Genomic Markers Distinguishing Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Insights from Pangenome and Phylogenomic Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
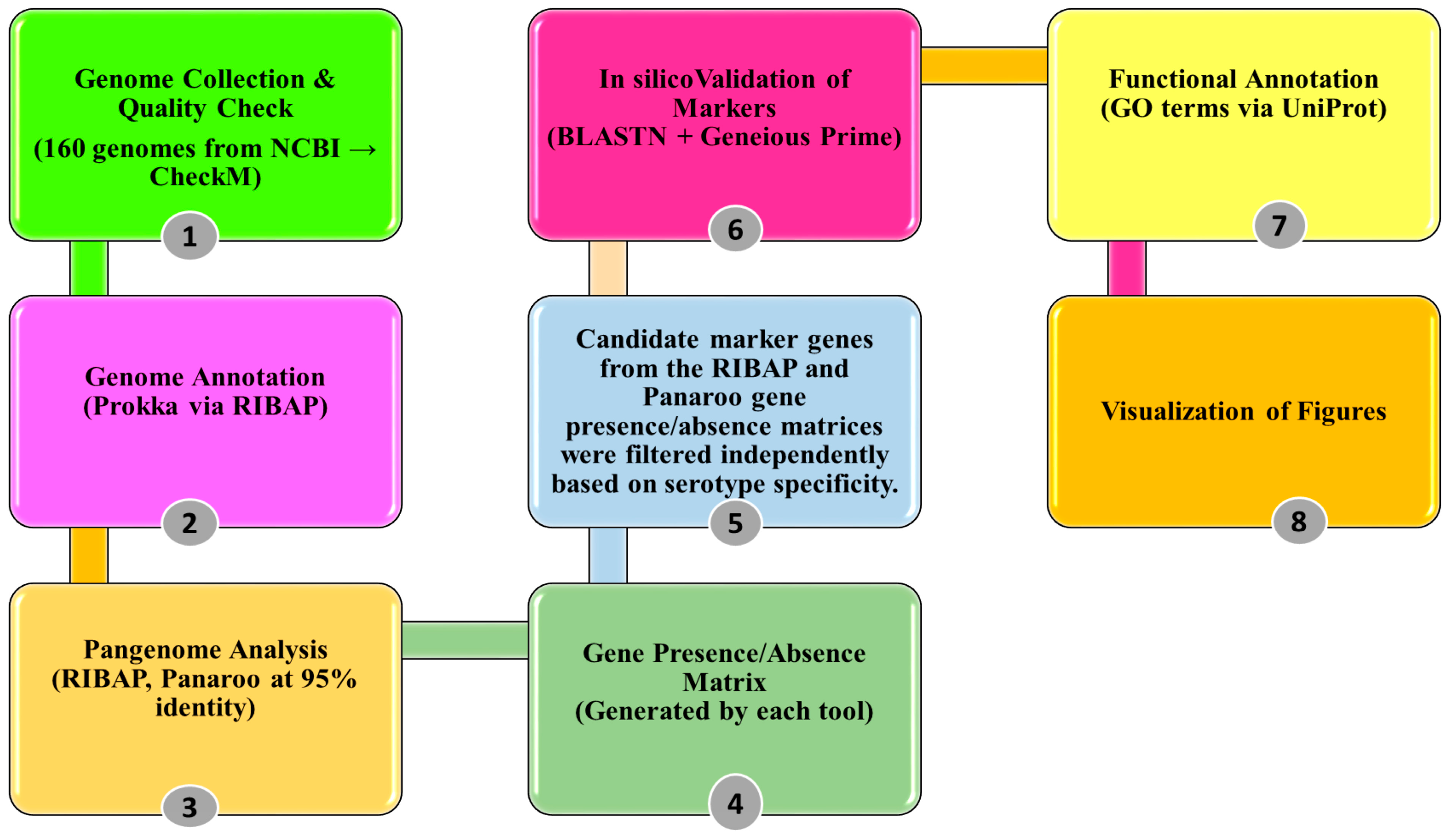
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Dataset Collection and Quality Filtering
2.2. Genome Annotation and Pangenome Analysis
2.3. Identification, Validation, and Cross-Verification of Candidate Marker Genes
2.4. Functional Characterization of Serogroup-Specific Genes via Gene Ontology Annotation
2.5. Visualization of Figures
3. Results
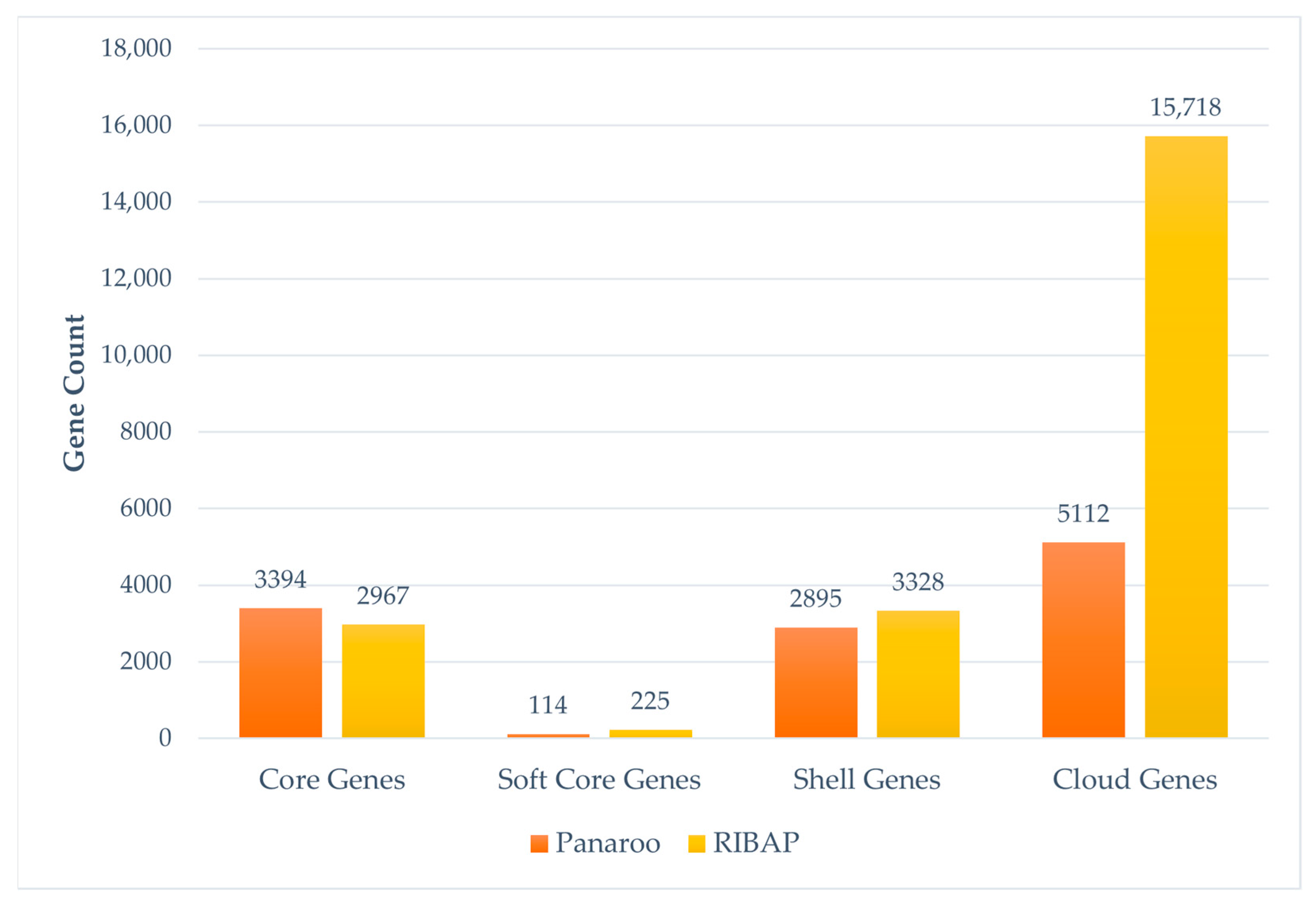
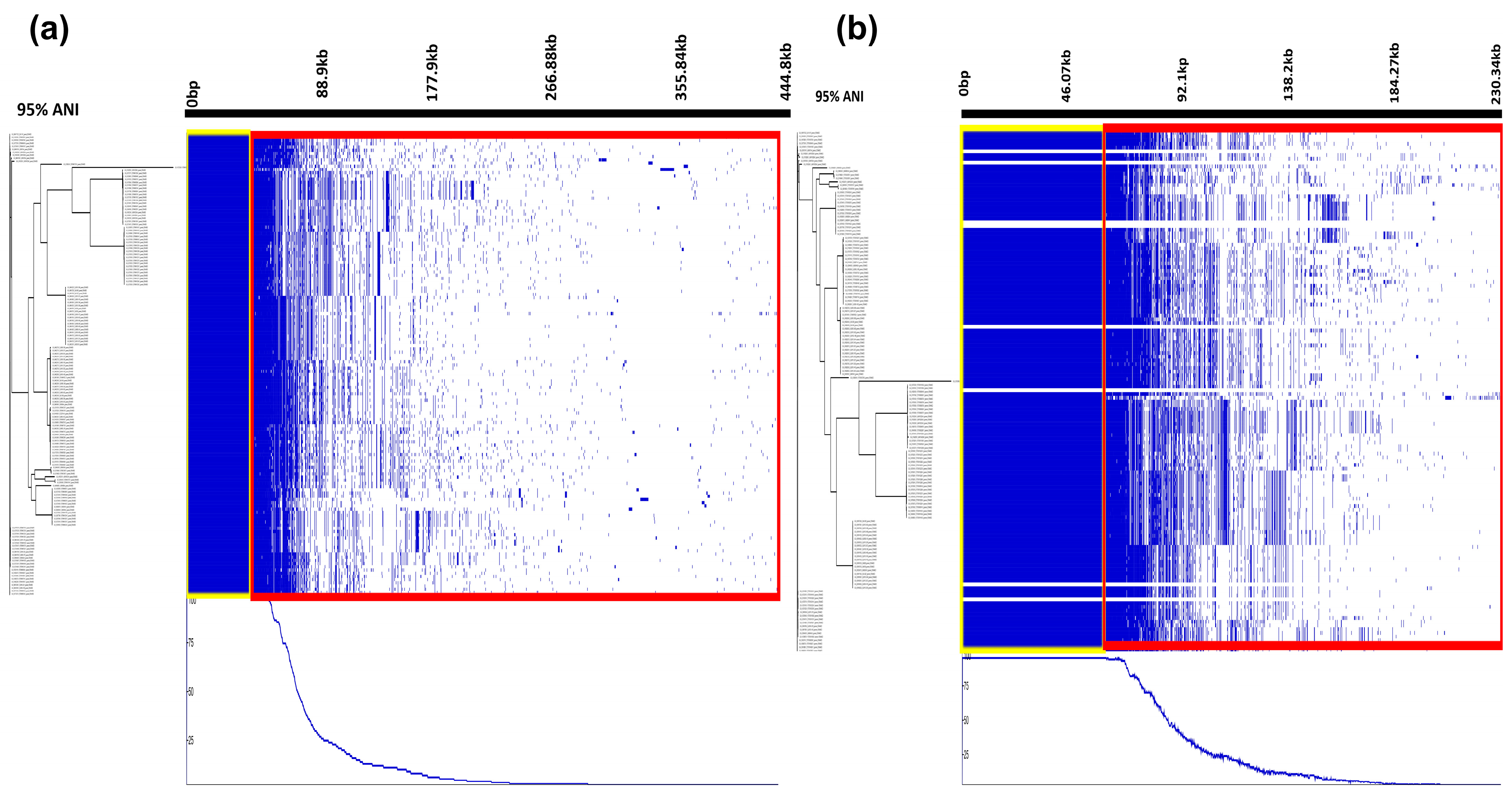
3.1. Comparative Pangenome Composition and Genomic Diversity of STEC Using RIBAP and Panaroo Tools
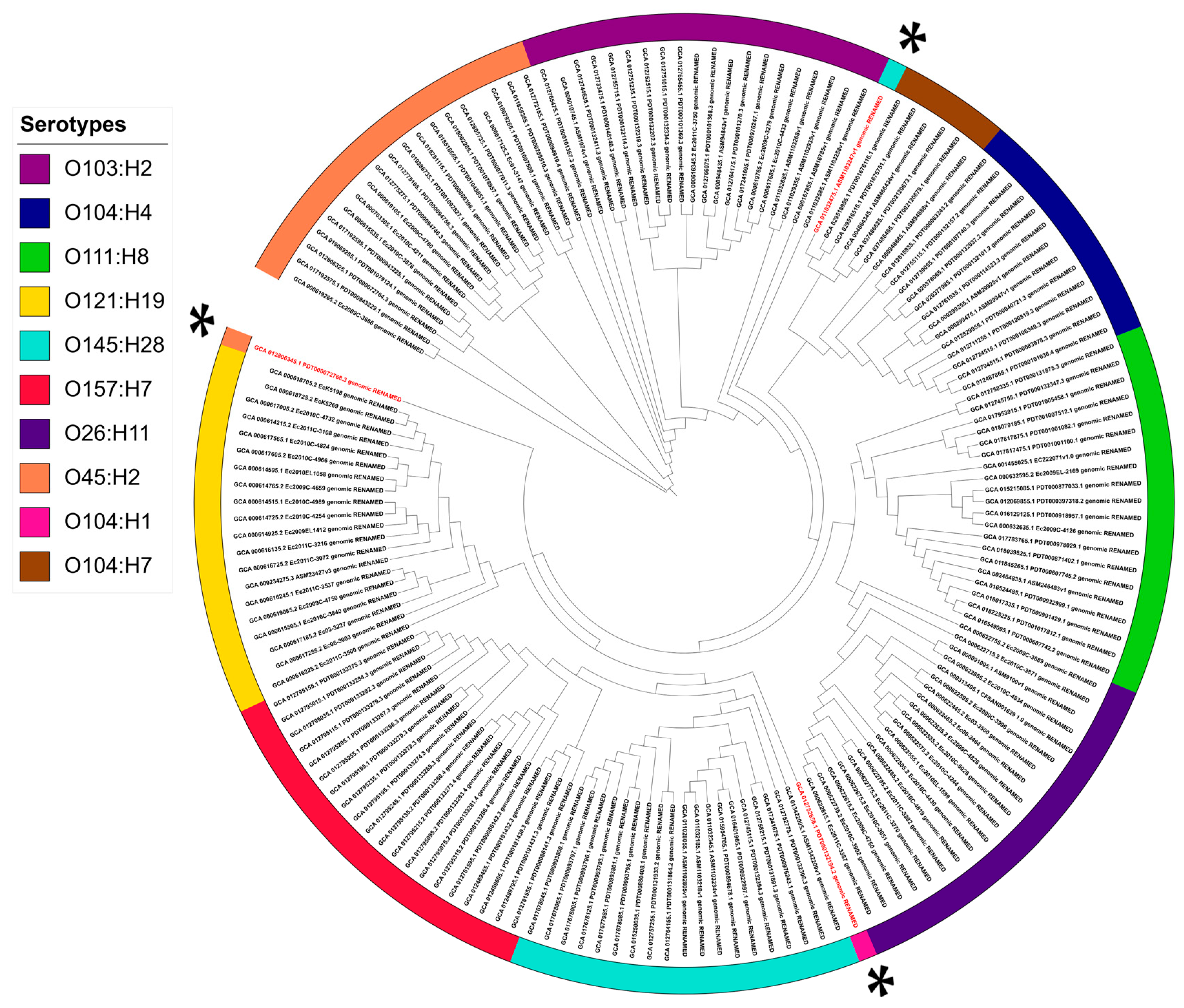
3.2. Identification and Validation of Specific Genetic Markers for Major Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Serogroups
3.3. Functional Characterization of Serogroup-Specific Genes via Gene Ontology Annotation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gunther, N.W., IV. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 86, 145–197. [Google Scholar]
- Alhadlaq, M.A.; Aljurayyad, O.I.; Almansour, A.; Al-Akeel, S.I.; Alzahrani, K.O.; Alsalman, S.A.; Yahya, R.; Al-Hindi, R.R.; Hakami, M.A.; Alshahrani, S.D. Overview of pathogenic Escherichia coli, with a focus on Shiga toxin-producing serotypes, global outbreaks (1982–2024) and food safety criteria. Gut Pathog. 2024, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Scallan, E.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Stapleton, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Yeung, D.H.; Kirk, M.D. Global incidence of human Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli infections and deaths: A systematic review and knowledge synthesis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.B.; Shi, X.; Shridhar, P.B.; Roberts, E.L.; DebRoy, C.; Phebus, R.K.; Bai, J.; Nagaraja, T. Multiplex PCR assays for the detection of one hundred and thirty seven serogroups of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli associated with cattle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Payne, M.; Kaur, S.; Lan, R. Improved genomic identification, clustering, and serotyping of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli using cluster/serotype-specific gene markers. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 772574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; O’Brien, A.D. Overview and historical perspectives. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valilis, E.; Ramsey, A.; Sidiq, S.; DuPont, H.L. Non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli—A poorly appreciated enteric pathogen: Systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 76, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capps, K.M.; Ludwig, J.B.; Shridhar, P.B.; Shi, X.; Roberts, E.; DebRoy, C.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Phebus, R.K.; Bai, J.; Nagaraja, T. Identification, Shiga toxin subtypes and prevalence of minor serogroups of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in feedlot cattle feces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.H.; Mody, R.K.; Ong, K.L.; Clogher, P.; Cronquist, A.B.; Garman, K.N.; Lathrop, S.; Medus, C.; Spina, N.L.; Webb, T.H. Increased recognition of non-O157 Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli infections in the United States during 2000–2010: Epidemiologic features and comparison with E. coli O157 infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, H.M.; Mosci, R.E.; Dietrich, S.; Burgess, E.; Wholehan, J.; McWilliams, K.; Pietrzen, K.; Benko, S.; Gatesy, T.; Rudrik, J.T. Population structure and genetic diversity of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) clinical isolates from Michigan. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Garcia, F.; Sperandio, V.; Hovde, C.J. Escherichia coli O104: H4 Pathogenesis: Enteroaggregative E. coli/Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli Explosive Cocktail of High Virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy, S.; Beutin, L.; Burgos, Y.; Fach, P. Specific detection of enteroaggregative hemorrhagic Escherichia coli O104: H4 strains by use of the CRISPR locus as a target for a diagnostic real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bielaszewska, M.; Kunsmann, L.; Mellmann, A.; Bauwens, A.; Köck, R.; Kossow, A.; Anders, A.; Gatermann, S.; Karch, H. Lability of the pAA virulence plasmid in Escherichia coli O104: H4: Implications for virulence in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, E.A.; Fadlallah, S.M.; Nassar, F.J.; Kazzi, N.; Matar, G.M. Approaches to treatment of emerging Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections highlighting the O104: H4 serotype. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, H.; Denamur, E.; Dobrindt, U.; Finlay, B.B.; Hengge, R.; Johannes, L.; Ron, E.Z.; Tønjum, T.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Vicente, M. The enemy within us: Lessons from the 2011 European Escherichia coli O104: H4 outbreak. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, J.J.; Siitonen, A.; Kaukoranta, S.-S. Usability and Performance of CHROMagar STEC Medium in Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3586–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyles, C. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: An overview. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, E45–E62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.M.; DebRoy, C.; Liu, Y.; Needleman, D.S.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Feng, P. Advances in molecular serotyping and subtyping of Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DebRoy, C.; Fratamico, P.M.; Yan, X.; Baranzoni, G.; Liu, Y.; Needleman, D.S.; Tebbs, R.; O’Connell, C.D.; Allred, A.; Swimley, M. Comparison of O-antigen gene clusters of all O-serogroups of Escherichia coli and proposal for adopting a new nomenclature for O-typing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147434. [Google Scholar]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and easy in silico serotyping of Escherichia coli isolates by use of whole-genome sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Achtman, M.; Brown, D.; Chattaway, M.; Dallman, T.; Delahay, R.; Kornschober, C. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didelot, X.; Wilson, D.J. ClonalFrameML: Efficient inference of recombination in whole bacterial genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.R.; Henderson, I.R. The evolution of the Escherichia coli phylogeny. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Moreira, C.G.; Li, D.R.; Reading, N.C.; Ritchie, J.M.; Waldor, M.K.; Williams, N.; Taussig, R.; Wei, S.; Roth, M. Targeting QseC signaling and virulence for antibiotic development. Science 2008, 321, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettelin, H.; Masignani, V.; Cieslewicz, M.J.; Donati, C.; Medini, D.; Ward, N.L.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Crabtree, J.; Jones, A.L.; Durkin, A.S. Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: Implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13950–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Hauser, L.; Jun, S.-R.; Nookaew, I.; Leuze, M.R.; Ahn, T.-H.; Karpinets, T.; Lund, O.; Kora, G.; Wassenaar, T. Insights from 20 years of bacterial genome sequencing. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordienko, E.N.; Kazanov, M.D.; Gelfand, M.S. Evolution of pan-genomes of Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., and Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Guttman, D.S.; Fitzgerald, J.R. Population genomics of bacterial host adaptation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassman, H.; Suttorp, V.; White, T.; Ziebell, K.; Kearney, A.; Bessonov, K.; Li, V.; Chui, L. Clinical Outcomes and Virulence Factors of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) from Southern Alberta, Canada, from 2020 to 2022. Pathogens 2024, 13, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockhurst, M.A.; Harrison, E.; Hall, J.P.; Richards, T.; McNally, A.; MacLean, C. The ecology and evolution of pangenomes. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1094–R1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Thuras, P.; Johnston, B.D.; Weissman, S.J.; Limaye, A.P.; Riddell, K.; Scholes, D.; Tchesnokova, V.; Sokurenko, E. The Pandemic H30 Subclone of Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Is Associated With Persistent Infections and Adverse Outcomes Independent From Its Multidrug Resistance and Associations With Compromised Hosts. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkiewicz, K.; Barf, L.-M.; Sachse, K.; Hölzer, M. RIBAP: A comprehensive bacterial core genome annotation pipeline for pangenome calculation beyond the species level. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Chatzou, M.; Floden, E.W.; Barja, P.P.; Palumbo, E.; Notredame, C. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin-Hill, G.; MacAlasdair, N.; Ruis, C.; Weimann, A.; Horesh, G.; Lees, J.A.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.; Beaudoin, C.; Floto, R.A. Producing polished prokaryotic pangenomes with the Panaroo pipeline. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Abricate [Internet]. Github. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Scan Contig Files Against PubMLST Typing Schemes. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez, R.L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Treangen, T.J.; Melsted, P.; Mallonee, A.B.; Bergman, N.H.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. Mash: Fast genome and metagenome distance estimation using MinHash. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Subgroup, G.P.D.P. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geue, L.; Menge, C.; Eichhorn, I.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Pickard, D.; Berens, C.; Barth, S.A. Evidence for contemporary switching of the O-antigen gene cluster between Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains colonizing cattle. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Sievert, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, T.L. Ggforce: Accelerating “ggplot2”. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggforce/index.html (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Garnier, S.; Ross, N.; Rudis, B.; Sciaini, M.; Camargo, A.P.; Scherer, C. R Package ‘Viridis’. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=viridis (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Chauhan, S.M.; Ardalani, O.; Hyun, J.C.; Monk, J.M.; Phaneuf, P.V.; Palsson, B.O. Decomposition of the pangenome matrix reveals a structure in gene distribution in the Escherichia coli species. mSphere 2025, 10, e00532-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Perrin, A.; De Sousa, J.A.M.; Vangchhia, B.; Burn, S.; O’Brien, C.L.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.; Rocha, E.P. Phylogenetic background and habitat drive the genetic diversification of Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, R.M.; Biggs, P.J.; Midwinter, A.C.; Browne, A.S.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Irshad, H.; French, N.P.; Brightwell, G.; Cookson, A.L. Genomic epidemiology and carbon metabolism of Escherichia coli serogroup O145 reflect contrasting phylogenies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, C.R.; Whiteside, M.D.; Gannon, V.P. Pan-genome analyses of the species Salmonella enterica, and identification of genomic markers predictive for species, subspecies, and serovar. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Aaresturp, F.M.; Ussery, D.W.; Friis, C. The Salmonella enterica pan-genome. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettelin, H.; Riley, D.; Cattuto, C.; Medini, D. Comparative genomics: The bacterial pan-genome. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, R.S.; Friis, C.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M. Estimating variation within the genes and inferring the phylogeny of 186 sequenced diverse Escherichia coli genomes. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Hoede, C.; Tenaillon, O.; Barbe, V.; Baeriswyl, S.; Bidet, P.; Bingen, E.; Bonacorsi, S.; Bouchier, C.; Bouvet, O. Organised genome dynamics in the Escherichia coli species results in highly diverse adaptive paths. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, D.J.; Valcanis, M.; Kuzevski, A.; Tauschek, M.; Inouye, M.; Stinear, T.; Levine, M.M.; Robins-Browne, R.M.; Holt, K.E. In silico serotyping of E. coli from short read data identifies limited novel O-loci but extensive diversity of O: H serotype combinations within and between pathogenic lineages. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.H.; Sahl, J.W.; Fraser, C.M.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Scheutz, F.; Rasko, D.A. Refining the pathovar paradigm via phylogenomics of the attaching and effacing Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12810–12815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, C.; Fruth, A.; Campbell, I.W.; Jenkins, C.; Smith, P.; Strockbine, N.; Weill, F.-X.; Nübel, U.; Grad, Y.H.; Waldor, M.K. O-antigen diversification masks identification of highly pathogenic shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104: H4-Like strains. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0098723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Barth, H.; Schmidt, H. Toxins of locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Toxins 2018, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuufire, E.; Bentum, K.E.; Nyarku, R.; Osei, V.; Elrefaey, A.; James, T.; Woube, Y.; Folitse, R.; Samuel, T.; Abebe, W. Identification of Novel Gene-Specific Markers for Differentiating Various Pathogenic Campylobacter Species Using a Pangenome Analysis Approach. Pathogens 2025, 14, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delannoy, S.; Tran, M.-L.; Fach, P. Insights into the assessment of highly pathogenic Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in raw milk and raw milk cheeses by high throughput real-time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 366, 109564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivarao, D.; Weiner, J.H. Dimethyl sulfoxide reductase of Escherichia coli: An investigation of function and assembly by use of in vivo complementation. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 5935–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, G.; Reeves, P. Biosynthesis of O-antigens: Genes and pathways involved in nucleotide sugar precursor synthesis and O-antigen assembly. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2503–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfiffer, V.; Sarenko, O.; Possling, A.; Hengge, R. Genetic dissection of Escherichia coli’s master diguanylate cyclase DgcE: Role of the N-terminal MASE1 domain and direct signal input from a GTPase partner system. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Perepelov, A.V.; Svensson, M.V.; Shevelev, S.D.; Guo, D.; Senchenkova, S.y.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; Weintraub, A.; Feng, L.; Widmalm, G. Genetic and structural relationships of Salmonella O55 and Escherichia coli O103 O-antigens and identification of a 3-hydroxybutanoyltransferase gene involved in the synthesis of a Fuc3N derivative. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, J.; Li, Y.; Larocque, R.; Schrag, J.D.; Cygler, M.; Matte, A. Crystal structure of histidinol phosphate aminotransferase (HisC) from Escherichia coli, and its covalent complex with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate and l-histidinol phosphate. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 311, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalynych, S.; Ruan, X.; Valvano, M.A.; Cygler, M. Structure-guided investigation of lipopolysaccharide O-antigen chain length regulators reveals regions critical for modal length control. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3710–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Islam, S.T.; Huszczynski, S.M.; Nugent, T.; Gold, A.C.; Lam, J.S. Conserved-residue mutations in Wzy affect O-antigen polymerization and Wzz-mediated chain-length regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Luo, P.; Zeng, H.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhai, R. The effect of O-antigen length determinant wzz on the immunogenicity of Salmonella Typhimurium for Escherichia coli O2 O-polysaccharides delivery. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cole, R.A.; Reeves, P.R. An O-antigen processing function for Wzx (RfbX): A promising candidate for O-unit flippase. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, N.M.; Blassick, C.M.; Andreani, V.; Lugagne, J.-B.; Dunlop, M.J. Dynamic gene expression and growth underlie cell-to-cell heterogeneity in Escherichia coli stress response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115032119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoldi, B.; Richardson, S.; Schneider, R.G.; Kurdmongkolthan, P.; Schneider, K.R. Preventing Foodborne Illness: E. coli “The Big Six”: FSHN13-09/FS233, rev. 1/2018. EDIS, University of Florida IFAS Extension. 2018. Available online: https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/FS233 (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Mainil, J.G.; Nakamura, K.; Ikeda, R.; Crombé, F.; Diderich, J.; Saulmont, M.; Piérard, D.; Thiry, D.; Hayashi, T. Emerging hybrid shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotype O80: H2 in humans and calves. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e00011-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonardi, S.; Conter, M.; Andriani, L.; Bacci, C.; Magagna, G.; Rega, M.; Lamperti, L.; Loiudice, C.; Pierantoni, M.; Filipello, V. Emerging of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O177: H11 and O177: H25 from cattle at slaughter in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 423, 110846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
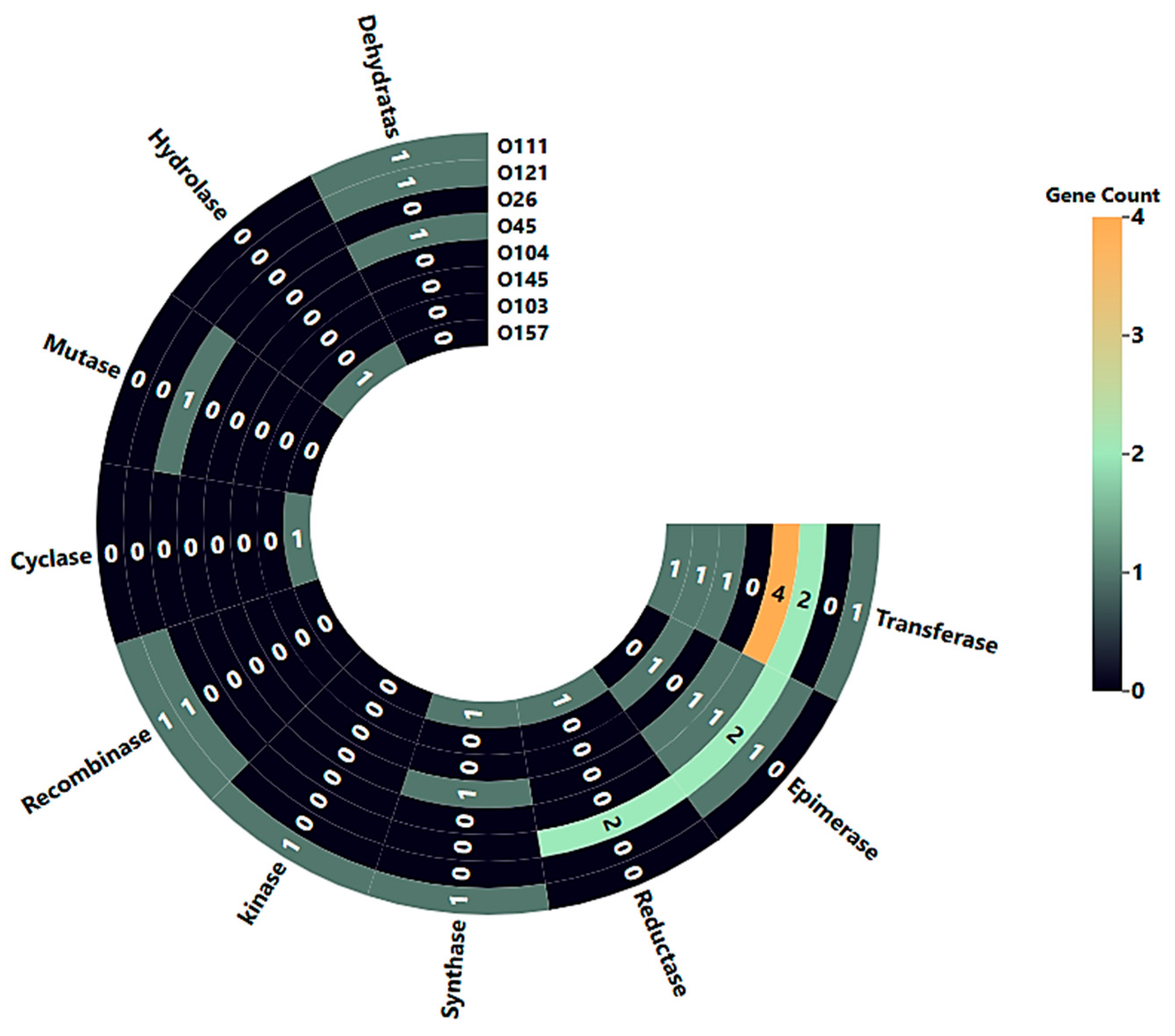
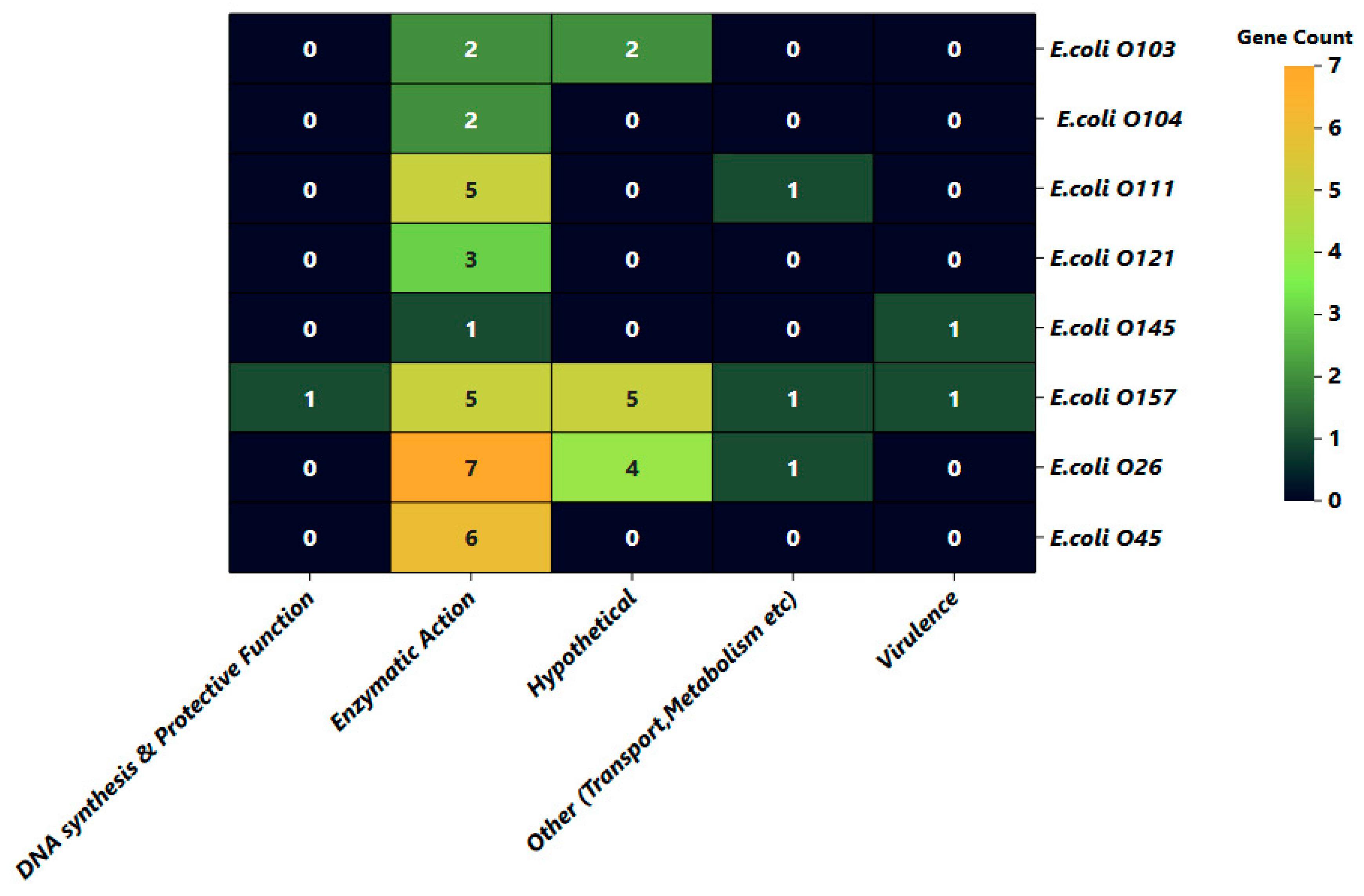
| Serogroups | Protein Name (Gene) | Accession No. | Size (bp) | Subcellular Localization | Functional Gene Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O157 | Hypothetical protein | AAG58872.1 | 624 | Unknown | Hypothetical |
| Hypothetical protein | WP_000369315.1 | 672 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| Hypothetical protein | EHV01783.1 | 135 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| Hypothetical protein | WP_000526425.1 | 300 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| YehF protein | WP_001215588. | 729 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| GDP-L-fucose synthase (fcl_2) | AAC32346.1 | 966 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| GDP-mannose mannosyl hydrolase (gmm_2) | WP_000478513.1 | 510 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase 1(manC1_2) | WP_001278239.1 | 1449 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Putative diguanylate cyclase DgcE (dgcE_2) | ASL58608.1 | 2808 | Inner cell membrane (cytosolic side) | Enzymatic Action | |
| Chitoporin (chiP_1) | ACI72635.1 | 480 | Outer membrane (porin) | Others (Transport, Metabolism, etc.) | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide reductase (dmsA_1) | WP_000380694.1 | 2382 | Periplasmic side of the inner cell membrane | Enzymatic action | |
| Toxin ParE4 | WP_000277484.1 | 282 | Cytoplasm | Virulence | |
| Protein YciF | AAG56012.1 | 501 | Cytoplasm | DNA synthesis and protection | |
| O103 | Hypothetical protein | WP_001064117.1 | 407 | Unknown | Hypothetical |
| Hypothetical protein | EJV1286191.1 | 528 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (lnpD) | WP_000996555.1 | 1029 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| N-acetylgalactosamine-N, N’-diacetylbacillosaminyl-diphospho-undecaprenol4-alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase(pglJ) | HGU3025143.1 | 1092 | Membrane-associated | Enzymatic action | |
| O145 | Putative fimbrial chaperone YehC (yehC 1) | EKO1170350.1 | 292 | Periplasmic space (inner-membrane-anchored chaperone) | Virulence |
| Histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase (hisC) | WP_001099213.1 | 1071 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| O104 | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase (neuC) | WP_000723247.1 | 1164 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action |
| CMP-N, N’-diacetyllegionaminic acid synthase (Legl) | EGT66549.1 | 330 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| O45 | Serine acetyltransferase (cysE_1) | EOV7831118.1 | 240 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action |
| dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase (rfbC) | WP_001100944.1 | 540 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine C6 dehydratase (pglF) | WP_001435027.1 | 1887 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| UDP-N-acetylbacillosamine N-acetyltransferase (pglD) | WP_000342233.1 | 561 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Undecaprenyl-phosphate alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyl 1-phosphate transferase (wecA_1) | WP_000966114.1 | 1035 | Inner cell membrane | Enzymatic action | |
| Glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase 2 (rffH_1) | WP_000676072.1 | 873 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| O26 | Hypothetical protein | AOM43287.1 | 508 | Unknown | Hypothetical |
| UDP-23-diacetamido-23-dideoxy-D-glucuronate 2-epimerase (wbpI) | WP_000734421.1 | 1131 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| UDP-2-acetamido-26-beta-L-arabino-hexul-4-ose reductase (wbjC) | WP_001429673.1 | 1107 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| UDP-glucose 4-epimerase (capD) | WP_000475914.1 | 1035 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| hypothetical protein | EET7051301.1 | 795 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| hypothetical protein | WP_000291456.1 | 1023 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| Putative O-antigen transporter (rfbX) | WP_000914145.1 | 1263 | Inner cell membrane | Others (Transport, Metabolism, etc.) | |
| Glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase 1 (rfbA) | WP_000857547.1 | 879 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose reductase (rfbD) | WP_001023633.1 | 900 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| hypothetical protein | WP_001116073.1 | 1214 | Unknown | Hypothetical | |
| D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase (mshA_1) | WP_000862644.1 | 1041 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Phosphomannomutase/phosphoglucomutase (algC) | KGM70217.1 | 836 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| O121 | dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (rfbB) | KDV82622.1 | 712 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action |
| Tyrosine recombinase (xerC_1) | WP_001234104.1 | 1212 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| dTDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-glucose 3,5-epimerase (wbtF) | EFF6995043.1 | 1116 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| O111 | GDP-mannose 46-dehydratase (gmd_1) | EGZ2997311.1 | 561 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action |
| Serine recombinase (PinR) | WP_000268365.1 | 549 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Tyrosine-protein kinase (wzc) | WP_000137212.1 | 2163 | Membrane-associated | Enzymatic action | |
| UTP--glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (galF) | WP_000609087.1 | 894 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action | |
| Chain length determinant protein (wzzB) | WP_000027959.1 | 984 | Inner cell membrane | Others (Transport, Metabolism etc.) | |
| GDP-L-colitose synthase (colC) | WP_000866332.1 | 924 | Cytoplasm | Enzymatic action |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elrefaey, A.; Bentum, K.E.; Kuufire, E.; James, T.; Nyarku, R.; Osei, V.; Woube, Y.; Samuel, T.; Abebe, W. Genomic Markers Distinguishing Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Insights from Pangenome and Phylogenomic Analyses. Pathogens 2025, 14, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090862
Elrefaey A, Bentum KE, Kuufire E, James T, Nyarku R, Osei V, Woube Y, Samuel T, Abebe W. Genomic Markers Distinguishing Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Insights from Pangenome and Phylogenomic Analyses. Pathogens. 2025; 14(9):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090862
Chicago/Turabian StyleElrefaey, Asmaa, Kingsley E. Bentum, Emmanuel Kuufire, Tyric James, Rejoice Nyarku, Viona Osei, Yilkal Woube, Temesgen Samuel, and Woubit Abebe. 2025. "Genomic Markers Distinguishing Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Insights from Pangenome and Phylogenomic Analyses" Pathogens 14, no. 9: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090862
APA StyleElrefaey, A., Bentum, K. E., Kuufire, E., James, T., Nyarku, R., Osei, V., Woube, Y., Samuel, T., & Abebe, W. (2025). Genomic Markers Distinguishing Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli: Insights from Pangenome and Phylogenomic Analyses. Pathogens, 14(9), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14090862







