Identification of Immunogenic Antigens of Naegleria fowleri Adjuvanted by Cholera Toxin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Survival and Protection
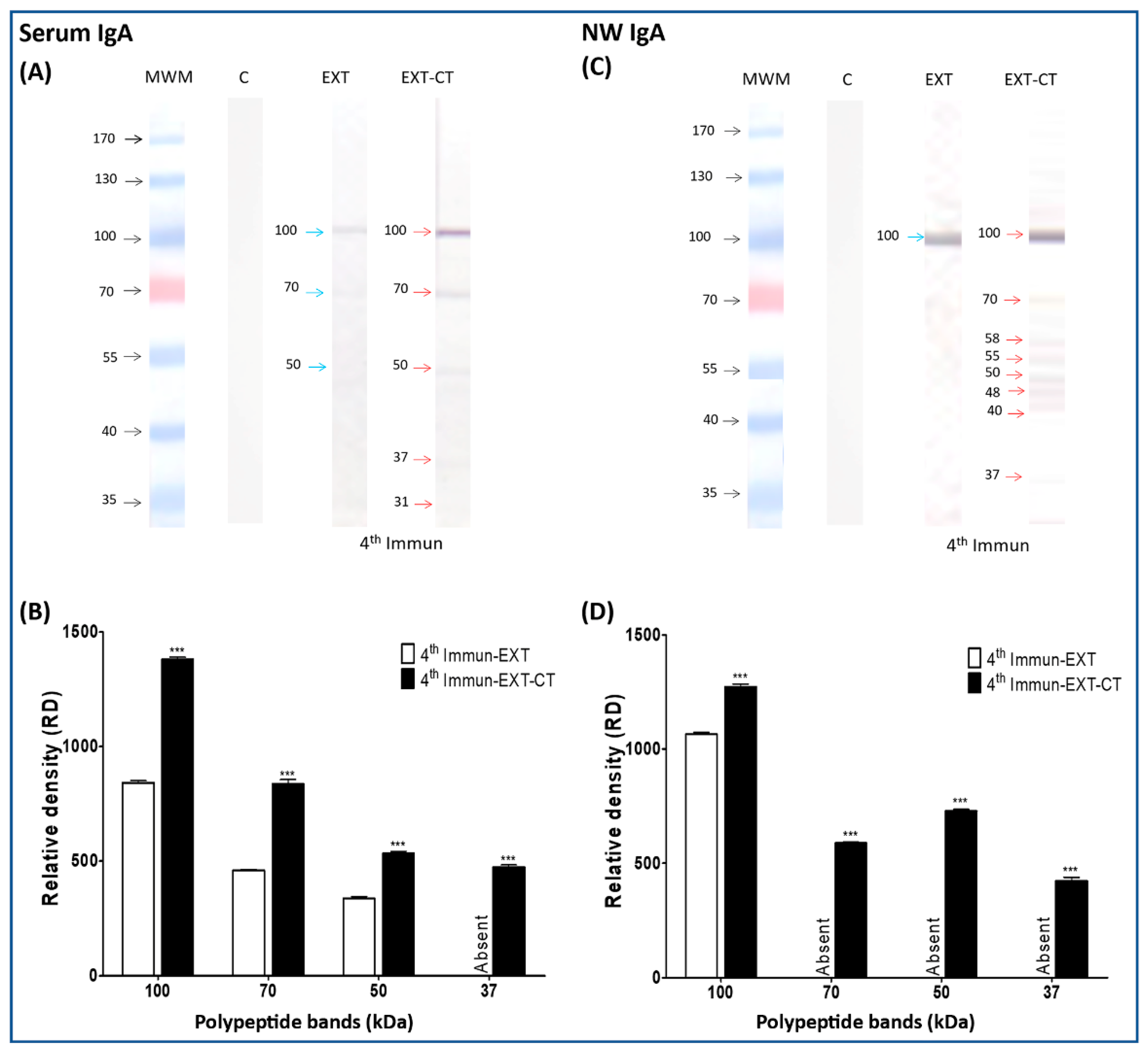
2.2. Immunogenic Polypeptide Bands of N. fowleri Recognized by IgA from Serum and Nasal Washes
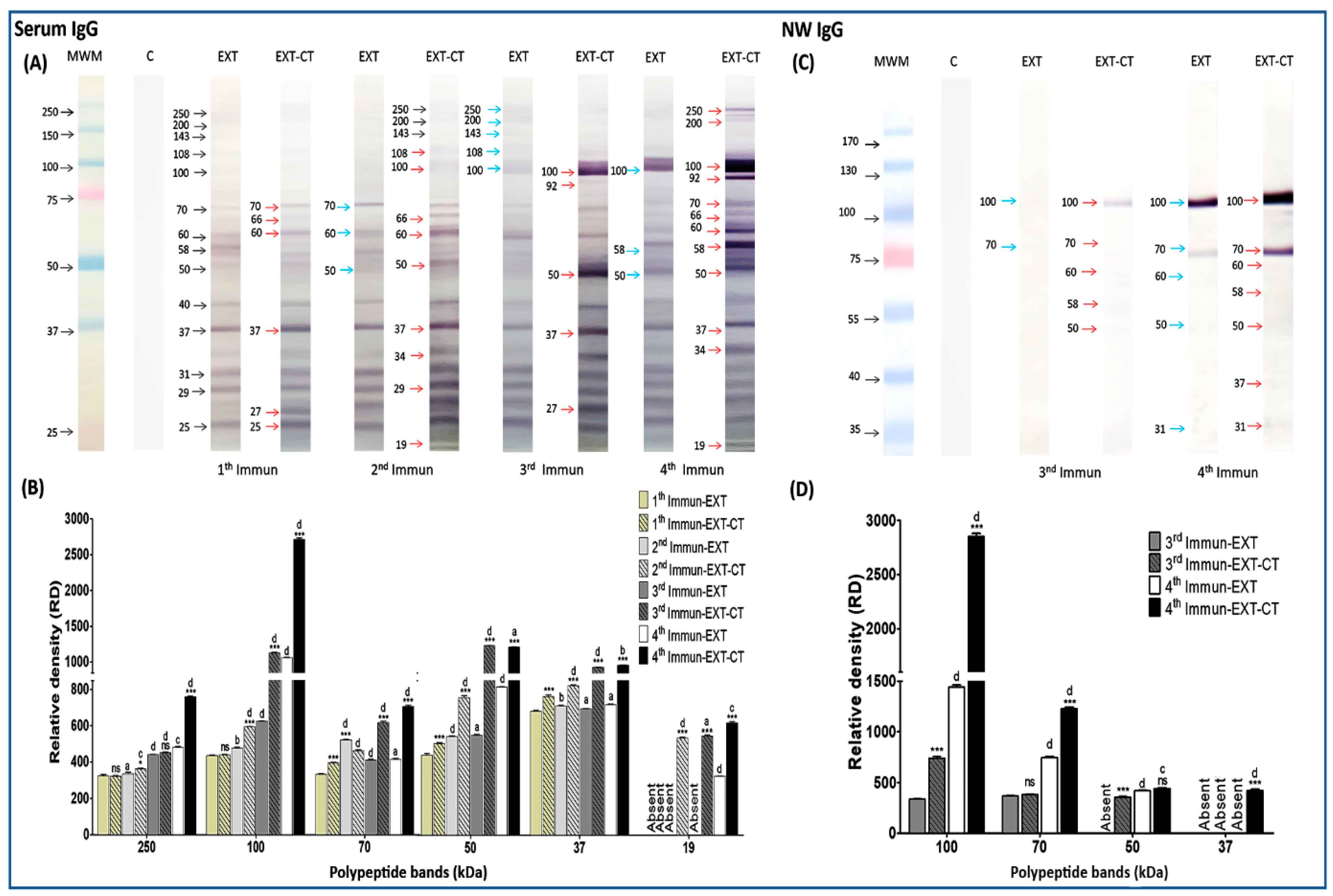
2.3. Immunogenic Polypeptide Bands of N. fowleri Recognized by IgG from Serum and Nasal Washes
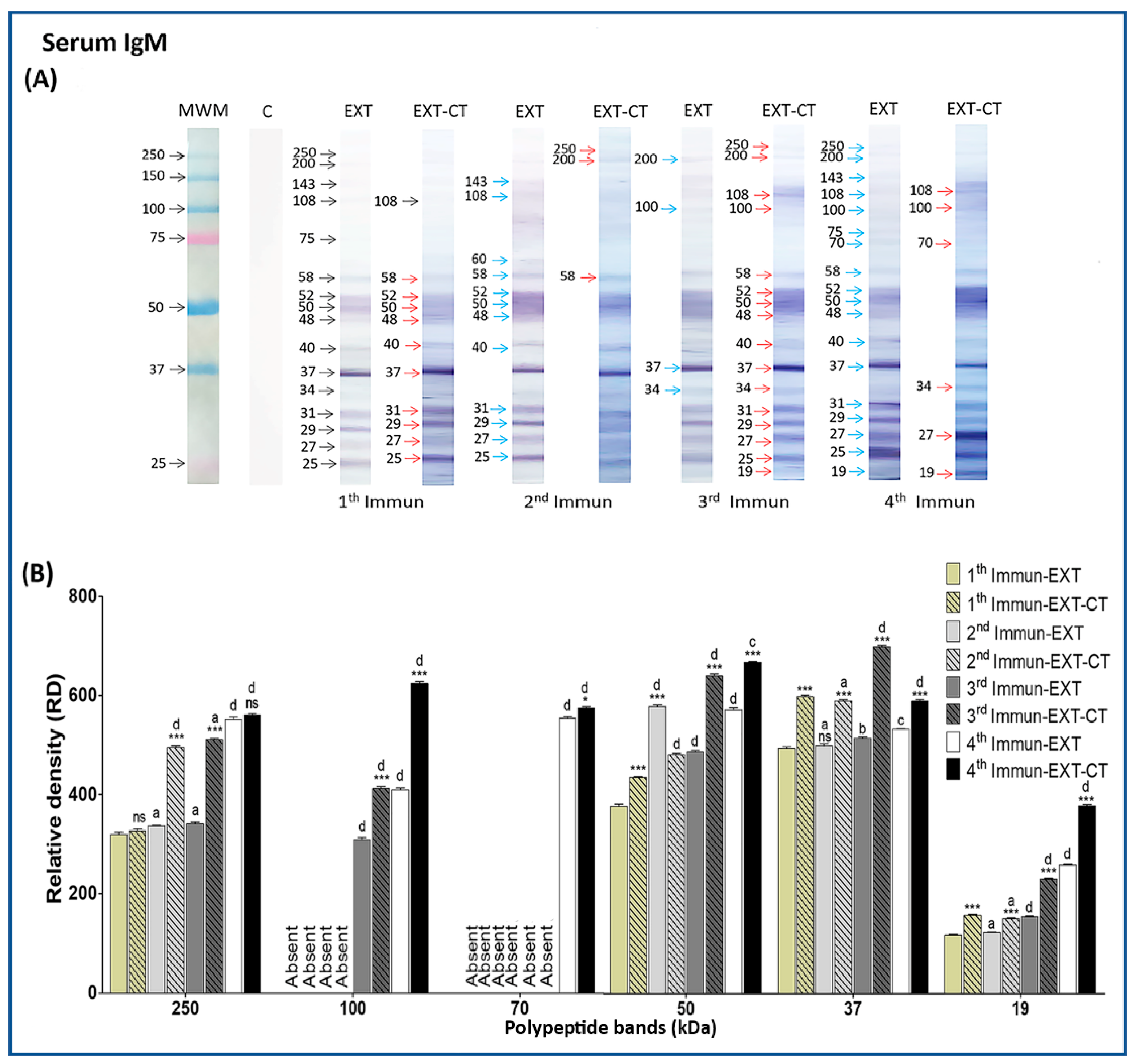
2.4. Immunogenic Polypeptide bands of N. fowleri Recognized by IgM from Serum
2.5. Identification of Immunogenic Polypeptide Bands by Mass Spectrometry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Naegleria fowleri Cultures
4.2. Animals
4.3. Immunization Scheme
4.4. Sample Collection
4.5. Anti-N. fowleri Antibodies by Western Blot
4.6. Identification of Immunogenic Bands by Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Survival Analysis, Densitometric Analysis by ImageLab and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gautam, P.L.; Sharma, S.; Puri, S.; Kumar, R.; Midha, V.; Bansal, R. A rare case of survival from primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 16, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.F. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis. An appraisal of present knowledge. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1972, 66, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Mori, H.; Popruk, S.; Roobthaisong, A.; Sutthikornchai, C.; Koompapong, K.; Siri, S.; Sukthana, Y.; Nacapunchai, D. Development of a rapid, simple method for detecting Naegleria fowleri visually in water samples by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyserman, I.; Mondal, D.; Sarabia, F.; McKerrow, J.H.; Roush, W.R.; Debnath, A. Identification of cysteine protease inhibitors as new drug leads against Naegleria fowleri. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 188, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Hernandez, S.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A.; Lopez-Revilla, R.; Resendiz-Albor, A.A.; Moreno-Fierros, L. Intranasal coadministration of the Cry1Ac protoxin with amoebal lysates increases protection against Nae0gleria fowleri meningoencephalitis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4368–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Yepez, M.; Campos-Rodriguez, R.; Lopez-Reyes, I.; Bonilla-Lemus, P.; Rodriguez-Cortes, A.Y.; Contis-Montes de Oca, A.; Jarillo-Luna, A.; Miliar-Garcia, A.; Rojas-Hernandez, S. Intranasal coadministration of Cholera toxin with amoeba lysates modulates the secretion of IgA and IgG antibodies, production of cytokines and expression of pIgR in the nasal cavity of mice in the model of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 145, S84–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Yepez, M.; Rojas-Hernandez, S.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A.; Terrazas, L.I.; Moreno-Fierros, L. Protection against Naegleria fowleri infection in mice immunized with Cry1Ac plus amoebic lysates is dependent on the STAT6 Th2 response. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Yepez, M.M.; Campos-Rodriguez, R.; Resendiz-Albor, A.A.; Pena-Juarez, C.; Contis-Montes de Oca, A.; Arciniega-Martinez, I.M.; Bonilla-Lemus, P.; Rojas-Hernandez, S. Naegleria fowleri immunization modifies lymphocytes and APC of nasal mucosa. Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Yoo, J.K.; Sohn, H.J.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.H. Protective immunity against Naegleria fowleri infection on mice immunized with the rNfa1 protein using mucosal adjuvants. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Huerta, N.; Sanchez-Monroy, V.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Shibayama, M. A comparative study of the membrane proteins from Naegleria species: A 23-kDa protein participates in the virulence of Naegleria fowleri. Eur. J. Protistol. 2020, 72, 125640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Sanchez, M.; Carrasco-Yepez, M.M.; Herrera-Diaz, J.; Rojas-Hernandez, S. Identification of differential protein recognition pattern between Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria lovaniensis. Parasite Immunol. 2020, 42, e12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasch, C.E.; Robbins, J.D. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. III. Immunogenicity of serotype 2 vaccines and specificity of protection in a guinea pig model. J. Exp. Med. 1978, 147, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briles, D.E.; Nahm, M.; Schroer, K.; Davie, J.; Baker, P.; Kearney, J.; Barletta, R. Antiphosphocholine antibodies found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous infection with type 3 streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Exp. Med. 1981, 153, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, E.J.; Robertson, S.M.; Gulig, P.A.; Frisch, C.F.; Haanes, E.J. Immunoprotection of rats against Haemophilus influenzae type B disease mediated by monoclonal antibody against a haemophilus outer-membrane protein. Lancet 1982, 1, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiro, L.L.; Kohlstadt, S.S.; Henri, S.S.; Dessein, H.H.; Matabiau, V.V.; Paris, P.P.; Bourgois, A.A.; Dessein, A.J. Identification of a candidate vaccine peptide on the 37 kDa Schistosoma mansoni GAPDH. Vaccine 2000, 18, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz-Laylin, L.K.; Prochnik, S.E.; Ginger, M.L.; Dacks, J.B.; Carpenter, M.L.; Field, M.C.; Kuo, A.; Paredez, A.; Chapman, J.; Pham, J.; et al. The genome of Naegleria gruberi illuminates early eukaryotic versatility. Cell 2010, 140, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zysset-Burri, D.C.; Muller, N.; Beuret, C.; Heller, M.; Schurch, N.; Gottstein, B.; Wittwer, M. Genome-wide identification of pathogenicity factors of the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarillo-Luna, A.; Moreno-Fierros, L.; Campos-Rodriguez, R.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A.; Lara-Padilla, E.; Rojas-Hernandez, S. Intranasal immunization with Naegleria fowleri lysates and Cry1Ac induces metaplasia in the olfactory epithelium and increases IgA secretion. Parasite Immunol. 2008, 30, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamerson, M.; Schmoyer, J.A.; Park, J.; Marciano-Cabral, F.; Cabral, G.A. Identification of Naegleria fowleri proteins linked to primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Microbiology 2017, 163, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakonova, M.; Bokoch, G.; Swanson, J.A. Dynamics of cytoskeletal proteins during Fcgamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, M.H.; Song, K.J.; Shin, H.J. The Nf-actin gene is an important factor for food-cup formation and cytotoxicity of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, H.J.; Song, K.J.; Kang, H.; Ham, A.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chwae, Y.J.; Kim, K.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, H.J. Cellular characterization of actin gene concerned with contact-dependent mechanisms in Naegleria fowleri. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.N.; Kopachik, W.; Band, R.N. Cloning and characterization of transcripts showing virulence-related gene expression in Naegleria fowleri. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancholi, V.; Chhatwal, G.S. Housekeeping enzymes as virulence factors for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 293, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, B.; Wang, S.; Peng, X. Rapid screening of highly efficient vaccine candidates by immunoproteomics. Proteomics 2004, 4, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloeckaert, A.; Vizcaino, N.; Paquet, J.Y.; Bowden, R.A.; Elzer, P.H. Major outer membrane proteins of Brucella spp.: Past, present and future. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Song, Y.P.; Boel, G.; Kochar, J.; Pancholi, V. Group A streptococcal surface GAPDH, SDH, recognizes uPAR/CD87 as its receptor on the human pharyngeal cell and mediates bacterial adherence to host cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 350, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunio, S.A.; Oldfield, N.J.; Ala’Aldeen, D.A.; Wooldridge, K.G.; Turner, D.P. The role of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GapA-1) in Neisseria meningitidis adherence to human cells. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Pandey, A.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. Identification of GAPDH on the surface of Plasmodium sporozoites as a new candidate for targeting malaria liver invasion. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; Johansen, F.E.; Brandtzaeg, P. The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal. Immunol. 2008, 1, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.K.; Clements, M.L.; Reimer, C.B.; Snyder, M.; Nelson, D.L.; Murphy, B.R. Analysis of immunoglobulin G antibody responses after administration of live and inactivated influenza A vaccine indicates that nasal wash immunoglobulin G is a transudate from serum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, S.Y. Mucosal vaccine adjuvants update. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2012, 1, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerkinsky, C.; Holmgren, J. Topical immunization strategies. Mucosal. Immunol. 2010, 3, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, J.; Czerkinsky, C.; Eriksson, K.; Mharandi, A. Mucosal immunisation and adjuvants: A brief overview of recent advances and challenges. Vaccine 2003, 21 (Suppl. 2), S89–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | Mice Death (in days) | % Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 6–8 | 0 |
| 1st immun-ext | 7–11 | 0 |
| 1st immun-ext-CT | 10–13 | 0 |
| 2nd immun-ext | 8–12 | 0 |
| 2nd immun-ext-CT | 11–13 | 20 |
| 3rd immun-ext | 11–13 | 20 |
| 3rd immun-ext-CT | 13 | 80 |
| 4th immun-ext | 11–13 | 60 |
| 4th immun-ext-CT | -- | 100 |
| Immunogenic Polypeptide Bands (kDa) | Protein Description with the Compared Species | |
|---|---|---|
| Naegleria fowleri | Naegleria gruberi | |
| 250 | Myosin II heavy chain Fragment (Q25561); Actin Fragment (B5M6J9); Actin 1 (ACT1), Unknown protein NF009 from 2D PAGE Fragment (NF09); Cpn 60 Fragment (Q94626); Ubiquitin Fragment (Q25558). | Cysteine protease Fragment (Q9TWP8). |
| 100 | Actin Fragment (B5M6J9); Ubiquitin Fragment (Q25558); Heat shock protein (Q25552); Membrane protein (Q95UJ2); Amino acid decarboxylase Fragment (C6L6E3); 26S proteasome subunit Fragment (Q95VC2); Penicillin amidase homolog Fragment (Q25548); ATP synthase subunit alpha (M4H5H9); Myosin II heavy chain Fragment (Q25561); Hsp70 (Q6B3P1); Ribosomal protein S3 (M4H5R4); Putative cytosolic carboxypeptidase 6 (M1H4M8). | Putative uncharacterized protein (D2UXB7); Predicted protein (D2VY23); Predicted protein (D2W5T0); Predicted protein (D2VU93); Polyubiquitin (D2VTG7); Calponin homology domain protein Fragment (D2V120); Predicted protein Fragment (D2UXT6); Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase (D2W142); Glutamate dehydrogenase (D2V2V3); AP complex subunit beta (D2VMT9); Catalase (D2VWQ6); Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase family protein (D2V5Y1); ATP synthase subunit beta (D2V5T0). |
| 70 | Actin 1 (ACT1); Actin 2 (ACT2); Membrane protein (Q95UJ2); Hsp70 (Q6B3P1). | Predicted protein (D2UZ33); Predicted protein (D2VWJ8); Predicted protein (D2VSC1); Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase (D2VDR3); Predicted protein (D2V9C6); AP complex subunit beta (D2VMT9); Clathrin heavy chain (D2V5V4); ATP synthase subunit beta (D2V5T0); Predicted protein (D2VGK9); Isovaleryl CoA dehydrogenase (D2UXG9); Predicted protein (D2VWE1). |
| 50 | Amino acid decarboxylase Fragment (C6L6E3); Actin 1 (ACT1); Pyrophosphate fructose 6 phosphate 1 phosphotransferase (PFP); Membrane protein (Q95UJ2); Thioredoxin homolog (Q25549); Hsp70 (Q6B3P1); Myosin II heavy chain Fragment (Q25561). | Glutamate dehydrogenase (D2V2V3); Putative uncharacterized protein (D2UXB7); Predicted protein (D2VT95); Predicted protein (D2VWF2); Pyrophosphate fructose 6 phosphate (D2V5S29); Predicted protein (D2V0Z9); Adenosylhomocysteinase (D2W1E4); Coronin (D2VLM1); Elongation factor Tu (D2V3J1); Predicted protein (D2VV89); ATP synthase subunit beta (D2V5T0); Predicted protein (D2V9Y7); Alanine aminotransferase (D2V3R0); Predicted protein (D2W0R2); Predicted protein (D2W1W8); Elongation factor 1 alpha Fragment (Q2MM01); Protein disulfide isomerase (D2VCZ2); Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (D2UYA5); Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor (D2V193); Actin related protein ARP3 (D2V7J7); RhoGEF domain containing protein (D2VJF9); Predicted protein (D2UXY9); Succinate CoA ligase ADP forming subunit beta mitochondrial (D2VP45); 4 aminobutyrate aminotransferase (D2UY50); Predicted protein (D2W3B8); Dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (D2V1E8); Predicted protein (D2VB42); Predicted protein (D2VBF6); Predicted protein (D2VLT8); Predicted protein (D2UZW5); Predicted protein (D2W2M7). |
| 37 | Actin 2 Fragment (ACT2); Actin Fragment (B5M6J9); ATP synthase subunit alpha (M4H5H9); Ubiquitin Fragment (Q25559); Myosin II heavy chain Fragment (Q25561). | Putative uncharacterized protein (D2UXB7); Putative uncharacterized protein (D2VE39); Putative uncharacterized protein (D2VZJ8); Conventional actin (D2VUS6); Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase (D2W142); Putative uncharacterized protein (D2V8I2); Predicted protein (D2VM36); Predicted protein (D2VKN7); Mitogen activated protein kinase (D2VK26); Predicted protein (D2VSP0); Malate dehydrogenase (D2VZB1); Prohibitin (D2W2C5); Isocitrate dehydrogenase NAD subunit mitochondrial (D2VQ70); Isocitrate dehydrogenase NADP dependent (D2VRD7); Mitochondrial trans-2 enoyl CoA reductase (D2VNA9); Inosine 5 monophosphate dehydrogenase (D2UY23); ATP synthase subunit beta (D2V5T0); Predicted protein (D2VKI4); ARF SAR family small GTPase (D2V115); Jun kinase activation domain binding protein (D2VD78); Predicted protein (D2VRL5); Elongation factor 1 alpha Fragment (Q2MM01); NAD dependent epimerase dehydratase family protein (D2V803); Putative uncharacterized protein (D2VEC2). |
| 19 | Membrane protein (Q95UJ2); Unknown protein NF016 from 2D PAGE Fragment (NF16); Calcineurin B (Q9NAY9); Fructose 1 6 bisphosphatase homolog Fragment (Q27706); Photoactivated adenylyl cyclase (W0SLB1). | 40S ribosomal protein S13 (D2VL67). |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojas-Hernández, S.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, M.; Rojas-Ortega, D.A.; Bonilla-Lemus, P.; Contis-Montes de Oca, A.; Herrera-Díaz, J.; López-Reyes, I.; Carrasco-Yépez, M.M. Identification of Immunogenic Antigens of Naegleria fowleri Adjuvanted by Cholera Toxin. Pathogens 2020, 9, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9060460
Rojas-Hernández S, Gutiérrez-Sánchez M, Rojas-Ortega DA, Bonilla-Lemus P, Contis-Montes de Oca A, Herrera-Díaz J, López-Reyes I, Carrasco-Yépez MM. Identification of Immunogenic Antigens of Naegleria fowleri Adjuvanted by Cholera Toxin. Pathogens. 2020; 9(6):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9060460
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas-Hernández, Saúl, Mara Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Diego Alexander Rojas-Ortega, Patricia Bonilla-Lemus, Arturo Contis-Montes de Oca, Jorge Herrera-Díaz, Israel López-Reyes, and María Maricela Carrasco-Yépez. 2020. "Identification of Immunogenic Antigens of Naegleria fowleri Adjuvanted by Cholera Toxin" Pathogens 9, no. 6: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9060460
APA StyleRojas-Hernández, S., Gutiérrez-Sánchez, M., Rojas-Ortega, D. A., Bonilla-Lemus, P., Contis-Montes de Oca, A., Herrera-Díaz, J., López-Reyes, I., & Carrasco-Yépez, M. M. (2020). Identification of Immunogenic Antigens of Naegleria fowleri Adjuvanted by Cholera Toxin. Pathogens, 9(6), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9060460







