The Malacosporean Myxozoan Parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A Threat to Wild Salmonids
Abstract
1. Introduction
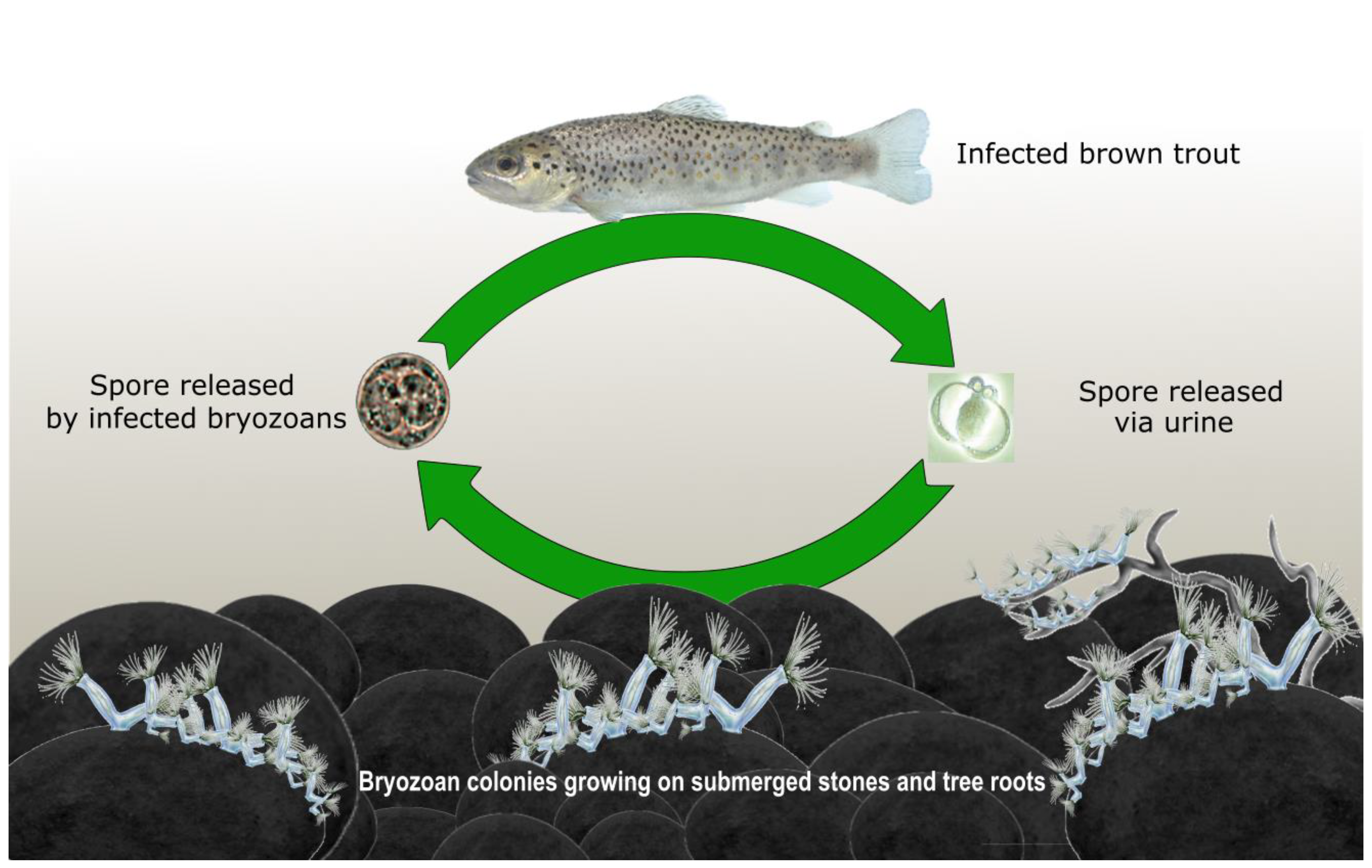
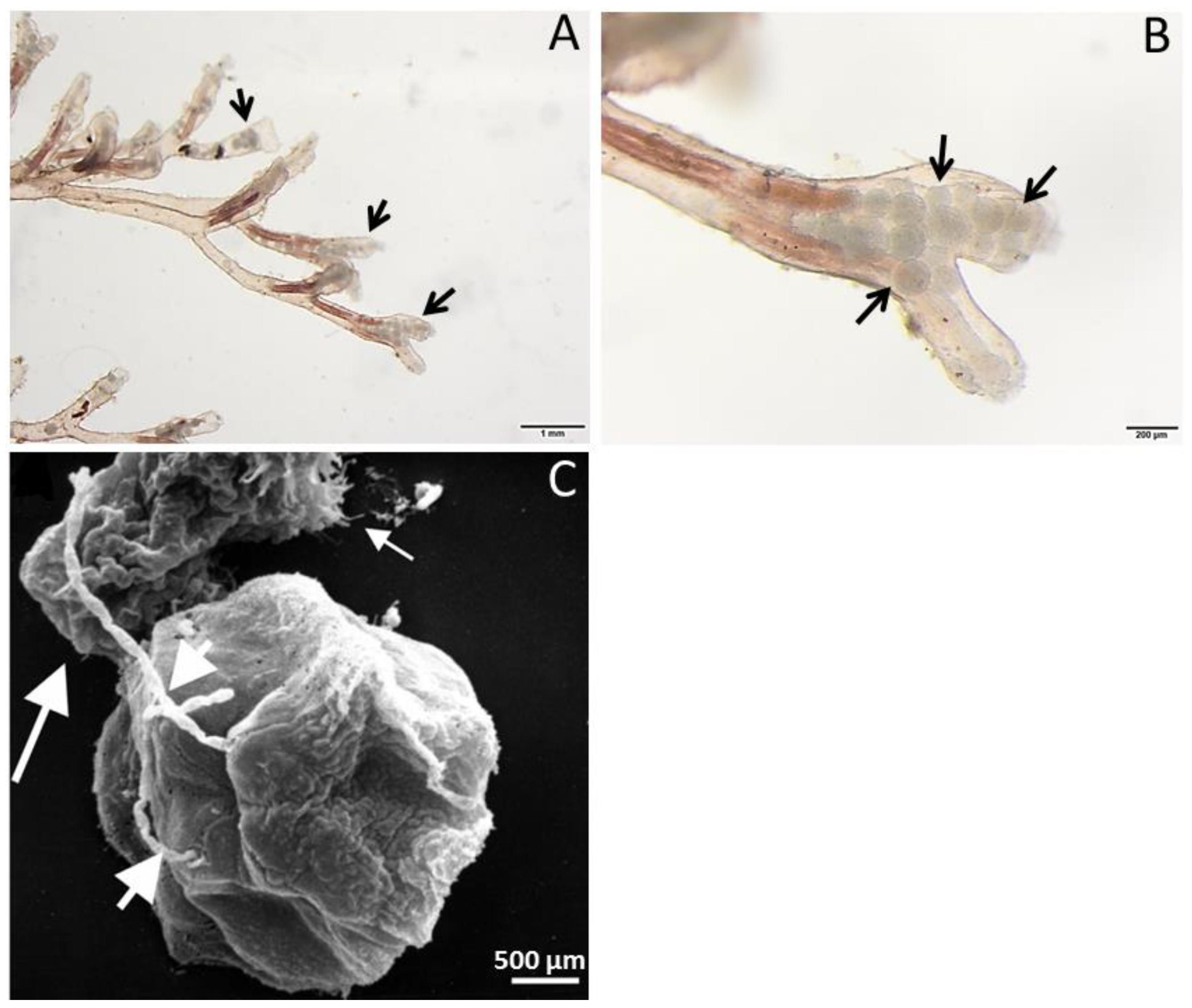
2. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae
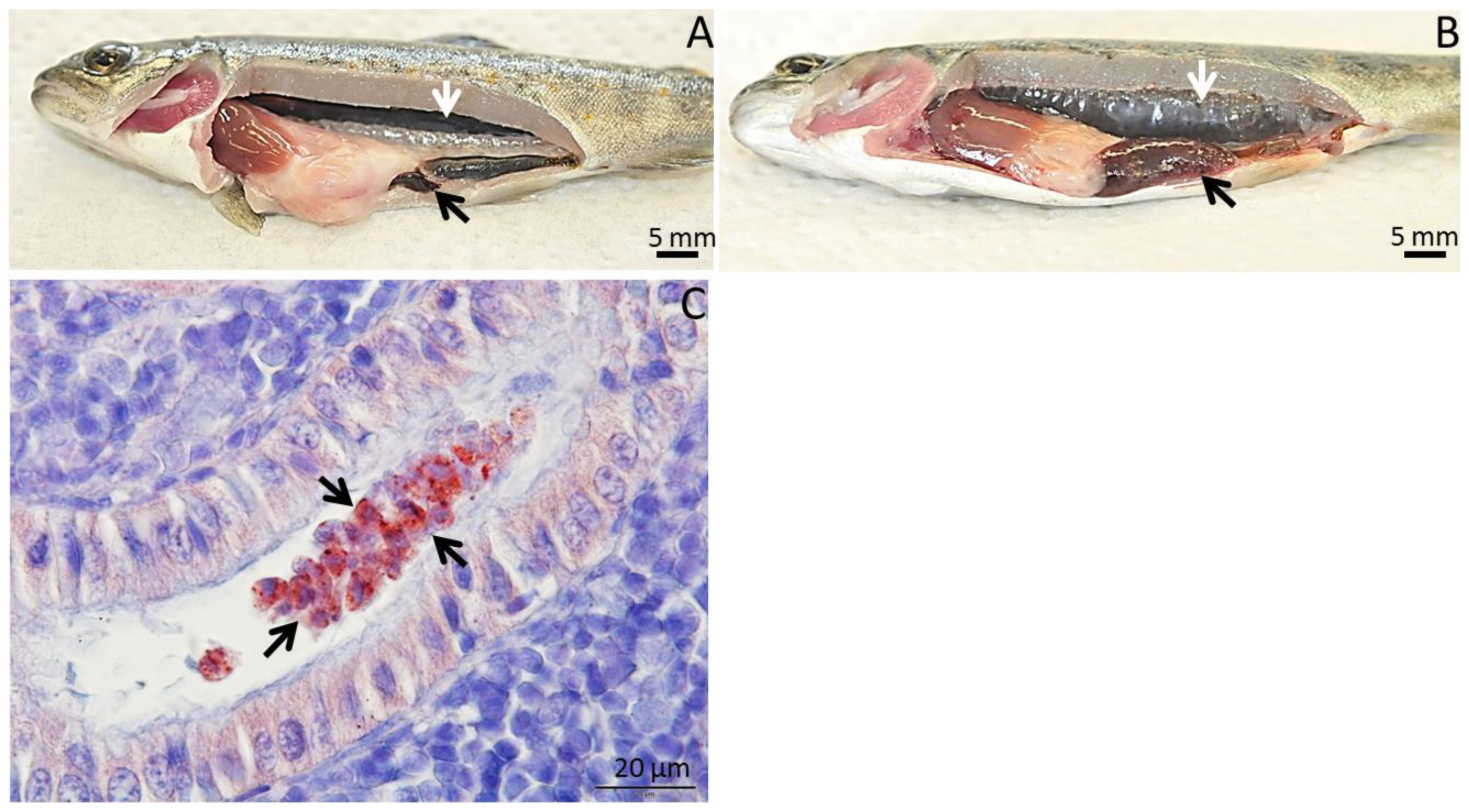
3. Geographic Distribution of T. bryosalmonae and Impact of PKD among Wild Salmonids
4. Effect of Temperature on T. bryosalmonae Infected Bryozoan and Fish Host
5. Aquatic Birds and Common Carp as Vectors of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae
6. Modelling Studies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canning, E.U.; Curry, A.; Feist, S.W.; Longshaw, M.; Okamura, B. Tetracapsula bryosalmonae n.sp. for PKX organism, the cause of PKD in Salmonid fish. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Pathol. 1999, 19, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.J.; Adams, A. Transmission of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa: Malacosporea), the causative organism of salmonid proliferative kidney disease, to the freshwater bryozoan Fredericella sultana. Parasitology 2006, 133, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, S.W.; Longshaw, M.; Canning, E.U.; Okamura, B. Induction of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss via the bryozoan Fredericella sultana infected with Tetracapsula bryosalmonae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 45, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longshaw, M.; Le Deuff, R.M.; Harris, A.F.; Feist, S.W. Development of proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), following short-term exposure to Tetracapsula bryosalmonae infected bryozoans. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; El-Matbouli, M. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa: Malacosporea) portal of entry into the fish host. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 90, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, R.P.; MacConnell, E.; de Kinkelin, P. Proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1993, 3, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Giger, W.; Güttinger, H.; Ochsenbein, U.; Peter, A.; Scheurer, K.; Segner, H.; Staub, E.; Suter, M.J.F. Where Have All the Fish Gone? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 441A–447A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuk, M.E.; Reichert, P.; Peter, A.; Schager, E.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Assessing the decline of brown trout (Salmo trutta) in Swiss rivers using a Bayesian probability network. Ecol. Model. 2006, 192, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, B.; Kotob, M.H.; Unfer, G.; El-Matbouli, M. First Proliferative Kidney Disease outbreak in Austria, linking to the aetiology of Black Trout Syndrome threatening autochthonous trout populations. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 119, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewisch, E.; Unfer, G.; Pinter, K.; Bechter, T.; El-Matbouli, M. Distribution and prevalence of T. bryosalmonae in Austria: A first survey of trout from rivers with a shrinking population. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellowstone River Fish Kill Fact Sheet-Updated. Available online: http://fwp.mt.gov/news/newsReleases/headlines/nr_4278.html (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Sage, J.L. Economic Contributions of the Yellowstone River to Park County, Montana; The Institute for Tourism and Recreation Research: Missoula, MT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gay, M.; Okamura, B.; De Kinkelin, P. Evidence that infectious stages of Tetracapsula bryosalmonae for rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss are present throughout the year. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2001, 46, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettge, K.; Segner, H.; Burki, R.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Wahli, T. Proliferative kidney disease (PKD) of rainbow trout: Temperature- and time-related changes of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae DNA in the kidney. Parasitology 2009, 136, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettge, K.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout: Time- and temperature-related renal pathology and parasite distribution. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 83, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tops, S.; Lockwood, W.; Okamura, B. Temperature-driven proliferation of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in bryozoan portends salmonid declines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 70, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effects of Elevated Water Temperatures on Salmonids. Available online: https://fortress.wa.gov/ecy/publications/publications/0010046.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2019).
- Plehn, M. Praktikum der Fischkrankheiten; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J.; Shepherd, C.J. Handbook of Trout and Salmon Diseases; Fishing News (Books) Ltd.: West Byfleet, Surrey, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, M.L.; Hedrick, R.P. PKX, the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in pacific salmonid fishes and its affinities with the Myxozoa. J. Protozool. 1985, 32, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.L.; Canning, E.U.; Okamura, B. Molecular data implicate bryozoans as hosts for PKX (Phylum Myxozoa) and identify a clade of bryozoan parasites within the Myxozoa. Parasitology 1999, 119, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, E.U.; Curry, A.; Feist, S.W.; Longshaw, M.; Okamura, B. A new class and order of myxozoans to accommodate parasites of bryozoans with ultrastructural observations on Tetracapsula bryosalmonae (PKX organism). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2000, 47, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, E.U.; Tops, S.; Curry, A.; Wood, T.S.; Okamura, B. Ecology, development and pathogenicity of Buddenbrockia plumatellae Schröder, 1910 (Myxozoa, Malacosporea) (syn. Tetracapsula bryozoides) and establishment of Tetracapsuloides n. gen. for Tetracapsula bryosalmonae. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2002, 49, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Guri, E.; Philippe, H.; Okamura, B.; Holland, P.W.H. Buddenbrockia is a cnidarian worm. Science 2007, 317, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Okamura, B. The phylogeography of salmonid proliferative kidney disease in Europe and North America. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, H.; Okamura, B. Ecology and evolution of malacosporean-bryozoan interactions. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2015; pp. 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, T.S.; Okamura, B. A new key to the freshwater bryozoans of Britain, Ireland and Continental Europe, with notes on their ecology. In Freshwater Biological Association; Sutcliffe, D.W., Ed.; Scientific Publication: Ambleside, UK, 2005; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Okamura, B.; Anderson, C.L.; Longshaw, M.; Feist, S.W.; Canning, E.U. Patterns of occurrence and 18s rDNA sequence variation of PKX (Tetracapsula bryosalmonae), the causative agent of salmonid proliferative kidney disease. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, H.; Gruhl, A.; Okamura, B. Diversification and repeated morphological transitions in endoparasitic cnidarians (Myxozoa: Malacosporea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 76, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.J.; Adams, A. Proliferative, presaccular stages of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (myxozoa: Malacosporea) within the invertebrate host Fredericella sultana (bryozoa: Phylactolaemata). J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, B.; Hartikainen, H.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Wahli, T. Life cycle complexity, environmental change and the emerging status of salmonid proliferative kidney disease. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.L.; Hedrick, R.P. Transmission of the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) with the blood and spleen of infected fish; further evidence that the PKX parasite belongs to the phylum Myxozoa. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1985, 5, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.J.; Adams, A. Sporogony of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in the brown trout Salmo trutta and the role of the tertiary cell during the vertebrate phase of myxozoan life cycles. Parasitology 2008, 135, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; El-Matbouli, M. Comparison of the susceptibility of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and four rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) strains to the myxozoan Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae, the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease (PKD). Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Abd-Elfattah, A.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Fate of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa) after infection of brown trout Salmo trutta and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 107, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, D.S.; El-Matbouli, M. Transmission of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa: Malacosporea) to Fredericella sultana (Bryozoa: Phylactolaemata) by various fish species. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 79, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Kumar, G.; El-Matbouli, M. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae persists in brown trout Salmo trutta for five years post exposure. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 127, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Hoffmann, R.W. Influence of water quality on the outbreak of proliferative kidney disease—Field studies and exposure experiments. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tops, S.; Hartikainen, H.L.; Okamura, B. The effects of infection by Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa) and temperature on Fredericella sultana (Bryozoa). Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt-Holm, P. Proliferative kidney disease: Why is it of interest for the Swiss project “Fishnet”? J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt-Holm, P. Decline of brown trout (Salmo trutta) in Switzerland - How to assess potential causes in a multi-factorial cause-effect relationship. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dash, M.; Vasemägi, A. Proliferative kidney disease (PKD) agent Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in brown trout populations in Estonia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 109, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristmundsson, Á.; Antonsson, T.; Árnason, F. First record of proliferative kidney disease in Iceland. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2010, 30, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lahnsteiner, F.; Haunschmid, R.; Mansour, N. Possible reasons for late summer brown trout (Salmo trutta Linnaeus 1758) mortality in Austrian prealpine river systems. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, T.; Bernet, D.; Segner, H.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Role of altitude and water temperature as regulating factors for the geographical distribution of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae infected fishes in Switzerland. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2184–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, T.; Bernet, D.; Steiner, P.A.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Geographic distribution of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae infected fish in Swiss rivers: An update. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zimmerli, S.; Bernet, D.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Vonlanthen, P.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H. Assessment of fish health status in four Swiss rivers showing a decline of brown trout catches. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, B.; Jonsson, N. Ecology of Atlantic Salmon and Brown Trout: Habitat as a Template for Life Histories; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Seagrave, C.P.; Bucke, D.; Hudson, E.B.; Mcgregor, D. A survey of the prevalence and distribution of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in England and Wales. J. Fish Dis. 1981, 4, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, R.; McVicar, A.H. Some preliminary observations on Proliferative Kidney Disease in wild brown trout, Salmo trutta L. in a Scottish stream. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1982, 2, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bucke, D.; Feist, S.W.; Clifton-Hadley, R.S. The occurrence of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in cultured and wild fish: Further investigations. J. Fish Dis. 1991, 14, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Morrison, J.K.; Ramsey, H.W.; Ferguson, H.W. Proliferative kidney disease: First reported outbreak in North America. J. Fish Dis. 1984, 7, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macconnell, E.; Peterson, J.E. Proliferative Kidney Disease in feral cutthroat trout from a remote Montana reservoir: A first case. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1992, 4, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahli, T.; Knuesel, R.; Bernet, D.; Segner, H.; Pugovkin, D.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Escher, M.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Proliferative kidney disease in Switzerland: Current state of knowledge. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterud, E.; Forseth, T.; Ugedal, O.; Poppe, T.T.; Jørgensen, A.; Bruheim, T.; Fjeldstad, H.P.; Mo, T.A. Severe mortality in wild Atlantic salmon Salmo salar due to proliferative kidney disease (PKD) caused by Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 77, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Steiner, P.; Müller, B.; Casanova-Nakayama, A. Complex interaction between proliferative kidney disease, water temperature and concurrent nematode infection in brown trout. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 104, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, I.; Hartikainen, H.; Williams, C.; Okamura, B. Persistence, impacts and environmental drivers of covert infections in invertebrate hosts. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Hirschi, R.; Schneider, E. Proliferative kidney disease in brown trout: Infection level, pathology and mortality under field conditions. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 114, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeler, E.J.; Feist, S.W.; Longshaw, M.; Thrush, M.A.; St-Hilaire, S. An assessment of the variation in the prevalence of renal myxosporidiosis and hepatitis in wild brown trout, Salmo trutta L., within and between rivers in South-West England. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.A.; Jørgensen, A. A survey of the distribution of the PKD-parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Cnidaria: Myxozoa: Malacosporea) in salmonids in Norwegian rivers—Additional information gleaned from formerly collected fish. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovgaard, A.; Buchmann, K. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and PKD in juvenile wild salmonids in Denmark. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2012, 101, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Braden, L.M.; Prosperi-Porta, G.; Kim, E.; Jones, S.R.M. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in spawning pink salmon, Oncorhynchus gorbuscha (Walbaum), in the Quinsam River, British Columbia, Canada. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debes, P.V.; Gross, R.; Vasemägi, A. Quantitative genetic variation in, and environmental effects on, pathogen resistance and temperature-dependent disease severity in a wild trout. Am. Nat. 2017, 190, 244–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenčič, V.; Zajc, U.; Kušar, D.; Ocepek, M.; Pate, M. A survey on Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae infections in Slovene fresh waters. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasemägi, A.; Nousiainen, I.; Saura, A.; Vähä, J.P.; Valjus, J.; Huusko, A. First record of proliferative kidney disease agent Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in wild brown trout and European grayling in Finland. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 125, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sobociński, B.; Huusko, A.; Vasemägi, A. First record of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa; Malacosporea) in European whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2018, 38, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, J.K. Spawning and Early Life History of Mountain Whitefish in the Madison River, Montana. Ph.D. Thesis, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- De Kinkelin, P.; Gerald, J.P. Reunion sur l’hepatonephrite parasitaire de la Truite Arc-en-Ciel. In Bulletin de l’Office International des Epizooties; Office International des Épizooties: Paris, France, 1977; Volume 87, pp. 489–490. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, T.K.; Ghittion, P. Proliferative Kidney Disease in Rainbow Trout From Italian Hatcheries; International Association for Aquatic Animal Medicine Proceedings: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Beraldo, P.; Berton, D.; Giavenni, R.; Galeotti, M. First report on proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in marble trout (Salmo trutta marmoratus, Cuvier 1817). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2006, 26, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Peribáñez, M.A.; Luco, D.F.; García, L.; Castillo, J.A. The prevalence of proliferative kidney disease from the kidney and muscle of rainbow and brown trout in Aragon (Spain). Prev. Vet. Med. 1997, 32, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, D.T.G.; McArdle, J.F. Management and control of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in a freshwater Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) farm in Ireland: A case history. Fish Vet. J. 1988, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Palikova, M.; Papezikova, I.; Markova, Z.; Navratil, S.; Mares, J.; Mares, L.; Vojtek, L.; Hyrsl, P.; Jelinkova, E.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under intensive breeding conditions: Pathogenesis and haematological and immune parameters. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 238, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Abd-Elfattah, A.; Soliman, H.; El-Matbouli, M. Establishment of medium for laboratory cultivation and maintenance of Fredericella sultana for in vivo experiments with Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa). J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, P.R.; Sepulveda, A.J.; Martin, R.M.; Hopper, L.R. A probe-based quantitative PCR assay for detecting Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae in fish tissue and environmental DNA water samples. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2018, 10, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, I.; Hartikainen, H.; Holland, J.; Secombes, C.; Okamura, B. Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae abundance in river water. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 124, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H.; Kumar, G.; El-Matbouli, M. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick for rapid detection of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae, the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease in salmonids. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.L.; Higgins, M.; Whitaker, D.J.; Yokoyama, H. Proliferative kidney disease and Sphaerospora oncorhynchi in wild-caught salmonids from the Puntledge river system, Vancouver-Island, British-Columbia. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, S.W.; Peeler, E.J.; Gardiner, R.; Smith, E.; Longshaw, M. Proliferative kidney disease and renal myxosporidiosis in juvenile salmonids from rivers in England and Wales. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, B.; Bailey, C.; Ferguson, J.A. First report of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and PKD in Alaskan salmonids. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Eastern Fish Health Workshop, New York, NY, USA, 1–5 April 2019; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, D.; Fux, R.; Blutke, A.; Schwaiger, J.; El-Matbouli, M.; Sutter, G.; Langenmayer, M.C. Proliferative kidney disease and proliferative darkening syndrome are linked with brown trout (Salmo trutta fario) mortalities in the Pre-Alpine Isar river. Pathogens 2019, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kutz, S.; Harvell, C.D. Climate change and infectious diseases: From evidence to a predictive framework. Science 2013, 341, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcogliese, D.J. The distribution and abundance of parasites in aquatic ecosystems in a changing climate: More than just temperature. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Segner, H.; Wahli, T.; Strepparava, N. Are brown trout Salmo trutta fario and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss two of a kind? A comparative study of salmonids to temperature-influenced Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae infection. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kinkelin, P.; Loriot, B. A water temperature regime which prevents the occurrence of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foott, J.S.; Hedrick, R.P. Seasonal occurrence of the infectious stage of proliferative kidney disease (PKD) and resistance of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, to reinfection. J. Fish Biol. 1987, 30, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton-Hadley, R.S.; Bucke, D.; Richards, R. Proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fish: A review. J. Fish Dis. 1984, 7, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, H.; Johnes, P.; Moncrieff, C.; Okamura, B. Bryozoan populations reflect nutrient enrichment and productivity gradients in rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2320–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Morvan, C.; Troutaud, D.; Deschaux, P. Differential effects of temperature on specific and nonspecific immune defences in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Köllner, B.; Kotterba, G. Temperature dependent activation of leucocyte populations of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, after intraperitoneal immunisation with Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002, 12, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen, S.; Bylund, G.; Lilius, E.M. Effect of environmental temperature on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) innate immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, Q.H.; Dixon, B. Impacts of low temperature on the teleost immune system. Biology 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilmonczyk, S.; Monge, D.; De Kinkelin, P. Proliferative kidney disease: Cellular aspects of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), response to parasitic infection. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Bettge, K.; Forster, U.; Segner, H.; Wahli, T. Kidney pathology and parasite intensity in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss surviving proliferative kidney disease: Time course and influence of temperature. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2012, 97, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macconnell, E.; Smith, C.E.; Hedrick, R.P.; Speer, C.A. Cellular inflammatory response of rainbow trout to the protozoan parasite that causes proliferative kidney disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1989, 1, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Segner, H.; Casanova-Nakayama, A.; Wahli, T. Who needs the hotspot? The effect of temperature on the fish host immune response to Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae the causative agent of proliferative kidney disease. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abos, B.; Estensoro, I.; Perdiguero, P.; Faber, M.; Hu, Y.; Rosales, P.D.; Granja, A.G.; Secombes, C.J.; Holland, J.W.; Tafalla, C. Dysregulation of B cell activity during proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneaux, M.; Visse, M.; Gross, R.; Pukk, L.; Saks, L.; Vasemägi, A. Parasite infection and decreased thermal tolerance: Impact of proliferative kidney disease on a wild salmonid fish in the context of climate change. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Strepparava, N.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H. Exploring the immune response, tolerance and resistance in proliferative kidney disease of salmonids. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 90, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Abd-Elfattah, A.; El-Matbouli, M. Identification of differentially expressed genes of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa). Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhagar, A.; Ertl, R.; Kumar, G.; El-Matbouli, M. Transcriptome profiling of posterior kidney of brown trout, Salmo trutta, during proliferative kidney disease. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; von Siebenthal, E.W.; Rehberger, K.; Segner, H. Transcriptomic analysis of the impacts of ethinylestradiol (EE2) and its consequences for proliferative kidney disease outcome in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 222, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuerola, J.; Green, A.J. Dispersal of aquatic organisms by waterbirds: A review of past research and priorities for future studies. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elfattah, A.; El-Matbouli, M.; Kumar, G. Structural integrity and viability of Fredericella sultana statoblasts infected with Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa) under diverse treatment conditions. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, I.G.; Jones, M.J. Movement of common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in a regulated lowland Australian river: Implications for management. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2006, 13, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elfattah, A.; Fontes, I.; Kumar, G.; Soliman, H.; Hartikainen, H.; Okamura, B.; El-Matbouli, M. Vertical transmission of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae (Myxozoa), the causative agent of salmonid proliferative kidney disease. Parasitology 2014, 141, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garner, M.G.; Hamilton, S.A. Principles of epidemiological modelling. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2011, 30, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Mari, L.; Hartikainen, H.; Strepparava, N.; Wahli, T.; Jokela, J.; Gatto, M.; Rinaldo, A.; Bertuzzo, E. An epidemiological model for proliferative kidney disease in salmonid populations. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Bertuzzo, E.; Mari, L.; Fontes, I.; Hartikainen, H.; Strepparava, N.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Wahli, T.; Jokela, J.; Gatto, M.; et al. Integrated field, laboratory, and theoretical study of PKD spread in a Swiss prealpine river. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11992–11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Mari, L.; Gatto, M.; Rinaldo, A.; Bertuzzo, E. Spread of proliferative kidney disease in fish along stream networks: A spatial metacommunity framework. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reported Year | Fish Species | Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | Grayling | United Kingdom | [49] |
| 1982 | Brown trout | United Kingdom | [50] |
| 1984 | Rainbow trout | USA | [52] |
| 1991 | Brown trout and grayling | United Kingdom | [51] |
| 1992 | Cutthroat trout | USA | [78] |
| 1995 | Kokanee salmon and chinook salmon | Canada | [53] |
| 2002 | Brown trout | United Kingdom | [79] |
| 2002 | Rainbow trout, brown trout and grayling | Switzerland | [54] |
| 2004 | Brown trout+ and cutthroat trout++ | United Kingdom+, Switzerland+ and USA++ | [25] |
| 2007 | Atlantic salmon | Norway | [55] |
| 2007 | Brown trout | Switzerland | [46] |
| 2007 | Brown trout | Switzerland | [47] |
| 2008 | Brown trout, rainbow trout and brook trout | Switzerland | [45] |
| 2008 | Brown trout | United Kingdom | [59] |
| 2010 | Arctic charr and brown trout | Iceland | [43] |
| 2010 | Brown trout and Atlantic salmon | Denmark | [61] |
| 2010 | Pink salmon | Canada | [62] |
| 2013 | Brown trout | Switzerland | [56] |
| 2014 | Brown trout | Estonia | [42] |
| 2014 | Brown trout and rainbow trout | Slovenia | [64] |
| 2015 | Brown trout | Switzerland | [58] |
| 2016 | Mountain white fish, rainbow trout, brown trout and cutthroat trout | USA | [11,12] |
| 2016 | Brown trout | Austria | [9] |
| 2017 | Brown trout and grayling | Finland | [65] |
| 2017 | Atlantic salmon, Arctic charr and brown trout | Norway | [60] |
| 2017 | Brown trout | Estonia | [63] |
| 2018 | Brown trout and rainbow trout | Austria | [10] |
| 2018 | European whitefish | Finland | [66] |
| 2019 | Chum salmon | USA (Alaska) | [80] |
| 2019 | Brown trout | Germany | [81] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sudhagar, A.; Kumar, G.; El-Matbouli, M. The Malacosporean Myxozoan Parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A Threat to Wild Salmonids. Pathogens 2020, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010016
Sudhagar A, Kumar G, El-Matbouli M. The Malacosporean Myxozoan Parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A Threat to Wild Salmonids. Pathogens. 2020; 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSudhagar, Arun, Gokhlesh Kumar, and Mansour El-Matbouli. 2020. "The Malacosporean Myxozoan Parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A Threat to Wild Salmonids" Pathogens 9, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010016
APA StyleSudhagar, A., Kumar, G., & El-Matbouli, M. (2020). The Malacosporean Myxozoan Parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A Threat to Wild Salmonids. Pathogens, 9(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9010016







