Design and Characterization of an Electrostatic Constant-Force Actuator Based on a Non-Linear Spring System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
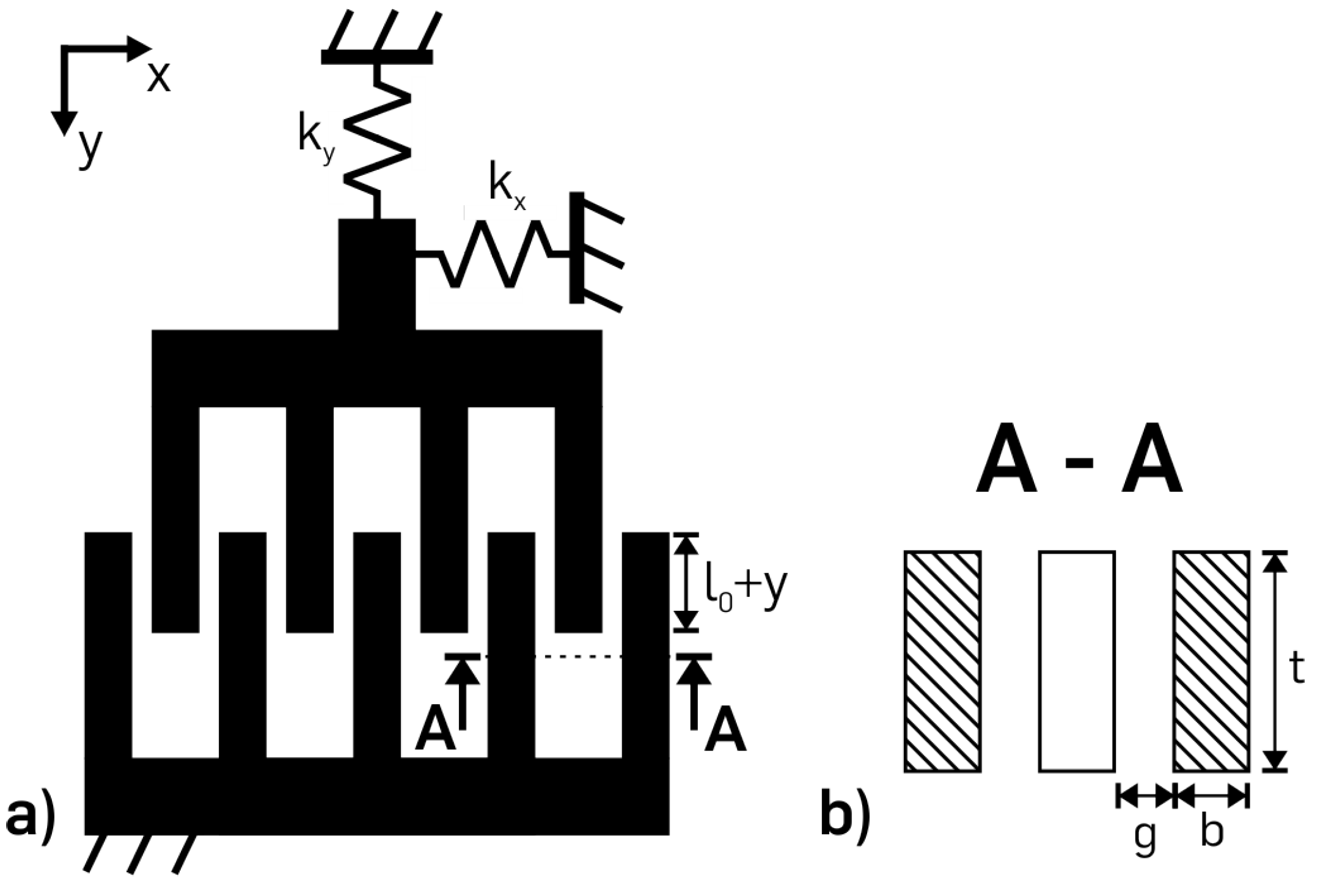
2.1. Electrostatic Comb Drive Actuator
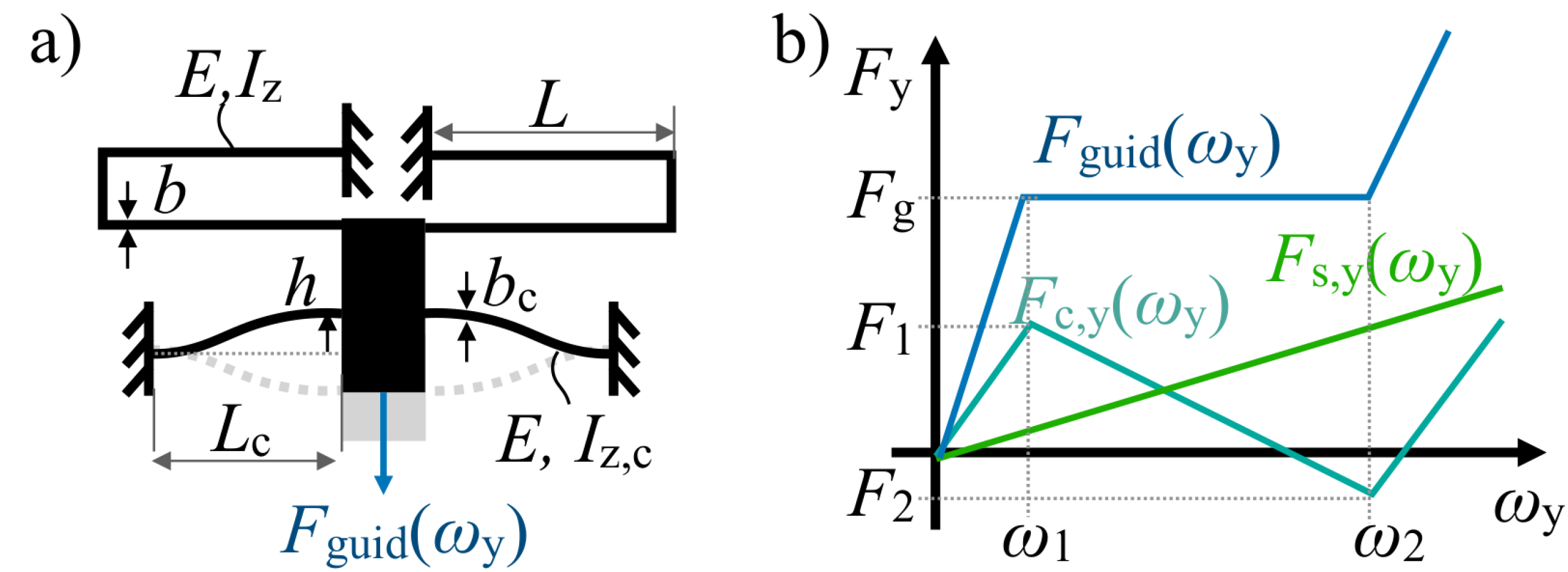
2.2. Non-Linear Spring System
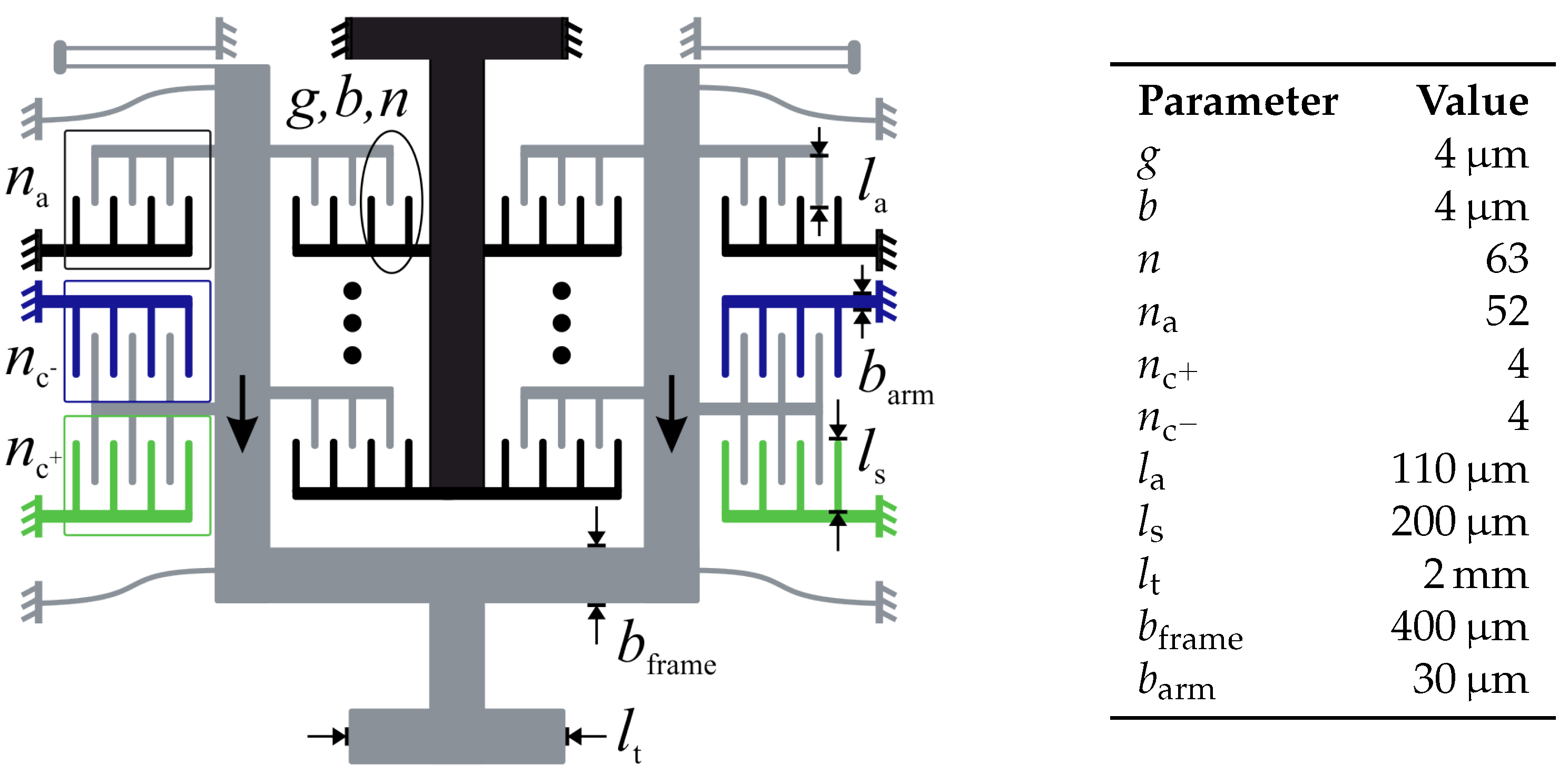
2.3. Design of the Constant-Force Generator
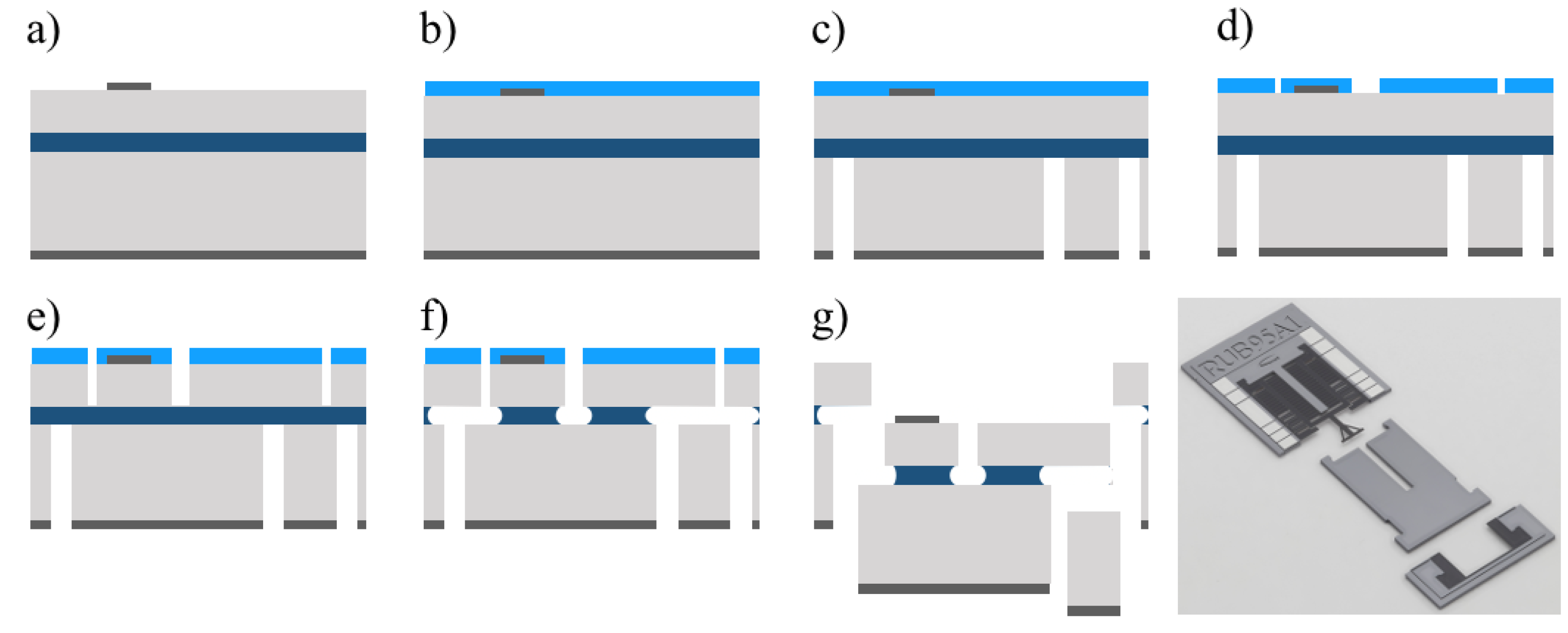
2.4. Fabrication Process
2.5. Electronical Voltage Control
2.6. Experimental Setup for the Force Measurement
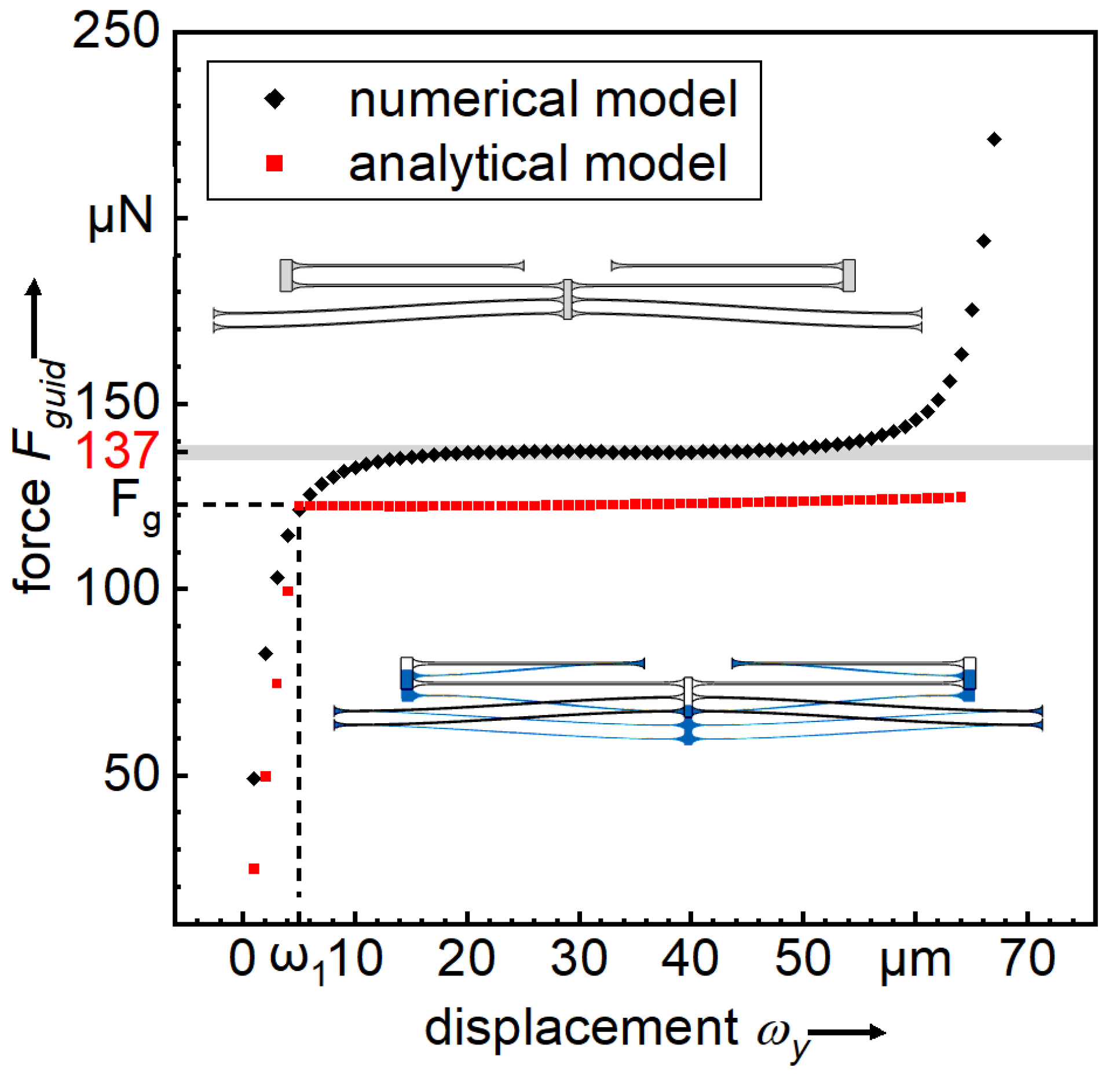
3. Experiments and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PWM | Pulse width modulation |
| SOI | Silicon-on-insulator |
| PCB | printed circuit board |
Appendix A. Electrical Components
| Component | Value | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 47 k | - | |
| 1 k | - | |
| 4.7 k | - | |
| 1 k | - | |
| NPN transistor | - | ON 2N5551 160 V bipolar junction transistor |
| 1 M | - | |
| 10 nF | - | |
| 1 M | - | |
| 10 nF | - | |
| Relay | - | KY-019 5V magnetic relay |
| 100 k | - | |
| 470 | - | |
| 1 M | - |
References
- Bueche, F. The Viscoelastic Properties of Plastics. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, N.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Mechanical stimulation of mesenchymal stem cells: Implications for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Qing, H.; Gao, C.F. Exact solutions for bending of Timoshenko curved nanobeams made of functionally graded materials based on stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Compos. Struct. 2020, 245, 112362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnola, F.; Faghidian, S.A.; Barretta, R.; de Sciarra, F.M. Variationally consistent dynamics of nonlocal gradient elastic beams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2020, 149, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apuzzo, A.; Barretta, R.; Faghidian, S.; Luciano, R.; de Sciarra, F.M. Nonlocal strain gradient exact solutions for functionally graded inflected nano-beams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Q. Design and simulation of a passive-type constant-force MEMS microgripper. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macao, China, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 1100–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, Q. Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism. Actuators 2018, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legtenberg, R.; Groeneveld, A.W.; Elwenspoek, M. Comb-drive actuators for large displacements. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1996, 6, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sari, I.; Zeimpekis, I.; Kraft, M. A dicing free SOI process for MEMS devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 95, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goj, B. Entwicklung Eines Dreiachsigen Taktilen Mikromesssystems in Siliicum-Technologie. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Ilmenau, Ilmenau, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, G. Die Grundlagen der Elektrostatik. In Elektromagnetische Feldtheorie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 43–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leondes, C.T. MEMS/NEMS: Handbook Techniques and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chang, I.C.M.; Chen, R.; Hou, M.T.K. On the side instability of comb-fingers in MEMS electrostatic devices. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2008, 148, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, W.K. Introduction to Microsystem Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, P.; Schmitt, L.; Tsivin, N.; Hoffmann, M. Highly Selective Guiding Springs for Large Displacements in Surface MEMS. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Lang, J.; Slocum, A. A Curved-Beam Bistable Mechanism. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, S.; Lahmer, T.; Rabczuk, T. Detection of flaws in piezoelectric structures using extended (FEM). Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2013, 96, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.; Schmitt, P.; Barowski, J.; Hoffmann, M. Stepwise Electrostatic Actuator System for THz Reflect Arrays. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR; International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications, Online, 17–19 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Lu, G. Analysis of lateral instability of in-plane comb drive MEMS actuators based on a two-dimensional model. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2004, 113, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, I.P.M.; Berg, J.M. Lateral stability of a periodically forced electrostatic comb drive. In Proceedings of the 2012 American Control Conference (ACC), Montréal, QC, Canada, 27–29 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, U.; Schenk, C.; Gamm, E. Halbleiter-Schaltungstechnik, 16th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Göbel, H. Einführung in die Halbleiter-Schaltungstechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments. FDC1004Q 4-Channel Capacitance-to-Digital Converter for Capacitive Sensing Solutions; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sartorius Mechatronics. Die WZA-N Serie—OEM Wägezellen; Sartorius Weighing Technology GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Physik Instrumente (PI). Q-Motion Präzisions-Lineartisch; Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co. KG: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, P.; Hoffmann, M. Engineering a Compliant Mechanical Amplifier for MEMS Sensor Applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2020, 29, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


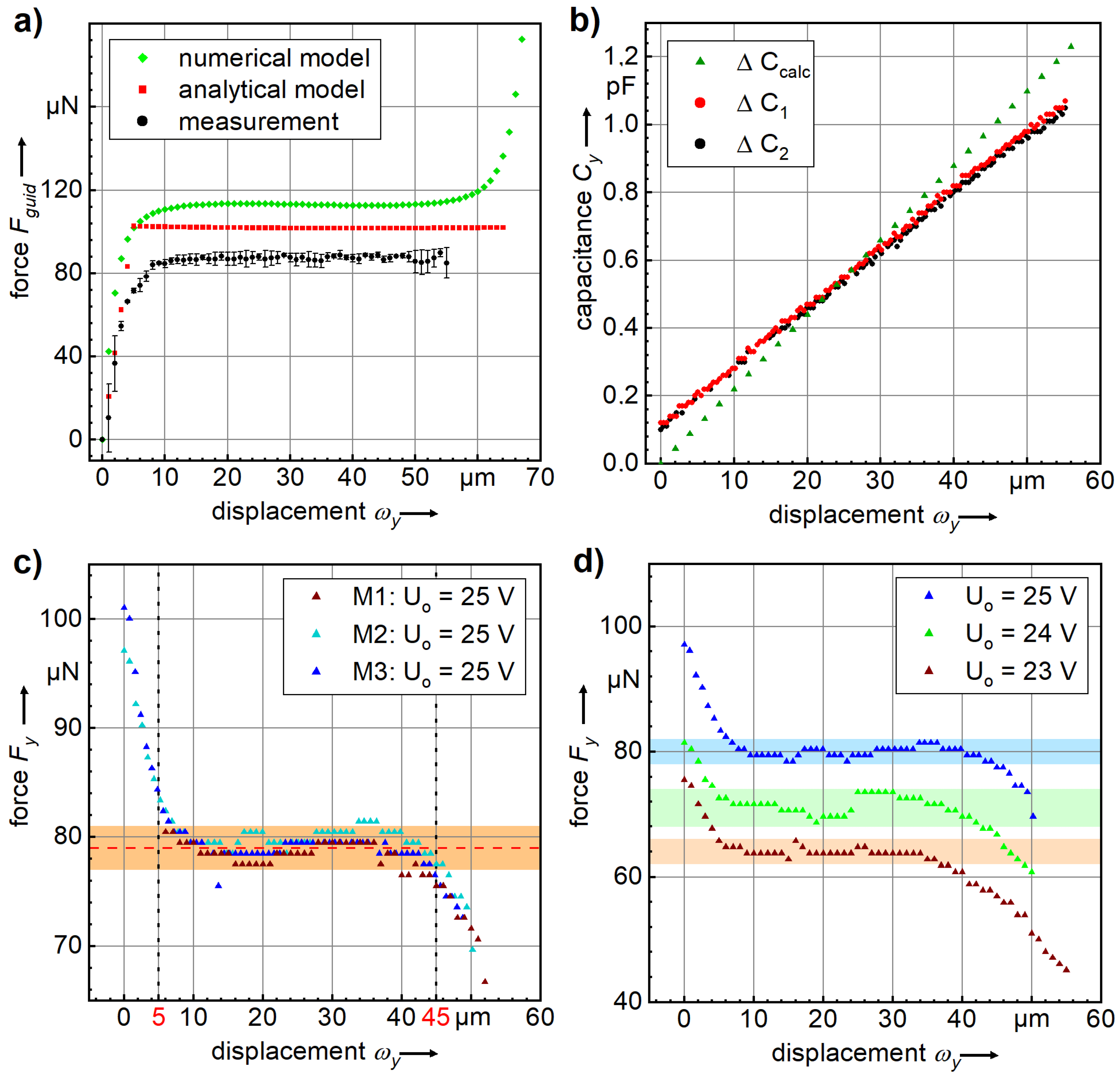
| Operating Voltage [V] | Constant-Force [N] | Displacement Range [m] |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | 35 | |
| 24 | 37 | |
| 25 | 40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thewes, A.C.; Schmitt, P.; Löhler, P.; Hoffmann, M. Design and Characterization of an Electrostatic Constant-Force Actuator Based on a Non-Linear Spring System. Actuators 2021, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080192
Thewes AC, Schmitt P, Löhler P, Hoffmann M. Design and Characterization of an Electrostatic Constant-Force Actuator Based on a Non-Linear Spring System. Actuators. 2021; 10(8):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080192
Chicago/Turabian StyleThewes, Anna Christina, Philip Schmitt, Philipp Löhler, and Martin Hoffmann. 2021. "Design and Characterization of an Electrostatic Constant-Force Actuator Based on a Non-Linear Spring System" Actuators 10, no. 8: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080192
APA StyleThewes, A. C., Schmitt, P., Löhler, P., & Hoffmann, M. (2021). Design and Characterization of an Electrostatic Constant-Force Actuator Based on a Non-Linear Spring System. Actuators, 10(8), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080192






