Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3. Sources of Phenotypic Diversification
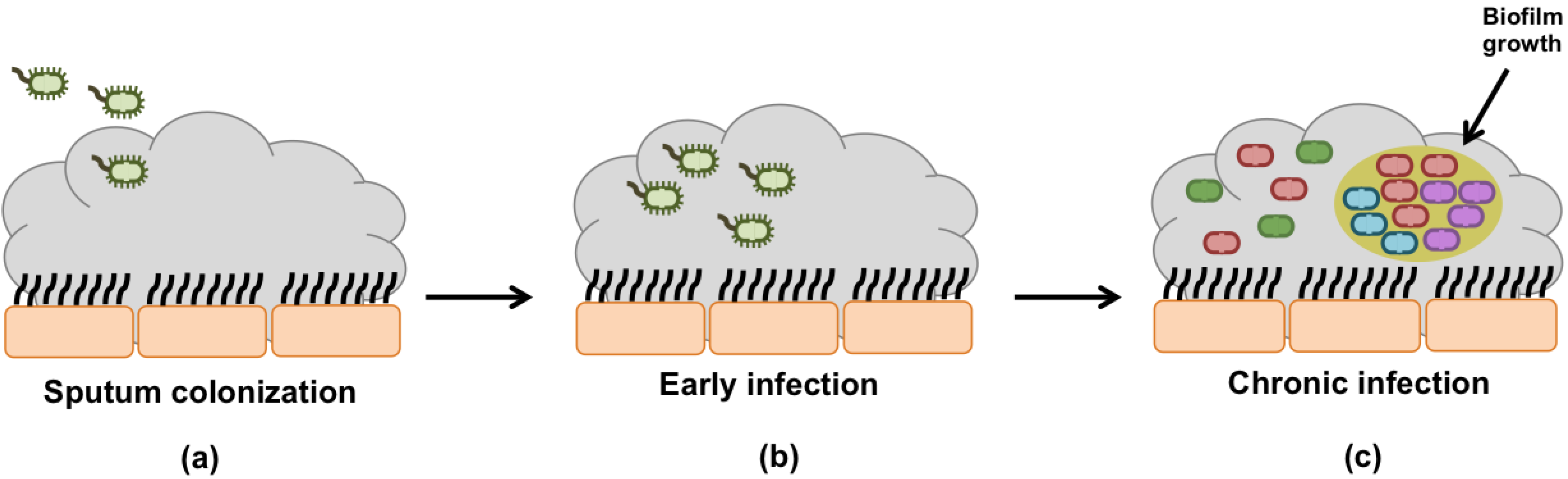
4. P. aeruginosa Evolution and Adaptation during Infection Development

4.1. Early Infection
4.2. Chronic Infection
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kreda, S.M.; Davis, C.W.; Rose, M.C. CFTR, mucins, and mucus obstruction in cystic fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009589. [Google Scholar]
- Folkesson, A.; Jelsbak, L.; Yang, L.; Johansen, H.K.; Ciofu, O.; Hoiby, N.; Molin, S. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis airway: An evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, F.A. Cystic fibrosis: Pathogenesis and future treatment strategies. Respir. Care 2009, 54, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubamba, B.; Dhooghe, B.; Noel, S.; Leal, T. Cystic fibrosis: Insight into CFTR pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, R.C. Targeted therapy for cystic fibrosis: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mutation-specific pharmacologic strategies. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2006, 10, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.I.; Prince, A. Opportunistic infections in lung disease: Pseudomonas infections in cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.L.; Mashburn, L.M.; Singh, P.K.; Whiteley, M. Cystic fibrosis sputum supports growth and cues key aspects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa physiology. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5267–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, D.D.; Lunsdorf, H.; Lam, J.S.; Romling, U. Microcolony formation: A novel biofilm model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the cystic fibrosis lung. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schobert, M.; Jahn, D. Anaerobic physiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the cystic fibrosis lung. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2010, 300, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittar, F.; Richet, H.; Dubus, J.C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Stremler, N.; Sarles, J.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M. Molecular detection of multiple emerging pathogens in sputa from cystic fibrosis patients. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Patient Registry 2011 Annual Report; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, M.; Cohen, R. New and investigational treatments in cystic fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2011, 5, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Smyth, A.R. Current dilemmas in antimicrobial therapy in cystic fibrosis. Exp. Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 407–422. [Google Scholar]
- Döring, G.; Flume, P.; Heijerman, H.; Elborn, J.S. Treatment of lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis: Current and future strategies. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.; Singh, M.; Dwan, K. Inhaled antibiotics for long-term therapy in cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 16, CD001021. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Signorovitch, J.E.; Zhang, J.; Latremouille-Viau, D.; von Wartburg, M.; Wu, E.Q.; Shi, L. Reduced mortality in cystic fibrosis patients treated with tobramycin inhalation solution. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, F.; Munck, A.; Kho, P.; Angyalosi, G. Treatment of early Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with cystic fibrosis: The ELITE trial. Thorax 2010, 65, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobell, J.T.; Waters, C.D.; Young, D.C.; Stockmann, C.; Ampofo, K.; Sherwin, C.M.; Spigarelli, M.G. Optimization of anti-pseudomonal antibiotics for cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: II. cephalosporins and penicillins. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, H.D.; Falcao-Silva, V.S.; Goncalves, G.F. Pulmonary bacterial pathogens in cystic fibrosis patients and antibiotic therapy: A tool for the health workers. Int. Arch. Med. 2008, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silby, M.W.; Winstanley, C.; Godfrey, S.A.; Levy, S.B.; Jackson, R.W. Pseudomonas genomes: Diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 652–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.H.; Hansen, S.K.; Johansen, H.K.; Thomsen, L.E.; Workman, C.T.; Nielsen, K.F.; Jelsbak, L.; Hoiby, N.; Yang, L.; Molin, S. Early adaptive developments of Pseudomonas aeruginosa after the transition from life in the environment to persistent colonization in the airways of human cystic fibrosis hosts. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Bjarnsholt, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in cystic fibrosis. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogardt, M.; Heesemann, J. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during persistence in the cystic fibrosis lung. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelstraete, P.; Haerynck, F.; van Daele, S.; Deseyne, S.; de Baets, F. Eradication therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization episodes in cystic fibrosis patients not chronically colonized by P. aeruginosa. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragonzi, A.; Paroni, M.; Nonis, A.; Cramer, N.; Montanari, S.; Rejman, J.; di Serio, C.; Doring, G.; Tummler, B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa microevolution during cystic fibrosis lung infection establishes clones with adapted virulence. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.A.; Fothergill, J.L.; Paterson, S.; Brockhurst, M.A.; Winstanley, C. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of some antibiotics can drive diversification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations in artificial sputum medium. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Mandsberg, L.F.; Wang, H.; Hoiby, N. Phenotypes selected during chronic lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients: Implications for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huse, H.K.; Kwon, T.; Zlosnik, J.E.; Speert, D.P.; Marcotte, E.M.; Whiteley, M. Parallel evolution in Pseudomonas aeruginosa over 39,000 generations in vivo. mBio 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, T.D.; Michel, J.B.; Aingaran, M.; Potter-Bynoe, G.; Roux, D.; Davis, M.R.J.; Skurnik, D.; Leiby, N.; LiPuma, J.J.; Goldberg, J.J.; et al. Parallel bacterial evolution within multiple patients identifies candidate pathogenicity genes. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, D.J.; Sutton, M.D.; Schurr, M.J.; Herr, A.B.; Caldwell, C.C.; Matu, J.O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa hypoxic or anaerobic biofilm infections within cystic fibrosis airways. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.O.; Fiandaca, M.J.; Pedersen, J.; Hansen, C.R.; Andersen, C.B.; Pressler, T.; Givskov, M.; Hoiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlitzsch, D.; Tarran, R.; Ulrich, M.; Schwab, U.; Cekici, A.; Meyer, K.C.; Birrer, P.; Bellon, G.; Berger, J.; Weiss, T.; et al. Effects of reduced mucus oxygen concentration in airway Pseudomonas infections of cystic fibrosis patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.D.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Palmer, J.N. Biofilms. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 43, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Alhede, M.; Alhede, M.; Eickhardt-Sørensen, S.R.; Moser, C.; Kühl, M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Høiby, N. The in vivo biofilm. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, S. Multicellular signalling and growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakioti, M.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Bacterial biofilms: Development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a010306. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F. Biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, Y.A.; Plakunov, V.K. Biofilm—“City of microbes” or an analogue of multicellular organisms? Microbiology 2007, 76, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, N.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Jensen, P.O.; Stub, C.; Hentzer, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O.; Givskov, M.; Johansen, H.K.; Hoiby, N. Novel mouse model of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection mimicking cystic fibrosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, J.; Meyer-Hoffert, U.; Teran, L.M.; Schwichtenberg, L.; Bartels, J.; Maune, S.; Schroder, J.M. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa, TNF-alpha, and IL-1beta, but not IL-6, induce human beta-defensin-2 in respiratory epithelia. Am. J. Respirat. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerke, C.; Wolz, C. Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to the cystic fibrosis lung. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 300, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, D.J.; Cuppoletti, J.; Trapnell, B.; Lymar, S.V.; Rowe, J.J.; Yoon, S.S.; Hilliard, G.M.; Parvatiyar, K.; Kamani, M.C.; Wozniak, D.J.; et al. Anaerobic metabolism and quorum sensing by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in chronically infected cystic fibrosis airways: Rethinking antibiotic treatment strategies and drug targets. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 1425–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.S.; Hennigan, R.F.; Hilliard, G.M.; Ochsner, U.A.; Parvatiyar, K.; Kamani, M.C.; Allen, H.L.; DeKievit, T.R.; Gardner, P.R.; Schwab, U.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa anaerobic respiration in biofilms: Relationships to cystic fibrosis pathogenesis. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Camper, A.K.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Costerton, J.W.; Davies, D.G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenkard, E. Antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbes. infect./Inst. Pasteur. 2003, 5, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouenne, T.; Vilain, S.; Cosette, P.; Junter, G.A. Proteomics of Biofilm Bacteria. Curr. Proteomics 2004, 1, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southey-Pillig, C.J.; Davies, D.G.; Sauer, K. Characterization of temporal protein production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8114–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Tian, X. Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms. Sensors 2012, 12, 2519–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, D.J.; Korfhagen, T.R.; Irvin, R.T.; Schurr, M.J.; Sauer, K.; Lau, G.W.; Sutton, M.D.; Yu, H.; Hoiby, N. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections in cystic fibrosis: Insights into pathogenic processes and treatment strategies. Exp. Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G.; Parsek, M.R.; Pearson, J.P.; Iglewski, B.H.; Costerton, J.W.; Greenberg, E.P. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 1998, 280, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, M.D.; Ceri, H.; Storey, D.G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa GacA, a factor in multihost virulence, is also essential for biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Gibbs, K.A.; Hager, P.W.; Phibbs, P.V.J.; Kolter, R. The global carbon metabolism regulator Crc is a component of a signal transduction pathway required for biofilm development by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 425–431. [Google Scholar]
- Whitchurch, C.B.; Erova, T.E.; Emery, J.A.; Sargent, J.L.; Harris, J.M.; Semmler, A.B.; Young, M.D.; Mattick, J.S.; Wozniak, D.J. Phosphorylation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa response regulator AlgR is essential for type IV fimbria-mediated twitching motility. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.M.; Machado, I.; Nicolau, A.; Pereira, M.O. Improvements on colony morphology identification towards bacterial profiling. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 95, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirov, S.M.; Webb, J.S.; O'May C, Y.; Reid, D.W.; Woo, J.K.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilm differentiation and dispersal in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3264–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, B.R.; Thoendel, M.; Singh, P.K. Self-generated diversity produces “insurance effects” in biofilm communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16630–16635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S.; Franklin, M.J. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Sociomicrobiology: The connections between quorum sensing and biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Rao, S.; Bansal, A.; Dang, S.; Gupta, S.; Gabrani, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: Potential therapeutic targets. Biologicals 2014, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.A.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Stoodley, P. Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Cullen, M.C.; Rickard, A.H.; Zeef, L.A.; Davies, D.G.; Gilbert, P. Characterization of nutrient-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7312–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.K.K.; Webb, J.S.; Kirov, S.M.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. Biofilm dispersal cells of a cystic fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate exhibit variability in functional traits likely to contribute to persistent infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Canton, R.; Campo, P.; Baquero, F.; Blazquez, J. High frequency of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis lung infection. Science 2000, 288, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rojas, A.; Oliver, A.; Blazquez, J. Intrinsic and environmental mutagenesis drive diversification and persistence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, A.; Smith, E.E.; Burns, J.L.; Speert, D.P.; Moskowitz, S.M.; Perez, J.L.; Oliver, A. Genetic adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients is catalyzed by hypermutation. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7910–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiers, A.J.; Buckling, A.; Rainey, P.B. The causes of Pseudomonas diversity. Microbiology 2000, 146 Pt 10, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet-Gougeon, A.; Kovacs, B.; le Gall-David, S.; le Bars, H.; Bousarghin, L.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Lobel, B.; Guille, F.; Soussy, C.J.; Tenke, P. Bacterial hypermutation: Clinical implications. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Riis, B.; Pressler, T.; Poulsen, H.E.; Hoiby, N. Occurrence of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients is associated with the oxidative stress caused by chronic lung inflammation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanski, M.A.; DePristo, M.A.; Collins, J.J. Sublethal antibiotic treatment leads to multidrug resistance via radical-induced mutagenesis. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, M.D.; Blanquer, D.; Togores, B.; Sauleda, J.; Perez, J.L.; Oliver, A. Hypermutation is a key factor in development of multiple-antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains causing chronic lung infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3382–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O.; Mandsberg, L.F.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Wassermann, T.; Hoiby, N. Genetic adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during chronic lung infection of patients with cystic fibrosis: Strong and weak mutators with heterogeneous genetic backgrounds emerge in mucA and/or lasR mutants. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driffield, K.; Miller, K.; Bostock, J.M.; O'Neill, A.J.; Chopra, I. Increased mutability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, A.M.; Macia, M.D.; Yang, L.; Molin, S.; Oliver, A.; Smania, A.M. Evolution and adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms driven by mismatch repair system-deficient mutators. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27842. [Google Scholar]
- Yachi, S.; Loreau, M. Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity in a fluctuating environment: The insurance hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogardt, M.; Hoboth, C.; Schmoldt, S.; Henke, C.; Bader, L.; Heesemann, J. Stage-specific adaptation of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates during chronic pulmonary infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Mena, A. Bacterial hypermutation in cystic fibrosis, not only for antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoboth, C.; Hoffmann, R.; Eichner, A.; Henke, C.; Schmoldt, S.; Imhof, A.; Heesemann, J.; Hogardt, M. Dynamics of adaptive microevolution of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa during chronic pulmonary infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiricny, N.; Molin, S.; Foster, K.; Diggle, S.P.; Scanlan, P.D.; Ghoul, M.; Johansen, H.K.; Santorelli, L.A.; Popat, R.; West, S.A.; et al. Loss of social behaviours in populations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infecting lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis. PLoS One 2014, 9, e83124. [Google Scholar]
- Workentine, M.L.; Sibley, C.D.; Glezerson, B.; Purighalla, S.; Norgaard-Gron, J.C.; Parkins, M.D.; Rabin, H.R.; Surette, M.G. Phenotypic heterogeneity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations in a cystic fibrosis patient. PLoS One 2013, 8, e60225. [Google Scholar]
- Doring, G.; Conway, S.P.; Heijerman, H.G.; Hodson, M.E.; Hoiby, N.; Smyth, A.; Touw, D.J. Antibiotic therapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: A European consensus. Eur. Respirat. J. 2000, 16, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manos, J.; Hu, H.; Rose, B.R.; Wainwright, C.E.; Zablotska, I.B.; Cheney, J.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Grimwood, K.; et al. Virulence factor expression patterns in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from infants with cystic fibrosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L.; Gibson, R.L.; McNamara, S.; Yim, D.; Emerson, J.; Rosenfeld, M.; Hiatt, P.; McCoy, K.; Castile, R.; Smith, A.L.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in young children with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramper-Stranders, G.A.; van der Ent, C.K.; Molin, S.; Yang, L.; Hansen, S.K.; Rau, M.H.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Wolfs, T.F. Initial Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with cystic fibrosis: Characteristics of eradicated and persistent isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, G.J.; Reis, R.S.; Fernandes, A.C.; da Rocha, S.L.; Pereira, M.D.; Perales, J.; Freire, D.M. Rhamnolipid production: Effect of oxidative stress on virulence factors and proteome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mawgoud, A.M.; Lepine, F.; Deziel, E. Rhamnolipids: Diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1323–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, S.; Oliver, A.; Salerno, P.; Mena, A.; Bertoni, G.; Tummler, B.; Cariani, L.; Conese, M.; Doring, G.; Bragonzi, A. Biological cost of hypermutation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis. Microbiol. Sgm 2007, 153, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.K.; Rau, M.H.; Johansen, H.K.; Ciofu, O.; Jelsbak, L.; Yang, L.; Folkesson, A.; Jarmer, H.O.; Aanaes, K.; von Buchwald, C.; et al. Evolution and diversification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the paranasal sinuses of cystic fibrosis children have implications for chronic lung infection. ISME J. 2012, 6, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, M.C.; Rijntjes, E.; el Bouazzaoui, L.H.; Fokkens, W.J.; Brimicombe, R.W.; Heijerman, H.G.M. Importance of bacteriology in upper airways of patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxler, R.B.; Hoover, W.C.; Britton, L.J.; Gerwin, A.M.; Rowe, S.M. Clearance of initial mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.J.; Dehnbostel, J.; Blackwell, T.S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Host defence in lung diseases. Respirology 2010, 15, 1037–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Buckley, D.G.; Wu, Z.; Saenphimmachak, C.; Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; Miller, S.I.; Ramsey, B.W.; Speert, D.P.; Moskowitz, S.M.; et al. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, G.; Parameswaran, I.G.; Murphy, T.F. Differential adaptation of microbial pathogens to airways of patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 124–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, N.; Klockgether, J.; Wrasman, K.; Schmidt, M.; Davenport, C.F.; Tummler, B. Microevolution of the major common Pseudomonas aeruginosa clones C and PA14 in cystic fibrosis lungs. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1690–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Eisinger, V.M.; Rowen, D.W.; Yu, H.D. Regulated proteolysis controls mucoid conversion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8107–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govan, J.R.; Deretic, V. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 539–574. [Google Scholar]
- Deretic, V.; Schurr, M.J.; Yu, H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, mucoidy and the chronic infection phenotype in cystic fibrosis. Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, D.M.; Wozniak, D.J. Understanding the control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate synthesis and the prospects for management of chronic infections in cystic fibrosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.W.; Schurr, M.J.; Mudd, M.H.; Govan, J.R.; Holloway, B.W.; Deretic, V. Mechanism of conversion to mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infecting cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8377–8381. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, L.F.; Ohman, D.E. Identification of genes in the σ²² regulon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa required for cell envelope homeostasis in either the planktonic or the sessile mode of growth. mBio 2012, 3, e00094-12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Badrane, H.; Arora, S.; Baker, H.V.; Jin, S. MucA-mediated coordination of type III secretion and alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7575–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragonzi, A.; Wiehlmann, L.; Klockgether, J.; Cramer, N.; Worlitzsch, D.; Doring, G.; Tummler, B. Sequence diversity of the mucABD locus in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. Microbiology 2006, 152, 3261–3269. [Google Scholar]
- Haussler, S.; Tummler, B.; Weissbrodt, H.; Rohde, M.; Steinmetz, I. Small-colony variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, S.; Ziegler, I.; Lottel, A.; von Gotz, F.; Rohde, M.; Wehmhohner, D.; Saravanamuthu, S.; Tummler, B.; Steinmetz, I. Highly adherent small-colony variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis lung infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, S. Biofilm formation by the small colony variant phenotype of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deziel, E.; Comeau, Y.; Villemur, R. Initiation of biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 57RP correlates with emergence of hyperpiliated and highly adherent phenotypic variants deficient in swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities 1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirisits, M.J.; Prost, L.; Starkey, M.; Parsek, M.R. Characterization of colony morphology variants isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4809–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, B.C. Small colony variants (SCVs) of Staphylococcus aureus—A bacterial survival strategy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, M.; Hickman, J.H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, N.; de Long, S.; Hinz, A.; Palacios, S.; Manoil, C.; Kirisits, M.J.; Starner, T.D.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa rugose small-colony variants have adaptations that likely promote persistence in the cystic fibrosis lung. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3492–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Medina, E.; Hussain, M.; Volker, W.; Heitmann, V.; Niemann, S.; Holzinger, D.; Roth, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Becker, K.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus phenotype switching: An effective bacterial strategy to escape host immune response and establish a chronic infection. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, P.; Proctor, R.A. Staphylococcus aureus as an intracellular pathogen: The role of small colony variants. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; McNamara, P.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G. Small colony variants: A pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, M.D.; Zhu, H.; Conibear, T.C.; Hume, E.B.; Givskov, M.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. Role of quorum sensing by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in microbial keratitis and cystic fibrosis. Microbiology 2008, 154, 2184–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Klockgether, J.; Tummler, B. An intragenic deletion in pilQ leads to nonpiliation of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from cystic fibrosis lung. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, A.U.; Dinesh, S.D.; Larbig, K.; Romling, U. Impact of large chromosomal inversions on the adaptation and evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronically colonizing cystic fibrosis lungs. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- D’Argenio, D.A.; Wu, M.; Hoffman, L.R.; Kulasekara, H.D.; Deziel, E.; Smith, E.E.; Nguyen, H.; Ernst, R.K.; Larson Freeman, T.J.; Spencer, D.H.; et al. Growth phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants adapted to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, J.A.; Carty, N.L.; McDonald, N.A.; Graham, E.D.; Cheluvappa, R.; Griswold, J.A.; Hamood, A.N. Analysis of quorum sensing-deficient clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimmersdorf, E.; Horatzek, S.; Pelnikevich, A.; Wiehlmann, L.; Schomburg, D. How Pseudomonas aeruginosa adapts to various environments: A metabolomic approach. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Ray, A.; Hodson, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Increased sputum amino acid concentrations and auxotrophy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in severe cystic fibrosis lung disease. Thorax 2000, 55, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.L.; Pitt, T.L. Auxotrophic variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are selected from prototrophic wild-type strains in respiratory infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mowat, E.; Paterson, S.; Fothergill, J.L.; Wright, E.A.; Ledson, M.J.; Walshaw, M.J.; Brockhurst, M.A.; Winstanley, C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa population diversity and turnover in cystic fibrosis chronic infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, G.; Kapil, A.; Kabra, S.K.; Das, B.K.; Dwivedi, S.N. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from chronically infected children with cystic fibrosis in India. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borriello, G.; Werner, E.; Roe, F.; Kim, A.M.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Stewart, P.S. Oxygen limitation contributes to antibiotic tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.R.; White, A.; Elborn, J.S.; Tunney, M.M. Effect of oxygen limitation on the in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown planktonically and as biofilms. Eur.J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 677–687. [Google Scholar]
- Bragonzi, A.; Worlitzsch, D.; Pier, G.B.; Timpert, P.; Ulrich, M.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Givskov, M.; Conese, M.; Doring, G. Nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa expresses alginate in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis and in a mouse model. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, B.R.; Singh, P.K. Endogenous oxidative stress produces diversity and adaptability in biofilm communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12503–12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwercman, B.; Meyer, C.; Lambert, P.A.; Reinert, C.; Hoiby, N. High-level beta-lactamase activity in sputum samples from cystic-fibrosis patients during antipseudomonal treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.; Ciofu, O.; Hoiby, N.; Gotoh, N.; Wretlind, B. Molecular mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, H.K.; Moskowitz, S.M.; Ciofu, O.; Pressler, T.; Høiby, N. Spread of colistin resistant non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa among chronically infected Danish cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Oh, H.; Jalal, S.; Karpati, F.; Ciofu, O.; Hoiby, N.; Wretlind, B. Chromosomal mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman, B.; Jensen, E.T.; Hoiby, N.; Kharazmi, A.; Costerton, J.W. Induction of beta-lactamase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagge, N.; Hentzer, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Ciofu, O.; Givskov, M.; Hoiby, N. Dynamics and spatial distribution of beta-lactamase expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengzhuang, W.; Ciofu, O.; Yang, L.; Wu, H.; Song, Z.; Oliver, A.; Hoiby, N. High beta-lactamase levels change the pharmacodynamics of beta-lactam antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia, V.; Borrell, N.; Macia, M.D.; Moya, B.; Perez, J.L.; Oliver, A. Influence of high mutation rates on the mechanisms and dynamics of in vitro and in vivo resistance development to single or combined antipseudomonal agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, A.M.; Pereira, M.O. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review. Pathogens 2014, 3, 680-703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030680
Sousa AM, Pereira MO. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review. Pathogens. 2014; 3(3):680-703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030680
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Ana Margarida, and Maria Olívia Pereira. 2014. "Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review" Pathogens 3, no. 3: 680-703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030680
APA StyleSousa, A. M., & Pereira, M. O. (2014). Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diversification during Infection Development in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs—A Review. Pathogens, 3(3), 680-703. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3030680



