Prions in Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy: An Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dominant Protease-Sensitive PrPSc Conformer
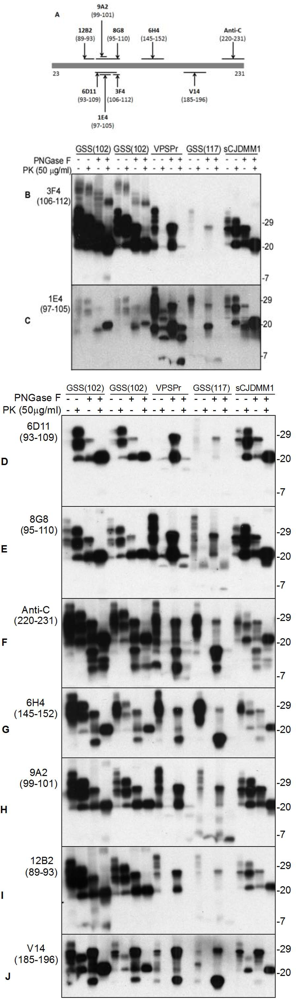
3. Pathognomonic Ladder-Like Electrophoretic Profile of Protease-Resistant PrPSc with a Peculiar Immunoreactivity Behavior
4. Polymorphism-Dependent PK-Sensitive and PK-Resistant PrPSc
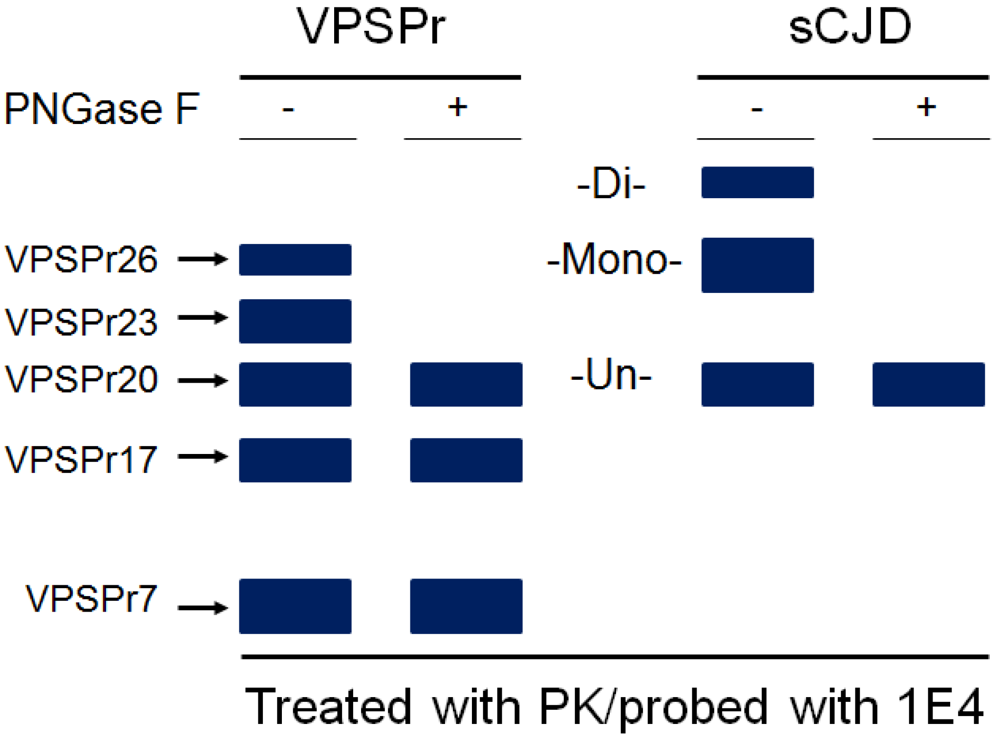
5. The Ladder-Like Electrophoretic Profile of 1E4-Detected rPrPSc Consisting of Five PrP Fragments
6. Glycoform-Selective Prion Formation in VPSPr and fCJDV180I
7. Transmissibility of VPSPr and fCJDV180I
8. Origin of Prions in VPSPr and fCJDV180I
9. Association between VPSPr and Other Prion Diseases
| MAbs | Epitopes | Human | Sheep | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPSPr | A117 | F198S | 102 | sCJD | Nor98 | ||
| SAF32 | Octarepeat | – | – | + | + | + | – |
| 12B2 | 89–93 | – | + | + | + | + | + |
| 9A2 | 99–101 | ± | + | + | + | + | + |
| 6D11 | 93–109 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 8G8 | 95–110 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| F89 | 139–142 | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| L42 | 145–150 | + | ± | ± | + | + | + |
| 12F10 | 143–152 | + | – | – | – | + | – |
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.Q.; Parchi, P.; Chen, S.G. Sporadic and inherited CJD: Classification and characterisation. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 213–239. [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone, G.; Di Fede, G.; Mangieri, M.; Limido, L.; Capobianco, R.; Suardi, S.; Grisoli, M.; Binelli, S.; Fociani, P.; Bugiani, O.; Tagliavini, F. A novel phenotype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetti, P.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, M.; Alshekhlee, A.; Castellani, R.; Cohen, M.; Barria, M.A.; Gonzalez-Romero, D.; Belay, E.D.; Schonberger, L.B.; Marder, K.; Harris, C.; Burke, J.R.; Montine, T.; Wisniewski, T.; Dickson, D.W.; Soto, C.; Hulette, C.M.; Mastrianni, J.A.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.Q. A novel human disease with abnormal prion protein sensitive to protease. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q; Puoti, G.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Qing, L.; Cali, I.; Shimoji, M.; Langeveld, J.P.; Castellani, R.; Notari, S.; Crain, B.; Schmidt, R.E.; Geschwind, M.; Dearmond, S.J.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.; Honig, L.; Torres, J.M.; Mastrianni, J.; Capellari, S.; Giaccone, G; Belay, E.D.; Schonberger, L.B.; Cohen, M.; Perry, G.; Kong, Q.; Parchi, P.; Tagliavini, F.; Gambetti, P. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy: A new sporadic disease of the prion protein. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Haïk, S.; Cali, I.; Zhan, Y.; Moudjou, M.; Li, B.; Laplanche, J.L.; Laude, H.; Langeveld, J.; Gambetti, P.; Kitamoto, T.; Kong, Q.; Brandel, J.P.; Cobb, B.A.; Petersen, R.B.; Zou, W.Q. Glycoform-selective prion formation in sporadic and familial forms of prion disease. PLoS One 2013, 8, e58786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benestad, S.L.; Sarradin, P.; Thu, B.; Schönheit, J.; Tranulis, M.A.; Bratberg, B. Cases of scrapie with unusual features in Norway and designation of a new type, Nor98. Vet Rec. 2003, 153, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirisinu, L.; Nonno, R.; Gambetti, P.; Agrimi, U.; Zou, W.Q. Comparative study of sheep Nor98 with human variably protease-sensitive prionopathy and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. Prion 5. 2011, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Langeveld, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, S.; McGeer, P.L.; Yuan, J.; Payne, M.C.; Kang, H.E.; McGeehan, J.; Sy, M.S.; Greenspan, N.S.; Kaplan, D.; Wang, G.X.; Parchi, P.; Hoover, E.; Kneale, G.; Telling, G.; Surewicz, W.K.; Kong, Q.; Guo, J.P. PrP conformational transitions alter species preference of a PrP-specific antibody. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13874–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Zheng, J.; Gray, D.M.; Gambetti, P.; Chen, S.G. Antibody to DNA detects scrapie but not normal prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth, J.D.; Joiner, S.; Hill, A.F.; Campbell, T.A.; Desbruslais, M.; Luthert, P.J.; Collinge, J. Tissue distribution of protease resistant prion protein in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease using a highly sensitive immunoblotting assay. Lancet 2001, 358, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasbon-Frodl, E.; Lorenz, H.; Mann, U.; Nitsch, R.M.; Windl, O.; Kretzschmar, H.A. Loss of glycosylation associated with the T183A mutation in human prion disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 108, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasseigneaux, S.; Haïk, S.; Laffont-Proust, I.; De Marco, O.; Lenne, M.; Brandel, J.P.; Hauw, J.J.; Laplanche, J.L.; Peoc'h, K. V180I mutation of the prion protein gene associated with atypical PrPSc glycosylation. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 408, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capellari, S.; Zaidi, S.I.; Long, A.C.; Kwon, E.E.; Petersen, R.B. The Thr183Ala mutation, not the loss of the first glycosylation site, alters the physical properties of the prion protein. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2000, 2, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zanusso, G.; Polo, A.; Farinazzo, A.; Nonno, R.; Cardone, F.; Di Bari, M.; Ferrari, S.; Principe, S.; Gelati, M.; Fasoli, E.; Fiorini, M.; Prelli, F.; Frangione, B.; Tridente, G.; Bentivoglio, M.; Giorgi, A.; Schininà, M.E.; Maras, B.; Agrimi, U.; Rizzuto, N.; Pocchiari, M.; Monaco, S. Novel prion protein conformation and glycotype in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudjou, M.; Treguer, E.; Rezaei, H.; Sabuncu, E.; Neuendorf, E.; Groschup, M.H.; Grosclaude, J.; Laude, H. Glycan-controlled epitopes of prion protein include a major determinant of susceptibility to sheep scrapie. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9270–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Féraudet, C.; Morel, N.; Simon, S.; Volland, H.; Frobert, Y.; Créminon, C.; Vilette, D.; Lehmann, S.; Grassi, J. Screening of 145 anti-PrP monoclonal antibodies for their capacity to inhibit PrPSc replication in infected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11247–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Bongarzone, S.; Giachin, G.; Rossetti, G.; Carloni, P.; Legname, G. Dominant-negative effects in prion diseases: insights from molecular dynamics simulations on mouse prion protein chimeras. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, M.K.; Dron, M.; Chapuis, J.; Langevin, C.; Laude, H. Prion propagation in cells expressing PrP glycosylation mutants. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzi, N.L.; Cancellotti, E.; Baybutt, H.; Blackford, L.; Bradford, B.; Plinston, C.; Coghill, A.; Hart, P.; Piccardo, P.; Barron, R.M.; Manson, J.C. Host PrP glycosylation: A major factor determining the outcome of prion infection. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, K.A.; Deleault, N.R.; Mahal, S.P.; Baskakov, I.; Luhrs, T.; Riek, R.; Supattapone, S. The stoichiometry of host PrPC glycoforms modulates the efficiency of PrPSc formation in vitro. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14129–14139. [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan, J.C.; Miller, M.B.; Kwak, A.H.; Harris, B.T.; Supattapone, S. Trans-dominant inhibition of prion propagation in vitro is not mediated by an accessory cofactor. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsukura, K.; Satoh, K.; Shirabe, S.; Tomita, I.; Fukutome, T.; Morikawa, M.; Iseki, M.; Sasaki, K.; Shiaga, Y.; Kitamoto, T.; Eguchi, K. Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with a V180I mutation: Comparative analysis with pathological findings and diffusion-weighted images. Dement Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2009, 28, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Head, M.W.; van Gool, W.A.; Baas, F.; Yull, H.; Ironside, J.W.; Rozemuller, A.J. The first case of protease-sensitive prionopathy (PSPr) in The Netherlands: A patient with an unusual GSS-like clinical phenotype. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telling, G.C.; Scott, M.; Mastrianni, J.; Gabizon, R.; Torchia, M.; Cohen, F.E.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Prion propagation in mice expressing human and chimeric PrP transgenes implicates the interaction of cellular PrP with another protein. Cell 1995, 83, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supattapone, S.; Miller, M.B. Cofactor Involvement in Prion Propagation. In Prions and Diseases: Physiology and Pathophysiology; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. Prion Protein Conversion and Lipids. In Prions and Diseases: Physiology and Pathophysiology; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Colby, D.W.; Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a006833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy and beyond (E-letter). Science. Available online: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/308/5727/1420.long/reply#sci_el_10316 (accessed on 20 September 2007).
- Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P. Modeling of human prions and prion diseases in vitro and in vivo. Drug Disc. Today: Dis. Mod. 2004, 1, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, S.B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science 1982, 216, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Asher, D.M.; Sulima, M.P.; Bacote, A.; Goldfarb, L.G.; Gajdusek, D.C. Human spongiform encephalopathy: The National Institutes of Health series of 300 cases of experimentally transmitted disease. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 35, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, J.; Kitamoto, T.; Hoque, M.Z.; Furukawa, H. Experimental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and related diseases to rodents. Neurology 1996, 46, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Chen, S.G.; Brown, P.; Zou, W.; Capellari, S.; Budka, H.; Hainfellner, J.; Reyes, P.F.; Golden, G.T.; Hauw, J.J.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gambetti, P. Different patterns of truncated prion protein fragments correlate with distinct phenotypes in P102L Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8322–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, P.; Manson, J.C.; King, D.; Ghetti, B.; Barron, R.M. Accumulation of prion protein in the brain that is not associated with transmissible disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4712–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P. From microbes to prions: The final proof of the prion hypothesis. Cell 2005, 121, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonno, R.; Di Bari, M.; Pirisinu, L.; D’Agostino, C.; Marcon, S.; Riccardi, G.; Vaccari, G.; Parchi, P.; Zou, W.Q.; Gambetti, P.; Agrimi, U. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy is transmissible in bank voles. Prion 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti, P.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Cali, I.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.Q. Variably protease-sensitive prionopathy: Transmissibility and PMCA studies. Prion 2011, 5, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Surewicz, W.K.; Petersen, R.B.; Zou, W.Q.; Chen, S.G.; Parchi, P.; Capellari, S.; Goldfarb, L.; Montagna, P.; Lugaresi, E.; Piccardo, P.; Ghetti, B.; Gambetti, P. Inherited Prion Diseases. In Prion Biology and Diseases; Prusiner, S.B., Ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 673–775. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, Z.; Guo, J.P.; McGeehan, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Cali, I.; McGeer, P.L.; Cashman, N.R.; Bessen, R.; Surewicz, W.K.; Kneale, G.; Petersen, R.B.; Gambetti, P.; Zou, W.Q. Accessibility of a critical prion protein region involved in strain recognition and its implications for the early detection of prions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xiao, X.; McGeehan, J.; Dong, Z.; Cali, I.; Fujioka, H.; Kong, Q.; Kneale, G.; Gambetti, P.; Zou, W.Q. Insoluble aggregates and protease-resistant conformers of prion protein in uninfected human brains. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34848–34858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.Q. Insoluble Cellular Prion Protein. In Prions and Diseases: Physiology and Pathophysiology; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.Q.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, X. Insoluble cellular prion protein and its association with prion and Alzheimer diseases. Prion 2011, 5, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavini, F.; Prelli, F.; Ghiso, J.; Bugiani, O.; Serban, D.; Prusiner, S.B.; Farlow, M.R.; Ghetti, B.; Frangione, B. Amyloid protein of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana kindred) is an 11 kd fragment of prion protein with an N-terminal glycine at codon 58. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Pirisinu, L.; Nonno, R.; Esposito, E.; Benestad, S.L.; Gambetti, P.; Agrimi, U.; Zou, W.Q. Small ruminant Nor98 prions share biochemical features with human Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease and variably protease-sensitive prionopathy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66405. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, W.-Q.; Gambetti, P.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, J.; Langeveld, J.; Pirisinu, L. Prions in Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy: An Update. Pathogens 2013, 2, 457-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030457
Zou W-Q, Gambetti P, Xiao X, Yuan J, Langeveld J, Pirisinu L. Prions in Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy: An Update. Pathogens. 2013; 2(3):457-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030457
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Wen-Quan, Pierluigi Gambetti, Xiangzhu Xiao, Jue Yuan, Jan Langeveld, and Laura Pirisinu. 2013. "Prions in Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy: An Update" Pathogens 2, no. 3: 457-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030457
APA StyleZou, W.-Q., Gambetti, P., Xiao, X., Yuan, J., Langeveld, J., & Pirisinu, L. (2013). Prions in Variably Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy: An Update. Pathogens, 2(3), 457-471. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030457




