Whole-Body Control for a Torque-Controlled Legged Mobile Manipulator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
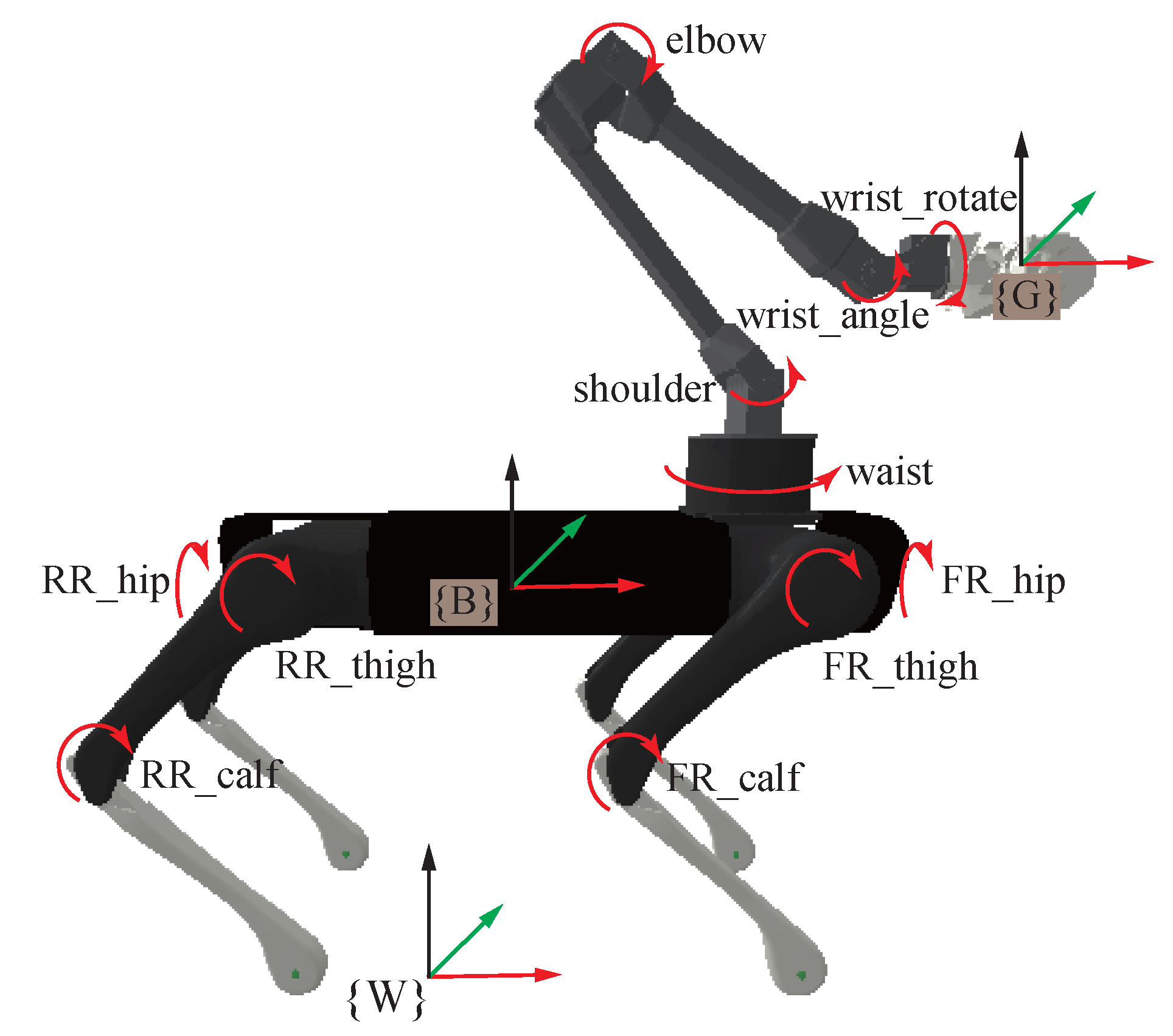
2. Model Formulation
3. Whole-Body Control
4. Simulation Studies
4.1. Walking Pivot
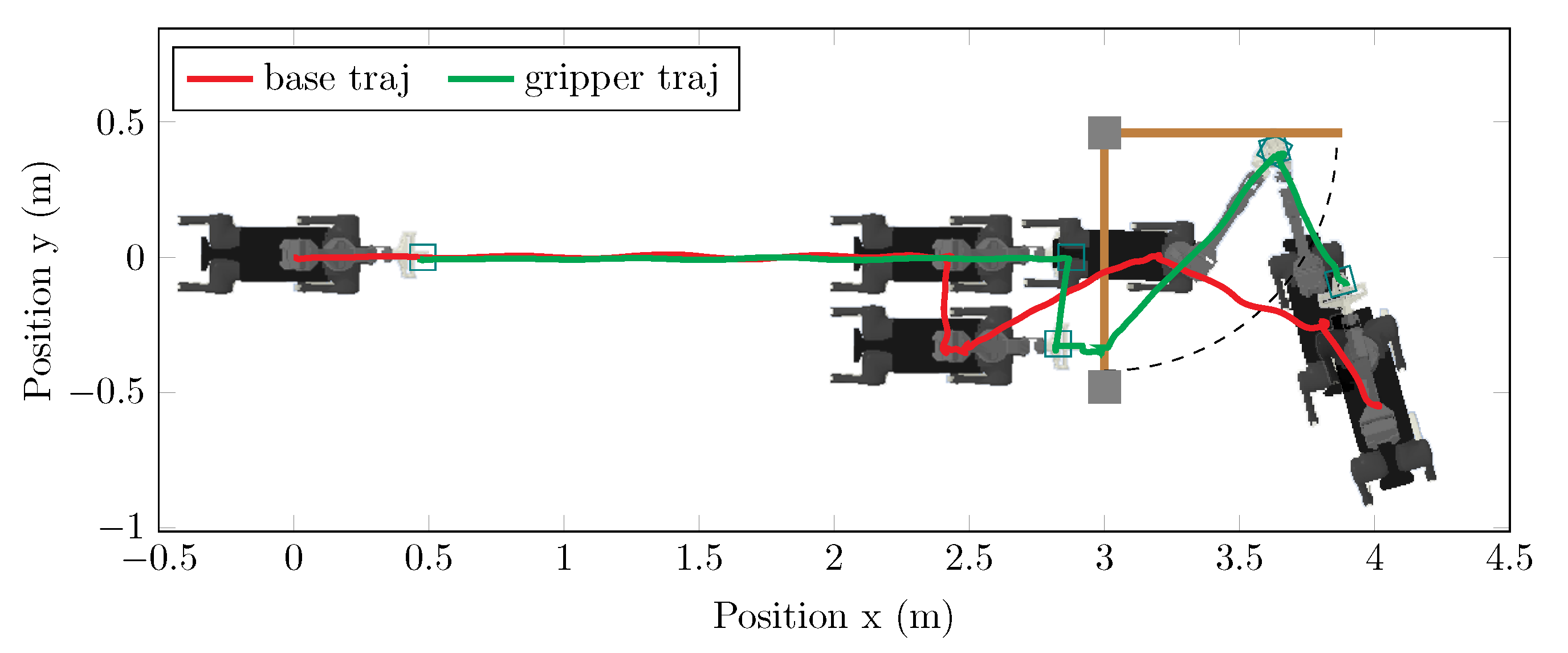
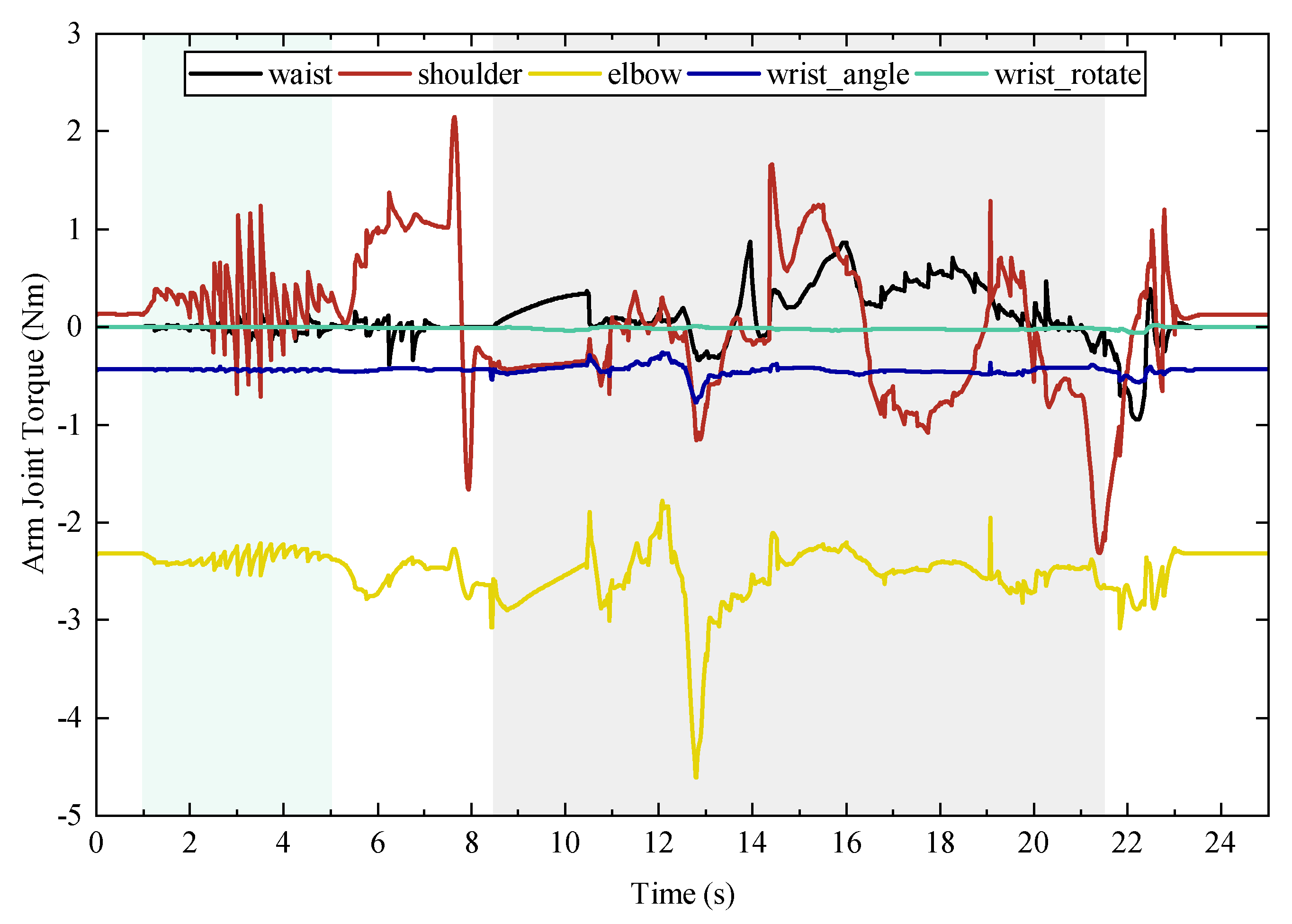
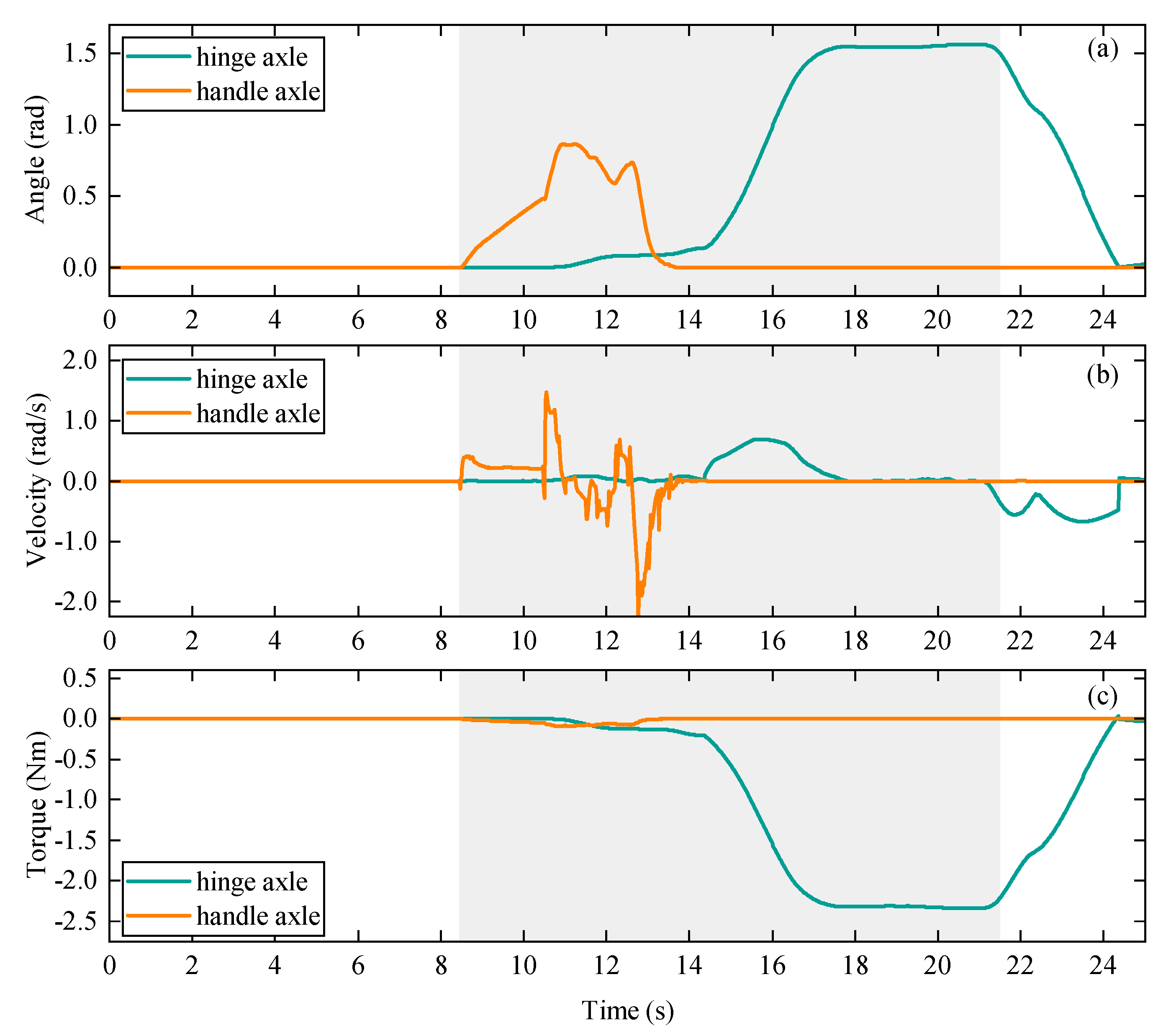
4.2. Spring-Loaded Door Opening
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| WBC | Whole body controller |
| IK | Inverse kinematics |
| ID | Inverse dynamics |
| QP | Quadratic Program |
| HQP | Hierarchical quadratic programming |
| SDK | Software development kit |
References
- Carlo, J.D.; Wensing, P.M.; Katz, B.; Bledt, G.; Kim, S. Dynamic Locomotion in the MIT Cheetah 3 Through Convex Model-Predictive Control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Carballo, D.; Di Carlo, J.; Katz, B.; Bledt, G.; Lim, B.; Kim, S. Vision Aided Dynamic Exploration of Unstructured Terrain with a Small-Scale Quadruped Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 2464–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B. Balance control based on six-dimensional spatial mechanics and velocity adjustment through region intervention and foot landing for quadruped robot. Robotica 2022, 40, 855–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, P.; Mohanty, P. Modeling and Effective Foot Force Distribution for the Legs of a Quadruped Robot. Robotica 2021, 39, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhornyak, L.; Emami, M. Gait Optimization for Quadruped Rovers. Robotica 2020, 38, 1263–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Liu, J.; Jia, Y. Dynamic Modeling and Control of Deformable Linear Objects for Single-Arm and Dual-Arm Robot Manipulations. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Liang, D.; Gao, H.; Li, W.; Tavakoli, M. Dual-User Haptic Teleoperation of Complementary Motions of a Redundant Wheeled Mobile Manipulator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 6283–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Whitman, E.; Xinjilefu, X.; Atkeson, C.G. Optimization-Based Full Body Control for the DARPA Robotics Challenge. J. Field Robot. 2015, 32, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuindersma, S.; Deits, R.; Fallon, M.; Valenzuela, A.; Dai, H.; Permenter, F.; Koolen, T.; Marion, P.; Tedrake, R. Optimization-Based Locomotion Planning, Estimation, and Control Design for the Atlas Humanoid Robot. Auton. Robot. 2016, 40, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, B.U.; Focchi, M.; Lee, J.; Dallali, H.; Caldwell, D.G.; Semini, C. Towards a multi-legged mobile manipulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3618–3624. [Google Scholar]
- Risiglione, M.; Barasuol, V.; Caldwell, D.G.; Semini, C. A Whole-Body Controller Based on a Simplified Template for Rendering Impedances in Quadruped Manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.A.; Kim, J.; Pandala, A. Quadrupedal Locomotion via Event-Based Predictive Control and QP-Based Virtual Constraints. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4463–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Stephens, B.; Murphy, M.P.; Rizzi, A.A. Dynamic whole-body robotic manipulation. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Systems Technology XV, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17 May 2013; pp. 3618–3624. [Google Scholar]
- Bellicoso, C.D.; Krämer, K.; Stäuble, M.; Sako, D.; Jenelten, F.; Bjelonic, M.; Hutter, M. ALMA-Articulated Locomotion and Manipulation for a Torque-Controllable Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 8477–8483. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiman, J.P.; Farshidian, F.; Minniti, M.V.; Hutter, M. A Unified MPC Framework for Whole-Body Dynamic Locomotion and Manipulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4688–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Zeng, F.; Qin, K. Loco-Manipulation Control for Arm-Mounted Quadruped Robots: Dynamic and Kinematic Strategies. Machines 2022, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Fang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Tsagarakis, N. A generic optimization-based framework for reactive collision avoidance in bipedal locomotion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 21–24 August 2016; pp. 1026–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, J.; Peers, C.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Sun, J.; Richardson, R.; Zhou, C. Teleoperating a Legged Manipulator through Whole-Body Control. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems, Oxford, UK, 1 September 2022; pp. 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Carlo, J.D.; Katz, B.; Bledt, G.; Kim, S. Highly dynamic quadruped locomotion via whole-body impulse control and model predictive control. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.06586. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Whitman, E.; Xinjilefu, X.; Atkeson, C.G. Optimization Based Full Body Control for the Atlas Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Xin, S.; Zhou, C.; Tsagarakis, N. Straight leg walking strategy for torque-controlled humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 2014–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bellicoso, C.D.; Gehring, C.; Hwangbo, J.H.; Fankhauser, P.; Hutter, M. Perception-less Terrain Adaptation through Whole Body Control and Hierarchical Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 November 2016; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Kuindersma, S.; Permenter, F.; Tedrake, R. An efficiently solvable quadratic program for stabilizing dynamic locomotion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 2589–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, A.; Rotella, N.; Mason, S.; Grimminger, F.; Schaal, S.; Righetti, L. Momentum control with hierarchical inverse dynamics on a torque-controlled humanoid. Auton. Robot. 2016, 40, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Peers, C.; Xin, S.; Zhou, C. Opening a Spring-Loaded Door with a Legged Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 5th UK Robotics and Autonomous Systems Conference, Aberystwyth, UK, 26 August 2022; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Peers, C.; Motawei, M.; Richardson, R.; Zhou, C. Development of a Teleoperative Quadrupedal Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 4th UK-RAS Conference, Hatfield, UK, 2 June 2021; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier, J.; Saurel, G.; Buondonno, G.; Mirabel, J.; Lamiraux, F.; Stasse, O.; Mansard, N. The Pinocchio C++ library: A fast and flexible implementation of rigid body dynamics algorithms and their analytical derivatives. In Proceedings of the IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, Paris, France, 14–16 January 2019; pp. 614–619. [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier, J.; Valenza, F.; Mansard, N. Pinocchio: Fast forward and Inverse Dynamics for Poly-Articulated Systems. 2015–2019. Available online: https://stack-of-tasks.github.io/pinocchio (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Ayusawa, K.; Venture, G.; Nakamura, Y. Identifiability and identification of inertial parameters using the underactuated base-link dynamics for legged multibody systems. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 446–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; An, H.; Ma, H. Modeling and base parameters identification of legged robots. Robotica 2022, 40, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, E.; Bai, Y. Pybullet, a Python Module for Physics Simulation for Games, Robotics and Machine Learning. 2016. Available online: https://pybullet.org/wordpress/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Stellato, B.; Banjac, G.; Goulart, P.; Bemporad, A.; Boyd, S. OSQP: An operator splitting solver for quadratic programs. Math. Program. Comput. 2020, 12, 637–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Priority | Task | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Dynamic consistency | 1 |
| Torque saturation limits | 1 | |
| Contact force limits | 1 | |
| 1 | Contact motion task | 1 |
| 2 | Base position control task | 1 |
| Base orientation control task | 1 | |
| Swing foot position control task | 0.5 | |
| Gripper position control task | 1 | |
| Gripper orientation control task | 0.65 | |
| 3 | Minimum motion task | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Gao, H.; Wan, Y.; Humphreys, J.; Peers, C.; Yu, H.; Zhou, C. Whole-Body Control for a Torque-Controlled Legged Mobile Manipulator. Actuators 2022, 11, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110304
Li J, Gao H, Wan Y, Humphreys J, Peers C, Yu H, Zhou C. Whole-Body Control for a Torque-Controlled Legged Mobile Manipulator. Actuators. 2022; 11(11):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jun, Haibo Gao, Yuhui Wan, Joseph Humphreys, Christopher Peers, Haitao Yu, and Chengxu Zhou. 2022. "Whole-Body Control for a Torque-Controlled Legged Mobile Manipulator" Actuators 11, no. 11: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110304
APA StyleLi, J., Gao, H., Wan, Y., Humphreys, J., Peers, C., Yu, H., & Zhou, C. (2022). Whole-Body Control for a Torque-Controlled Legged Mobile Manipulator. Actuators, 11(11), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11110304









