Modeling and Control of Hysteresis Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform Based on Duhem Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
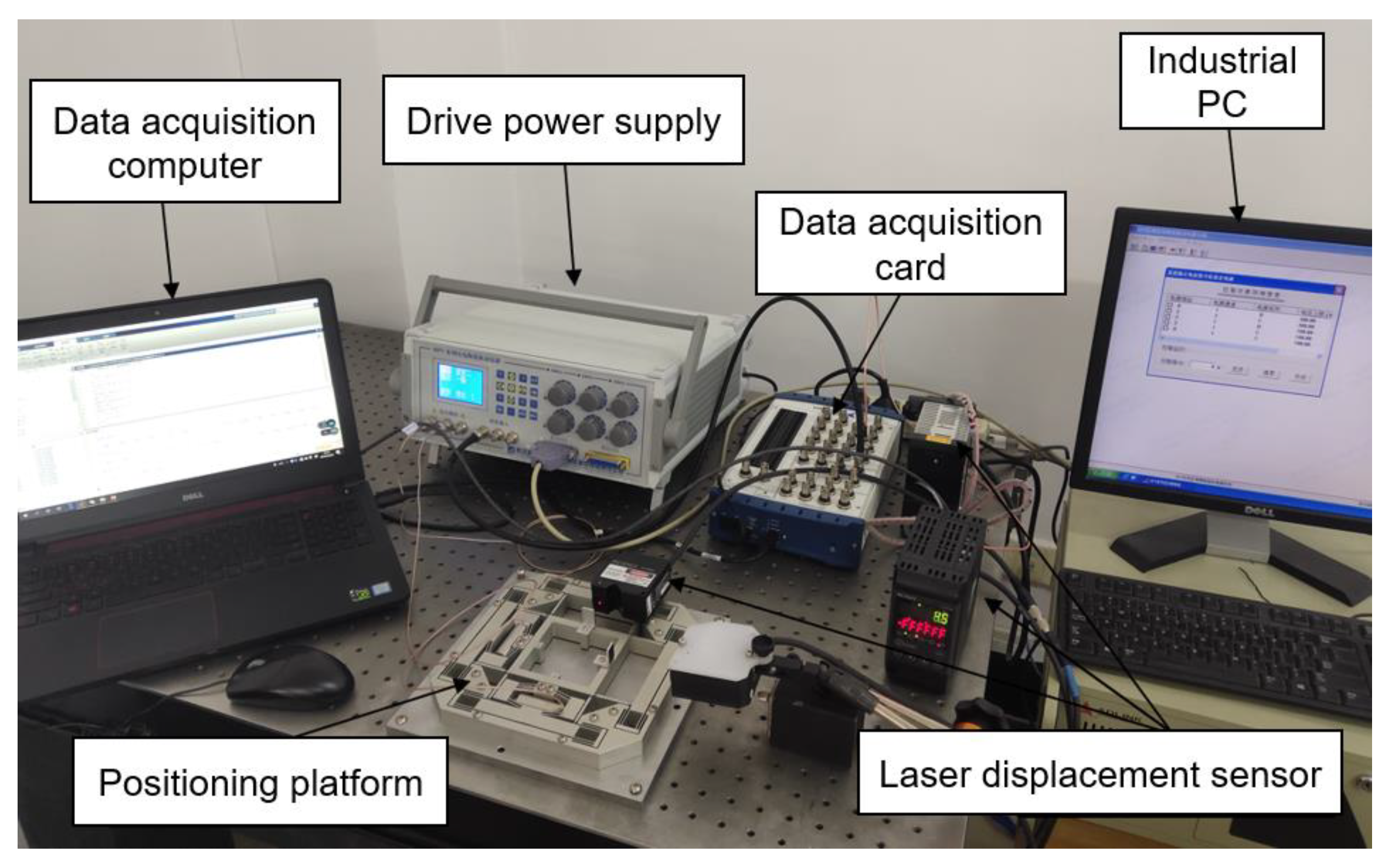
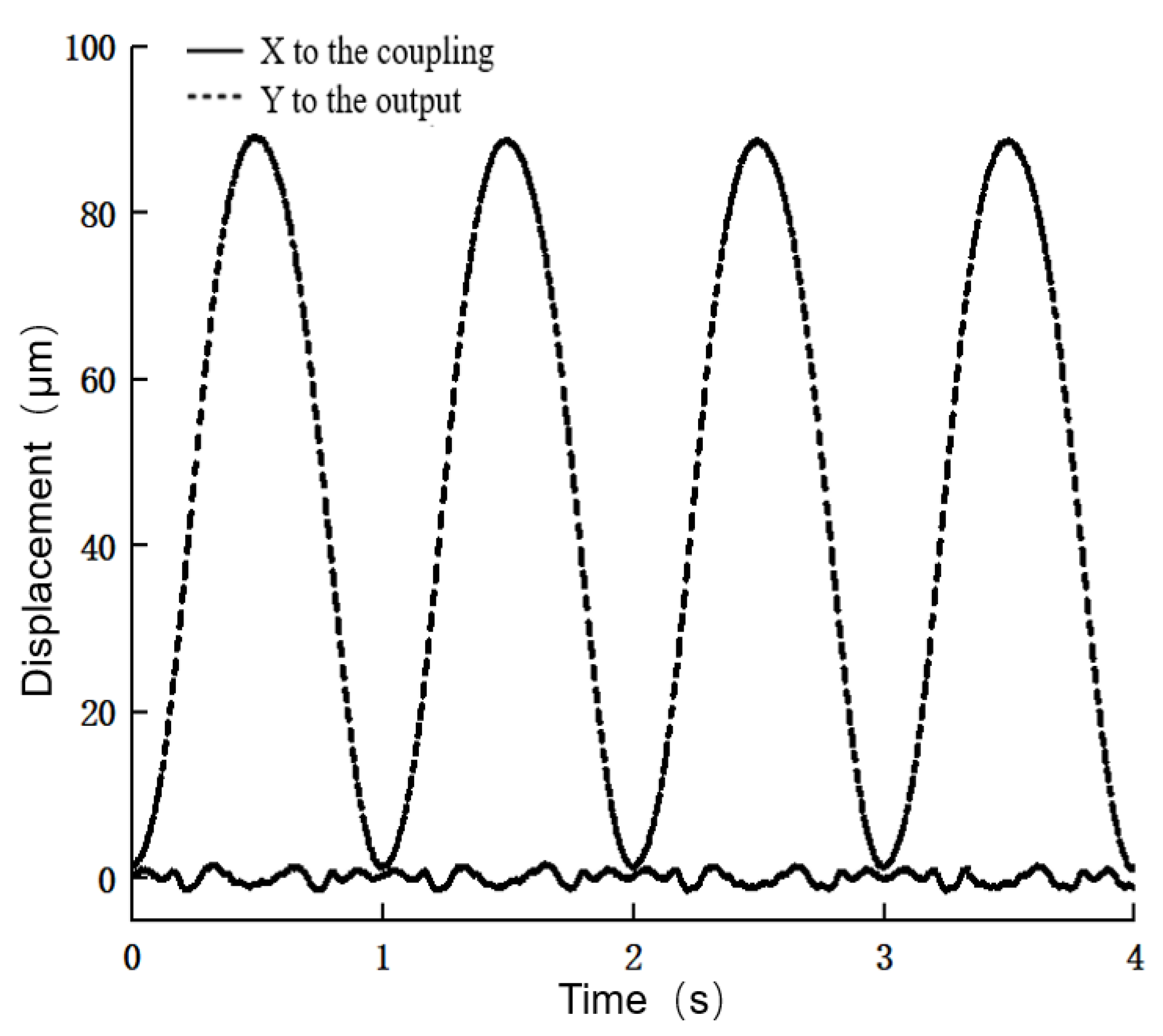
2. Research on the Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform
3. Hysteresis Modeling and Parameter Identification
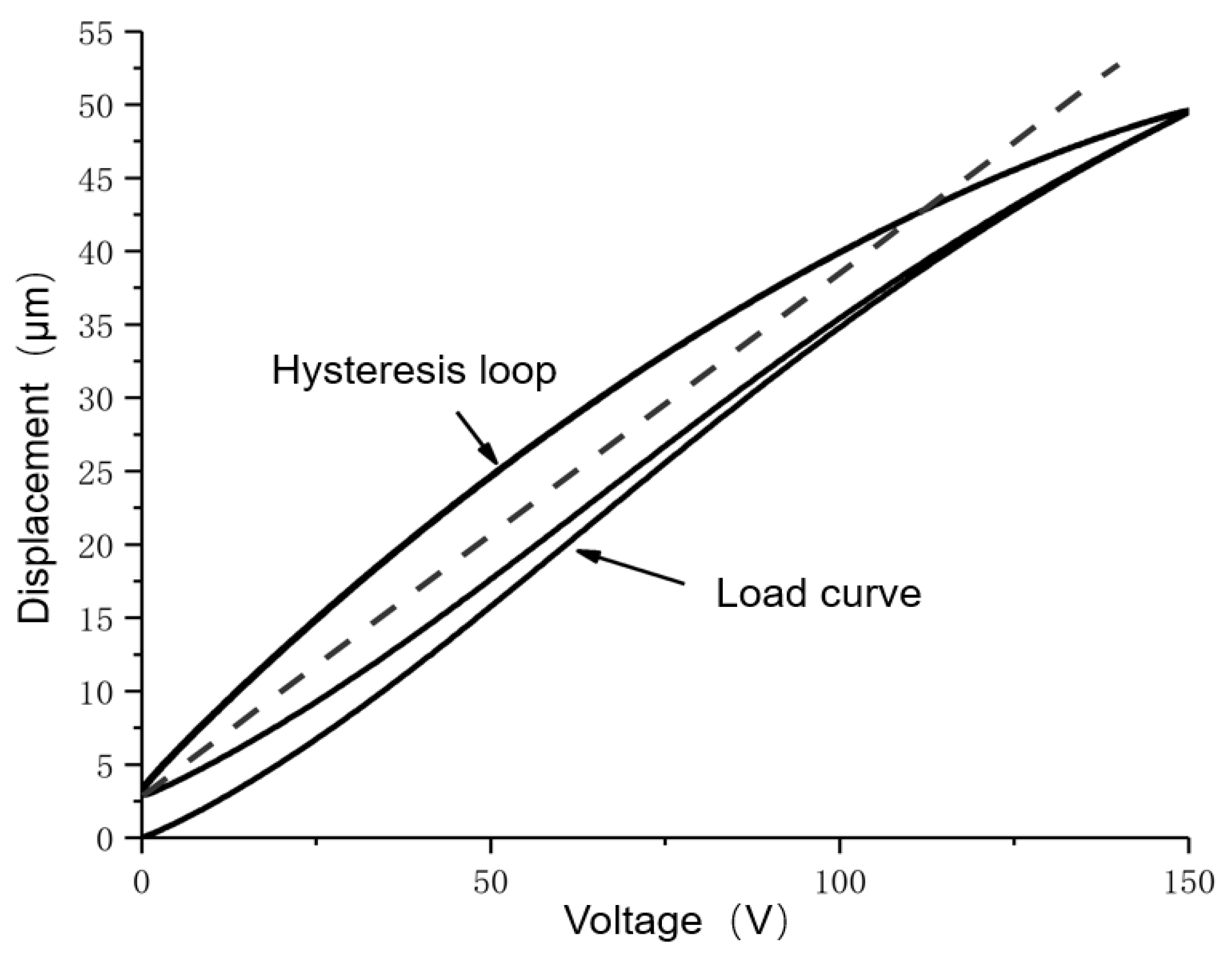
3.1. Duhem Model
3.2. Segment Identification Model Parameters
- Initialize the algorithm parameters.
- The bulletin board is assigned an initial value. Calculate the fitness value of the current position of each artificial fish, record the state of the artificial fish in the optimal position and its fitness value to the bulletin board, and judge whether the termination condition is satisfied. If satisfied, go to step 5, if not, go to step 3.
- Update the artificial fish position.
- Bulletin board information update: Calculate the fitness value of each artificial fish in the new state, compare it with the bulletin board information, and update the bulletin board information if it is better than the bulletin board. It is judged whether the termination condition is met; if so, go to step 5, if not, go to step 3.
- The algorithm terminates.
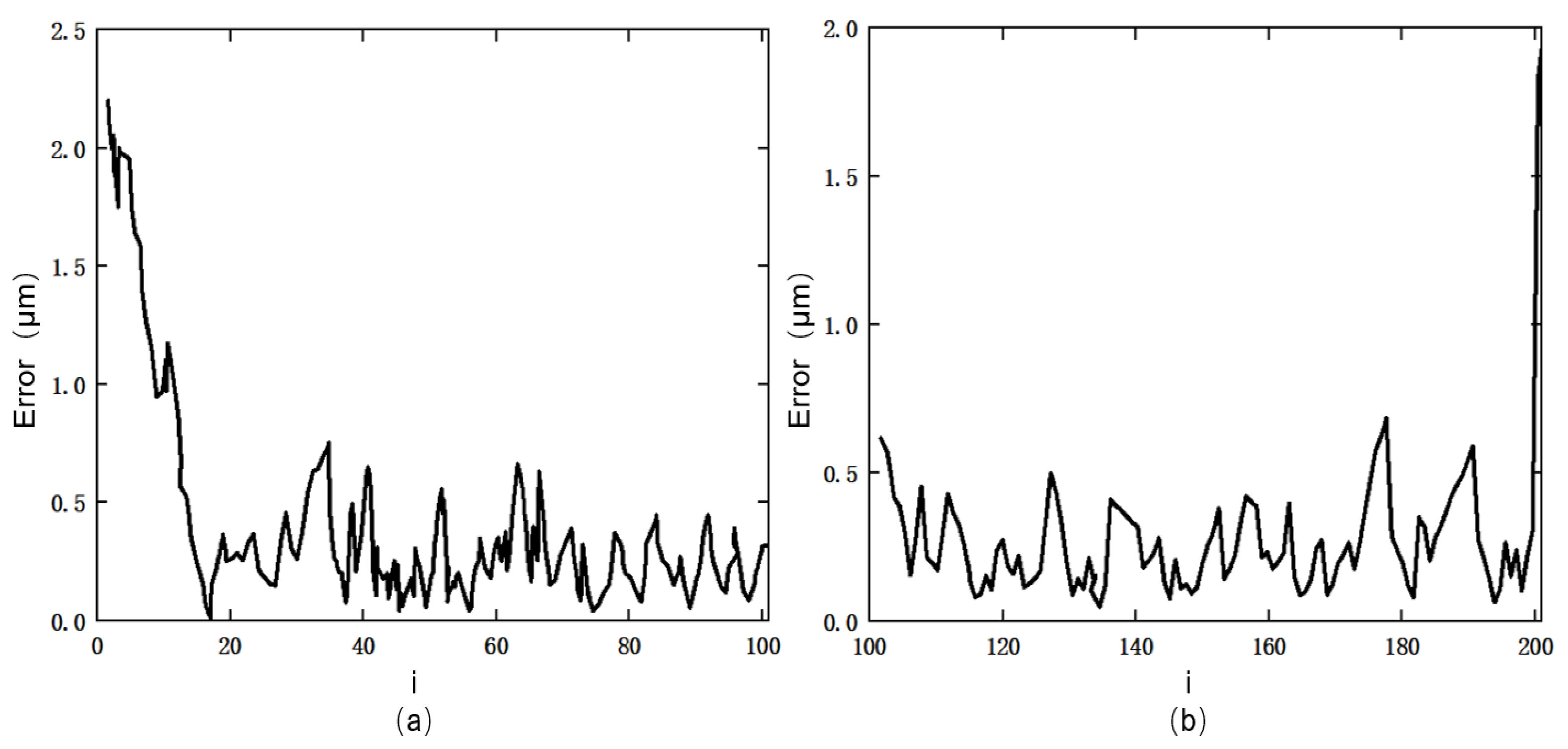
3.3. Parameter Identification Results and Analysis
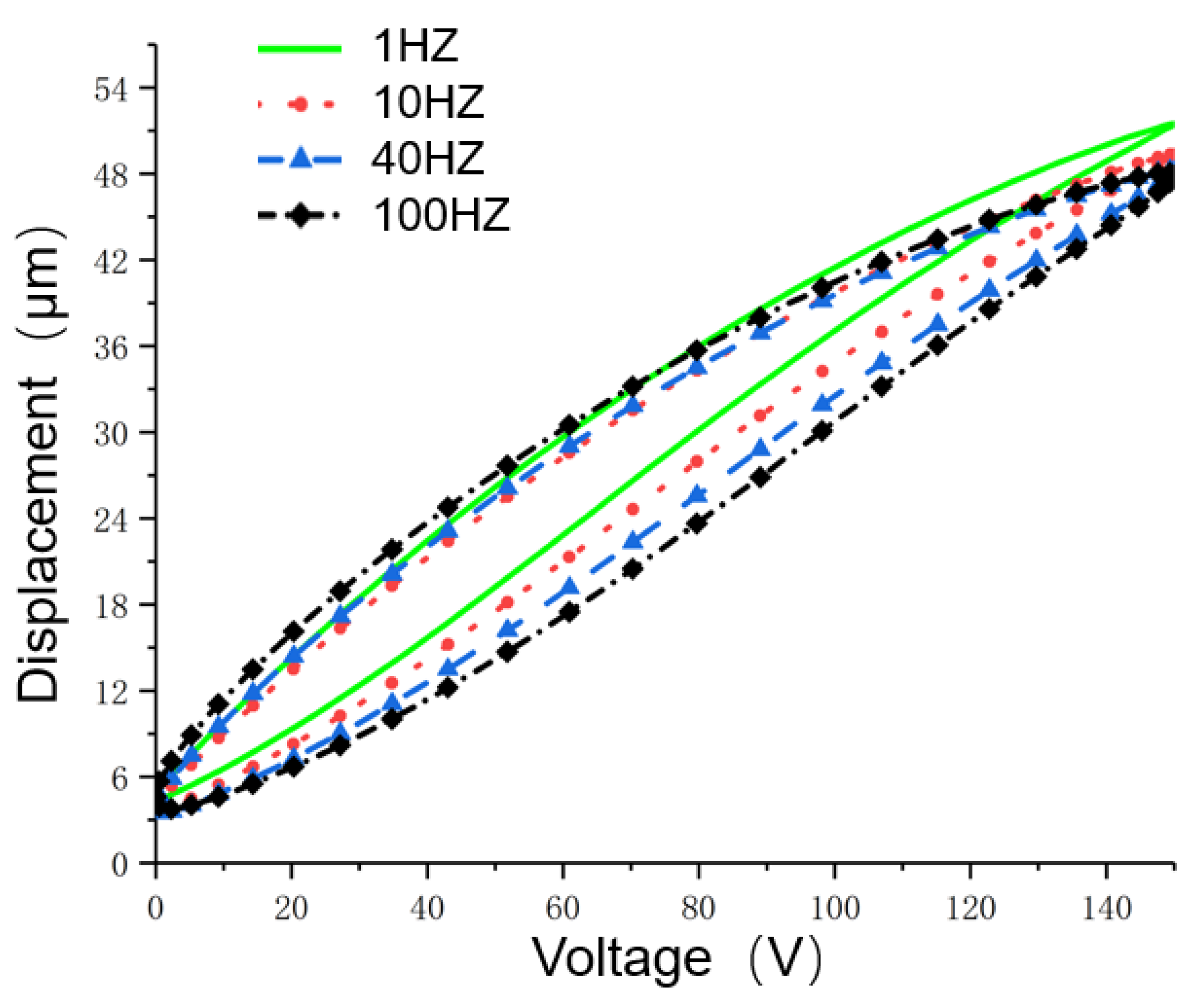
3.4. Rate Correlation Validation
4. Controller Design
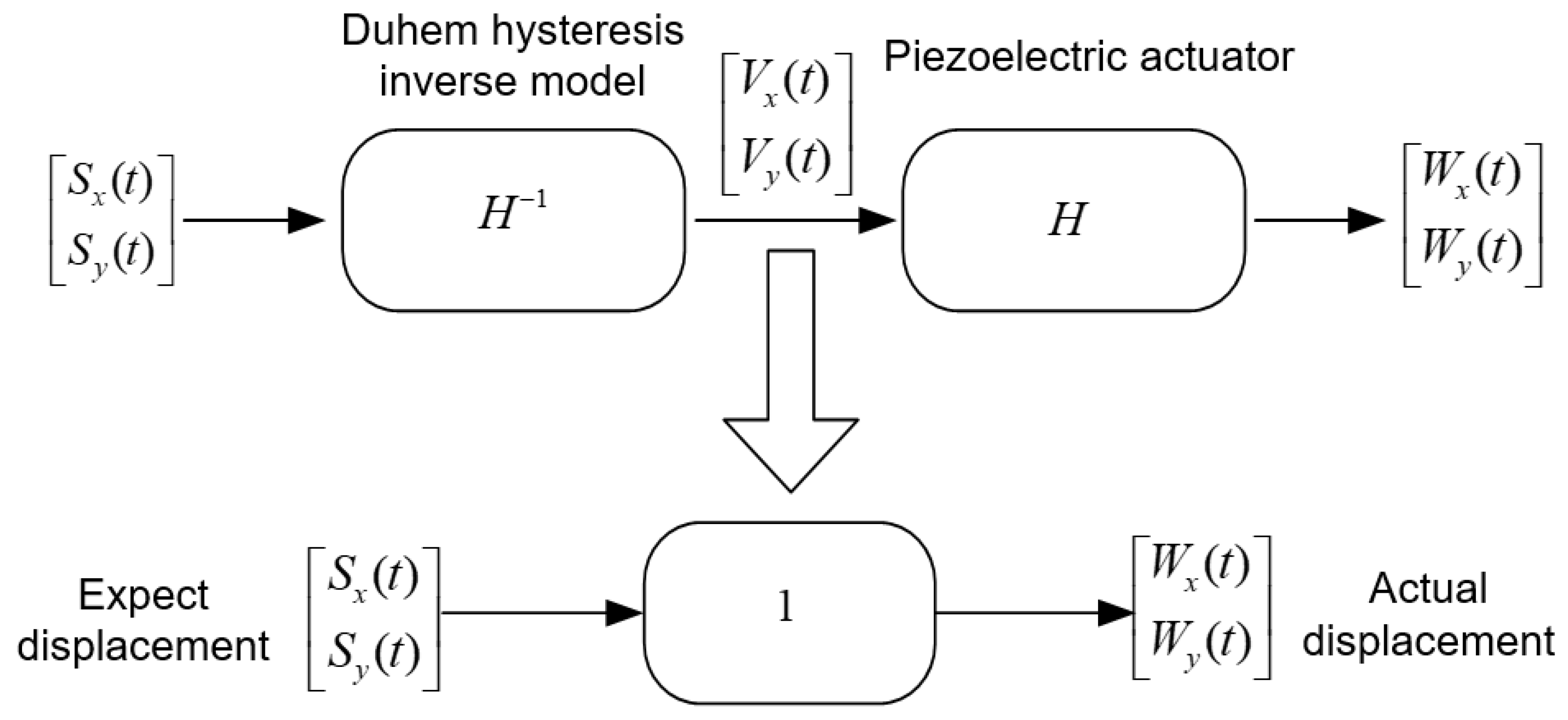
4.1. Feedforward Controller Design
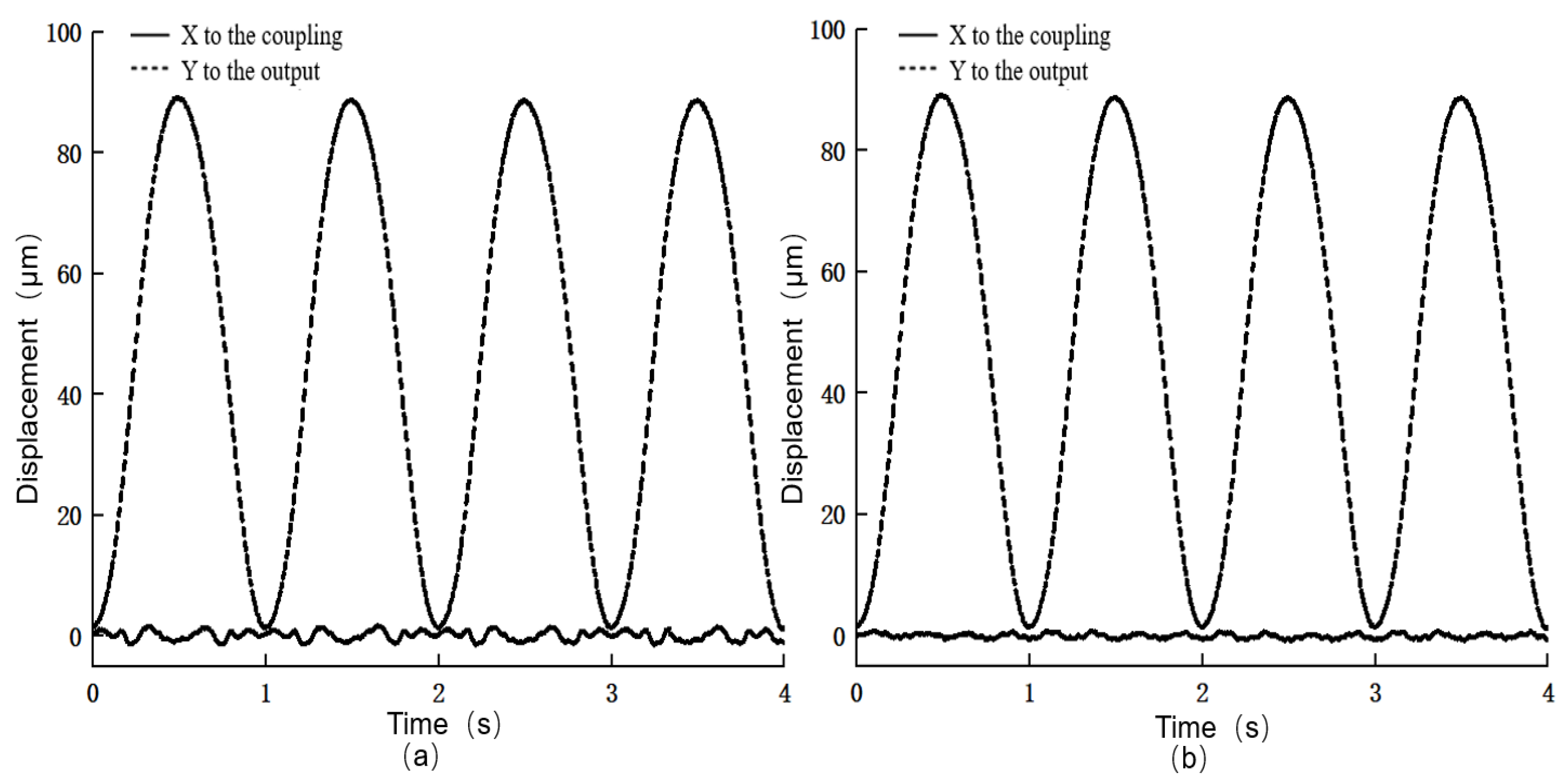
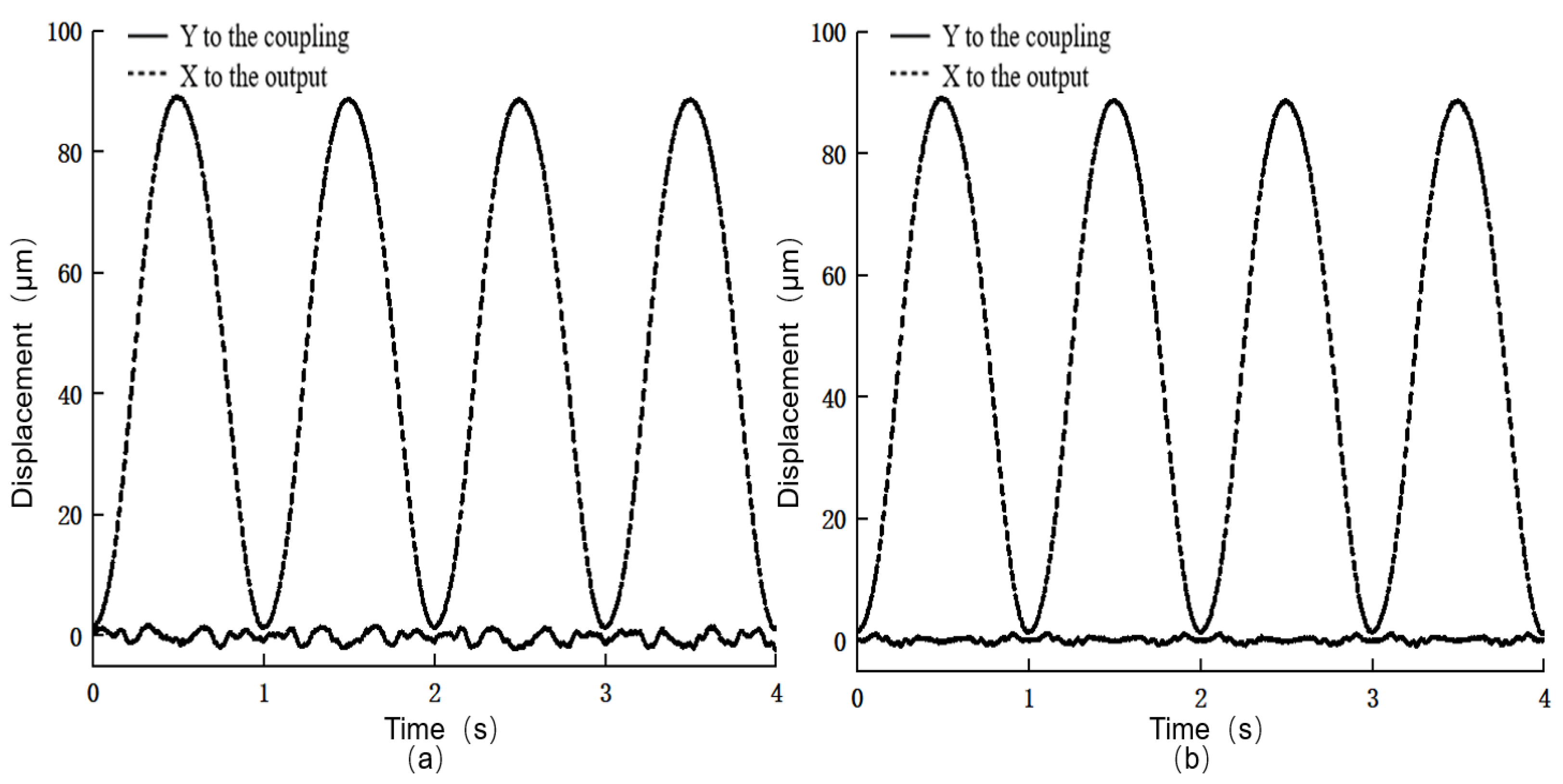
4.2. Decoupled Controller Design
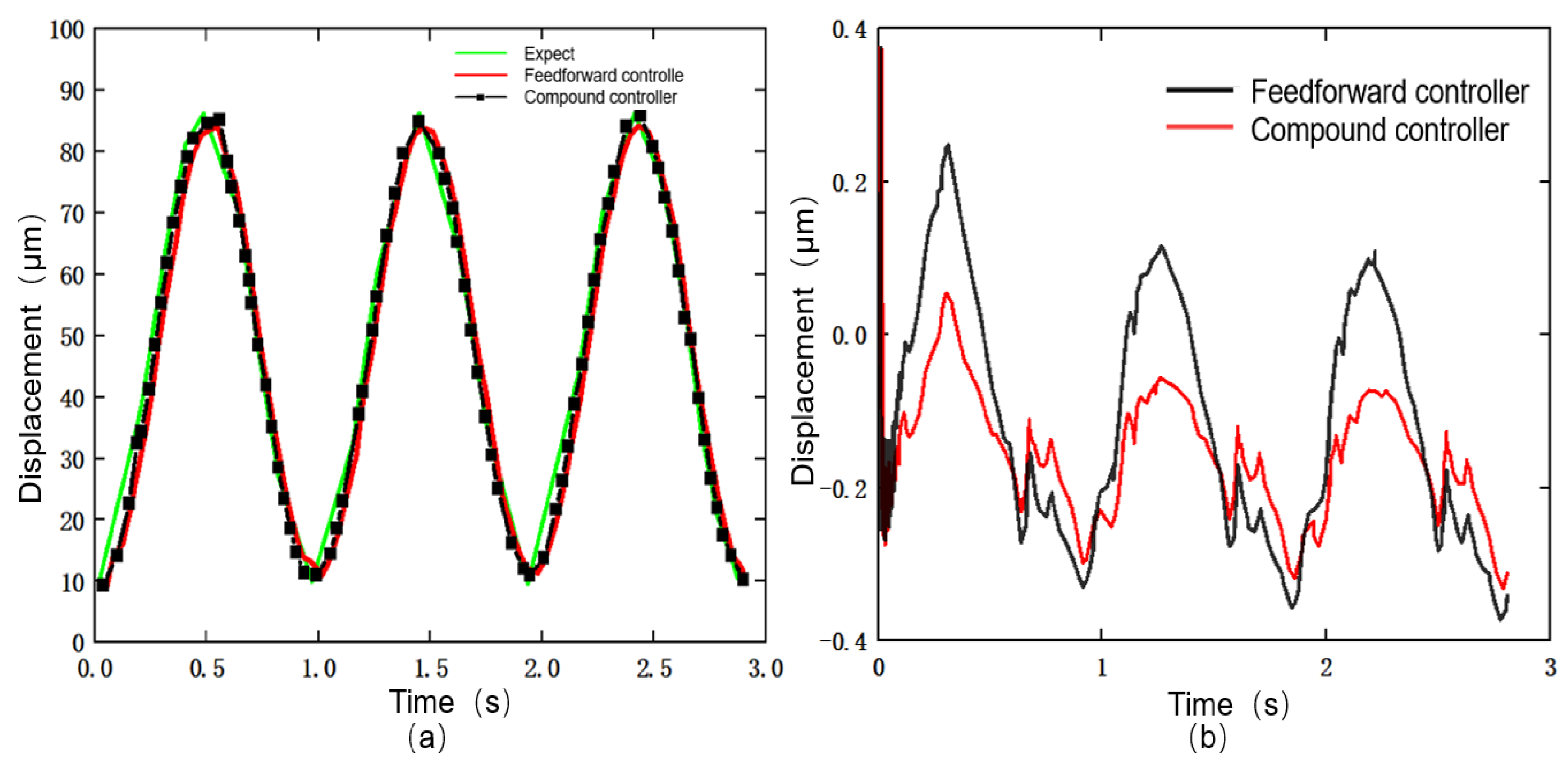
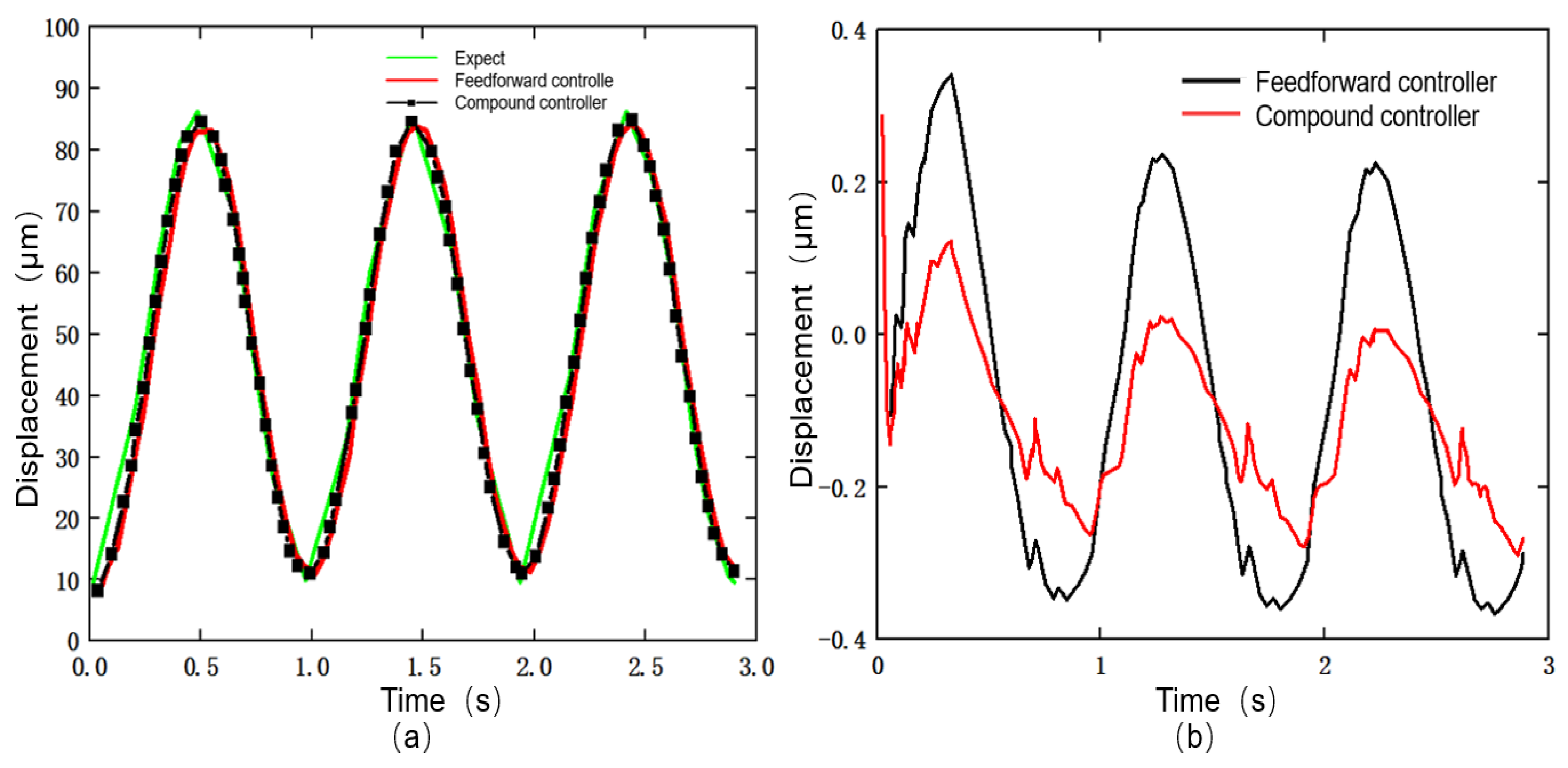
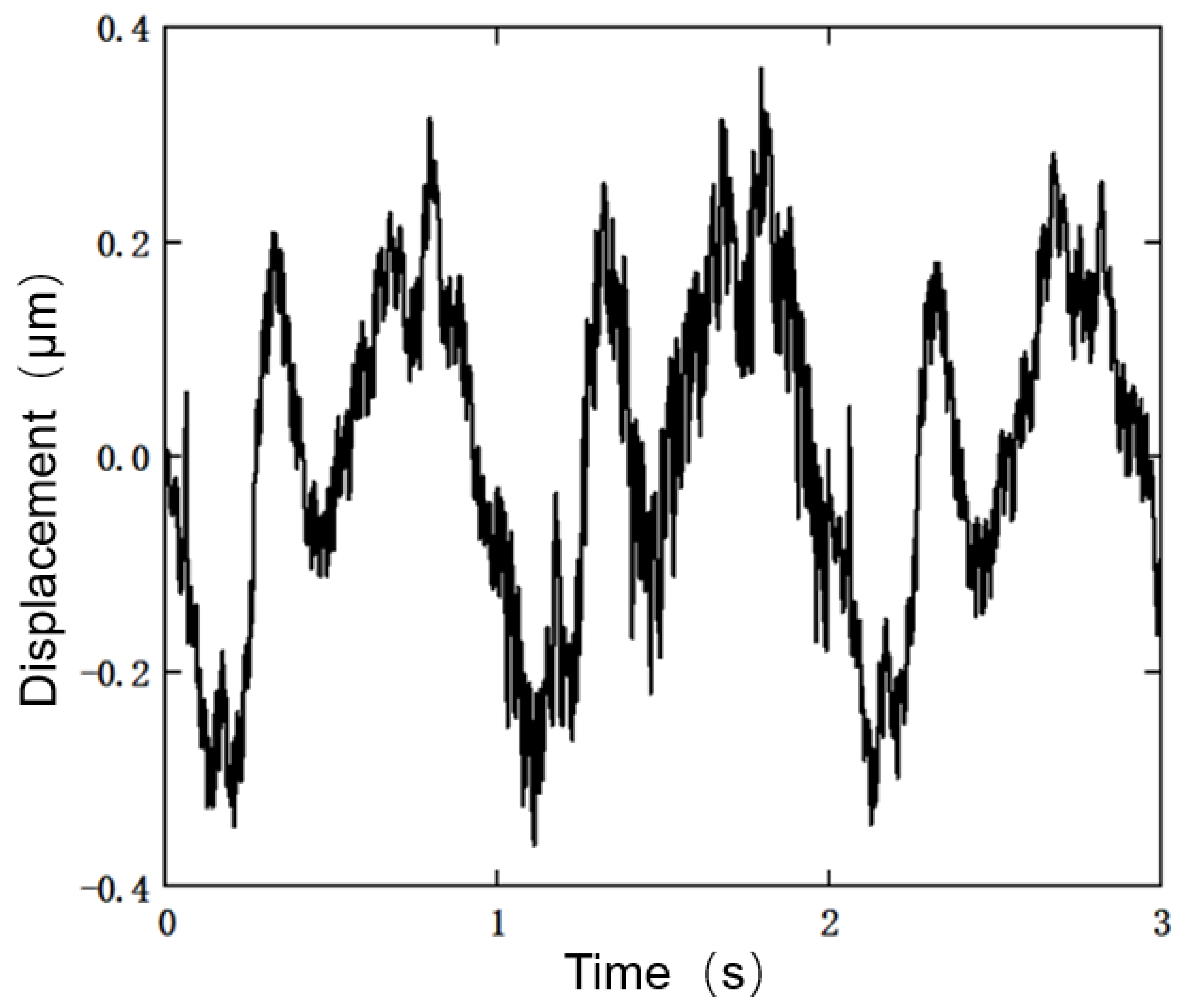
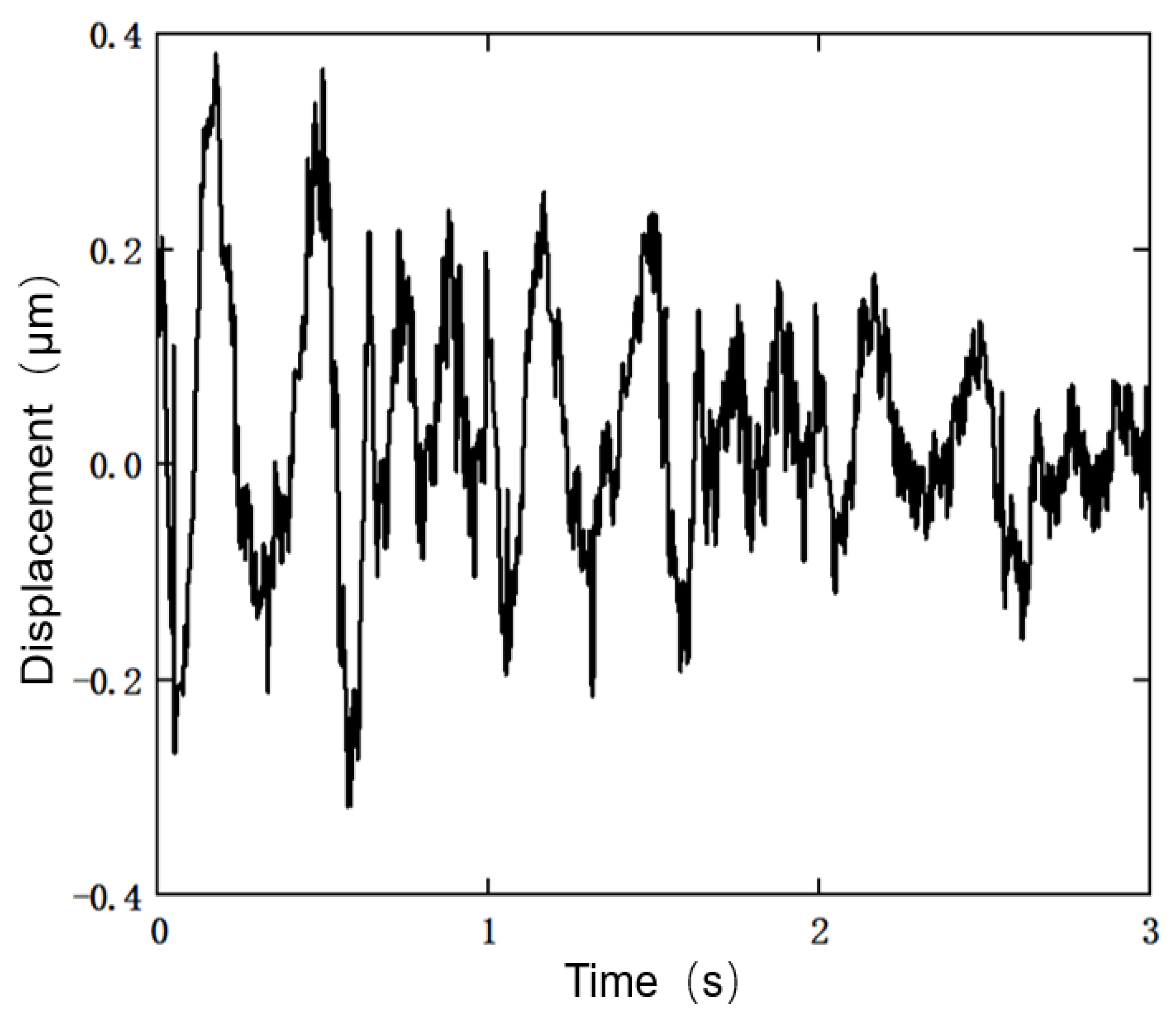
4.3. Composite Controller Design and Testing
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The hysteresis curve was divided into the step-up section and the step-down section for model parameter identification. The segmented Duhem model established from this can more accurately describe the hysteresis characteristics of the positioning platform, and the modeling accuracy was improved by 69.62%.
- (2)
- After introducing the bat algorithm to optimize the artificial fish swarm algorithm, the identification accuracy of the model parameters greatly improved, and the modeling error was reduced by 48.97%.
- (3)
- The composite controller designed based on the established Duhem inverse model, which integrates feedforward, decoupling and feedback control, has displacement errors under both constant and variable-amplitude sinusoidal signals within 0.25%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, C. Identification and control for Hammerstein systems with hysteresis non-linearity. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, G.; Wei, Z. Influence of High Voltage DC Transmission on Measuring Accuracy of Current Transformers. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 72629–72634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinc, U.; Klemenc, J.; Nagode, M.; Seruga, D. A direct approach to modelling the complex response of magnesium AZ31 alloy sheets to variable strain amplitude loading using Prandtl-Ishlinskii operators. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 127, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatawneh, N.; Al Janaideh, M. A Frequency-Dependent Prandtl-Ishlinskii Model of Hysteresis Loop Under Rotating Magnetic Fields. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2019, 34, 2263–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Sang, Z.; Lu, K.; Han, F.; Wang, J.; Ju, B. A new hysteresis modeling and optimization for piezoelectric actuators based on asymmetric Prandtl-Ishlinskii model. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2020, 316, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L. Development of a combined Prandtl Ishlinskii-Preisach model. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2020, 304, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, J.; Dai, X.; Li, Z. Hysteresis compensation of the Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for piezoelectric actuators using modified particle swarm optimization with chaotic map. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 075003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zhang, X. An enhanced Bouc-Wen model for characterizing rate-dependent hysteresis of piezoelectric actuators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, C. Description of asymmetric hysteretic behavior based on the Bouc-Wen model and piecewise linear strength-degradation functions. Eng. Struct. 2019, 181, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, C.; Feng, F.; Na, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q. Deep Neural Network Technique for High-Dimensional Microwave Modeling and Applications to Parameter Extraction of Microwave Filters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 4140–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Kinematics model identification and motion control of robot based on fast learning neural network. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 6145–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Xia, P.; Lang, K.; Smith, E.C.; Rahh, C.D. Neural Network Based Hysteresis Compensation of Piezoelectric Stack Actuator Driven Active Control of Helicopter Vibration. Sensor Actuators A-Phys. 2020, 302, 111809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Mei, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, M. A Modified Duhem Model for Rate-Dependent Hysteresis Behaviors. Micromachines 2019, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, K.; Yan, P.; Li, S. Duhem Model-Based Hysteresis Identification in Piezo-Actuated Nano-Stage Using Modified Particle Swarm Optimization. Micromachines 2021, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Hong, K.; Hu, K. Generalized regression neural network modeling based on inverse Duhem operator and adaptive sliding mode control for hysteresis in piezoelectric actuators. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2022, 236, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleuteri, M.; Klein, O.; Krejci, P. Outward pointing inverse Preisach operators. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H. A generalized Prandtl-Ishlinskii model for characterizing the rate-independent and rate-dependent hysteresis of piezoelectric actuators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, Y. Modeling and High Dynamic Compensating the Rate-Dependent Hysteresis of Piezoelectric Actuators via a Novel Modified Inverse Preisach Model. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshat, M.; Sepidnam, G.; Sargolzaei, M.; Toosi, A.N. Artificial fish swarm algorithm: A survey of the state-of-the-art, hybridization, combinatorial and indicative applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2014, 42, 965–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Huang, F.; Shen, X.; Jiang, C.; Lin, X. An adaptive stochastic resonance detection method with a knowledge-based improved artificial fish swarm algorithm. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 11773–11794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabba, A.; Tari, A.; Zouache, D. Multiobjective artificial fish swarm algorithm for multiple sequence alignment. Inf. Syst. Oper. Res. 2020, 58, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lian, L.; Zhu, F. Parameter fitting of variogram based on hybrid algorithm of particle swarm and artificial fish swarm. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 116, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gandomi, A.H. Bat algorithm: A novel approach for global engineering optimization. Eng. Comput. 2012, 29, 464–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; He, X. Bat algorithm: Literature review and applications. Int. J. Bio-Inspir. Comput. 2013, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, S.; Zhang, H. A hybrid grasshopper optimization algorithm with bat algorithm for global optimization. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 3863–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xiang, Z. Modified constant modulus algorithm based on bat algorithm. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 4493–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Shao, M.; Guo, L.; An, D. analysis for hysteresis of piezoelectric actuator based on microscopic mechanism. IOP conference series. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 399, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, J. Fast and Precise Control for the Vibration Amplitude of an Ultrasonic Transducer Based on Fuzzy PID Control. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.K.; Parhi, D.R. Particle Swarm Optimization aided PID gait controller design for a humanoid robot. ISA Trans. 2021, 114, 306–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
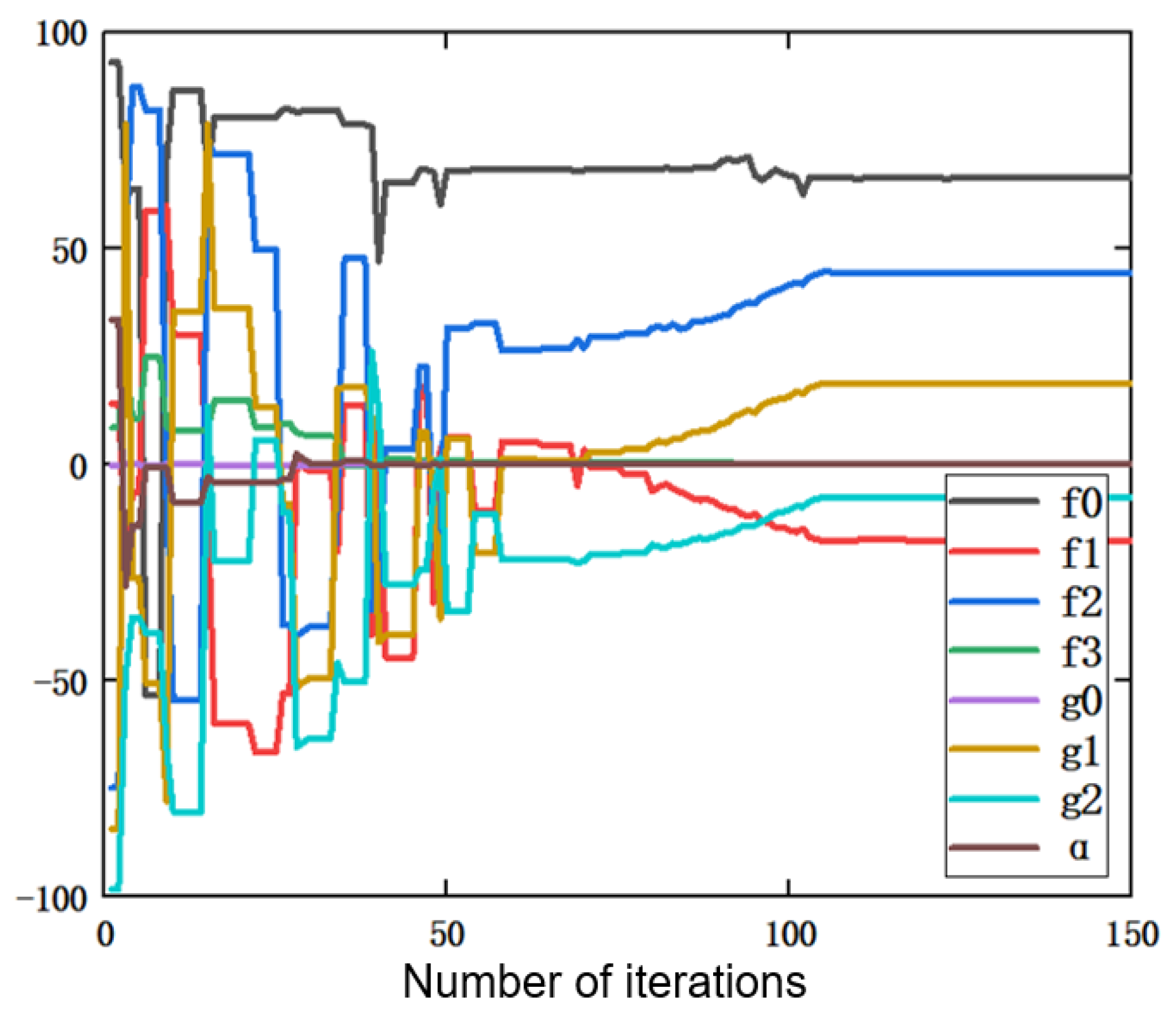

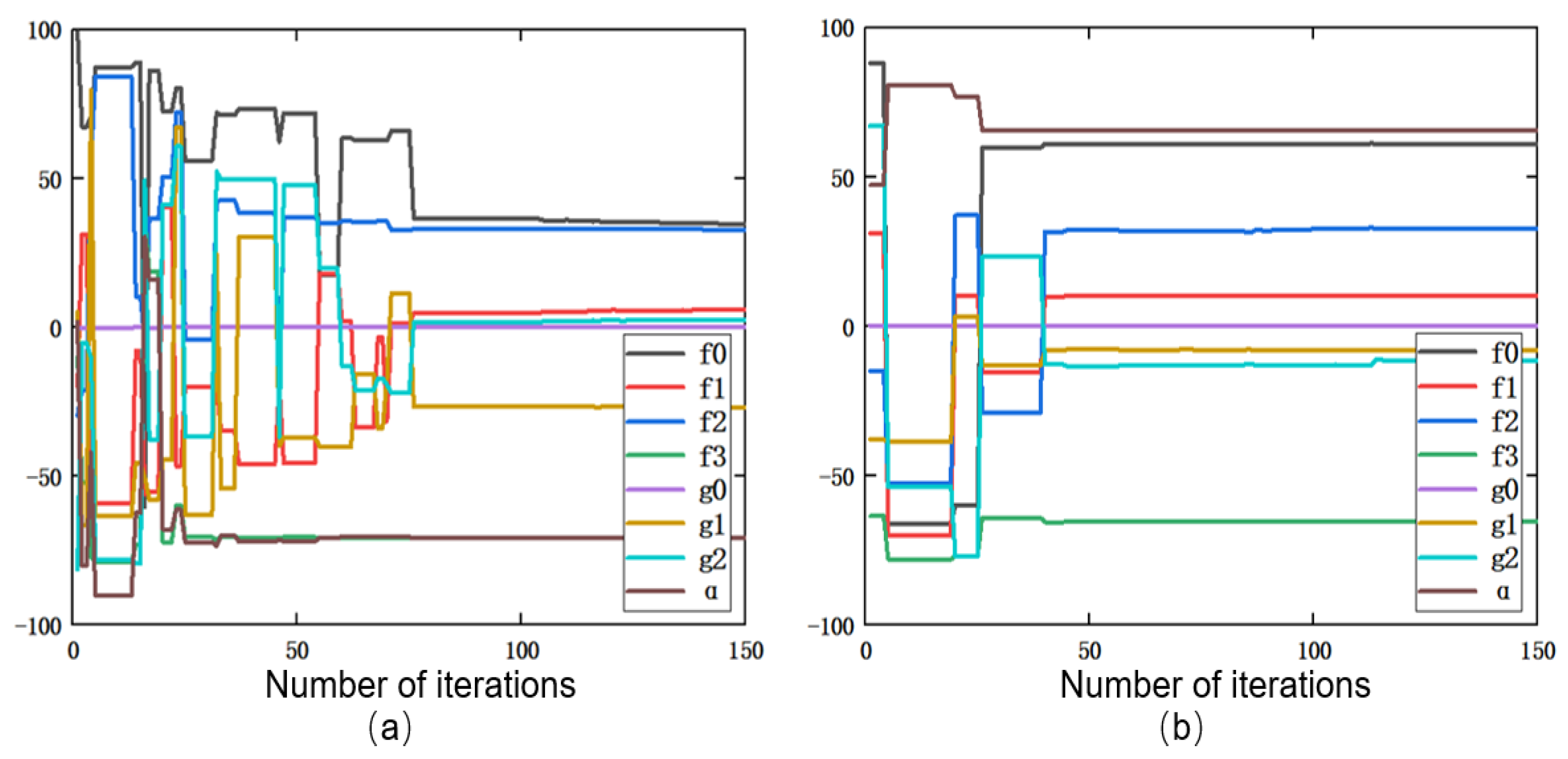
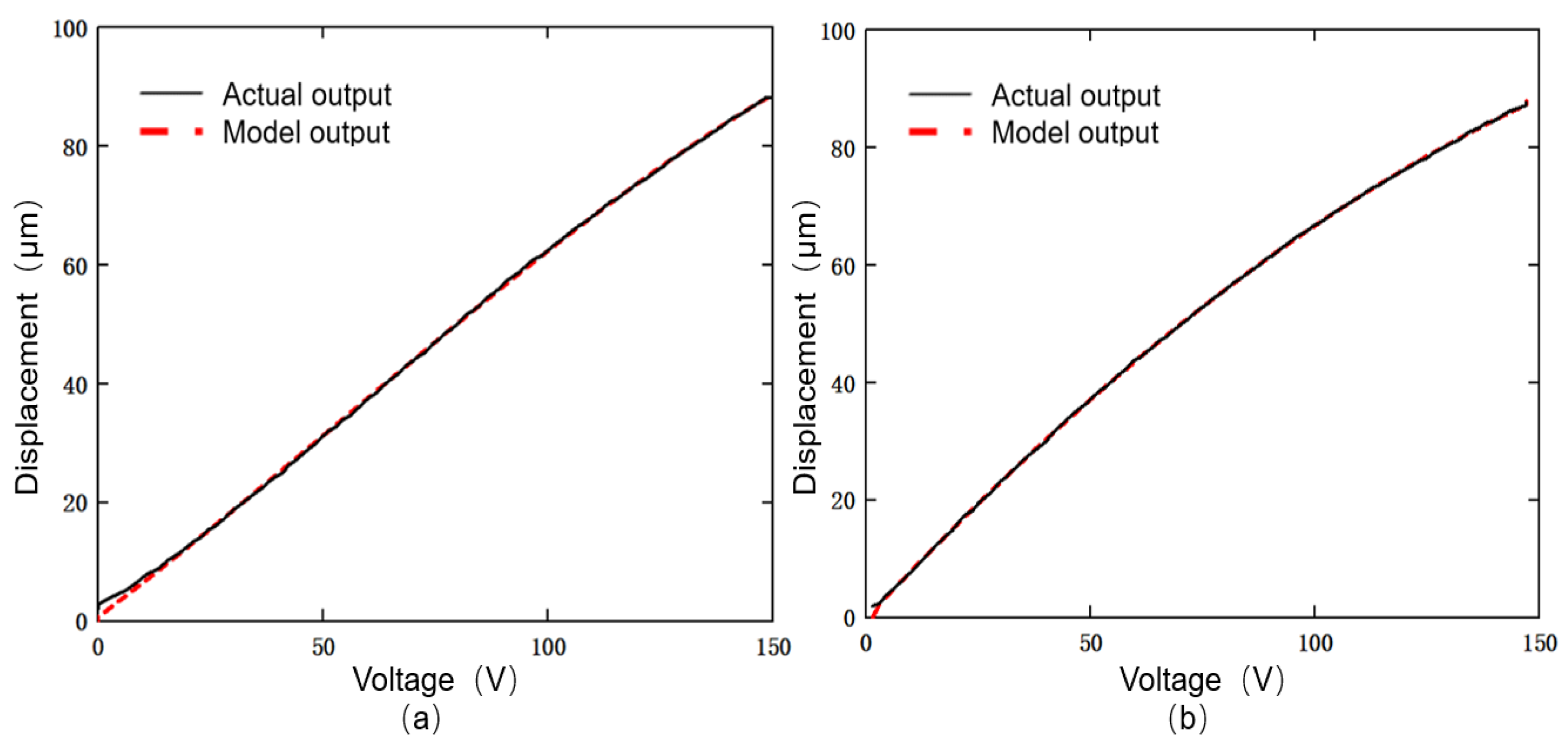
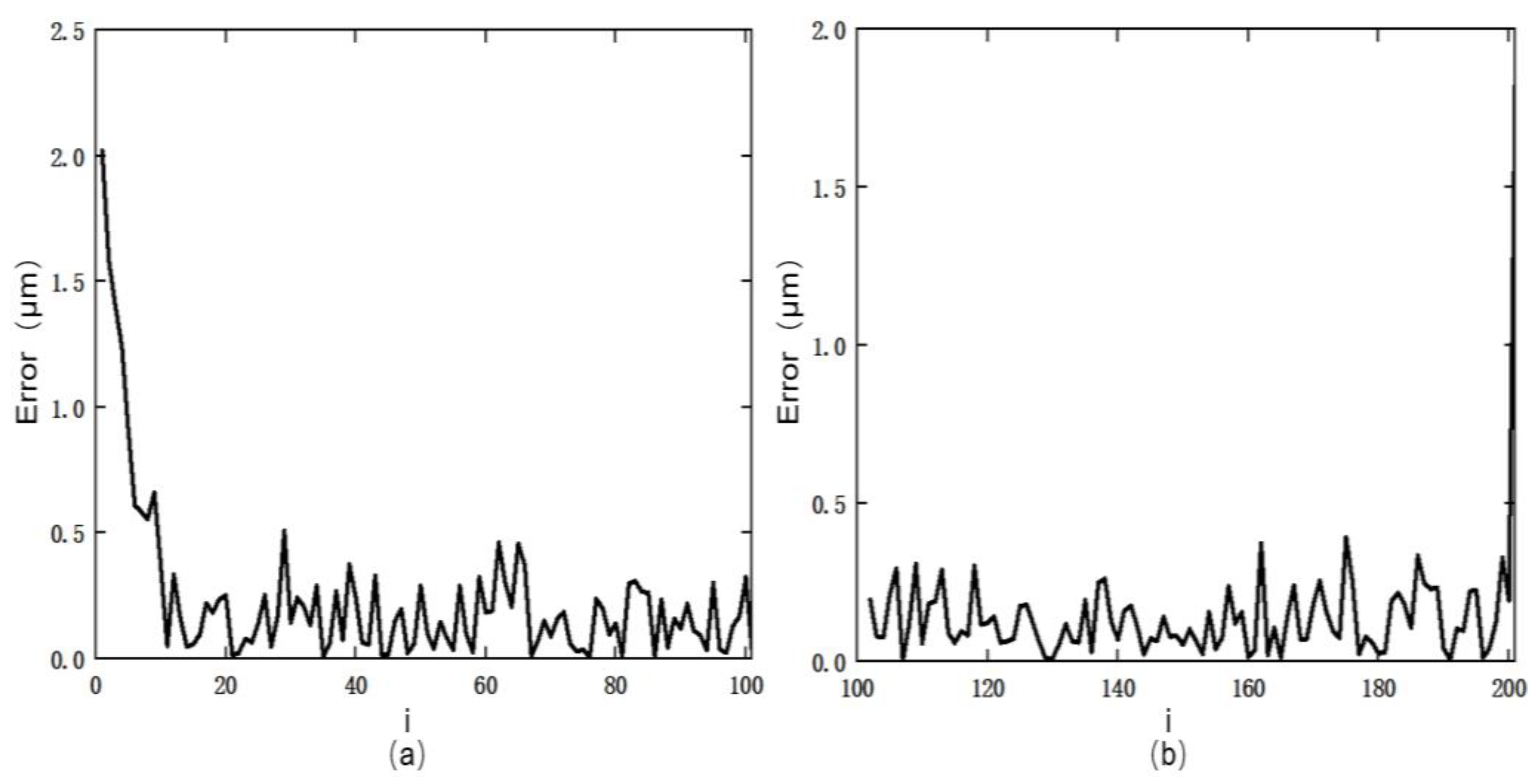
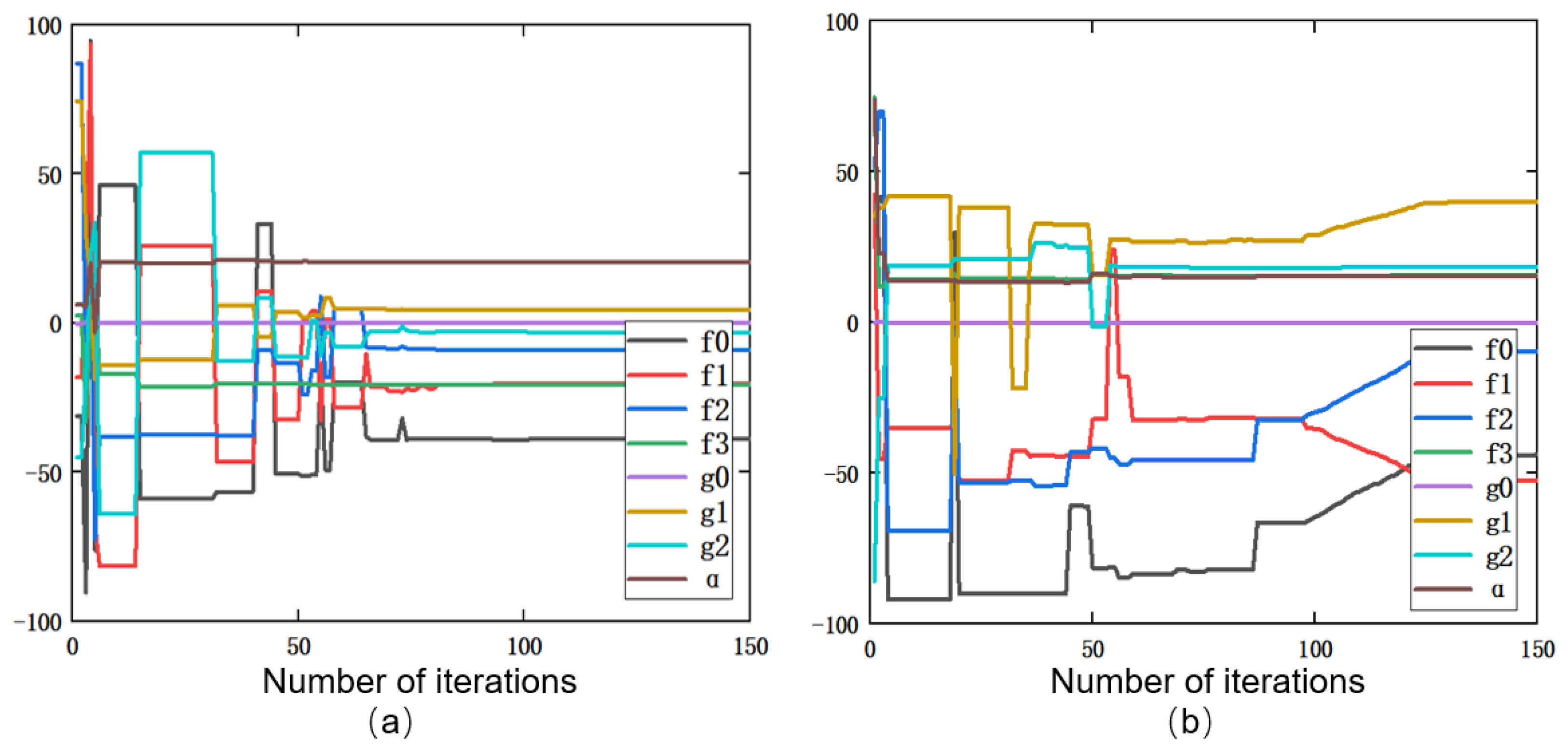
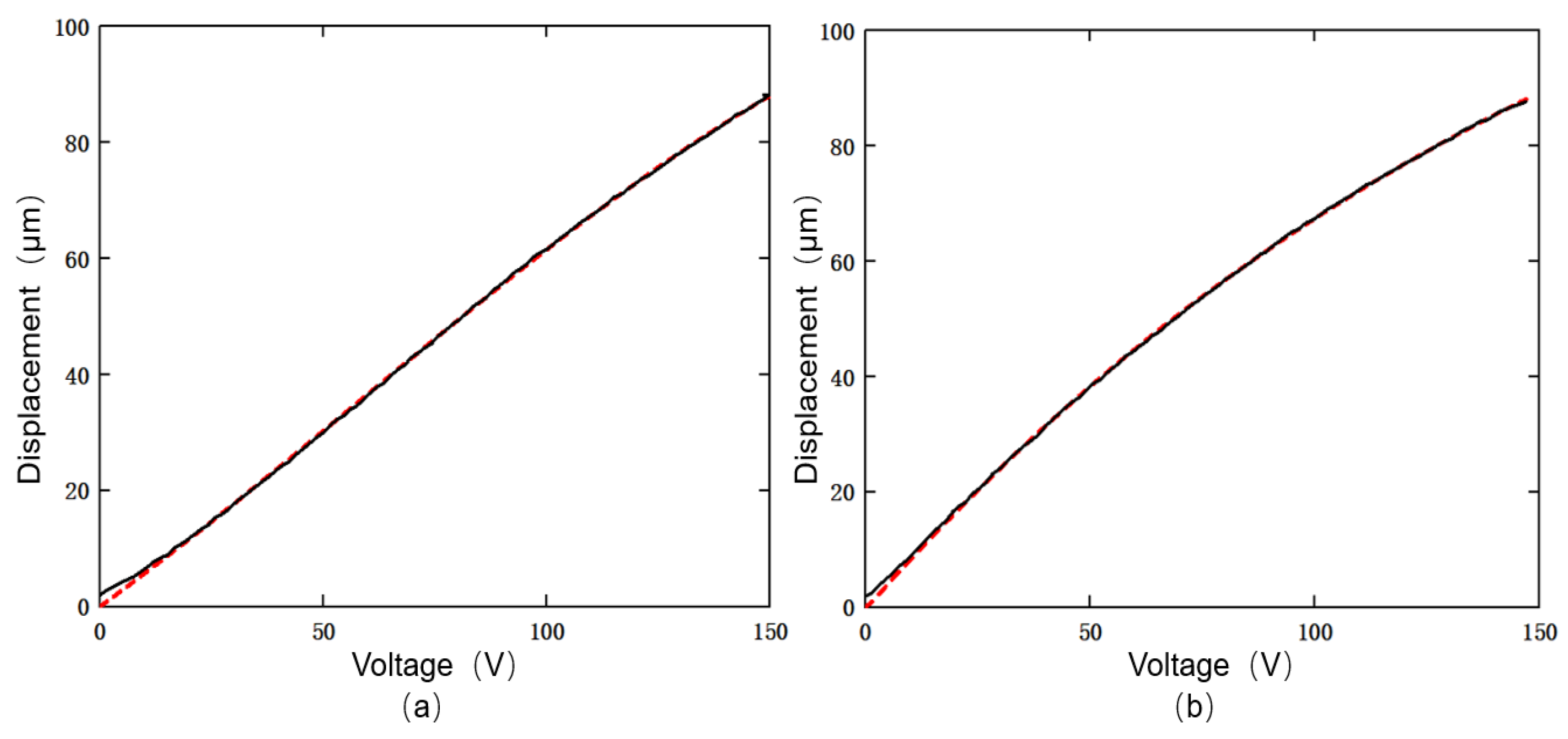
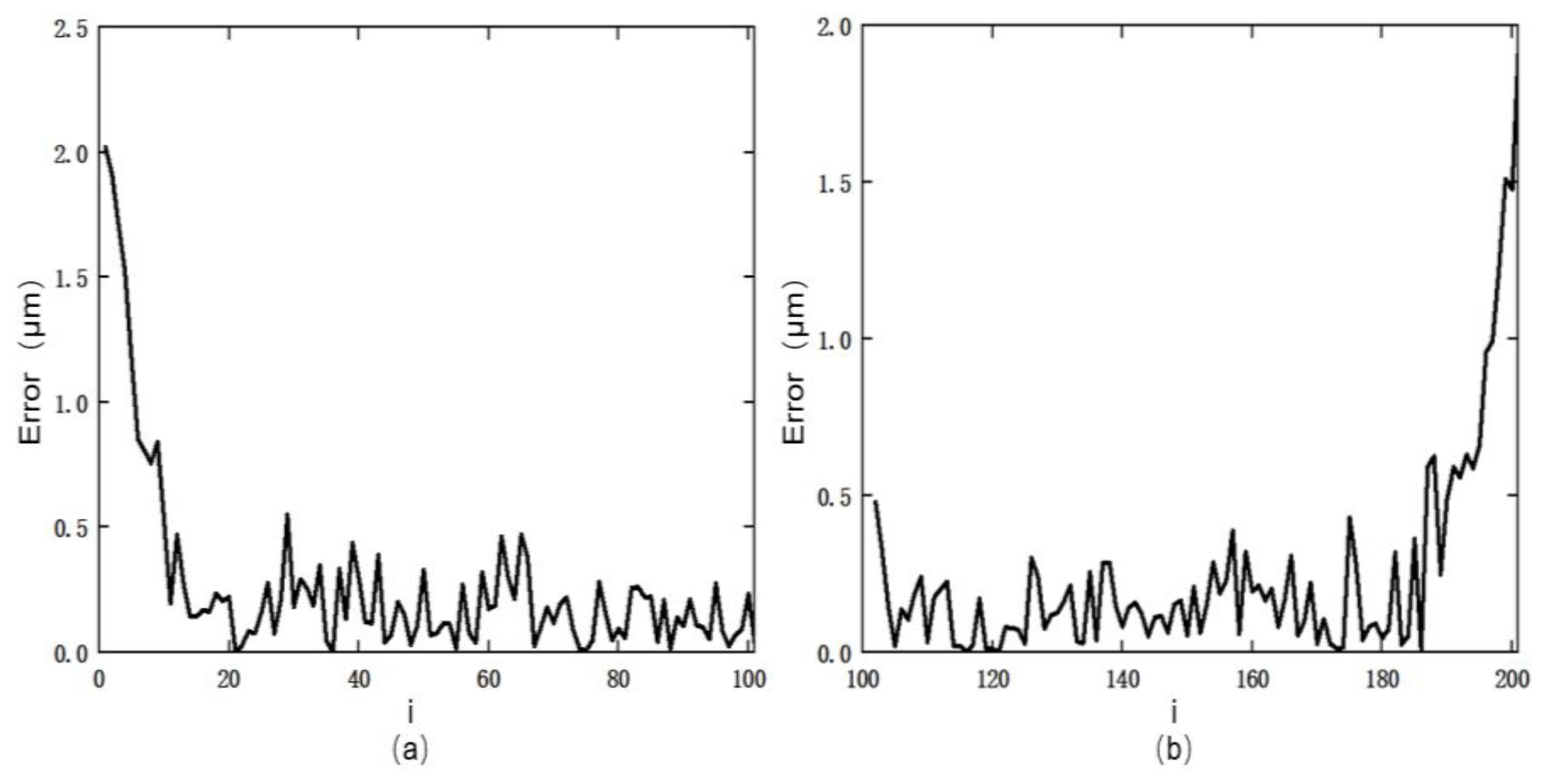

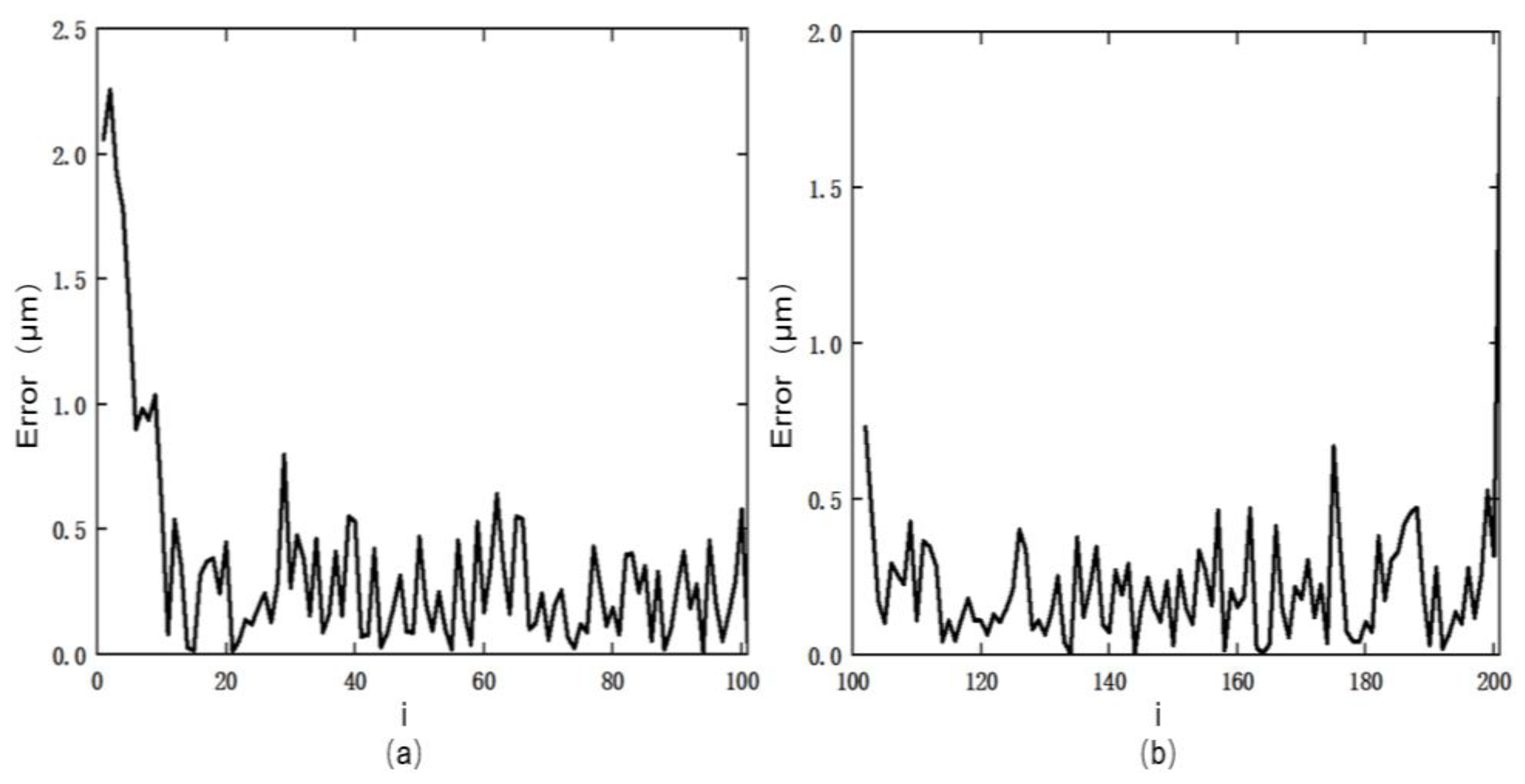

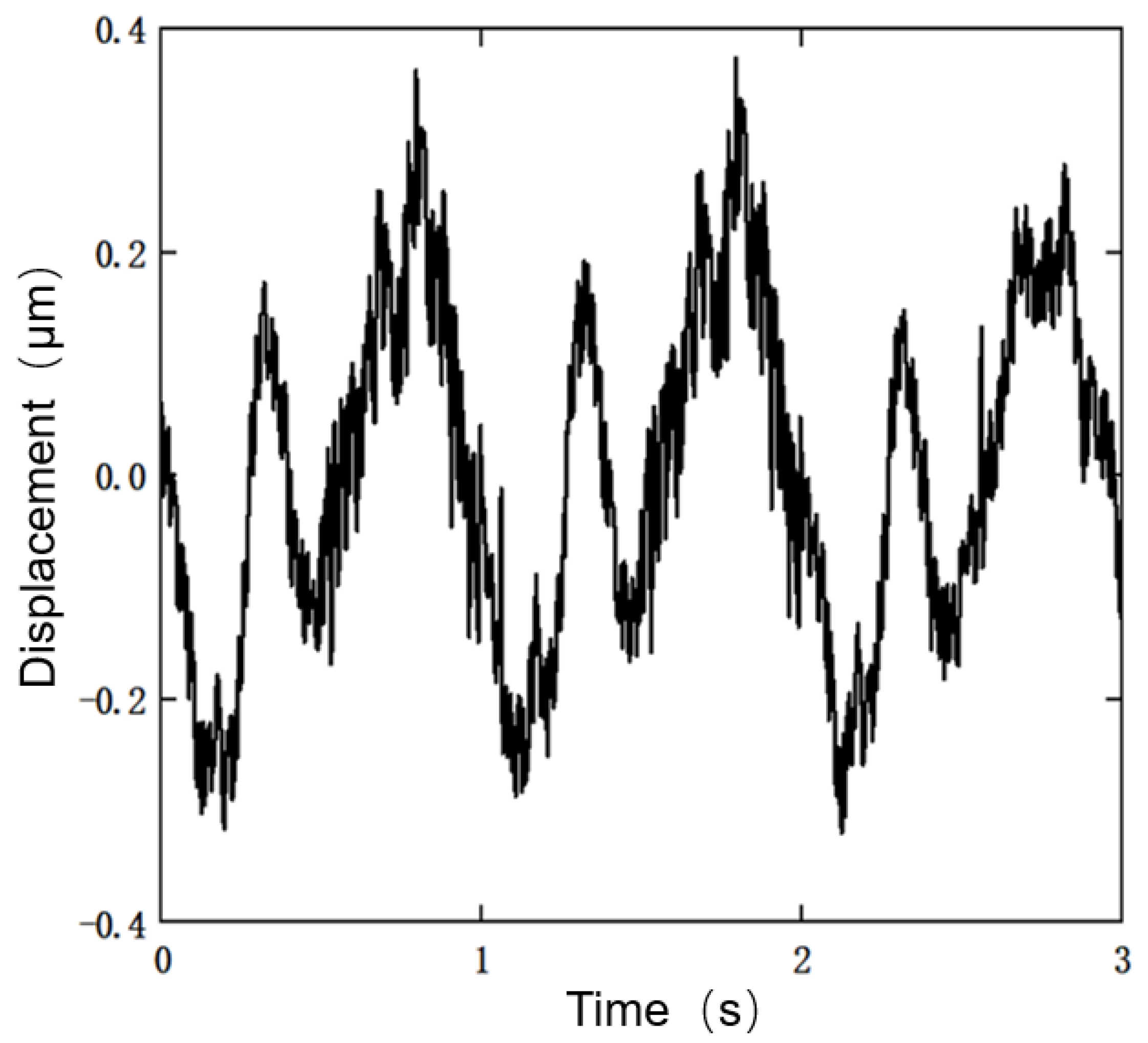
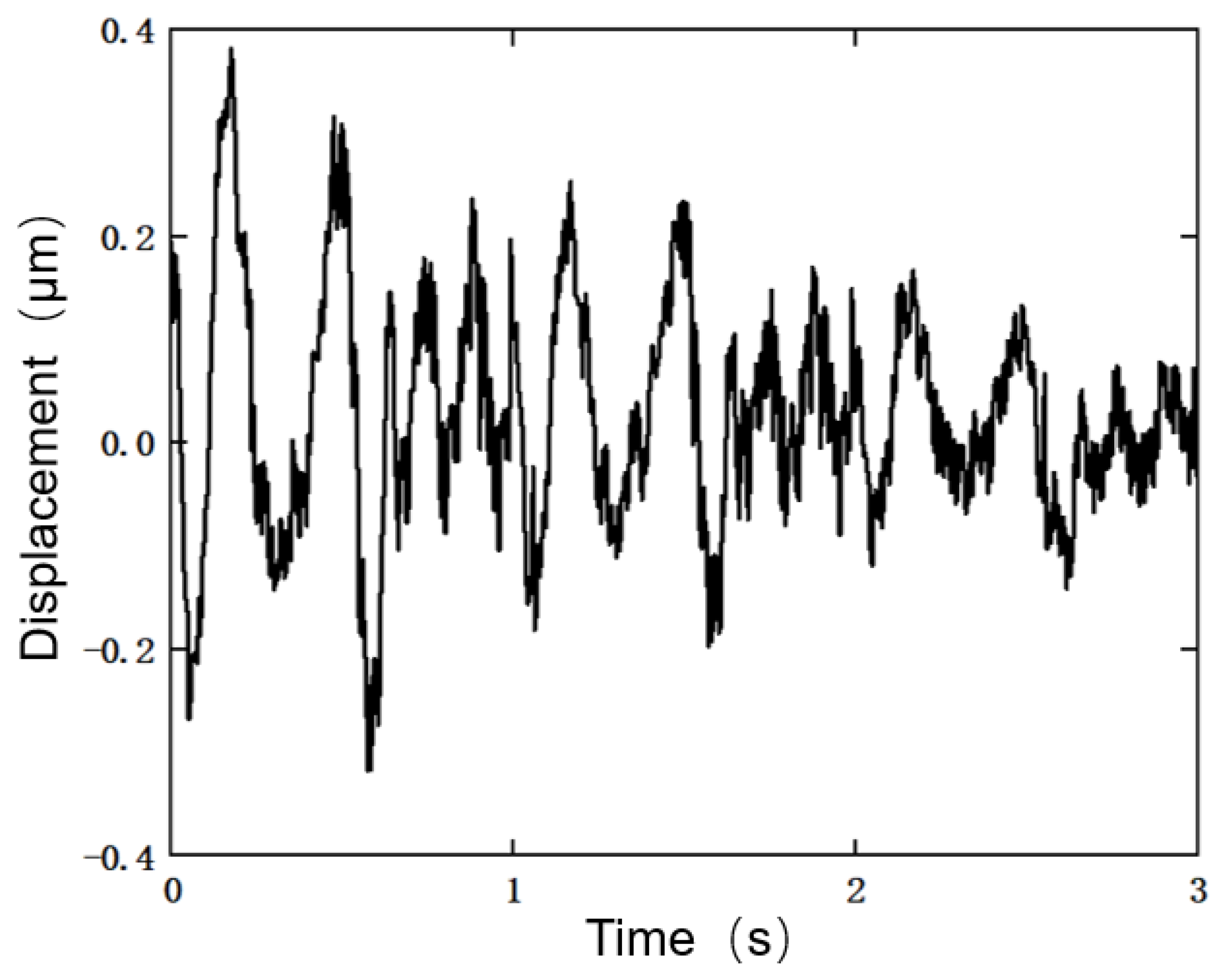
| Parameter | Identify the Results |
|---|---|
| 66.1302 | |
| −17.4632 | |
| 44.4025 | |
| 0.039727 | |
| 0.0485549 | |
| 5.03691 × 10−4 | |
| 18.7986 | |
| −7.53645 |
| Parameter | Identify the Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Rising Segment | Failing Segment | |
| −70.5414 | 65.5115 | |
| 34.5487 | 60.9669 | |
| 6.078683 | 10.2623 | |
| 32.7450 | 32.6779 | |
| −70.6247 | −65.3047 | |
| 1.044 × 10−4 | −9.615 × 10−4 | |
| −26.88 | −7.82026 | |
| 2.4939 | −11.5234 | |
| Parameter | Identify the Results | |
|---|---|---|
| Rising Segment | Failing Segment | |
| 20.5173 | 15.5066 | |
| −38.9701 | −43.9303 | |
| −20.4347 | −52.5417 | |
| −9.12629 | −9.69358 | |
| −20.6836 | 15.5562 | |
| 8.599 × 10−4 | 3.55 × 10−4 | |
| 4.4955 | 39.8547 | |
| −3.00583 | 18.4739 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, H.; Lv, B.; Ding, H.; Yang, F.; Qi, A.; Wu, X.; Ni, J. Modeling and Control of Hysteresis Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform Based on Duhem Model. Actuators 2022, 11, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050122
Ji H, Lv B, Ding H, Yang F, Qi A, Wu X, Ni J. Modeling and Control of Hysteresis Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform Based on Duhem Model. Actuators. 2022; 11(5):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050122
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Huawei, Bo Lv, Hanqi Ding, Fan Yang, Anqi Qi, Xin Wu, and Jing Ni. 2022. "Modeling and Control of Hysteresis Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform Based on Duhem Model" Actuators 11, no. 5: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050122
APA StyleJi, H., Lv, B., Ding, H., Yang, F., Qi, A., Wu, X., & Ni, J. (2022). Modeling and Control of Hysteresis Characteristics of Piezoelectric Micro-Positioning Platform Based on Duhem Model. Actuators, 11(5), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050122






