Escherichia coli Strains with Virulent Factors Typical for Uropathogens were Isolated from Sinuses from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis—Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient’s Medical History
2.1.1. Case 1 Presentation
2.1.2. Case 2 Presentation
2.1.3. Case 3 Presentation
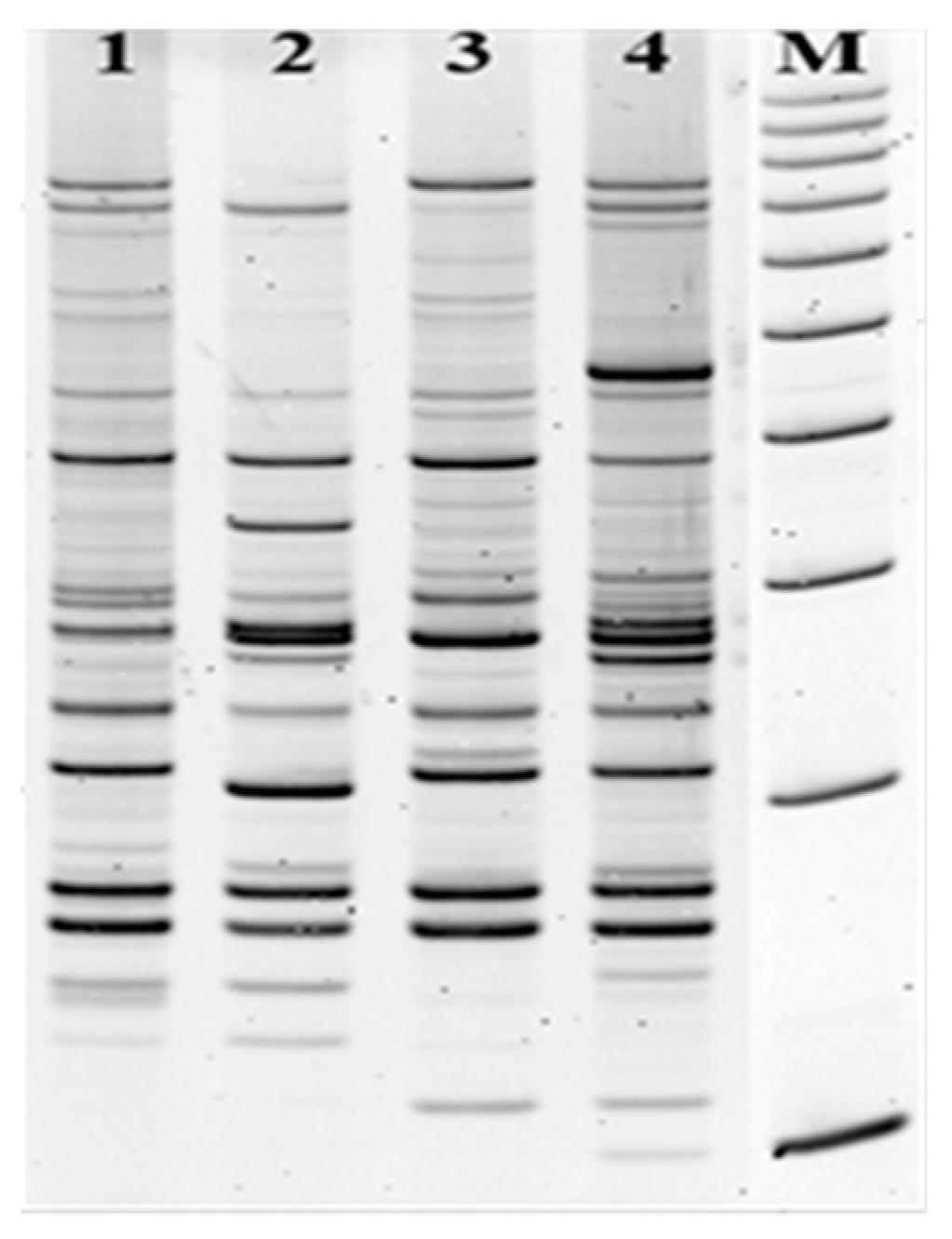
2.2. Genetic Characterization of Escherichia coli
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Genetic Characterization of E. coli Strains
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barshak, M.B.; Durand, M.L. The Role of Infection and Antibiotics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, E.; Kennedy, D.W. Rhinosinusitis: A Guide for Diagnosis and Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Finegold, S.M.; Flynn, M.J.; Rose, F.V.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Jakielaszek, C.; McTeague, M.; Wexler, H.M.; Berkowitz, E.; Wynne, B. Bacteriological findings associated with chronic bacterial maxillary sinusitis in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, M.; Samet, A.; Marszałek, A.; Krawczyk, B.; Kotłowski, R.; Nowicki, A.; Anyszek, T.; Nowicki, S.; Kur, J.; Nowicki, B. Intra-operative biopsy in chronic sinusitis detects pathogenic Escherichia coli that carry fimG/H, fyuA and agn43 genes coding biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtsig, E.I.; Sel’kova, E.P.; Malygina, L.V.; Lapitskaia, A.S. The role of respiratory viruses in etiology of rhinosinisitis in the children. Vestn. Otorinolaringol. 2014, 6, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, B.; Śledzińska, A.; Szemiako, A.; Samet, A.; Nowicki, B.; Kur, J. Characterisation of Escherichia coli isolates from the blood of haematological adult patients with bacteraemia: Translocation from gut to blood requires the cooperation of multiple virulence factors. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, R.P.; Martinez, F.J.; Huffangle, G.B. The role of the microbiome in exacerbations of chronic lung diseases. Lancet 2014, 384, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasubramaniam, R.; Douglas, R. The microbiome and chronic rhinosinusitis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 4, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.L.; Henderson, T.A.; Vigil, P.D.; Mobley, H.L. Genomic islands of uropathogenic Escherichia coli contribute to virulence, J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3469–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil, P.D.; Stapleton, A.E.; Johnson, J.R.; Hooton, T.M.; Hodges, A.P.; He, Y.; Mobley, H.L. Presence of putative repeat-in-toxin gene tosA in Escherichia coli predicts successful colonization of the urinary tract. MBio 2011, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Cruz-Córdova, A.; Cázares-Domínguez, V.; Escalona-Venegas, G.; Zavala-Vega, S.; Arellano-Galindo, J.; Romo-Castillo, M.; Hernández-Castro, R.; Ochoa, S.A.; Luna-Pineda, V.M. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains harboring tosA gene were associated to high virulence genes and a multidrug-resistant profile. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 134, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogyiova, E.; Siegfried, L.; Kmeťová, M.; <monospace> </monospace>Šandorčinová, Z.; Liptakova, A.; Biroš, E. Occurrence and genetic association of selected virulence factors in clinical Escherichia coli isolates. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szemiako, K.; Krawczyk, B.; Samet, A.; Śledzińska, A.; Nowicki, B.; Nowicki, S.; Kur, J. A subset of two adherence systems, acute pro-inflammatory pap genes and invasion coding dra, fim, or sfa, increases the risk of Escherichia coli translocation to the bloodstream. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, A.; Boase, S.; Psaltis, A.; Wormald, P.J. Role of bacterial and fungal biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyer, D.M.; Henderson, I.R.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Identification of sat, an autotransporter toxin produced by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, N.J.; Srinivasan, U.; Desvaux, M.; Foxman, B.; Marrs, C.F.; Henderson, I.R. PicU, a second serine protease autotransporter of uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 230, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Chi, F.; Wang, L.; Jong, T.D.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.H. Involvement of IbeA in Meningitic Escherichia coli K1-Induced Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Transmigration Across Brain Endothelial Cells. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Leibner-Ciszak, J.; Stojowska, K.; Kur, J. The New LM-PCR/shifter Method for the Genotyping of Microorganisms Based on the Use of a Class IIS Restriction Enzyme and Ligation Mediated PCR. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Kur, J.; Stojowska-Swędrzyńska, K.; Śpibida, M. Principles and applications of Ligation Mediated PCR methods for DNA-based typing of microbial organisms. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamus-Białek, W.; Wojtasik, A.; Majchrzak, M.; Sosnowski, M.; Parniewski, P. (CGG) 4-based PCR as a novel tool for discrimination of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains: Comparison with enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3937–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.L.Y.; Ulett, G.C.; Mabbett, A.N.; Beatson, S.A.; Webb, R.I.; Monaghan, W.; Nimmo, G.R.; Looke, D.F.; McEwan, A.G.; Schembri, M.A. Identification of type 3 fimbriae in uropathogenic Escherichia coli reveals a role in biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotłowski, R.; Bernstein, C.N.; Sepehri, S.; Krause, D.O. High prevalence of Escherichia coli belonging to the B2+D phylogenetic group in inflammatory bowel disease. GUT 2007, 56, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Characteristic of Patients | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic demographics | |||
| Age | 41 | 44 | 18 |
| Gender | M | M | M |
| Underlying diseases | chronic sinusitis | chronic sinusitis | chronic sinusitis |
| Duration of illness | 7 years | 3 years | 5 years |
| Duration of symptoms | >12 weeks | >12 weeks | >12 weeks |
| Episodes within a one-year period | >4 | >4 | >4 |
| Symptoms | |||
| Purulent drainage | + | + | + |
| Facial/dental pain | + | + | + |
| Nasal obstruction | + | + | + |
| Hyposmia | + | + | + |
| Nasal congestion | + | − | + |
| Halitosis | + | − | - |
| Cough, sore throat | + | + | + |
| Ear pain | − | − | + |
| Patient-associated risk factors | |||
| Nasal polyps | + | − | + |
| Lower nasal concha hypertrophy | − | + | + |
| Cigarette smoking: Currently (C)/in the past (P) | + (P) | + (P) | + (P) |
| Sleep apnea | - | + | - |
| Allergy | + | - | - |
| Snoring | − | − | − |
| GERD | − | − | − |
| * Outpatient procedures within 6 months in violation of tissue integrity | dental treatment | - | - |
| Surgery | functional endoscopic sinus surgery | functional endoscopic nasal and nasal sinuses surgery, nasal segmental correction, correction of soft palate by coblation method | functional endoscopic sinus surgery, correction of nasal septum and conchae by coblation method |
| CBCT 3D | CBCT 3D | CBCT 3D | |
| Radiodiagnostics | |||
| Clinical outcome | |||
| Relapse | + | − | − |
| Duration of clinical remission | 6 months | − | − |
| Postoperative period | functional endoscopic sinus surgery with the opening of ethmoid cells, frontal sinuses | − | − |
| Histopathological data | |||
| Polypoid mucosal | + | − | + |
| Cylindrical epithelium | − | + | + |
| Infiltration with monocytes | − | + | + |
| Metaplasia | − | − | − |
| Blood count/NEU% [range 45–70] | 64 | 51.7 | 51.5 |
| Blood count/EOS% [range 1–5] | 4.9 | 2.7 | 6.3 |
| Blood count/MONO% [range 3–8] | 9.4 | 8.5 | 5.4 |
| Clinical sample | specimen/swab | specimen/swab | specimen/swab |
| Microbiological cultures - characteristic | |||
| Polymicrobial infections | E. coli; S. aureus | E. coli; E. faecium | E. coli; S. aureus |
| Empiric Therapy | AMC | AMC | AMC |
| Inflammation of the urinary system | + | + | + |
| Episodes/ recurrence of infection | >10/+ | 2/− | 1/− |
| Genetic Characteristic of Isolates | Isolate 1 | Isolate 2 | Isolate 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | from left maxillary sinus | from right maxillary sinus | from left maxillary sinus |
| Antibiotic resistance profile of E. coli | - | AM, AMC, P, AMX, TRC, TR | - |
| Virulence -associated genes of E. coli | |||
| Adhesins (fimbrial and nonfimbrial adhesin) | fimG/H, sfa, papC, tosA | fimG/H, sfa, focG | fimG/H, sfa, focG |
| Toxins | hlyA, usp, cnf1, tosB | hlyA, usp, cnf1, tosB | hlyA, usp, cnf1, tosB |
| Iron acquisition system | fyuA, irp2, entB, fepA, iroN, chuA | fyuA, irp2, entB, fepA, iroN, iha, chuA, fecA | fyuA, irp2, entB, fepA, iroN, iha, chuA, fecA |
| K capsule | kspMTII | kspMTII | kspMTII |
| Autotransporter and biofilm | ag43a (flu) | ag43a (flu) | ag43a (flu) |
| Serine protease autotransporters | vat, pic | vat, pic | vat, pic |
| Invasin | ibeA | - | - |
| E. coli phylogenetic group | B2 | B2 | B2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krawczyk, B.; Michalik, M.; Fordon, M.; Wysocka, M.; Samet, A.; Nowicki, B. Escherichia coli Strains with Virulent Factors Typical for Uropathogens were Isolated from Sinuses from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis—Case Report. Pathogens 2020, 9, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9050318
Krawczyk B, Michalik M, Fordon M, Wysocka M, Samet A, Nowicki B. Escherichia coli Strains with Virulent Factors Typical for Uropathogens were Isolated from Sinuses from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis—Case Report. Pathogens. 2020; 9(5):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9050318
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrawczyk, Beata, Michał Michalik, Magdalena Fordon, Magdalena Wysocka, Alfred Samet, and Bogdan Nowicki. 2020. "Escherichia coli Strains with Virulent Factors Typical for Uropathogens were Isolated from Sinuses from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis—Case Report" Pathogens 9, no. 5: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9050318
APA StyleKrawczyk, B., Michalik, M., Fordon, M., Wysocka, M., Samet, A., & Nowicki, B. (2020). Escherichia coli Strains with Virulent Factors Typical for Uropathogens were Isolated from Sinuses from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis—Case Report. Pathogens, 9(5), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9050318





