Abstract
Electromagnetic active suspension is an important technique used in vehicles to improve ride comfort and handling stability. To achieve satisfactory suspension performance, the active suspension control requires strong robustness against the vehicle uncertainties and external disturbances. The voice coil motor (VCM) is applied to the active suspension. A suspension model considering the actuator is established. An active suspension controller based on the active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) method is proposed. Through the test platform built, it is demonstrated that the ADRC of VCM active suspension has better performance than the PID. The results indicate that the overshoot and adjustment time of ADRC controller is reduced by 80% and 50%, respectively. The body vertical displacement of the ADRC is 50% smaller than PID.
1. Introduction
Suspension system is an important part of the automobile, which is mainly used to transfer the force and torque between the body and the wheel. It has the characteristics of reducing impact and vibration [1,2]. The performance of the system will directly affect the dynamic performance of the vehicle such as ride comfort and driving safety [3]. It is difficult for the passive or semi-active suspension with traditional spring damping structure to improve the dynamic performance of vehicles. For hydroelectric active suspension and air suspension, the dynamic performance of vehicles can be greatly improved. However, they have common problems such as high energy consumption, response delay, and small controllable bandwidth [4,5]. Because of the active control characteristics of electromagnetic suspension, it has attracted extensive attention [6,7].
Lin et al. [8] developed a gray predictive self-organizing fuzzy controller (SOFC) for active suspension systems, which solves the problem of improper selection of SOFC parameters. Ning et al. [9] proposed a Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy controller based on a disturbance observer, which shows that it can significantly improve the ride comfort of heavy drivers. Mustafa et al. [10] investigated a new model-free fuzzy logic controller for nonlinear active suspension systems based on particle swarm optimization (PSO-MFFLC). Based on different road disturbances, PSO-MFFLC was compared with classic PID, intelligent PID and time-delay estimation control. Shao et al. [11] established a multi-objective reliable fuzzy H-∞ control for in-wheel motors driving EV active suspension, and proved its effectiveness by computer simulation. In order to cope with the uncertainty of the suspension, adaptive control strategy was applied. Liu et al. designed an adaptive sliding fault-tolerant controller to improve ride comfort [12]. Huang et al. [13] developed a new adaptive law for vehicle active suspension systems with unknown nonlinear dynamics to estimate two NN weights. Hua et al. [14] proposed a new adaptive control scheme for the half-vehicle active suspension system with unknown dead zone inputs. Pan et al. [15] studied an adaptive tracking control strategy for vehicle suspension, which has the advantage of not requiring the assumption of measurable actuator output. Sun et al. [16] designed adaptive rear-step level-based tracking control to stabilize the vertical and pitch movements of the body by introducing virtual control inputs and reference trajectories. For active suspension systems, the control design objective is not simply to improve ride comfort, but also to keep suspension stroke and tire deflection within an acceptable level. Therefore, robust control is also widely used in active suspension control [17]. The robust controller for the electromagnetic suspension system was proposed by Sande et al. [18], which verified the accuracy of the model through the test bench built. Comfort can be improved by 53% when driving over a 3 cm speed bump. The μ synthetic controller designed by Zhang et al. [19] can significantly improve ride comfort compared with passive suspension. Wang et al. [20] applied robust non-fragile finite frequency H∞ static output feedback control to a quarter-car active suspension model. Pan et al. [15] introduced an adaptive tracking control strategy for vehicle suspensions that eliminates unintended nonlinear effects. Gordon et al. [21] hypothesized that vehicle sensors could be used to measure the road height profile in front of the car, and used model predictive control to improve the performance of semi-active and active suspension systems. Chen et al. used the optimal sliding mode control of the active suspension of nonlinear vehicles. Moreover, multi-objective optimization control was also used [22,23]. Nevertheless, most of the control methods mentioned above are based on the suspension model, which is extremely difficult to obtain when taking all uncertain factors into account. Additionally, those complex control algorithms are difficult to implemented in practical control systems because the suspension control system requires a lot of time and stability.
In the 1990s, Han [24] proposed a novel general active disturbance rejection control method based on the widely used PID controller. ADRC is completely independent of the model and has real-time similarity to PID, which makes ADRC widely be used in engineering in recent years [25,26,27,28,29]. ADRC can automatically estimate the internal model uncertainties and the external disturbances. It compensates for it by a special extended state observer (ESO). Yuan et al. [30] introduced ADRC into the control of active suspension of tracked vehicles and gave simulation results to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. While the existing work gives excellent results in active suspension control, the actuators were not taken into consideration. That is to say, the effect of actuator dynamics in those papers was neglected, and the actuator was modeled as an ideal force generator. This assumption results in inaccuracies of controller design in actual engineering. Voice coil motor (VCM) is a kind of linear motor, which has many good features as it can generate force with high accuracy and acceleration over a sufficient range of movement [31]. Numerous applications have shown the feasibility and significant effectiveness of VCMs used as the actuator of active vibration isolation systems [32].
According to the above analysis, active disturbance rejection control is used to the control of the voice coil motor active suspension. The main contributions of this paper are as follows. First, the voice coil motor is applied to the active suspension and a suspension model considering the actuator is established. Second, an ADRC controller is designed to estimate and compensate the vehicle uncertainties and external disturbances of voice coil motor active suspension. Third, through the simulation and experiment, the actual control effect of the proposed control strategy is verified.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 establishes the voice coil motor active suspension model. Section 3 designs ADRC controller for the active suspension. The simulated and experimental results are presented in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 presents the conclusion of this research.
2. Mathematical Model
The two-degree-of-freedom (2-DOF) model is adopted to simulate a quarter-vehicle suspension. Although the 2DOF model is simple, it is effective to have a good understanding of suspension performance, such as ride comfort and road holding. The quarter-car voice coil motor active suspension model is shown in Figure 1.
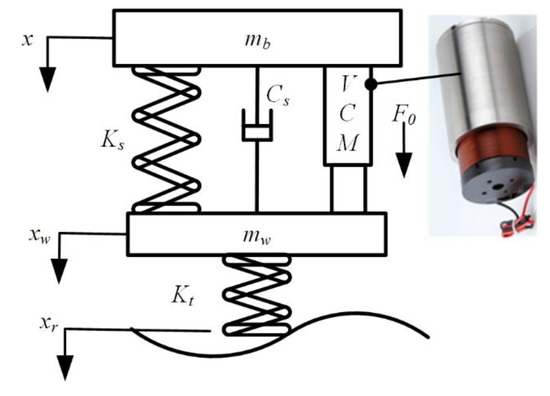
Figure 1.
Model of quarter-car voice coil motor active suspension.
According to Newton’s second law, the suspension model is given by
where x is the vertical displacement of the body relative to its static equilibrium position, xw is the vertical displacement of the wheel relative to its static equilibrium position, xr is the vertical displacement of the road relative to its initial position; Ks, Kt is the suspension spring stiffness and the wheel equivalent stiffness, respectively. Cs is the suspension damping coefficient. mb and mw represent the mass of the vehicle and the quality of the wheel, respectively. The active control force F0 is generated by the voice coil motor.
Voice coil motor is a special type of linear drive motor with simple structure, small size, and fast response. The structure diagram is presented in Figure 2a. The outer part is stator, a permanent magnet is fixed inside the stator. The inside part is mover, a coil winding is arranged on the mover. The mover and the stator can linearly move in the axial direction. When the energized coil (conductor) is positioned in the magnetic field, a force is generated. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the current passing through the conductor. The direction of the motor force can be changed by modifying the direction of the current. The circuit equivalent model of the voice coil motor is illustrated in Figure 2b.
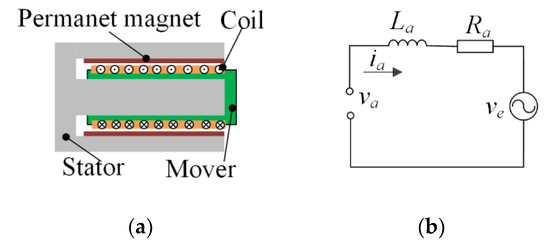
Figure 2.
Voice coil motor: (a) Structure diagram; (b) Circuit equivalent model.
The voltage balance equation can be expressed as
where ia is the coil current, va is the motor input voltage, La is the coil inductance, Ra is the coil resistance, and ve is the induced electro-motive force. The induced electromotive force is proportional to the relative motion speed of the stator and mover of the motor. Since the stator and mover of the motor are fixed to the body and the wheel respectively, the induced electromotive force can be expressed as
where vr is the relative motion speed between the motor mover and the stator, and kb is the induced electromotive force (EMF) coefficient.
The force generated by the voice coil motor is proportional to the current
where kF is the motor driving force coefficient.
3. Controller Design
The road excitation makes the vehicle body vibrate. It reduces the comfort of the human body, especially in the harsh road environment. Therefore, the main goal of the active suspension aims to reduce the vibration of the body and keep the body smooth to improve ride comfort. According to the suspension dynamics equation and the motor model, the body is a second-order system and the motor is a first-order system. Therefore, the two models constitute a third-order cascade system. The system state variables are selected as follows
The goal of the control system is to reduce the vibration of the body, so the vertical displacement of the body is chosen as the system output.
The force of the active suspension is provided by the voice coil motor, so the control variable is selected as the motor input voltage.
The effect of wheel motion on the body is considered to be an external disturbance, then the system state equation is
It can be recognized from Equation (8) that the wheel motion displacement and the motion speed are external disturbances of the vehicle body. The motion state of the wheel is not just related to the motion state of the vehicle body, but also related to the road excitation. Moreover, the motion state of the wheel is often difficult to directly measure. Therefore, the active disturbance rejection control method is used to estimate and compensate the system uncertainties and external disturbances. For the 3rd-order cascade system, two cascade controllers could be designed. The body displacement is used as the input to the outer ADRC, and the suspension demand force is used as its output. The inner layer ADRC is used to follow the demand force. However, cascade control means that the parameters of the two ADRC controllers have to be adjusted. It will undoubtedly increase the control difficulty. Fortunately, the ADRC controller does not rely on accurate models. The most notable feature of ADRC is that all internal uncertainties and external disturbances of the system are considered to be total disturbances. In addition, a special extended state observer (ESO) is applied to estimate the total disturbance and compensate it. To simplify the control system, the third-order system shown in Equation (8) is reduced to a second-order system to control. All un-modeled parts and external disturbances in the system are treated as unknown total disturbances of the system.
Letting
Then
Letting
Then Equation (11) is simplified to:
The third-order object of Equation (8) is simplified to a second-order system, where P is the total unknown disturbance of the system, including uncertainties and external disturbance; b is the coefficient of the control variable.
Since the actual value of the total disturbance P of the system is difficult to measure, the ADRC scheme is used to estimate and compensate it. The complete algorithm of the ADRC controller includes tracking differentiator (TD), extended state observer (ESO) and nonlinear state error feedback control (NLSEF). ESO is the core part of ADRC design. There is linear extended state observer (LESO) and nonlinear extended state observer (NLESO). LESO is relatively simple and the parameters are easy to adjust, but its estimation accuracy is not as good as NLESO. Therefore, NLESO is adopted there. The block diagram of ADRC is illustrated in Figure 3.
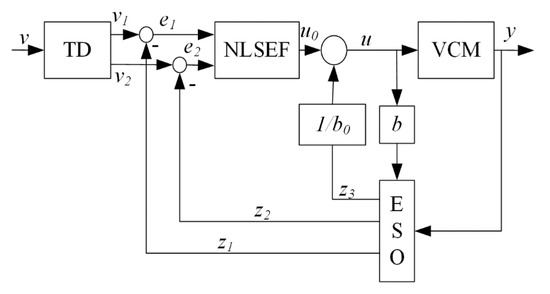
Figure 3.
Block diagram of ADRC.
First, TD is used to arrange the transition process for input variables and extract its differential signal, the implementation algorithm of the TD is as follows
where
Second, the implementation algorithm of the ESO is as follows
where
h is sampling step size.
Third, the implementation algorithm of the NLESO is as follows
where z3 is the estimate total disturbance; b0 is the “compensation factor” that determines the strength of compensation. It is a tunable parameter. The parameters in Equations (16) and (18) are calculated by the following formula:
Among them, r0 determines how fast the transition process follows the input. The parameters in ESO are determined by the sampling step size. The value of b0 affects the compensation strength of estimated z3. If the value is too small, then the compensation of z3 is too large. It will result in serious instability or oscillation of the system. In addition, its value should not be too large, otherwise the compensation effect on the disturbance is too small. β11, β12 are two coefficients in the nonlinear feedback, which is similar to the proportional and derivative terms in the PID, respectively.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Apparatus
To verify the control algorithm, a single-wheel electromagnetic active suspension system is designed. The experimental schematic diagram is presented in Figure 4a, and the experimental apparatus is demonstrated in Figure 4b. The device mainly includes a voice coil motor for providing control force, a coil spring for supporting the vehicle body, and a cam and servo motor for simulating road surface excitation. The wheel is attached to the mover of the voice coil motor, and the body is connected to the stator of the VCM.
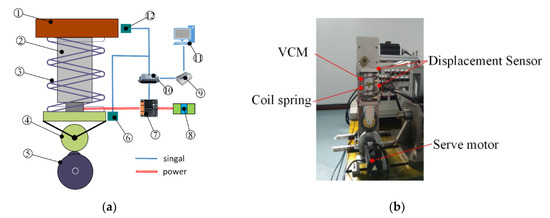
Figure 4.
Experimental Section apparatus: (a) schematic diagram; (b) Physical diagram. ① body; ② voice coil motor; ③ spring; ④ wheel; ⑤ servo motor and cam; ⑥ linear displacement sensor 1; ⑦ motor drive H-bridge; ⑧ battery; ⑨ USB-CAN module; ⑩ controller; ⑪ computer; ⑫ linear displacement sensor 2.
Two displacement sensors are used in the experiment to measure the body displacement and suspension travel. The voice coil motor is a single-phase DC motor driven by an H-bridge. The power supply voltage is 24V DC. The main control chip of the controller is the NXP 32-bit microprocessor MPC5744. The controller communicates with the computer through the CAN-USB module. The computer is used to record and calibrate the parameters of the controller in real time. The parameters of the system are given in Table 1. The suspension stiffness, damping coefficient, suspension mass and unsprung mass are from the design parameters. The motor parameters are from the product specifications. In addition, the measuring devices technical feature are given in Table 2.

Table 1.
System parameters in the quarter-car active suspension.

Table 2.
The measuring devices technical feature.
4.2. Simulation and Experimental Validation
One of the principal functions of the active suspension is to adjust the height of the car. Therefore, the vehicle step response is used to adjust the parameters of the controller. After careful adjustment, the proportional coefficient, integral coefficient, and differential coefficient of the PID controller are 2000, 10, and 60,000, respectively. In addition, the ADRC controller parameters are given in Table 3.

Table 3.
ADRC Controller parameters.
Figure 5 shows the comparison of the body step response of the two controllers. The overshoot of the PID controller and ADRC controller is approximately 0.005 m and 0.001 m, respectively. The overshoot of ADRC is 80% smaller than PID. This happens because the ADRC has arranged a transition to the input signal so that the output signal follows a smooth curve, thereby effectively preventing the large overshoot problem of the step response. However, this takes such ADRC control response slightly slower than the PID in the initial stage of the step response. The regulation time of ADRC is about 0.25 s, and the PID adjustment time is about 0.5 s. ADRC adjustment time is 50% lower than the PID. Because the extended state observer in ADRC controller can predict the system state and correct it in the control, it can achieve the stability faster.
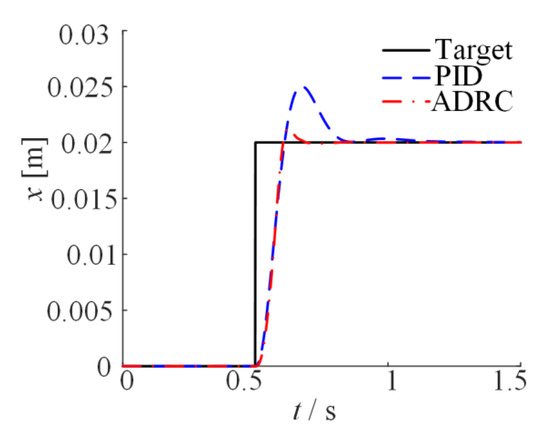
Figure 5.
Simulated body vertical displacement of ADRC and PID controller under step signal.
With the same controller parameters, the two control strategies are compared on a typical semi-sinusoidal road. Road excitation xr is shown in Figure 6, the excitation amplitude is 0.02 m, and the frequency of the sine wave is 10 rad/s.
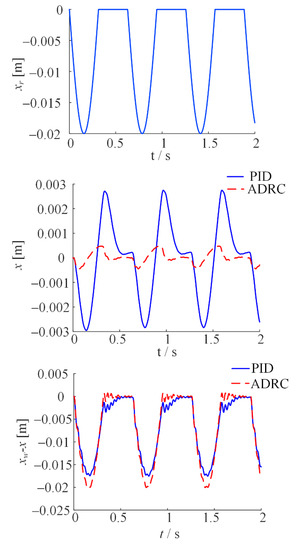
Figure 6.
Performance of the ADRC scheme and the PID controller under half sine road excitation.
The vehicle body displacement x and the suspension dynamic deflection xw-x under the two control strategies are shown in Figure 6. It can be observed that the displacement of the body under the ADRC control is about 0.5mm, and the displacement of the body under the PID control is about 3mm. The vibration amplitude of the ADRC decreases by 83%. The amplitude of body vibration is significantly smaller under the control of ADRC. This is because the PID controller only adjusts the control variable in real time through feedback. This leads to a certain delay of PID control force. Road impact can be regarded as an external disturbance, the extended state observer in ADRC can estimate the system disturbance in real time and compensate it in the control output. So ADRC achieving better control performance. It can be seen that the peak value of suspension dynamic deflection of ADRC is larger than 17.15% PID. which indicates that although ADRC provides better body stability, the impact will be slightly larger.
To verify the real-time performance and control ability of ADRC controller in practical application. The ADRC and PID control methods are compared in the test bench. In the test, the cam shown in the following figure is used as the road excitation, the servo motor drives the cam to rotate, and the motor speed is set as 50 rpm. Then the control model is converted into C code through the rapid prototype controller (RCP). The cam and the controller as shown in Figure 7. The controller collects the body displacement as feedback, and sets the body target position through the upper computer. Then record the body displacement. In the experiment, ADRC controller and PID both use the same control parameters as the simulation. In addition, experimental results of the PID controller and the ADRC controller are demonstrated in Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively.

Figure 7.
The cam for simulating road excitation and the RCP controller.
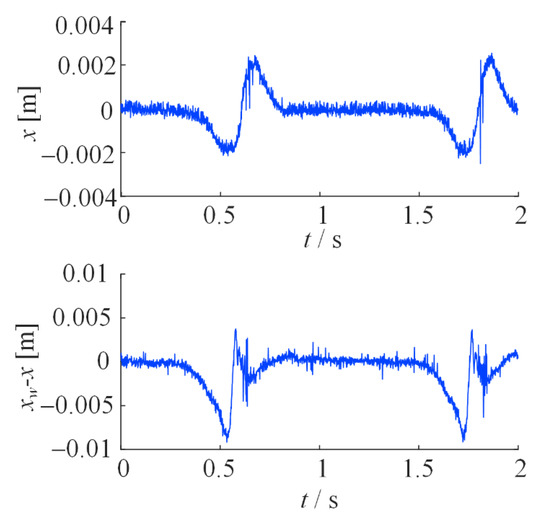
Figure 8.
Test results of PID control.
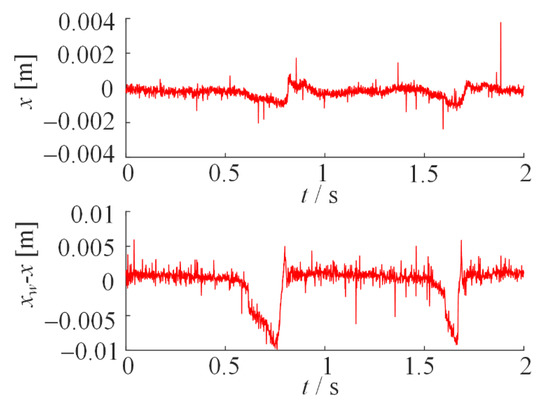
Figure 9.
Test results of ADRC control.
It can be observed that in the actual controller system, ADRC can still achieve better control effects than PID. The body displacement of the PID control is about 2mm, while the ADRC controls the body displacement to less than 1mm. The vibration amplitude of ADRC is reduced by more than 50%. This verifies that ADRC has good real-time performance and can be used in the actual control system. It also shows that the controller has strong adaptive ability. Although there are some deviations between the model and the real object, it has achieved good control results.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the VCM active suspension model is established. The ADRC method is used to control the active suspension with a VCM. In addition, the ADRC controller is designed to estimate and compensate for system uncertainties and disturbances. The simulation and experiment results indicate that the ADRC is able to estimate the disturbance in real time and compensate it actively. The ADRC controller has better dynamic response performance and stronger suppression of disturbance in comparison of PID controller. The overshoot and adjustment time of ADRC controller is reduced by 80% and 50%, respectively. The vibration amplitude of ADRC is decreased by more than 50% under the same road excitation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P. and W.W.; methodology, J.L. and F.P.; validation, J.L.; data curation, F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, F.P.; funding acquisition, W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: U1864210).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Theunissen, J.; Tota, A.; Gruber, P.; Dhaens, M.; Sorniotti, A. Preview-based techniques for vehicle suspension control: A state-of-the-art review. Annu. Rev. Control. 2021, 51, 206–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysen, B.; Paulides, J.; Janssen, J.; Lomonova, E.A. Active Electromagnetic Suspension System for Improved Vehicle Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2010, 59, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.K.; Wang, R.C.; Meng, X.P.; Liu, W.; Chen, L. Intelligent switching control of hybrid electromagnetic active suspension based on road identification. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 152, 107355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkareem, M.; Xu, L.; Guo, X.X.; Ali, M.; Elagouz, A.; Hassan, M.A.; Essa, F.A.; Zou, J.Y. Energy harvesting sensitivity analysis and assessment of the potential power and full car dynamics for different road modes. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2018, 110, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.K.; Wang, R.C.; Meng, X.P.; Chen, L. Study on coordinated control of the energy regeneration and the vibration isolation in a hybrid electromagnetic suspension. J. Automob. Eng. 2017, 231, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.H.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.C.; Jiang, H.B.; Shen, Y.J. Design and experiment study of a semi-active energy-regenerative suspension system. Smart Mater Struct. 2015, 24, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Pisu, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, R. Control design and fuel economy investigation of power split HEV with energy regeneration of suspension. Appl. Energ. 2016, 182, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lian, R.J. Design of a grey-prediction self-organizing fuzzy controller for active suspension systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 4162–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Du, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. Disturbance observer based Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy control for an active seat suspension. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 93, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.I.; Wang, H.P.; Tian, Y. Vibration control of an active vehicle suspension systems using optimized model-free fuzzy logic controller based on time delay estimation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 127, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.X.; Naghdy, F.; Du, H.P. Reliable fuzzy H-infinity control for active suspension of in-wheel motor driven electric vehicles with dynamic damping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 87, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Luo, X.X.; Xiao, J. Adaptive sliding fault tolerant control for nonlinear uncertain active suspension systems. J Franklin I 2016, 353, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Na, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.Q.; Guo, Y. Adaptive control of nonlinear uncertain active suspension systems with prescribed performance. ISA Trans. 2015, 54, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.C.; Chen, J.N.; Li, Y.F.; Li, L. Adaptive prescribed performance control of half-car active suspension system with unknown dead-zone input. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 111, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.H.; Sun, W.C.; Jing, X.J.; Gao, H.J.; Yao, J.Y. Adaptive tracking control for active suspension systems with non-ideal actuators. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 399, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.C.; Gao, H.J.; Kaynak, O. Adaptive Backstepping Control for Active Suspension Systems With Hard Constraints. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 18, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, C.C. Road-adaptive algorithm design of half-car active suspension system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sande, T.; Gysen, B.; Besselink, I.; Paulides, J.; Lomonova, E.A.; Nijmeijer, H. Robust control of an electromagnetic active suspension system: Simulations and measurements. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, G.G.; Yu, F. Modeling and μ Synthesis Control of Vehicle Active Suspension with Motor Actuator. Wseas Trans. Syst. 2012, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Chen, C.Z.; Yu, S.B. Robust non-fragile finite-frequency H-infinity static output-feedback control for active suspension systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 91, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T.J.; Sharp, R.S. On improving the performance of automotive semi-active suspension systems through road preview. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 217, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.A.; Wang, J.C.; Yao, M.; Kim, Y.B. Improved optimal sliding mode control for a non-linear vehicle active suspension system. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 395, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, L.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.N.; Xiong, Z.B. Multi-objective optimization of active suspension system in electric vehicle with In-Wheel-Motor against the negative electromechanical coupling effects. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 116, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H. Multi-objective control for uncertain nonlinear active suspension systems. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. From PID to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Duan, B.Y. Automatic disturbances rejection controller for precise motion control of permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 52, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Gao, L.Q.; Gao, Z. On stability analysis of active disturbance rejection control for nonlinear time-varying plants with unknown dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2007 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 3501–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.C.; Bai, W.Y.; Yang, S.; Song, K.; Huang, Y.; Xie, H. ADRC With Adaptive Extended State Observer and its Application to Air-Fuel Ratio Control in Gasoline Engines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5847–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.Q.; Pu, F.; Li, S.F.; Gao, Y. Lateral Path Tracking Control of Autonomous Land Vehicle Based on ADRC and Differential Flatness. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.Q.; Fu, M.Y.; Li, C.M.; Pu, F.; Xu, Y.W. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Active Suspension System of Tracked Vehicles with Gun. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Fuh, C.C.; Tung, P.C. Application of voice coil motors in active dynamic vibration absorbers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.C.; Cao, D.Q.; Wang, D.W.; Tang, J.; Nie, Y.F.; Huang, W.H. Design and Experimental Study of a VCM-Based Stewart Parallel Mechanism Used for Active Vibration Isolation. Energies 2015, 8, 8001–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).