Parasitic Nematode Immunomodulatory Strategies: Recent Advances and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
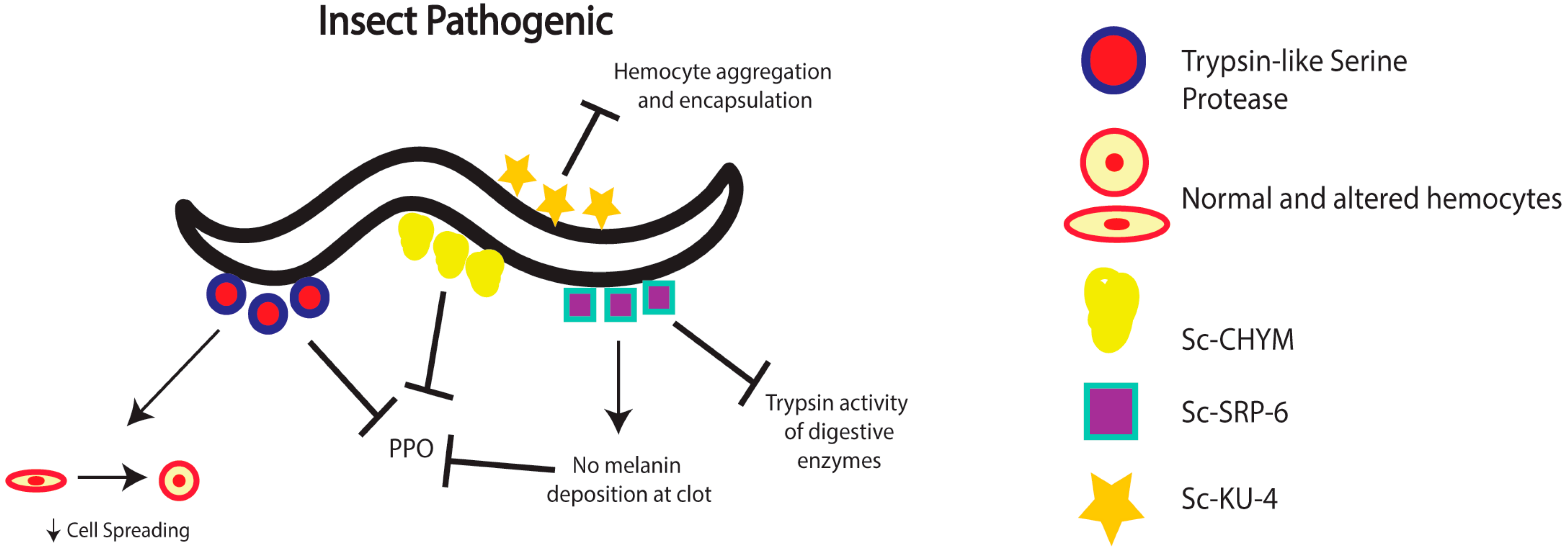
2. Nematode Immunomodulation in Insects
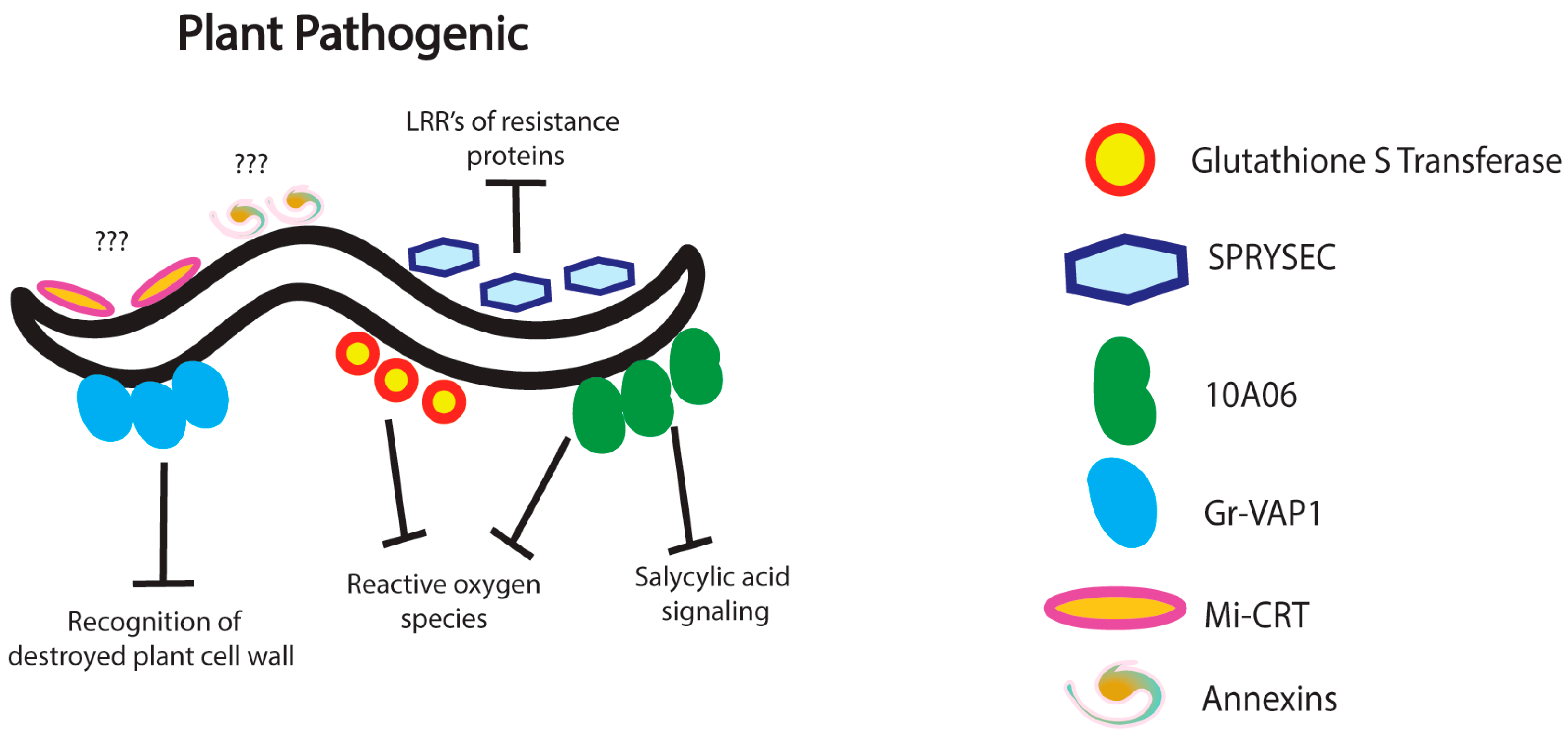
3. Nematode Immunomodulation in Plants
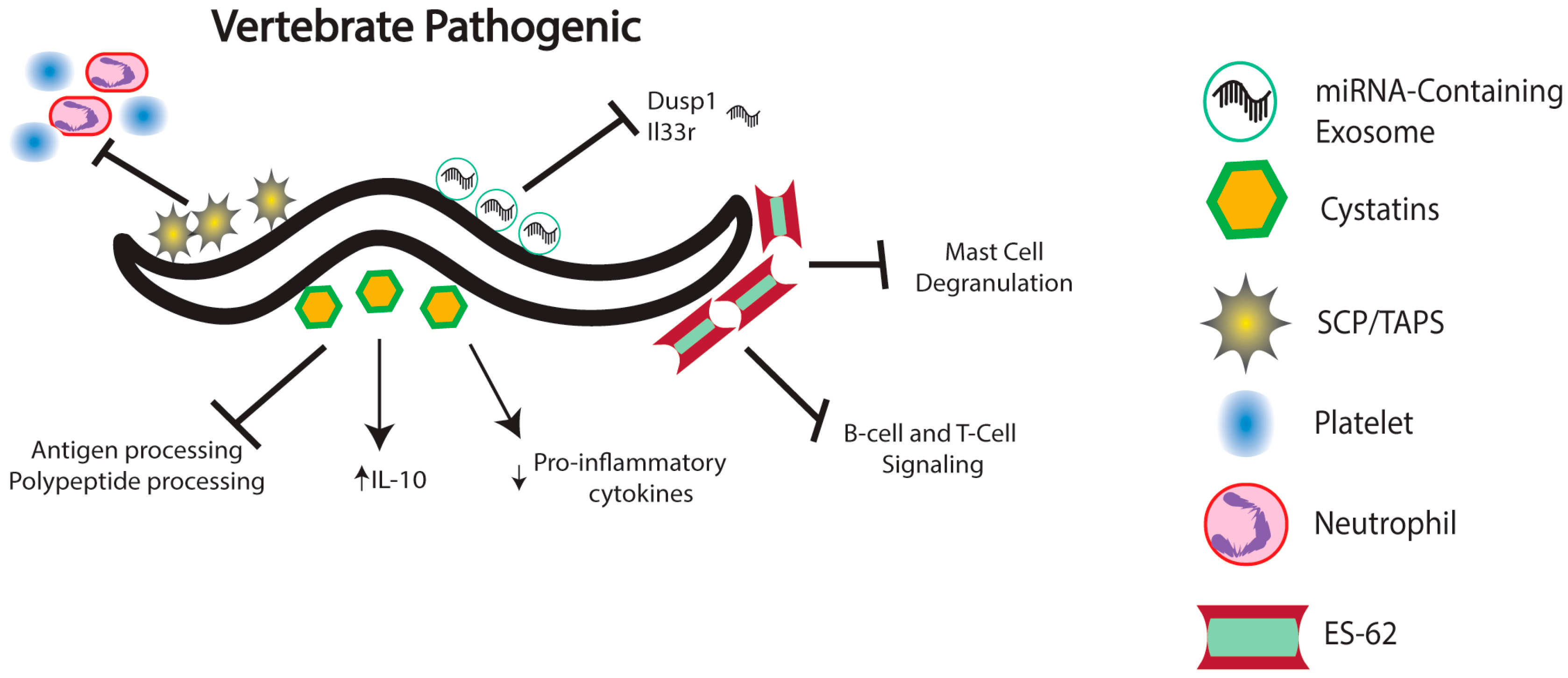
4. Nematode Immunomodulation in Vertebrates
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maizels, R.M.; Blaxter, M.L.; Scott, A.L. Immunological genomics of Brugia malayi: Filarial genes implicated in immune evasion and protective immunity. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, I.M.; Bradley, J.E.; Jackson, J.A. Macroparasites, innate immunity and immunoregulation: Developing natural models. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.C.; Reynolds, S.E.; Eleftherianos, I. Insect immune responses to nematode parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, R.M.; Gomez-Escobar, N.; Gregory, W.F.; Murray, J.; Zang, X. Immune evasion genes from filarial nematodes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitson, J.P.; Grainger, J.R.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth immunoregulation: The role of parasite secreted proteins in modulating host immunity. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klei, T.R. Immunological control of gastrointestinal nematode infections. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 72, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Lucius, R. Modulation of host immune responses by nematode cystatins. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSorley, H.J.; Hewitson, J.P.; Maizels, R.M. Immunomodulation by helminth parasites: Defining mechanisms and mediators. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deehan, M.R.; Frame, M.J.; Parkhouse, R.M.; Seatter, S.D.; Reid, S.D.; Harnett, M.M.; Harnett, W. A phosphorylcholine-containing filarial nematode-secreted product disrupts B lymphocyte activation by targeting key proliferative signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.H.; Deehan, M.R.; Katz, E.; Brown, K.S.; Houston, K.M.; O’Grady, J.; Harnett, M.M.; Harnett, W. Hyporesponsiveness of murine B lymphocytes exposed to the filarial nematode secreted product ES-62 in vivo. Immunology 2003, 109, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.E.; Horohov, D.W. Immunological aspects of nematode parasite control in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, E124–E132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.F.; Araújo, C.A. Helminth products as a potential therapeutic strategy for inflammatory diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansell, B.R.; Schnyder, M.; Deplazes, P.; Korhonen, P.K.; Young, N.D.; Hall, R.S.; Mangiola, S.; Boag, P.R.; Hofmann, A.; Sternberg, P.W.; et al. Insights into the immuno-molecular biology of Angiostrongylus vasorum through transcriptomics--prospects for new interventions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, A.H.; Coakley, G.; Simbari, F.; McSorely, H.J.; Quintana, J.F.; Le Bihan, T.; Kumar, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Lear, M.; Harcus, Y.; et al. Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.A.; Turner, J.D.; Kamal, M.; Wright, V.; Bickle, Q.; Else, K.J.; Ramsan, M.; Bradley, J.E. Gastrointestinal nematode infection is associated with variation in innate immune responsiveness. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, R.A.K.; Hartmann, S.; Rausch, S. Nematode modulation of inflammatory bowel disease. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Segura, M.; Morgan, K.; Loredo-Osti, J.C.; Stevenson, M.M. Impairment of protective immunity to blood-stage malaria by concurrent nematode infection. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3531–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnett, W. Secretory products of helminth parasites as immunomodulators. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 195, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, H.K.; Gaugler, R. Entomopathogenic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1993, 38, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, A.R.; Sternberg, P.W. Entomopathogenic nematodes. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R430–R431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich-Blair, H.; Clarke, D.J. Mutualism and pathogenesis in Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus: Two roads to the same destination. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterfield, N.R.; Ciche, T.; Clarke, D. Photorhabdus and a host of hosts. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodou, A.; Ankrah, D.O.; Stathopoulos, C. Toxins and secretion systems of Photorhabdus luminescens. Toxins 2010, 2, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, R.H.; ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Clarke, D.J.; Dowling, A.J.; Reynolds, S.E. Dissecting the immune response to the entomopathogen Photorhabdus. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kanost, M.R. Immunity in lepidopteran insects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 708, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imler, J.L.; Bulet, P. Antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila: Structures, activities and gene regulation. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2005, 86, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casanova-Torres, Á.M.; Goodrich-Blair, H. Immune signaling and antimicrobial peptide expression in Lepidoptera. Insects 2013, 4, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolff, J.; Schmid-Hempel, P. Perspectives on the evolutionary ecology of arthropod antimicrobial peptides. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Brehélin, M. Insect haemocytes: What type of cell is that? J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmaras, V.J.; Lampropoulou, M. Regulators and signalling in insect haemocyte immunity. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honti, V.; Csordás, G.; Kurucz, É.; Márku, R.; Andó, I. The cell-mediated immunity of Drosophila melanogaster: Hemocyte lineages, immune compartments, microanatomy and regulation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Revenis, C. Role and importance of phenoloxidase in insect hemostasis. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Wu, K.; Xie, W.; Luan, Y.X.; Ling, E. Insect prophenoloxidase: The view beyond immunity. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brivio, M.F.; Mastore, M.; Pagani, M. Parasite-host relationship: A lesson from a professional killer. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2005, 2, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, N.; Toubarro, D.; Simões, N. Biochemical study and in vitro insect immune suppression by a trypsin-like secreted protease from the nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, D.; Haas, E.; Miller, J. Eicosanoids: Exploiting insect immunity to improve biological control programs. Insects 2012, 3, 492–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubarro, D.; Avila, M.M.; Hao, Y.; Balasubramanian, M.; Jing, Y.; Montiel, R.; Faria, T.Q.; Brito, R.M.; Simões, M. A serpin released by an entomopathogen impairs clot formation in insect defense system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theopold, U.; Krautz, R.; Dushay, M.S. The Drosophila clotting system and its messages for mammals. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyavathi, V.V.; Minz, A.; Nagaraju, J. Nodulation: An unexplored cellular defense mechanism in insects. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, N.; Hao, Y.J.; Toubarro, D.; Nascimento, G.; Simões, N. Purification, biochemical and molecular analysis of a chymotrypsin protease with prophenoloxidase suppression activity from the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubarro, D.; Avila, M.M.; Montiel, R.; Simões, N. A pathogenic nematode targets recognition proteins to avoid insect defenses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, V.M.; Gleason, C.A. Plant-nematode interactions. Cur. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, E.; Eleftherianos, I. Entomopathogenic and plant pathogenic nematodes as opposing forces in agriculture. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, V.M.; Kumar, A. Nematode resistance in plants: The battle underground. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, W.S.; Kieran, S.R.; Zasada, I.A. The relationship between temperature and development in Globodera ellingtonae. J. Nematol. 2015, 47, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goverse, A.; Smant, G. The activation and suppression of plant innate immunity by parasitic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Dickman, M. Plant programmed cell death: Can’t live with it; Can’t live without it. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaouannet, M.; Rosso, M.N. Effectors of root sedentary nematodes target diverse plant cell compartments to manipulate plant functions and promote infection. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e25507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Torres, J.L.; Wilbers, R.H.P.; Warmerdam, S.; Finkers-Tomczak, A.; Diaz-Granados, A.; van Schaik, C.C.; Helder, J.; Bakker, J.; Goverse, A.; Schots, A.; et al. Apoplastic venom allergen-like proteins of cyst nematodes modulate the activation of basal plant innate immunity by cell surface receptors. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Goyal, A.K. Identification and functional analysis of secreted effectors from phytoparasitic nematodes. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Postma, W.; Tytgat, T.; Prins, P.; Qin, L.; Overmars, H.; Vossen, J.; Spiridon, L.N.; Petrescu, A.J.; Goverse, A.; et al. A secreted SPRY domain-containing protein (SPRYSEC) from the plant-parasitic nematode Globodera rostochiensis interacts with a CC-NB-LRR protein from a susceptible tomato. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubreuil, G.; Magliano, M.; Deleury, E.; Abad, P.; Rosso, M.N. Transcriptome analysis of root-knot nematode functions induced in the early stages of parasitism. New Phytol. 2007, 176, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewezi, T.; Howe, P.J.; Maier, T.R.; Hussey, R.S.; Mitchum, M.G.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J. Arabidopsis spermidine synthase is targeted by an effector protein of the cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaouannet, M.; Magliano, M.; Arguel, M.J.; Gourgues, M.; Evangelisti, E.; Abad, P.; Rosso, M.N. The root-knot nematode calreticulin Mi-CRT is a key effector in plant defense suppression. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Gantasala, N.P.; Roychowdhury, T.; Thakur, P.K.; Banakar, P.; Shukla, R.N.; Jones, M.G.; Rao, U. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the cereal cyst nematode, Heterodera avenae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, A.; Jones, J.T.; Blok, V.C.; Beauchamp, J.; McDermott, L.; Cooper, A.; Kennedy, M.W. A surface-associated retinol- and fatty acid-binding protein (Gp-FAR-1) from the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida: Lipid binding activities, structural analysis and expression pattern. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Allen, R.; Maier, T.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J.; Hussey, R.S. The parasitome of the phytonematode Heterodera glycines. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, N.R.; Brooker, S.; Hotez, P.J.; Montresor, A.; Engels, D.; Savioli, L. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: Updating the global picture. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 12, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Fenwick, A.; Savioli, L.; Molyneux, D.H. Rescuing the bottom billion through control of neglected tropical diseases. Lancet 2009, 373, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Helming, L.; Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages: An immunologic functional perspective. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrigoue, J.G.; Marshall, F.A.; Artis, D. On the hunt for helminths: Innate immune cells in the recognition and response to helminth parasites. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Veer, M.J.; Kemp, J.M.; Meeusen, E.N.T. The innate host defence against nematode parasites. Parasite Immunol. 2007, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grencis, R.K. Immunity to helminths: Resistance, regulation, and susceptibility to gastrointestinal nematodes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maizels, R.M.; Balic, A.; Gomez-Escobar, N.; Nair, M.; Taylor, M.D.; Allen, J.E. Helminth parasites–masters of regulation. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 201, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall, E.; Brandstetter, H. Structure and function of legumain in health and disease. Biochimie 2016, 122, 126–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierack, P.; Lucius, R.; Sonnenburg, B.; Schilling, K.; Hartmann, S. Parasite-specific immunomodulatory functions of filarial cystatin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2422–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Su, Z. Modulation of dendritic cell function and immune response by cysteine protease inhibitor from murine nematode parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus. Immunology 2012, 138, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flávia Nardy, A.; Freire-de-Lima, C.G.; Morrot, A. Immune evasion strategies of Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 178947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendt, P.; Arnold, P.; Brueck, M.; Rickert, U.; Lucius, R.; Hartmann, S.; Klotz, C.; Lucius, R. A helminth protease inhibitor modulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory phenotype of microglia in vitro. Neuroimmunomodulation 2016, 23, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Korhonen, P.K.; Campbell, B.E.; Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Jabbar, A.; Hall, R.S.; Mondal, A.; Howe, A.C.; Pell, J.; et al. The genome and developmental transcriptome of the strongylid nematode Haemonchus contortus. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foth, B.J.; Tsai, I.J.; Reid, A.J.; Bancroft, A.J.; Nichol, S.; Tracey, A.; Holroyd, N.; Cotton, J.A.; Stanley, E.J.; Zarowiecki, M.; et al. Whipworm genome and dual-species transcriptome analyses provide molecular insights into an intimate host-parasite interaction. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, V.L.; Tsai, I.J.; Coghlan, A.; Reid, A.J.; Holroyd, N.; Foth, B.J.; Tracey, A.; Cotton, J.A.; Stanley, E.J.; Beasley, H.; et al. The genomic basis of parasitism in the Strongyloides clade of nematodes. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantacessi, C.; Mitreva, M.; Campbell, B.E.; Hall, R.S.; Young, N.D.; Jex, A.R.; Ranganathan, S.; Gasser, R.B. First transcriptomic analysis of the economically important parasitic nematode, Trichostrongylus colubriformis, using a next-generation sequencing approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyle, M.; Foster, D.L.; McGrath, D.E.; Brown, S.M.; Laroche, Y.; De Meutter, J.; Stanssens, P.; Bogowitz, C.A.; Fried, V.A.; Ely, J.A.; et al. A hookworm glycoprotein that inhibits neutrophil function is a ligand of the integrin CD11b/CD18. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10008–10015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, A.; Jones, B.F.; Harrison, L.M.; Chadderdon, R.C.; Cappello, M. Isolation and molecular cloning of a secreted hookworm platelet inhibitor from adult Ancylostoma caninum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 129, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, M.A.; Lumb, F.; Harnett, M.M.; Harnett, W. ES-62, a therapeutic anti-inflammatory agent evolved by the filarial nematode Acanthocheilonema viteae. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 194, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Riyami, L.; Harnett, W. Immunomodulatory properties of ES-62, a phosphorylcholine-containing glycoprotein secreted by Acanthocheilonema viteae. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodridge, H.S.; Marshall, F.A.; Else, K.J.; Houston, K.M.; Egan, C.; Al-Riyami, L.; Liew, F.Y.; Harnett, W.; Harnett, M.M. Immunomodulation via novel use of TLR4 by the filarial nematode phosphorylcholine-containing secreted product, ES-62. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendez, A.J.; Harnett, M.M.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Wong, W.S.; Tay, H.K.; McSharry, C.P.; Harnett, W. Inhibition of Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell responses by ES-62, a product of parasitic filarial nematodes. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnett, W.; Harnett, M.M. Filarial nematode secreted product ES-62 is an anti-inflammatory agent: Therapeutic potential of small molecule derivatives and ES-62 peptide mimetics. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Riyami, L.; Pineda, M.A.; Rzepecka, J.; Huggan, J.K.; Khalaf, A.I.; Suckling, C.J.; Scott, F.J.; Rodgers, D.T.; Harnett, M.M.; Harnett, W. Designing anti-inflammatory drugs from parasitic worms: A synthetic small molecule analogue of the Acanthocheilonema viteae product ES-62 prevents development of collagen-induced arthritis. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9982–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beninson, L.A.; Fleshner, M. Exosomes: An emerging factor in stress-induced immunomodulation. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanian, M.; Fraser, L.M.; Agbedanu, P.N.; Harischandra, H.; Moorhead, A.R.; Day, T.A.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Kimber, M.J. Release of small RNA-containing exosome-like vesicles from the human filarial parasite Brugia malayi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.F.; Makepeace, B.L.; Babayan, S.A.; Ivens, A.; Pfarr, K.M.; Blaxter, M.; Debrah, A.; Wanji, S.; Ngangyung, H.F.; Bah, G.S.; et al. Extracellular Onchocerca-derived small RNAs in host nodules and blood. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cooper, D.; Eleftherianos, I. Parasitic Nematode Immunomodulatory Strategies: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Pathogens 2016, 5, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens5030058
Cooper D, Eleftherianos I. Parasitic Nematode Immunomodulatory Strategies: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Pathogens. 2016; 5(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens5030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleCooper, Dustin, and Ioannis Eleftherianos. 2016. "Parasitic Nematode Immunomodulatory Strategies: Recent Advances and Perspectives" Pathogens 5, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens5030058
APA StyleCooper, D., & Eleftherianos, I. (2016). Parasitic Nematode Immunomodulatory Strategies: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Pathogens, 5(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens5030058





