Brucella abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Increasing Cell Transmigration through the Erk1/2 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
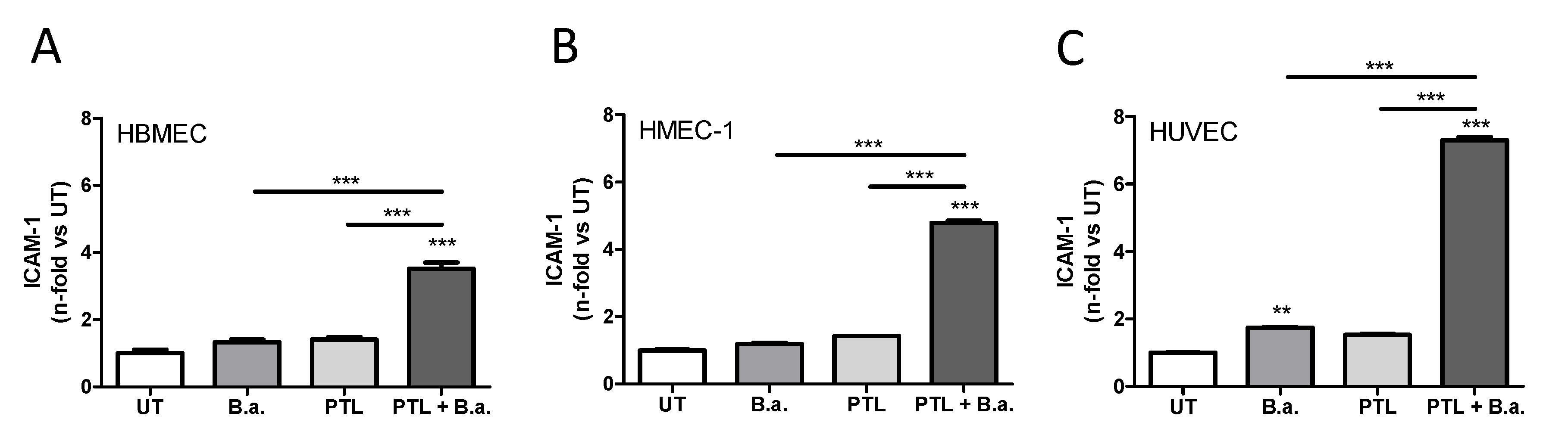
2.1. Interaction with Platelets Enhances the Activation of Endothelial Cells in the Context of B. abortus Infection
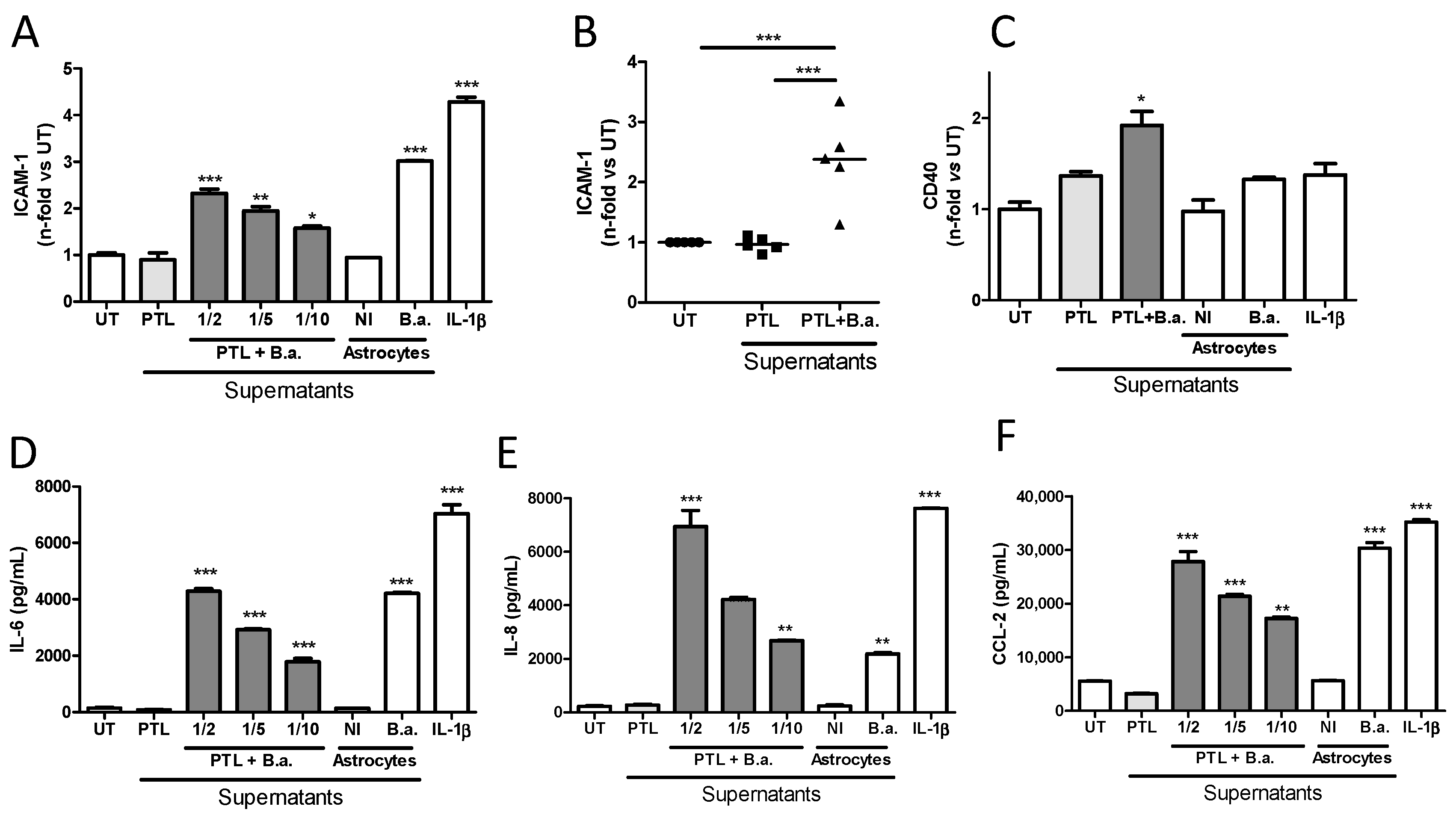
2.2. Supernatants from B. abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
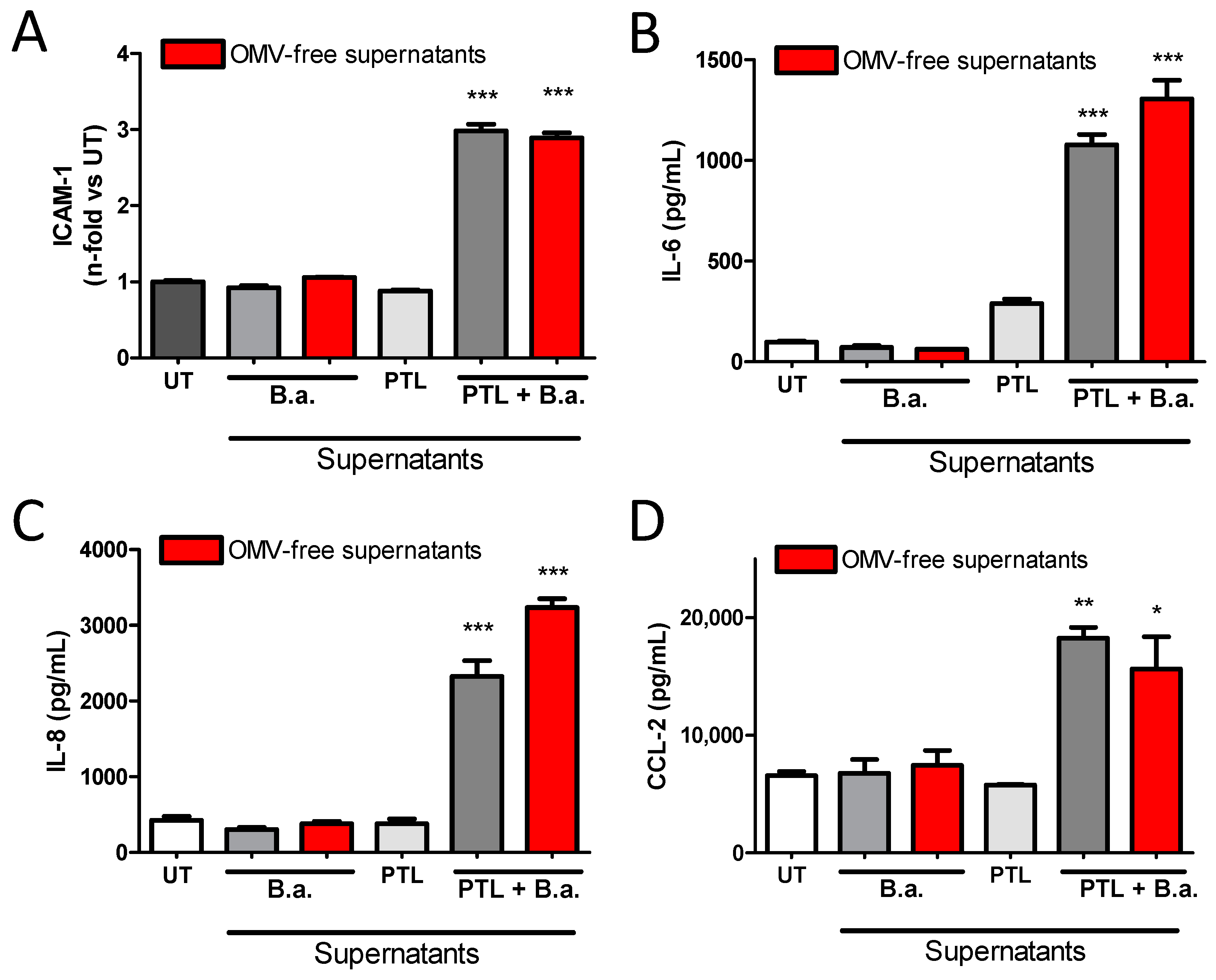
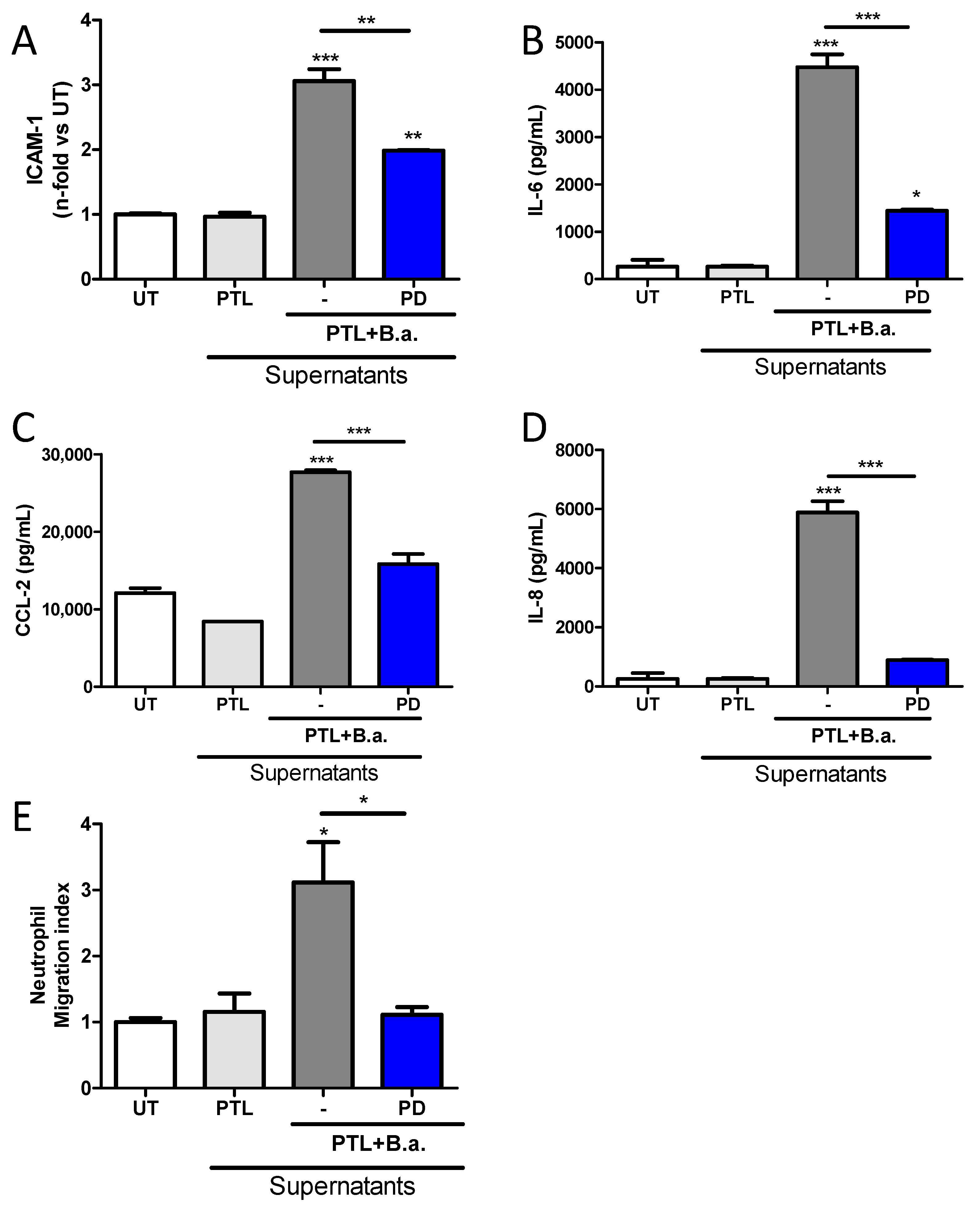
2.3. Secreted Factors from B. abortus-Activated Platelets Activate HBMECs
2.4. B. abortus Lipoprotein-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
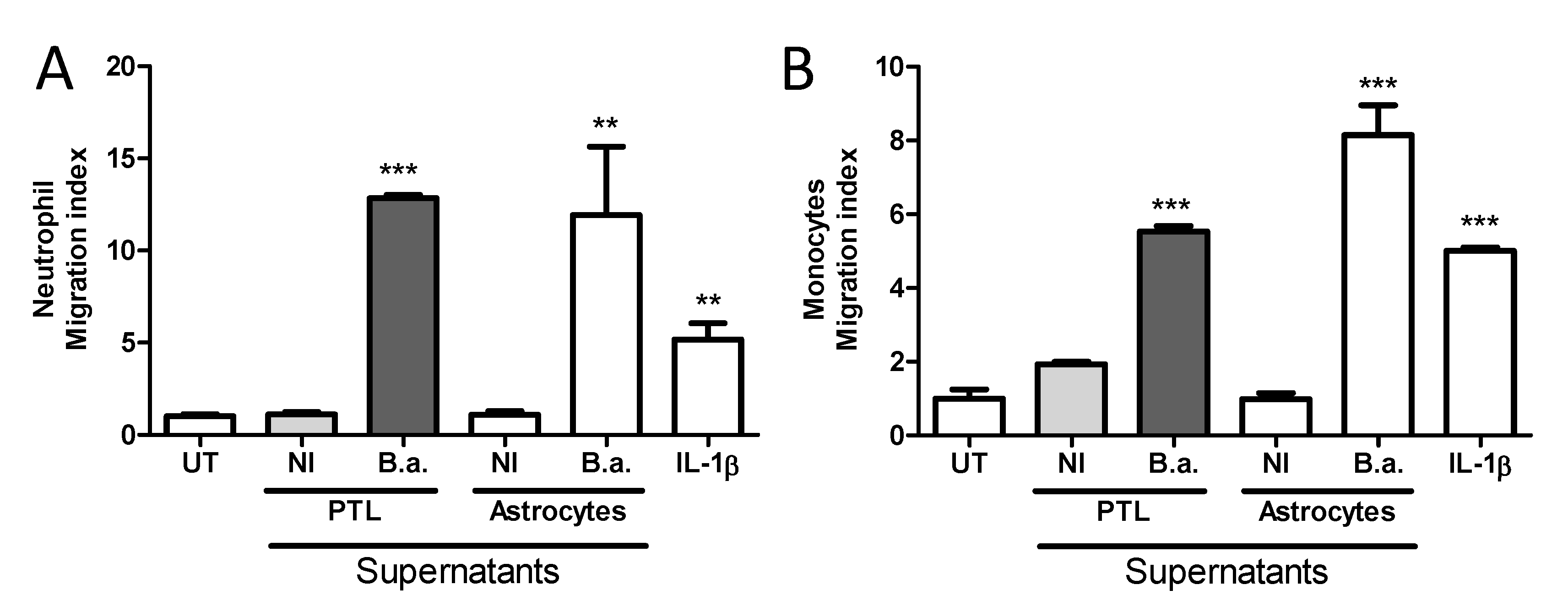
2.5. Platelet-Stimulated HBMECs Induce Transendothelial Migration of Neutrophils and Monocytes
2.6. The Erk1/2 Pathway Is Involved in HMBEC Activation Induced by B. abortus-Stimulated Platelets and It Is Implicated in Transendothelial Migration of Neutrophils
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Bacteria and Lipoproteins
4.3. Cell Lines
4.4. Platelet Purification and Stimulation
4.5. Endothelial Cell Treatment
4.6. Erk1/2 Signaling Pathway
4.7. Measurement of Cytokine and Chemokine Concentrations
4.8. Determination of Cell Surface Molecules by Flow Cytometry
4.9. Neutrophil and Monocytes Transendothelial Migration Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johansson, B.B. The Physiology of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurotransm. Interact. Cogn. Funct. 1990, 274, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M.A.; Gong, C.; Xu, Y.G.; Chang, Y.; Shi, H. Factors controlling permeability of the blood–brain barrier. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 73, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.J.; Corbel, M.J. Brucellosis in Latin America. Brucellosis: Clinical and Laboratory Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Giambartolomei, G.H.; Wallach, J.C.; Baldi, P.C. Neurobrucellosis. In Encephalitis: Diagnosis and Treatment; The Egerton Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 14, pp. 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- Miraglia, M.C.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Barrionuevo, P.; Rodríguez, J.; Kim, K.S.; Dennis, V.A.; Delpino, M.V.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Brucella abortus Traverses Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Using Infected Monocytes as a Trojan Horse. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samartino, C.G.; Delpino, M.V.; Godoy, C.P.; Di Genaro, M.S.; Pasquevich, K.A.; Zwerdling, A.; Barrionuevo, P.; Mathieu, P.; Cassataro, J.; Pitossi, F.; et al. Brucella abortus Induces the Secretion of Proinflammatory Mediators from Glial Cells Leading to Astrocyte Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, M.C.; Scian, R.; Samartino, C.G.; Barrionuevo, P.; Rodriguez, A.M.; E Ibañez, A.; Coria, L.M.; Velásquez, L.N.; Baldi, P.C.; Cassataro, J.; et al. Brucella abortus induces TNF-α-dependent astroglial MMP-9 secretion through mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.M.; Delpino, M.V.; Miraglia, M.C.; Franco, M.M.C.; Barrionuevo, P.; Dennis, V.A.; Oliveira, S.C.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Brucella abortus-activated microglia induce neuronal death through primary phagocytosis. Glia 2017, 65, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, M.C.; Franco, M.M.C.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Bellozi, P.M.Q.; Ferrari, C.C.; Farias, M.I.; Dennis, V.A.; Barrionuevo, P.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Pitossi, F.; et al. Glial Cell-Elicited Activation of Brain Microvasculature in Response to Brucella abortus Infection Requires ASC Inflammasome-Dependent IL-1beta Production. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3794–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landoni, V.I.; Schierloh, P.; Nebel, M.D.C.; Fernandez, G.C.; Calatayud, C.; Lapponi, M.J.; Isturiz, M.A. Shiga Toxin 1 Induces on Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Astrocytes the Release of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha that Alter Brain-Like Endothelium Integrity. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions and blood-brain barrier permeability. J. Anat. 2002, 200, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holinstat, M. Normal platelet function. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carestia, A.; Kaufman, T.; Rivadeneyra, L.; Landoni, V.I.; Pozner, R.G.; Negrotto, S.; D’Atri, L.P.; Gómez, R.M.; Schattner, M. Mediators and molecular pathways involved in the regulation of neutrophil extracellular trap formation mediated by activated platelets. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 99, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, A.; Velásquez, L.N.; Milillo, M.A.; Delpino, M.V.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Landoni, V.I.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Pozner, R.G.; Barrionuevo, P. Platelets Promote Brucella abortus Monocyte Invasion by Establishing Complexes with Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.E.; Seizer, P.; Gawaz, M. Platelets: Inflammatory Firebugs of Vascular Walls. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, s5–s10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchette, J.-P.; Martineau, I.; Gagnon, G. Platelet-rich Plasmas: Growth Factor Content and Roles in Wound Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2005, 84, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.; McConkey, S.; McConkey, S. The role of platelets in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 67, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.C.; Hirschman, M.P.; Sun, A.; Singh, M.V.; Kasischke, K.; Maggirwar, S.B. Excess Soluble CD40L Contributes to Blood Brain Barrier Permeability In Vivo: Implications for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garciarena, C.D.; McHale, T.M.; Watkin, R.L.; Kerrigan, S.W. Coordinated Molecular Cross-Talk between Staphylococcus aureus, Endothelial Cells and Platelets in Bloodstream Infection. Pathogens 2015, 4, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, A.; Milillo, M.A.; Serafino, A.; Castillo, L.A.; Weiss, F.B.; Delpino, M.V.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Fernández, G.C.; Barrionuevo, P. Brucella abortus–infected platelets modulate the activation of neutrophils. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyck, R.; Enzmann, G. The physiological roles of ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in neutrophil migration into tissues. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Reichenbach, N.; Del Valle, L.; Potula, R.; Phipps, R.P.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Persidsky, Y. Dyad of CD40/CD40 ligand fosters neuroinflammation at the blood-brain barrier and is regulated via JNK signaling: Implications for HIV-1 encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9454–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, C.N.; Delpino, M.V.; Fossati, C.A.; Baldi, P.C. Outer Membrane Vesicles from Brucella abortus Promote Bacterial Internalization by Human Monocytes and Modulate Their Innate Immune Response. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, G.H.; Zwerdling, A.; Cassataro, J.; Bruno, L.; Fossati, C.A.; Philipp, M.T. Lipoproteins, not lipopolysaccharide, are the key mediators of the proinflammatory response elicited by heat-killed Brucella abortus. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4635–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwerdling, A.; Delpino, M.V.; Pasquevich, K.A.; Barrionuevo, P.; Cassataro, J.; Samartino, C.G.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Brucella abortus activates human neutrophils. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fang, W.; Shang, D.; Liu, D.; Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.-H. VEGF Increases Paracellular Permeability in Brain Endothelial Cells via Upregulation of EphA2. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2014, 297, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets: Signaling cells in the immune continuum. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity by the Innate Immune System. Science 2010, 327, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawaz, M.; Langer, H.; May, A.E. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.W.; Italiano, J.E.; Freedman, J. Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Dejana, E.; Fiocchi, C. Immune regulation by microvascular endothelial cells: Directing innate and adaptive immunity, coagulation, and inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6017–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.V.; Davidson, D.C.; Jackson, J.W.; Singh, V.B.; Silva, J.; Ramirez, S.H.; Maggirwar, S.B. Characterization of platelet-monocyte complexes in HIV-1-infected individuals: Possible role in HIV-associated neuroinflammation. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4674–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Watson, S. Platelets and the innate immune system: Mechanisms of bacterial-induced platelet activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.R.; Foster, T.J.; Cox, D. The interaction of bacterial pathogens with platelets. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 4, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawaz, M.; Neumann, F.-J.; Dickfeld, T.; Koch, W.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Adelsberger, H.; Langenbrink, K.; Page, S.; Neumeier, D.; Schoömig, A.; et al. Activated Platelets Induce Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Secretion and Surface Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 on Endothelial Cells. Circulation 1998, 98, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Reutershan, J. Leucocyte-Endothelial Interactions in Health and Disease. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2006, 176, 97–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-De-Abreu, A.; Campbell, R.A.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets: Versatile effector cells in hemostasis, inflammation, and the immune continuum. Semin. Immunopathol. 2011, 34, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, V.; Slupsky, J.R.; Gräfe, M.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Foörster, R.; Müller-Berghaus, G.; Kroczek, R.A. CD40 ligand on activated platelets triggers an inflammatory reaction of endothelial cells. Nature 1998, 391, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuchtriegel, G.; Uhl, B.; Puhr-Westerheide, D.; Pörnbacher, M.; Lauber, K.; Krombach, F.; Reichel, C.A. Platelets Guide Leukocytes to Their Sites of Extravasation. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, S.M.; Peterson-Burch, B.D.; Bricker, B.J.; Zuerner, R.L.; Qing, Z.; Li, L.-L.; Kapur, V.; Alt, D.P.; Olsen, S.C. Completion of the Genome Sequence of Brucella abortus and Comparison to the Highly Similar Genomes of Brucella melitensis and Brucella suis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2715–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibor, A.; Decelle, B.; Letesson, J.-J. Outer Membrane Proteins Omp10, Omp16, and Omp19 of Brucella spp. Are Lipoproteins. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4960–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.-Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H.-F. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramoto, H.; Breslin, J.W.; Pappas, P.J.; Hobson, R.W.; Durán, W.N. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates differential signaling pathways in in vivo microcirculation. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H1590–H1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, F.C.; Irving, E.; Ray, A.; Lee, J.; Kassis, S.; Kumar, S.; Badger, A.; Legos, J.J.; A Erhardt, J.; Ohlstein, E.; et al. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in cerebral focal ischemia. Med. Res. Rev. 2001, 21, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stins, M.F.; Gilles, F.; Kim, K.S. Selective expression of adhesion molecules on human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 76, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stins, M.F.; Badgera, J.; Kim, K.S. Bacterial invasion and transcytosis in transfected human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microb. Pathog. 2001, 30, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizet, V.; Kim, K.S.; Stins, M.; Jonas, M.; Chi, E.Y.; Nguyen, D.; Rubens, C.E. Invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells by group B streptococci. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 5074–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, M.C.; Bregante, J.; Delpino, M.V.; Barrionuevo, P.; A Fossati, C.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Baldi, P.C. Proinflammatory response of human endothelial cells to Brucella infection. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, A.M.; Trotta, A.; Melnyczajko, A.P.; Miraglia, M.C.; Kim, K.S.; Delpino, M.V.; Barrionuevo, P.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Brucella abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Increasing Cell Transmigration through the Erk1/2 Pathway. Pathogens 2020, 9, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090708
Rodríguez AM, Trotta A, Melnyczajko AP, Miraglia MC, Kim KS, Delpino MV, Barrionuevo P, Giambartolomei GH. Brucella abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Increasing Cell Transmigration through the Erk1/2 Pathway. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090708
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Ana María, Aldana Trotta, Agustina P. Melnyczajko, M. Cruz Miraglia, Kwang Sik Kim, M. Victoria Delpino, Paula Barrionuevo, and Guillermo Hernán Giambartolomei. 2020. "Brucella abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Increasing Cell Transmigration through the Erk1/2 Pathway" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090708
APA StyleRodríguez, A. M., Trotta, A., Melnyczajko, A. P., Miraglia, M. C., Kim, K. S., Delpino, M. V., Barrionuevo, P., & Giambartolomei, G. H. (2020). Brucella abortus-Stimulated Platelets Activate Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Increasing Cell Transmigration through the Erk1/2 Pathway. Pathogens, 9(9), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090708





