Reemerging Rice Orange Leaf Phytoplasma with Varying Symptoms Expressions and Its Transmission by a New Leafhopper Vector—Nephotettix virescens Distant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
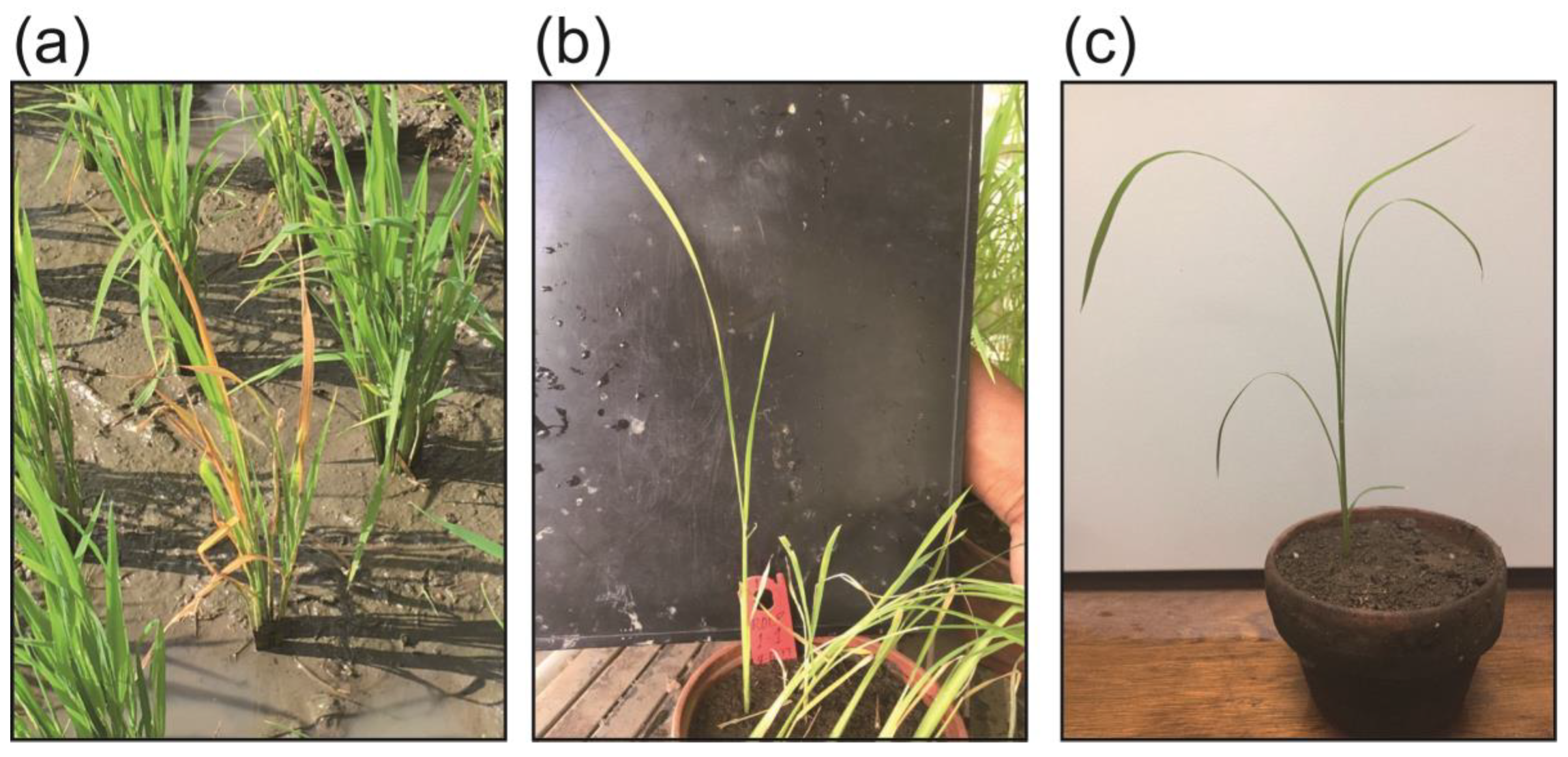
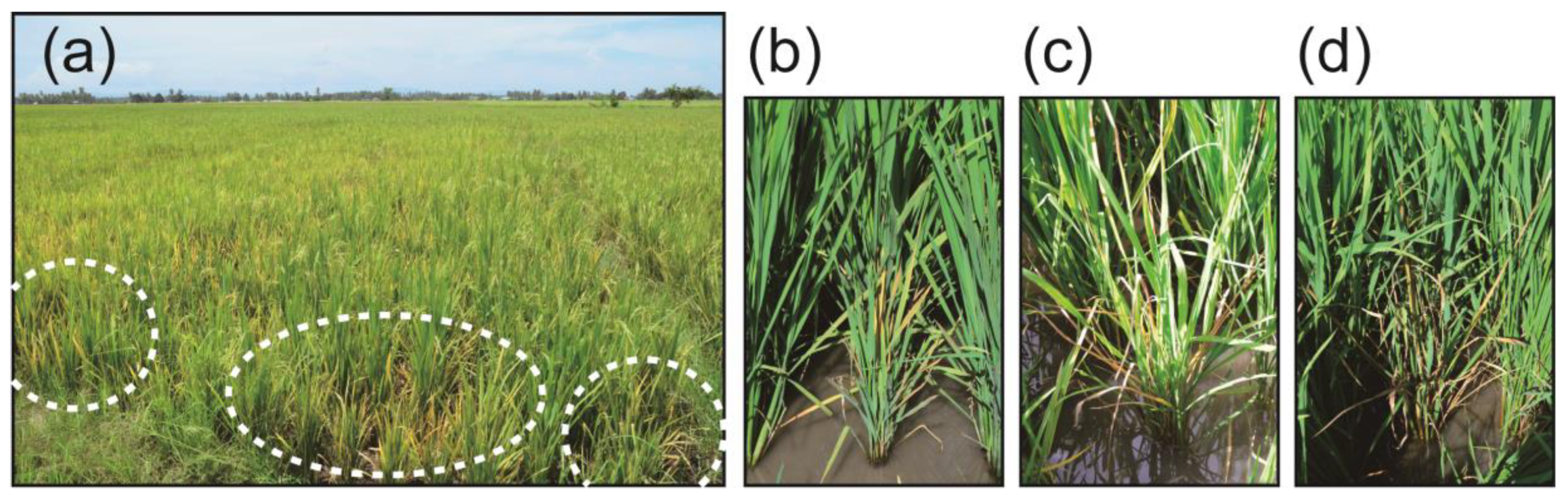
2.1. ROLD Prevalence and Field Symptoms
2.2. Transmission of ROLP by N. virescens
2.3. Trend Analysis of ROLP Transmission by N. virescens
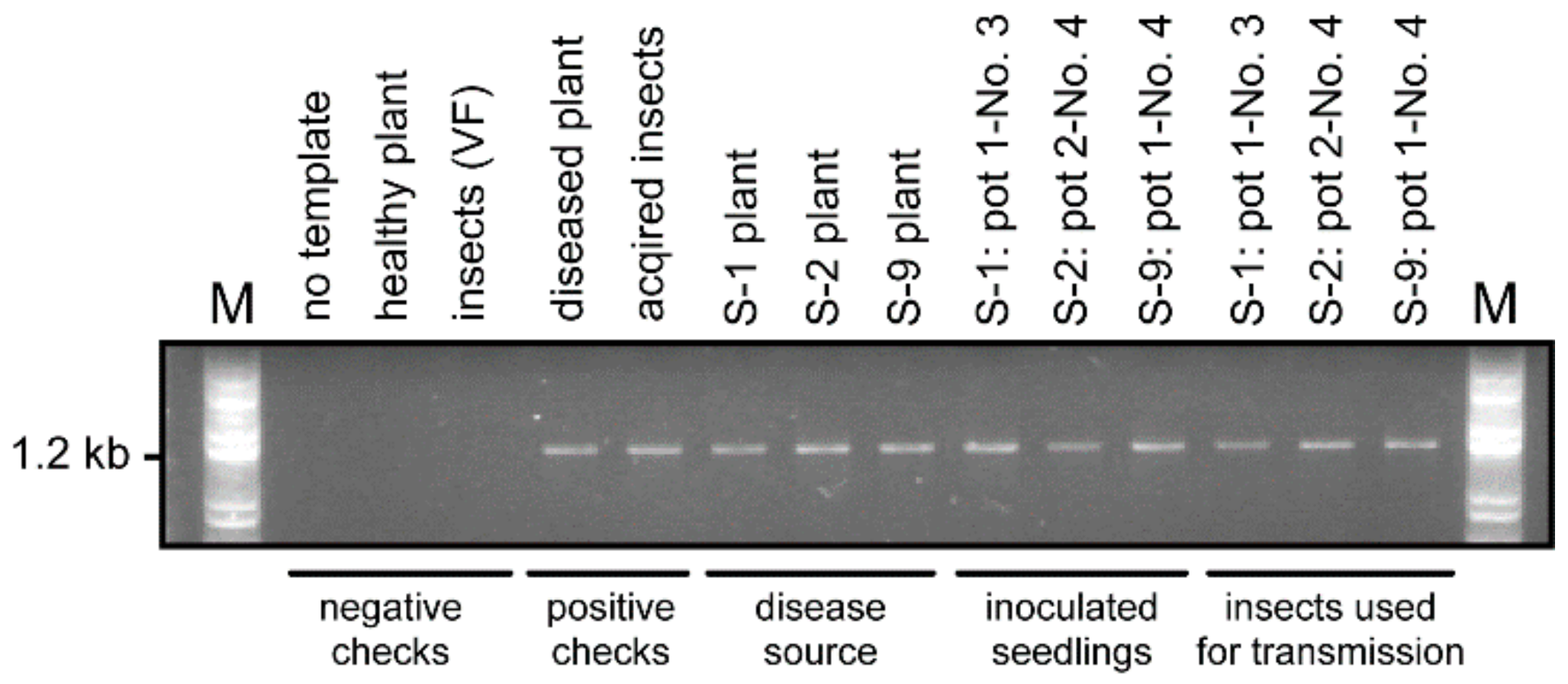
2.4. Confirmation of ROLP Transmission by 16S rDNA Sequencing
3. Discussion
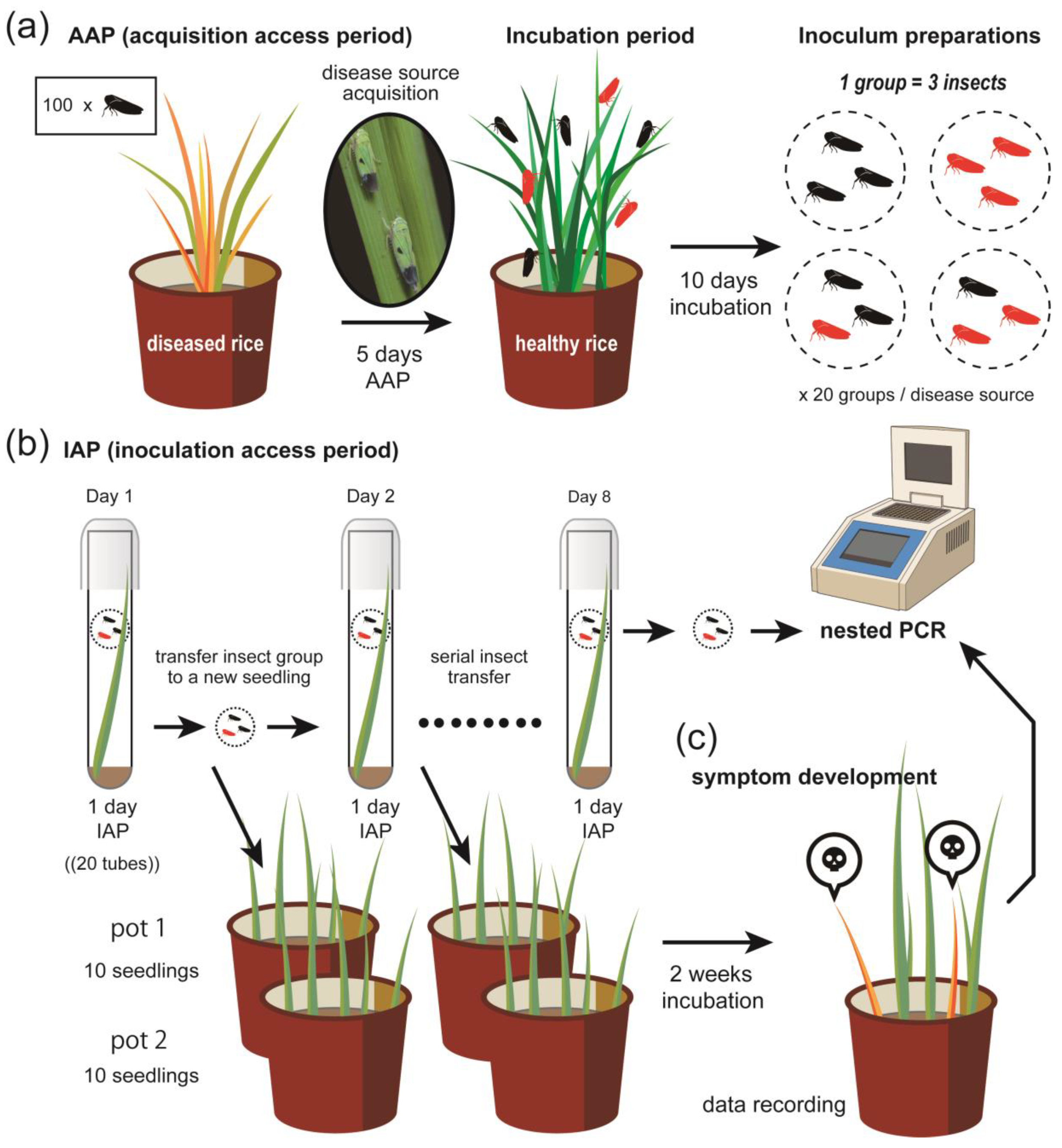
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Source and Leaf Sample Collection
4.2. DNA Sample Preparation
4.3. Detection of Rice Tungro Viruses
4.4. Detection of ROLP
4.5. ROLP Insect Transmission Test
4.6. Sequence Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rivera, C.; Ou, S.; Pathak, M. Transmission studies of the orange leaf disease of rice. Plant Dis. Rep. 1963, 47, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Hibino, H.; Jonson, G.; Sta Cruz, F. Association of mycoplasmalike organisms with rice orange leaf in the Philippines. Plant Dis. 1987, 71, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.-C. (Ed.) Orange Leaf Disease. In Rice Virus Diseases; International Rice Research Institute: Los Banõs, Philippines, 1972; pp. 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- IRPCM Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma Working Team—Phytoplasma Taxonomy Group. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’, a taxon for the wall-less, non-helical prokaryotes that colonize plant phloem and insects. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-M.; Hammond, R.; Davis, R.; Gundersen, D. Universal amplification and analysis of pathogen 16S rDNA for classification and identification of mycoplasmalike organisms. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, D.; Lee, I. Ultrasensitive detection of phytoplasmas by nested-PCR assays using two universal primer pairs. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 1996, 35, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.-M.; Davis, R.E.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E. Phytoplasma: Phytopathogenic mollicutes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 221–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Sawayanagi, T.; Wongkaew, P.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Wei, W.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, S.-I.; Ugaki, M.; Hibi, T. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma oryzae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with rice yellow dwarf disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarmathi, P.; Rabindran, R.; Velazhahan, R.; Suresh, S.; Robin, S. First report of rice orange leaf disease phytoplasma (16 SrI) in rice (Oryza sativa) in India. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2013, 8, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hao, W.; Lu, G.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G. Occurrence and identification of a new vector of rice orange leaf phytoplasma in South China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Murata, N. Destructive plant diseases caused by mycoplasma-like organisms in Asia. Outlook Agric. 1993, 22, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, V.; Raychaudhuri, S. Rice yellow dwarf disease. In Mycoplasma Diseases of Crops; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 233–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cabauatan, P.; Koganezawa, H.; Cabunagan, R.; Sta Cruz, F. Rice dwarf (RDV), a new virus disease in the Philippines. IRRN 1993, 18, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Hibino, H.; Saleh, N.; Roechan, M. Transmission of two kinds of RTD viruses. Phytopathology 1979, 69, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, O.; Chancellor, T.-C. The biology, epidemiology, and management of rice tungro disease in Asia. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasuji, F. Epidemiological study on rice dwarf virus transmitted by the green rice leafhopper Nephotettix cincticeps. JARQ 1974, 8, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Han, N.; Dang, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Yao, H.; Peng, Y.; Stanley, D.; Ye, G. Combined influence of Bt rice and rice dwarf virus on biological parameters of a non-target herbivore, Nephotettix cincticeps (Uhler) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, H.-V.; Hai, N.-V.; Man, V.-T.; Matsumoto, M. Rice dwarf disease in North Vietnam in 2009 is caused by southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus (SRBSDV). Bull. Inst. Trop. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2009, 32, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hibino, H. Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-T.; Hoat, T.-X.; Quan, M.-V. Molecular detection and characterization of 16SrI phytoplasma associated with rice orange leaf symptom in Vietnam. Phytopathog. Mollicutes 2016, 6, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkong, S.; Reanwarakorn, K.; Khwantongyim, C. Molecular classification of Phytoplasma associated with rice orange leaf disease in Thailand. Agric. Sci. J. 2016, 47, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, G. Draft genome sequence of rice orange leaf phytoplasma from Guangdong, China. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Lee, M.; Zhao, Y. Computer-simulated RFLP analysis of 16S rRNA genes: Identification of ten new phytoplasma groups. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valarmathi, P.; Rabindran, R. Nested PCR assay for detection of Rice Orange Leaf phytoplasma in the Zigzag leafhopper vector, Recilia dorsalis (Motschulsky): A first report. Ecoscan 2015, 9, 837–839. [Google Scholar]
- CABI. Invasive Species Compendium (Nephotettix Virescens (Green Paddy Leafhopper)). Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/36198 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Ishii, Y.; Kakizawa, S.; Hoshi, A.; Maejima, K.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. In the non-insect-transmissible line of onion yellows phytoplasma (OY-NIM), the plasmid-encoded transmembrane protein ORF3 lacks the major promoter region. Microbiology 2009, 155, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanboonsong, Y.; Ritthison, W.; Choosai, C.; Sirithorn, P. Transmission of sugarcane white leaf phytoplasma by Yamatotettix flavovittatus, a new leafhopper vector. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Hibino, H. Orange leaf symptoms on rice. IRRN 1988, 13, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkaew, P. Sugarcane white leaf disease characterization, diagnosis development, and control strategies. Funct. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 6, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Trivellone, V.; Filippin, L.; Narduzzi-Wicht, B.; Angelini, E. A regional-scale survey to define the known and potential vectors of grapevine yellow phytoplasmas in vineyards South of Swiss Alps. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, Y.; Canel, A.; Bertaccini, A.; Contaldo, N. Molecular diversity of phytoplasmas associated with grapevine yellows disease in north-eastern Italy. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malembic-Maher, S.; Desqué, D.; Khalil, D.; Salar, P.; Bergey, B.; Danet, J.-L.; Duret, S.; Dubrana-Ourabah, M.-P.; Beven, L.; Ember, I. When a Palearctic bacterium meets a Nearctic insect vector: Genetic and ecological insights into the emergence of the grapevine Flavescence dorée epidemics in Europe. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1007967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.; Thompson, W.-F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajet, N.; Daquioag, R.; Hibino, H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to diagnose rice tungro. J. Plant Prot. Trop. 1985, 2, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, Y.; Cabunagan, R.-C.; Cabauatan, P.-Q.; Choi, I.-R. Characterization of Oryza rufipogon-derived resistance to tungro disease in rice. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.-A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Lee, M.; Shao, J.; Suo, X.; Davis, R.-E. The iPhyClassifier, an interactive online tool for phytoplasma classification and taxonomic assignment. In Phytoplasma. Methods in Molecular Biology; Dickinson, M., Hodgetts, J., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 329–338. [Google Scholar]


| Year | Province | Municipality | Barangay a | Rice Variety | Detection b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Laguna (IRRI), Luzon | Los Baños | College | unknown | 49/60 |
| 2019 | Davao del Sur, Mindanao | Hagonoy | Sinayawan | Nsic Rc 286 | 8/8 |
| Davao del Sur, Mindanao | Matanao | New Murcia | Nsic Rc 224 | 2/2 | |
| CompostelaValley, Mindanao | Compostela | Tamia | Nsic Rc 160 | 7/9 | |
| Davaodel Norte, Mindanao | Sto Tomas | Kinamayan | unknown | 9/9 | |
| Davao Oriental, Mindanao | Banaybanay | Mobongcogon | Nsic Rc 160 | 3/3 | |
| Davao Oriental, Mindanao | Banaybanay | Cabangcalan | unknown | 7/7 |
| Disease Source Plants | ROLP-Detection (Rice Seedlings) a | ROLP-Detection (Insect Groups) b | Symptom Development by ROLP-Positive Insect Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+) c | (−) d | |||
| S-1 | 27/153 | 13/20 | 10 | 3 |
| S-2 | 14/155 | 9/20 | 5 | 4 |
| S-9 | 8/157 | 5/20 | 5 | 0 |
| H-control e | 0/149 | 0/20 | NA f | NA f |
| Disease Source | Pot No. | Insect Group No. | Days of Serial Inoculation a | No. Insect Left | ROLP in Insect c | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 b | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | |||||
| S-1 | 1 | 1 | − d | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | − |
| 2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | − | ||
| 3 | + d | + | + | + | − | + | − | d | 2 | + | ||
| 4 | − | − | − | − | − | d | − | d | 1 | + | ||
| 5 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | d | 2 | − | ||
| 6 | − | x | − | d d | − | − | − | − | 2 | − | ||
| 7 | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 8 | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 9 | x d | − | − | − | − | − | − | d | 2 | + | ||
| 10 | x | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | − | ||
| 2 | 1 | − | − | x | − | − | − | − | d | 2 | + | |
| 2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | − | ||
| 3 | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 4 | − | − | x | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | − | ||
| 5 | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | 3 | + | ||
| 6 | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 7 | + | + | x | − | + | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 8 | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | + | ||
| 9 | − | + | x | − | − | − | − | d | 2 | + | ||
| 10 | − | + | − | − | − | d | − | d | 2 | + | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonson, G.B.; Matres, J.M.; Ong, S.; Tanaka, T.; Choi, I.-R.; Chiba, S. Reemerging Rice Orange Leaf Phytoplasma with Varying Symptoms Expressions and Its Transmission by a New Leafhopper Vector—Nephotettix virescens Distant. Pathogens 2020, 9, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9120990
Jonson GB, Matres JM, Ong S, Tanaka T, Choi I-R, Chiba S. Reemerging Rice Orange Leaf Phytoplasma with Varying Symptoms Expressions and Its Transmission by a New Leafhopper Vector—Nephotettix virescens Distant. Pathogens. 2020; 9(12):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9120990
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonson, Gilda B., Jerlie M. Matres, Socheath Ong, Toshiharu Tanaka, Il-Ryong Choi, and Sotaro Chiba. 2020. "Reemerging Rice Orange Leaf Phytoplasma with Varying Symptoms Expressions and Its Transmission by a New Leafhopper Vector—Nephotettix virescens Distant" Pathogens 9, no. 12: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9120990
APA StyleJonson, G. B., Matres, J. M., Ong, S., Tanaka, T., Choi, I.-R., & Chiba, S. (2020). Reemerging Rice Orange Leaf Phytoplasma with Varying Symptoms Expressions and Its Transmission by a New Leafhopper Vector—Nephotettix virescens Distant. Pathogens, 9(12), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9120990






