On the Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation in Electromagnetically Levitating Hybrid Micro-Actuator: Theory and Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
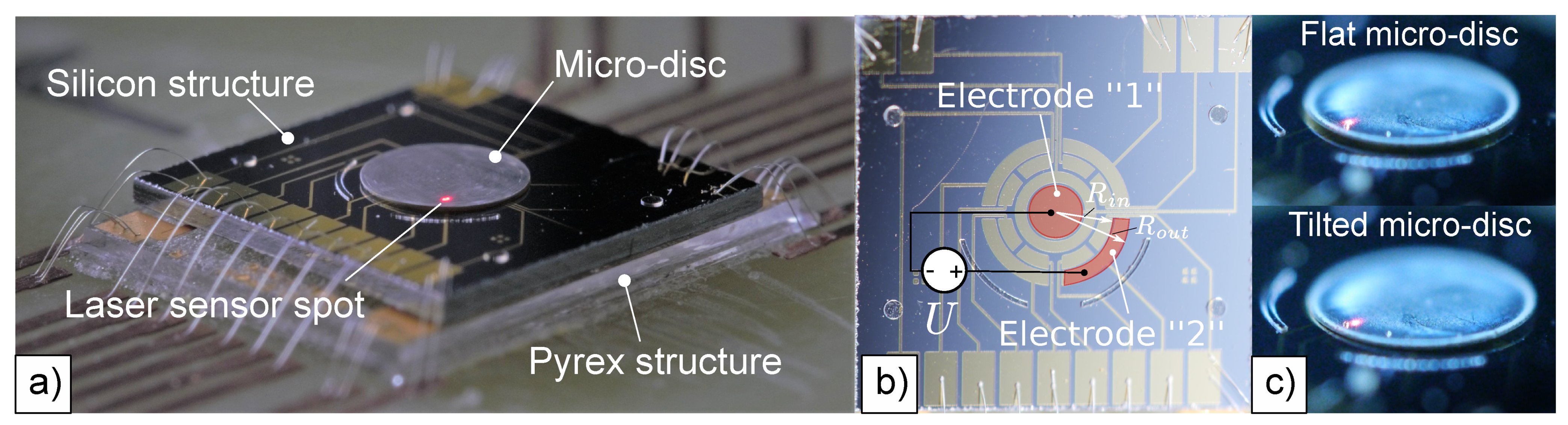
2. Fabrication and Measurements
3. Simulation and Modeling
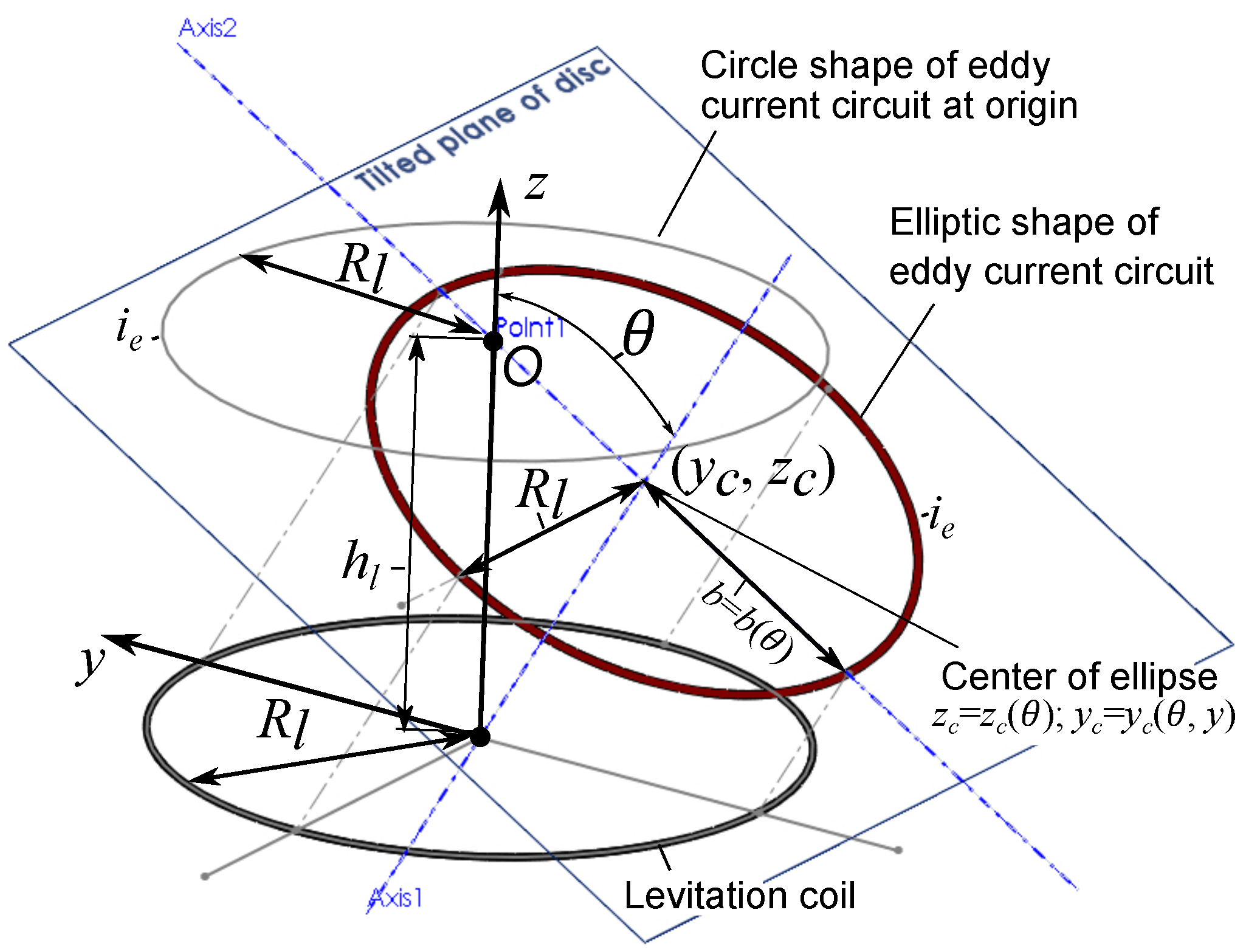
3.1. Simulation of Induced Eddy Current within the Tilting Proof Mass
3.2. Mutual Inductance between Two Filaments of Circular and Elliptic Shapes
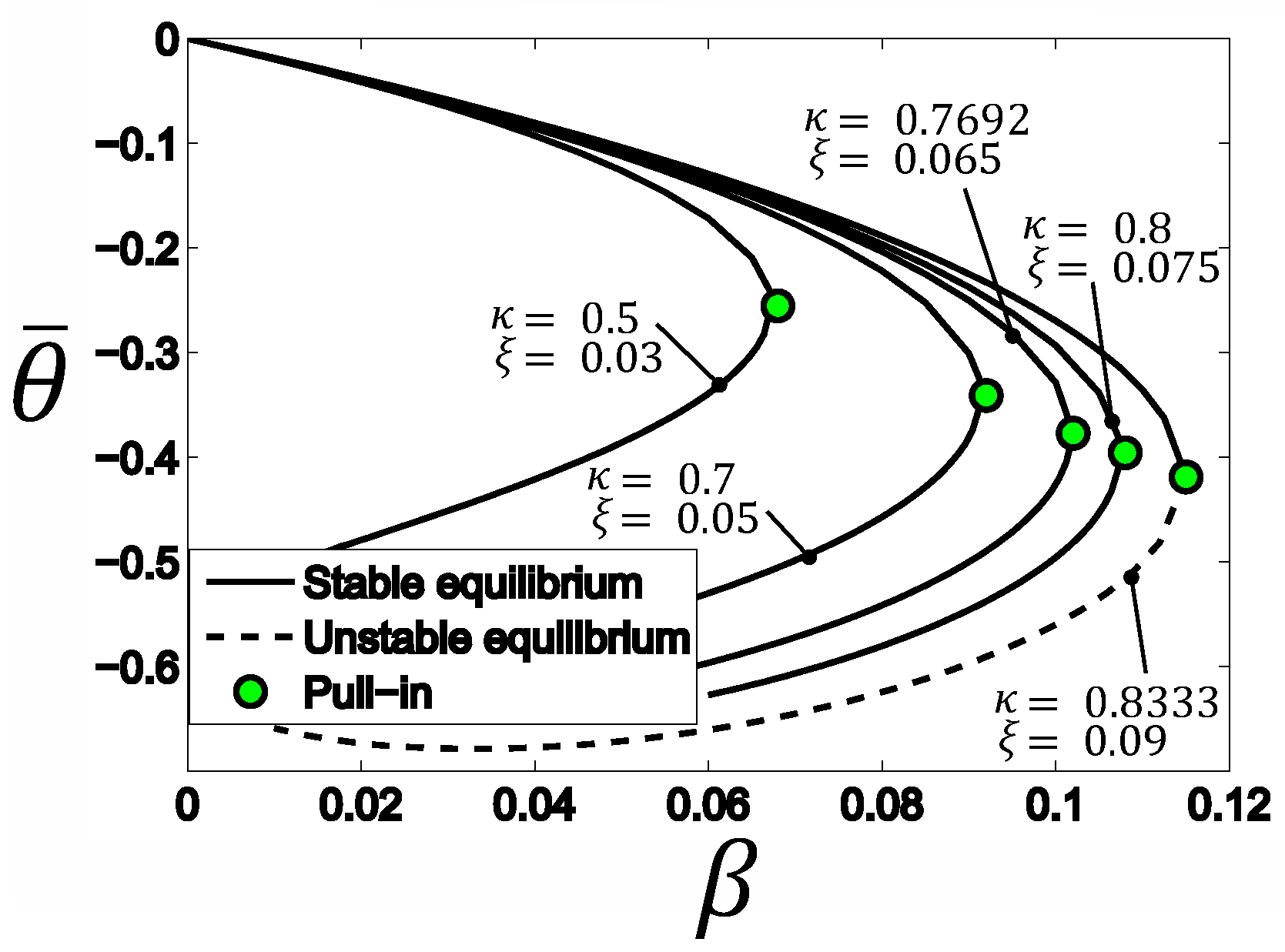
3.3. Model of Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation
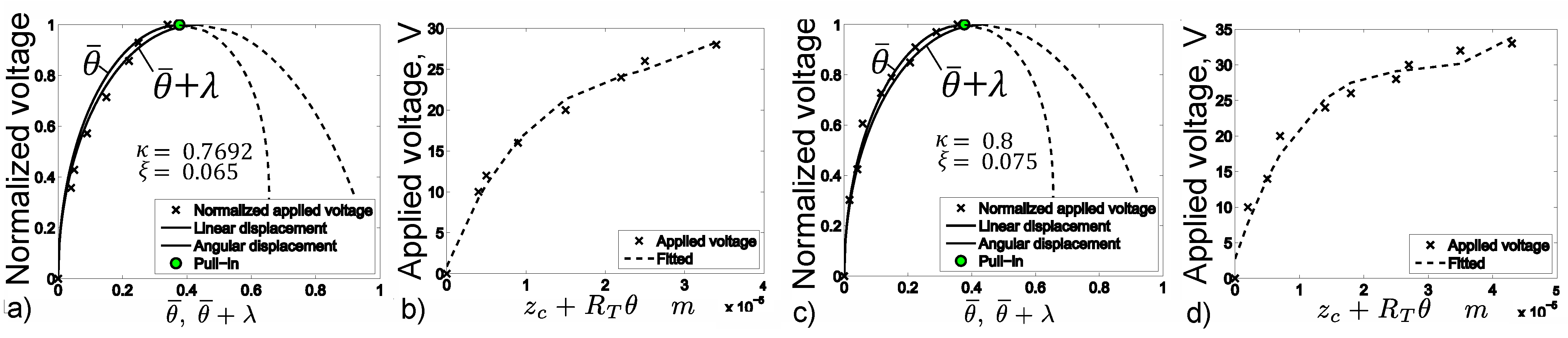
4. Analysis of the Derived Model
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILMA | Inductive Levitation Micro-Actuator |
| HLMA | Hybrid Levitation Micro-Actuator |
| PM | Proof Mass |
| MLMA | Magnetic Levitation Micro-Actuator |
| ELMA | Electric Levitation Micro-Actuator |
Appendix A. Nomenclature
- area of the electrode “1” ()
- area of the electrode “2” ()
- a
- dimensionless parameter
- capacitance of capacitor build on electrode “1” ()
- capacitance of capacitor build on electrode “2” ()
- E
- the complete elliptic function of the second kind
- generalized force () ()
- gravity acceleration vector ()
- height of levitation ()
- h
- space between the electrode surface and cm of levitated disc ()
- i
- induced eddy current ()
- I
- AC current in the levitation coil ()
- magnitude of AC current in the levitation coil ()
- j
- imaginary unit
- K
- complete elliptic function of the first kind
- N
- number of wire loops
- n
- number of finite elements
- L
- Lagrange function ()
- self-inductance of the eddy current circuit ()
- self-inductance of the j-wire loop ()
- self-inductance of the finite circular element ()
- mutual inductance between k- and s-finite circular elements ()
- M
- between two filaments of circular and elliptic shapes ()
- m
- mass of levitated object ()
- Q
- electric charges ()
- electrical resistance of the eddy current circuit ()
- radius of circular element ()
- inner radius of sector electrode ()
- radius of levitation coil ()
- outer radius of sector electrode ()
- mean distance ()
- thickness of micro-object ()
- U
- voltage ()
- coordinate of the centre of the ellipse along the y-axis ()
- coordinate of the centre of the ellipse along the z-axis ()
- Matrices
- unit matrix of size
- matrix of eddy currents of size ()
- matrix of coil currents of size ()
- symmetric hollow matrix of size whose elements are () ()
- mutual inductance between coils and finite elements of size ()
- Greek symbols
- dimensionless square voltage
- angular displacement of the levitated disc ()
- dimensionless angle
- dimensionless parameter
- dimensionless displacement
- dimensionless parameter
- dissipation function ()
- frequency of AC current ()
References
- Jin, J.; Yih, T.C.; Higuchi, T.; Jeon, J.U. Direct electrostatic levitation and propulsion of silicon wafer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1998, 34, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakoshi, T.; Endo, Y.; Fukatsu, K.; Nakamura, S.; Esashi, M. Electrostatically levitated ring-shaped rotational gyro/accelerometer. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 2468–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.T.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.Y. Micromachined electrostatically suspended gyroscope with a spinning ring-shaped rotor. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Asadollahbaik, A.; Kampmann, R.; Korvink, J.G. Levitating Micro-Actuators: A Review. Actuators 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coombs, T.A.; Samad, I.; Ruiz-Alonso, D.; Tadinada, K. Superconducting micro-bearings. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2005, 15, 2312–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Poletkin, K.; den Hartogh, B.; Wallrabe, U.; Badilita, V. 3D micro-machined inductive contactless suspension: Testing and modeling. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 220, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Lu, Z.; Moazenzadeh, A.; Mariappan, S.G.; Korvink, J.G.; Wallrabe, U.; Badilita, V. Polymer Magnetic Composite Core Boosts Performance of Three-Dimensional Micromachined Inductive Contactless Suspension. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearwood, C.; Williams, C.B.; Mellor, P.H.; Chang, K.Y.; Woodhead, J. Electro-magnetically levitated micro-discs. In Proceedings of the IEE Colloquium on Microengineering Applications in Optoelectronics, London, UK, 27 February 1996; pp. 6/1–6/3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dricot, S.; Kraft, M. Design and experiment of an electromagnetic levitation system for a micro mirror. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearwood, C.; Ho, K.Y.; Williams, C.B.; Gong, H. Development of a levitated micromotor for application as a gyroscope. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 83, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Ye, Z.; Takahata, K. Micromachined Graphite Rotor Based on Diamagnetic Levitation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmire, D.; Choo, H.; Kant, R.; Govindjee, S.; Sequin, C.; Muller, R.; Demmel, J. Diamagnetically levitated MEMS accelerometers. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference (TRANSDUCERS 2007), Lyon, France, 10–14 June 2007; pp. 1203–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Dieppedale, C.; Desloges, B.; Rostaing, H.; Delamare, J.; Cugat, O.; Meunier-Carus, J. Magnetic bistable micro-actuator with integrated permanent magnets. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE SENSORS, Vienna, Austria, 24–27 October 2004; Volume 1, pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Abadie, J.; Piat, E.; Oster, S.; Boukallel, M. Modeling and experimentation of a passive low frequency nanoforce sensor based on diamagnetic levitation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 173, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Lu, Z.; Wallrabe, U.; Korvink, J.G.; Badilita, V. A qualitative technique to study stability and dynamics of micro-machined inductive contactless suspensions. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, I.; Kraft, M. A MEMS Linear Accelerator for Levitated Micro-objects. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 222, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.; Lu, Z.; Wallrabe, U.; Badilita, V. A New Hybrid Micromachined Contactless Suspension With Linear and Angular Positioning and Adjustable Dynamics. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Kan, R.; Bleuler, H.; Zhou, J. Realization of a Diamagnetically Levitating Rotor Driven by Electrostatic Field. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bleuler, H.; Kan, R. Passive diamagnetic contactless suspension rotor with electrostatic glass motor. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Keskekler, A.; Alijani, F.; Steeneken, P.G. Rigid body dynamics of diamagnetically levitating graphite resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 243505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratt, K.; Badilita, V.; Burger, T.; Korvink, J.; Wallrabe, U. A fully MEMS-compatible process for 3D high aspect ratio micro coils obtained with an automatic wire bonder. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 015021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlnieska, V.; Voigt, A.; Wadhwa, S.; Korvink, J.; Kohl, M.; Poletkin, K. Development of Control Circuit for Inductive Levitation Micro-Actuators. Proceedings 2020, 64, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.; Lu, Z.; Wallrabe, U.; Badilita, V. Hybrid electromagnetic and electrostatic micromachined suspension with adjustable dynamics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 660, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K.V. A novel hybrid Contactless Suspension with adjustable spring constant. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Shalati, R.; Korvink, J.G.; Badilita, V. Pull-in actuation in hybrid micro-machined contactless suspension. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1052, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K.; Lu, Z.; Wallrabe, U.; Korvink, J.; Badilita, V. Stable dynamics of micro-machined inductive contactless suspensions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 131–132, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K.V. Static Pull-In Behavior of Hybrid Levitation Microactuators: Simulation, Modeling, and Experimental Study. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Korvink, J.G. Efficient calculation of the mutual inductance of arbitrarily oriented circular filaments via a generalisation of the Kalantarov-Zeitlin method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 483, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K.V.; Korvink, J.G. Modeling a Pull-In Instability in Micro-Machined Hybrid Contactless Suspension. Actuators 2018, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poletkin, K. Simulation of Static Pull-in Instability of Hybrid Levitation Microactuators. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR; International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications 2021, Online, 17–19 February 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Poletkin, K.V. Levitation Micro-Systems: Applications to Sensors and Actuators, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; p. 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Measurement I | Measurement II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measured | Levitation height, | 130 | 150 |
| parameters | Spacing, h | 100 | 120 |
| Results of medelling | Pull-in displacement | 34 | 45 |
| Pull-in voltage,U | 27 | 33 | |
| Parameters of medelling | 0.065 | 0.075 | |
| 0.7692 | 0.8 | ||
| Results of medelling | Pull-in displacement | 38 | 48 |
| Pull-in voltage,U | 28 | 33 | |
| Device design | Diameter of levitation coil, | 2 | |
| Area of electrodes, and | 0.8 and 0.43 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poletkin, K. On the Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation in Electromagnetically Levitating Hybrid Micro-Actuator: Theory and Experiment. Actuators 2021, 10, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10100256
Poletkin K. On the Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation in Electromagnetically Levitating Hybrid Micro-Actuator: Theory and Experiment. Actuators. 2021; 10(10):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10100256
Chicago/Turabian StylePoletkin, Kirill. 2021. "On the Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation in Electromagnetically Levitating Hybrid Micro-Actuator: Theory and Experiment" Actuators 10, no. 10: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10100256
APA StylePoletkin, K. (2021). On the Static Pull-In of Tilting Actuation in Electromagnetically Levitating Hybrid Micro-Actuator: Theory and Experiment. Actuators, 10(10), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10100256






