sergeev, I.; Celse, J.P.; Rüffer, R.; Lesourd, M.; Zhang, L.; Sánchez del Río, M. Performance of a silicon monochromator under high heat load. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2014, 21, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeren, F.; Bruijnen, D.; van Dijk, N.; Oomen, T. Joint input shaping and feedforward for point-to-point motion: Automated tuning for an industrial nanopositioning system. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Feng, Z.; Zheng, D.; Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Xiao, X. Robust adaptive motion tracking of piezoelectric actuated stages using online neural-network-based sliding mode control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 150, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, M.; Liang, W.; Feng, Z.; Ling, J.; Al Mamun, A.; Xiao, X. PID-type sliding mode-based adaptive motion control of a 2-DOF piezoelectric ultrasonic motor driven stage. Mechatronics 2021, 76, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Hu, J.; Yao, J. Adaptive neural network output feedback robust control of electromechanical servo system with backlash compensation and disturbance rejection. Mechatronics 2022, 84, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loof, J.; Besselink, I.; Nijmeijer, H. Automated lane changing with a controlled steering-wheel feedback torque for low lateral acceleration purposes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2019, 4, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liang, W.; Ling, J.; Xiao, X.; Tan, K.K.; Lee, T.H. Integral terminal sliding-mode-based adaptive integral backstepping control for precision motion of a piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarem, S.; Delibas, B.; Koc, B. Data-driven tuning of PID controlled piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. Actuators 2021, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; De Silva, C.; Lee, T.H. Global iterative sliding mode control of an industrial biaxial gantry system for contouring motion tasks. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2021, 27, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.M. Dual-Notch Based Repetitive Control for Tracking Lissajous Scan Trajectories with Piezo-Actuated Nano-Scanners. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Fowler, A.G.; Yong, Y.K.; Moheimani, S.R. A feedback controlled MEMS nanopositioner for on-chip high-speed AFM. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 23, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. A two-DOF ultrasonic motor using a longitudinal–bending hybrid sandwich transducer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 3041–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, S. A cylindrical traveling wave ultrasonic motor using longitudinal and bending composite transducer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 161, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, J.A.; Pao, L.Y.; Abramovitch, D.Y. Analysis and comparison of three discrete-time feedforward model-inverse control techniques for nonminimum-phase systems. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizuka, M. Zero phase error tracking algorithm for digital control. J. Dyn. Sys. Meas. Control 1987, 109, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Fatikow, S. A novel direct inverse modeling approach for hysteresis compensation of piezoelectric actuator in feedforward applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 18, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fleming, A.J.; Yong, Y.K.; Aphale, S.S.; Zhu, L. High performance raster scanning of atomic force microscopy using Model-free Repetitive Control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 173, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jin, Z. Trajectory Tracking Control for Reaction–Diffusion System with Time Delay Using P-Type Iterative Learning Method. Actuators 2021, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yu, P.; Chen, X.; She, J. Design of repetitive-control system with input dead zone based on generalized extended-state observer. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2017, 139, 071008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaei, A.; Yong, Y.K.; Moheimani, S.R.; Sebastian, A. Tracking of triangular references using signal transformation for control of a novel AFM scanner stage. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 20, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, Y.; Shen, D.; Li, L.; Tan, J. Learning Control for Motion Coordination in Wafer Scanners: Towards Gain Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Zou, Q. A modeling-free inversion-based iterative feedforward control for precision output tracking of linear time-invariant systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 18, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolder, J.; Kleinendorst, S.; Oomen, T. Data-driven multivariable ILC: Enhanced performance by eliminating L and Q filters. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 3728–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, D.A.; Tharayil, M.; Alleyne, A.G. A survey of iterative learning control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 96–114. [Google Scholar]
- van Zundert, J.; Oomen, T. On inversion-based approaches for feedforward and ILC. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Shao, Q.; Qi, J.; Peng, Y. Smooth and time-optimal S-curve trajectory planning for automated robots and machines. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 137, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



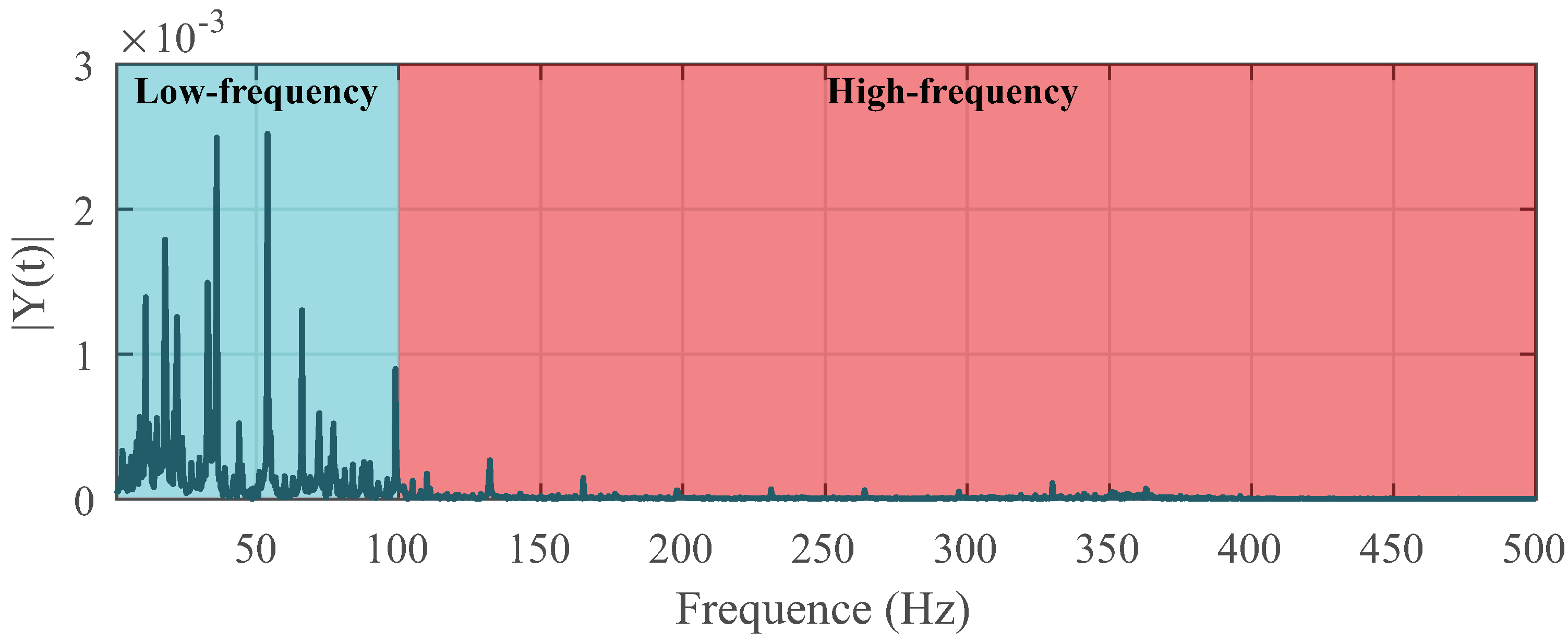
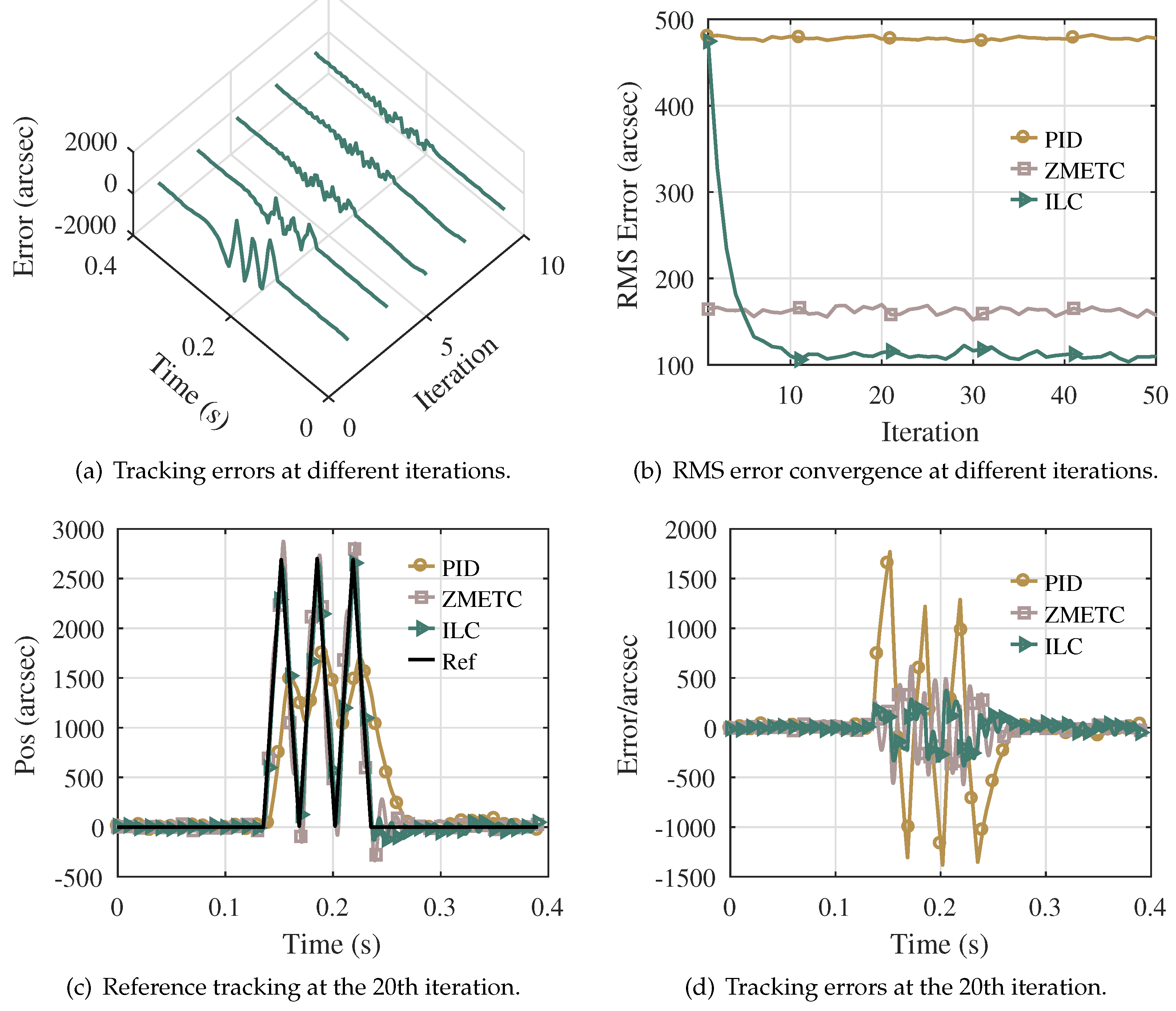
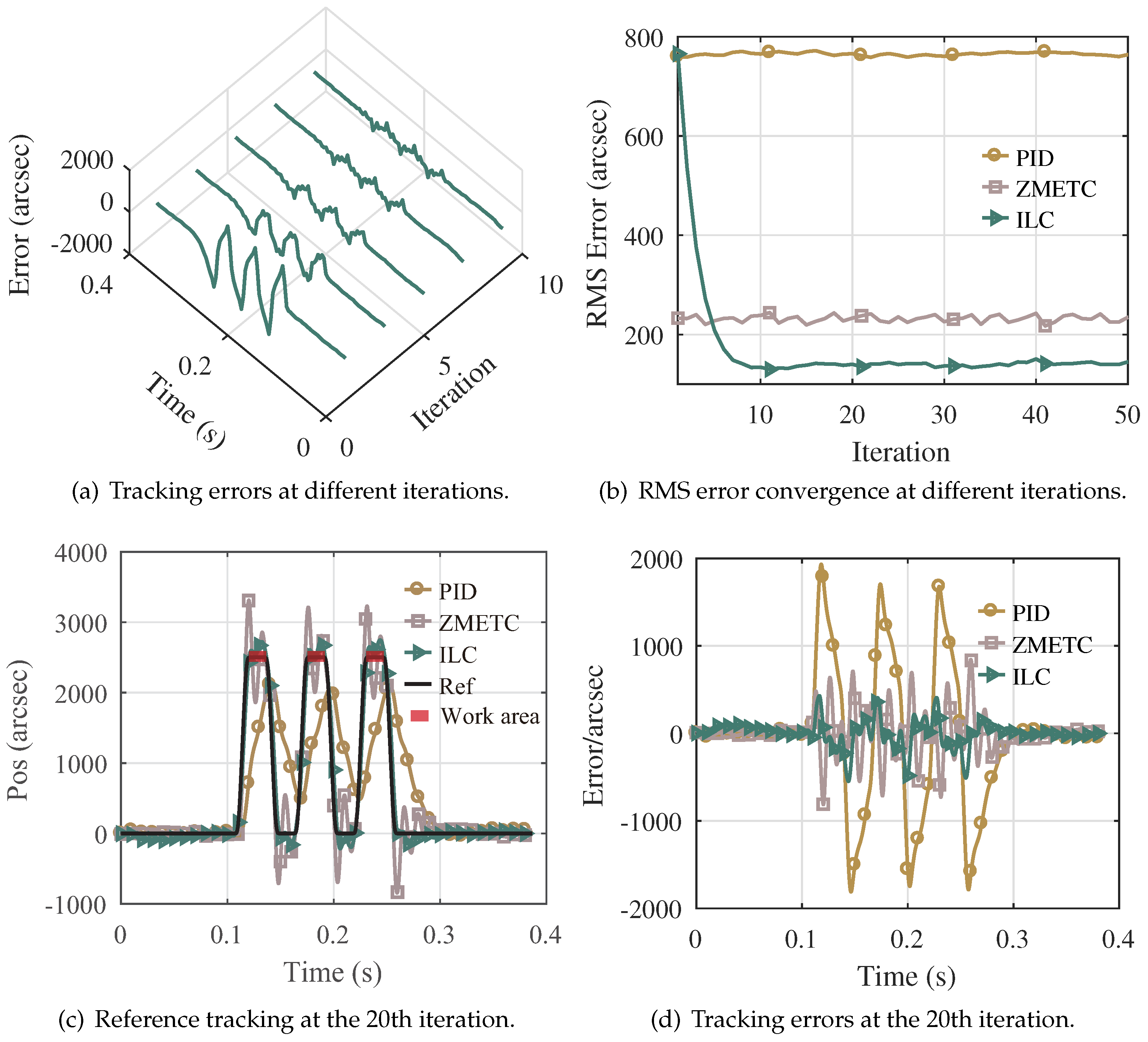
| Frequency (Hz) | RMS Error (arcsec) | MAX Error (arcsec) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID | ZMETC | ILC | PID | ZMETC | ILC | |
| 10 | 593.28 | 57.60 | 52.56 | 779.4 | 188.64 | 116.28 |
| 20 | 545.27 | 91.33 | 80.02 | 1366.6 | 293.57 | 185.17 |
| 30 | 474.42 | 151.93 | 103.27 | 1736.4 | 560.97 | 306.14 |
| Frequency (Hz) | RMS Error (arcsec) | MAX Error (arcsec) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID | ZMETC | ILC | PID | ZMETC | ILC | |
| 18 | 819.25 | 68.26 | 76.83 | 1581.1 | 137.38 | 142.56 |
| 24 | 842.11 | 102.29 | 89.48 | 1761.4 | 237.37 | 203.77 |
| 36 | 758.09 | 220.98 | 127.89 | 1925.0 | 716.16 | 406.96 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, S.; Lu, H.; Feng, Z.; Xiao, X. Position Tracking for Multi-Channel Double-Crystal Monochromator Scanning Based on Iterative Learning Control. Actuators 2022, 11, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11070177
He S, Lu H, Feng Z, Xiao X. Position Tracking for Multi-Channel Double-Crystal Monochromator Scanning Based on Iterative Learning Control. Actuators. 2022; 11(7):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11070177
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Siyu, Haolin Lu, Zhao Feng, and Xiaohui Xiao. 2022. "Position Tracking for Multi-Channel Double-Crystal Monochromator Scanning Based on Iterative Learning Control" Actuators 11, no. 7: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11070177
APA StyleHe, S., Lu, H., Feng, Z., & Xiao, X. (2022). Position Tracking for Multi-Channel Double-Crystal Monochromator Scanning Based on Iterative Learning Control. Actuators, 11(7), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11070177






