Design and Characterization of a Planar Motor Drive Platform Based on Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shell Resonators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
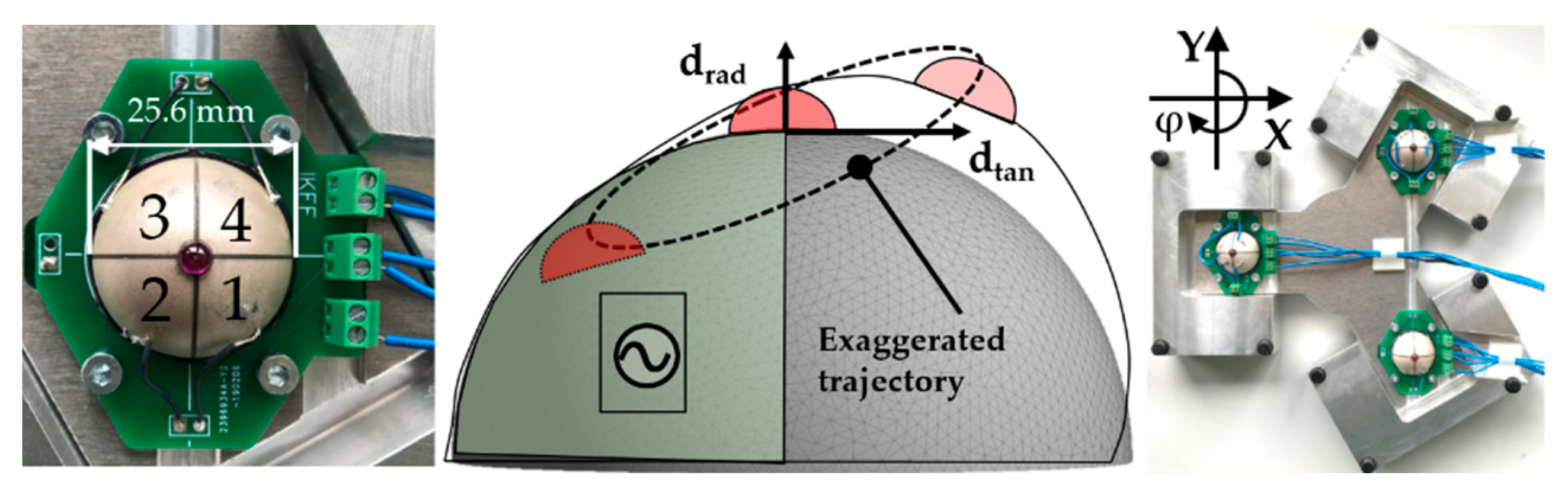
2.1. Ultrasonic Standing Wave Resonators Made of Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shells
2.2. Mechanical Design of the Planar Motor Drive Platform
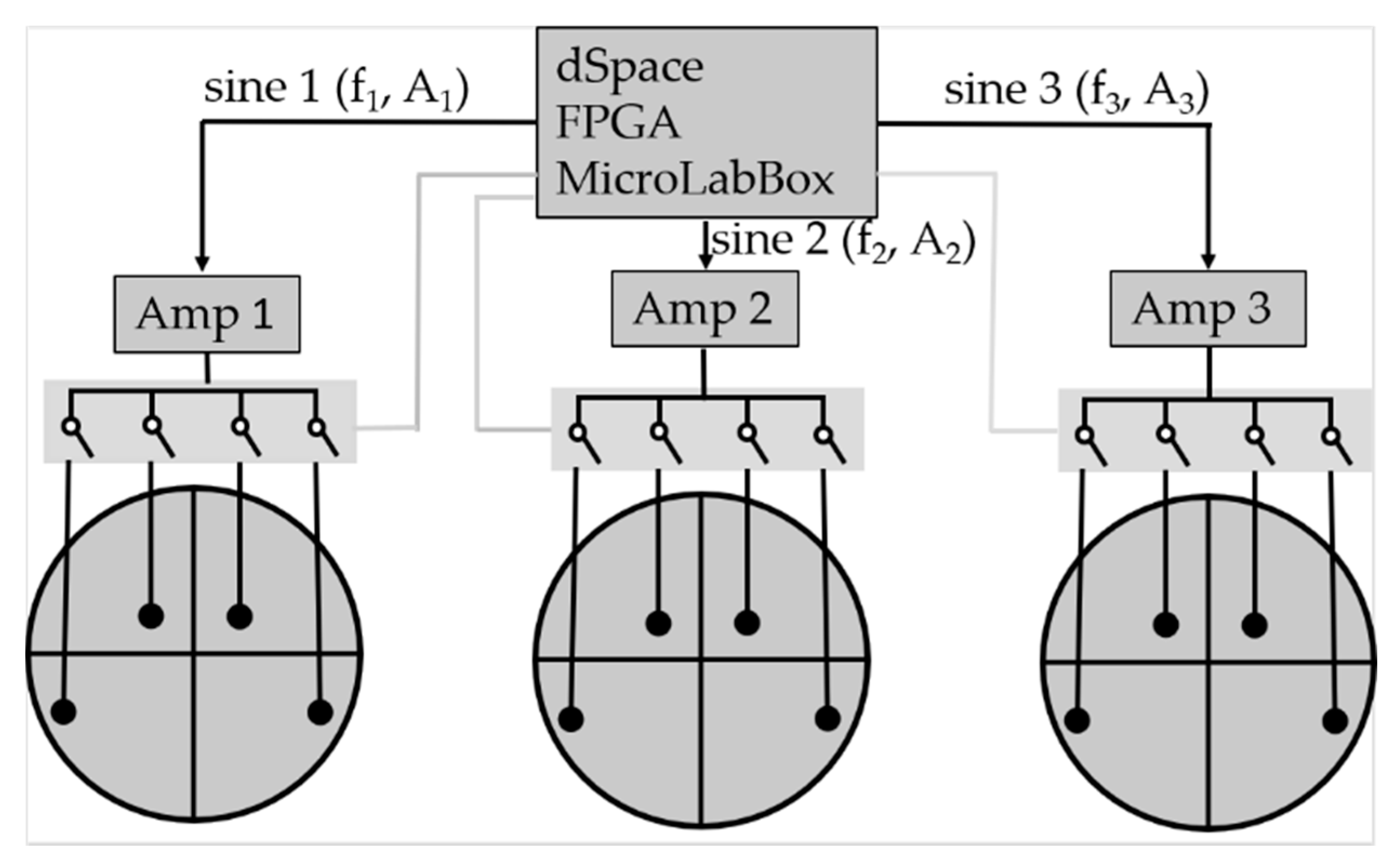
2.3. Electrical Design to Control the Platform
3. Measurements and Results
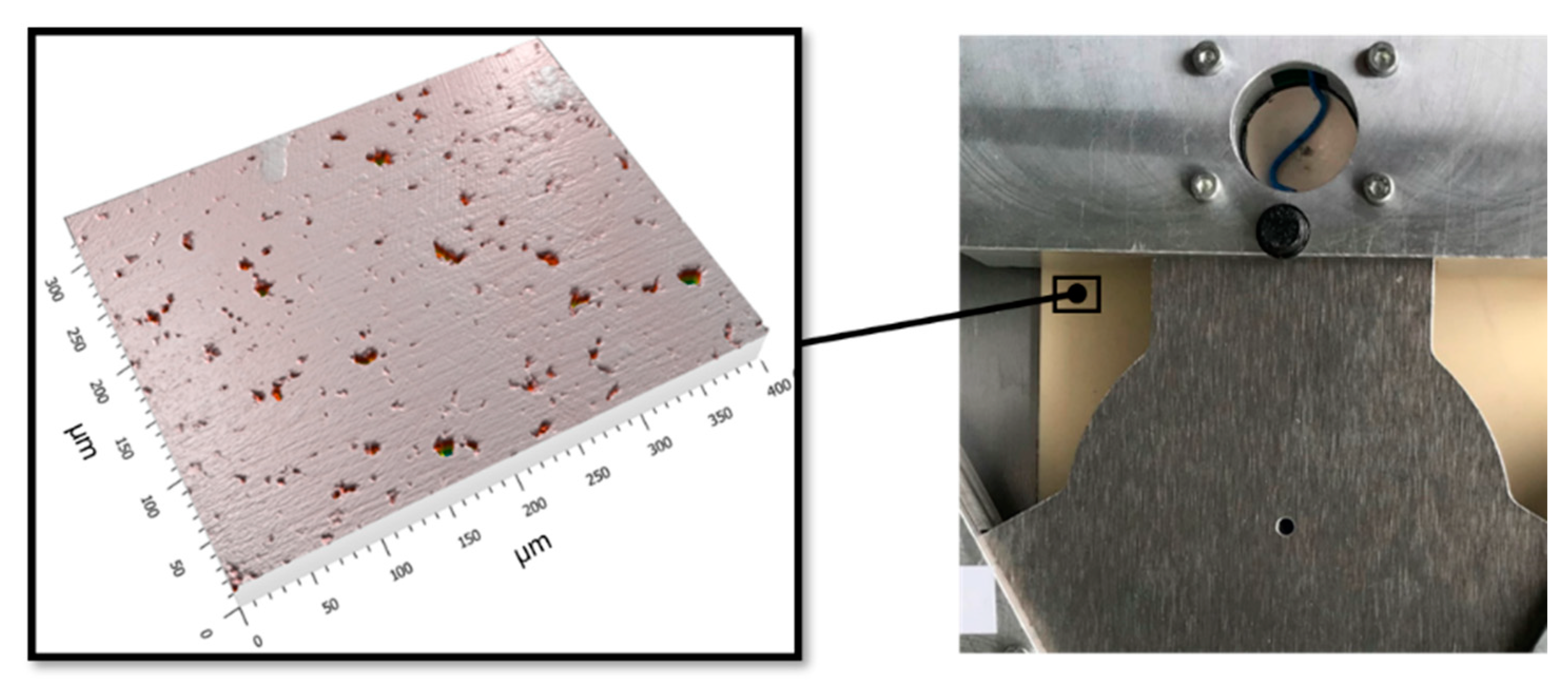
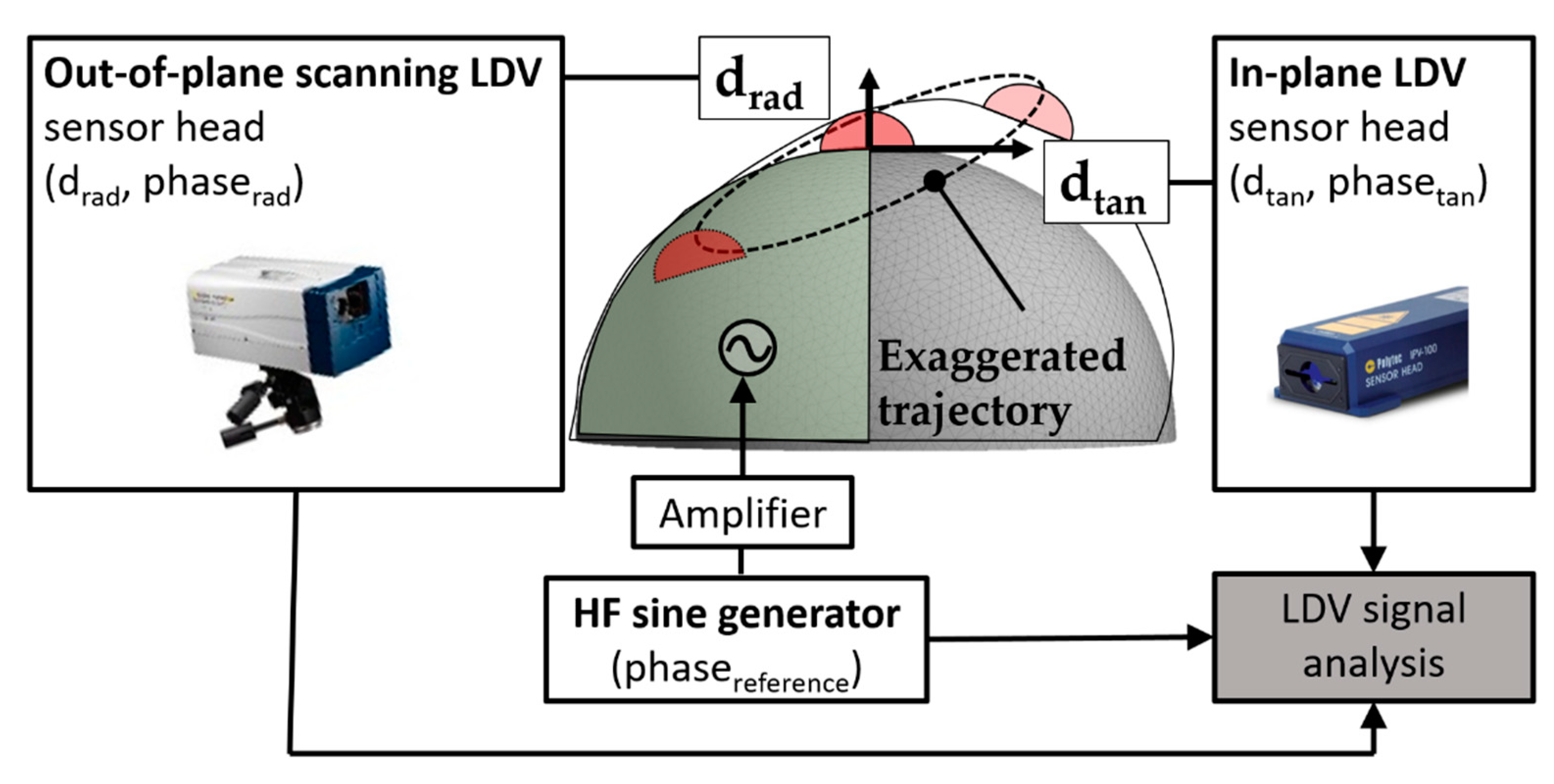
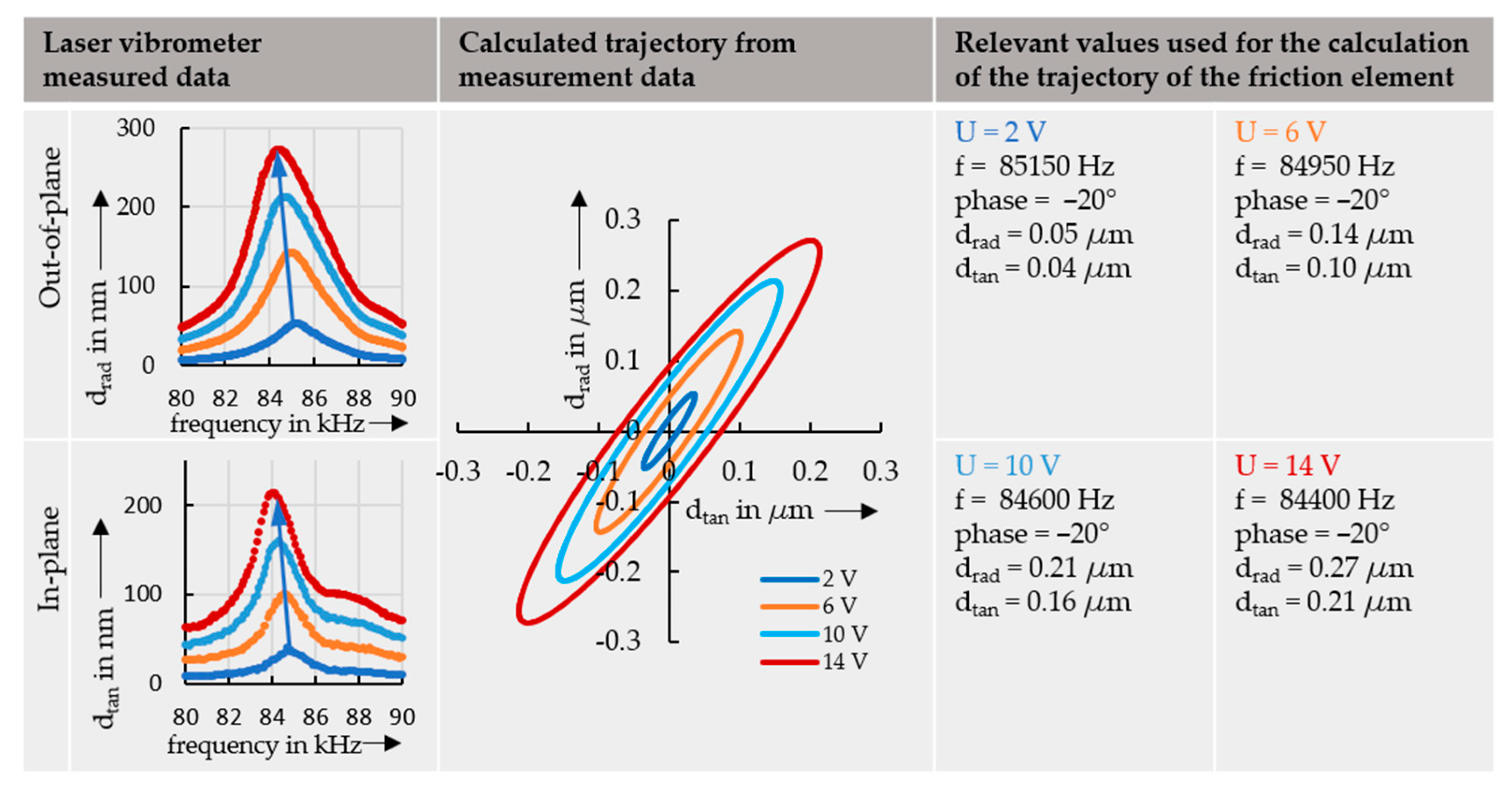
3.1. Measurements of Deflection of the Friction Contact in Free-Swinging Mode
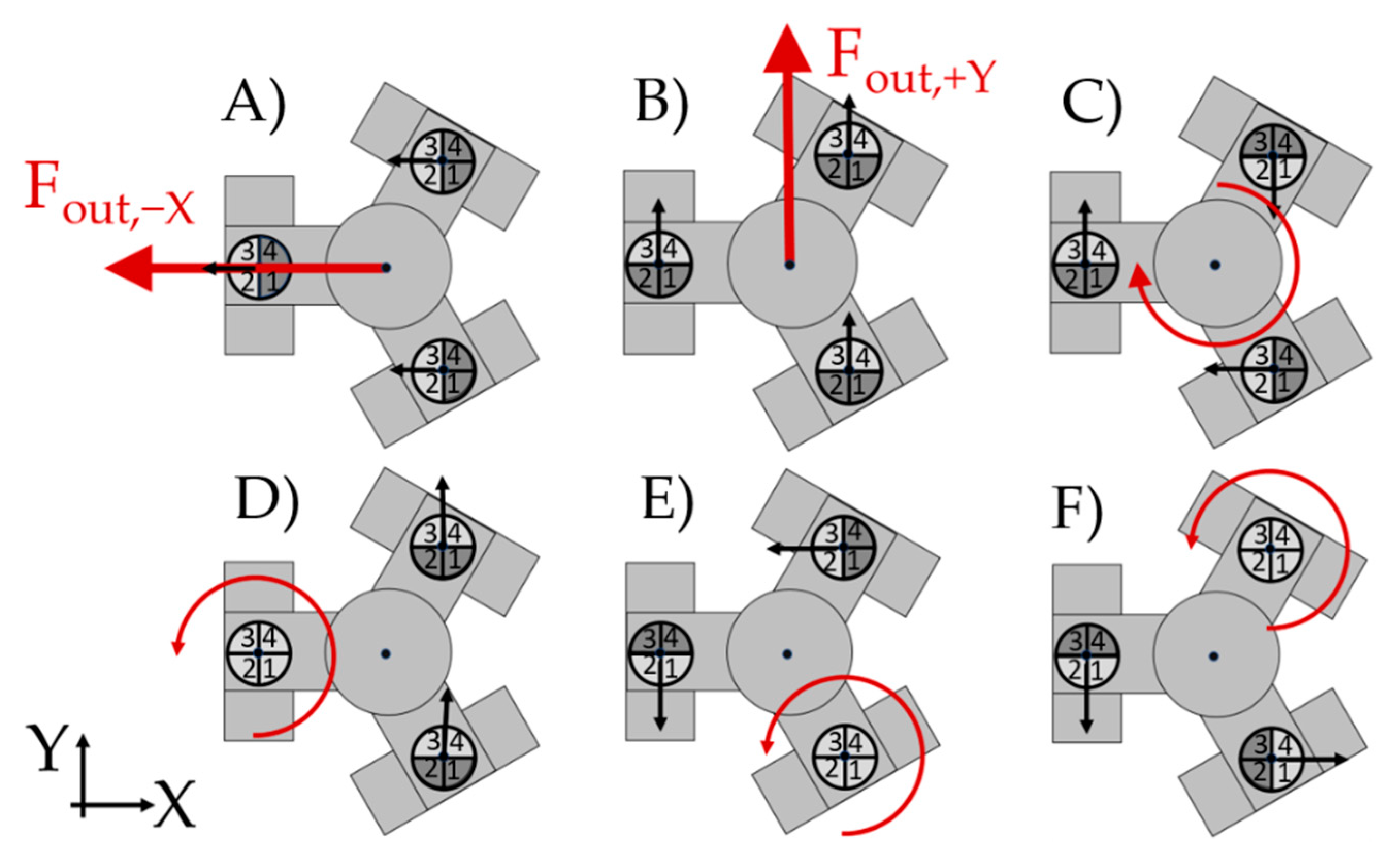
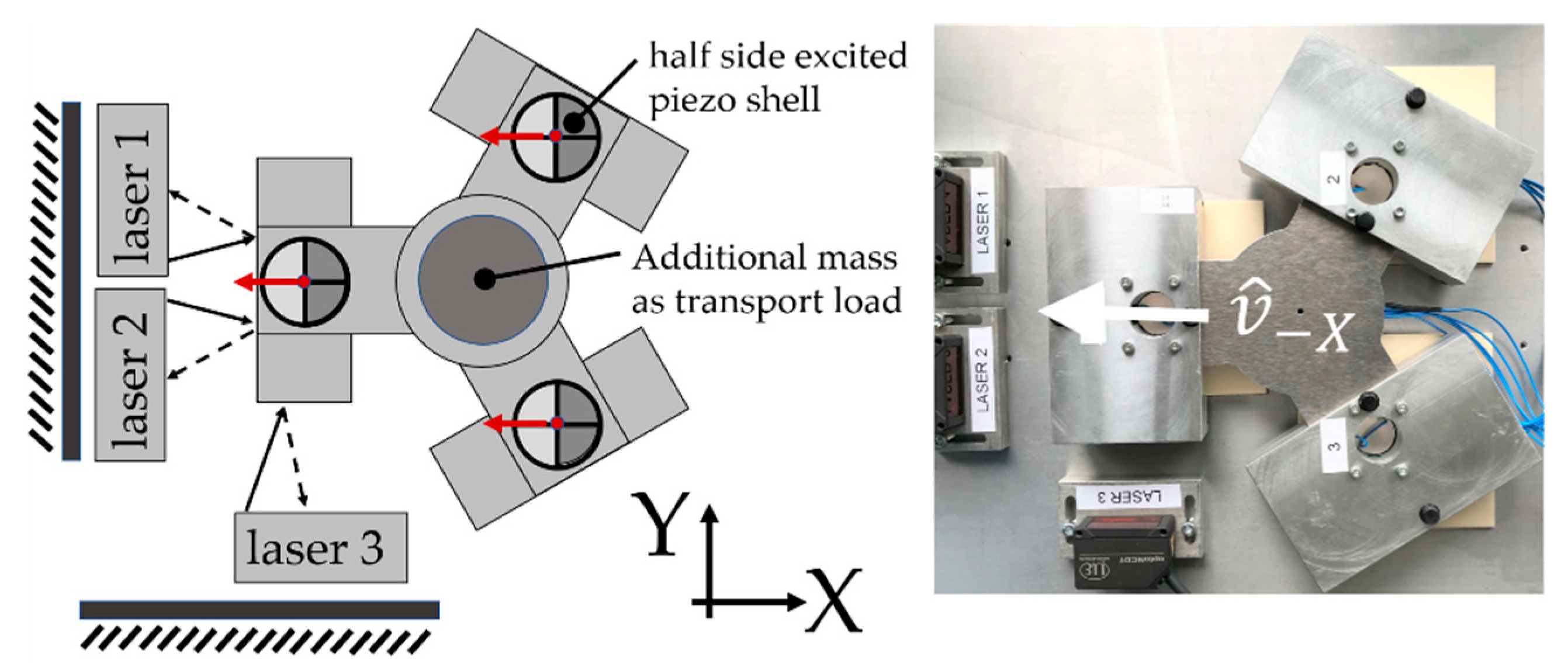
3.2. Measurements of the Maximum Drive Velocity
3.2.1. Velocity Measurements in the −X Direction
3.2.2. Velocity Measurements in the +Y Direction
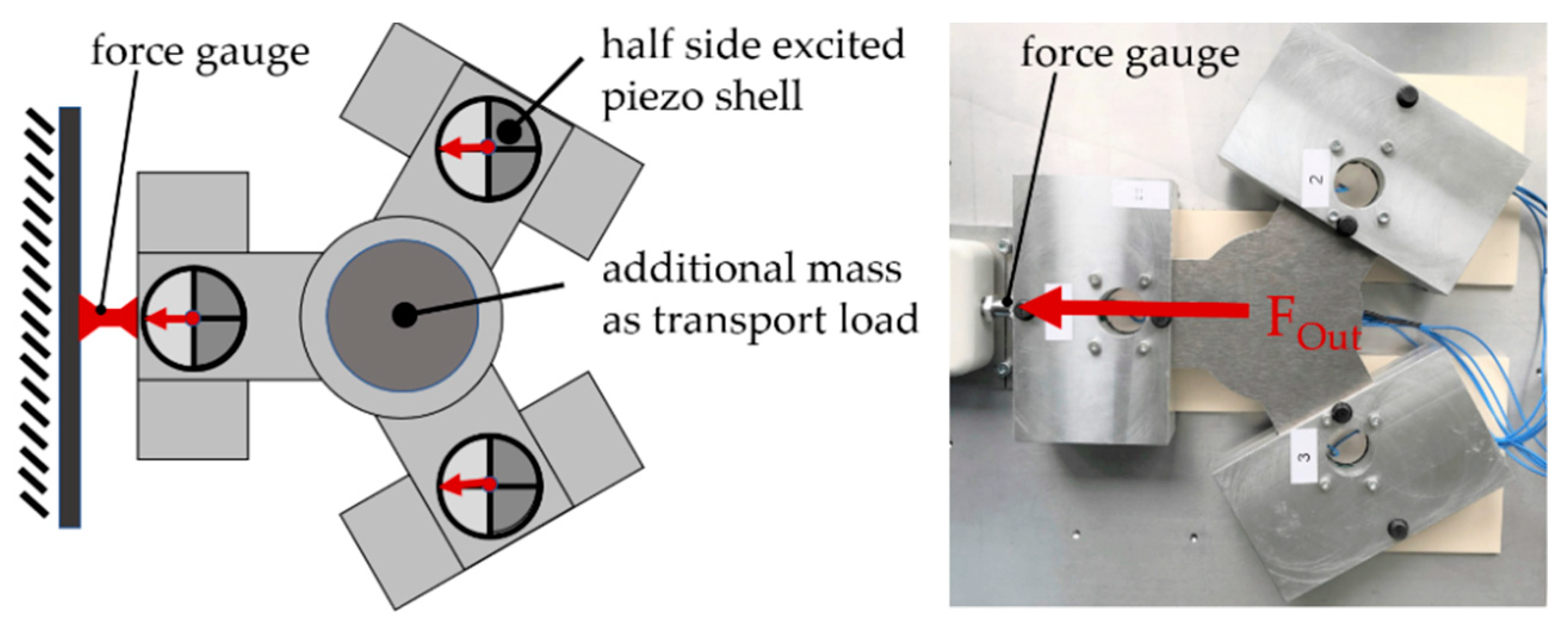
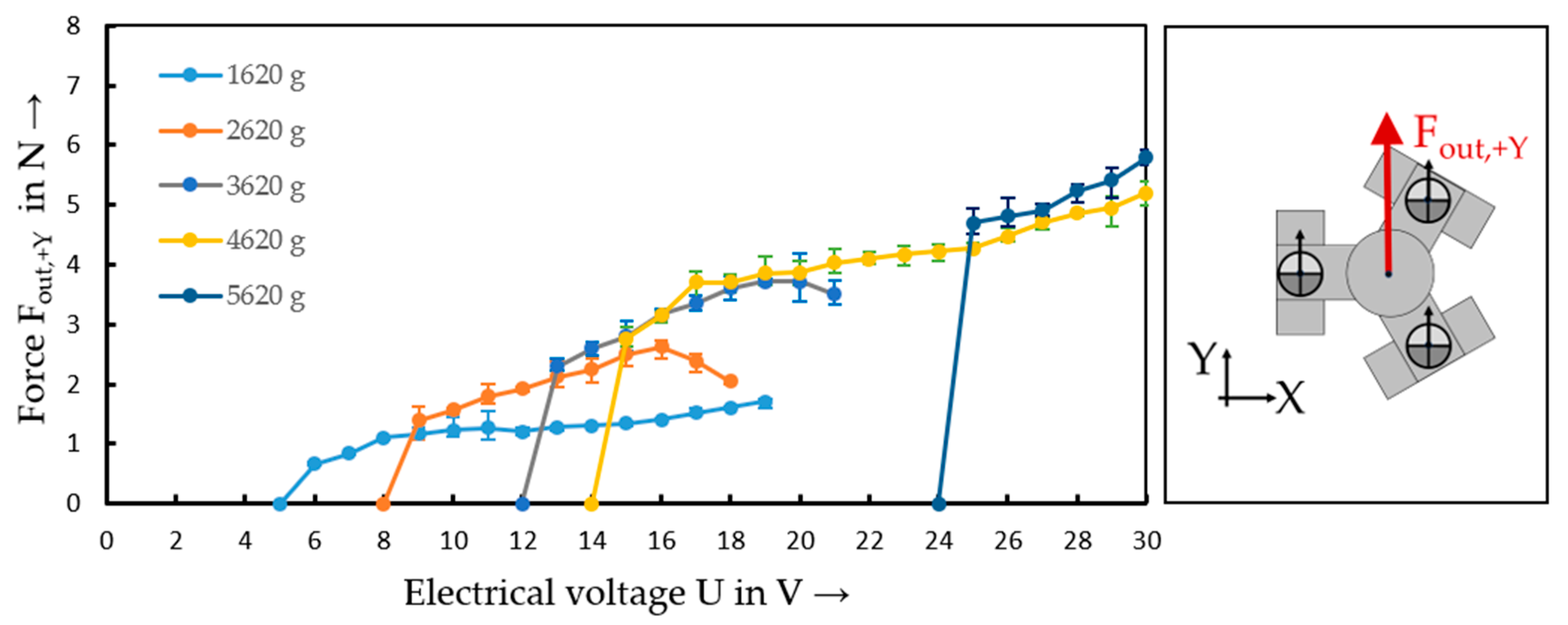
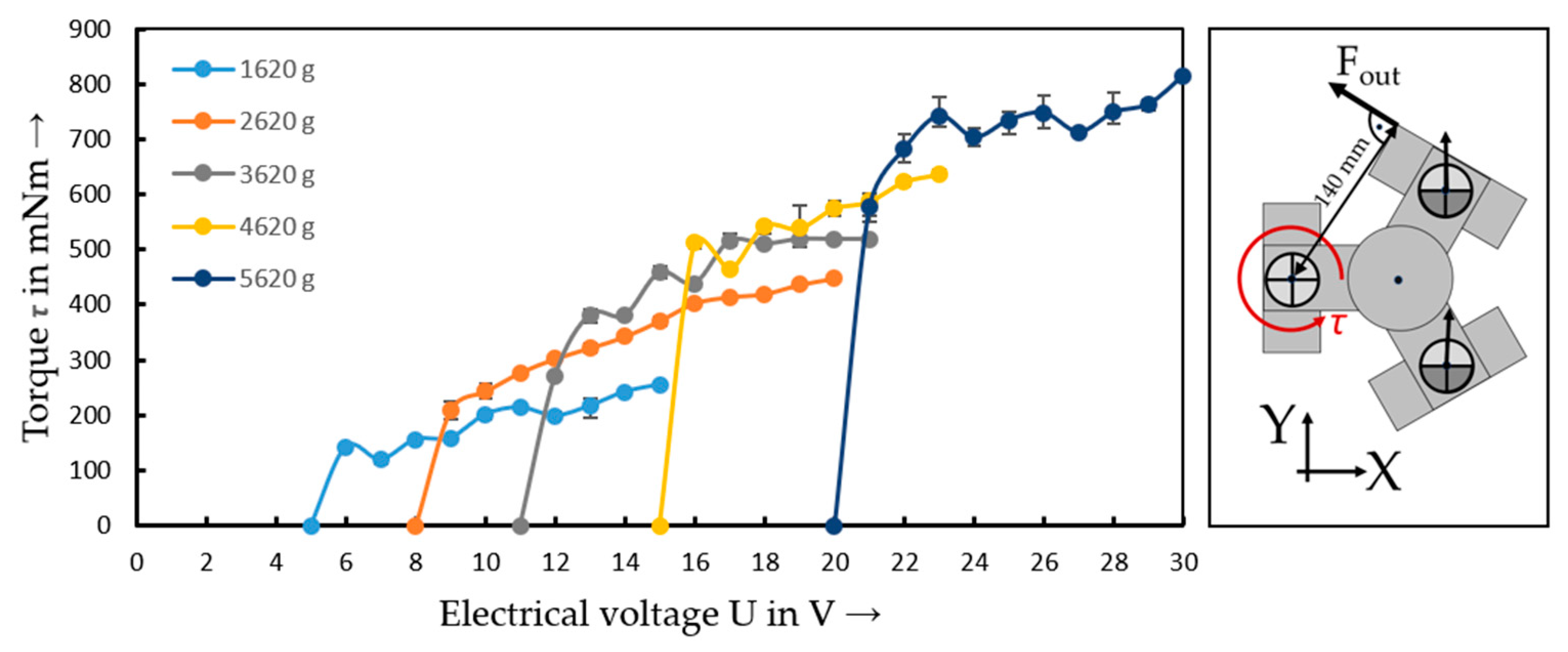
3.3. Measurements of the Output Force
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric ultrasonic motors: Overview. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bein, T.; Breitbach, E.J.; Uchino, K. A linear ultrasonic motor using the first longitudinal and the fourth bending mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 1997, 6, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, B.; Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motors. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Hashmi, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 36, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Vyshnevskyy, O.; Kovalev, S.; Wischnewskiy, W. A novel, single-mode piezoceramic plate actuator for ultrasonic linear motors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapelke, S. A Vibro-Impact Approach to Piline®Ultrasonic Motors. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications 2021, ACTUATOR 2021 Proceedings, Online, 17–19 February 2021; Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0825/10/7/148/htm (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Spanner, K.; Koc, B. Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview. Actuators 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, G.; Yasinov, R.; Karasikov, N. Performance and Applications of L1B2 Ultrasonic Motors. Actuators 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, G.S.; Cole, G.; Su, H. Approaches to creating and controlling motion in MRI. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 6687–6690. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Cardona, D.C.; Shang, W.; Camilo, A.; Cole, G.A.; Rucker, D.C.; Webster, R.J.; Fischer, G.S. A MRI-guided concentric tube continuum robot with piezoelectric actuation: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 1939–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer Mechatronik Dresden. Manipulatoren. Available online: https://www.steinmeyer-mechatronik.de/positioniersysteme/standardsysteme/manipulatoren/mp53-2-1/ (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, J. Sandwich-Type Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Ultrasonic Motor with Hybrid Excitation. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-C.; Huang, J.-C. Design and Fabrication of a High-Power Eyeball-Like Microactuator Using a Symmetric Piezoelectric Pusher Element. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woern, H.; Seyfried, J.; Fahlbusch, S.; Buerkle, A.; Schmoeckel, F. Flexible microrobots for micro assembly tasks. In Proceedings of the MHS2000, Proceedings of 2000 International Symposium on Micromechatronics and Human Science (Cat. No.00TH8530), Nagoya, Japan, 22–25 October 2000; IEEE: Nagoya, Japan, 2000; pp. 135–143, ISBN 0-7803-6498-8. [Google Scholar]
- Devos, S.; Van de Vijver, W.; Decoster, K.; Reynaerts, D.; Van Brussel, H. A planar piezoelectric drive with a stepping and a resonant operation mode. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of the European Society for Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology, Glasgow, UK, 31 May–2 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Large-stroke piezo-actuated planar motor for nanopositioning applications. In Proceedings of the ASPE 2014 Annual Meeting, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 22–25 June 2014; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.-X.; Yao, Z.-Y. Structure design and finite element analysis of a new multi-degree-of-freedom ultrasonic motor. In Proceedings of the 2015 Symposium on Piezoelectricity, Acoustic Waves and Device Applications, Jinan, China, 30 October–2 November 2015; Tao, X., Ed.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 318–321, ISBN 978-1-4799-8807-5. [Google Scholar]
- Van Brussel, H.; Van de Vijver, W.; Volder, M.; de Devos, S.; Reynaerts, D. A Fast, High-stiffness and High-resolution Piezoelectric Motor with Integrated Bearing and Driving Functionality. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.S.; Youcef-Toumi, K. Modeling of an omni-directional high precision friction drive positioning stage. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.98CH36146), Leuven, Belgium, 20 May 1998; Volume 1, pp. 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Juhas, L.; Vujanic, A.; Adamovic, N.; Nagy, L.; Borovac, B. Development of platform for micro-positioning actuated by piezo-legs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, B. Nutzung Piezoelektrischer Gewölbestrukturen für Multidimensionale Ultraschallmotoren. Ph.D. Thesis, IKFF, Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schiele, F.; Gundelsweiler, B. Piezo-Actuated XYPhi-Motor based on Hemispherical Resonators. In Proceedings of the IKMT Innovative small Drives and Micro-Motor Systems; 12. ETG/GMM-Symposium, Wuerzburg, Germany, 10–11 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schiele, F.; Gundelsweiler, B. Hemispherical Resonators Made of Soft and Hard Piezo Material for Planar Ultrasonic Motors. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications 2021, Online, 17–19 February 2021; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9400551 (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Heywang, W.; Lubitz, K.; Wersing, W.; Hull, R.; Osgood, R.M.; Parisi, J. Piezoelectricity: Evolution and Future of a Technology, 1. Aufl; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 3540686800. [Google Scholar]
- Ceramtec Company. Piezoceramic Soft Matarials Material Data; Ceramtec Company: Catalog, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Di Maio, Y.; Colombier, J.P.; Cazottes, P.; Audouard, E. Ultrafast laser ablation characteristics of PZT ceramic: Analysis methods and comparison with metals. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallaschek, J. Contact mechanics of piezoelectric ultrasonic motors. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Matsuo, E.; Nakamura, K.; Ueha, S.; Ohnishi, K. Characteristics of Ultrasonic Motors Driven in a Vacuum. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, 2956–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporation, W.U.M. Wischnewskyi Ultrasonic Motors Corporation. Available online: http://wumotors.ca/ultrasonic-motor-friction-rail.html (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Cosmo Electronics Corp. KAQY212 Series: Solid State Relay-MOSFET-Output. Data Sheet, Docment No. 69M00001.8. Available online: http://www.cosmo-ic.com/object/products/KAQY212.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Rothberg, S.J.; Allen, M.S.; Castellini, P.; Di Maio, D.; Dirckx, J.J.J.; Ewins, D.J.; Halkon, B.J.; Muyshondt, P.; Paone, N.; Ryan, T.; et al. An international review of laser Doppler vibrometry: Making light work of vibration measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 99, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpelson, M.; Wei, G.-Y.; Wood, R.J. Driving high voltage piezoelectric actuators in microrobotic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 176, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Viehland, D.; Carazo, A.V.; Ryu, J.; Uchino, K. High-power resonant measurements of piezoelectric materials: Importance of elastic nonlinearities. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollett, R.S.; Leblanc, C.L. Ferroelectric Nonlinearities in Transducer Ceramics. IEEE Trans. Son. Ultrason. 1973, 20, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material Property | SONOX P5 (Soft Piezoceramic) |
|---|---|
| Stiffness | c33D: 14.5 × 1010 N/m2; c55D: 5.8 × 1010 N/m2 |
| Qm | 90 |
| Relative permittivity | εS11/ε0: 1220; εS33/ε0: 865 |
| Charge constant | d33: 450 × 10−12 C/N; d31: −180 × 10−12 C/N; d15: 550 × 10−12 C/N |
| Total Weight | 1620 g | 2620 g | 3620 g | 4620 g | 5620 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umin | 7 V | 10 V | 13 V | 15 V | 17 V |
| Umax | 19 V | 27 V | 28 V | 30 V | 30 V |
| v−X,min | 5.7 mm/s | 7.7 mm/s | 8.6 mm/s | 6 mm/s | 5 mm/s |
| v−X,max | 59 mm/s | 61.3 mm/s | 77 mm/s | 67.3 mm/s | 51 mm/s |
| Total Weight | 1620 g | 2620 g | 3620 g | 4620 g | 5620 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umin | 7 V | 10 V | 13 V | 18 V | 19 V |
| Umax | 20 V | 22 V | 27 V | 30 V | 30 V |
| v+Y,min | 5.3 mm/s | 6.3 mm/s | 5 mm/s | 10 mm/s | 5 mm/s |
| v+Y,max | 74 mm/s | 73 mm/s | 77 mm/s | 75 mm/s | 61 mm/s |
| Total Weight | 1620 g | 2620 g | 3620 g | 4620 g | 5620 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umin | 6 V | 10 V | 12 V | 15 V | 24 V |
| Umax | 20 V | 25 V | 27 V | 30 V | 30 V |
| Fout, min | 0.30 N | 2.10 N | 2.68 N | 4.10 N | 4.46 N |
| Fout, max | 3.53 N | 5.10 N | 6.1N | 6.53 N | 7 N |
| Total Weight | 1620 g | 2620 g | 3620 g | 4620 g | 5620 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umin | 6 V | 9 V | 13 V | 15 V | 25 V |
| Umax | 19 V | 16 V | 19 V | 30 V | 30 V |
| Fout, min | 0.66 N | 1.39 N | 2.3 N | 2.76 N | 4.7 N |
| Fout, max | 1.7 N | 2.62 N | 3.72 N | 5.2 N | 5.8 N |
| Total Weight | 1620 g | 2620 g | 3620 g | 4620 g | 5620 g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umin | 6 V | 9 V | 12 V | 16 V | 21 V |
| Umax | 15 V | 20 V | 21 V | 23 V | 30 V |
| τmin | 142 mNm | 209 mNm | 270 mNm | 512 mNm | 577 mNm |
| τmax | 255 mNm | 448 mNm | 577 mNm | 636 mNm | 815 mNm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiele, F.; Gundelsweiler, B. Design and Characterization of a Planar Motor Drive Platform Based on Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shell Resonators. Actuators 2021, 10, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080187
Schiele F, Gundelsweiler B. Design and Characterization of a Planar Motor Drive Platform Based on Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shell Resonators. Actuators. 2021; 10(8):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiele, Frank, and Bernd Gundelsweiler. 2021. "Design and Characterization of a Planar Motor Drive Platform Based on Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shell Resonators" Actuators 10, no. 8: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080187
APA StyleSchiele, F., & Gundelsweiler, B. (2021). Design and Characterization of a Planar Motor Drive Platform Based on Piezoelectric Hemispherical Shell Resonators. Actuators, 10(8), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080187






