Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material
Abstract
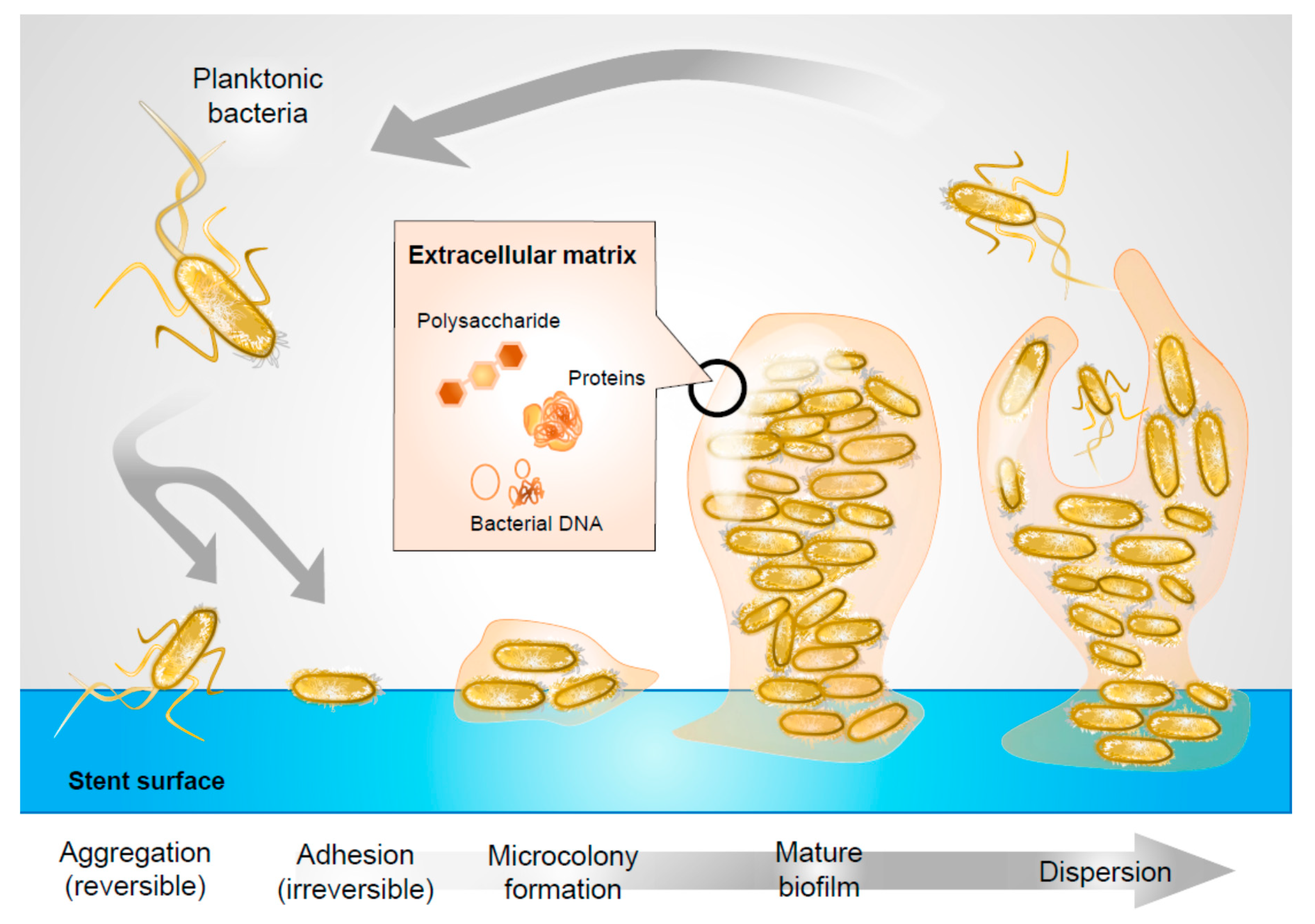
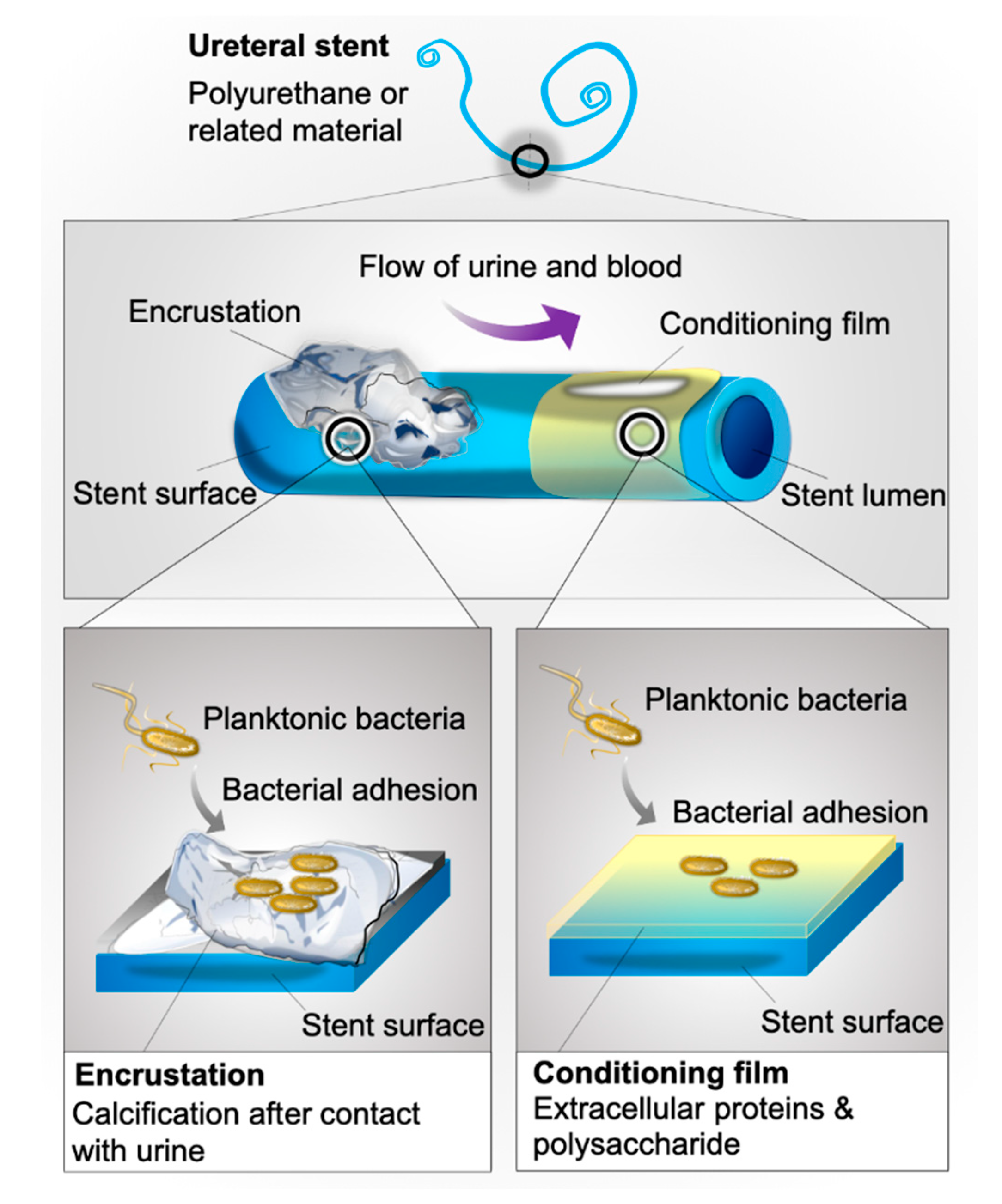
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Stent Management
2.1.1. Stent Retrieval
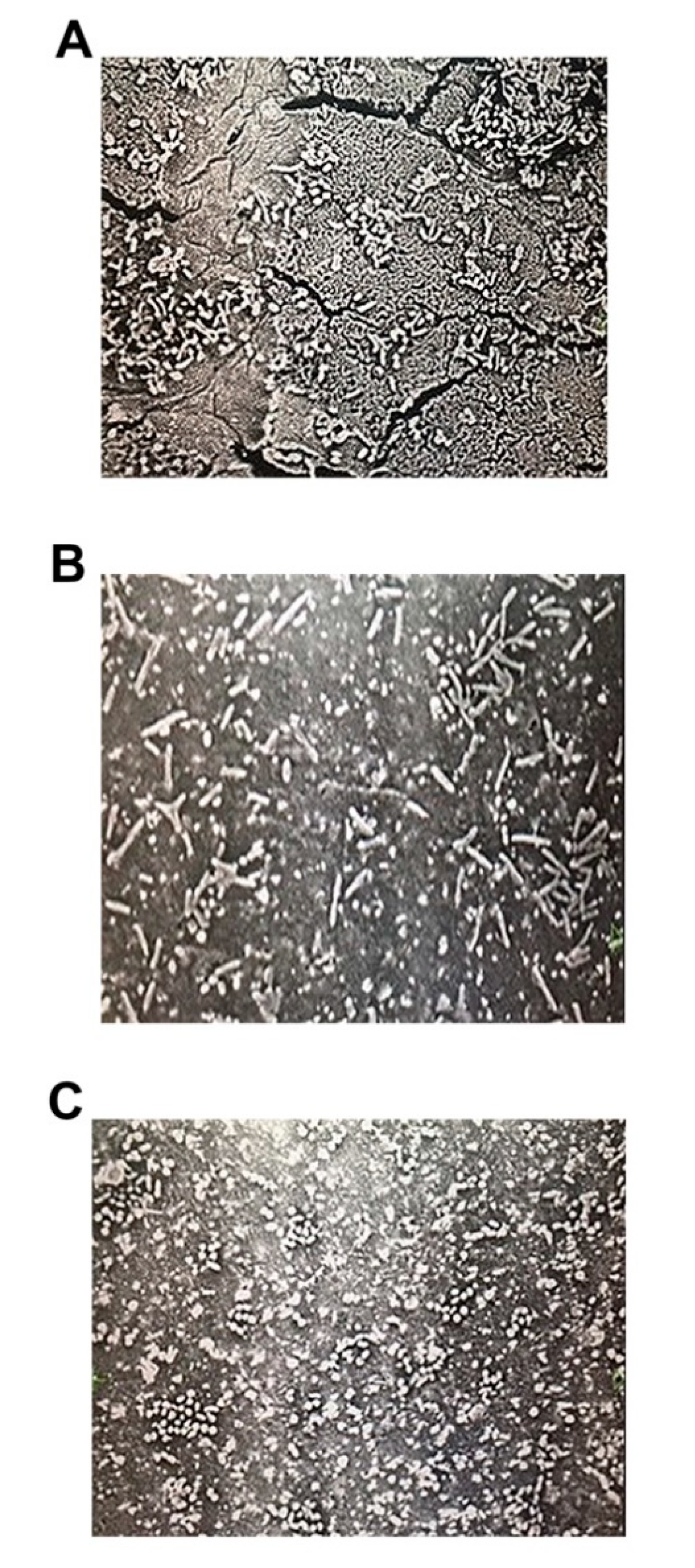
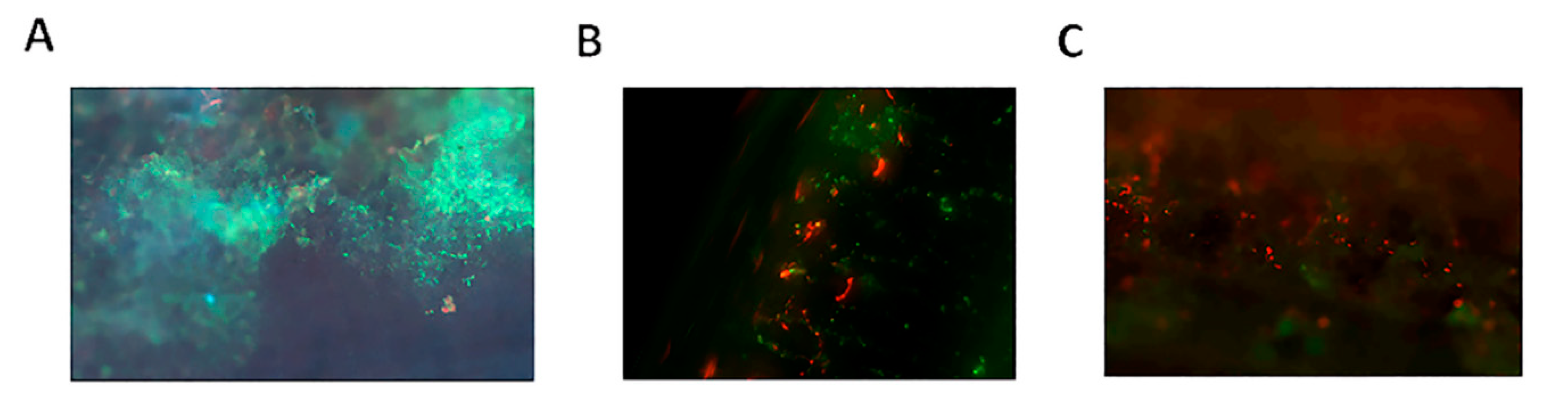
2.1.2. Bacterial Attachment
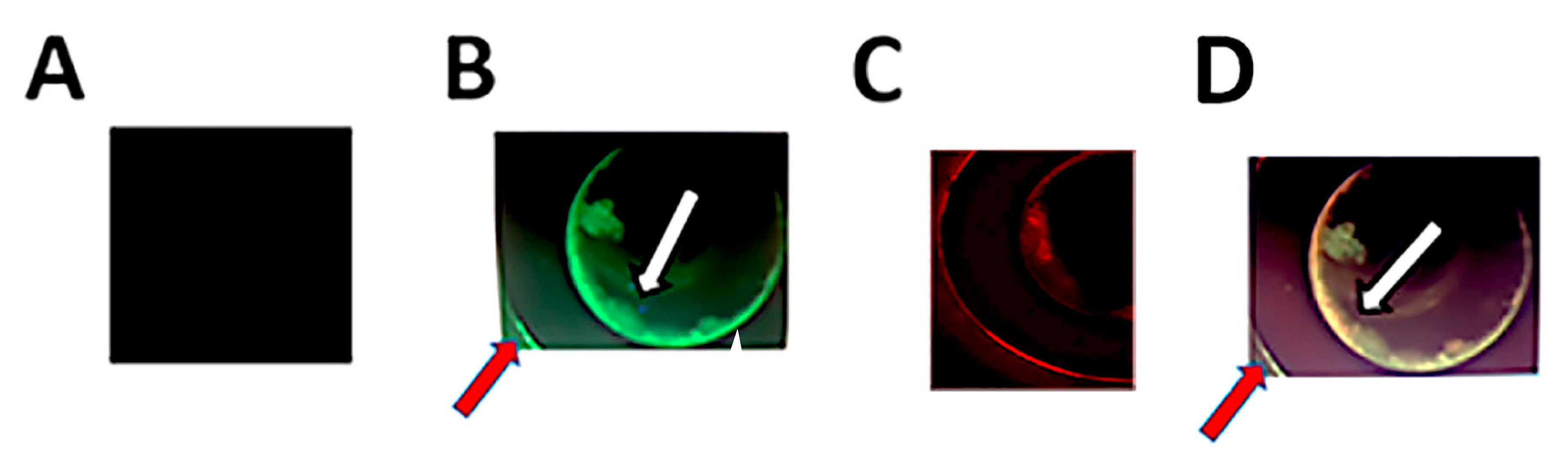
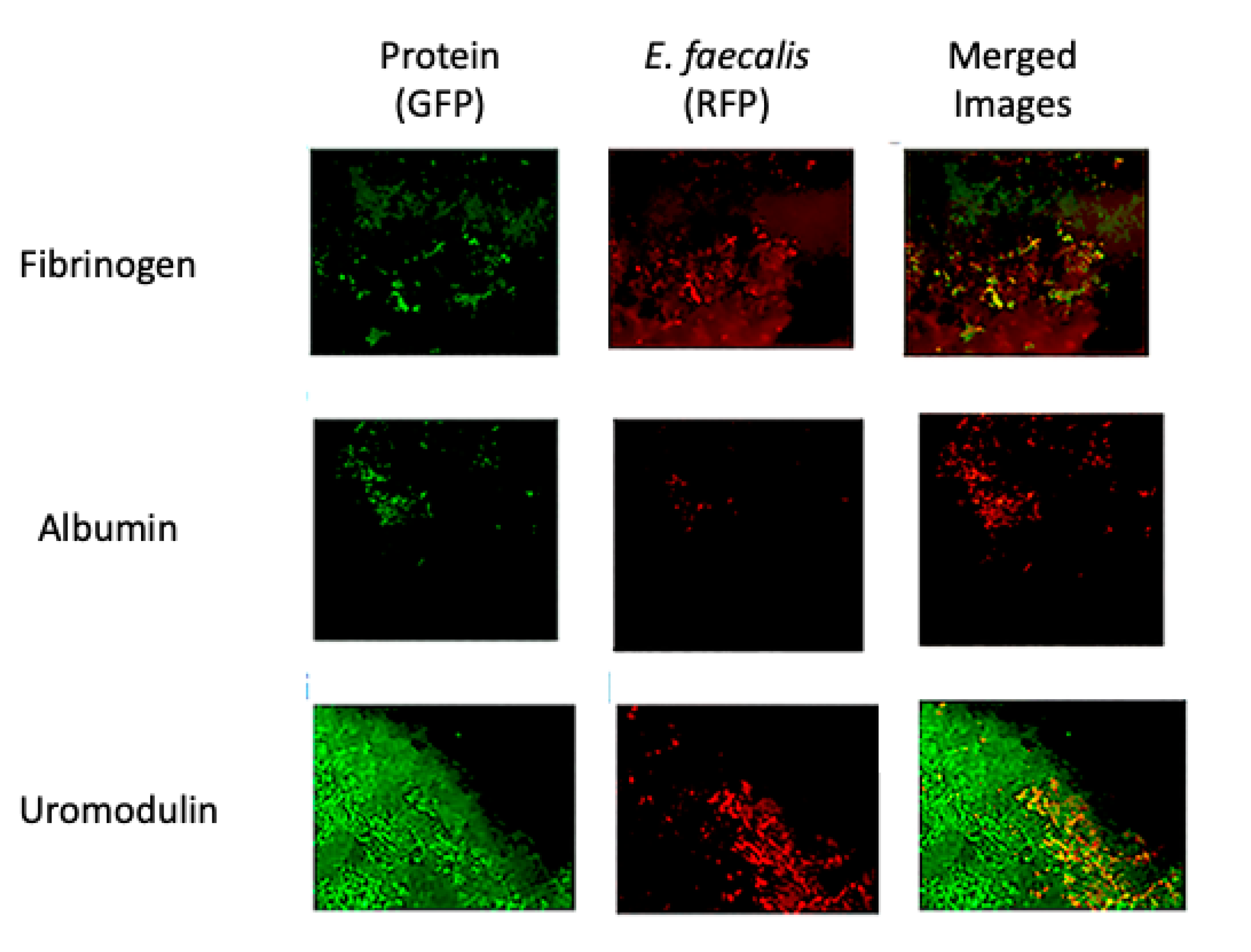
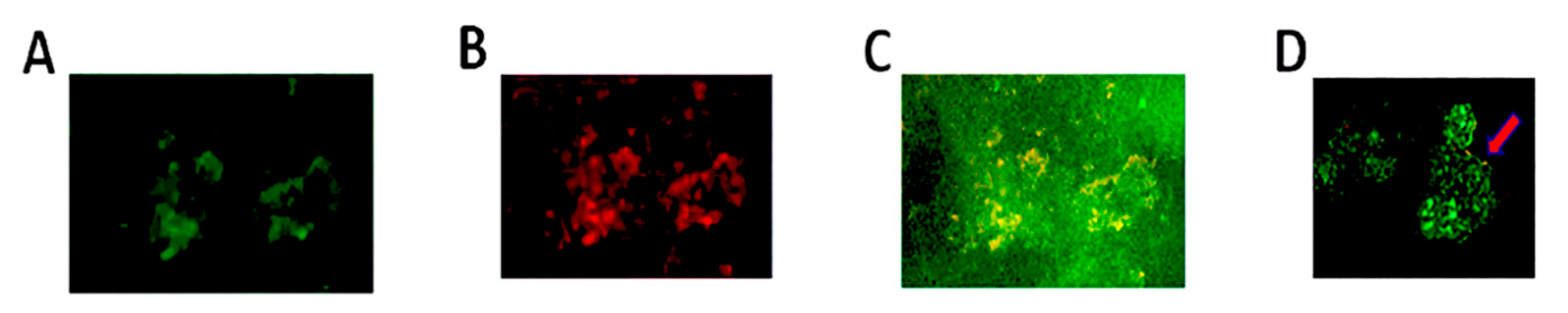
2.2. Double Immunofluorescent Staining and Confocal Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Overview of the Study
4.2. Stent Retrieval
4.3. Bacterial Culture
4.4. Immunofluorescence Double Staining and Confocal Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costerton, J.W.; Geesey, G.G.; Cheng, K.-J. How Bacteria Stick. Sci. Am. 1978, 238, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumstein, V.; Betschart, P.; Albrich, W.C.; Buhmann, M.T.; Ren, Q.; Schmid, H.-P.; Abt, D. Biofilm formation on ureteral stents—Incidence, clinical impact, and prevention. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2017, 147, w14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenke, P.; Koves, B.; Nagy, K.; Hultgren, S.J.; Mendling, W.; Wullt, B.; Grabe, M.; Wagenlehner, F.M.E.; Cek, M.; Pickard, R.; et al. Update on biofilm infections in the urinary tract. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, K.K. What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. Biofilm exopolysaccharides: A strong and sticky framework. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenke, P.; Kovács, B.; Jackel, M.; Nagy, E. The role of biofilm infection in urology. World J. Urol. 2006, 24, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.G.; Blacker, A.J.; Kumar, P. Ureteric stents: The past, present and future. J. Clin. Urol. 2018, 11, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paick, S.H.; Park, H.K.; Oh, S.-J.; Kim, H.H. Characteristics of bacterial colonization and urinary tract infection after indwelling of double-J ureteral stent. Urology 2003, 62, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Denstedt, J.D.; Kang, Y.S.; Lam, D.; Nause, C. Microbial Adhesion and Biofilm Formation on Ureteral Stents in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Urol. 1992, 148, 1592–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, C.R.; Plas, E.; Hübner, W.A.; Zimmerl, H.; Ulrich, W.; Pflüger, H. Bacterial colonization of ureteral stents. Eur. Urol. 1999, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunal, N.; Willke, A.; Hamzaoğlu, O. Ureteral stent infections: A prospective study. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, J.; Anson, K.; Giusti, G.; Grasso, M.; Kamphuis, G.; Lahme, S.; Liatsikos, E.; Patel, A.; Pearle, M.S.; Valiquette, L.; et al. Update of the ICUD-SIU consultation on stone technology behind ureteroscopy. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A. Implant-Associated Infection. In Biofilm Infections; Bjarnsholt, T., Jensen, P.Ø., Moser, C., Høiby, N., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Elwood, C.N.; Lo, J.; Chou, E.; Crowe, A.; Arsovska, O.; Adomat, H.; Miyaoka, R.; Tomlinson-Guns, E.; Monga, M.; Chew, B.H.; et al. Understanding urinary conditioning film components on ureteral stents: Profiling protein components and evaluating their role in bacterial colonization. Biofouling 2013, 29, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holá, V.; Ruzicka, F.; Horká, M. Microbial diversity in biofilm infections of the urinary tract with the use of sonication techniques. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehinde, E.O.; Rotimi, V.O.; Al-Hunayan, A.; Abdul-Halim, H.; Boland, F.; Al-Awadi, K.A. Bacteriology of Urinary Tract Infection Associated with Indwelling J Ureteral Stents. J. Endourol. 2004, 18, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttner, H.; Mack, D.; Rohde, H.; Büttner, H. Structural basis of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation: Mechanisms and molecular interactions. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristina, A.; Giridhar, G.; Gabriel, B.; Naylor, P.; Myrvik, Q. Cell Biology and Molecular Mechanisms in Artificial Device Infections. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1993, 16, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickler, D.; Ganderton, L.; King, J.; Nettleton, J.; Winters, C. Proteus mirabilis biofilms and the encrustation of urethral catheters. Urol. Res. 1993, 21, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Pinkner, J.S.; Caparon, M.G.; Hultgren, S.J. EbpA vaccine antibodies block binding of Enterococcus faecalis to fibrinogen to prevent catheter-associated bladder infection in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 254ra127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.G.; Kim, H.K.; Burts, M.L.; Krausz, T.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D.M. Genetic requirements for Staphylococcus aureus abscess formation and persistence in host tissues. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Moreno, A.M.; Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J.; Gonzalez-Martin, M.L.; Bruque, J.M.; Perez-Giraldo, C. Adhesion of Enterococcus faecalis 1131 grown under subinhibitory concentrations of ampicillin and vancomycin to a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic substratum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 203, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velraeds, M.M.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Reid, G.; Busscher, H.J. Inhibition of initial adhesion of uropathogenic Enterococcus faecalis by biosurfactants from Lactobacillus isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, S.A.; Dave, S.; Reid, G.; Burton, J.P. Ibuprofen lacks direct antimicrobial properties for the treatment of urinary tract infection isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.; Elwood, C.N.; Choi, K.; Hendlin, K.; Monga, M.; Chew, B.H. Uropathogen Interaction with the Surface of Urological Stents Using Different Surface Properties. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orskov, I.; Orskov, F.; Birch-Andersen, A. Comparison of Escherichia coli fimbrial antigen F7 with type 1 fimbriae. Infect. Immun. 1980, 27, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, W.R.; Lehmann, L.; McCormick, J. Transcriptional Activation of the Staphylococcus aureus putP Gene by Low-Proline-High Osmotic Conditions and during Infection of Murine and Human Tissues. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanassche, T.; Peetermans, M.; Van Aelst, L.N.L.; Peetermans, W.E.; Verhaegen, J.; Missiakas, D.M.; Schneewind, O.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Verhamme, P. The Role of Staphylothrombin-Mediated Fibrin Deposition in Catheter-Related Staphylococcus aureus Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liatsikos, E.; Kallidonis, P.; Kyriazis, I.; Constantinidis, C.; Hendlin, K.; Stolzenburg, J.-U.; Karnabatidis, D.; Siablis, D. Ureteral Obstruction: Is the Full Metallic Double-Pigtail Stent the Way to Go? Eur. Urol. 2010, 57, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunney, M.M. Comparative assessment of ureteral stent biomaterial encrustation. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kram, W.; Buchholz, N.; Hakenberg, O.W. Ureteral stent encrustation. Pathophysiology. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2016, 69, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scotland, K.B.; Kung, S.H.; Chew, B.H.; Lange, D. Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material. Pathogens 2020, 9, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090764
Scotland KB, Kung SH, Chew BH, Lange D. Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090764
Chicago/Turabian StyleScotland, Kymora B, Sonia HY Kung, Ben H Chew, and Dirk Lange. 2020. "Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090764
APA StyleScotland, K. B., Kung, S. H., Chew, B. H., & Lange, D. (2020). Uropathogens Preferrentially Interact with Conditioning Film Components on the Surface of Indwelling Ureteral Stents Rather than Stent Material. Pathogens, 9(9), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090764






