Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies and Cryoglobulins in Patients with Acute and Chronic HEV Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
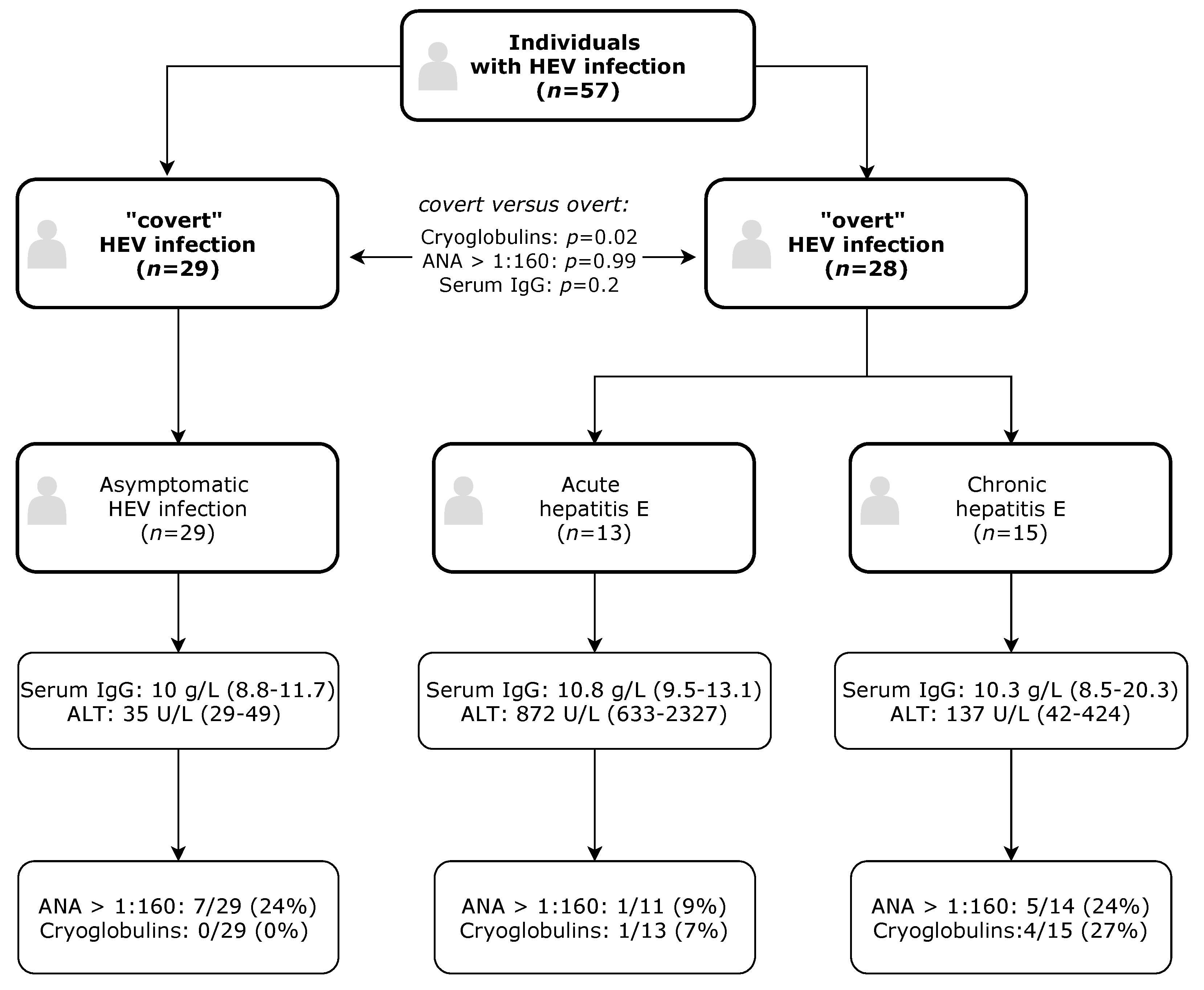
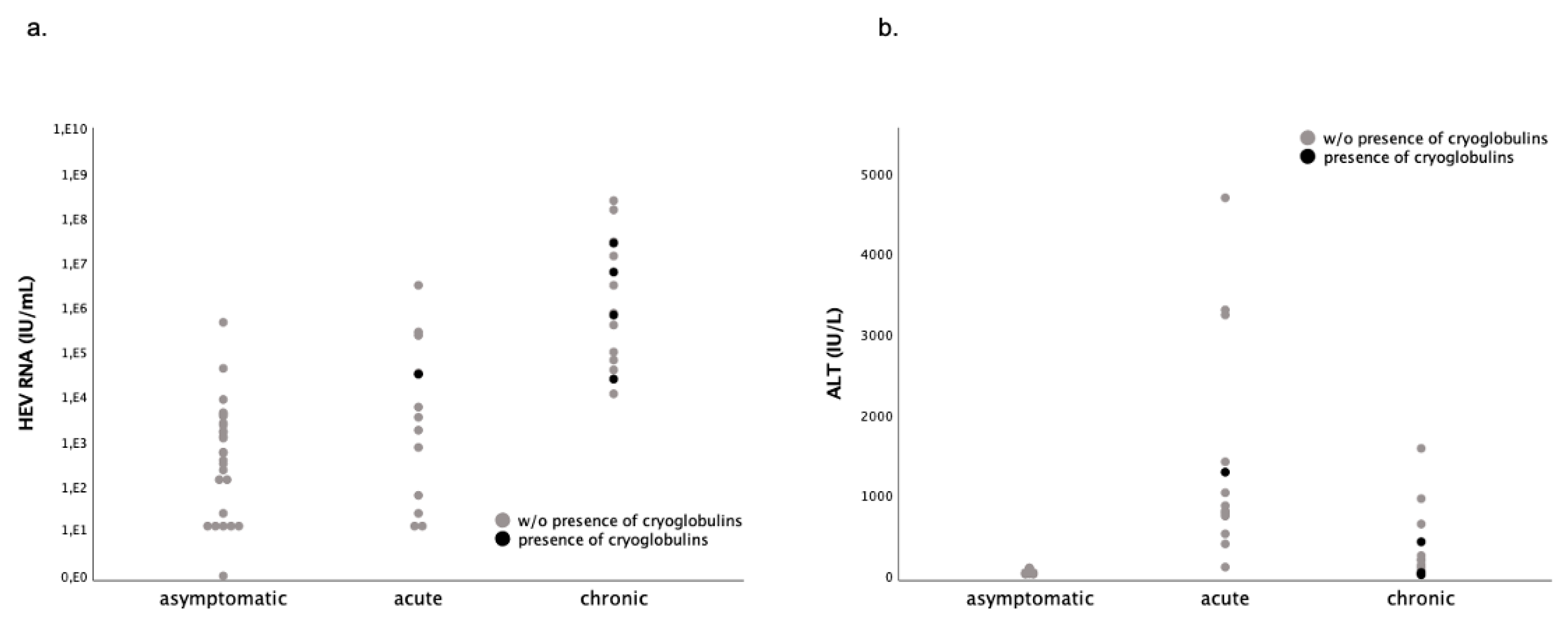
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Testing for HEV and Definition of Hepatitis E
4.3. Recruitment and Testing of a Control Cohort of HBV- or HCV-Infected Untreated Patients
4.4. Testing for Autoantibodies and Cryoglobulins
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Nelson, K.E.; Purcell, R.H. Hepatitis E. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pischke, S. The Clinical Perspective on Hepatitis E. Viruses 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, R.; Kini, D.; Sofat, S.; Naik, S.R.; Krawczynski, K. Duration of viraemia and faecal viral excretion in acute hepatitis E. Lancet 2000, 356, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, J.M.; Bureau, C.; Poirson, H.; Mansuy, J.M.; Alric, L.; Selves, J.; Dupuis, E.; Izopet, J.; Vinel, J.P. Fulminant liver failure from acute autochthonous hepatitis E in France: Description of seven patients with acute hepatitis E and encephalopathy. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, B.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Pas, S.D.; Hunter, J.G.; Madden, R.G.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; Dalton, H.R.; Jacobs, B.C. Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with preceding hepatitis E virus infection. Neurology 2014, 82, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, Q.; Gu, S.; Tang, L. Guillain-Barre syndrome caused by hepatitis E infection: Case report and literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroszewicz, J.; Flisiak, R.; Kalinowska, A.; Wierzbicka, I.; Prokopowicz, D. Acute hepatitis E complicated by acute pancreatitis: A case report and literature review. Pancreas 2005, 30, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanth, S.S.; Khan, Z.; Rau, N.R.; Rao, K. Acute hepatitis E complicated by acute pancreatitis and multiorgan dysfunction. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014203875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijk, J.J.J.; Dalton, H.R.; Ripellino, P.; Madden, R.G.; Jones, C.; Fritz, M.; Gobbi, C.; Melli, G.; Pasi, M.; Herrod, J.; et al. Clinical phenotype and outcome of hepatitis E virus-associated neuralgic amyotrophy. Neurology 2017, 89, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijk, J.J.J.; Madden, R.G.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Hunter, J.G.; Reimerink, J.H.J.; Bendall, R.P.; Pas, S.D.; Ellis, V.; van Alfen, N.; Beynon, L.; et al. Neuralgic amyotrophy and hepatitis E virus infection. Neurology 2014, 82, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Guo, N.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Fan, J.; Yu, J.; Pan, Q.; et al. Seroprevalence of AIH-related autoantibodies in patients with acute hepatitis E viral infection: A prospective case-control study in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Ripellino, P.; Gobbi, C.; Cerny, A.; Baserga, A.; Di Bartolomeo, C.; Bihl, F.; Deleonardi, G.; Melidona, L.; Grondona, A.G.; et al. Autoimmune liver disease serology in acute hepatitis E virus infection. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, L.P.; Gratacos-Gines, J.; Ortiz, O.; Rodriguez-Tajes, S.; Lens, S.; Reverter, E.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Costa, J.; Vinas, O.; Forns, X.; et al. Higher seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in autoimmune hepatitis: Role of false-positive antibodies. Liver Int. 2019, 40, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubert, R.; Diestelhorst, J.; Junge, N.; Kirstein, M.M.; Pischke, S.; Vogel, A.; Bantel, H.; Baumann, U.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Increased seroprevalence of HAV and parvovirus B19 in children and of HEV in adults at diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Gisa, A.; Suneetha, P.V.; Wiegand, S.B.; Taubert, R.; Schlue, J.; Wursthorn, K.; Bantel, H.; Raupach, R.; Bremer, B.; et al. Increased HEV seroprevalence in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gerven, N.M.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Pas, S.D.; Zaaijer, H.L.; de Boer, Y.S.; Witte, B.I.; van Nieuwkerk, C.M.J.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Bouma, G.; de Man, R.A.; et al. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients in the Netherlands. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. JGLD 2016, 25, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, M.; Strassl, R.; Beinhardt, S.; Stattermayer, A.F.; Kozbial, K.; Lagler, H.; Holzmann, H.; Trauner, M.; Hofer, H. High seroprevalence of anti-Hepatitis E antibodies in Austrian patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee. European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebode, M.; Pischke, S.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Polywka, S.; Quaas, A.; Lohse, A.W.; Wege, H. New foe treated with old guns—Supportive role of steroids in the treatment of acute severe hepatitis E. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Honer zu Siederdissen, C.; Pischke, S.; Schlue, J.; Deterding, K.; Hellms, T.; Schuler-Luttmann, S.; Schwarz, A.; Manns, M.P.; Cornberg, M.; Wedemeyer, H. Chronic hepatitis E virus infection beyond transplantation or human immunodeficiency virus infection. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1112–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkoff, N.Z.; Buzzi, K.; Williamson, A.K.; Hagmann, S.H.F. Case Report: Acute Hepatitis E in a Pediatric Traveler Presenting with Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisti, G.; Irish, D.N.; Ijaz, S.; Tedder, R.S.; Moore, K. Acute Hepatitis E Mimicking a Flare of Disease in a Patient with Chronic Autoimmune Hepatitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.L.; Baldaia, C.; Fatela, N.; Ramalho, F.; Cardoso, C. Case of acute hepatitis E with concomitant signs of autoimmunity. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, F.; Ueno, Y.; Kanno, N.; Okamoto, H.; Shimosegawa, T. A case of acute hepatitis with positive autoantibodies who actually had hepatitis E virus infection. Hepatol. Res. 2005, 32, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.; Ching Companioni, R.; Bansal, R.; Vyas, N.; Catalano, C.; Aron, J.; Walfish, A. Acute hepatitis E presenting with clinical feature of autoimmune hepatitis. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2016, 6, 33342. [Google Scholar]
- Thodou, V.; Buechter, M.; Manka, P.; Gerken, G.; Kahraman, A. Course of hepatitis E infection in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune hepatitis: A case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Behrendt, P.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. HEV-associated cryoglobulinaemia and extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis E. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 678–679. [Google Scholar]
- Bazerbachi, F.; Leise, M.D.; Watt, K.D.; Murad, M.H.; Prokop, L.J.; Haffar, S. Systematic review of mixed cryoglobulinemia associated with hepatitis E virus infection: Association or causation? Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 5, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Del Bello, A.; Esposito, L.; Lhomme, S.; Puissant-Lubrano, B.; Alric, L.; Faguer, S.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Hepatitis E virus-associated cryoglobulinemia in solid-organ-transplant recipients. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccatello, D.; Saadoun, D.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Fervenza, F.C.; Cacoub, P.; Zignego, A.L.; Ferri, C. Cryoglobulinaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Stone, J.H.; Cid, M.C.; Bosch, X. The cryoglobulinaemias. Lancet 2012, 379, 348–360. [Google Scholar]
- Muchtar, E.; Magen, H.; Gertz, M.A. How I treat cryoglobulinemia. Blood 2017, 129, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sansonno, D.; Carbone, A.; De Re, V.; Dammacco, F. Hepatitis C virus infection, cryoglobulinaemia, and beyond. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pischke, S.; Polywka, S.; Haag, F.; Iking-Konert, C.; Sterneck, M.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Dammermann, W.; Luth, S.; Schimer, J.H. Association of hepatitis E virus and essential cryoglobulinemia? J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 67, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilman, A.J.; Le, A.K.; Zhao, C.; Hoang, J.; Yasukawa, L.A.; Weber, S.C.; Vierling, J.M.; Nguyen, M.H. Autoantibodies in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: Impact on clinical outcomes and extrahepatic manifestations. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018, 5, e000203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pischke, S.; Hartl, J.; Pas, S.D.; Lohse, A.W.; Jacobs, B.C.; Van der Eijk, A.A. Hepatitis E virus: Infection beyond the liver? J. Hepatol. 2016, 66, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westholter, D.; Hiller, J.; Denzer, U.; Polywka, S.; Ayuk, F.; Rybczynski, M.; Horvatits, T.; Gundlach, S.; Blöcker, J.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; et al. HEV-positive blood donations represent a relevant infection risk for immunosuppressed recipients. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Akmatov, M.K.; Rober, N.; Ahrens, W.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Fricke, J.; Greiser, H.; Günther, K.; Kaaks, R.; Kemmling, Y.; Krone, B.; et al. Anti-nuclear autoantibodies in the general German population: Prevalence and lack of association with selected cardiovascular and metabolic disorders-findings of a multicenter population-based study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Woods-Burnham, L.; Ortiz, G.; Rios-Colon, L.; Figueroa, J.; Albesa, R.; Andrade, L.E.; Mahler, M.; Casiano, C.A. Specificity of antinuclear autoantibodies recognizing the dense fine speckled nuclear pattern: Preferential targeting of DFS70/LEDGFp75 over its interacting partner MeCP2. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 161, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Grygiel-Gorniak, B.; Rogacka, N.; Puszczewicz, M. Antinuclear antibodies in healthy people and non-rheumatic diseases—Diagnostic and clinical implications. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Im, J.H.; Chung, M.H.; Park, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.S. Antinuclear antibodies in infectious diseases. Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, C.M.; Binder, S.R. ANA testing in the presence of acute and chronic infections. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2016, 37, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, L.E.; Yoon, J.C.; Raghuraman, S.; Moir, S.; Sneller, M.C.; Rehermann, B. B cell homeostasis in chronic hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia is maintained through naive B cell apoptosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Felden, J.; Alric, L.; Pischke, S.; Aitken, C.; Schlabe, S.; Spengler, U.; Giordani, M.T.; Schnitzler, P.; Bettinger, D.; Thimme, R.; et al. The burden of hepatitis E among patients with haematological malignancies: A retrospective European cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, J.; Pas, S.D.; Agteresch, H.J.; de Man, R.A.; Maaskant, J.; Schipper, M.E.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Cornelissen, J.J.; van der Eijk, A.A. Hepatitis E virus: An underestimated opportunistic pathogen in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2013, 122, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yan, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, L. Presence and persistence of hepatitis E virus RNA and proteins in human bone marrow. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalit, M.; Wollner, S.; Levo, Y. Cryoglobulinemia in acute type-A hepatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1982, 47, 613–616. [Google Scholar]
- Florin-Christensen, A.; Roux, M.E.; Aarana, R.M. Cryoglobulins in acute and chronic liver diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1974, 16, 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Saadoun, D.; Asselah, T.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Charlotte, F.; Bedossa, P.; Valla, D.; Piette, J.C.; Marcellin, P.; Cacoub, P. Cryoglobulinemia is associated with steatosis and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, U.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Gulli, F.; Santini, S.A.; Todi, L.; Marino, M.; Rapaccini, G.L. Serological profile of asymptomatic HCV positive patients with low level of cryoglobulins. Biofactors 2018, 45, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olyaei, A.J.; de Mattos, A.M.; Bennett, W.M. Nephrotoxicity of immunosuppressive drugs: New insight and preventive strategies. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2001, 7, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonwa, T.A.; Mai, M.L.; Melton, L.B.; Hays, S.R.; Goldstein, R.M.; Levy, M.F.; Klintmalm, G.B. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLTX) using calcineurin-based immunotherapy: Risk of development and treatment. Transplantation 2001, 72, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beddhu, S.; Bastacky, S.; Johnson, J.P. The clinical and morphologic spectrum of renal cryoglobulinemia. Medicine 2002, 81, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, S.A.; Blumel, J.; Mizusawa, S.; Matsubayashi, K.; Sakata, H.; Okada, Y.; Nübling, C.M.; Hanschmann, K.M.; HEV Collaborative Study Group. World Health Organization International Standard to harmonize assays for detection of hepatitis E virus RNA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaski, J.; Weiler-Normann, C.; Schakat, M.; Zachou, K.; Muratori, P.; Lampalzer, S.; Haag, F.; Schramm, C.; Lenzi, M.; Dalekos, G.N.; et al. Update of the simplified criteria for autoimmune hepatitis: Evaluation of the methodology for immunoserological testing. J. Hepatol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyckova, G.; Murali, M. Laboratory testing for cryoglobulins. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of HEV infection | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Asymptomatic | Acute | Chronic |
| Patients, (%) | 29 (51) | 13 (23) | 15 (26) |
| Age, years #,+ | 40 (29–51) | 51 (47–61) | 58 (46–63) |
| Female, (%) | 9 (31) | 3 (23) | 5 (33) |
| AST, U/L #,+ | 23 (20–26) | 189 (49–707) | 139 (36–227) |
| ALT, U/L #, | 35 (29–49) | 872 (633–2327) | 137 (42–424) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL #,+ | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 0.9 (0.7–1.2) | 1.6 (1.3–1.8) |
| Bilirubin, mg/dL # | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 1 (0.6–2.6) | 0.8 (0.5-1) |
| Serum IgG, g/L | 10 (8.8–11.7) | 10.8 (9.5–13.1) | 10.3 (8.5–20.3) |
| Serum IgA, g/L | 2.2 (1.4–3.1) | 2.4 (1.6–3.8) | 1.8 (1.2–2.2) |
| Serum IgM, g/L # | 0.8 (0.5–1.1) | 1.3 (0.8–2.4) | 1 (0.5–1.3) |
| Anti-HEV IgG, (%) #, | 13/25 (52) | 8/8 (100) | 10/12 (83) |
| Anti-HEV IgM, (%) #,+,* | 13/25 (52) | 10/10 (100) | 12/12 (100) |
| HEV-RNA, IU/mL #,+ | 580 (24–3,735) | 3500 (43–134,624) | 740,000 (66,000–27,000,000) |
| Variable | Cryoglobulins | w/o Cryoglobulins | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 5 | 52 | |
| Age, years | 55 (46–57) | 49 (35–55) | 0.31 |
| Female, (%) | 0 (0) | 17 (33) | 0.31 |
| AST, U/L | 36 (22–238) | 28 (21–135) | 0.63 |
| ALT, U/L | 42 (22–856) | 56 (33–492) | 0.69 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.6 (1.3–2.8) | 0.9 (0.8–1.2) | 0.007 |
| Bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.5 (0.3–1.2) | 0.6 (0.4–0.9) | 0.47 |
| Serum IgG, g/L | 13 (8.2–22.8) | 10.3 (8.9–12.3) | 0.41 |
| Serum IgA, g/L | 1.7 (1.2–7.6) | 1.9 (1.5–3.2) | 0.91 |
| Serum IgM, g/L | 1.6 (1.1–2.5) | 0.9 (0.5–1.2) | 0.024 |
| HEV-RNA, IU/mL | 670,000 (28,500–16,550,000) | 2467 (140–74,500) | 0.018 |
| ANA titers * | 2 (40) | 11 (21) | 0.58 |
| Rheumatoid factor | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 1.0 |
| Patient | Sex | Age | Acute/Chronic | Type of Tx | Immuno-Suppression | PLT (109/L) | WBC (109/L) | Lymph. (109/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | M | 55 | Acute | - | - | 155 | 4.3 | 1.36 |
| #2 | M | 45 | Chronic | Kidney | Tac/MMF/S | 227 | 3.8 | 1.55 |
| #3 | M | 56 | Chronic | Heart | Eve/MMF | 230 | 5.8 | 1.21 |
| #4 | M | 58 | Chronic | Kidney | S * | 153 | 4.7 | 1.05 |
| #5 | M | 46 | Chronic | Heart | Eve/MMF/S | 348 | 6.4 | NA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horvatits, T.; Schulze zur Wiesch, J.; Polywka, S.; Buescher, G.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Hussey, E.; Horvatits, K.; Peine, S.; Haag, F.; Addo, M.M.; et al. Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies and Cryoglobulins in Patients with Acute and Chronic HEV Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090755
Horvatits T, Schulze zur Wiesch J, Polywka S, Buescher G, Lütgehetmann M, Hussey E, Horvatits K, Peine S, Haag F, Addo MM, et al. Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies and Cryoglobulins in Patients with Acute and Chronic HEV Infection. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090755
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorvatits, Thomas, Julian Schulze zur Wiesch, Susanne Polywka, Gustav Buescher, Marc Lütgehetmann, Elaine Hussey, Karoline Horvatits, Sven Peine, Friedrich Haag, Marylyn M. Addo, and et al. 2020. "Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies and Cryoglobulins in Patients with Acute and Chronic HEV Infection" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090755
APA StyleHorvatits, T., Schulze zur Wiesch, J., Polywka, S., Buescher, G., Lütgehetmann, M., Hussey, E., Horvatits, K., Peine, S., Haag, F., Addo, M. M., Lohse, A. W., Weiler-Normann, C., & Pischke, S. (2020). Significance of Anti-Nuclear Antibodies and Cryoglobulins in Patients with Acute and Chronic HEV Infection. Pathogens, 9(9), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090755







