Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
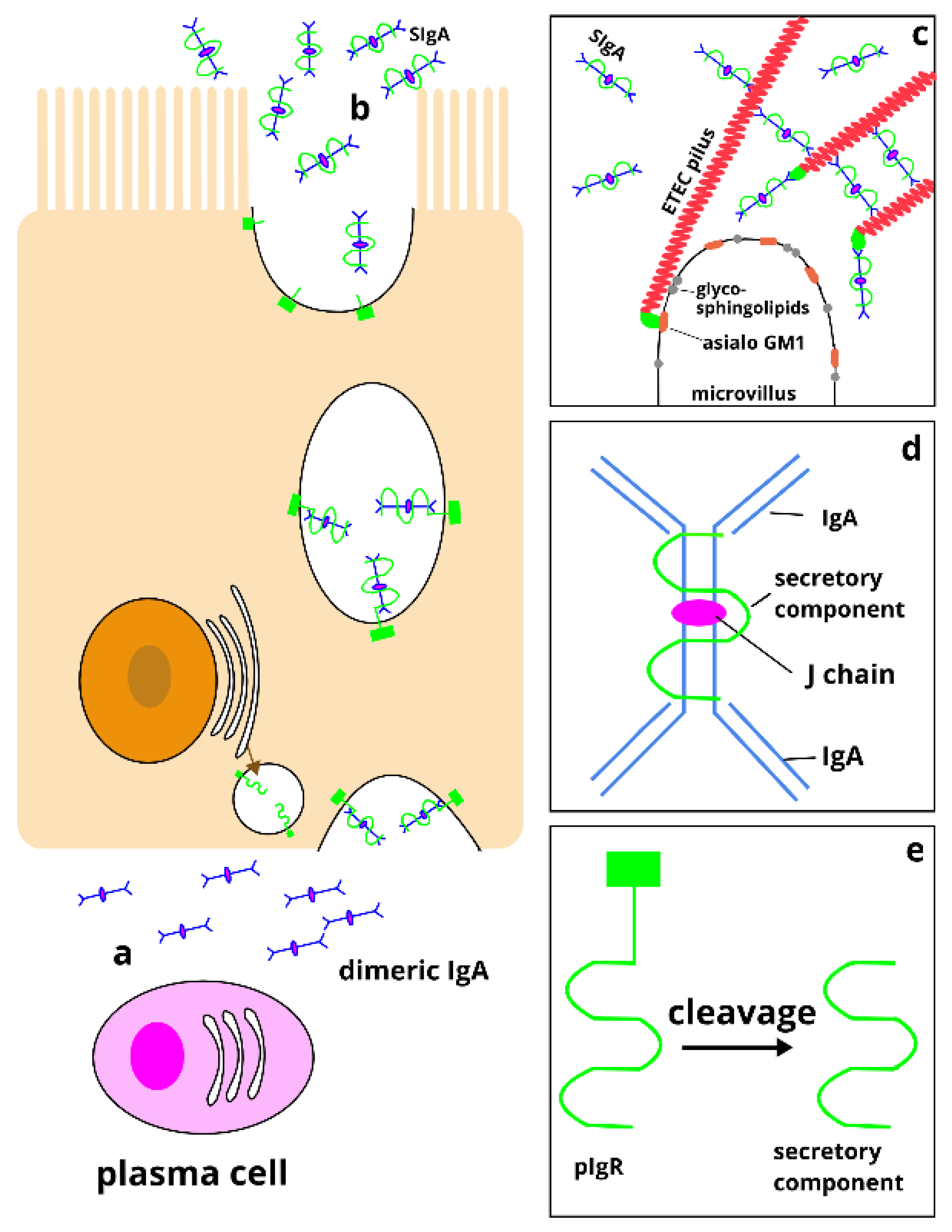
2. Importance and Origins of IgA Responses
3. Direct and Indirect Measurements of Small Intestinal SIgA Responses
4. SIgA Responses to ETEC Infection
| IgA Responses, Day of Peak (Fold Increase) (No. of Responders/No. of Volunteers) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigens | Serum | ALS/ASC | Salivary | Intestinal a | Strains | Dose (log10) | References |
| WC O78 | d10(9)(5/6) | H10407 | 6 | 1978 Evans [55] | |||
| WC O78 | d10(14)(6/7) | H10407 | 8 | 1978 Evans [55] | |||
| O167 | ng(2)(3/5) *J | 214-4 | 6, 8, 10 | 1977 Levine [56] | |||
| O148 | ng(9)(20/29) | B7A | 5, 6, 9 | 1979 Levine [19] | |||
| O25 | ng(6,6)(2/6) | E2528C-1 | 5, 6, 9 | 1979 Levine [19] | |||
| O78 | d10(7/7)ng | H10407 | 8 | 1982 Levine [57] | |||
| O78 | d7(>2.5)(22/27) | H10407 | 7 | 2012 Darsley [58] | |||
| O78 | d10(59.8)(42/44) | d7(1093)(42/44) | d10(4.5)(6/10) | d10(86.3)(5/5) *F | H10407 | 7.3, 8 | 2016 Chakraborty [17] |
| O78 | d9(16)(9/15) | d9(125)(10/15) | d9(5.3)(9/15) *F | H10407 | 5 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| O78 | d9(10)(7/15) | d7(116)(12/15) | d9(9.3)(11/15) *F | H10407 | 6 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| WC O6 | d10(24)(29/30) | TW10589 | 6, 7, 8, 9 | 2014 Skrede [53] | |||
| WC O6 | d10(5.6)(26/30) | d10(10.4)(25/27) | d10(7.7)(26/29) *L | TW10589 | 6, 7, 8, 9 | 2016 Aase [32] | |
| LT | d30(2.5)(2/6) | H10407 | 6 | 1977 Evans [55] | |||
| LT | d10(3)(4/7) | H10407 | 8 | 1977 Evans [55] | |||
| LT | ng(28)(20/29) | B7A | 5, 6, 9 | 1979 Levine [19] | |||
| LT | ng(8)(4/6) | E2528C-1 | 5, 6, 9 | 1979 Levine [19] | |||
| LT | d21(6/7)ng | H10407 | 8 | 1982 Levine [57] | |||
| LT (EltB) | d14(6.3)(12/15) | d10(10)(12/15) * | H10407 | 8, 9 | 2007 Coster [60] | ||
| LT (EltB) | d10(6.1)(13/15) | d7(9)(14/16) * | B7A | 8, 10 | 2007 Coster [60] | ||
| LT | d28(3.3)(1/6) | d7(23)ng * | E24377A | 8, 9 | 2008 McKenzie [61] | ||
| LT | d10(>4)(13/14) | LSN03, WS011 | 8–10 | 2019 Savarino [62] | |||
| LT (EltB) | ng(>2.5)(3/27) | ng(>4)(17/27) | H10407 | 7 | 2011 Darsley [58] | ||
| LT (EltB) | d10(2.5)(28/44) | d7(14.2)(35/44) | d28(1)(3/8) | d28(3.6)(4/5) *F | H10407 | 7.3, 8 | 2016 Chakraborty [17] |
| LT | ng(17.4)(10/11) | H10407 | 9 | 2017 Savarino [63] | |||
| LT (EltB) | ng(>2)(11/20) | d7(1.7)(6/20) | H10407 | 7 | 2018 Chakraborty [64] | ||
| LT (EltB) | d9(1.6)(3/15) | d9(2.6)(9/15) | ng(ng)(4/15) *F | H10407 | 5 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| LT (EltB) | d28(1.63)(4/15) | d9(1.44)(5/15) | ng(ng)(4/15) *F | H10407 | 6 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| LT | ng(>2)(5/12) | LSN03, WS011 | 8–10 | 2019 Savarino [62] | |||
| CFA/I fim | d30(2.6)(3/6) | H10407 | 6 | 1977 Evans [55] | |||
| CFA/I fim | d10(6.6)(4/6) | H10407 | 8 | 1977 Evans [55] | |||
| CFA/I | d8(6/7)ng | H10407 | 8 | 1982 Levine [57] | |||
| CFA/I | d28(40)(15/15) | d14–28(26)(14/15) * | H10407 | 8, 9 | 2007 Coster [60] | ||
| CFA/I | ng(>2.5)(10/27) | ng(>4)(18/27) | H10407 | 7 | 2012 Darsley [58] | ||
| CFA/I | d28(2)(22/44) | d7(4.1)(21/44) | d28(0.55)(0/5) *F | H10407 | 7.3, 8 | 2016 Chakraborty [17] | |
| CFA/I | ng(8.9)(4/11) | H10407 | 9 | 2017 Savarino [63] | |||
| CFA/I | ng(ng)(1/15) | d9(2.9)(10/15) | no rise(4/15) *F | H10407 | 5 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| CFA/I | ng(ng)(3/15) | d7(2.5)(7/15) | no rise(4/15) *F | H10407 | 6 | 2018 Chakraborty [59] | |
| CFA/I | ng(>2)(12/20) | d7(3.3)(16/20) | H10407 | 7 | 2018 Chakraborty [64] | ||
| CFA/I(CfaB) | 3m(9.6)(8/9) | d10(2.9)ng | TW11681 | 6,7,8 | 2019 Sakkestad [54] | ||
| CFAII | d7(88)(9/10) * | d7(72)(6/9) *J | E23477A | 9 | 1994 Tacket [65] | ||
| CS1 | d7(58)(4/10) * | E23477A | 9 | 1994 Tacket [65] | |||
| CS1 | d28(5.89)(7/17) | d7(66){14/17) * | ng(ng)(13/17) | E24377A | 8,9 | 2008 McKenzie [61] | |
| CS1 + CS3 | ng(ng)(6/9) | d7(4)(2/8) *J | E24377A | 8,7 | 1984 Levine [38] | ||
| CS3 | d7(161)(9/10) * | E23477A | 9 | 1994 Tacket [65] | |||
| CS3 | d28(4.4)(7/17) | d7(53)(10/17) * | ng(ng)(10/17) | E24377A | 8,9 | 2008 McKenzie [61] | |
| CS5 (CsfA) | d28(5.2)(17/21) | TW10722 | 6,7,8,9,10 | 2019 Sakkestad [54] | |||
| CS6 | d10(15)(5/16) | d7–10(12)(8/16) * | B7A | 8,10 | 2007 Coster [60] | ||
| CS6 (CssA + B) | d10(1.3)(5/21) | TW10722 | 6,7,8,9,10 | 2019 Sakkestad [54] | |||
| CS17 | ng(>2)(12/12) | LSNO3, WSO11 | 8–10 | 2019 Savarino [62] | |||
| YghJ | d7(7.62)18/20 | H10407 | 7 | 2018 Chakraborty [64] | |||
| YghJ | d10(3.7)(17/21) | TW10722 | 6,7,8,9,10 | 2019 Sakkestad [54] | |||
| YghJ | d10{3.2)(7/9) | d7(267)ng | TW11681 | 6,7,8 | 2019 Sakkestad [54] | ||
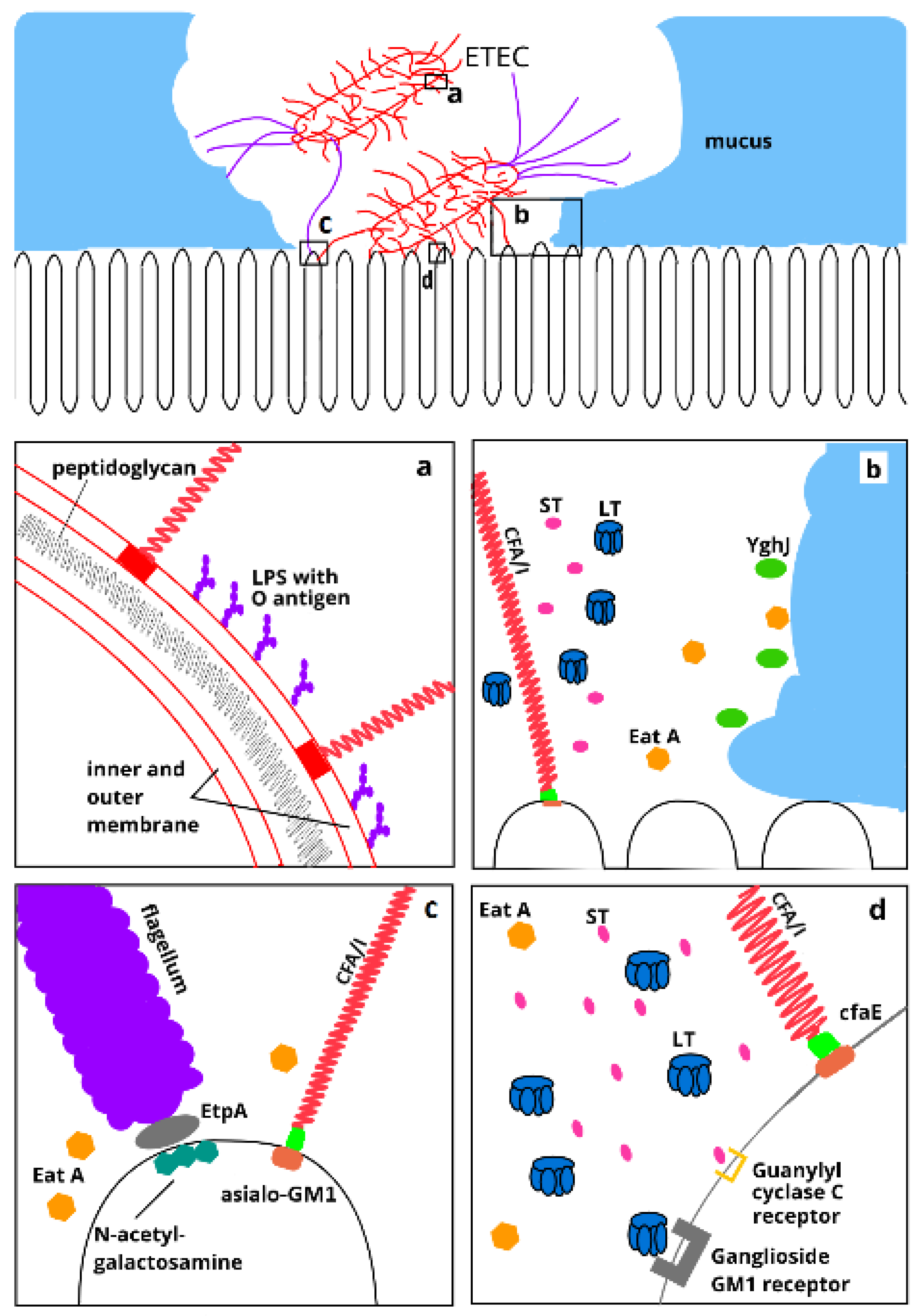
4.1. O-Antigen
4.2. Toxins
4.3. Colonization Factors
4.4. Nonclassical Antigens
5. SIgA and Protective Immunity
6. Limitations of ETEC CHIM Studies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIEC | Adherent-invasive Escherichia Coli |
| ALS | Antibody in lymphocyte supernatant |
| ASC | Antibody secreting cell |
| CFA/I | Colonization factor 1 |
| CHIM | Controlled human infection model |
| CS | Coli surface antigen |
| DAEC | Diffusely adherent Escherichia Coli |
| dmLT | Double mutant labile toxin |
| EAEC | Enteroaggregative Escherichia Coli |
| EHEC | Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli |
| EIEC | Enteroinvasive Escherichia Coli |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ELISPOT | Enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot |
| EPEC | Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli |
| ETEC | Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli |
| GALT | Gut-associated lymphoid tissue |
| GM1 | Monosialotetrahexosylganglioside 1 |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| LMICs | Lower-Middle income countries |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LT | Labile toxin |
| pIgR | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor |
| PMBC | Periphral blood mononuclear cell |
| SC | Secretory component |
| SIgA | Secretory immunoglobulin A |
| ST | Stable toxin |
| STEC | Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia Coli |
| WC | Whole cell |
References
- Shulman, S.T.; Friedmann, H.C.; Sims, R.H. Theodor Escherich: The First Pediatric Infectious Diseases Physician? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Johnson, J.R. Proposal for a New Inclusive Designation for Extraintestinal Pathogenic Isolates of Escherichia coli: ExPEC. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1753–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.; Mazumder, A. Pathogenic Potential, Genetic Diversity, and Population Structure of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from a Forest-Dominated Watershed (Comox Lake) in British Columbia, Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, R.N.; Taylor, L.S.; Tauschek, M.; Robins-Browne, R. Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection and Prolonged Diarrhea in Children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent Advances in Understanding Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, T.P.; Sakellaris, H. Colonization factors of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 90, 155–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, H.L.; Formal, S.B.; Hornick, R.B.; Snyder, M.J.; Libonati, J.P.; Sheahan, D.G.; LaBrec, E.H.; Kalas, J.P. Pathogenesis ofEscherichia coliDiarrhea. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sack, R.B.; Gorbach, S.L.; Banwell, J.G.; Jacobs, B.; Chatterjee, B.D.; Mitra, R.C. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with severe cholera-like disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1971, 123, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalzadeh, N.; Salmanian, A.H.; Ahangari, G.; Sadeghi, M.; Amani, J.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Jafari, M. Design and characterization of a chimeric multiepitope construct containing CfaB, heat-stable toxoid, CssA, CssB, and heat-labile toxin subunit B of enterotoxigenicEscherichia coli: A bioinformatic approach. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2014, 61, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.S.; Lentaigne, J.; Hill, N.E.; Harrison, J.J.; MacKenzie, H.; Akorli, E.; Burns, D.S.; Hutley, E.J.; Connor, P.; Woods, D.R. Epidemiology and etiology of diarrhea in UK military personnel serving on the United Nations Mission in South Sudan in 2017: A prospective cohort study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 28, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, W.; Najnigier, B.; Stelmasiak, T.; Robins-Browne, R.M. Randomized control trials using a tablet formulation of hyperimmune bovine colostrum to prevent diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in volunteers. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, M.E.; Adcock, P.M.; Smith, S.W.; Quinlan, K.; Kamimoto, L.A.; Rowe, S.Y.; Scott, K.; Conover, C.; Varchmin, T.; Bopp, C.A.; et al. Epidemic Diarrhea due to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roels, T.H.; Proctor, M.E.; Robinson, L.C.; Hulbert, K.; Bopp, C.A.; Davis, J.P. Clinical features of infections due to Escherichia coli producing heat-stable toxin during an outbreak in Wisconsin: A rarely suspected cause of diarrhea in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravioto, A.; Reyes, R.E.; Trujillo, F.; Uribe, F.; Navarro, A.; De La Roca, J.M.; Hernandez, J.M.; Perez, G.; Vazquez, V. Risk of diarrhea during the first year of life associated with initial and subsequent colonization by specific enteropathogens. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 131, 886–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Harro, C.; DeNearing, B.; Ram, M.; Feller, A.; Cage, A.; Bauers, N.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.; Sack, D.A. Characterization of Mucosal Immune Responses to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Antigens in a Human Challenge Model: Response Profiles after Primary Infection and Homologous Rechallenge with Strain H10407. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Frech, S.A.; Flyer, D.C.; Bloom, A.; Kazempour, K.; Glenn, G.M. Transcutaneous immunization with the heat-labile toxin (LT) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC): Protective efficacy in a double-blind, placebo-controlled challenge study. Vaccine 2007, 25, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.M.; Nalin, D.R.; Hoover, D.L.; Bergquist, E.J.; Hornick, R.B.; Young, C.R. Immunity to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1979, 23, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Merson, M.H.; Rowe, B.; Taylor, P.R.; Alim, A.R.M.A.; Gross, R.J.; Sack, D.A. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: Acquired immunity and transmission in an endemic area. Bull. World Health Organ. 1981, 59, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, M.M.; Barry, E.M.; Chen, W.H. A roadmap for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine development based on volunteer challenge studies. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1357–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Bartels, S.; Qadri, F.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Elicits Immune Responses to Multiple Surface Proteins. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3027–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Randall, A.; Vickers, T.J.; Molina, D.; Harro, C.D.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Sack, D.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Felgner, P.L.; et al. Interrogation of a live-attenuated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine highlights features unique to wild-type infection. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; He, B.; Chiu, A.; Chadburn, A.; Shan, M.; Buldys, M.; Ding, A.; Knowles, D.M.; Santini, P.A.; Cerutti, A. Epithelial cells trigger frontline immunoglobulin class switching through a pathway regulated by the inhibitor SLPI. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandtzaeg, P.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Morton, H.C. From B to A the mucosal way. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, B.J.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Gothefors, L.; Barua, D.; Huda, S.; Holmgren, J. Local and Systemic Antibody Responses to Naturally Acquired Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Diarrhea in an Endemic Area. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 153, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.; Evans, D.J., Jr.; Opekun, A.R.; Graham, D.Y. Non-replicating oral whole cell vaccine protective against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) diarrhea: Stimulation of anti-CFA (CFA/I) and anti-enterotoxin (anti-LT) intestinal IgA and protection against challenge with ETEC belonging to heterologous serotypes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1988, 47, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; Johansen, F.-E.; Brandtzaeg, P. The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Secretory immunity with special reference to the oral cavity. J. Oral Microbiol. 2013, 5, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmeier, W.; Hennemann, A.; Caspary, W.F. IgA and IgM V(H) repertoires in human colon: Evidence for clonally expanded B cells that are widely disseminated. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, C.; Wahl, B.; Fohse, L.; Suerbaum, S.; Macpherson, A.J.; Prinz, I.; Pabst, O. Age, microbiota, and T cells shape diverse individual IgA repertoires in the intestine. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aase, A.; Sommerfelt, H.; Petersen, L.B.; Bolstad, M.; Cox, R.J.; Langeland, N.; Guttormsen, A.B.; Steinsland, H.; Skrede, S.; Brandtzaeg, P. Salivary IgA from the sublingual compartment as a novel noninvasive proxy for intestinal immune induction. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.; Sollid, L.M. The human intestinal B-cell response. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, F.-E.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Carlsen, H.S.; Farstad, I.N.; Soler, D.; Brandtzaeg, P. Regional induction of adhesion molecules and chemokine receptors explains disparate homing of human B cells to systemic and mucosal effector sites: Dispersion from tonsils. Blood 2005, 106, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boysen, A.; Palmisano, G.; Krogh, T.J.; Duggin, I.G.; Larsen, M.R.; Moller-Jensen, J. A novel mass spectrometric strategy “BEMAP” reveals Extensive O-linked protein glycosylation in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Engstrom, F.; Hall, E.; Chang, H.S.; Gomes, J.G.; Kyle, J.L.; Cassels, F.; Turner, A.K.; Randall, R.; et al. Comparative Safety and Immunogenicity of Two Attenuated Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Strains in Healthy Adults. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qadri, F.; Akhtar, M.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Chowdhury, M.I.; Ahmed, T.; Rafique, T.A.; Khan, A.; Rahman, S.I.A.; Khanam, F.; Lundgren, A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the oral, inactivated, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine ETVAX in Bangladeshi children and infants: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.M.; Ristaino, P.; Marley, G.; Smyth, C.; Knutton, S.; Boedeker, E.; Black, R.E.; Young, C.; Clements, M.L.; Cheney, C. Coli surface antigens 1 and 3 of colonization factor antigen II-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: Morphology, purification, and immune responses in humans. Infect. Immun. 1984, 44, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jertborn, M.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Holmgren, J. Saliva, breast milk, and serum antibody responses as indirect measures of intestinal immunity after oral cholera vaccination or natural disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 24, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantele, A.; Arvilommi, H.; Jokinen, I. Specific immunoglobulin-secreting human blood cells after peroral vaccination against Salmonella typhi. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 153, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantele, A. Antibody-secreting cells in the evaluation of the immunogenicity of an oral vaccine. Vaccine 1990, 8, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åhrén, C.; Jertborn, M.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Intestinal Immune Responses to an Inactivated Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine and Associated Immunoglobulin A Responses in Blood. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3311–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Ahmed, T.; Ahmed, F.; Bradley Sack, R.; Sack, D.A.; Svennerholm, A.M. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral, inactivated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli plus cholera toxin B subunit vaccine in Bangladeshi children 18–36 months of age. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S.; Sack, D.A. Development of a Novel In Vitro Assay (ALS Assay) for Evaluation of Vaccine-Induced Antibody Secretion from Circulating Mucosal Lymphocytes. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Carpenter, C.; Hall, E.; Randall, R.; McKenzie, R.; Cassels, F.; Diaz, N.; Thomas, N.; Bedford, P.; Darsley, M.; Gewert, C.; et al. Comparison of the antibody in lymphocyte supernatant (ALS) and ELISPOT assays for detection of mucosal immune responses to antigens of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in challenged and vaccinated volunteers. Vaccine 2006, 24, 3709–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsland, H.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Gjessing, H.K.; Aaby, P.; Molbak, K.; Sommerfelt, H. Protection from natural infections with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: Longitudinal study. Lancet 2003, 362, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, C.D.; Chakraborty, S.; Feller, A.; DeNearing, B.; Cage, A.; Ram, M.; Lundgren, A.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.I.; et al. Refinement of a Human Challenge Model for Evaluation of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.K.; Riddle, M.S.; Alcala, A.N.; Sack, D.A.; Harro, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Gutiérrez, R.L.; Savarino, S.J.; Darsley, M.; McKenzie, R.; et al. An Evidenced-Based Scale of Disease Severity following Human Challenge with Enteroxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersing, B.K.; Porter, C.K.; Kotloff, K.; Neels, P.; Cravioto, A.; MacLennan, C.A. How can controlled human infection models accelerate clinical development and policy pathways for vaccines against Shigella? Vaccine 2019, 37, 4778–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.W.; Gyles, C.L. The Relationship Between Two Apparently Different Enterotoxins Produced By Enteropathogenic Strains Of Escherichia Coli Of Porcine Origin. J. Med. Microbiol. 1970, 3, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, H.W.; Halls, S. The transmissible nature of the genetic factor in Escherichia coli that controls haemolysin production. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1967, 47, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vedoy, O.B.; Hanevik, K.; Sakkestad, S.T.; Sommerfelt, H.; Steinsland, H. Proliferation of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain TW11681 in stools of experimentally infected human volunteers. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrede, S.; Steinsland, H.; Sommerfelt, H.; Aase, A.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Langeland, N.; Cox, R.; Sævik, M.; Wallevik, M.; Skutlaberg, D.H.; et al. Experimental infection of healthy volunteers with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coliwild-type strain TW10598 in a hospital ward. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkestad, S.T.; Steinsland, H.; Skrede, S.; Lillebø, K.; Skutlaberg, D.H.; Guttormsen, A.B.; Zavialov, A.; Paavilainen, S.; Søyland, H.; Sævik, M.; et al. A new human challenge model for testing heat-stable toxin-based vaccine candidates for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea—Dose optimization, clinical outcomes, and CD4+ T cell responses. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.; Satterwhite, T.K.; Evans, D.J.; Jr DuPont, H.L. Differences in serological responses and excretion patterns of volunteers challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with and without the colonization factor antigen. Infect. Immun. 1978, 19, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.M.; Caplan, E.S.; Waterman, D.; Cash, R.A.; Hornick, R.B.; Snyder, M.J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1977, 17, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.M.; Black, R.E.; Brinton, C.C.; Jr Clements, M.L.; Fusco, P.; Hughes, T.P.; Odonnell, S.; Robins-Browne, R.; Wood, S.; Young, C.R. Reactogenicity, immunogenicity and efficacy studies of Escherichia coli type 1 somatic pili parenteral vaccine in man. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 1982, 33, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Darsley, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; DeNearing, B.; Sack, D.A.; Feller, A.; Buchwaldt, C.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.; Harro, C.D. The Oral, Live Attenuated Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine ACE527 Reduces the Incidence and Severity of Diarrhea in a Human Challenge Model of Diarrheal Disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Harro, C.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Connor, S.; Maier, N.; Dally, L.; Flores, J.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Walker, R.; et al. Impact of lower challenge doses of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli on clinical outcome, intestinal colonization and immune responses in adult volunteers. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacket, C.O.; Losonsky, G.; Link, H.; Hoang, Y.; Guesry, P.; Hilpert, H.; Levine, M.M. Protection by Milk Immunoglobulin Concentrate against Oral Challenge with EnterotoxigenicEscherichia coli. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.; Darsley, M.; Thomas, N.; Randall, R.; Carpenter, C.; Forbes, E.; Finucane, M.; Sack, R.B.; Hall, E.; Bourgeois, A.L. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of PTL-003, an attenuated enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) vaccine strain, in protecting against challenge with virulent ETEC. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, S.J.; McKenzie, R.; Tribble, D.R.; Porter, C.K.; O’Dowd, A.; Sincock, S.A.; Poole, S.T.; DeNearing, B.; Woods, C.M.; Kim, H.; et al. Hyperimmune Bovine Colostral Anti-CS17 Antibodies Protect Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Diarrhea in a Randomized, Doubled-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Human Infection Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, S.J.; McKenzie, R.; Tribble, D.R.; Porter, C.K.; O’Dowd, A.; Cantrell, J.A.; Sincock, S.A.; Poole, S.T.; DeNearing, B.; Woods, C.M.; et al. Prophylactic Efficacy of Hyperimmune Bovine Colostral Antiadhesin Antibodies Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Diarrhea: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1 Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Randall, A.; Vickers, T.J.; Molina, D.; Harro, C.D.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Sack, D.A.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Felgner, P.L.; et al. Human Experimental Challenge With Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Elicits Immune Responses to Canonical and Novel Antigens Relevant to Vaccine Development. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacket, C.O.; Reid, R.H.; Boedeker, E.C.; Losonsky, G.; Nataro, J.P.; Bhagat, H.; Edelman, R. Enteral immunization and challenge of volunteers given enterotoxigenic E. coli CFA/II encapsulated in biodegradable microspheres. Vaccine 1994, 12, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.P.; Wang, L. Genomic organization of LPS-specific loci. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 264, 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.K. Occurrence, distribution, and associations of O and H serogroups, colonization factor antigens, and toxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 569–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, R.S.; Grimont, F.; Lenormand, P.; Burguiere, P.; Beutin, L.; Grimont, P.A. Identification of Escherichia coli O-serogroups by restriction of the amplified O-antigen gene cluster (rfb-RFLP). Res. Microbiol. 2000, 151, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-R.; Wu, F.-T.; Tsai, J.-L.; Mu, J.-J.; Lin, L.-F.; Chen, K.-L.; Kuo, S.H.-S.; Chiang, C.-S.; Wu, H.-S. Comparison between O Serotyping Method and Multiplex Real-Time PCR To Identify Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Taiwan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, Y.; Narimatsu, H.; Miyazato, T.; Nakasone, N.; Higa, N.; Toma, C.; Iwanaga, M. The relationship between O-antigens and pathogenic genes of diarrhea-associated Escherichia coli. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaro, M.A.S.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Mathias-Santos, C.; Guth, B.E.C.; Rãgua-Mangia, A.; Ferreira, A.J.P.; Takagi, M.; Crespo, J.C.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.E.; Ferreira, L.C.D.S. Production and release of heat-labile toxin by wild-type human-derived enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 48, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasaro, M.A.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Mathias-Santos, C.; Guth, B.E.C.; Balan, A.; Sbrogio-Almeida, M.E.; Ferreira, L. Genetic Diversity of Heat-Labile Toxin Expressed by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Humans. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, A.; Young, J.C.; Constantinou, N.; Frankel, G. Infection strategies of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffré, E.; Sjöling, Å. The LT1 and LT2 variants of the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) heat-labile toxin (LT) are associated with major ETEC lineages. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotloff, K.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsland, H.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Perch, M.; Dias, F.; Fischer, T.K.; Aaby, P.; Mølbak, K.; Sommerfelt, H. EnterotoxigenicEscherichia coliInfections and Diarrhea in a Cohort of Young Children in Guinea-Bissau. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.D.; Savarino, S.; Abu-Elyazeed, R.; Safwat, M.; Rao, M.; Wierzba, T.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Holmgren, J.; Frenck, R.; Park, E.; et al. Development of Pathogenicity-Driven Definitions of Outcomes for a Field Trial of a Killed Oral Vaccine against EnterotoxigenicEscherichia coliin Egypt: Application of an Evidence-Based Method. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Lu, T.; Nandre, R.M.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, W. Immunogenicity characterization of genetically fused or chemically conjugated heat-stable toxin toxoids of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in mice and pigs. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, Y.; Govasli, M.L.; Zegeye, E.D.; Sommerfelt, H.; Steinsland, H.; Puntervoll, P. Immunizations with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Toxin Conjugates Engender Toxin-Neutralizing Antibodies in Mice That Also Cross-React with Guanylin and Uroguanylin. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Von Mentzer, A.; Frykberg, P.L.; Aslett, M.; Page, A.J.; Sjöling, Å.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Stability of the Encoding Plasmids and Surface Expression of CS6 Differs in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Encoding Different Heat-Stable (ST) Enterotoxins (STh and STp). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Canto, F.; O’Ryan, M.; Pardo, M.; Torres, A.; Gutierrez, D.; Cádiz, L.; Valdés, R.; Mansilla, A.; Martinez, R.; Hernandez, D.; et al. Chaperone-Usher Pili Loci of Colonization Factor-Negative Human Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Canto, F.; Valenzuela, P.; Cantero, L.; Bronstein, J.; Blanco, J.; Prado, V.; Levine, M.; Nataro, J.; Sommerfelt, H.; Vidal, R.; et al. Distribution of Classical and Nonclassical Virulence Genes in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Chilean Children and tRNA Gene Screening for Putative Insertion Sites for Genomic Islands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3198–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, R.M.; Muhsen, K.; Tennant, S.M.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Faruque, A.S.G.; Saha, D.; Adegbola, R.; et al. Colonization factors among enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from children with moderate-to-severe diarrhea and from matched controls in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS). PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, H.I.; Kamal, K.A.; Wasfy, M.O.; El-Ghorab, N.M.; Lowe, B.; Steffen, R.; Kodkani, N.; Amsler, L.; Waiyaki, P.; David, J.C.; et al. Phenotypic diversity of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) isolated from cases of travelers’ diarrhea in Kenya. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.H.; Nagaraj, S.; Sen, S.; Permala-Booth, J.; Del Canto, F.; Vidal, R.; Barry, E.M.; Bitoun, J.; Chen, W.H.; Tennant, S.M.; et al. Genome and Functional Characterization of Colonization Factor Antigen I- and CS6-Encoding Heat-Stable Enterotoxin-Only Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Reveals Lineage and Geographic Variation. mSystems 2019, 4, e00329-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-F.; Poole, S.; Rasulova, F.; McVeigh, A.L.; Savarino, S.J.; Xia, D. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analyses of several forms of the CfaB major subunit of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CFA/I fimbriae. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Boil. Cryst. Commun. 2009, 65, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Nandre, R.M.; Nietfeld, J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, W. Antibodies induced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) adhesin major structural subunit and minor tip adhesin subunit equivalently inhibit bacteria adherence in vitro. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalouie, F.; Mousavi, S.L.; Nazarian, S.; Amani, J.; Pourfarzam, P. Immunogenic evaluation of chimeric recombinant protein against ETEC, EHEC and Shigella. Mol. Boil. Res. Commun. 2017, 6, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gheibi Hayat, S.M.; Mousavi Gargari, S.L.; Nazarian, S. Construction and immunogenic properties of a chimeric protein comprising CfaE, CfaB and LTB against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Biologicals 2016, 44, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha, R.P.; McVeigh, A.L.; Lee, L.H.; Agnew, M.K.; Cassels, F.J.; Scott, D.A.; Whittam, T.S.; Savarino, S.J. Evolutionary and Functional Relationships of Colonization Factor Antigen I and Other Class 5 Adhesive Fimbriae of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7190–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, S.; Lundgren, A.; Carlin, N.; Löfstrand, M.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Cross-reactivity and avidity of antibody responses induced in humans by the oral inactivated multivalent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine ETVAX. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Wierzba, T.F.; Savarino, S.J.; Abu-Elyazeed, R.; El-Ghoreb, N.; Hall, E.R.; Naficy, A.; Abdel-Messih, I.; Frenck, J.R.W.; Svennerholm, A.; et al. Serologic Correlates of Protection against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güereña-Burgueño, F.; Hall, E.R.; Taylor, D.N.; Cassels, F.J.; Scott, D.A.; Wolf, M.K.; Roberts, Z.J.; Nesterova, G.V.; Alving, C.R.; Glenn, G.M. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Prototype Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Vaccine Administered Transcutaneously. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, A.; Wenneras, C.; Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.M. Antibody responses in humans against coli surface antigen 6 of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 4507–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, D.E.; DeLorimier, A.J.; Wolf, M.K.; Hall, E.R.; Cassels, F.J.; van Hamont, J.E.; Newcomer, R.L.; Davachi, M.A.; Taylor, D.N.; McQueen, C.E. Oral immunization of adult volunteers with microencapsulated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) CS6 antigen. Vaccine 2003, 21, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozen, T.G.; Li, G.; Howard, S.P. YghG Is a Novel Pilot Protein Required for Localization of the GspS Type II Secretion System Secretin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2608–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Luo, Q.; Vickers, T.J.; Sheikh, A.; Lewis, W.G.; Fleckenstein, J.M. EatA, an Immunogenic Protective Antigen of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Degrades Intestinal Mucin. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Hilliard, G.M.; Hamilton, D.J.; Luo, J.; Ostmann, M.M.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli EtpA mediates adhesion between flagella and host cells. Nature 2009, 457, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Luo, Q.; Roy, K.; Shabaan, S.; Kumar, P.; Qadri, F.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Contribution of the Highly Conserved EaeH Surface Protein to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevance, F.F.V.; Hughes, K.T. Coordinating assembly of a bacterial macromolecular machine. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 6, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Roy, K.; Woo-Rasberry, V.; Hamilton, D.J.; Kansal, R.; Qadri, F.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Directed Evaluation of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Autotransporter Proteins as Putative Vaccine Candidates. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lindenthal, C.; Elsinghorst, E.A. Identification of a glycoprotein produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Baldi, D.L.; Tauschek, M.; Strugnell, R.A.; Robins-Browne, R.M. Transcriptional Regulation of the yghJ-pppA-yghG-gspCDEFGHIJKLM Cluster, Encoding the Type II Secretion Pathway in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Qadri, F.; Kansal, R.; Rasko, D.A.; Sheikh, A.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Conservation and immunogenicity of novel antigens in diverse isolates of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Kansal, R.; Bartels, S.R.; Hamilton, D.J.; Shaaban, S.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Adhesin degradation accelerates delivery of heat-labile toxin by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Boil. Chem. 2011, 286, 29771–29779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Hamilton, D.J.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Cooperative role of antibodies against heat-labile toxin and the EtpA Adhesin in preventing toxin delivery and intestinal colonization by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, F.M.; Martin, J.; Hazen, T.H.; Vickers, T.J.; Pashos, M.; Okhuysen, P.C.; Gómez-Duarte, O.G.; Cebelinski, E.; Boxrud, D.; Del Canto, F.; et al. Conservation and global distribution of non-canonical antigens in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, E.B.; Branco, L.M.; Clements, J.D. Evaluating the A-Subunit of the Heat-Labile Toxin (LT) As an Immunogen and a Protective Antigen Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K.; Gentry, L.O. Double-blind comparison of bismuth subsalicylate and placebo in the prevention and treatment of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in volunteers. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Dotson, J.; Allen, K.P.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Identification and molecular characterization of EatA, an autotransporter protein of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, C.; Louis Bourgeois, A.; Sack, D.; Walker, R.; DeNearing, B.; Brubaker, J.; Maier, N.; Fix, A.; Dally, L.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. Live attenuated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine with dmLT adjuvant protects human volunteers against virulent experimental ETEC challenge. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coria, L.M.; Martinez, F.L.; Bruno, L.A.; Pasquevich, K.A.; Cassataro, J. U-Omp19 from Brucella abortus increases dmLT immunogenicity and improves protection against Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin (LT) oral challenge. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, E.B.; Lawson, L.B.; Freytag, L.C.; Clements, J.D. Characterization of a Mutant Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin, LT(R192G/L211A), as a Safe and Effective Oral Adjuvant. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, A.; Bourgeois, L.; Carlin, N.; Clements, J.; Gustafsson, B.; Hartford, M.; Holmgren, J.; Petzold, M.; Walker, R.; Svennerholm, A.-M. Safety and immunogenicity of an improved oral inactivated multivalent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine administered alone and together with dmLT adjuvant in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled Phase I study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 7077–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, D.R.; Goggins, J.A.; Sabbagh, L.M.; Freytag, L.C.; Clements, J.D.; McLachlan, J.B. Adjuvant selection regulates gut migration and phenotypic diversity of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells following parenteral immunization. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppato, M.; Gaspar, C.; Regeimbal, J.; Nunez, R.G.; Giuntini, S.; Schiller, Z.A.; Gawron, M.A.; Pondish, J.R.; Martin, J.C.; Schneider, M.I.; et al. Oral administration of an anti-CfaE secretory IgA antibody protects against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrheal disease in a nonhuman primate model. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Kumru, O.S.; Xiong, J.; Antunez, L.R.; Hickey, J.; Wang, Y.; Cavacini, L.; Klempner, M.; Joshi, S.B.; Volkin, D.B. Preformulation Characterization and Stability Assessments of Secretory IgA Monoclonal Antibodies as Potential Candidates for Passive Immunization by Oral Administration. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riaz, S.; Steinsland, H.; Hanevik, K. Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Pathogens 2020, 9, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090714
Riaz S, Steinsland H, Hanevik K. Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090714
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiaz, Saman, Hans Steinsland, and Kurt Hanevik. 2020. "Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090714
APA StyleRiaz, S., Steinsland, H., & Hanevik, K. (2020). Human Mucosal IgA Immune Responses against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Pathogens, 9(9), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090714





