Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection of Sources of Evidence
2.5. Data Charting Process and Data Items
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HEV | Hepatitis E virus |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
| PCC | Population, Concept, and Context |
| PRISMA-ScR | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Debing, Y.; Moradpour, D.; Neyts, J.; Gouttenoire, J. Update on Hepatitis E Virology: Implications for Clinical Practice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis E. 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). Acute Hepatitis E—Level 4 Cause. 2021. Available online: https://www.healthdata.org/research-analysis/diseases-injuries-risks/factsheets/2021-acute-hepatitis-e-level-4-disease (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.-J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis E Virus: Host Tropism and Zoonotic Infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Bendall, R.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Xia, N.S.; Ijaz, S.; Izopet, J.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E. Lancet. 2012, 379, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; El Costa, H.; Schvartz, B.; Peron, J.-M.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Rabbit Hepatitis E Virus Infections in Humans, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velavan, T.P.; Pallerla, S.R.; Johne, R.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E.; Schemmerer, M.; Wenzel, J.J.; Hofmann, J.; Shih, J.W.K.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis E: An Update on One Health and Clinical Medicine. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, D.F.d.S.D.; Mesquita, J.R.; Dutra, V.; Nascimento, M.S.J. Systematic Review of Hepatitis E Virus in Brazil: A One-Health Approach of the Human-Animal-Environment Triad. Animals 2021, 11, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Dalton, H.R.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 116–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, C.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Ulrich, R.G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E Virus and Related Viruses in Wild, Domestic and Zoo Animals: A Review. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 65, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Ma, Z.; Bramer, W.M.; Cao, W.; de Man, R.A.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. The Global Epidemiology of Hepatitis E Virus Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, M.C.; Manchiero, C.; Dantas, B.P.; Bernardo, W.M.; Abdala, E.; Tengan, F.M. Prevalence of Hepatitis E in Latin America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Public Health 2025, 244, 105745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, A.M.; Heringer, T.P.; Medina-Pestana, J.O.; Ferraz, M.L.G.; Granato, C.F.H. First Report and Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Renal Transplant Recipients in Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parana, R.; Cotrim, H.P.; Trepo, C.; Cortey-Boennec, M.L.; Lyra, L. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus IgG Antibodies in Patients from a Referral Unit of Liver Diseases in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Caridad Montalvo Villalba, M.; Owot, J.C.; Benedito, E.C.; Corredor, M.B.; Flaquet, P.P.; Frometa, S.S.; Wong, M.S.; Rodriguez Lay, L.d.L. Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Humans and Swine, Cuba. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengan, F.M.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Nunes, A.K.S.; Manchiero, C.; Dantas, B.P.; Magri, M.C.; Prata, T.V.G.; Nascimento, M.; Mazza, C.C.; Abdala, E.; et al. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E in Adults in Brazil: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, D.; Rocha, J.; Crispim, M. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies Among Different Groups in the Amazonian Basin. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 96, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos-Castilho, A.M.; de Sena, A.; Geraldo, A.; Spada, C.; Granato, C.F. High Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies Among Blood Donors in Southern Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 88, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songtanin, B.; Molehin, A.J.; Brittan, K.; Manatsathit, W.; Nugent, K. Hepatitis E Virus Infections: Epidemiology, Genetic Diversity, and Clinical Considerations. Viruses 2023, 15, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.; Godfrey, C.; McInerney, P.; Khalil, H.; Larsen, P.; Marnie, C.; Pollock, D.; Tricco, A.C.; Munn, Z. Best Practice Guidance and Reporting Items for the Development of Scoping Review Protocols. JBI Evid. Synth. 2022, 20, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-Compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitral, C.L.; da Silva-Nunes, M.; Pinto, M.A.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Gaspar, A.M.C.; Pereira, R.C.C.; Ferreira, M.U. Hepatitis A and E Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Survey in Rural Amazonia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, M.P.A.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Sánchez-Arcila, J.C.; Faria, S.C.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Perce-Da-Silva, D.; Rezende-Neto, J.; Pinto, M.A.; Maia-Herzog, M.; Banic, D.M.; et al. Seroprevalence of the Hepatitis E Virus in Indigenous and Non-Indigenous Communities from the Brazilian Amazon Basin. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.J.S.; de Oliveira, C.M.A.; Sarmento, V.P.; das Chagas, A.A.C.; Nonato, N.S.; de Brito, D.C.N.; Barbosa, K.M.V.; Soares, M.D.C.P.; Nunes, H.M. Hepatitis E Virus Infection Among Rural Afro-Descendant Communities from the Eastern Brazilian Amazon. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2018, 51, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.J.S.; Malheiros, A.P.; Sarmento, V.P.; Resende, F.d.S.; Alves, M.M.; Nunes, H.M.; Soares, M.D.C.P.; de Sá, L.R.M. Serological and Molecular Retrospective Analysis of Hepatitis E Suspected Cases from the Eastern Brazilian Amazon 1993–2014. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, R.S.; Baia, K.L.N.; de Souza, S.B.; Fontoura, G.M.G.; Nunes, P.F.; Machado, L.F.A.; Kupek, E.; Fischer, B.; Martins, L.C.; Oliveira-Filho, A.B. Hepatitis E Virus in People Who Use Crack-Cocaine: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Remote Region of Northern Brazil. Viruses 2021, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraná, R.; Vitvitski, L.; Andrade, Z.; Trepo, C.; Cotrim, H.; Bertillon, P.; Silva, F.; Silva, L.; de Oliveira, I.R.; Lyra, L. Acute Sporadic Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis in Northeastern Brazil: Etiology and Natural History. Hepatology 1999, 30, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, A.; Pinho, J.; Silva, L.; Sousa, L.; Saraceni, C.; Braga, E.; Pereira, J.; Zarife, M.; Reis, M.; Lyra, L.; et al. HEV, TTV and GBV-C/HGV Markers in Patients with Acute Viral Hepatitis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Passos-Castilho, A.M.; de Sena, A.; Domingues, A.L.C.; Lopes-Neto, E.P.; Medeiros, T.B.; Granato, C.F.H.; Ferraz, M.L. Hepatitis E Virus Seroprevalence Among Schistosomiasis Patients in Northeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, L.A.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Silva, J.V.J.; Morais, V.M.S.; Gonçales, J.P.; da Silva, D.M.; Coêlho, M.R.C.D. Risk Analysis and Seroprevalence of HEV in People Living with HIV/AIDS in Brazil. Acta Trop. 2019, 189, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, G.G.; Bezerra, L.A.; Júnior, J.V.J.S.; Gonçales, J.P.; Montreuil, A.C.B.; Côelho, M.R.C.D. Analysis of Seroprevalence and Risk Factors for Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) in Donation Candidates and Blood Donors in Northeast Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, L.R.M.G.; Batista, A.D.; Côelho, M.R.C.D.; Santos, J.C.; Cunha, G.G.; Leal, G.R.A.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Domingues, A.L.C.; Lopes, E.P. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 55, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.T.d.O.; Mariz, C.A.; Batista, A.D.; de Morais, C.N.L.; Araújo, L.; Barreto, A.V.M.S.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Domingues, A.L.; Lopes, E.P. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Among Schistosomiasis mansoni Patients Residing in Endemic Zone in Brazil. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva-Sampaio, J.P.; Sinimbu, R.B.; Marques, J.T.; Neto, A.F.d.O.; Villar, L.M. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Blood Donors from Piauí State, Northeast Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 29, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Freitas, N.; Kozlowski, A.; Reis, N.; Lopes, C.; Teles, S.; Gardinali, N.; Pinto, M. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Antibodies in a Population of Recyclable Waste Pickers in Brazil. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 59, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, N.R.; Santana, E.B.; Silva, Á.M.; da Silva, S.M.; Teles, S.A.; Gardinali, N.R.; Pinto, M.A.; Martins, R.M.B. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Patients with Acute Non-A, Non-B, Non-C Hepatitis in Central Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, N.R.; Teles, S.A.; Caetano, K.A.A.; de Matos, M.A.; Carneiro, M.A.d.S.; Gardinali, N.R.; Pinto, M.A.; Martins, R.M.B. Hepatitis E Seroprevalence and Associated Factors in Rural Settlers in Central Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2017, 50, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.M.N.S.; de Freitas, N.R.; Teles, S.A.; Bottino, F.d.O.; Lemos, A.S.; de Paula, V.; Pinto, M.A.; Martins, R.M.B. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus RNA and Antibodies in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients in Central Brazil. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, S.A.; Caetano, K.A.A.; Carneiro, M.A.D.S.; Villar, L.M.; Stacciarini, J.M.; Martins, R.M.B. Hepatitis E Prevalence in Vulnerable Populations in Goiânia, Central Brazil. Viruses 2023, 15, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, S.B.; Souto, F.J.; Fontes, C.J.; Gaspar, A.M. Prevalence of Hepatitis A and E Virus Infection in School Children of an Amazonian Municipality in Mato Grosso State. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2002, 35, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.M.T.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Vitral, C.L.; Vieira, K.d.A.; Pinto, M.A.; Souto, F.J.D. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies in Individuals Exposed to Swine in Mato Grosso, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2012, 107, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Castro, V.O.L.; Tejada-Strop, A.; Weis, S.M.S.; Stábile, A.C.; de Oliveira, S.M.V.L.; Teles, S.A.; Kamili, S.; Motta-Castro, A.R.C. Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infections Among Persons Who Use Crack Cocaine from the Midwest Region of Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 91, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis-Torres, S.M.d.S.; França, A.d.O.; Granato, C.; Passarini, A.; Motta-Castro, A.R.C. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection Among Volunteer Blood Donors in Central Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focaccia, R.; da Conceição, O.J.; Sette, H., Jr.; Sabino, E.; Bassit, L.; Nitrini, D.R.; Lomar, A.V.; Lorenço, R.; Vieira De Souza, F.; Kiffer, C.R.; et al. Estimated Prevalence of Viral Hepatitis in the General Population of the Municipality of São Paulo, Measured by a Serologic Survey of a Stratified, Randomized and Residence-Based Population. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 2, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçales, N.S.L.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Moreira, R.C.; Saraceni, C.P.; Spina, A.M.M.; Stucchi, R.B.; Filho, A.D.R.; Magna, L.A.; Júnior, F.L.G. Hepatitis E Virus Immunoglobulin G Antibodies in Different Populations in Campinas, Brazil. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, T.; Passos, A.M.; Perez, R.M.; Bilar, J.; Fragano, D.; Granato, C.; Medina-Pestana, J.O.; Ferraz, M.L.G. Past and Current Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Renal Transplant Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos-Castilho, A.M.; de Sena, A.; Reinaldo, M.R.; Granato, C.F.H. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: Results of Laboratory-Based Surveillance from 1998 to 2013. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015, 48, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos-Castilho, A.M.; Reinaldo, M.R.; de Sena, A.; Granato, C.F. High Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies in Sao Paulo, Southeastern Brazil: Analysis of a Group of Blood Donors Representative of the General Population. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricks, G.; Senise, J.F.; Junior, H.P.; Grandi, G.; Passarini, A.; Caldeira, D.B.; Junior, D.C.; de Moraes, H.A.B.; Granato, C.F.H.; Castelo, A. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Chronic Hepatitis C in Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Lisboa-Neto, G.; Mendes-Correa, M.C.J.; Picone, C.M.; Salles, N.A.; Mendrone-Junior, A.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pinho, J.R.R. Serological and Molecular Markers of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in HIV-Infected Patients in Brazil. Arch. Virol. 2017, 163, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricks, G.; Senise, J.F.; Pott, H., Jr.; Grandi, G.; Carnaúba, D., Jr.; de Moraes, H.A.B.; Granato, C.F.H.; Castelo, A. Previous Hepatitis E Virus Infection, Cirrhosis and Insulin Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, D.C.d.A.e.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Haddad, S.K.; da Roza, D.L.; Bottino, F.d.O.; Faria, S.B.S.C.; Bellíssimo-Rodrigues, F.; Passos, A.D.C. Declining Prevalence of Hepatitis A and Silent Circulation of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Southeastern Brazil. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, D.D.; Luna, L.K.d.S.; Passarini, A.; Alves, V.R.G.; Caldeira, D.B.; Cruz, J.S.; Gouveia, V.A.; Bellei, N.; Granato, C.F. Hepatitis E Virus Infection Among Patients with Altered Levels of Alanine Aminotransferase. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, A.C.P.; Gouvea, M.G.; Ferreira, A.C.; Pinho, J.R.R.; de Mello, E.S.; D’ALbuquerque, L.A.C.; Terrabuio, D.; Abdala, E.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pessoa, M.G. The Impact of Hepatitis E Infection on Hepatic Fibrosis in Liver Transplanted Patients for Hepatitis C Infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura Zitelli, P.M.; Gomes-Gouvea, M.; Mazo, D.F.; Singer, J.d.M.; Oliveira, C.P.M.S.; Farias, A.Q.; Pinho, J.R.; Tanigawa, R.Y.; Ferreira Alves, V.A.; Carrilho, F.J.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Infection Increases the Risk of Diabetes and Severity of Liver Disease in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clinics 2021, 76, e3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.B.; Reche, L.A.; Nastri, A.C.d.S.S.; Malta, F.d.M.; Amgarten, D.E.; Casadio, L.V.B.; Gonzalez, M.P.; Ono, S.K.; Mendes-Correa, M.C.; Carrilho, F.J.; et al. Acute Hepatitis Related to Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3f Infection in Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e70024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zicker, M.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Welter, E.A.R.; Guardia, B.D.; da Silva, P.G.T.M.; da Silveira, L.B.; Camargo, L.F.A. The Risk of Reinfection or Primary Hepatitis E Virus Infection at a Liver Transplant Center in Brazil: An Observational Cohort Study. Viruses 2024, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinta, K.S.; Liberto, M.I.M.; de Paula, V.S.; Yoshida, C.F.; Gaspar, A.M.C. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Selected Brazilian Populations. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2001, 96, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Santos, D.C.; Souto, F.J.; Santos, D.R.; Vitral, C.L.; Gaspar, A.M. Seroepidemiological Markers of Enterically Transmitted Viral Hepatitis A and E in Individuals Living in a Community Located in the North Area of Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2002, 97, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bortoliero, A.L.; Bonametti, A.M.; Morimoto, H.K.; Matsuo, T.; Reiche, E.M.V. Seroprevalence for Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Infection Among Volunteer Blood Donors of the Regional Blood Bank of Londrina, State of Paraná, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo. 2006, 48, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardtke, S.; Rocco, R.; Ogata, J.; Braga, S.; Barbosa, M.; Wranke, A.; Doi, E.; da Cunha, D.; Maluf, E.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Risk Factors and Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Evaluated in Frozen-Serum Samples (2002–2003) of Pregnant Women Compared with Female Blood Donors in a Southern Region of Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.M.; Oliveira, J.M.; Mendoza-Sassi, R.A.; Figueiredo, A.S.; da Mota, L.D.; Nader, M.M.; Gardinali, N.R.; Kevorkian, Y.B.; Salvador, S.B.S.; Pinto, M.A.; et al. Detection and Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in HIV-Infected Patients and Blood Donors from Southern Brazil. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 86, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.B.; Gouvêa, M.S.G.; Chuffi, S.; Dellavia, G.H.; Ornel, F.; Von Diemen, L.; Kessler, F.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Álvares-Da-Silva, M.R. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Risk Populations and Blood Donors in a Referral Hospital in the South of Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzetto, R.; Klein, R.L.; Erpen, L.M.S.; Klein, B.D.; Giacobbo, I.; da Silveira, R.A.; Frandoloso, R.; Kreutz, L.C. Unusual High Prevalence of Antibodies to Hepatitis E Virus in South Brazil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368, fnab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, A.J.S.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Soares, M.D.C.P.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Malheiros, A.P.; Carneiro, L.A.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; Pereira, W.L.A. HEV Infection in Swine from Eastern Brazilian Amazon: Evidence of Co-Infection by Different Subtypes. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Lopes, K.G.S.; Cunha, D.S.; Silva, V.S.; Barbosa, C.N.; Brandespim, D.F.; Junior, J.W.P.; Bertani, G.R.; Gil, L.H.V.G. Risk Analysis and Occurrence of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) in Domestic Swine in Northeast Brazil. Food Environ. Virol. 2017, 9, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; dos Santos, D.R.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; da Silva, A.; de Lima, G.B.; Filho, A.F.B.B.; Pena, L.J.; Gil, L.H. Evolutionary Study of Potentially Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 from Swine in Northeast Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2019, 114, e180585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, M.V.d.C.; Gardinali, N.R.; da Cruz, R.A.S.; Lopes, L.L.; Silva, G.S.; Júnior, J.G.C.; de Oliveira, A.C.S.; Souza, M.d.A.; Colodel, E.M.; Alfieri, A.A.; et al. Evaluation of Hepatitis E Virus Infection Between Different Production Systems of Pigs in Brazil. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2013, 46, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, C.G.; Silveira, S.; Schenkel, D.M.; Carvalho, H.; Teixeira, E.A.; Souza, M.d.A.; Dutra, V.; Nakazato, L.; Canal, C.W.; Pescador, C.A. Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Pigs from Subsistence Farms in the State of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 58, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitral, C.L.; Pinto, M.A.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Khudyakov, Y.E.; dos Santos, D.R.; Gaspar, A.M.C. Serological Evidence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Different Animal Species from the Southeast of Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2005, 100, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.R.; de Paula, V.S.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Marchevsky, R.S.; Pinto, M.A. Hepatitis E Virus in Swine and Effluent Samples from Slaughterhouses in Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 149, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.R.; Mendes, G.S.; Pena, G.P.A.; Santos, N. Hepatitis E Virus Infection of Slaughtered Healthy Pigs in Brazil. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, A.; Metorima, C.S.; Miyagi, S.A.T.; Sousa, A.O.; Peyser, A.V.; Castro, A.M.M.G.; Baldisseri, F.A., Jr.; Souza Filho, A.F.; Brandão, P.E.; Heinemann, M.B. High Genetic Diversity of Hepatitis E Virus in Swine in São Paulo State, Brazil. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2021, 73, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinali, N.; Barry, A.; da Silva, P.; de Souza, C.; Alfieri, A. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Hepatitis E Virus in Naturally Infected Pigs from Brazilian Herds. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos-Castilho, A.M.; Granato, C.F.H. High Frequency of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Swine from South Brazil and Close Similarity to Human HEV Isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.S.; Silveira, S.; Caron, V.S.; Mósena, A.C.S.; Weber, M.N.; Cibulski, S.P.; Medeiros, A.A.R.; Silva, G.S.; Corbellini, L.G.; Klein, R.; et al. Backyard Pigs are a Reservoir of Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus in Southern Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 112, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariz, C.d.A.; Braga, C.; Albuquerque, M.d.F.P.M.d.; Luna, C.F.; Salustiano, D.M.; Freire, N.M.; de Morais, C.N.L.; Lopes, E.P. Occurrence of Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection in Socioeconomic Population Strata from Recife, Pernambuco, Northeast Brazil. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2024, 27, e240033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators. Global Change in Hepatitis C Virus Prevalence and Cascade of Care Between 2015 and 2020: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocruz. Ciência e Saúde Pela Vida. Solicitar Diagnóstico de Referência em Hepatite E—Fiocruz IOC/RJ. 2025. Available online: https://fiocruz.br/sites/fiocruz.br/files/servicos/servico/solicitar-diagnostico-de-referencia-em-hepatite-e-fiocruz-ioc-rj.html (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Nunes, K.; e Silva, M.A.C.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Lemes, R.B.; Pezo-Valderrama, P.; Kimura, L.; de Sena, L.S.; Krieger, J.E.; Varela, M.C.; de Azevedo, L.O.; et al. Admixture’s Impact on Brazilian Population Evolution and Health. Science 2025, 388, eadl3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Dos Santos, D.R.L.; Pinto, M.A. Hepatitis E Virus Research in Brazil: Looking Back and Forwards. Viruses 2023, 15, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Minimum Social Indicators. 2025. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/en/statistics/social/education/21484-minimum-social-indicators.html?lang=en-GB (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Villalobos, N.V.F.; Kessel, B.; Rodiah, I.; Ott, J.J.; Lange, B.; Krause, G.; Chemin, I. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in the Americas: Estimates from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, J.; Otto, B.; Madden, R.G.; Webb, G.; Woolson, K.L.; Kriston, L.; Vettorazzi, E.; Lohse, A.W.; Dalton, H.R.; Pischke, S. Hepatitis E Seroprevalence in Europe: A Meta-Analysis. Viruses 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Luchs, A.; Azevedo, L.S.; Silva, V.C.M.; Lemos, M.F.; Costa, A.C.; Compri, A.P.; França, Y.; Viana, E.; Malta, F.; et al. Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Feces of Capybaras (Hydrochoeris hydrochaeris) in Brazil. Viruses 2023, 15, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, C.; Eisen, A.K.A.; Demoliner, M.; Heldt, F.H.; Filippi, M.; Pereira, V.M.d.A.G.; Teixeira, T.A.M.; Roth, L.O.; Gularte, J.S.; Spilki, F.R. Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 in Bovine Livers Slaughtered in the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, N.S. Hepatitis E: Discovery, Global Impact, Control and Cure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7030–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, J.A.A.A.; Kampa, K.C.; Morsoletto, D.G.B.; Pissaia, A., Jr.; Ivantes, C.A.P. Hepatitis E: A Literature Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treagus, S.; Wright, C.; Baker-Austin, C.; Longdon, B.; Lowther, J. The Foodborne Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus to Humans. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
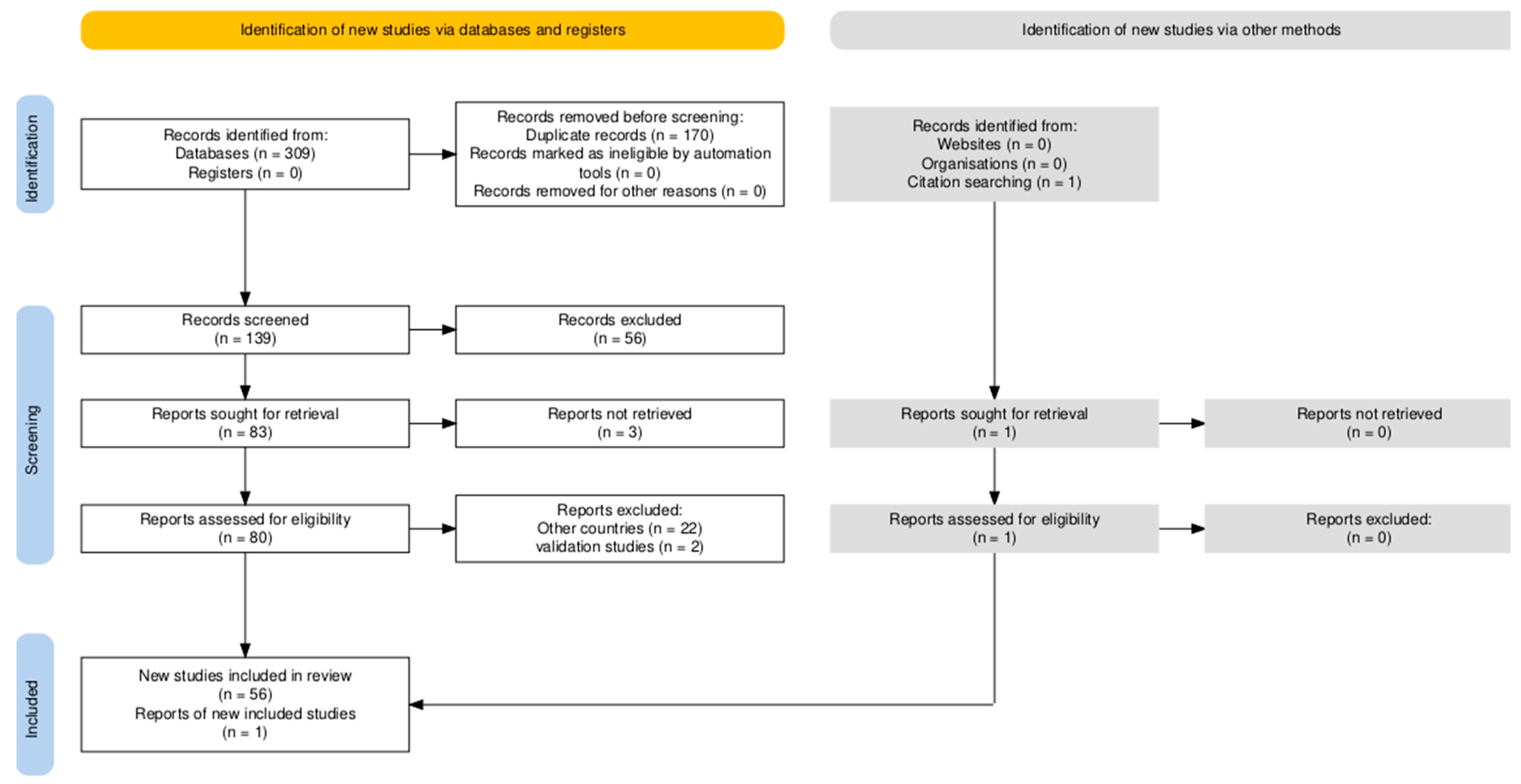
| Objective/ Problem | To investigate the epidemiological characteristics of HEV in Brazil, including modes of transmission, by reviewing genotyping studies in humans and swine/What are the epidemiological characteristics of HEV infection across the regions of Brazil? | ||
| P | C | C* | |
| Extraction | Epidemiology | Hepatitis E | Brazil |
| Combination | epidemiology; epidemiologia | hepatitis E; hepatitis E virus; Hepatite E; vírus da hepatite E | brazil; brasil |
| Construction | (“epidemiology” OR “epidemiologia”) | (“hepatitis E” OR “hepatitis E vírus” OR “hepatite E” OR “vírus da hepatite E”) | (“Brazil” OR “Brasil”) |
| Use | (“epidemiology” OR “epidemiologia”) AND (“hepatitis E” OR “hepatitis E vírus” OR “hepatite E” OR “vírus da hepatite E”) AND (“Brazil” OR “Brasil”); (“hepatitis E” OR “hepatitis E vírus”) AND (“Brazil” OR “Brasil”); (“hepatitis E/epidemiology” OR “hepatitis E vírus”) AND (“Brazil”) | ||
| Brazil Region | Type of Study | Selected Population | Epidemiological Characteristics | Sample Size | Anti-HEV Prevalence | RNA | Genotype | Author/Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG n (%) | IgM n (%) | ||||||||
| North | |||||||||
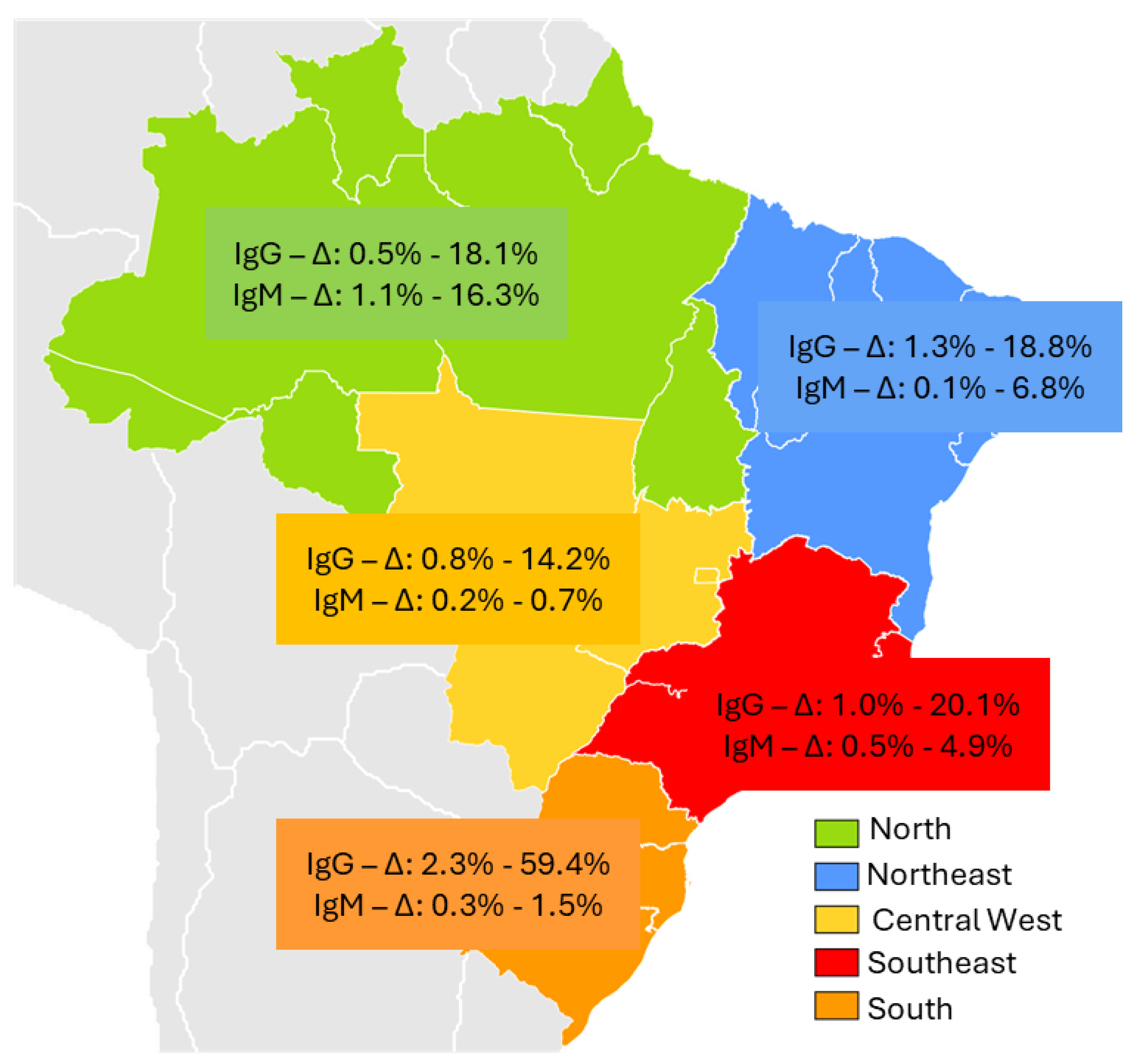
| Acre | Retrospective cross-sectional | Residents of an agricultural settlement in 2004 | Age > 21 years | 388 | 50 12.8% | 7 16.3% | n/a | n/a | Vitral CL et al., 2014 [24] |
| Amazônia/ Rondônia | Cross-sectional | Yanomani Indians Urban and rural areas | HEV in urban areas (2.9%), rural areas (14.2%) and village areas (2.8%) | 811 | 55 6.8% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Vasconcelos MP et al., 2024 [25] |
| Pará | Cross-sectional | Afro-descendant community | Young men reported eating bushmeat | 535 | 3 0.5% | 6 1.1% | negative | n/a | Souza AJS et al., 2018 [26] |
| Cross-sectional | Suspected cases of acute hepatitis | Male gender (55.2%) | 318 | 29 9.1% | 16 5.0% | negative | n/a | Souza AJS et al., 2019 [27] | |
| Cross-sectional | Crack cocaine users | Poorer and homeless; longer use of crack cocaine | 437 | 79 18.1% | 6 1.4% | positive | 3c | Nascimento RS et al., 2021 [28] | |
| Northeast | |||||||||
| Bahia | Retrospective cross-sectional | Blood donors (n = 200) Hemodialyzed (n = 392) | Blood donors | 200 | 4 2% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Paraná R et al., 1997 [15] |
| Cross-sectional | Acute sporadic non-A, non-B (NANB) | Aminotransferases elevation | 43 | 5 12% | negative | n/a | n/a | Paraná R et al., 1999 [29] | |
| Cross-sectional | Patients with acute viral hepatitis | Higher prevalence of HEV in patients with acute hepatitis | 73 | 21 28.8% | 5 6.8% | n/a | n/a | Lyra AC et al., 2005 [30] | |
| Pernambuco | Retrospective cross-sectional | Patients with schistosomiasis mansoni | Patients treated at a referral hospital with advanced forms of the disease | 80 | 15 18.8% | negative | negative | n/a | Passos -Castilho AM et al., 2016 [31] |
| Cross-sectional | People living with HIV/AIDS | Higher HIV infection time | 366 | 15 4.1% | n/a | negative | n/a | Bezerra LA et al., 2019 [32] | |
| Cross-sectional | Blood candidates and donors | All male gender, consumption of pork and chicken | 996 | 9 0.9% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Cunha GG et al., 2022 [33] | |
| Cross-sectional | Patients with chronic liver disease | Contact with swine and more advanced liver disease | 227 | 7 3.1% | n/a | negative | n/a | Araújo LRMG et al., 2024 [34] | |
| Retrospective cross-sectional | Patients with schistosomiasis mansoni | More advanced periportal fibrosis | 286 | 15 5.2% | negative | negative | n/a | Gomes CTO et al., 2024 [35] | |
| Piaui | Cross-sectional | Blood donors | Male gender (66.7%), age ≥ 30 years (75%) | 890 | 12 1.3% | 1 0.1% | negative | n/a | Silva-Sampaio JP et al., 2025 [36] |
| Central West | |||||||||
| Goiás | Prevalence survey | Recyclable material collectors | Contact with human feces (87.5%) and animal feces (75%) | 431 | 22 5.1% | 3 0.7% | negative | n/a | Martins RM et al., 2014 [37] |
| Cross-sectional | Patients with acute viral hepatitis | Pork consumption (95%) and wild animal (75%) | 379 | 20 5.3% | 1 0.3% | negative | n/a | Freitas NR et al., 2016 [38] | |
| Cross-sectional | Rural settlement | Male gender (75%), Time in rural settlement >5 years | 464 | 16 3.4% | n/a | negative | n/a | Freitas NR et al., 2017 [39] | |
| Cohort | Kidney transplant recipients | Previous hemodialysis (100%); Consumption of wild animal (87.5%) | 316 | 8 2.5% | 1 0.3% | negative | n/a | Oliveira JMNS et al., 2018 [40] | |
| Cross-sectional | Recyclers, immigrants, refugees, and homeless people | Homeless; recyclers | 459 | 4 0.87% | 1 0.2% | negative | Teles AS et al. 2023 [41] | ||
| Mato Grosso | Prevalence survey | School children | Absence of sanitary sewage. | 487 | 22 4.5% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Assis SB et al., 2002 [42] |
| Cross-sectional | Swine handlers | age ≥ 50 years, longer exposure to swine | 310 | 26 8.4% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Silva SM et al., 2022 [43] | |
| Mato Grosso do Sul | Cross-sectional | Crack users | Low education level (73.7%), unprotected sexual intercourse | 698 | 99 14.2% | 2 0.3% | negative | n/a | Castro VOL et al., 2018 [44] |
| Retrospective cross-sectional | Blood donors | Male (75%), age ≥ 30 years (70%): lack of sewage system | 250 | 16 6.4% | Negative | n/a | n/a | Weis-Torres SMDS et al., 2022 [45] | |
| Southeast | |||||||||
| São Paulo | Prevalence survey | General population | n/a | 1059 | 1.68% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Focaccia R et al.,1998 [46] |
| Cross-sectional | Blood donors and staff at a university hospital, | Blood donors with elevated ALT, and cleaning staff | 375 | 18 4.8% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Gonçales NS et al., 2000 [47] | |
| Cross-sectional | Kidney transplant | Transplant patients with elevated aminotransferases | 192 | 28 15% | n/a | 20 10% | n/a | Hering T et al., 2014 [48] | |
| Retrospective cross-sectional | Patients with clinical suspicion of HEV | age ≥ 40 years | 2.271 | 47 2.1% | 27 4.9% | 1 | 3b | Passos-Castilho AM et al., 2015 [49] | |
| Cross-sectional | Blood donors | age ≥ 45 years | 500 | 49 9.8% | 1 | negative | n/a | Passos -Castilho AM et al., 2017 [50] | |
| Cross-sectional | Chronic HCV patients | Contact with swines and consumption of pork | 618 | 63 10.2% | negative | n/a | n/a | Bricks G et al., 2018 [51] | |
| Cross-sectional | People living with HIV | Age ≥ 40 years | 354 | 38 10.7% | 5 1.4% | negative | n/a | Ferreira AC et al., 2018 [52] | |
| Cross-sectional | Chronic HCV patients | Age ≥ 60 years; contact with swine | 618 | 63 10.2% | negative | n/a | n/a | Bricks G et al., 2019 [53] | |
| Cross-sectional | Residents of a small municipality in São Paulo | Consumption of raw meat | 248 | 50 20.7% | negative | n/a | n/a | Araújo DCA et al., 2020 [54] | |
| Cross-sectional | Patients in the Emergency Room with altered levels of ALT | Altered levels of ALT | 401 | n/a | 2 of 90 2.2% | 16 of 311 5.1% | n/a | Conte DD et al., 2021 [55] | |
| Cohort | Liver transplants | HBV/HCV coinfected | 294 | 24 8.2% | 6 2% | 17 5.8% | n/a | Moraes ACP et al., 2021 [56] | |
| Cross-sectional | Chronic HCV patients | More advanced liver disease; more Type 2 DM, | 181 | 22 12% | 3 1.6% | 9 4.9% | n/a | Zitelli PMY et al., 2021 [57] | |
| Cross-sectional | Patients with acute viral hepatitis | Elevated aminotransferases | 91 | 12 13.2% | 4 4.4% | 1 | 3f | Ribeiro LB et al., 2024 [58] | |
| Prospective | Liver transplanted and donors | n/a | 190 | 19 10% | 1 0.5% | negative | n/a | Zicker M et al., 2024 [59] | |
| Rio de Janeiro | Retrospective cross-sectional | Acute viral hepatitis; hemodialysis; intravenous drug users; blood donors; | n/a | 1115 | Acute viral hepatitis (2.1%) hemodialysis (6.2%); UDIVs (11.8%); blood donors (4.3%) | n/a | n/a | n/a | Trinta KS et al., 2001 [60] |
| Cross-sectional | Manguinhos Community | Age ≥ 40 years | 699 | 17 2.4% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Santos DC et al., 2002 [61] | |
| South | |||||||||
| Paraná | Cross-sectional | Blood donors | There was no association with sociodemographic variables | 996 | 23 2.3% | n/a | n/a | n/a | Bortoliero AL et al., 2006 [62] |
| Cross-sectional | pregnant women (n = 209); female blood donor (n = 199) | Age ≥ 40 years; >3 number of pregnancies | 408 | 91 22.5% | n/a | negative | n/a | Hardtke S et al., 2018 [63] | |
| Santa Catarina | Cross-sectional | Blood donors | 300 | 30 10% | 1 0.3% | negative | n/a | Passos-Castilho AM et al., 2016 [19] | |
| Rio Grande do Sul | Cross-sectional | PLWHA Blood donors | Age ≥ 40 years; poor sanitation; alcohol use | 601 | 42 6.9% | n/a | 8 1.3% | 3 | Moss da Silva SC et al., 2019 [64] |
| Cross-sectional | Cirrhosis; crack users; liver transplanted; blood donors | Higher in cirrhosis; crack users; liver transplanted patients and blood donors | 400 | 78 19.5% | 6 1.5% | negative | n/a | Costa et al., 2021 [65] | |
| Cross-sectional | Blood samples were from laboratories | Age ≥ 40 years | 3.000 | 1.783 59.4% | n/a | negative | n/a | Zorzeto R et al., 2021 [66] | |
| Brazil Region | State | Herd Characteristics | Biological Sample Tested | Total (n=) | Prevalence HEV | RNA | Genotype | Author/Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG n (%) | IgM n (%) | Subtype | |||||||
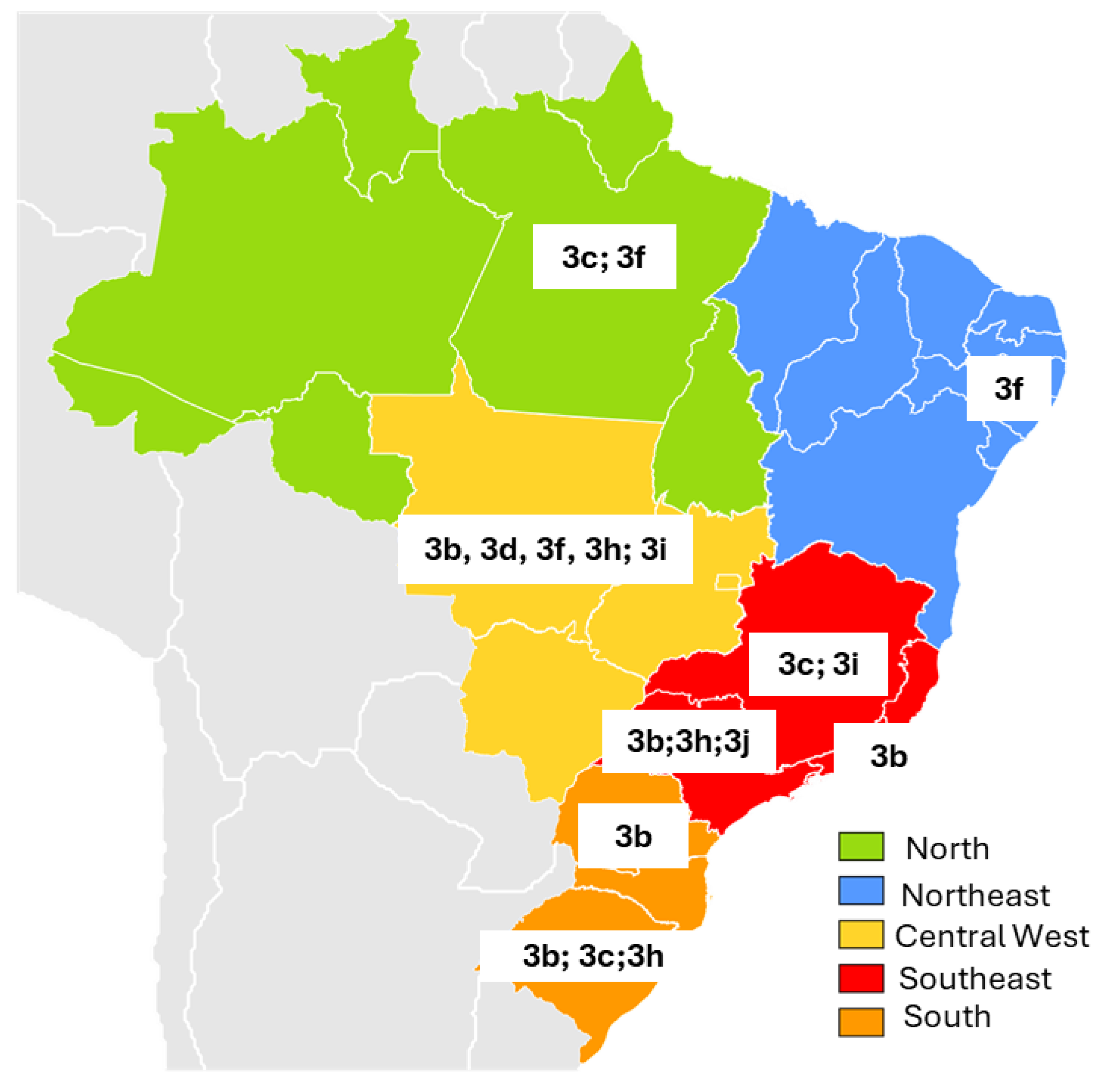
| North | Pará | Six-month-old swine from a licensed slaughterhouse (60%) and a slaughterhouse not registered with health regulatory agencies (40%). Samples collected during slaughter. | Serum, feces and liver | 151 | 13 8.6% | 0 | 15 * 9.9% | 3c; 3f | Souza AJ et al., 2012 [67] |
| Northeast | Pernambuco | Coming from a slaughterhouse located in the metropolitan region of Recife (30%) and farms in the rural region of the state (70%) | Serum | 325 | 266 82% | - | n/a | n/a | Oliveira-Filho EF et al., 2017 [68] |
| Pernambuco | Animals aged two to six months, from farms that use intensive and extensive production systems. | Feces | 119 | - | - | 2 (1.68%) | 3f | Oliveira-Filho EF et al., 2019 [69] | |
| Central West | Mato Grosso | Four-month-old animals from large-scale farms (50%) and family farms (50%). Overall, 18 (72%) of the 25 swine presented microscopic liver lesions, characterized by fibrosis and portal inflammation. | Bile, liver and feces | 25 | - | - | 15 ** 83.3% | 3b; 3f | Costa Lana et al., 2014 [70] |
| Mato Grosso | Growing piglets of both sexes, between three and four months of age, and breeding females, between eight and twenty-four months of age, from subsistence farms. | Serum and feces | 150 | - | - | 12 8% | 3d; 3h; 3i | Campos CG et al., 2018 [71] | |
| Southeast | Rio de Janeiro | Swine ranging in age from 1 to >25 week in four commercial herds | Serum | 357 | 227 63.6% | n/a | n/a | Vitral CL et al., 2005 [72] | |
| Rio de Janeiro | Healthy animals aged > five months, from three legal slaughterhouses. | Bile | 115 | 11 *** 9.6% | 3b | dos Santos DR et al., 2011 [73] | |||
| Minas Gerais | Healthy animals for slaughter at a state slaughterhouse. No macroscopic lesions were observed in the livers of slaughtered swine during bile collection. | Bile | 335 | - | - | 51 15.2% | 3c; 3i | Amorim AR et al., 2018 [74] | |
| São Paulo | Samples from a state swine biobank. | Feces | 89 | - | - | 7 7.86% | 3b; 3h; 3j | Cortez A et al., 2021 [75] | |
| South | Paraná | Samples came from maturation cycle farms (58.3%) and grow-to-slaughter farms (41.7%). All swine were asymptomatic. | Feces | 170 | - | - | 26 15.3% | 3b | Gardinali NR et al., 2012 [76] |
| Paraná | Animals aged between four and 16 weeks old from a small rural property in the region. | Feces | 170 | - | - | 34 20% | 3b | Passos-Castilho AM et al., 2017 [77] | |
| Rio Grande do Sul | Animals from farms located near peri-urban areas or landfills, indigenous reservations, and farms that feed swine with food scraps. Samples from two different periods were analyzed: 2012 (50.6%) and 2014 (49.4%) | Serum | 1444 | 1034 71.6% | - | 6 **** 0.8% | 3b; 3c; 3h | da Silva MS et al., 2018 [78] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mariz, C.A.; de Araújo, L.R.M.G.; Lopes, E.P. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Features. Pathogens 2025, 14, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090895
Mariz CA, de Araújo LRMG, Lopes EP. Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Features. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090895
Chicago/Turabian StyleMariz, Carolline Araujo, Lílian Rose Maia Gomes de Araújo, and Edmundo Pessoa Lopes. 2025. "Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Features" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090895
APA StyleMariz, C. A., de Araújo, L. R. M. G., & Lopes, E. P. (2025). Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Brazil: A Scoping Review of Epidemiological Features. Pathogens, 14(9), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090895







