Abstract
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection sometimes results in the occurrence of acute liver failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), which is often fatal, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus or elderly individuals. ACLF is observed in patients with cirrhosis who occasionally have zinc deficiency. However, effective drugs for hepatitis A are currently unavailable. Glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is an antiviral agent that has been reported to prevent HAV replication. The effects of zinc acetate on HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication and changes in GRP78 levels in human hepatocytes with or without HAV infection were examined. Zinc acetate inhibited HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication in both Huh7 and GL37 cells. Zinc acetate also inhibited HAV replication in both low- and high-glucose media. Zinc acetate increased the expression of GRP78, in response to HAV replication. The combination of zinc acetate with ribavirin led to greater suppression of both HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA and HAV HM175/18f genotype IB replication in Huh7 cells than that of ribavirin alone. In conclusion, zinc acetate inhibits HAV replication in accompany with the elevation of GRP78 expression without causing cellular toxicity. Zinc compounds may be useful for the treatment of ACLF caused by HAV infection.
1. Introduction
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection is a major cause of acute hepatitis with mild to severe symptoms and, rarely, acute liver failure (ALF) and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), which are often fatal [1]. ACLF is observed in cirrhotic patients who occasionally have zinc deficiency [2]. In 2016, 7134 people died from hepatitis A worldwide [1]. Effective vaccines for hepatitis A have been developed to prevent HAV infection; however, effective drugs for hepatitis A are currently not available. Considering this background information, we decided to investigate the effects of zinc compounds as antiviral agents on HAV replication.
HAV is a positive-sense RNA virus, belonging to the Picornaviridae family, and is classified into the Hepatovius genus [3]. HAV RNA genome is approximately 7.6 kb in length and encodes structural (VP4, VP2, VP3, and VP1) and nonstructural (2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3C, and 3D) proteins. HAV RNA has an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES), which is composed mainly of a 5′-nontranslational region (5′-NTR) and a 3′-NTR, and HAV proteins are generated via HAV IRES-mediated translation [3].
Zinc compounds, such as zinc oxide nanoparticles, zinc sulfate, and zinc chloride, protect against virus infection [4,5,6,7]. Zinc sulfate and zinc chloride suppress HAV RNA replication in human hepatocytes [4,5,6,7]. We previously demonstrated that Japanese rice-koji extracts, which induce the expression of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), have an inhibitory effect on HAV replication [8]. GRP78, a cell-protective ER chaperone protein, is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway and is also known as heat shock protein family A member 5 (HSPA5) or binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP). Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq) analysis revealed that miso extracts also affect the zinc homeostasis pathways [8]. Zinc sulfate could inhibit HAV replication in association with increased GRP78 expression [8].
HAV replication is sensitive to the interferon and interferon signaling pathways [9,10]. It has been recently reported that GRP78 can enhance the activation of the interferon/Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway during influenza A virus infection [11]. In the present study, the effects of zinc acetate on HAV replication were examined and the changes in GRP78 levels were also investigated in human hepatocytes infected with HAV.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
The human hepatoma cell line Huh7 [12] and African green monkey kidney cell line GL37 [13] were used in the present study. Huh7 and GL37 were kindly gifted by Prof. Ralf Bartenschlager (Universität Mainz, Mainz, Germany) and Dr. Tomoko Kiyohara (National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan), respectively.
The cells were maintained in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 medium (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan), Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)-low glucose (1000 mg/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) or DMEM-high-glucose (4500 mg/L) (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Serana, Pessin, Germany) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (FUJIFILM Wako). Cells were cultured at 37 °C with a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
Zinc acetate, zinc chloride, and zinc sulfate or ribavirin were purchased from FUJIFILM Wako or Sigma-Aldrich, respectively. Zinc acetate, zinc chloride, zinc sulfate, and ribavirin were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich) for the use in cell culture.
2.2. HAV Infection
The cells were infected with HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 as previously described [8]. Approximately 1 × 106 cells were infected with 1 × 104 copies/mL HAV RNA. MOI was determined by the methods as previously described [13,14].
Briefly, Huh7 cells were seeded 24 h prior to infection at a density of 0.5 × 106 cells/well in 6-well plates (AGC Techno Glass, Haibara-gun, Shizuoka, Japan). The cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; FUJIFILM Wako) and infected with HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA in serum-free medium [8]. At 4 h after infection, the cells were washed twice with PBS, and incubated with fresh media. At 24 h after infection, the media was exchanged by DMEM supplemented with 5% FBS with or without zinc compounds at different concentrations. At 48 h after infection, total cellular RNAs were extracted to measure HAV RNA [8].
To examine the effect of a combination of zinc acetate and ribavirin, cells were infected with HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA or HAV HM175/18f genotype IB at an MOI of 0.01; HAV HM175/18f genotype IB was provided by Prof. Stanley M Lemon (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA) and Dr. Asuka Hirai-Yuki (National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan).
2.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative PCR (qPCR) for HAV RNA
Total cellular RNAs were extracted via a QIAshredder (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) as previously described [7]. Reverse transcription was performed using PrimeScript RT reagent (Perfect Real Time; TaKaRa Bio, Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) at 37 °C for 15 min, followed by incubation at 85 °C for 5 s. For the quantification of HAV RNA, the following primers were used: sense primer, 5′-AGGCTACGGGTGAAACCTCTTAG-3′ and antisense primer, 5′-GCCGCTGTTACCCTATCCAA-3′ [14]. For the quantification of β-actin mRNA, the following primers were used: sense primer, 5′-CAGCCATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGG-3′ and antisense primer, 5′-AGGTCCAGACGCAGGATGGCATG-3′ [15]. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed using PowerSYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Tokyo, Japan) on a 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) or a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) [6]. Real-time PCR assays were performed in triplicate. Huh7 and GL37 cells were analyzed via the ddCt method and standard curve method, respectively.
2.4. Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50)
IC50, which is the concentration of each drug that produces 50% of the maximal inhibitory effect against HAV, was calculated by the formula as previously described [15].
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
For the evaluation of cell viability, we performed a dimethylthiazol carboxymethoxyphenyl sulfophenyl tetrazolium (MTS) assay (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) in triplicate. The absorbance of each well at 490 nm was measured with an iMark Microplate Reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) [8].
2.6. Quantitative Detection of the GRP78 Concentration in Conditioned Medium
GRP78 was quantified in conditioned medium from Huh7 cells cultured with a human GRP78/Bip sandwich ELISA kit (Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA) [5]. The sensitivity and range were 0.02 ng/mL and 0.156 ng/mL–10 ng/mL, respectively. The absorbance of each well at 450 nm was measured [5].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Enhancement of HAV RNA Replication in High-Concentration Glucose Media
In the present study, Huh7 or GL37 cells were infected with HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA at an MOI of 0.01 in high-glucose DMEM (4500 mg/L) or low-glucose DMEM (1000 mg/L). At 48 h of infection, the level of intracellular HAV RNA was measured by real-time RT-PCR. In Huh7 cells, HAV RNA levels were increased 1.30-fold with 4500 mg/L glucose medium compared with those with 1000 mg/L glucose medium (Figure 1A). HAV RNA levels were enhanced by 1.24-fold in GL37 cells cultured with 4500 mg/L glucose compared with those cultured with 1000 mg/L glucose (Figure 1B). Together, these results support a previous report that high-concentration glucose enhances HAV RNA replication in Huh7 cells infected with HAV at 96 h after infection [16].
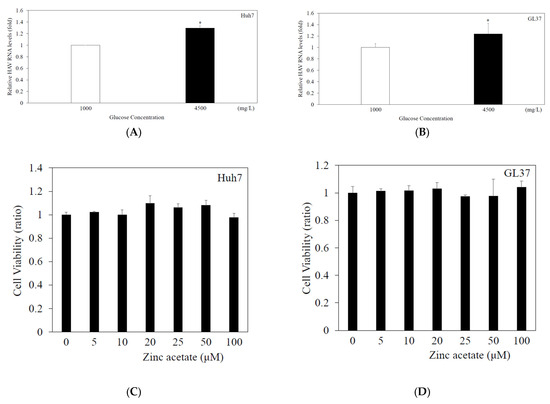
Figure 1.
High-concentration glucose enhances HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA RNA replication, and zinc acetate has no cytotoxicity. Compared with low-glucose (1000 mg/L) DMEM, high-glucose (4500 mg/L) Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) enhanced HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication in both Huh7 cells (A) and GL37 cells (B). HAV RNA was measured by real-time RT-PCR after 48 h of infection. * p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference between two groups. Zinc acetate (at the indicated concentration) had no effect on cytotoxicity in either Huh7 cells (C) or GL37 cells (D). An MTS assay was performed for evaluation after 48 h of incubation. There was no statistically significant difference compared with cells without zinc acetate treatment.
3.2. Zinc Acetate Had No Effect on the Viability of GL37 or Huh7 Cells at 5–100 μM for 48 H
To examine the effects of zinc acetate on cell proliferation (Figure 1C,D), Huh7 and GL37 cells were incubated with different concentrations of zinc acetate (5, 10, 20, 25, 50 and 100 μM) for 48 h, and cell viability was evaluated via the MTS assay. Cellular viabilities were not reduced when Huh7 or GL37 cells were incubated with zinc acetate. We selected concentrations of zinc acetate 10–20 µM for further studies.
3.3. Zinc Acetate Significantly Inhibited HAV HA11-1299 Genotype IIIA Replication in Huh7 Cells in High-Concentration Glucose Media
To examine the effects of zinc acetate on HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication (Figure 2A,B), Huh7 cells were incubated with different concentrations of zinc acetate (10–20 µM) for 24 h. With 1000 mg/L glucose, HAV replication was reduced to 69% and 51% by 10 μM and 20 μM zinc acetate, respectively, compared with that of the control (100%) (Figure 2A). With 4500 mg/L glucose, HAV replication was reduced to 57% and 53% by 10 μM and 20 μM zinc acetate, respectively, compared with that of the control (100%) (Figure 2B). Thus, in Huh7 cells, despite the high concentration of glucose, zinc sulfate suppressed HAV replication.
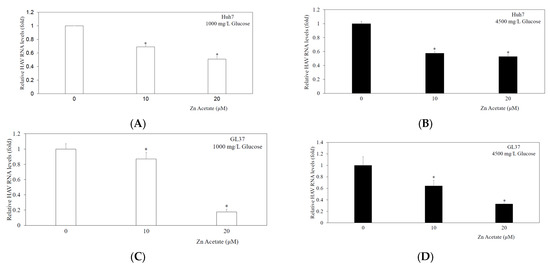
Figure 2.
Zinc acetate inhibits HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA RNA replication in both Huh7 cells (A,B) and GL37 cells (C,D). Cells were cultured in low-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (A,C); or high-glucose DMEM (B,D). HAV RNA was measured by real-time RT-PCR after 48 h of infection. Zinc acetate was used at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. * p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference, compared with those without zinc acetate treatment according to Student’s t test.
3.4. Zinc Acetate Significantly Inhibited HAV HA11-1299 Genotype IIIA Replication in GL37 Cells in High-Concentration Glucose Media
To examine the effects of zinc acetate on HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication (Figure 2C,D), GL37 cells were incubated with different concentrations of zinc acetate (10–20 µM) for 24 h. With 1000 mg/L glucose, HAV replication was reduced to 87% and 18% by 10 μM and 20 μM zinc acetate, respectively, compared with that of the control (100%) (Figure 2C). With 4500 mg/L glucose, HAV replication was reduced to 64% and 33% by 10 μM and 20 μM zinc acetate, respectively, compared with that of the control (100%) (Figure 2D). The IC50 value was 13.6 μM. Thus, in GL37 cells, despite the high concentration of glucose, zinc acetate suppressed HAV replication.
3.5. Zinc Compounds Significantly Inhibited HAV HA11-1299 Genotype IIIA Replication in Huh7 Cells
To examine the effects of zinc chloride, zinc sulfate, and zinc acetate on HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication, Huh7 cells were incubated with zinc chloride, zinc sulfate and zinc acetate at 20 μM for 24 h. HAV replication was reduced to 64%, 64%, and 64% by 20 μM zinc chloride, zinc sulfate and zinc acetate, respectively, compared with the control (100%) (Figure 3). There were no differences in the inhibitory effects of the selected zinc compounds against HAV replication in the present study.
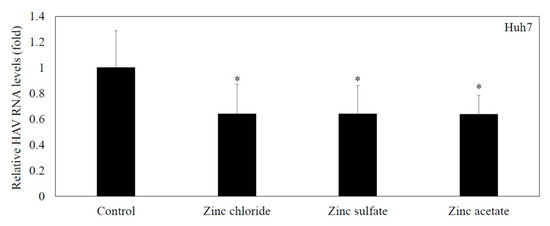
Figure 3.
Zinc compounds significantly inhibited HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA replication in Huh7 cells. Zinc compounds (zinc chloride, zinc sulfate and zinc acetate) significantly inhibited HAV RNA replication in Huh7 cells compared with cells without treatment. HAV RNA was measured by real-time RT-PCR after 48 h of infection. Zinc compounds were used at 20 μM. * p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference, compared with cells without treatment according to Student’s t test.
3.6. Zinc Acetate Increases GRP78 Concentrations in HAV-Infected Huh7 Cells
We previously reported that zinc sulfate inhibits HAV subgenomic RNA replication in HuhT7 cells, which are Huh7 cells stably expressing T7 polymerase, and that this effect is accompanied by an increase in the GRP78 concentration [5].
In the present study, the concentration of GRP78 in conditioned medium from zinc acetate-treated Huh7 cells infected with HAV was determined by ELISA (Figure 4). In Huh7 cells infected with HAV, the GRP78 concentration in the conditioned medium gradually increased with increasing zinc acetate concentration.
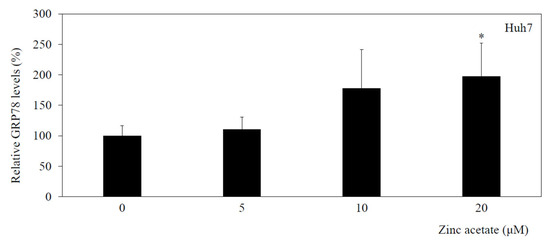
Figure 4.
Zinc acetate enhances or inhibits GRP78 concentrations in HAV-infected Huh7 cells. GRP78 was quantified in conditioned medium from cultured Huh7 cells via a human GRP78/Bip sandwich ELISA kit. Black columns, conditioned media from HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA-infected cells. * p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference, compared with cells without treatment according to Student’s t test.
3.7. Effects of Zinc Acetate With or Without Ribavirin on HAV Replication in Huh7 Cells
To further determine the effects of the combination of zinc acetate with ribavirin on HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA or HAV HM175/18f genotype IB replication in Huh7 cells, we performed an HAV infectivity assay (Figure 5). Huh7 cell monolayers in 6-well culture plates were infected with HAV at 0.01 MOI and treated with 0 or 10 μM ribavirin and 0 or 10 μM zinc acetate for 24 h.
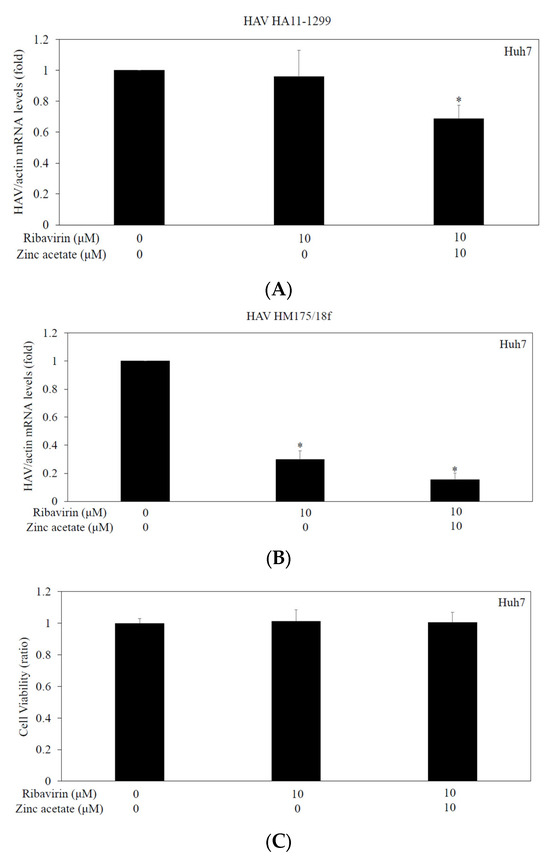
Figure 5.
Effects of zinc acetate with or without ribavirin on HAV replication in Huh7 cells. Cells infected with HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA (A) or HAV HM175/18f genotype IB (B) were used. HAV RNA was determined by real-time RT-PCR after 48 h of infection. Zinc acetate and ribavirin were used at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. * p < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference, compared with those without treatment according to Student’s t test. (C) The combination of ribavirin and zinc acetate (at the indicated concentrations) had no effect on cell viability of Huh7 cells. An MTS assay was performed for evaluation after 72 h of incubation. There were no statistically significant differences, compared with cells without treatment according to Student’s t test.
Suppression of both the HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA and HAV HM175/18f genotype IB replication by the combination of ribavirin and zinc acetate was greater than that of ribavirin alone or the untreated control (Figure 5A,B). No effects of the combination of ribavirin and zinc acetate on the cell viability of Huh7 cells were observed (Figure 5C).
4. Discussion
GRP78 is an antiviral protein that prevents HAV replication [16,17]. We previously verified the enhancement of HAV replication under GRP78 functional inhibition experiments (siRNA knockdown or knockout by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9)-mediated genome editing) [17], and the inhibition of HAV replication with GRP78 overexpression by [16]. In the present study, we observed that zinc acetate inhibited HAV replication, along with the enhancement of GRP78 protein expression.
We have previously shown that zinc sulfate, zinc chloride and Japanese rice-koji miso have inhibitory effects on HAV replication [5,6,7,8,18] and that zinc sulfate increases GRP78 expression in HAV-infected hepatocytes [5]. Zinc chloride decreases the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (MAP2K3), resulting in inhibiting HAV replication [7]. We observed that zinc acetate inhibited HAV HA11-1299 replication in both Huh7 and GL37 cells, although zinc acetate is useful for the treatment of Wilson’s disease and zinc deficiency in clinical settings [19,20]. However, in the present study, we did not observe any differences in the inhibitory effects of zinc sulfate, zinc chloride, or zinc acetate on HAV HA11-1299 replication.
In human, a serum zinc level < 60 μg/dL, 60–80 μg/dL and >80 μg/dL indicate zinc deficiency, marginal zinc deficiency, and the normal zinc status, respectively [20]. It is expected that 10–20 μM zinc acetate includes approximately 60–120 μg/dL zinc, because the molecular weight of zinc acetate and zinc are 183.5 g/mol and 65.38 g/mol, respectively. These are reasons for selecting 10–20 µM zinc acetate concentrations in the present study.
We previously reported that high concentrations of glucose enhanced HAV replication, in association with a reduction in GRP78 expression [16]. Nakao et al. [21] reported that diabetes mellitus was more common among deceased patients with HAV-ALF than among rescued patients with HAV-ALF (29% vs. 8%; p < 0.05). Kumar et al. [22] reported that diabetes leads to adverse outcomes in patients with metabolic dysfunction associated with fatty liver disease-related ACLF. We reconfirmed that a high concentration of glucose enhances HAV replication in both cultured Huh7 and in GL37 cells.
The increase in HAV replication under high-glucose conditions is modest (1.30-fold in Huh7, 1.24-fold in GL37) (Figure 1A,B). Glucose metabolism plays an important role in driving immune responses against viral infections [23]. HAV may evolve mechanisms to use host metabolism, by hijacking glucose-dependent pathways, and HAV may continue replication and modify immune responses.
Furthermore, in the present study, zinc acetate inhibited HAV replication in both low- and high-glucose media. These results indicate that zinc acetate may be useful for the treatment of severe acute hepatitis, although it may be ineffective for the treatment of end-stage liver diseases [19].
We also observed that zinc acetate increased the GRP78 concentration in the context of HAV infection. While GRP78 upregulation is highlighted, the exact pathway by which zinc acetate induces GRP78 and inhibits HAV remains unclear. It is possible that zinc deficiency could lead to oxidative stress, endoplasmic stress, apoptosis in hepatocytes and inflammation in the liver [24]. Endoplasmic stress is associated with HAV replication [8,17,25].
GRP78 can increase the activation of the interferon/JAK-STAT pathway during influenza A virus infection [11]. Zinc acetate may be more useful for treating diseases in which GRP78 is inhibited [18]. Interferon signaling plays an important role in controlling HAV replication in vivo [26]. Further studies may be needed to show whether GRP78 is the main factor or just one part of a wider antiviral effect of zinc acetate.
We also observed that the combination of zinc acetate with ribavirin affected HAV HA11-1299 genotype IIIA or HAV HM175/18f genotype IB replication in Huh7 cells. Although ribavirin is useful for the inhibition of HAV replication [27,28], it is associated with adverse events, such as hemolytic anemia. The addition of zinc acetate to ribavirin therapies may decrease the dose of ribavirin that patients receive, reducing the occurrence of adverse events.
GRP78 is an antiviral factor in several viral infections, such as influenza A virus [11], hepatitis B virus [29], hepatitis C virus [30] and Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) [31]. Several reports have shown that GRP78 enhances interferon signaling during viral infection, including HAV infection [7,11,29,30]. Silencing GRP78 expression in persistently JEV-infected cells led to C/EBP homologous binding protein (CHOP) induction, followed by a severe reduction in cell viability [31]. In general, HAV infection does not induce cellular apoptosis [32], except for some cases [33]. However, further studies on the mechanism underlying the association between GRP78 and anti-HAV agents are needed.
In general, patients with ACLF often have advanced chronic liver diseases, such as liver cirrhosis [22]. Patients with cirrhosis possess hypozincemia [2,20]. It may be useful for ACLF-patients infected with HAV to be treated by zinc compounds.
Zinc chloride, zinc sulfate, and zinc acetate which are water soluble, include 48%, 28%, 30% of element zinc content, respectively [34]. Zinc is primarily absorbed at duodenum and jejunum [35]. It was reported that the highest zinc plasma concentrations were observed with zinc acetate at a low pH in the stomach [36]. Japan’s Health Insurance system has approved zinc acetate hydrate for the safe treatment of patients with zinc deficiency. We showed that zinc acetate inhibits HAV replication, and our studies shed new light on the lack of effective treatments for hepatitis A, although there have been several reports about anti-HAV compounds [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46].
In the present study, high-glucose medium was used to mimic HAV severity in diabetic patients, but we do not know whether this culture condition accurately reflects the intracellular hepatic environment in actual diabetic patients. Particularly, diabetic patients have complex metabolic abnormalities including not only simple hyperglycemia but also insulin resistance, increased inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress. This may be one of the limitations of study.
5. Conclusions
We demonstrated that zinc acetate inhibits HAV replication, which is accompanied by increased GRP78 expression. The inhibitory effect of zinc acetate on HAV replication may be related to a known mechanism [47,48] without any serious toxicity to hepatocytes or renal cells. However, further understanding of the complex mechanism by which zinc acetate affects the expression of GRP78 in the context of HAV infection is needed. Bioavailability of zinc acetate could be a key practical challenge in patients with cirrhosis. Further studies at this point are needed in animal models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.K. and R.S.-T.; methodology, T.K. and R.S.-T.; software, T.K.; validation, T.K. and R.S.-T.; formal analysis, T.K.; investigation, T.K.; resources, T.K., R.S.-T., R.M., H.K. (Hirofumi Kogure), H.O. and S.T.; data curation, T.K.; interpretation of data, T.K., R.S.-T., H.A., T.Y., A.S., K.H., H.K. (Hiroteru Kamimura), A.T., R.M., H.K. (Hirofumi Kogure), H.O. and S.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.K.; writing—review and editing, T.K., R.S.-T., H.A., T.Y., A.S., K.H., H.K. (Hiroteru Kamimura), A.T., R.M., H.K. (Hirofumi Kogure), H.O. and S.T.; visualization, T.K.; supervision, R.S.-T., A.T., R.M., H.K. (Hirofumi Kogure), H.O. and S.T.; project administration, T.K.; funding acquisition, T.K., R.S.-T., H.O. and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) under Grant numbers JP24fk0210132 and JP25fk0210132. Reina Sasaki-Tanaka was also supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under grant number JP23K15055.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ralf Bartenschlager, Tomoko Kiyohara, Stanley M. Lemon and Asuka Hirai-Yuki for providing us the cell lines or viruses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HAV | hepatitis A virus |
| ACLF | acute-on-chronic liver failure |
| GRP78 | glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| ALF | acute liver failure |
| IRES | internal ribosomal entry site |
| NTR | nontranslational region |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| BiP | binding immunoglobulin protein |
| HSPA5 | heat shock protein family A member 5 |
| RNA-Seq | transcriptome sequencing |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| MTS | dimethylthiazol carboxymethoxyphenyl sulfophenyl tetrazolium |
| MOI | multiplicity of infection |
| MAP2K3 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
| poly(I:C) | polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis A. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-a/ (accessed on 3 August 2025).
- Moriyama, M.; Matsumura, H.; Fukushima, A.; Ohkido, K.; Arakawa, Y.; Nirei, K.; Yamagami, H.; Kaneko, M.; Tanaka, N.; Arakawa, Y. Clinical significance of evaluation of serum zinc concentrations in C-viral chronic liver disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusov, Y.; Kanda, T.; Palmenberg, A.; Sgro, J.Y.; Gauss-Müller, V. Silencing of hepatitis A virus infection by small interfering RNAs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5599–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, G.H.; Moemen, Y.S.; Youns, M.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Abdou, R.; El Raey, M.A. Antiviral zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated by hesperidin and in silico comparison study between antiviral phenolics as anti-SARS-CoV-2. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Kanda, T.; Suganami, A.; Nakamoto, S.; Win, N.N.; Tamura, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Yokosuka, O.; Kato, N.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Zinc Sulfate Against Hepatitis A Virus Replication. Future Virol. 2019, 14, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Sasaki, R.; Masuzaki, R.; Takahashi, H.; Fujisawa, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Okamoto, H.; Moriyama, M. Additive Effects of Zinc Chloride on the Suppression of Hepatitis A Virus Replication by Interferon in Human Hepatoma Huh7 Cells. In Vivo 2020, 34, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Sasaki-Tanaka, R.; Masuzaki, R.; Matsumoto, N.; Okamoto, H.; Moriyama, M. Knockdown of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 3 Negatively Regulates Hepatitis A Virus Replication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, N.N.; Kanda, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Moriyama, M.; Jiang, X.; Suganami, A.; Tamura, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Shirasawa, H. Inhibitory effect of Japanese rice-koji miso extracts on hepatitis A virus replication in association with the elevation of glucose-regulated protein 78 expression. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser-Nobis, K.; Harak, C.; Schult, P.; Kusov, Y.; Lohmann, V. Novel perspectives for hepatitis A virus therapy revealed by comparative analysis of hepatitis C virus and hepatitis A virus RNA replication. Hepatology 2015, 62, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai-Yuki, A.; Hensley, L.; McGivern, D.R.; González-López, O.; Das, A.; Feng, H.; Sun, L.; Wilson, J.E.; Hu, F.; Feng, Z.; et al. MAVS-dependent host species range and pathogenicity of human hepatitis A virus. Science 2016, 353, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Wu, W.; Pang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Qiu, J.; Fang, Z. GRP78 exerts antiviral function against influenza A virus infection by activating the IFN/JAK-STAT signaling. Virology 2024, 600, 110249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, V.; Körner, F.; Koch, J.; Herian, U.; Theilmann, L.; Bartenschlager, R. Replication of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science 1999, 285, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kiyohara, T.; Kanda, T.; Imazeki, F.; Fujiwara, K.; Gauss-Müller, V.; Ishii, K.; Wakita, T.; Yokosuka, O. Inhibitory effects on HAV IRES-mediated translation and replication by a combination of amantadine and interferon-alpha. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Basu, A.; Steele, R.; Wakita, T.; Ryerse, J.S.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Generation of infectious hepatitis C virus in immortalized human hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4633–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki-Tanaka, R.; Masuzaki, R.; Okamoto, H.; Shibata, T.; Moriyama, M.; Kogure, H.; Kanda, T. Drug Screening for Hepatitis A Virus (HAV): Nicotinamide Inhibits c-Jun Expression and HAV Replication. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0198722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwe Win, N.; Kanda, T.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamoto, S.; Okamoto, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Shirasawa, H. Free fatty acids or high-concentration glucose enhances hepatitis A virus replication in association with a reduction in glucose-regulated protein 78 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Kanda, T.; Haga, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Nakamura, M.; Wu, S.; Nakamoto, S.; Shirasawa, H.; Okamoto, H.; Yokosuka, O. Glucose-regulated protein 78 is an antiviral against hepatitis A virus replication. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3305–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ren, Q.; Chen, S.P.; Tong, X.B.; Dong, M.; Sugaya, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kita, K.; Suzuki, N. UVC mutagenicity is suppressed in Japanese miso-treated human RSa cells, possibly via GRP78 expression. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, C.K.; Miah, S.A.; Hasan, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.; Miah, A.R. Prolonged Jaundice in a Patient with Coexisting Hepatitis A Virus Infection and Wilson’s Disease. Mymensingh Med. J. 2021, 30, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kodama, H.; Tanaka, M.; Naito, Y.; Katayama, K.; Moriyama, M. Japan’s Practical Guidelines for Zinc Deficiency with a Particular Focus on Taste Disorders, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, and Liver Cirrhosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Nakayama, N.; Uchida, Y.; Tomiya, T.; Oketani, M.; Ido, A.; Tsubouchi, H.; Takikawa, H.; Mochida, S. Deteriorated outcome of recent patients with acute liver failure and late-onset hepatic failure caused by infection with hepatitis A virus: A subanalysis of patients seen between 1998 and 2015 and enrolled in nationwide surveys in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Arora, A.; Choudhury, A.; Arora, V.; Rela, M.; Jothimani, D.K.; Mahtab, M.A.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eapen, C.E.; Goel, A.; et al. APASL ACLF Research Consortium (AARC) for APASL ACLF Working Party. Impact of Diabetes, Drug-Induced Liver Injury, and Sepsis on Outcomes in Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Fatty Liver Disease-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 120, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darweesh, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Rahmati, M.; Al-Hamadani, M.; Al-Harrasi, A. Metabolic reprogramming in viral infections: The interplay of glucose metabolism and immune responses. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1578202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Xu, T.; Lv, H.; Guo, M.Y. Zinc deficiency causes oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and inflammation in hepatocytes in grass carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasaki, T.; Lenarcic, E.; Misumi, I.; Xie, L.; Fusco, W.G.; Yonish, B.; Das, A.; Kim, H.; Cameron, C.E.; Léger-Abraham, M.; et al. Hepatovirus translation requires PDGFA-associated protein 1, an eIF4E-binding protein regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadq6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai-Yuki, A.; Whitmire, J.K.; Joyce, M.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Lemon, S.M. Murine Models of Hepatitis A Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widell, A.; Hansson, B.G.; Oberg, B.; Nordenfelt, E. Influence of twenty potentially antiviral substances on in vitro multiplication of hepatitis A virus. Antivir. Res. 1986, 6, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki-Tanaka, R.; Shibata, T.; Okamoto, H.; Moriyama, M.; Kanda, T. Favipiravir Inhibits Hepatitis A Virus Infection in Human Hepatocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, J.; Chan, H.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Go, M.Y.; Tsai, S.N.; Ngai, S.M.; et al. Glucose-regulated protein 78 is an intracellular antiviral factor against hepatitis B virus. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 2582–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Li, N.L.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, B.; Kumthip, K.; Wang, T.T.; Huo, D.; Ingels, J.F.; Lu, L.; Shang, J.; et al. The Molecular Chaperone GRP78 Contributes to Toll-like Receptor 3-mediated Innate Immune Response to Hepatitis C Virus in Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12294–12309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyoo, H.R.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, Y.S. Constant up-regulation of BiP/GRP78 expression prevents virus-induced apoptosis in BHK-21 cells with Japanese encephalitis virus persistent infection. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Yokosuka, O.; Kato, N.; Imazeki, F.; Fujiwara, K.; Kawai, S.; Saisho, H.; Omata, M. Hepatitis A virus VP3 may activate serum response element associated transcription. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Egger, D.; Bienz, K. A cytopathic and a cell culture adapted hepatitis A virus strain differ in cell killing but not in intracellular membrane rearrangements. Virology 2000, 266, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarshi, P.P.; Mao, Q.; Grant, R.W.; Hazels Mitmesser, S. Comparative Absorption and Bioavailability of Various Chemical Forms of Zinc in Humans: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, M.; Hatsuyama, K.; Tajima, M.; Ueki, R.; Tsuji, Y.; Suzuki, T. Efficacy of Zinc Acetate in the Treatment of Zinc Deficiency in Elderly Inpatients and Effect of Total Dose on Its Replacement Therapy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.M.; Brewer, G.J.; Dressman, J.B.; Swidan, S.Z.; DuRoss, D.J.; Adair, C.H.; Barnett, J.L.; Berardi, R.R. Effect of intragastric pH on the absorption of oral zinc acetate and zinc oxide in young healthy volunteers. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; D’Souza, D.H. Grape seed extract for control of human enteric viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3982–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debing, Y.; Neyts, J.; Thibaut, H.J. Molecular biology and inhibitors of hepatitis A virus. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 895–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.S.; Dice, L.; D’Souza, D.H. Aqueous Extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa Calyces Decrease Hepatitis A Virus and Human Norovirus Surrogate Titers. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 7, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, P.; Gao, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.; Lin, J.; Su, D.; Rao, Z.; et al. Structural basis for neutralization of hepatitis A virus informs a rational design of highly potent inhibitors. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, M.; Morgan, M.T.; Dia, V.; D’Souza, D.H. Heat sensitization of hepatitis A virus and Tulane virus using grape seed extract, gingerol and curcumin. Food Microbiol. 2020, 90, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkousy, R.H.; Said, Z.N.A.; Abd El-Baseer, M.A.; Abu El Wafa, S.A. Antiviral activity of castor oil plant (Ricinus communis) leaf extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Sarowska, J.; Wojnicz, D.; Choroszy-Król, I.; Frej-Mądrzak, M. Natural Products and Their Potential Anti-HAV Activity. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SHI, S.; Zheng, X.; Suzuki, R.; Li, Z.; Shiota, T.; Wang, J.; Hirai-Yuki, A.; Liu, Q.; Muramatsu, M.; Song, S.J. Novel flavonoid hybrids as potent antiviral agents against hepatitis A: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleman, D.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Ogaly, H.A.; Galal, H.M.; Batiha, G.E.; Elkousy, R.H. GC/MS Analysis, Cytotoxicity, and Antiviral Activities of Annona glabra Hexane Extract Supported by In Silico Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, A.; Elshazly, E.H.; Slima, D.F.; Elnosary, M.E.; Sadek, A.M.; Khamis, M.; Gong, Y.; Tian, Q.; Gouda, G.A.; Zhu, G.P. Bioactive Compounds from Vicia sativa L. and Vicia monantha Retz. with Unveiling Antiviral Potentials in Newly Green Synthesized CdO Nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2025, 26, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davuluri, K.S.; Shukla, S.; Kakade, M.; Cherian, S.; Alagarasu, K.; Parshar, D. Explorations on the antiviral potential of zinc and magnesium salts against chikungunya virus: Implications for therapeutics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1335189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, M.; George, A.; Sivadas, A.; Karunakaran, K.; N., S.; Byradeddy, S.N.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; Mudgal, P.P.; Kulkarni, M. Development and characterization of formulations based on combinatorial potential of antivirals against genital herpes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 3103–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).