Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Rodent and Tick Species
2.2. Detection of the Borrelia spp.
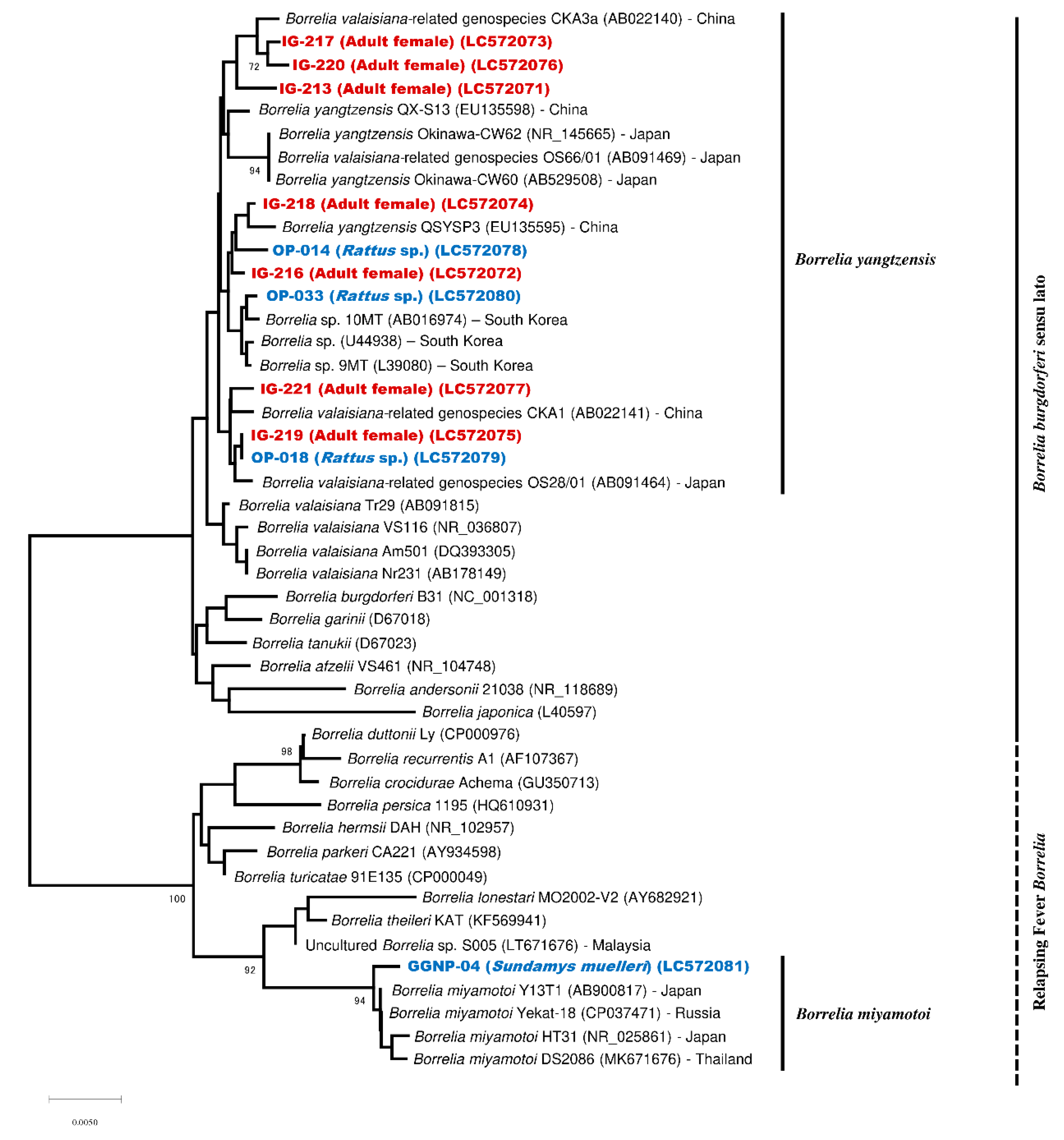
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of the Borrelia spp.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approvals
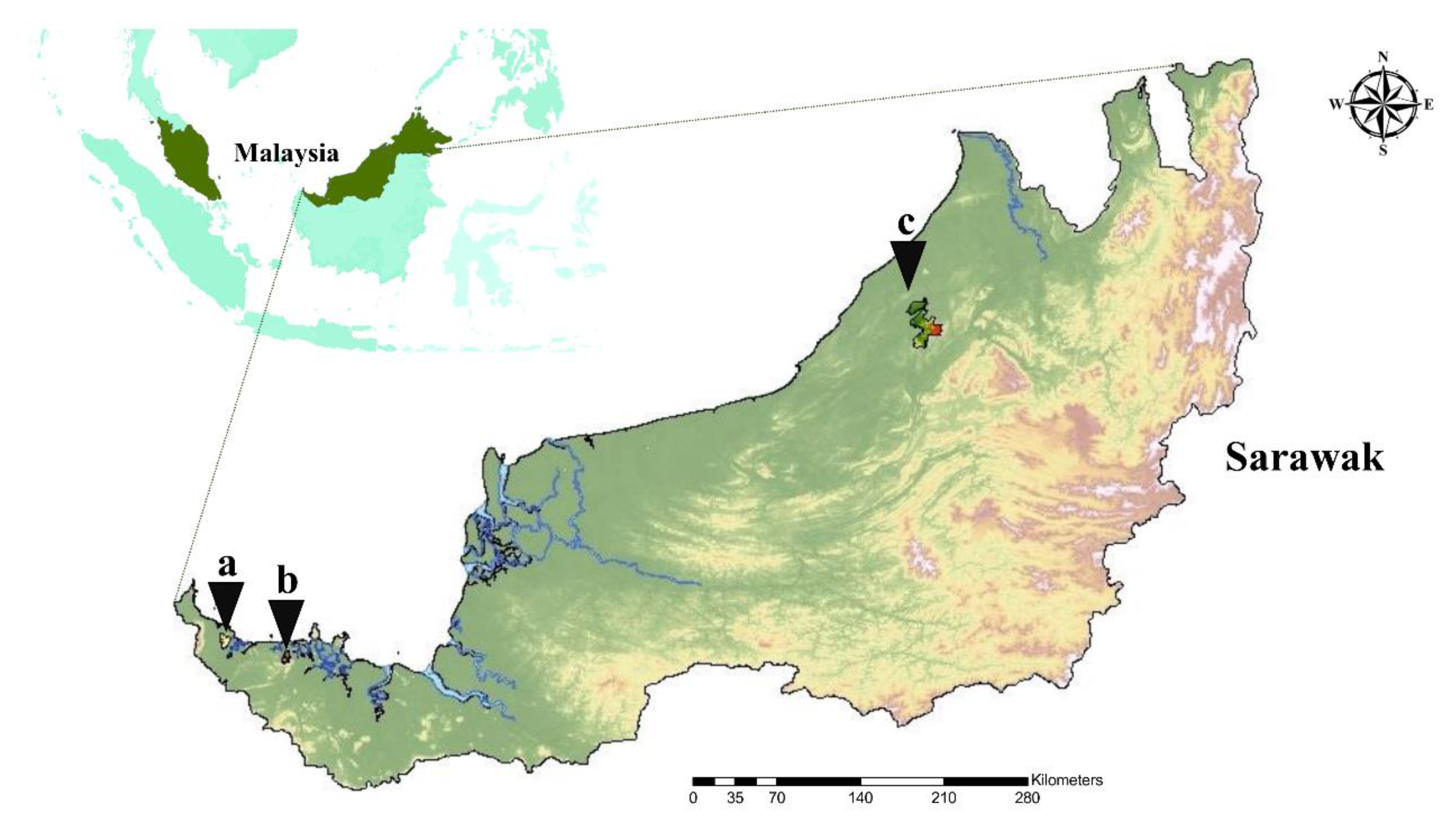
4.2. Survey Sites and Sample Collection
4.3. DNA Preparation and Species Identification of Rodents and Ticks
4.4. Screening of the Borrelia spp.
4.5. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of the Borrelia spp.
4.6. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Margos, G.; Gofton, A.; Wibberg, D.; Dangel, A.; Marosevic, D.; Loh, S.M.; Oskam, C.; Fingerle, V. The genus Borrelia reloaded. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Cutler, S.; Gofton, A.; Stevenson, B.; Estrada-Pena, A. Controversies in bacterial taxonomy: The example of the genus Borrelia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge, U.R.; Tannapfel, A.; Tyring, S.K.; Erbel, R.; Arendt, G.; Ruzicka, T. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesman, J.; Gern, L. Lyme borreliosis in Europe and North America. Parasitology 2004, 129, S191–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesler, M.C.; Shah, J.S.; Middelveen, M.J.; du Cruz, I.; Burrascano, J.J.; Stricker, R.B. Lyme disease: Diversity of Borrelia species in California and Mexico detected using a novel immunoblot assay. Healthcare 2020, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Margos, G.; Lane, R.S.; Fedorova, N.; Koloczek, J.; Piesman, J.; Hojgaard, A.; Sing, A.; Fingerle, V. Borrelia bissettiae sp. nov. and Borrelia californiensis sp. nov. prevail in diverse enzootic transmission cycles. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Hojgaard, A.; Lane, R.S.; Cornet, M.; Fingerle, V.; Rudenko, N.; Ogden, N.; Aanensen, D.M.; Fish, D.; Piesman, J. Multilocus sequence analysis of Borrelia bissettiae strains from North America reveals a new Borrelia species, Borrelia kurtenbachii. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2010, 1, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritt, B.S.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, M.E.; Replogle, A.J.; Bjork, J.; Liu, G.; Kingry, L.C.; Mead, P.S.; Neitzel, D.F.; et al. Borrelia mayonii sp. nov., a member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex, detected in patients and ticks in the upper midwestern United States. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4878–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Postic, D.; Sertour, N.; Livey, I.; Matuschka, F.-R.; Baranton, G. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species by multilocus sequence analysis and confirmation of the delineation of Borrelia spielmanii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, M.; Honig, V.; Ruzek, D.; Grubhoffer, L.; Rego, R.O.M. Europe-wide meta-analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato prevalence in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00609–e00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, M.; Baba, S.; Iguchi, K.; Yamaguti, N.; Russell, H. Lyme disease in Japan and its possible incriminated tick vector, Ixodes persulcatus. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 156, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzawa, T. Terrestrial distribution of the Lyme Borreliosis agent Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in east Asia. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 57, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbour, A.G. Relapsing fever. In Tick-Borne Diseases of Human; Jesse, L., Goodman, D.T.D., Sonenshine, D.E., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 268–291. [Google Scholar]
- Trape, J.F.; Diatta, G.; Arnathau, C.; Bitam, I.; Sarih, M.; Belghyti, D.; Bouattour, A.; Elguero, E.; Vial, L.; Mane, Y.; et al. The epidemiology and geographic distribution of relapsing fever borreliosis in West and North Africa, with a review of the Ornithodoros erraticus complex (Acari: Ixodida). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.D.; Brener, J.; Osorno, M.; Ristic, M. Pathobiology of Borrelia theileri in the tropical cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1978, 32, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Tsuruta, Y.; Matsushita, O.; Ralph, D.; McClelland, M.; Nakao, M. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of Borrelia miyamotoi sp. nov., isolated from the ixodid tick Ixodes persulcatus, the vector for Lyme disease in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, P.M.; Rich, S.M.; Smith, R.D.; Hartl, D.L.; Spielman, A.; Telford, S.R. A new Borrelia infecting Lone Star ticks. Lancet 1996, 347, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platonov, A.E.; Karan, L.S.; Kolyasnikova, N.M.; Makhneva, N.A.; Toporkova, M.G.; Maleev, V.V.; Fish, D.; Krause, P.J. Humans infected with relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia miyamotoi, Russia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.D.; Miranpuri, G.S.; Adams, J.H.; Ahrens, E.H. Borrelia theileri: Isolation from ticks (Boophilus microplus) and tick-borne transmission between splenectomized calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1985, 46, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Hovius, J.W.R.; de Wever, B.; Sohne, M.; Brouwer, M.C.; Coumou, J.; Wagemakers, A.; Oei, A.; Knol, H.; Narasimhan, S.; Hodiamont, C.J.; et al. A case of meningoencephalitis by the relapsing fever spirochaete Borrelia miyamotoi in Europe. Lancet 2013, 382, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, P.J.; Narasimhan, S.; Wormser, G.P.; Rollend, L.; Fikrig, E.; Lepore, T.; Barbour, A.; Fish, D. Human Borrelia miyamotoi infection in the United States. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Takano, A.; Konnai, S.; Nakao, M.; Ito, T.; Koyama, K.; Kaneko, M.; Ohnishi, M.; Kawabata, H. Human infections with Borrelia miyamotoi, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.G.; Jia, N.; Jiang, J.F.; Zheng, Y.C.; Chu, Y.L.; Jiang, R.R.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, H.B.; Wei, R.; Zhang, W.H.; et al. Borrelia miyamotoi infections in humans and ticks, Northeastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, K.; Tukur, S.M.; Watanabe, M.; Abd Rani, P.A.M.; Lau, S.F.; Shettima, Y.M.; Watanabe, M. Factors influencing the prevalence and distribution of ticks and tick-borne pathogens among domestic animals in Malaysia. Pertanika J. Sch. Reserve Rev. 2016, 2, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, J.E.; Shearman, P.L.; Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Aoro, G.; Lokes, B. Extreme differences in forest degradation in Borneo: Comparing practices in Sarawak, Sabah, and Brunei. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaveau, D.L.A.; Sloan, S.; Molidena, E.; Yaen, H.; Sheil, D.; Abram, N.K.; Ancrenaz, M.; Nasi, R.; Quinones, M.; Wielaard, N.; et al. Four decades of forest persistence, clearance and logging on Borneo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcox, B.A.; Duane, J.; Gubler, D.J. Disease ecology and the global emergence of zoonotic pathogens. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2005, 10, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohdy, S.; Schwartz, T.S.; Oaks, J.R. The coevolution effect as a driver of spillover. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, J.J.; Lim, F.S.; Tan, K.K.; Chen, F.S.; Phoon, W.H.; Khor, C.S.; Pike, B.L.; Chang, L.Y.; AbuBakar, S. Detection in Malaysia of a Borrelia sp. from Haemaphysalis hystricis (Ixodida: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, J.J.; Ishak, S.N.; Lim, F.S.; Mohd-Taib, F.S.; Khor, C.S.; Loong, S.K.; AbuBakar, S. Detection of a Borrelia sp. from Ixodes granulatus ticks collected from rodents in Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tay, S.T.; Kamalanathan, M.; Rohani, M.Y. Borrelia burgdorferi (strain B. afzelli) antibodies among Malaysian blood donor and patients. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2002, 33, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Khor, C.S.; Hassan, H.; Mohd-Rahim, N.F.; Chandren, J.R.; Nore, S.S.; Johari, J.; Loong, S.K.; Abd-Jamil, J.; Khoo, J.J.; Lee, H.Y.; et al. Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi among the indigenous people (Orang Asli) of peninsular Malaysia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Chu, C.Y.; Takano, A.; Jiang, B.G.; Liu, W.; Kurtenbach, K.; Masuzawa, T.; Fingerle, V.; Cao, W.C.; Kawabata, H. Borrelia yangtzensis sp. nov., a rodent-associated species in Asia, is related to Borrelia valaisiana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3836–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; van Dam, A.P.; Schwartz, I.; Dankert, J. Molecular typing of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: Taxonomic, epidemiological, and clinical implications. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 633–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, H.; Takano, A.; Kadosaka, T.; Fujita, H.; Nitta, Y.; Gokuden, M.; Honda, T.; Tomida, J.; Kawamura, Y.; Masuzawa, T.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing and DNA similarity analysis implicates that a Borrelia valaisiana-related sp. isolated in Japan is distinguishable from European, B. valaisiana. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuzawa, T.; Pan, M.J.; Kadosaka, T.; Kudeken, M.; Takada, N.; Yano, Y.; Imai, Y.; Yanagihara, Y. Characterization and identification of Borrelia isolates as Borrelia valaisiana in Taiwan and Kinmen Islands. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 44, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuzawa, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Kudeken, M.; Kadosaka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kawabata, H.; Koizumi, N.; Imai, Y. New genomospecies related to Borrelia valaisiana, isolated from mammals in Okinawa archipelago, Japan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, T.; Fukui, T.; Miyake, M.; Oh, H.B.; Cho, M.K.; Chang, W.H.; Imai, Y.; Yanagihara, H. Determination of members of a Borrelia afzelii-related group isolated from Ixodes nipponensis in Korea as Borrelia valaisiana. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, B.G.; Wang, D.M.; Jiang, W.J.; Zhao, Q.M.; Zhang, P.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Tang, G.P.; Yang, H.; et al. Novel genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato from rodents and ticks in southwestern China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3130–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takhampunya, R.; Korkusol, A.; Pongpichit, C.; Yodin, K.; Rungrojn, A.; Chanarat, N.; Promsathaporn, S.; Monkanna, T.; Thaloengsok, S.; Tippayachai, B.; et al. Metagenomic approach to characterizing disease epidemiology in a disease-endemic environment in northern Thailand. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.; Lin, Y.; Yao, C.; Shih, H.; Chung, L.; Liao, H.; Hsu, Y.; Wang, H. Tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from birds in Taiwan. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyamoto, K.; Sato, Y.; Okada, K.; Fukunaga, M.; Sato, F. Competence of a migratory bird, red-bellied thrush (Turdus chrysolaus), as an avian reservoir for the Lyme disease spirochetes in Japan. Acta Tropica 1997, 65, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, C.Y.; Nam, H.Y.; Chae, H.Y.; Chong, S.T.; Klein, T.A.; Ko, S.; Chae, J.S. Molecular detection of Anaplasma, Bartonella, and Borrelia species in ticks collected from migratory birds from Hong-do Island, Republic of Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movila, A.; Alekseev, A.N.; Dubinina, H.V.; Toderas, I. Detection of tick-borne pathogens in ticks from migratory birds in the Baltic region of Russia. Med Vet. Entomol. 2013, 27, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Foley, J.E.; Bierman, B.C.; Durden, L.A. Far-reaching dispersal of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato-infected Blacklegged ticks by migratory songbirds in Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.D.; Clark, K.L.; Foley, J.E.; Anderson, J.F.; Bierman, B.C.; Durden, L.A. Extensive distribution of the Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, in multiple tick species parasitizing avian and mammalian hosts across Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margos, G.; Gatewood, A.G.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanincova, K.; Terekhova, D.; Vollmer, S.A.; Cornet, M.; Piesman, J.; Donaghy, M.; Bormane, A.; et al. MLST of housekeeping genes captures geographic population structure and suggests a European origin of Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8730–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mtierova, Z.; Derdakova, M.; Chvostac, M.; Didyk, Y.M.; Mangova, B.; Taragelova, V.R.; Selyemova, D.; Sujanova, A.; Vaclav, R. Local population structure and seasonal variability of Borrelia garinii genotypes in Ixodes ricinus ticks, Slovakia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norte, A.C.; Margos, G.; Becker, N.S.; Albino Ramos, J.; Núncio, M.S.; Fingerle, V.; Araújo, P.M.; Adamík, P.; Alivizatos, H.; Barba, E.; et al. Host dispersal shapes the population structure of a tick-borne bacterial pathogen. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margos, G.; Sing, A.; Fingerle, V. Published data do not support the notion that Borrelia valaisiana is human pathogenic. Infection 2017, 45, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ito, T.; Asashima, N.; Ohno, M.; Nagai, R.; Fujita, H.; Koizumi, N.; Takano, A.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Case report: Borrelia valaisiana infection in a Japanese man associated with traveling to foreign countries. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.B.; Jia, N.; Jiang, B.G.; Sun, T.; Zheng, Y.C.; Huo, Q.B.; Liu, K.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Q.M.; Yang, H.; et al. Lyme borreliosis caused by diverse genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in northeastern China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.M.; Lee, W.G.; Ryou, J.; Yang, S.C.; Park, S.W.; Roh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, C.; Han, M.G. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks collected from humans, South Korea, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskul, P.; Stark, H.E.; Inlao, I. A checklist of ticks of Thailand (Acari: Metastigmata: Ixodoidea). J. Med. Entomol. 1983, 20, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, P.J.; Fish, D.; Narasimhan, S.; Barbour, A.G. Borrelia miyamotoi infection in nature and in humans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pukhovskaya, N.M.; Morozova, O.V.; Vysochina, N.P.; Belozerova, N.B.; Ivanov, L.I. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato and Borrelia miyamotoi in ixodid ticks in the far east of Russia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibernardo, A.; Cote, T.; Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R. The prevalence of Borrelia miyamotoi infection, and co-infections with other Borrelia spp. In Ixodes scapularis ticks collected in Canada. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.R.; Takano, A.; Konnai, S.; Shimozuru, M.; Kawabata, H.; Tsubota, T. Borrelia miyamotoi infections among wild rodents show age and month independence and correlation with Ixodes persulcatus larval attachment in Hokkaido, Japan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lommano, E.; Dvorak, C.; Vallotton, L.; Jenni, L.; Gern, L. Tick-borne pathogens in ticks collected from breeding and migratory birds in Switzerland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagemakers, A.; Staarink, P.J.; Sprong, H.; Hovius, J.W.R. Borrelia miyamotoi: A wide spread tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, A.G.; Bunikis, J.; Travinsky, B.; Hoen, A.G.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A.; Fish, D.; Tsao, J.I. Niche partitioning of Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia miyamotoi in the same tick vector and mammalian reservoir species. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zawada, S.G.; von Fricken, M.E.; Weppelmann, T.A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Optimization of tissue sampling for Borrelia burgdorferi in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibb, R.; Redding, D.W.; Chin, K.Q.; Donnelly, C.A.; Blackburn, T.M.; Newbold, T.; Jones, K.E. Zoonotic host diversity increases in human-dominated ecosystems. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoGiudice, K.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Schmidt, K.A.; Keesing, F. The ecology of infectious disease: Effects of host diversity and community composition on Lyme disease risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robins, J.H.; Hingston, M.; Matisoo-Smith, E.; Ross, H.A. Identifying Rattus species using mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohls, G.M. Tick (Ixodoidae) of Borneo and Malaya. Malays. Parasites 1957, 28, 65–94. [Google Scholar]
- Che Lah, E.F.; Yaakop, S.; Ahmad, M.; George, E.; Md Nor, S. Precise identification of different stages of a tick, Ixodes granulatus Supino, 1897 (Acari: Ixodidae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ushijima, Y.; Oliver, J.H.; Keirans, J.E.; Tsurumi, M.; Kawabata, H.; Watanabe, H.; Fukunaga, M. Mitochondrial sequence variation in Carlos capensis (Neumann), a parasite of seabirds, collected on Torishima Island in Japan. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtambo, J.; Van Bortel, W.; Madder, M.; Roelants, P.; Backeljau, T. Comparison of preservation methods of Rhipicephalus appendiculatus (Acari: Ixodidae) for reliable DNA amplification by PCR. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 38, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. Bold: The barcode of life data system (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takano, A.; Goka, K.; Une, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Fujita, H.; Shiino, T.; Watanabe, H.; Kawabata, H. Isolation and characterization of a novel Borrelia group of tick-borne borreliae from imported reptiles and their associated ticks. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roux, V.; Raoult, D. Body lice as tools for diagnosis and surveillance of reemerging diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Nakao, R.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Sato, K.; Kajihara, M.; Kanchela, S.; Changula, K.; Eto, Y.; Ndebe, J.; Sasaki, M.; et al. Human borreliosis caused by a New World Relapsing Fever Borrelia-like organism in the Old World. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sampling Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| November 2018 | March 2019 | |||
| Rodent Species | GGNP | KNP | OP Plantation | Total |
| Leopodamys sabanus | 0/2 | 0/2 | N/A | 0/4 |
| Maxomys rajah | N/A | 0/2 | N/A | 0/2 |
| Maxomys whiteheadi | 0/2 | N/A | N/A | 0/2 |
| Rattus spp. | N/A | 0/3 | 4/42 | 4/45 |
| Sundamys muelleri | 1/2 | N/A | 0/1 | 1/3 |
| Total | 1/6 | 0/7 | 4/43 | 5/56 |
| Ixodes granulatus | GGNP | KNP | OP Plantation | Total |
| Female | 0/3 | 1/9 | 10/10 | 11/22 |
| Nymph | N/A | 0/2 | 1/3 | 1/5 |
| Larva | N/A | N/A | 2/5 | 2/5 |
| Total | 0/3 | 1/11 | 13/18 | 14/32 |
| Gene | Sample ID | BLASTn | Identity | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| flaB | IG-204 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 |
| IG-206 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 | |
| IG-208 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 | |
| IG-213 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 | |
| IG-217 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 | |
| IG-218 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QTMP2 (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | EU135602 | |
| IG-215 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies (Japan) | 99.3% (298/300 bp) | AB091710 | |
| IG-219 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies (Japan) | 100% (300/300 bp) | AB091710 | |
| IG-214 | Borrelia sp. TKM-30 from Ixodes granulatus (Taiwan) | 99.3% (298/300 bp) | HM853004 | |
| IG-216 | Borrelia sp. TKM-30 from Ixodes granulatus (Taiwan) | 99.3% (298/300 bp) | HM853004 | |
| IG-220 | Uncultured Borrelia sp. clone Borr65 from Ixodes granulatus (China) | 100% (300/300 bp) | MG717514 | |
| IG-221 | Uncultured Borrelia sp. clone BorrIg from Ixodes granulatus (China) | 99.0% (297/300 bp) | MG717513 | |
| IG-222 | Uncultured Borrelia sp. from Ixodes granulatus (Malaysia) | 99.7% (299/300 bp) | LT969779 | |
| IG-228 | Uncultured Borrelia sp. from Ixodes granulatus (Malaysia) | 100% (300/300 bp) | LT969779 | |
| 16S rDNA | IG-213 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QX-S13 (China) | 99.5% (1347/1354 bp) | EU135598 |
| IG-216 | Borrelia sp. 9MT (South Korea) | 99.8% (1351/1354 bp) | L39080 | |
| IG-217 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies from rodent Apodemus agrarius (China) | 99.6% (1348/1354 bp) | AB022140 | |
| IG-220 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies from rodent Apodemus agrarius (China) | 99.6% (1346/1352 bp) | AB022140 | |
| IG-218 | Borrelia yangtzensis strain QSYSP3 (China) | 99.8% (1351/1354 bp) | EU135595 | |
| IG-219 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies from rodent Apodemus agrarius (China) | 99.7% (1350/1354 bp) | AB022141 | |
| IG-221 | Borrelia valaisiana-related genospecies from rodent Apodemus agrarius (China) | 99.6% (1349/1354 bp) | AB022141 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Target Gene (PCR Type) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mt-rrs1 | CTGCTCAATGATTTTTTAAATTGCTGTGG | Mitochondrial 16S rDNA of tick (Single PCR) | 55 | ~400 | [68] |
| mt-rrs2 | CCGGTCTGAACTCAGATCAAGTA | ||||
| BatL5310 | CCTACTCRGCCATTTTACCTATG | CO1 of rodents (Single PCR) | 48 | 750 | [70] |
| R6036R | ACTTCTGGGTGTCCAAAGAATCA | ||||
| BflaPAD | GATCARGCWCAAYATAACCAWATGCA | flaB of Borrelia (1st PCR) | 55 | 800 | [71] |
| BflaPDU | AGATTCAAGTCTGTTTTGGAAAGC | ||||
| BflaPBU | GCTGAAGAGCTTGGAATGCAACC | flaB of Borrelia (2nd PCR) | 50 | 345 | [71] |
| BflaPCR | TGATCAGTTATCATTCTAATAGCA | ||||
| fD1 | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | Universal primer for 16S rDNA of bacteria (1st PCR for rodent samples) | 55 | 1400 | [72] |
| rp2 | ACGGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT | ||||
| BF1 | GCTGGCAGTGCGTCTTAAGC | 16S rDNA of Borrelia (Single PCR for tick and 2nd PCR for rodent samples) | 55 | 1371 | [73] |
| BR1 | GCTTCGGGTATCCTCAACTC | ||||
| * BF3_seq | AGATACCCTGGTAGTCTACGCT | 16S rDNA of Borrelia | N/A | N/A | This study |
| * BR3_seq | GCTGCTGGCACGTAATTAGC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, A.C.C.; Qiu, Y.; Moustafa, M.A.M.; Nakao, R.; Shimozuru, M.; Onuma, M.; Mohd-Azlan, J.; Tsubota, T. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. Pathogens 2020, 9, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100846
Lau ACC, Qiu Y, Moustafa MAM, Nakao R, Shimozuru M, Onuma M, Mohd-Azlan J, Tsubota T. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. Pathogens. 2020; 9(10):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100846
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Alice C. C., Yongjin Qiu, Mohamed Abdallah Mohamed Moustafa, Ryo Nakao, Michito Shimozuru, Manabu Onuma, Jayasilan Mohd-Azlan, and Toshio Tsubota. 2020. "Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi" Pathogens 9, no. 10: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100846
APA StyleLau, A. C. C., Qiu, Y., Moustafa, M. A. M., Nakao, R., Shimozuru, M., Onuma, M., Mohd-Azlan, J., & Tsubota, T. (2020). Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato and Relapsing Fever Borrelia in Feeding Ixodes Ticks and Rodents in Sarawak, Malaysia: New Geographical Records of Borrelia yangtzensis and Borrelia miyamotoi. Pathogens, 9(10), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100846





